Abstract
Preclinical evidence, accumulated over the past decade, indicates that the angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R) stimulation exerts significant neuroprotective effects in various animal models of neuronal injury, notably in the central nervous system. While the atypical G protein-coupled receptor superfamily nature of AT2R and its related signaling are still under investigation, pharmacological studies have shown that stimulation of AT2R leads to neuritogenesis in vitro and in vivo. In this review, we focus on the potential neuroprotective and neuroregenerative roles of AT2R specifically in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The first section describes the evidence for AT2R expression in the PNS and highlights current controversies concerning the cellular distribution of the receptor. The second section focuses on AT2R signaling implicated in neuronal survival and in neurite outgrowth. The following sections review the relatively few preclinical studies highlighting the putative neuroprotective and neuroregenerative effects of AT2R stimulation in the context of peripheral neuropathy.
1. Introduction
There is a large unmet clinical need for novel therapeutic approaches to reduce disabilities (sensory impairment, motor deficit) and to improve overall quality of life in patients with peripheral neuropathies. The development of effective therapeutic solutions is hampered by the vast etiological spectrum of underlying causes and the persistent gaps in our understanding of the pathophysiological processes involved in peripheral neuropathy. However, accumulating evidence suggests a significant contribution of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) in both neuroprotection and neuroregeneration.
The RAS is well-described and known to regulate arterial blood pressure and ionic homeostasis [1]. The sequential enzymatic cascade of RAS is initiated with renin, a catalytic enzyme produced by kidney and secreted into the systemic circulation, which cleaves liver-derived angiotensinogen (AGT) to produce the decapeptide angiotensin I (Ang I). Pulmonary angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) converts Ang I into angiotensin II (Ang II), the main active component of the RAS. Ang II binds with high and similar affinity to its two principal receptors in humans, the Ang II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and the Ang II type 2 receptor (AT2R) [2]. Other angiotensinogen-derived peptides have been described and are shown in Figure 1. The RAS was first described as an endocrine system. However, it is now considered to be a “ubiquitous” system that is expressed locally in many tissues exerting multiple autocrine/paracrine effects with implications in tissue physiology and homeostasis. The first demonstration of Ang II presence in tissues, in the arterial wall of sheep, dates back to 1980 [3]. Subsequent studies have quantified the synthesis of Ang II by the use of radiolabeled ligands in the heart, kidneys and adrenal glands [4,5,6,7]. Additionally, components of a local RAS have been detected in several tissues including skin, bone, adipose tissue and inflammatory cells [8,9,10]. The localization and effects of local RAS are described in further detail elsewhere [11].
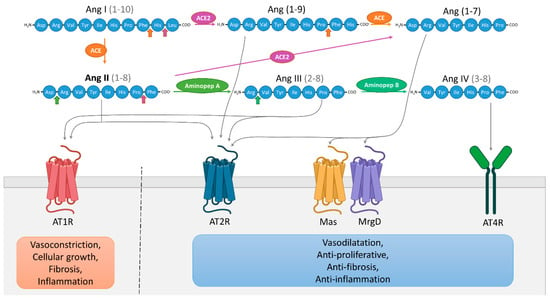
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS). Angiotensin (Ang) I is cleaved by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) to Ang II which can be then cleaved to Ang III by aminopeptidase A, then further cleaved to Ang IV by aminopeptidase B. Ang I can also be cleaved by ACE2 to produce Ang (1–9) which can be cleaved into Ang (1–7) by ACE. Ang (1–7) can be directly generated from Ang II by ACE2. Ang (1–7) binds and activates the receptors Mas and Mas-related G protein-coupled receptor member D (MrgD), Ang IV binds to AT4R, Ang III activates AT1R and AT2R and Ang (1–9) directly activates AT2R. Functionally, it is possible to simplify the RAS into two distinctive pathways [12]. The first involves over-activation of AT1R by Ang II/Ang III, promoting cellular growth, vasoconstriction, fibrosis and inflammation. The second involves the interactions between AT2R and Ang II/Ang (1–9)/Ang III, but also Ang (1–7) and Mas/MrgD receptors, and Ang IV and AT4R, leading to vasodilatation and anti-proliferative, anti-fibrotic, anti-inflammatory effects.
AT1R and AT2R are both seven-transmembrane receptors displaying a similar affinity to Ang II although these two receptors differ in their amino acid sequence, tissue-specific expression and functional effects. The main role of AT2R is to inhibit actions mediated by AT1R by decreasing cell growth and proliferation while promoting cell differentiation, in addition to a vasodilatory action and a decrease in blood pressure [12]. As demonstrated in several studies, AT2R expression is temporally regulated. Ligand binding, in situ hybridization and autoradiography studies show that AT2R is widely expressed during fetal life, whereas its expression is maintained at low levels in all organs in adults, contrary to AT1R which is preferentially expressed in adults [13,14]. On the other hand, recent western blot and RT-PCR studies show that AT2R shows significantly higher expression in adult than in fetal and neonatal rodent tissues, with the exception of skin [15,16]. Such a discrepancy challenges the role of AT2R during development. Moreover, inverse expression profiles of AT1R and AT2R during development have been reported, with decreased expression of AT1R and an increased expression of AT2R in the adult versus fetal stage, suggesting a crucial interacting role between the two receptors [16]. Moreover, AT1R/AT2R heterodimerization has previously been shown in non-neuronal cell types, illustrating the strong link between these two receptors [17]. AT2R expression is also dramatically increased in tissue under pathological conditions, for example during nerve crush injury or inflammation, suggesting a possible role of AT2R in tissue repair and more particularly in neuroregeneration [18,19,20].
While numerous studies have focused on protective and regenerative properties of AT2R in the central nervous system [21,22,23], very few have considered a role for AT2R in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Several reports have emphasized the role of peripheral AT2R in the modulation of pain [24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. However, the potential effects of Ang II/AT2R in neuroprotection/neuroregeneration in the PNS have been understudied and remains poorly understood. A few pharmacological studies, some from our team, highlight the beneficial effect of AT2R stimulation in a rodent model of traumatic- and drug-induced peripheral neuropathy [19,31,32,33,34]. Here, we aim to review the current knowledge on the role of AT2R and the therapeutic effect of respective agonists or antagonists in the treatment of various types of peripheral neuropathies. Basic information concerning the AT2R and its distribution within the PNS are introduced first.
2. Evidence for AT2R Expression in the Peripheral Nervous System
Over the past fifteen years, many studies have supported the concept of a local RAS and its potential role in the PNS, and particularly in the sensory nervous system [27,35,36,37,38]. Nevertheless, the distribution and expression level of AT2R in the PNS has been subject of controversy.
In rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG), AT2R expression, at the mRNA and protein levels, is tightly regulated throughout development to switch later to a restricted subpopulation of C-nociceptor neurons during adult life [39]. Recently, preferential expression of AT2R in non-peptidergic isolectin B4 (IB4+) C-nociceptor neurons was confirmed in adult rat DRG neurons [18]. The authors showed that AT2R is also expressed by some peptidergic small C- and medium Aδ-neurons as well as by a few large Aα- and Aβ-neurons, and that almost all AT2R+ DRG neurons co-expressed AT1R [18] (Figure 2). In humans, positive AT2R-immunolabelling was also shown in small-diameter DRG neurons and in nerve endings in the sub-epidermis and dermis, in urinary bladder, in vestibule and in the myenteric plexus [27,38,40]. This expression profile of AT2R in the PNS suggests its involvement in the development of sensory and nociceptive functions. However, immunohistochemistry (IHC)-based results must be viewed with caution due to the poor specificity of commercially-available AT2R antibodies [24,40]. One study has demonstrated the specificity of one commercial AT2R antibody, ab19134 (Abcam), using AT2R-expressing HEK-cells vs. non-transfected HEK-cells [41]. Nevertheless, recently, a research group reported no difference in AT2R signal intensity in DRG sections from wild type- and agtr2 (the AT2R gene) KO-mice using these same AT2R antibodies [24].
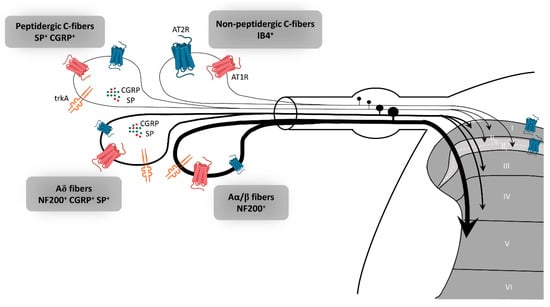
Figure 2.
Expression of AT2R in the sensory peripheral nervous system. According to the most recent immunohistochemistry study on the expression of AT2R in DRG and in the spinal cord of rat, AT2R would be expressed by almost all types of sensory neurons, though to different degrees [18]. Non-peptidergic C-nociceptors expressing IB4 are strongly stained for AT2R. Some small and medium DRG neurons co-expressed AT2R and trkA, a marker of nociceptive neurons (peptidergic C and Aδ neurons). The few large neurons which express AT2R are stained for NF200 and trkA, markers of Aα/β nociceptive neurons. Most ATR2+ neurons are also AT1R+. AT1R: angiotensin II type 1 receptor, AT2R: angiotensin II type 2 receptor, CGRP: calcitonin gene-related peptide, DRG: dorsal root ganglion, IB4: isolectin 4, NF200: neurofilament 200, SP: substance P, trkA: tropomyosin receptor kinase type A.
At the mRNA level, AT2R is upregulated in pathological conditions in the PNS, as has been shown in other tissues such as infarcted heart and regenerating skeletal muscle [42,43]. In response to nerve axotomy and crush injury, AT2R mRNA levels are strongly increased in adult DRG and sciatic nerve fibers in rats [44]. A role for AT2R in Schwann cell (SC)-mediated healing actions has been evoked since the kinetics of AT2R mRNA expression is closely linked to the kinetics of SCs differentiation during nerve recovery. It is important to note that quantification of total AT2R mRNA from DRG encompasses different cell types (i.e., sensory neurons, satellite cells, immune cells, and SCs). SCs themselves have been shown to express AT1R and AT2R in vitro and in fresh samples of rat sciatic nerve, with a higher proportion of AT2R than AT1R [45].
Recently, Shepherd et al. demonstrated that mouse and human DRG neurons do not express AT2R [24]. By combining different technical approaches to investigate the expression of AT2R, the authors pointed out the lack of AT2R expression in mouse DRG neurons, either at the protein- or mRNA-level. In line with this, Ang II did not induce either calcium influx and electrophysiological responses or intracellular signaling in cultured primary mouse DRG neuron. In addition, a lack of GFP signal was observed in DRG sections from AT2R-EGFP reporter mice, suggesting that agtr2 was not expressed either in neurons or in non-neuronal cells of mouse DRG. However, they revealed that peripheral macrophages express a functional AT2R and these could be implicated in Ang II-induced peripheral mechanical pain sensitization [24]. One could envision a paracrine system between DRG neurons that synthesize Ang II and non-neuronal AT2R+ cells such as SCs and/or immune cells that are recruited only during nerve injury [46]. In this respect, the CD3+ T-cells which are involved in mechanical pain in response to chronic constriction injury (CCI) [41] might express AT2R. This cell-cell dialogue, mediated by AT2R in the PNS, could play a key role in neuroprotective and neuroregenerative processes.
With regard to the expression of AT2R by DRG neurons, it appears that species differences likely exist. Most studies conducted in rats have found AT2R to be expressed in DRG neurons while studies performed in mouse DRG neurons have given opposite results [24]. One explanation might be that two isoforms of AT2R exist in mice, as is the case for AT1R (AT1a and AT1b) in mice and rats, and as has already been suggested in the rat brain [47]. In this respect, AT2R-antibodies could detect another isoform of AT2R, which could be expressed in DRG neurons of AT2R KO-mice. It is also important to note that AT2R-deficient mice often only have part of the receptor affected, thus potentially allowing the expression of a truncated form of the protein, which is possibly detected by some antibodies [48,49]. Another hypothesis is that AT2R mRNA is synthesized in DRG neurons under pathological conditions (lesion, crush, section) and transported along microtubules to nerve terminals where it is then translated by a local system [50]. This would provide a rationale for the discrepancies in results obtained from IHC on cultured DRG and DRG sections. Further studies are required to elucidate the questions concerning AT2R expression in the PNS and to understand their function.
3. AT2R Signaling
The AT2R gene was cloned in the early 90′s and the receptor has been attributed numerous functions. However, its signaling pathway remains difficult to elucidate [51,52]. AT2R belongs to the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily (GPCR). However, aside from signaling through G-protein-dependent mechanisms, activation of this receptor by G protein-independent intracellular signaling in neurons makes it an “atypical” or “non-canonical” GPCR. The recently described crystal structure of human AT2R bound to either Ang II or an AT2R-selective ligand, allowed the receptor to be captured in an active-like conformation and provided structural insights into a moderate coupling to G proteins [53,54]. Continuing efforts investigating the conformational arrangement of this receptor are necessary to complete our understanding of AT2R activation and signaling and will aid in better design of targeted compounds [55]. In the following section, we will specifically review the role of AT2R signaling implicate in neuronal survival and neurite outgrowth and summarize the current findings in a schematic (Figure 3).
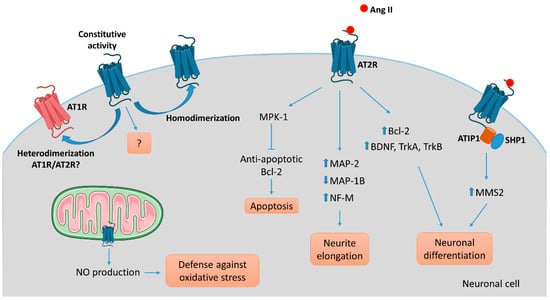
Figure 3.
AT2R-mediated intracellular signaling pathways involved in neuronal cells. Several intracellular signaling pathways are associated with AT2R activation in neuronal cells leading to apoptosis via activation of the phosphatase MPK-1, neurite elongation via reorganization of the cytoskeleton, or neuronal differentiation in part via upregulation of growth-factors, depending on the cell type, the context, and the environment. To date, ATIP1 is identified as a partner of AT2R involved in intracellular signaling pathway and trafficking in neuronal cells. While the evidence of an ATIP/AT2R complex comes from experiments on central nervous system neurons, we could hypothesize that a similar system exists in PNS neurons. AT2R signaling may antagonize AT1R-mediated signaling by a direct heterodimerization between the two. As well, homodimerization of AT2R might result in ligand-independent signaling.
To understand AT2R signal transduction, several cellular tools have been used. Among them, the rat pheochromocytoma PC12W cell line, of neuronal origin, has been particularly useful since these cells mostly express AT2R rather than AT1R. Several studies, focused on the effect of Ang II on PC12W cells, have demonstrated that AT2R mediates programmed cell death through inactivation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibition of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein resulting eventually in induction of apoptosis [56,57]. This apoptotic function of AT2R was once hypothesized to be involved in developmental biology and pathophysiology. However, it was later demonstrated that AT2R stimulation by C21, a specific agonist [58], induced RNA expression of Bcl-2 and increased the level of neurotrophins (BDNF, TrkA and TrkB) in vitro in primary neurons and in vivo in a model of spinal cord injury [59]. In quiescent PC12W cells, AT2R stimulation by Ang II treatment leads to neurite formation [60]. In this case, the signaling involves an increase in polymerized β-tubulin, upregulation of microtubule-associated protein (MAP)-2 and down-regulation of MAP-1B levels. Similar observations were made in PC12W cells differentiated by nerve growth factor (NGF) and in undifferentiated NG108-15 cells (mouse neuroblastoma x rat glioma hybrid cell line) [60,61]. MAP-2 proteins are known to interact with microtubules, neurofilaments and actin, and contribute to the maintenance of the neuronal cytoskeleton. Similarly, MAP-1B regulates branching and neurite direction during DRG neuron regeneration [62]. A significant decrease in MAP-2 expression was observed in DRG following CCI to the sciatic nerve in rats, suggesting the involvement of MAP-2 in the early response to nerve injury [63]. Ang II treatment also diminishes the expression of neurofilament-M at the protein and mRNA levels in PC12W cells, and this effect is suppressed by preventive treatment with PD123177 (an AT2R antagonist) [64]. Thus, AT2R stimulation in vitro decreases proliferation and leads to neuronal differentiation and to anarchic neurite elongation via reorganization of cytoskeletal components. In undifferentiated NG108-15 and PC12W cells, both cell types expressing AT2R but not AT1R, Ang II-induced neuronal differentiation, and thus neurite elongation, is counteracted by AT1R stimulation in differentiated neuronal cells expressing AT1R [61]. Therefore, these data highlight the precise regulation existing between AT2R and AT1R during neuronal differentiation and neurite elongation. In NG108-15 cells, Ang II/AT2R interaction leads to neurite outgrowth through a sustained activation of p42/p44 MAPK and phosphorylation of trkA [65,66]. The link between AT2R and activation of p42/p44 MAPK leading to neurite outgrowth was further confirmed in cultured adult rat DRG neurons, another optimal in vitro model in which to investigate the effects of AT2R modulation on PNS neurons [67]. In this later study, neurons treated with Ang II presented denser and much longer neurites than controls, confirming results obtained in neuronal cell lines.
It has also been demonstrated that the morphological differentiation induced by Ang II/AT2R involves an increase in nitric oxide (NO) production in the NG108-05 cell line [68]. An increase of neuronal NO synthase (nNOS) was observed in cultures of rat DRG neurons under stress conditions [69]. The neuroprotective role of NO has already been described in vitro and in vivo in rat DRG neurons [69,70,71]. In vivo, inhibition of nNOS aggravates DRG neuron injuries, such as in a rat model of sciatic nerve transection, suggesting a neuroprotective role of NO [71]. A more detailed review of the role of NO in neuronal proliferation, survival and differentiation can be found elsewhere [72]. A functional mitochondrial angiotensin system has been reported in several cellular types, including neuronal cells [73]. AT2R was localized on the inner mitochondrial membrane by immunogold electron microscopy, and its stimulation increased NO production, thus decreasing mitochondrial respiration [74]. This phenomenon could represent a defense against oxidative stress, and a neuroprotective function of AT2R. However, the presence of AT2R in mitochondria from PNS neurons has not thus far been investigated.
In 2007, Li et al., showed, in neuronal cells, that AT2R interacts with ATIP1, the first member of the AT2-interacting protein (ATIP) family, to induce neuronal differentiation via upregulation of methane methylsulfonate-sensitive 2 (MMS2) [75]. ATIPs are a family of proteins encoded by alternative splicing of a single gene called mtus1 (Microtubule associated tumor suppressor 1); ATIP1, ATIP3 and ATIP4 being the major isoforms. ATIP1 and ATIP3 are widely distributed whereas ATIP4 is restricted to the central nervous system [76]. The ATIPs are cytosolic proteins that constitutively interact with the C-terminal domain of AT2R and are involved in intracellular transport and signaling pathways of AT2R, depending on the cell-type and on the isoform [77,78]. ATBP50, the murine ATIP1, was identified as a Golgi-associated protein involved in the transport of the AT2R to the cell membrane [78]. In neuronal cells, AT2R activation induces the ATIP1-Src homology phosphatase 1 (SHP1) complex, leading to transcriptional activation of the DNA repair enzyme MMS2, and then induction of neuronal differentiation [75].
While progress has been made in understanding AT2R signaling, this receptor remains an enigma. Other review articles have emphasized in great detail the limitations of AT2R signaling studies [12,79,80,81].
4. Neuroprotection
Neuroprotection is defined as the ability for a therapy to prevent neuronal cell death by intervening in and inhibiting the pathogenic cascade that results in cell dysfunction and eventually in neuronal death. Most peripheral neuropathies are axon length dependent and result in distal axonal degeneration rather than loss of neuronal cell bodies. Thus, the ideal neuroprotective molecule should limit distal axonal degeneration, favor axon-glia interactions, and promote axonal regeneration and connection with the target cells. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory axes are key mechanisms involved in neuroprotection.
In the central nervous system, blockade of AT1R protects against ischemic brain damage, notably by reversing oxidative stress and inflammation [82,83]. These neuroprotective effects during AT1R blocker treatment are associated with a relative increase of AT2R stimulation by Ang II [84]. Further studies evaluating direct AT2R stimulation by the agonists CGP42112 or C21 have confirmed anti-inflammatory and tissue repair effects of AT2R in rodent models of stroke using middle cerebral artery occlusion [85,86,87]. Protective effects of AT2R modulation in diverse neuronal populations in a wide range of brain injuries including ischemic strokes, ischemia/reperfusion injury, inflammation and others, have already been reviewed elsewhere [88,89].
A small number of in vivo preclinical studies have highlighted the putative neuroprotective effect of AT2R stimulation on peripheral neuropathies. In the first study, candesartan (an AT1R antagonist) treatment prevented functional sensory neuropathy in a rat model of type 2 diabetes of fructose-induced insulin resistance [32]. In this model, the peripheral neuropathy was characterized by hypoalgesia in response to a noxious thermal stimulus. These authors also showed that insulin resistance resulted in a decrease of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-immunoreactive nerves in mesenteric arteries and an increase of AT2R expression and dysfunction in DRG neurons. This significant increase of AT2R expression in the DRG of fructose drinking rats (FDR) reinforces the concept that AT2R plays an important role in nerves under pathological conditions. When candesartan was administered at the same time as fructose in FDR, sensory nerve disorders were improved, the density of CGRP+ nerves was increased to match control levels and the high AT2R expression in DRG neurons was suppressed. Moreover, in FDR, AT1R blockade improved AT2R-mediated neurite outgrowth and restored Akt signaling [32]. Once again, these results reveal the strong functional interconnection that is present between AT1R and AT2R in peripheral nerves.
In our previous studies, we have shown several lines of evidence that direct or indirect stimulation of AT2R could prevent the development of sensory impairment in mouse models of toxin-induced neuropathies. First, in a mouse model of resiniferatoxin (RTX)-induced functional neuropathy, we showed that AT1R blockade by preventive administration of candesartan restored the RTX-induced thermal hypoalgesia and improved the depletion of substance P (SP) and CGRP in intraepidermal nerve fibers (IENFs) and in DRG neurons. This effect of candesartan was blocked by PD123319 (or EMA200), an AT2R blocker, and also in the AT2R KO mouse model. Therefore, we concluded that the neuroprotective effect of AT1R blockade was mediated by the promotion of AT2R activation by Ang II and the increase in tissue Ang II level [31]. Secondly, in a mouse model of vincristine (VCR)-induced tactile allodynia, administration of candesartan and C21 accelerated the recovery of normal tactile sensitivity. This beneficial effect of candesartan and C21 was abolished by PD123319. Both drugs also prevented VCR-induced non-peptidergic IENF loss [19]. We also showed that direct AT2R stimulation by C21 prevented myelinated fiber loss and the enlargement of myelinated axonal diameter induced by VCR in our mouse model [19].
Interestingly, all of the above studies which highlight the neuroprotective effect of AT2R in the PNS were performed using rodent models of “toxin”-induced neuropathy, rather than traumatic models.
5. Neuroregeneration
In contrast to the central nervous system, injured axons in the PNS maintain regenerative capacities. Neuroregeneration involves neuronal and non-neuronal responses resulting in restoration of neuronal connectivity and functional recovery. Injured peripheral axons have to regrow over long distances to reestablish synaptic connections with their targets in the periphery. Failure of axonal regrowth contributes to muscle atrophy or to loss of function of end-organs. In order to combat these effects and improve functional outcomes following PNS injury, the goal of an ideal treatment would be to accelerate axonal regeneration.
5.1. In Vitro
The neuroregenerative properties of AT2R stimulation were first highlighted in the PC12W neuronal cell line, which is responsive to NGF treatment. Data in PC12W cells showed that AT2R stimulation by Ang II enhances neurite elongation and promotes NGF-induced neuronal differentiation. AT2R stimulation inhibits growth factor-induced proliferation and enhances NGF-mediated growth arrest. All of the effects of Ang II in PC12W and NG108-15 cells were suppressed by pretreatment with PD123319 [90,91]. The same neuroregenerative effect of Ang II was observed in primary cultures of neonatal rat DRG neurons. This Ang II effect is inhibited by PD123177 (an AT2R blocker) treatment but not by losartan (an AT1R blocker) [20]. Using the same experimental paradigm, others have recently shown that the neuritogenesis properties of Ang II are counteracted by AT2R (PD123312)- as well as by AT1R (azilsartan)- antagonism [18]. Moreover, addition of Ang II in the culture medium induced neurite outgrowth in small to medium sized neurons positive for peripherin and this neuritogenesis was inhibited by PD123319 [37]. Hashikawa-Hobara and Hashikawa (2016) showed that AT2R-stimulation by CGP42112, a selective agonist of AT2R, induced neurite outgrowth in a primary culture of adult mouse DRG cells [92]. This result was also previously reported using rat and human DRG cell cultures treated with C21 or Ang II [27,67]. This positive effect of AT2R stimulation on neurite length and neurite density, shown with Gap43 staining (an axonal regeneration marker), was reduced after EMA401 (an AT2R antagonist) treatment [67].
5.2. In Vivo
To explore the neuroregenerative effects of drugs on the PNS, nerve transection and crush injury models in rodents have been widely used as the most representative models of traumatic peripheral neuropathy allowing the identification of key repair mechanisms. Local administration of Ang II in a rat model of sciatic nerve crush showed enhanced neuroregenerative mechanisms by accelerating recovery of sensorimotor function and by enhancing axonal regeneration and myelination [34]. All of these Ang II-mediated regenerating effects were blocked by PD123319. The authors concluded that this AT2R-dependent neuroregenerative effect could be due to the stimulation of AT2R in SCs with subsequent nuclear translocation of NF-κb, which is essential for myelin formation. In a rat model of inflammatory pain, one study has reported that hind paw injection of complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) induced cutaneous hyper-innervation associated with mechanical and thermal hypersensitivity at 3 days post-CFA injection. Simultaneous infusion of an AT2R blocker (PD123319) with CFA abolished dermal and epidermal hyper-innervation and reduced associated-hypersensitivity [93,94]. These results highlight the involvement of AT2R activation in inflammation-induced cutaneous hyper-innervation. The authors also demonstrated that a local RAS is expressed by the inflammatory cells, which have been recruited at the CFA injection site. Further investigations were performed on tissue from patients with provoked vulvodynia (PVD) [38]. PVD is characterized as a localized provoked pain in the vulvar vestibule, attributed to an increase of nociceptors in the vestibular endoderm and elevated numbers of inflammatory cells [95,96,97]. Tender tissue from PVD patient shows hyper-innervation and an increased number of T-cells, B-cells and macrophages compared with non-tender areas. The authors demonstrated that all of the necessary RAS components to synthesize Ang II are present in tender tissue and provided by inflammatory cell migration and/or proliferation. They also showed that neurite outgrowth is induced by tender tissue-conditioned medium in primary cultures of neonatal rat DRG neurons, and that this effect is prevented by adding Ang II antibody or PD123319 [38]. Recently, Benitez et al. 2020 showed that pharmacological inhibition of AT1R has greater impact on CGRP+ axonal endings whereas inhibition of AT2R has more effect on IB4+ nociceptors under physiological conditions [18]. They reported that AT2R but also AT1R are involved in neuritogenesis of these nociceptors. These data confirm, in vivo, both the neuroregenerative properties of AT2R stimulation in the PNS and the interplay of AT1R and AT2R.
6. Concluding Remarks
Recent data have provided evidence that AT2R plays an important role in the protection and regeneration of the sensory nervous system. The complex and enigmatic nature of AT2R, as coined by Sadybekov and Katritch, and its related signaling, leaves many unanswered questions about its function [55]. Intracellular events generated by what is considered as an atypical GPCR are numerous and tissue-type dependent. A better understanding of AT2R ligand-independent activity and signaling cascades is critical and would enable us to define the physiological and functional contributions of this receptor.
Despite controversies about the expression of AT2R in the PNS, mainly due to the poorly characterized antibodies that are commercially available, pharmacological studies have shown that stimulation of AT2R leads to neuritogenesis in vitro and in vivo (Table 1), supporting the rationale that the peripheral AT2R may be an effective therapeutic target. In this instance, development of AT2R agonists could be beneficial in the case of traumatic or toxic peripheral neuropathies involving sensory axon loss. On the other hand, AT2R agonists may be deleterious in the case of inflammatory disease involving hyper-innervation. Thus, in vestibulodynia, treatment with PD123319 (an AT2R blocker) appears to be effective in reducing AT2R-dependent hyper-innervation and associated pain.

Table 1.
Neuroprotective and neuroregenerative effect of AT2R stimulation in the peripheral nervous system.
However, the relevance of AT2R targeting remains to be fully established since the latest clinical trials with EMA401 performed by Novartis have been terminated prematurely due to safety issues [28]. A similar contradiction applies to our understanding of AT2R involvement in modulation of pain [98]. While some studies have reported an analgesic effect following AT2R blockade, others have shown that AT2R stimulation prevents neuropathic pain [98]. Improved knowledge of the RAS and particularly of AT2Rs in the PNS provide possible new approaches, novel methods and promising targets to address unmet medical needs among patients with peripheral neuropathy.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, A.D. (Aurore Danigo), A.R.; writing—review and editing, A.D. (Aurore Danigo), A.R., F.B., H.B., A.B., A.D. (Alexis Desmoulière), C.D.; visualization, F.S., L.M., S.B.; supervision, C.D., A.D. (Alexis Desmoulière), L.M.; project administration, C.D., A.D. (Aurore Danigo); funding acquisition, C.D., A.D. (Aurore Danigo), F.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from CHU de Limoges [APREL (Appel à projets équipes émergentes/équipes labellisées) « 2018 »], sponsored by ARS Nouvelle Aquitaine and from the association “La Ligue Contre le Cancer 87”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
Claire Demiot is part of the French neuropsychopharmacology consortium of SFPT (“Société Française de Pharmacologie et de Thérapeutique”).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
References
- Rettig, R.; Healy, D.P.; Printz, M.P. Cardiovascular Effects of Microinjections of Angiotensin II into the Nucleus Tractus Solitarii. Brain Res. 1986, 364, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosnyak, S.; Jones, E.S.; Christopoulos, A.; Aguilar, M.I.; Thomas, W.G.; Widdop, R.E. Relative Affinity of Angiotensin Peptides and Novel Ligands at AT1 and AT2 Receptors. Clin. Sci. (Lond. Engl. 1979) 2011, 121, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, D.T.; Coghlan, J.P.; Fernley, R.T.; Scoggins, B.A.; Tregear, G.W. Peripheral Production of Angiotensin II and III in Sheep. Circ Res 1980, 46, I135–I137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, C.; Lindell, K.; Ottosson, M.; Carlsson, B.R.; Carlsson, L.M.S. Human Adipose Tissue Expresses Angiotensinogen and Enzymes Required for Its Conversion to Angiotensin II. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 3925–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kats, J.P.; Danser, A.H.; van Meegen, J.R.; Sassen, L.M.; Verdouw, P.D.; Schalekamp, M.A. Angiotensin Production by the Heart: A Quantitative Study in Pigs with the Use of Radiolabeled Angiotensin Infusions. Circulation 1998, 98, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kats, J.P.; van Meegen, J.R.; Verdouw, P.D.; Duncker, D.J.; Schalekamp, M.A.; Danser, A.H. Subcellular Localization of Angiotensin II in Kidney and Adrenal. J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Thiel, B.S.; Góes Martini, A.; Te Riet, L.; Severs, D.; Uijl, E.; Garrelds, I.M.; Leijten, F.P.; van der Pluijm, I.; Essers, J.; Qadri, F.; et al. Brain Renin–Angiotensin System. Hypertension 2017, 69, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurewicz, M.; McDermott, D.H.; Sechler, J.M.; Tinckam, K.; Takakura, A.; Carpenter, C.B.; Milford, E.; Abdi, R. Human T and Natural Killer Cells Possess a Functional Renin-Angiotensin System: Further Mechanisms of Angiotensin II-Induced Inflammation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steckelings, U.M.; Wollschläger, T.; Peters, J.; Henz, B.M.; Hermes, B.; Artuc, M. Human Skin: Source of and Target Organ for Angiotensin II. Exp. Dermatol. 2004, 13, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, A.; Zouein, F.A.; Zayeri, Z.D.; Zibara, K. An Update on the Tissue Renin Angiotensin System and Its Role in Physiology and Pathology. JCDD 2019, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Poyan Mehr, A.; Kreutz, R. Physiology of Local Renin-Angiotensin Systems. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 747–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouet, S.; Nahmias, C. Signal Transduction from the Angiotensin II AT2 Receptor. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, E.F.; Sechi, L.A.; Griffin, C.A.; Schambelan, M.; Kalinyak, J.E. Expression of AT2 Receptors in the Developing Rat Fetus. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 88, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenkei, Z.; Palkovits, M.; Corvol, P.; Llorens-Cortès, C. Expression of Angiotensin Type-1 (AT1) and Type-2 (AT2) Receptor MRNAs in the Adult Rat Brain: A Functional Neuroanatomical Review. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 1997, 18, 383–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Chao, J.; Parbhu, K.-J.K.; Yu, L.; Xiao, L.; Gao, F.; Gao, L. Ontogeny of Angiotensin Type 2 and Type 1 Receptor Expression in Mice. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2012, 13, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Shao, C.; Gao, L. Developmental Expression Patterns for Angiotensin Receptors in Mouse Skin and Brain. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. JRAAS 2014, 15, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdAlla, S.; Lother, H.; Abdel-tawab, A.M.; Quitterer, U. The Angiotensin II AT2 Receptor Is an AT1 Receptor Antagonist. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 39721–39726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benitez, S.G.; Seltzer, A.M.; Messina, D.N.; Foscolo, M.R.; Patterson, S.I.; Acosta, C.G. Cutaneous Inflammation Differentially Regulates the Expression and Function of Angiotensin-II Types 1 and 2 Receptors in Rat Primary Sensory Neurons. J. Neurochem. 2020, 152, 675–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessaguet, F.; Danigo, A.; Bouchenaki, H.; Duchesne, M.; Magy, L.; Richard, L.; Sturtz, F.; Desmoulière, A.; Demiot, C. Neuroprotective Effect of Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor Stimulation in Vincristine-Induced Mechanical Allodynia. PAIN 2018, 159, 2538–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucius, R.; Gallinat, S.; Rosenstiel, P.; Herdegen, T.; Sievers, J.; Unger, T. The Angiotensin II Type 2 (AT2) Receptor Promotes Axonal Regeneration in the Optic Nerve of Adult Rats. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimond, M.-O.; Gallo-Payet, N. How Does Angiotensin AT2 Receptor Activation Help Neuronal Differentiation and Improve Neuronal Pathological Situations? Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namsolleck, P.; Recarti, C.; Foulquier, S.; Steckelings, U.M.; Unger, T. AT(2) Receptor and Tissue Injury: Therapeutic Implications. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2014, 16, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilms, H.; Rosenstiel, P.; Unger, T.; Deuschl, G.; Lucius, R. Neuroprotection with Angiotensin Receptor Antagonists: A Review of the Evidence and Potential Mechanisms. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2005, 5, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, A.J.; Copits, B.A.; Mickle, A.D.; Karlsson, P.; Kadunganattil, S.; Haroutounian, S.; Tadinada, S.M.; de Kloet, A.D.; Valtcheva, M.V.; McIlvried, L.A.; et al. Angiotensin II Triggers Peripheral Macrophage-to-Sensory Neuron Redox Crosstalk to Elicit Pain. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 7032–7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, A.J.; Mickle, A.D.; Golden, J.P.; Mack, M.R.; Halabi, C.M.; de Kloet, A.D.; Samineni, V.K.; Kim, B.S.; Krause, E.G.; Gereau, R.W.; et al. Macrophage Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor Triggers Neuropathic Pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8057–E8066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.K.; O’Hara, C.L.; Stucky, C.L. Mechanical Sensitization of Cutaneous Sensory Fibers in the Spared Nerve Injury Mouse Model. Mol. Pain 2013, 9, 1744–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, U.; Yiangou, Y.; Sinisi, M.; Fox, M.; MacQuillan, A.; Quick, T.; Korchev, Y.E.; Bountra, C.; McCarthy, T.; Anand, P. Mechanisms Underlying Clinical Efficacy of Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor (AT2R) Antagonist EMA401 in Neuropathic Pain: Clinical Tissue and in Vitro Studies. Mol. Pain 2015, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.S.C.; Dworkin, R.H.; McCarthy, T.D.; Anand, P.; Bountra, C.; McCloud, P.I.; Hill, J.; Cutter, G.; Kitson, G.; Desem, N.; et al. EMA401, an Orally Administered Highly Selective Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor Antagonist, as a Novel Treatment for Postherpetic Neuralgia: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Clinical Trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, E.; Song, O.R.; Christophe, T.; Babonneau, J.; Fenistein, D.; Eyer, J.; Letournel, F.; Henrion, D.; Clere, N.; Paille, V.; et al. Mycobacterial Toxin Induces Analgesia in Buruli Ulcer by Targeting the Angiotensin Pathways. Cell 2014, 157, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, O.-R.; Kim, H.-B.; Jouny, S.; Ricard, I.; Vandeputte, A.; Deboosere, N.; Marion, E.; Queval, C.J.; Lesport, P.; Bourinet, E.; et al. A Bacterial Toxin with Analgesic Properties: Hyperpolarization of DRG Neurons by Mycolactone. Toxins 2017, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessaguet, F.; Danigo, A.; Magy, L.; Sturtz, F.; Desmoulière, A.; Demiot, C. Candesartan Prevents Resiniferatoxin-Induced Sensory Small-Fiber Neuropathy in Mice by Promoting Angiotensin II-Mediated AT2 Receptor Stimulation. Neuropharmacology 2017, 126, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashikawa-Hobara, N.; Hashikawa, N.; Inoue, Y.; Sanda, H.; Zamami, Y.; Takatori, S.; Kawasaki, H. Candesartan Cilexetil Improves Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor-Mediated Neurite Outgrowth via the PI3K-Akt Pathway in Fructose-Induced Insulin-Resistant Rats. Diabetes 2012, 61, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobara, N.; Goda, M.; Yoshida, N.; Takatori, S.; Kitamura, Y.; Mio, M.; Kawasaki, H. Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptors Facilitate Reinnervation of Phenol-Lesioned Vascular Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide-Containing Nerves in Rat Mesenteric Arteries. Neuroscience 2007, 150, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinecke, K.; Lucius, R.; Reinecke, A.; Rickert, U.; Herdegen, T.; Unger, T. Angiotensin II Accelerates Functional Recovery in the Rat Sciatic Nerve in Vivo: Role of the AT2 Receptor and the Transcription Factor NF-KappaB. Faseb J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2003, 17, 2094–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, J.; Tang, H.; Brimijoin, S.; Moughamian, A.; Nishioku, T.; Benicky, J.; Saavedra, J.M. Expression and Transport of Angiotensin II AT1 Receptors in Spinal Cord, Dorsal Root Ganglia and Sciatic Nerve of the Rat. Brain Res. 2008, 1246, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, J.; Schwab, A.; Nussberger, J.; Schaffner, T.; Saavedra, J.M.; Imboden, H. Intraneuronal Angiotensinergic System in Rat and Human Dorsal Root Ganglia. Regul. Pept. 2010, 162, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, A.; Blacklock, A.; Svojanovsky, S.; Smith, P.G. Estrogen Elicits Dorsal Root Ganglion Axon Sprouting via a Renin-Angiotensin System. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 3452–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Chakrabarty, A.; Mu, Y.; Bhattacherjee, A.; Goestch, M.; Leclair, C.M.; Smith, P.G. A Local Inflammatory Renin-Angiotensin System Drives Sensory Axon Sprouting in Provoked Vestibulodynia. J. Pain 2017, 18, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benitez, S.; Seltzer, A.; Acosta, C. Nociceptor-like Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons Express the Angiotensin-II AT2 Receptor throughout Development. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. Off. J. Int. Soc. Dev. Neurosci. 2017, 56, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafko, R.; Villapol, S.; Nostramo, R.; Symes, A.; Sabban, E.L. Commercially Available Angiotensin II At 2 Receptor Antibodies Are Nonspecific. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 69234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Muralidharan, A.; Smith, M.T. Attenuation of the Infiltration of Angiotensin II Expressing CD3+ T-Cells and the Modulation of Nerve Growth Factor in Lumbar Dorsal Root Ganglia—A Possible Mechanism Underpinning Analgesia Produced by EMA300, An Angiotensin II Type 2 (AT2) Receptor Ant. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nio, Y.; Matsubara, H.; Murasawa, S.; Kanasaki, M.; Inada, M. Regulation of Gene Transcription of Angiotensin II Receptor Subtypes in Myocardial Infarction. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Huq, T.S.; Delafontaine, P. Angiotensin Type 2 Receptor Signaling in Satellite Cells Potentiates Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 26239–26248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallinat, S.; Yu, M.; Dorst, A.; Unger, T.; Herdegen, T. Sciatic Nerve Transection Evokes Lasting Up-Regulation of Angiotensin AT2 and AT1 Receptor MRNA in Adult Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia and Sciatic Nerves. Mol. Brain Res. 1998, 57, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleuel, A.; de Gasparo, M.; Whitebread, S.; Püttner, I.; Monard, D. Regulation of Protease Nexin-1 Expression in Cultured Schwann Cells Is Mediated by Angiotensin II Receptors. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Bembrick, A.L.; Keay, K.A.; McLachlan, E.M. Immune Cell Involvement in Dorsal Root Ganglia and Spinal Cord after Chronic Constriction or Transection of the Rat Sciatic Nerve. Brain Behav. Immun. 2007, 21, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, K.; Saavedra, J.M. Heterogeneity of Angiotensin II AT2 Receptors in the Rat Brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 1992, 41, 290–297. [Google Scholar]
- Hein, L.; Barsh, G.S.; Pratt, R.E.; Dzau, V.J.; Kobilka, B.K. Behavioural and Cardiovascular Effects of Disrupting the Angiotensin II Type-2 Receptor in Mice. Nature 1995, 377, 744–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiki, T.; Labosky, P.A.; Shiota, C.; Okuyama, S.; Imagawa, Y.; Fogo, A.; Niimura, F.; Ichikawa, I.; Hogan, B.L.; Inagami, T. Effects on Blood Pressure and Exploratory Behaviour of Mice Lacking Angiotensin II Type-2 Receptor. Nature 1995, 377, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.H.W.; Lin, J.Q.; Ströhl, F.; Roque, C.G.; Cioni, J.M.; Cagnetta, R.; Turner-Bridger, B.; Laine, R.F.; Harris, W.A.; Kaminski, C.F.; et al. RNA Docking and Local Translation Regulate Site-Specific Axon Remodeling In Vivo. Neuron 2017, 95, 852–868.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, M.; Mukoyama, M.; Pratt, R.E.; Horiuchi, M.; Dzau, V.J. Cloning of CDNA and Analysis of the Gene for Mouse Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 197, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukoyama, M.; Nakajima, M.; Horiuchi, M.; Sasamura, H.; Pratt, R.E.; Dzau, V.J. Expression Cloning of Type 2 Angiotensin II Receptor Reveals a Unique Class of Seven-Transmembrane Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 24539–24542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, H.; Horita, S.; Hirata, K.; Shiroishi, M.; Shiimura, Y.; Iwanari, H.; Hamakubo, T.; Shimamura, T.; Nomura, N.; Kusano-Arai, O.; et al. Crystal Structure of the Human Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor Bound to an Angiotensin II Analog. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, H.; Inoue, A.; Ngako Kadji, F.M.; Hirata, K.; Shiimura, Y.; Im, D.; Shimamura, T.; Nomura, N.; Iwanari, H.; Hamakubo, T.; et al. The Crystal Structure of Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor with Endogenous Peptide Hormone. Structure 2020, 28, 418–425.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadybekov, A.; Katritch, V. Breaking the Enigma Code of Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor Signaling. Structure 2020, 28, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Horiuchi, M.; Dzau, V.J. Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor Mediates Programmed Cell Death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, M.; Hayashida, W.; Kambe, T.; Yamada, T.; Dzau, V.J. Angiotensin Type 2 Receptor Dephosphorylates Bcl-2 by Activating Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase-1 and Induces Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 19022–19026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Wallinder, C.; Plouffe, B.; Beaudry, H.; Mahalingam, A.K.; Wu, X.; Johansson, B.; Holm, M.; Botoros, M.; Karlén, A.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation, of the First Selective Nonpeptide AT2 Receptor Agonist. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 5995–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namsolleck, P.; Boato, F.; Schwengel, K.; Paulis, L.; Matho, K.S.; Geurts, N.; Thöne-Reineke, C.; Lucht, K.; Seidel, K.; Hallberg, A.; et al. AT2-Receptor Stimulation Enhances Axonal Plasticity after Spinal Cord Injury by Upregulating BDNF Expression. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 51, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroth, U.; Meffert, S.; Gallinat, S.; Unger, T. Angiotensin II and NGF Differentially Influence Microtubule Proteins in PC12W Cells: Role of the AT2 Receptor. Mol. Brain Res. 1998, 53, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laflamme, L.; de Gasparo, M.; Gallo, J.-M.; Payet, M.D.; Gallo-Payet, N. Angiotensin II Induction of Neurite Outgrowth by AT 2 Receptors in NG108-15 Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 22729–22735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouquet, C.; Soares, S.; von Boxberg, Y.; Ravaille-Veron, M.; Propst, F.; Nothias, F. Microtubule-Associated Protein 1B Controls Directionality of Growth Cone Migration and Axonal Branching in Regeneration of Adult Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 7204–7213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Ji, F.; Liu, L.; Li, F. Expression Changes of Parvalbumin and Microtubule- Associated Protein 2 Induced by Chronic Constriction Injury in Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia. Chin. Med. J. 2011, 124, 2184–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallinat, S.; Csikos, T.; Meffert, S.; Herdegen, T.; Stoll, M.; Unger, T. The Angiotensin AT2 Receptor Down-Regulates Neurofilament M in PC12W Cells. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 227, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron, L.; Laflamme, L.; Rivard, N.; Asselin, C.; Payet, M.D.; Gallo-Payet, N. Signals from the AT2 (Angiotensin Type 2) Receptor of Angiotensin II Inhibit P21ras and Activate MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase) to Induce Morphological Neuronal Differentiation in NG108-15 Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plouffe, B.; Guimond, M.O.; Beaudry, H.; Gallo-Payet, N. Role of Tyrosine Kinase Receptors in Angiotensin II AT2 Receptor Signaling: Involvement in Neurite Outgrowth and in P42/P44mapk Activation in NG108-15 Cells. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 4646–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, U.; Facer, P.; Yiangou, Y.; Sinisi, M.; Fox, M.; McCarthy, T.; Bountra, C.; Korchev, Y.E.; Anand, P. Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor (AT2R) Localization and Antagonist-Mediated Inhibition of Capsaicin Responses and Neurite Outgrowth in Human and Rat Sensory Neurons. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 1012–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, F.; Laflamme, L.; Payet, M.D.; Gallo-Payet, N. Nitric Oxide, a New Second Messenger Involved in the Action of Angiotensin II on Neuronal Differentiation of NG108-15 Cells. Endocr. Res. 1998, 24, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thippeswamy, T.; Morris, R. Nerve Growth Factor Inhibits the Expression of Nitric Oxide Synthase in Neurones in Dissociated Cultures of Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 230, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron, L.; Côté, F.; Payet, M.D.; Gallo-Payet, N. Nitric Oxide and Cyclic GMP Are Involved in Angiotensin II AT(2) Receptor Effects on Neurite Outgrowth in NG108-15 Cells. Neuroendocrinology 2002, 75, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thippeswamy, T.; Jain, R.K.; Mumtaz, N.; Morris, R. Inhibition of Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase Results in Neurodegenerative Changes in the Axotomised Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons: Evidence for a Neuroprotective Role of Nitric Oxide in Vivo. Neurosci Res. 2001, 40, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contestabile, A.; Ciani, E. Role of Nitric Oxide in the Regulation of Neuronal Proliferation, Survival and Differentiation. Neurochem. Int. 2004, 45, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadir, P.M.; Foster, D.B.; Crow, M.; Cooke, C.A.; Rucker, J.J.; Jain, A.; Smith, B.J.; Burks, T.N.; Cohn, R.D.; Fedarko, N.S.; et al. Identification and Characterization of a Functional Mitochondrial Angiotensin System. Cell Biol. 2011, 108, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, R.; Costa-Besada, M.A.; Iglesias-Gonzalez, J.; Perez-Costas, E.; Villar-Cheda, B.; Garrido-Gil, P.; Melendez-Ferro, M.; Soto-Otero, R.; Lanciego, J.L.; Henrion, D.; et al. Mitochondrial Angiotensin Receptors in Dopaminergic Neurons. Role in Cell Protection and Aging-Related Vulnerability to Neurodegeneration. Cell Death Dis 2016, 7, e2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-M.; Mogi, M.; Tsukuda, K.; Tomochika, H.; Iwanami, J.; Min, L.-J.; Nahmias, C.; Iwai, M.; Horiuchi, M. Angiotensin II-Induced Neural Differentiation via Angiotensin II Type 2 (AT 2 ) Receptor-MMS2 Cascade Involving Interaction between AT 2 Receptor-Interacting Protein and Src Homology 2 Domain-Containing Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Benedetto, M.; Bièche, I.; Deshayes, F.; Vacher, S.; Nouet, S.; Collura, V.; Seitz, I.; Louis, S.; Pineau, P.; Amsellem-Ouazana, D.; et al. Structural Organization and Expression of Human MTUS1, a Candidate 8p22 Tumor Suppressor Gene Encoding a Family of Angiotensin II AT2 Receptor-Interacting Proteins, ATIP. Gene 2006, 380, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouet, S.; Amzallag, N.; Li, J.-M.; Louis, S.; Seitz, I.; Cui, T.-X.; Alleaume, A.-M.; Di Benedetto, M.; Boden, C.; Masson, M.; et al. Trans-Inactivation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases by Novel Angiotensin II AT2 Receptor-Interacting Protein, ATIP. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 28989–28997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wruck, C.J.; Funke-Kaiser, H.; Pufe, T.; Kusserow, H.; Menk, M.; Schefe, J.H.; Kruse, M.L.; Stoll, M.; Unger, T. Regulation of Transport of the Angiotensin AT2 Receptor by a Novel Membrane-Associated Golgi Protein. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, S.J.; Booz, G.W.; Sigmund, C.D.; Coffman, T.M.; Kawai, T.; Rizzo, V.; Scalia, R.; Eguchi, S. Angiotensin II Signal Transduction: An Update on Mechanisms of Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol Rev. 2018, 98, 1627–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porrello, E.R.; Delbridge, L.M.D.; Thomas, W.G. The Angiotensin II Type 2 (AT2) Receptor: An Enigmatic Seven Transmembrane Receptor. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2009, 14, 958–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumners, C.; Fleegal, M.A.; Zhu, M. Angiotensin AT1 Receptor Signalling Pathways in Neurons. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 29, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Hirooka, K.; Nakamura, T.; Itano, T.; Nishiyama, A.; Nagai, Y.; Shiraga, F. Neuroprotective Effects of Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor (AT1-R) Blocker via Modulating AT1-R Signaling and Decreased Extracellular Glutamate Levels. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 4099–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zhu, Y.-Z.; Wong, P.T.-H. Neuroprotective Effects of Candesartan against Cerebral Ischemia in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Neuroreport 2005, 16, 1963–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, M.; Liu, H.-W.; Chen, R.; Ide, A.; Okamoto, S.; Hata, R.; Sakanaka, M.; Shiuchi, T.; Horiuchi, M. Possible Inhibition of Focal Cerebral Ischemia by Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor Stimulation. Circulation 2004, 110, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.-Y.; Yin, L. Neuroprotective Effect of Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor during Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion. Neural Regen Res. 2016, 11, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, L.; Perez-Alvarez, M.J.; Wandosell, F. Angiotensin II Type-2 Receptor Stimulation Induces Neuronal VEGF Synthesis after Cerebral Ischemia. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016, 1862, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwengel, K.; Namsolleck, P.; Lucht, K.; Clausen, B.H.; Lambertsen, K.L.; Valero-esquitino, V.; Thöne-reineke, C.; Müller, S.; Widdop, R.E.; Denton, K.M.; et al. Angiotensin AT2-Receptor Stimulation Improves Survival and Neurological Outcome after Experimental Stroke in Mice. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matavelli, L.C.; Siragy, H.M. AT2 Receptor Activities and Pathophysiological Implications. J. Cardiovasc. Pharm. 2015, 65, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumners, C.; Horiuchi, M.; Widdop, R.E.; McCarthy, C.; Unger, T.; Steckelings, U.M. Protective Arms of the Renin-Angiotensin-System in Neurological Disease. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2013, 40, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimond, M.-O.; Wallinder, C.; Alterman, M.; Hallberg, A.; Gallo-Payet, N. Comparative Functional Properties of Two Structurally Similar Selective Nonpeptide Drug-like Ligands for the Angiotensin II Type-2 (AT(2)) Receptor. Effects on Neurite Outgrowth in NG108-15 Cells. Eur J. Pharm. 2013, 699, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meffert, S.; Stolf, M.; Steckelings, U.M.; Bottari, S.P.; Unger, T. The Angiotensin II AT2 Receptor Inhibits Proliferation and Promotes Differentiation in PC12W Cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1996, 122, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashikawa-Hobara, N.; Hashikawa, N. Angiotensin II AT2receptors Regulate NGF-Mediated Neurite Outgrowth via the NO-CGMP Pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, A.; Liao, Z.; Smith, P.G. Angiotensin II Receptor Type 2 Activation Is Required for Cutaneous Sensory Hyperinnervation and Hypersensitivity in a Rat Hind Paw Model of Inflammatory Pain. J. Pain 2013, 14, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, A.; Liao, Z.; Mu, Y.; Smith, P.G. Inflammatory Renin-Angiotensin System Disruption Attenuates Sensory Hyperinnervation and Mechanical Hypersensitivity in a Rat Model of Provoked Vestibulodynia. J. Pain 2018, 19, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm-Starke, N.; Hilliges, M.; Falconer, C.; Rylander, E. Increased Intraepithelial Innervation in Women with Vulvar Vestibulitis Syndrome. GOI 1998, 46, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohm-Starke, N.; Hilliges, M.; Falconer, C.; Rylander, E. Neurochemical Characterization of the Vestibular Nerves in Women with Vulvar Vestibulitis Syndrome. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 1999, 48, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadha, S.; Gianotten, W.L.; Drogendijk, A.C.; Weijmar Schultz, W.C.; Blindeman, L.A.; van der Meijden, W.I. Histopathologic Features of Vulvar Vestibulitis. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 1998, 17, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulakat, L.; Sumners, C. Angiotensin Type 2 Receptors: Painful, or Not? Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 571994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).