Schisandrol A Suppresses Catabolic Factor Expression by Blocking NF-κB Signaling in Osteoarthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
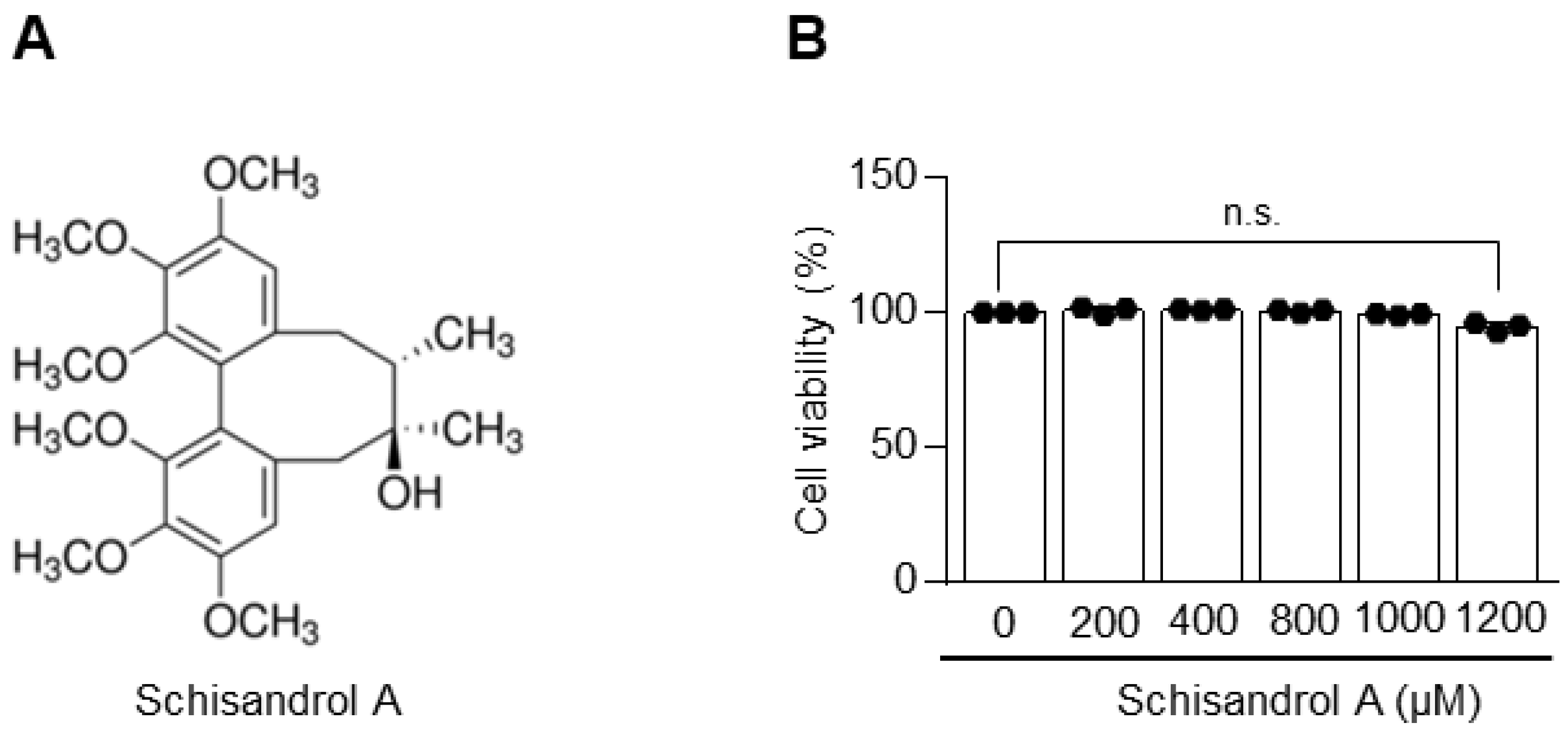
2.1. Schisandrol A Is Not Toxic to Chondrocytes
2.2. Schisandrol A Inhibits IL-1β-Induced MMPs and COX-2 in Chondrocytes
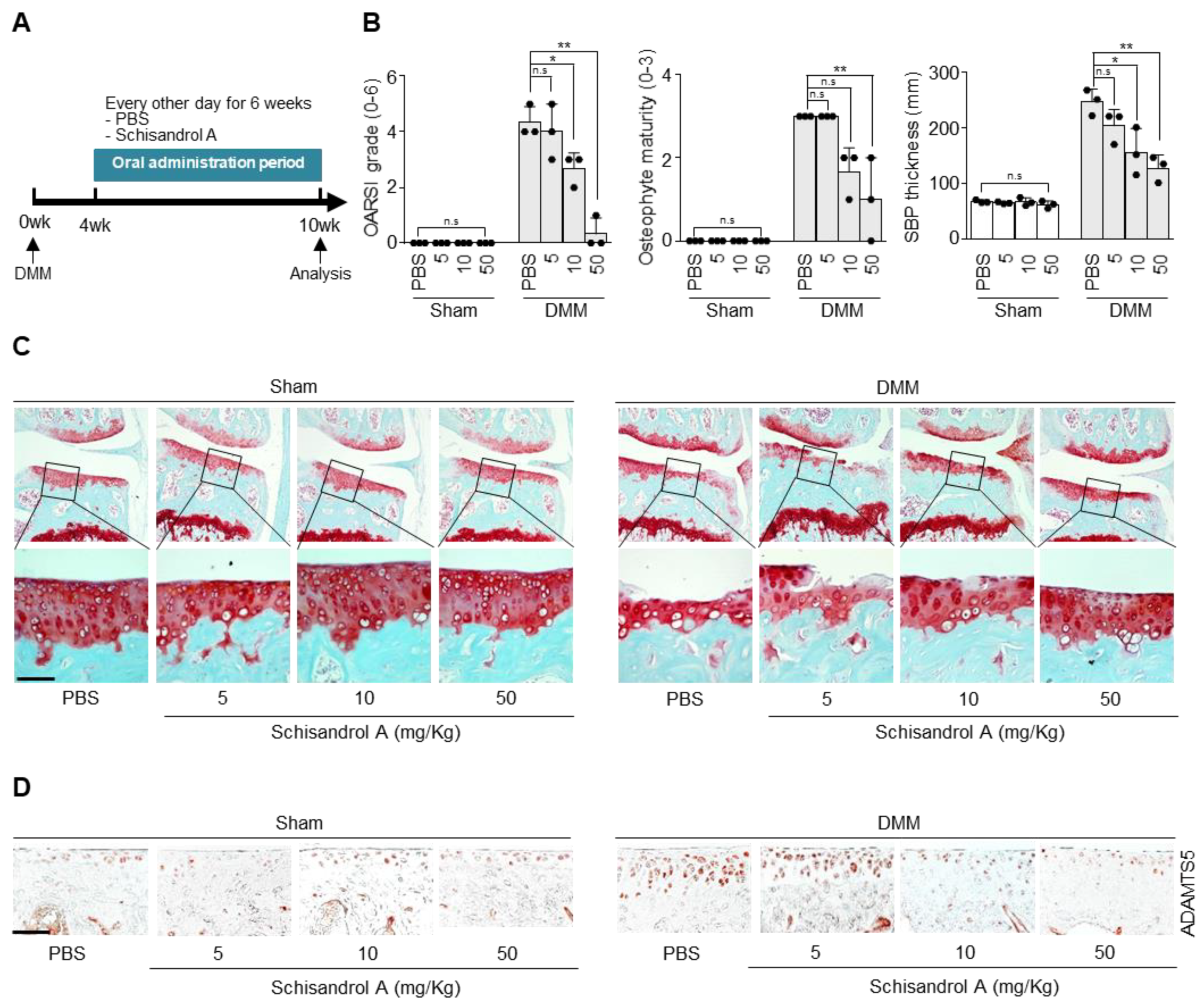
2.3. Oral Gavage of Schisandrol A Inhibits Cartilage Degradation in the Destabilization of the Medial Meniscus (DMM)-Induced Arthritis Model
2.4. Schisandrol A Prevents Activation of IL-1β-Induced NF-κB Signaling in Mouse Articular Chondrocytes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Culture of Articular Chondrocytes and Viability Analysis
4.3. Reagents and Treatment
4.4. Quantitative Reverse Transcription–Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.5. Protein Isolation and Western Blotting
4.6. PGE2, Collagenase, and Reporter Gene Assays
4.7. Experimental OA Mouse Model and Oral Administration
4.8. Evaluation of Cartilage Destruction
4.9. Immunohistochemistry
4.10. Protein Structural Homology Modeling
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feldmann, M. Pathogenesis of arthritis: Recent research progress. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 771–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeser, R.F.; Goldring, S.R.; Scanzello, C.R.; Goldring, M.B. Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belluzzi, E.; Macchi, V.; Fontanella, C.G.; Carniel, E.L.; Olivotto, E.; Filardo, G.; Sarasin, G.; Porzionato, A.; Granzotto, M.; Pozzuoli, A.; et al. Infrapatellar fat pad gene expression and protein production in patients with and without osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, M.A.; Loeser, R.F. Aging-related inflammation in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1966–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeser, R.F.; Collins, J.A.; Diekman, B.O. Ageing and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.Y.; Ahmad, N.; Haqqi, T.M. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieppe, P.A.; Lohmander, L.S. Pathogenesis and management of pain in osteoarthritis. Lancet 2005, 365, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldring, M.B.; Otero, M. Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, Y.; Maeno, M.; Suzuki, N.; Shiratsuchi, H.; Motohashi, M.; Matsumura, H. The effect of IL-1β on the expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases in human chondrocytes. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 3210–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Squires, G.R.; Mousa, A.; Tanzer, M.; Zukor, D.J.; Antoniou, J.; Feige, U.; Poole, A.R. Role of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor? In matrix degradation of human osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Sampson, E.R.; Jin, H.; Li, J.; Ke, Q.H.; Im, H.-J.; Chen, D. MMP13 is a critical target gene during the progression of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosset, M.; Pigenet, A.; Salvat, C.; Berenbaum, F.; Jacques, C. Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-3 and -13 synthesis induced by IL-1β in chondrocytes from mice lacking microsomal prostaglandin e synthase-1. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 6244–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosang, A.J.; Rogerson, F.M. Identifying the human aggrecanase. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchetina, E.V.; Di Battista, J.A.; Zukor, D.J.; Antoniou, J.; Poole, A.R. Prostaglandin PGE2 at very low concentrations suppresses collagen cleavage in cultured human osteoarthritic articular cartilage: This involves a decrease in expression of proinflammatory genes, collagenases and COL10A1, a gene linked to chondrocyte hypertrophy. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2007, 9, R75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, M.M.; Seibert, K.; Manning, P.T.; Currie, M.G.; Woerner, B.M.; Edwards, D.; Koki, A.; Tripp, C.S. Cyclooxygenase 2-dependent prostaglandin E2 modulates cartilage proteoglycan degradation in human osteoarthritis explants. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 1789–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.-C.; Jo, J.; Park, Y.; Kang, H.K. NF-B signaling pathways in osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Cells 2019, 8, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Tanaka, S. Molecular mechanisms underlying osteoarthritis development: Notch and NF-κB. Arthritis Res. 2017, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. NF-B, the first quarter-century: Remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincenti, M.P.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. Transcriptional regulation of collagenase (MMP-1, MMP-13) genes in arthritis: Integration of complex signaling pathways for the recruitment of gene-specific transcription factors. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torzilli, P.A.; Bhargava, M.; Chen, C.T. Mechanical loading of articular cartilage reduces IL-1-induced enzyme expression. Cartilage 2011, 2, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Men, L.; Sun, Y.; Wei, M.; Fan, X. Pharmacodynamic effects and molecular mechanisms of lignans from Schisandra chinensis Turcz. (Baill.), a current review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 892, 173796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szopa, A.; Ekiert, R.; Ekiert, H. Current knowledge of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. (Chinese magnolia vine) as a medicinal plant species: A review on the bioactive components, pharmacological properties, analytical and biotechnological studies. Phytochem. Rev. 2016, 16, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Yu, X.; Chen, C. Schizandrol A: A lignan from Schisandra chinensis. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E Struct. Rep. Online 2008, 64, o1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Cong, L.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Guan, X.; Liu, P.; Xie, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, J. Pharmacokinetics and distribution of schisandrol A and its major metabolites in rats. Xenobiotica 2019, 49, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Choi, B.R.; Bak, Y.O.; Zhang, L.T.; Zhou, L.X.; Huang, Y.R.; Zhao, C.; Park, J.K. Cavernosum smooth muscle relaxation induced by Schisandrol A via the NO-cGMP signaling pathway. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2016, 62, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Piao, Z.; Yao, L.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y. Schisandrin ameliorates cognitive deficits, endoplasmic reticulum stress and neuroinflammation in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced Alzheimer’s disease rats. Exp. Anim. 2020, 69, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Ju, W.; Chen, J.; Sun, J. Characteristics and antioxidant activity of lignans in Schisandra chinensis and Schisandra sphenanthera from different locations. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1800030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Yao, L.; Zhang, L.; Piao, Z.; Lu, Y. Schizandrol A protects against Aβ1–42-induced autophagy via activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in SH-SY5Y cells and primary hippocampal neurons. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 1739–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, N.-R.; Moon, P.-D.; Kim, N.-R.; Kim, H.-Y.; Jeong, H.-J.; Kim, H.-M. Schisandra chinensis and its main constituent schizandrin attenuate allergic reactions by down-regulating caspase-1 in ovalbumin-sensitized mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2017, 45, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; Sun, Y.; Gong, G.; Li, Y.; Fan, K.; Wu, B.; Bi, K.; Jia, Y. The neuroprotective effect of schisandrol A on 6-OHDA-induced PD mice may be related to PI3K/AKT and IKK/IκBα/NF-κB pathway. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 128, 110743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Tan, Y.-S.; Chen, H.-L.; Yan, Y.; Zhai, K.-F.; Li, D.-P.; Kou, J.-P.; Yu, B.-Y. Identification of schisandrin as a vascular endothelium protective component in YiQiFuMai powder injection using HUVECs binding and HPLC-DAD-Q-TOF-MS/MS analysis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 129, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-Y.; Hsieh, M.-T.; Wu, C.-R.; Tsai, F.-H.; Lu, T.-C.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Li, W.-C.; Lin, Y.-T.; Peng, W.-H. Schizandrin protects primary cultures of rat cortical cells from glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 107, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shijin, L.; Xungang, X.; Minghua, C. Matrine inhibits IL-1β-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases by sup-pressing the activation of MAPK and NF-κB in human chondrocytes in vitro. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 4764–4772. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, C.; Kang, L.; Jang, D.; Jeon, J.; Lee, H.; Choi, S.; Han, S.J.; Oh, E.; Nam, J.; Kim, C.S.; et al. Cirsium japonicum var. maackii and apigenin block Hif-2α-induced osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 5369–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musumeci, G.; Aiello, F.C.; Szychlinska, M.A.; Di Rosa, M.; Castrogiovanni, P.; Mobasheri, A. Osteoarthritis in the XXIst century: Risk factors and behaviours that influence disease onset and progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 6093–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchi, S.; Palumbo, P.; Sponta, A.; Coppolino, M. Clinical pharmacology of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: A review. Anti-Inflam. Anti-Allergy Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 11, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, R.; Siracusa, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Genovese, T.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Mandalari, G.; Impellizzeri, D.; et al. The role of cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) nuts on an experimental model of painful degenerative joint disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Crupi, R.; Rizzarelli, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. The protective effect of new carnosine-hyaluronic acid conjugate on the inflammation and cartilage degradation in the experimental model of osteoarthritis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manicone, A.M.; McGuire, J.K. Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 19, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Dubois, R.N. The role of COX-2 in intestinal inflammation and colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2009, 29, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huo, D.-S.; Cai, Z.-P.; Shao, G.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Yang, Z.-J. The effect of schizandrol A-induced DNA methylation on SH-SY5YAB 1–40 altered neuronal cell line: A potential use in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2015, 78, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Cheng, X.; Jing, H.; Yan, T.; Xiao, F.; Wu, B.; Bi, K.; Jia, Y. Combination of schisandrin and nootkatone exerts neuroprotective effect in Alzheimer’s disease mice model. Metab. Brain Dis. 2019, 34, 1689–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Y.; Jin, Y.; Pan, L.; Zhang, A.; Liu, F. Schisandrin A ameliorates MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease in a mouse model via regulation of brain autophagy. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 2019, 42, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.-B.; Liu, M.-Y.; Chen, Z.-X.; Wei, M.-J. Schisandrin ameliorates cognitive impairment and attenuates Aβ deposition in APP/PS1 transgenic mice: Involvement of adjusting neurotransmitters and their metabolite changes in the brain. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Yu, B.; Kou, J. Schizandrin protects against OGD/R-induced neuronal injury by suppressing autophagy: Involvement of the AMPK/mTOR pathway. Molecules 2019, 24, 3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Huang, R.; Yan, L.; Li, D.-T.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wei, X.-H.; Cui, Y.-C.; Pan, C.-S.; Fan, J.-Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Schisandrin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury by regulating TLR-4 and Akt/FoxO1 signaling pathways. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Peng, L.-Y.; Wu, S.-C.; Li, J.-H.; Song, K.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.-N.; Yu, J.-L.; An, Q.; Yi, P.-F.; et al. Schizandrin attenuates inflammation induced by avian pathogenic Escherichia coli in chicken type II pneumocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 81, 106313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.Y.; Hung, T.M.; Bae, K.H.; Shin, E.M.; Zhou, H.Y.; Na Hong, Y.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, H.P.; Kim, Y.S. Anti-inflammatory effects of schisandrin isolated from the fruit of Schisandra chinensis Baill. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 591, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasser, M.I.; Zhu, S.; Chen, C.; Zhao, M.; Huang, H.; Zhu, P. A comprehensive review on Schisandrin B and its biological properties. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, N.-N.; Wang, Z.-Z.; Zhu, X.-C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, W.-Q.; Yang, R.; Zhang, X.-M. Schisandrin A and B enhance the dentate gyrus neurogenesis in mouse hippocampus. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2020, 105, 101751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; An, F.; Wei, X.; Hong, M.; Lu, Y. Comparative effects of Schisandrin A, B, and C on acne-related inflammation. Inflammation 2017, 40, 2163–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Song, M.; Ma, Y.; Yan, J.; You, H.; Wu, H. Schisandrin A inhibits the IL-1β-induced inflammation and cartilage degradation via suppression of MAPK and NF-κB signal pathways in rat chondrocytes. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.-C.; Tu, S.-L.; Zheng, B.-A.; Dong, Q.-J.; Wan, Z.-A.; Dai, Q.-Q. Schizandrin A exhibits potent anticancer activity in colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting heat shock factor 1. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, J.; Ma, C.; Xu, K.; Xu, L.; He, Y.; Moqbel, S.A.A.; Hu, P.; Jiang, L.; Chen, W.; Bao, J.; et al. Schisandrin B ameliorated chondrocytes inflammation and osteoarthritis via suppression of NF-κB and MAPK signal pathways. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Yin, Y.; Cao, F.-L.; Chen, Y.-F.; Peng, Y.; Hou, W.-G.; Sun, S.-K.; Luo, Z.-J. Tanshinone IIA attenuates the inflammatory response and apoptosis after traumatic injury of the spinal cord in adult rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.S.; Gedin, P.; Hugo, A.; Bakalkin, G.; Kanar, A.; Hart, D.A.; Druid, H.; Svensson, C.; Kosek, E. Activation of NF-κB in Synovium versus cartilage from patients with advanced knee osteoarthritis: A potential contributor to inflammatory aspects of disease progression. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Acquisto, F. Inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-B): An emerging theme in anti-inflammatory therapies. Mol. Interv. 2002, 2, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csaki, C.; Mobasheri, A.; Shakibaei, M. Synergistic chondroprotective effects of curcumin and resveratrol in human articular chondrocytes: Inhibition of IL-1β-induced NF-κB-mediated inflammation and apoptosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.; Kang, L.-J.; Lee, K.M.; Cho, C.; Song, E.K.; Kim, W.; Park, T.J.; Yang, S. 3′-Sialyllactose protects against osteoarthritic development by facilitating cartilage homeostasis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 22, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasi, S.; Ea, H.-K.; So, A.; Busso, N. Revisiting the role of interleukin-1 pathway in osteoarthritis: Interleukin-1α and -1β, and NLRP3 inflammasome are not involved in the pathological features of the murine menisectomy model of osteoarthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Zhu, N.; Sun, R.; Liao, W.; Fan, S.; Shi, F.; Lin, H.; Jiang, S.; Ying, Y. Metformin inhibits chemokine expression through the AMPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2018, 38, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.D. The diverse and complex roles of NF-κB subunits in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sueishi, T.; Akasaki, Y.; Goto, N.; Kurakazu, I.; Toya, M.; Kuwahara, M.; Uchida, T.; Hayashida, M.; Tsushima, H.; Bekki, H.; et al. GRK 5 inhibition attenuates cartilage degradation via decreased NF-κB signaling. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 72, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasson, S.; Blanchet, T.; Morris, E. The surgical destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) model of osteoarthritis in the 129/SvEv mouse. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2007, 15, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, J.; Xiao, K.; Xu, Y.; Guo, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, H. β-TrCP restricts lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced activation of TRAF6-IKK pathway upstream of IκBα signaling. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanarek, N.; Ben-Neriah, Y. Regulation of NF-κB by ubiquitination and degradation of the IκBs. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; Beer, T.A.P.D.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bryant, S.H.; Cheng, T.; Wang, J.; Gindulyte, A.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; He, S.; Zhang, J. PubChem BioAssay: 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, D955–D963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S.J.; Jun, J.; Eyun, S.-i.; Lee, C.-G.; Jeon, J.; Pan, C.-H. Schisandrol A Suppresses Catabolic Factor Expression by Blocking NF-κB Signaling in Osteoarthritis. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030241
Han SJ, Jun J, Eyun S-i, Lee C-G, Jeon J, Pan C-H. Schisandrol A Suppresses Catabolic Factor Expression by Blocking NF-κB Signaling in Osteoarthritis. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(3):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030241
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Seong Jae, Jimoon Jun, Seong-il Eyun, Choong-Gu Lee, Jimin Jeon, and Cheol-Ho Pan. 2021. "Schisandrol A Suppresses Catabolic Factor Expression by Blocking NF-κB Signaling in Osteoarthritis" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 3: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030241
APA StyleHan, S. J., Jun, J., Eyun, S.-i., Lee, C.-G., Jeon, J., & Pan, C.-H. (2021). Schisandrol A Suppresses Catabolic Factor Expression by Blocking NF-κB Signaling in Osteoarthritis. Pharmaceuticals, 14(3), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030241





