Obtusifolin, an Anthraquinone Extracted from Senna obtusifolia (L.) H.S.Irwin & Barneby, Reduces Inflammation in a Mouse Osteoarthritis Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
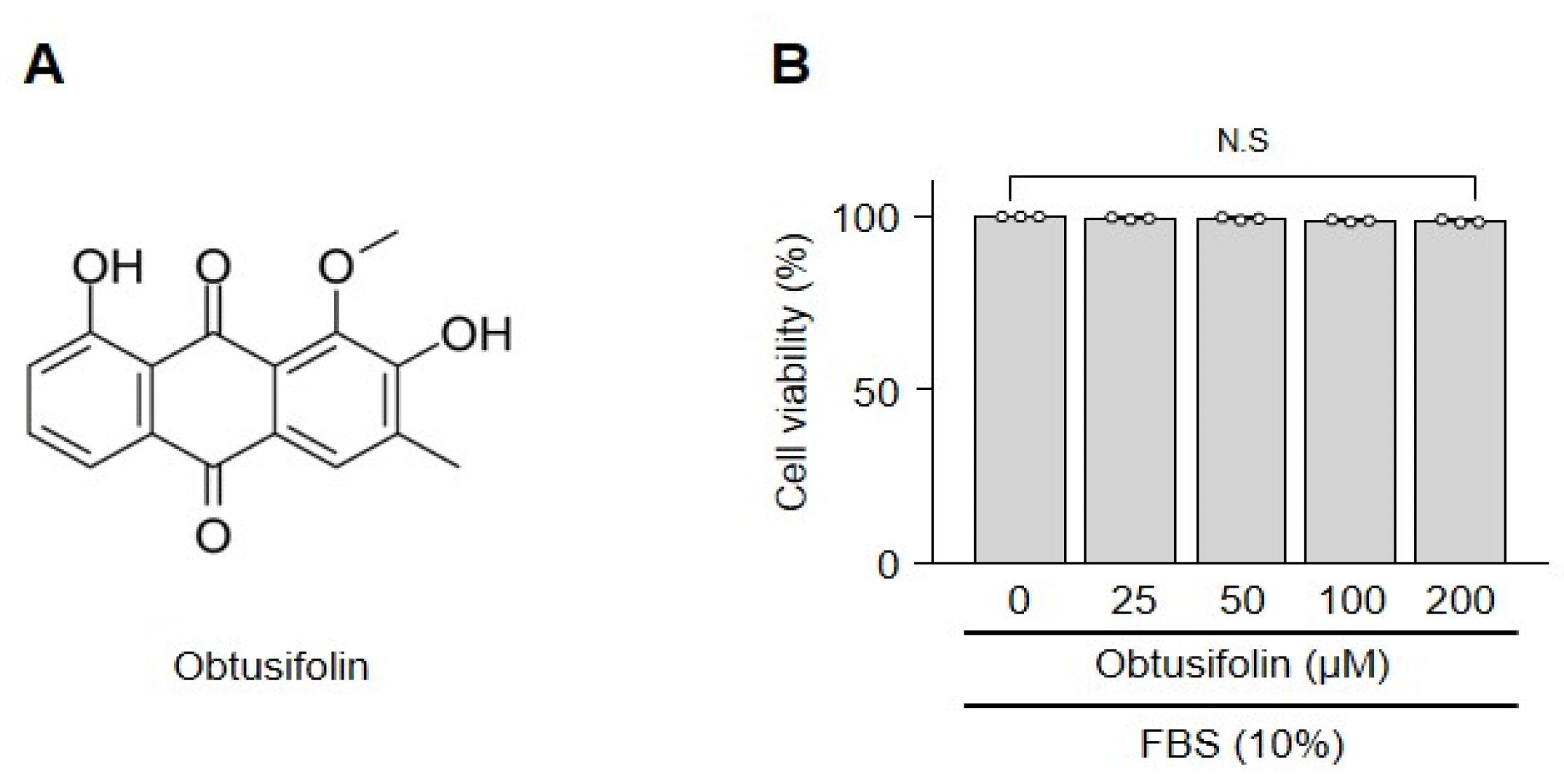
2.1. Obtusifolin Does Not Affect the Viability of Chondrocytes
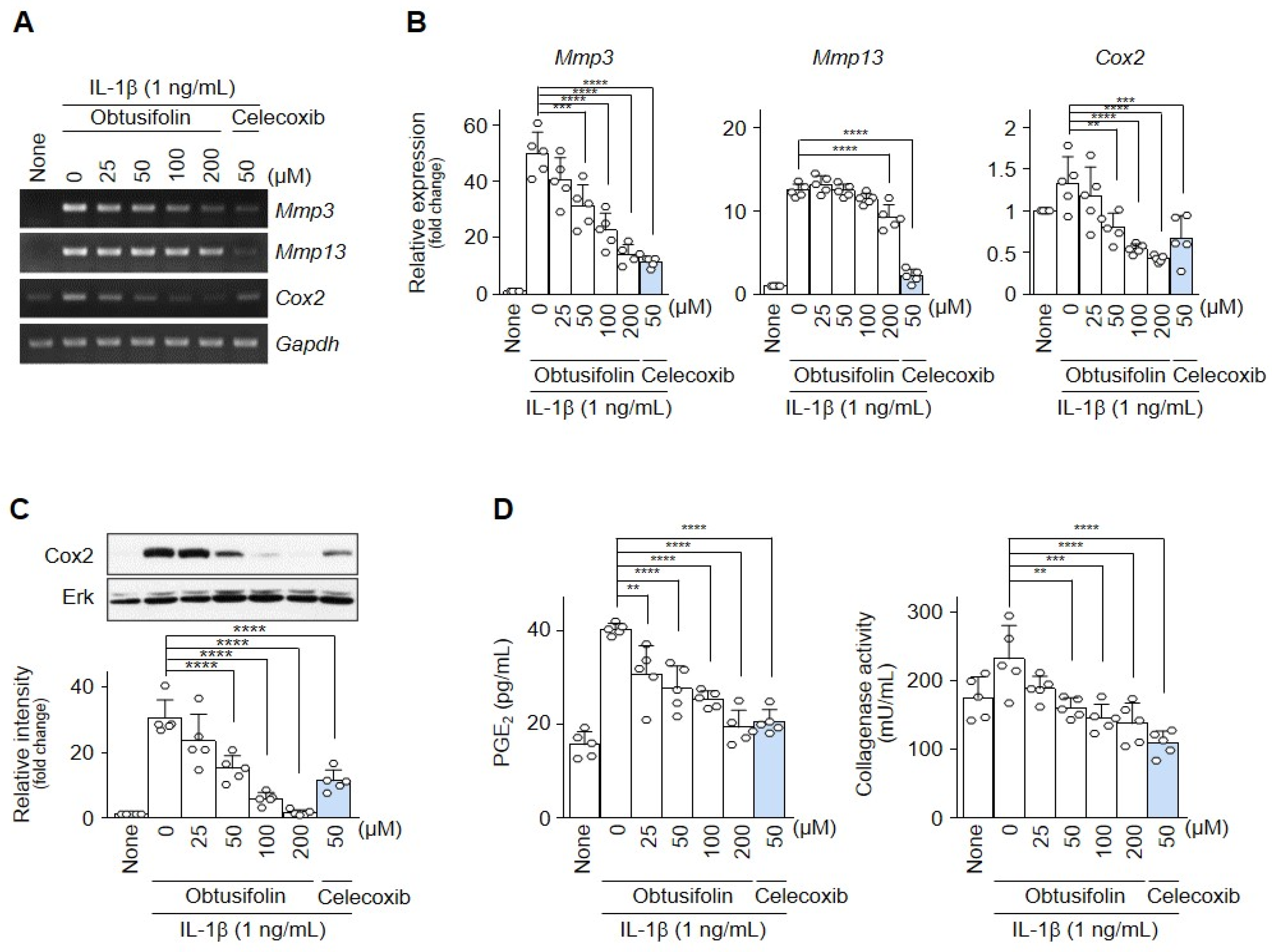
2.2. Obtusifolin Inhibits Factors Involved in OA Pathogenesis
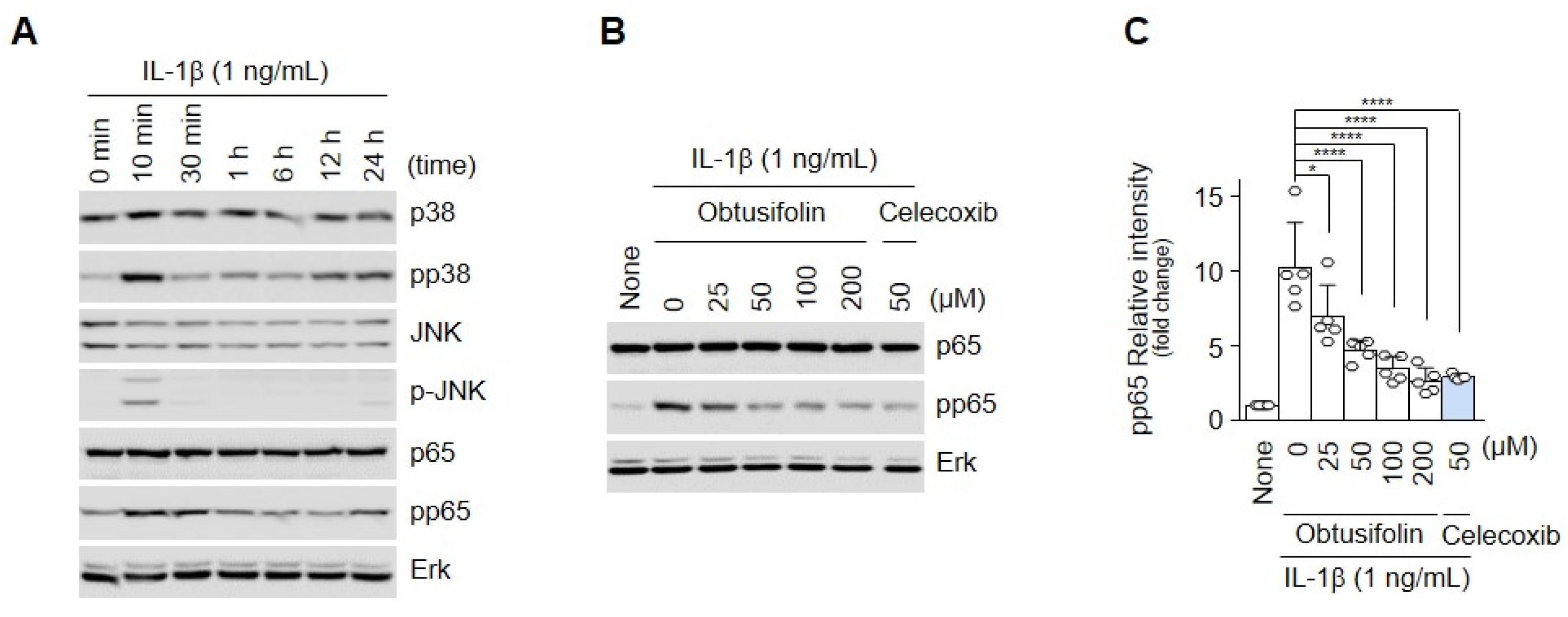
2.3. Obtusifolin Regulates OA through the NF-κB Signaling Pathway
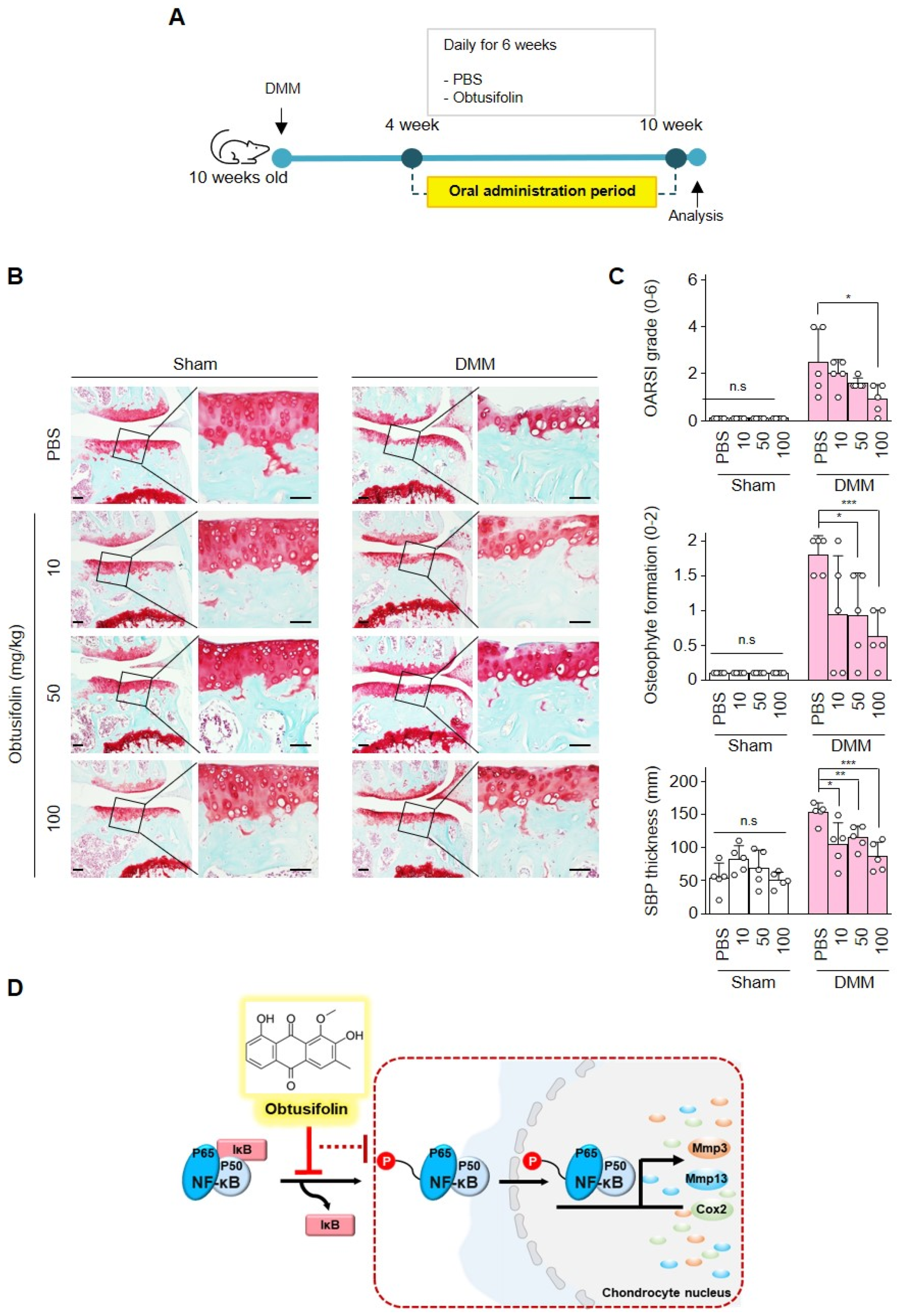
2.4. Effects of Obtusifolin In Vivo and Summary of Mechanism
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Primary Culture of Mouse Articular Chondrocytes and Animals
4.2. In Vitro Chondrocyte Treatment and Reagents
4.3. Cell Cytotoxicity Assay (Lactate Dehydrogenase Assay)
4.4. Transcription and Protein Analyses
4.5. Collagenase Activity and PGE2 Assay
4.6. Experimental OA-Induced Mice and Oral Administration
4.7. Histology Analysis
4.8. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Negoi, T. The epidemiology and impact of pain in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neogi, T.; Zhang, Y. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 39, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeser, R.F.; Goldring, S.R.; Scanzello, C.R.; Goldring, M.B. Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeser, R.F. Aging and osteoarthritis: The role of chondrocyte senescence and aging changes in the cartilage matrix. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2009, 17, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Kim, J.; Ryu, J.H.; Oh, H.; Chun, C.H.; Kim, B.J.; Min, B.H.; Chun, J.S. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha is a catabolic regulator of osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeser, R.F.; Collins, J.A.; Diekman, B.O. Ageing and the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrage, P.S.; Mix, K.S.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. Matrix metalloproteinases: Role in arthritis. Front. Biosci. 2006, 1, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.; Kang, L.J.; Lee, K.M.; Cho, C.; Song, E.K.; Kim, W.; Park, T.J.; Yang, S. 3′-Sialyllactose protects against osteoarthritic development by facilitating cartilage homeostasis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.C.; Jo, J.; Park, J.; Kang, H.K.; Park, Y. NF-κB signaling pathways in osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Cells 2019, 8, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigoglou, S.; Papavassiliou, A.G. The NF-κB signaling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2580–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivitto, E.; Otero, M.; Marcu, K.B.; Goldring, M.B. Pathophysiology of osteoarthritis: Canonical NF-κB/IKKβ-dependent and kinase-independent effects of IKKα in cartilage degradation and chondrocyte differentiation. RMD 2015, 15 (Suppl. S1), e000061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman-Blas, J.A.; Jimemez, S.A. NF-KappaB as a potential therapeutic target in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthr. Carti. 2006, 14, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadass, V.; Vaiyapuri, T.; Tergaonkar, V. Small molecule NF-κB pathway inhibitors in clinic. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haseeb, A.; Chen, D.; Haqqi, T.M. Delphinidin inhibits IL-1β-induced activation of NF-κB by modulating the phosphorylation of IRAK-1Ser376 in human articular chondrocytes. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, M.; Cibere, J.; Sayre, E.C.; Kopec, J.A. Efficacy of commonly prescribed analgesics in the management of osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol. Int. 2018, 38, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, E.M.; Muller, C.E. Anthraquinones as pharmacological tools and drugs. Med. Res. Rev. 2016, 36, 705–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Y.; You, L.; Yin, X.; Fu, J.; Ni, J. Aloe-emodin: A review of its pharmacology, toxicity, and pharmacokinetics. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrimali, D.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Kumar, A.P.; Zhang, J.; Tan, B.K.; Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G. Targeted abrogation of diverse signal transduction cascades by emodin for the treatment of inflammatory disorders and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 341, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshisagar, A.D.; Panchal, P.V.; Harle, U.N.; Nanda, R.K.; Shaikh, H.M. Anti-inflammatory and antiarthritic activity of anthraquinone derivatives in rodents. Int. J. Inflam. 2014, 2014, 690596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zeng, K.; Qiu, Y.; Yan, F.; Lin, C. Therapeutic effect of emodin on collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Inflammation 2013, 36, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.G.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, Y.H.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, Y.; Hong, S.; Kim, K.H.; Yoo, B.C.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of anthraquinone-2-carboxylic acid. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 1903849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savarino, L.; Fioravanti, A.; Leo, G.; Aloisi, R.; Mian, M. Anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonic acid as a disease-modifying osteoarthritis drug: And in vitro and in vivo study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2007, 461, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panova, E.; Jones, G. Benefit-risk assessment of diacerein in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Drug Saf. 2015, 38, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhong, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Sheng, G.T. Obtusifolin inhibits high glucose-induced mitochondrial apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3011–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Hyun, S.K.; Yoon, B.H.; Seo, J.H.; Lee, K.T.; Cheong, J.H.; Jung, S.Y.; Jin, C.; Choi, J.S.; Ryu, J.H. Gluco-obtusifolin and its aglycon, obtusifolin, attenuate scopolamine-induced memory impairment. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 111, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.L.; Tsai, E.M.; Hou, M.F.; Wang, T.N.; Hung, J.Y.; Kuo, P.L. Obtusifolin suppresses phthalate esters-induced breast cancer bone metastasis by targeting parathyroid hormone-related protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11933–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, C.J. Obtusifolin isolated from the seeds of cassia obtusifolia regulates the gene expression and production of MUC5AC mucin in airway epithelial cells via affecting NF-kappaB pathway. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Yang, S.; Shin, Y.; Rhee, J.; Chun, C.H.; Chun, J.S. Interleukin-6 plays an essential role in hypoxia-inducible factor 2a-induced experimental osteoarthritis. Atrhritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2732–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.C.; Xie, Z.J.; Tang, Q.; Li, X.B.; Fu, X.; Feng, Z.H.; Xuan, J.W.; Ni, W.F.; Wu, A.M. Hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA) targets the NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways and ameliorates the development of osteoarthritis. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4443–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklatvala, J. Inflammatory signaling in cartilage: MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways in chondrocytes and the use of inhibitors for research into pathogenesis and therapy of osteoarthritis. Curr. Drug Targets 2007, 8, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.X.; Zou, F.M.; Li, Y.; Liu, A.M.; Tu, M. JNK pathway in osteoarthritis: Pathological and therapeutic aspects. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2017, 37, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.Y.; Hsieh, H.L.; Jou, M.J.; Yang, C.M. Involvement of p42/p44 MAPK, p38 MAPK, JNK and nuclear factor-kappa B in interleukin-1beta-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in rat brain astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2004, 90, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchi, S.; Palumbo, P.; Sponta, A.; Coppolino, M.F. Clinical pharmacology of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; a review. Antiinflamm. Antiallergy Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 11, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, L.D.; Thiele, G.M.; Tian, J.; Wang, D. The development of novel therapies for rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2008, 18, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogoveanu, O.C.; Streba, C.T.; Vere, C.C.; Petrescu, L.; Traistaru, R. Superior digestive tract side effects after prolonged treatment with NSAIDs in patients with osteoarthritis. J. Med. Life 2015, 8, 458–461. [Google Scholar]
- Puljak, L.; Marin, A.; Vrdoljak, D.; Markotic, F.; Utrobicic, A.; Tugwell, P. Celecoxib for osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 5, CD009865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasselt, M.; Baerwald, C. Celecoxib for the treatment of musculoskeletal arthritis. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2019, 20, 168–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellegen, A.R.; Rudnik-Jansen, I.; Pouran, B.; De Visser, H.M.; Weinans, H.H.; Thomas, R.E.; Kik, M.J.L.; Grinwis, G.C.M.; Thies, J.C.; Woike, N.; et al. Controlled release of celecoxib inhibits inflammation, bone cysts and osteophyte formation in a preclinical model of osteoarthritis. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chan, C.O.; Lau, C.C.; Yu, Z.; Mok, D.K.; Chen, S. Simultaneous determination of eight anthraquinones in semen cassia by HPLC-DAD. Phytochem. Anal. 2012, 23, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, T.; Sitarek, P.; Toma, M.; Picot, L.; Wielanek, M.; Skała, E.; Śliwiński, T. An extract of transgenic Senna obtusifolia L. hairy roots with overexpression of Pgss1 gene in combination with chemotherapeutic agent induces apoptosis in the leukemia cell line. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Huo, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Li, X. Anti-inflammatory effects of aurantio-obtusin from seed of cassia obtusifolia L. through modulation of the NF-κB pathway. Molecules 2018, 23, 3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Du, G.; Lu, Y. Anti-inflammatory effects and mechanisms of rhein, and anthraquinone compound, and its applications in treating arthritis: A review. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2020, 10, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.H.; Ye, C.Y.; Chen, E.M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.H. Emodin ameliorates cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis by inhibiting NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling in-vitro and in-vivo. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 61, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.; Noh, H.J.; Lee, H.; Park, H.H.; Ha, Y.J.; Park, S.H.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.J.; Kang, H.C.; Eyun, S.I.; et al. TRIM24-RIP3 axis perturbation accelerates osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, J.; Grassel, S. Experimental osteoarthritis models in mice. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1194, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.; Kang, L.J.; Jang, D.; Jeon, J.; Lee, H.; Choi, S.; Han, S.J.; Oh, E.; Nam, J.; Kim, C.S.; et al. Cirsium japonicum var. maackii and apigenin block Hif-2α-induced osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 5369–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nam, J.; Seol, D.-W.; Lee, C.-G.; Wee, G.; Yang, S.; Pan, C.-H. Obtusifolin, an Anthraquinone Extracted from Senna obtusifolia (L.) H.S.Irwin & Barneby, Reduces Inflammation in a Mouse Osteoarthritis Model. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030249
Nam J, Seol D-W, Lee C-G, Wee G, Yang S, Pan C-H. Obtusifolin, an Anthraquinone Extracted from Senna obtusifolia (L.) H.S.Irwin & Barneby, Reduces Inflammation in a Mouse Osteoarthritis Model. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(3):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030249
Chicago/Turabian StyleNam, Jiho, Dong-Won Seol, Choong-Gu Lee, Gabbine Wee, Siyoung Yang, and Cheol-Ho Pan. 2021. "Obtusifolin, an Anthraquinone Extracted from Senna obtusifolia (L.) H.S.Irwin & Barneby, Reduces Inflammation in a Mouse Osteoarthritis Model" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 3: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030249
APA StyleNam, J., Seol, D.-W., Lee, C.-G., Wee, G., Yang, S., & Pan, C.-H. (2021). Obtusifolin, an Anthraquinone Extracted from Senna obtusifolia (L.) H.S.Irwin & Barneby, Reduces Inflammation in a Mouse Osteoarthritis Model. Pharmaceuticals, 14(3), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030249






