Α Multicenter Retrospective Study Evaluating Brivaracetam in the Treatment of Epilepsies in Clinical Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographic and Clinical Data
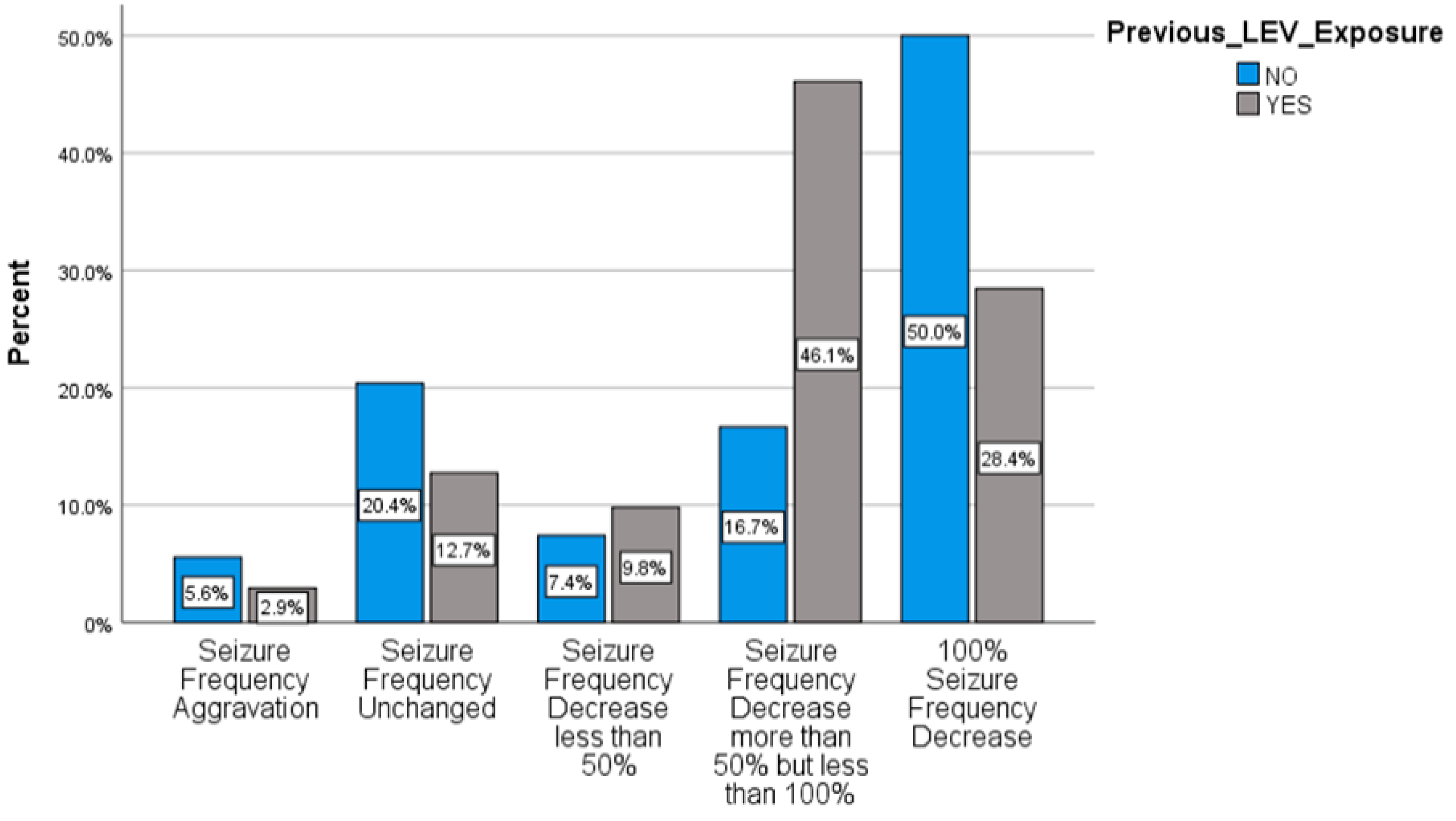
2.2. Brivaracetam and Levetiracetam
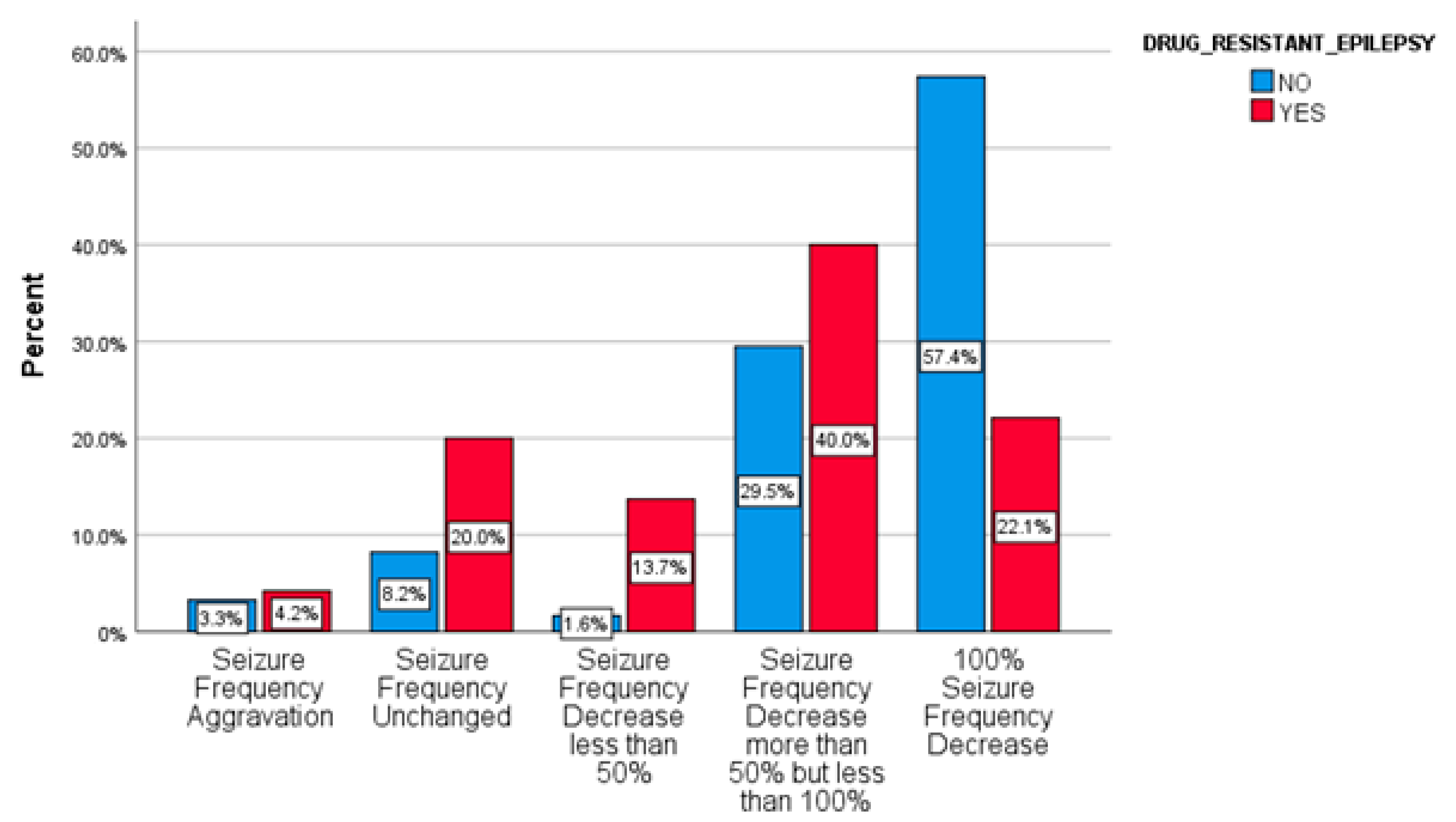
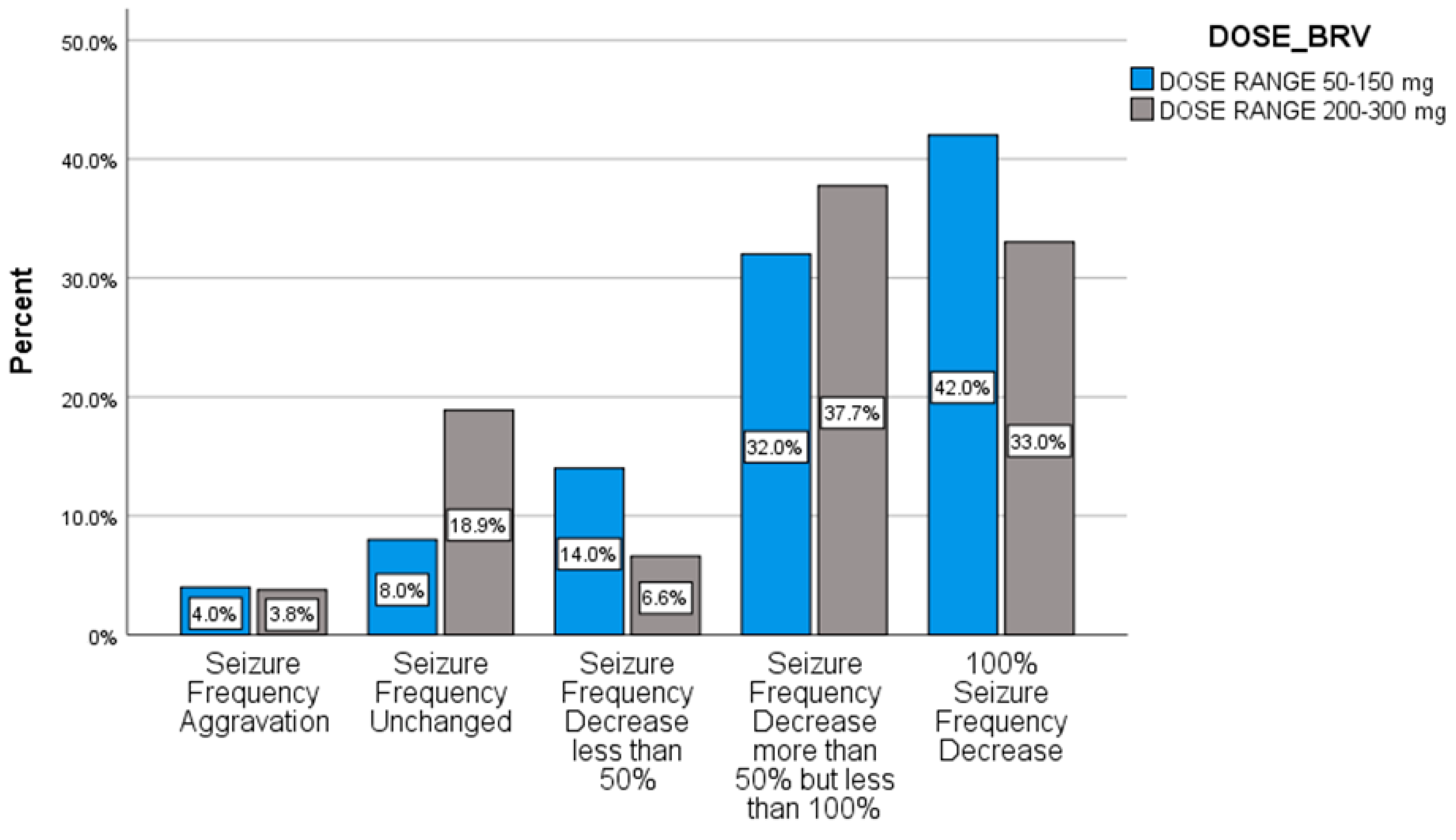
2.3. Responsiveness
2.4. Treatment-Emerged Adverse Events
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Study Cohort
4.3. Treatment Regimen
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moshé, S.L.; Perucca, E.; Ryvlin, P.; Tomson, T. Epilepsy: New advances. Lancet 2015, 385, 884–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, M.J.; Barry, S.J.E.; Bamagous, G.A.; Norrie, J.D.; Kwan, P. Patterns of treatment response in newly diagnosed epilepsy. Neurology 2012, 78, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, N.; Heath, C.A.; Greene, J. A review of medication adherence in people with epilepsy. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2017, 135, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillard, M.; Fuks, B.; Leclercq, K.; Matagne, A. Binding characteristics of brivaracetam, a selective, high affinity SV2A ligand in rat, mouse and human brain: Relationship to anti-convulsant properties. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 664, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UCBPharma. Briviact®(brivaracetam) Summary of Product Characteristics. 2018. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/briviact-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Biton, V.; Berkovic, S.F.; Abou-Khalil, B.; Sperling, M.R.; Johnson, M.E.; Lu, S. Brivaracetam as adjunctive treatment for uncontrolled partial epilepsy in adults: A phase III randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryvlin, P.; Werhahn, K.J.; Blaszczyk, B.; Johnson, M.E.; Lu, S. Adjunctive brivaracetam in adults with uncontrolled focal epilepsy: Results from a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, P.; Schiemann, J.; Sperling, M.R.; Whitesides, J.; Liang, W.; Stalvey, T.; Brandt, C.; Kwan, P. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, parallel-group study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of adjunctive brivaracetam in adult patients with uncontrolled partial-onset seizures. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, P.; Trinka, E.; Van Paesschen, W.; Rektor, I.; Johnson, M.E.; Lu, S. Adjunctive brivaracetam for uncontrolled focal and generalized epilepsies: Results of a phase III, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, flexible-dose trial. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelczyk, A.; Klein, K.M.; Willems, L.M.; Rosenow, F.; Bauer, S. Brivaracetam in the treatment of focal and idiopathic generalized epilepsies and of status epilepticus. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 9, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, S.L.; Fakhoury, T.; Liang, W.; Eckhardt, K.; Borghs, S.; D’Souza, J. An open-label, prospective, exploratory study of patients with epilepsy switching from levetiracetam to brivaracetam. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 52, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, E.; Guzmán, L.; Quintana, M.; Abraira, L.; Santamarina, E.; Salas-Puig, X.; Toledo, M. Efficacy, retention, and safety of brivaracetam in adult patients with genetic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 102, 106657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Menachem, E.; Mameniškienė, R.; Quarato, P.P.; Klein, P.; Gamage, J.; Schiemann, J.; Johnson, M.E.; Whitesides, J.; McDonough, B.; Eckhardt, K. Efficacy and safety of brivaracetam for partial-onset seizures in 3 pooled clinical studies. Neurology 2016, 87, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.C.; Sander, J.W. Difficulties in extrapolating from clinical trial data to clinical practice: The case of antiepileptic drugs. Neurology 1997, 49, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhoff, B.J.; Staack, A.M.; Hillenbrand, B.C. Randomized controlled antiepileptic drug trials miss almost all patients with ongoing seizures. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 66, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinig, I.; von Podewils, F.; Möddel, G.; Bauer, S.; Klein, K.M.; Paule, E.; Reif, P.S.; Willems, L.M.; Zöllner, J.P.; Kunz, R.; et al. Postmarketing experience with brivaracetam in the treatment of epilepsies: A multicenter cohort study from Germany. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, M.; Hintz, M.; Specht, A.; Schulze-Bonhage, A. Tolerability, efficacy and retention rate of brivaracetam in patients previously treated with levetiracetam: A monocenter retrospective outcome analysis. Seizure 2018, 61, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, V.; López-González, F.J.; Mauri, J.A.; Rodriguez-Uranga, J.; Olivé-Gadea, M.; Montoya, J.; Ruiz-Giménez, J.; Zurita, J.; The BRIVA-LIFE Study Group. BRIVA-LIFE—A multicenter retrospective study of the long-term use of brivaracetam in clinical practice. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2019, 134, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matagne, A.; Margineanu, D.G.; Kenda, B.; Michel, P.; Klitgaard, H. Anti-convulsive and antiepileptic properties of brivaracetam (ucb 34714), a high-affinity ligand for the synaptic vesicle protein, SV2A. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adewusi, J.; Burness, C.; Ellawela, S.; Emsley, H.; Hughes, R.; Lawthom, C.; Maguire, M.; McLean, B.; Mohanraj, R.; Oto, M.; et al. Brivaracetam efficacy and tolerability in clinical practice: A UK-based retrospective multicenter service evaluation. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 106, 106967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, R.M.; Wammes-van der Heijden, E.A.; Schelhaas, H.J.; Tan, I.Y.; Festen, D.A.; Majoie, M.H. Efficacy and tolerability of brivaracetam in patients with intellectual disability and epilepsy. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matagne, A.; Kenda, B.; Michel, P.; Klitgaard, H. UCB 34714, a new pyrrolidone derivative, suppresses seizures epileptogenesis in animal models of chronic epilepsy in vivo. Epilepsia 2003, 44, 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- Trenité, D.K.N.; Genton, P.; Parain, D.; Masnou, P.; Steinhoff, B.J.; Jacobs, T.; Pigeolet, E.; Stockis, A.; Hirsch, E. Evaluation of brivaracetam, a novel SV2A ligand, in the photosensitivity model. Neurology 2007, 69, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.N.; Chen, D.; Chen, T.; Xu, D.; Chen, S.H.; Liu, L. The adverse event profile of brivaracetam:a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Seizure 2017, 45, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigo, J.; Nguyen, L.; HANS, G.; Belachew, S.; Moonen, G.; Klitgaard, H. UCB 34714: Effect on inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmission. Epilepsia 2004, 45, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Carunchio, I.; Pieri, M.; Ciotti, M.T.; Albo, F.; Zona, C. Modulation of AMPA receptors in cultured cortical neurons induced by the antiepileptic drug levetiracetam. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, P.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Berg, A.T.; Brodie, M.J.; Allen Hauser, W.; Mathern, G.; Moshé, S.L.; Perucca, E.; Wiebe, S.; French, J. Definition of drug resistant epilepsy: Consensus proposal by the ad hoc task force of the ILAE Commission on Therapeutic Strategies. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Baseline, n = 156 (%) |
|---|---|
| Age (years), M(SD) | 39.69 (13.63) |
| Gender | n = 156 (%) |
| -Male | 82 (52.6) |
| -Female | 74 (47.4) |
| Period of follow-up (months), M(SD) | 3.9 (2.76) |
| Epilepsy Duration (years), M(SD) | 21.43 (13.66) |
| Drug Resistant Epilepsy | n = 156 (%) |
| -Yes | 61 (39.1) |
| -No | 95 (60.9) |
| Cosponsored AED, M(SD) | 2.28 (1.40) |
| BRV Monotherapy | 9 (5.8) |
| Types of Seizures | n = 156 (%) |
| -Focal Seizures | 88 (56.41) |
| -Focal Seizures with secondary generalization | 39 (25) |
| -Generalized Seizures | 25 (16.03) |
| -Unclassified Seizures | 4 (2.56) |
| Syndromes | n = 156 (%) |
| -Idiopathic Epilepsy | 69 (44.2) |
| -Symptomatic Epilepsy | 71 (45.5) |
| -Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy | 4 (2.6) |
| -Special Syndromes | 12 (7.7) |
| BRV in mg | n = 156 (%) |
|---|---|
| 50 | 6 (3.8) |
| 100 | 27 (17.3) |
| 150 | 17 (10.9) |
| 200 | 105 (67.3) |
| 300 | 1 (0.6) |
| Mean BRV Dose in mg, M(SD) | 172.12 (46.57) |
| Median BRV Dose in mg, M(SD) | 200 |
| Reasons for BRV Prescription | n = 156 (%) |
| - Seizures | 119 (76.3) |
| - Adverse Events | 23 (14.7) |
| - Both | 14 (9) |
| LEV medication at BL | n = 156 (%) |
| Treated with LEV in the past | 102 (65.38) |
| LEV intake at BL | 85 (83.33) |
| -Immediate switch to BRV | 83 (97.64) |
| -Gradual switch | 2 (2.36) |
| LEV in (past) medical history | 17 (16.6) |
| LEV naive | 54 (34.61) |
| Mean LEV dose in mg, M(SD) | 1278.85 (1326.21) |
| Median LEV dose in mg, M(SD) | 1000 |
| Discontinuation reasons of LEV | n = 156 (%) |
| - Seizures | 60 (38.5) |
| - Adverse Events | 27 (17.3) |
| - Both | 15 (9.6) |
| - No previous treatment | 54 (34.6) |
| Seizure Frequency Change after BRV Treatment | n = 156 (%) |
|---|---|
| - Seizure Frequency Unchanged | 24 (15.4) |
| - Seizure Freedom | 56 (35.9) |
| - Seizure Frequency Aggravation | 6 (3.8) |
| - Seizure Frequency Responder < 50% | 14 (9) |
| - Seizure Frequency Responder ≥ 50% | 56 (35.9) |
| - Seizure Frequency Unchanged | 24 (15.4) |
| Seizure Frequency Change after BRV Treatment in Switching Group | n = 85 (%) |
|---|---|
| - Seizure Freedom | 26 (30.6) |
| - Seizure Frequency Responder ≥ 50% | 41 (48.2) |
| - Seizure Frequency Responder < 50% | 9 (10.6) |
| - Seizure Frequency Unchanged | 8 (9.4) |
| - Seizure Frequency Aggravation | 1 (1.2) |
| Adverse Events | Baseline, n = 156 (%) |
|---|---|
| - Yes | 26 (16.6) |
| - No | 130 (83.3) |
| Types of Adverse Events | n = 156 (%) |
| - Non-Behavioral Adverse Events | 18 (11.5) |
| - Behavioral Adverse Events | 8 (5.1) |
| Switching Patients | n = 85 (%) |
|---|---|
| -No Adverse Events | 75 (88.2) |
| -Behavioral Adverse Events | 3 (3.5) |
| -Non-Behavioral Adverse Events | 7 (8.2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stefanatou, M.; Vasileiadou Kapetanou, E.; Kimiskidis, V.K.; Papaliagkas, V.; Polychronopoulos, P.; Markoula, S.; Charisiou, K.; Kazis, D.; Verentzioti, A.; Patrikelis, P.; et al. Α Multicenter Retrospective Study Evaluating Brivaracetam in the Treatment of Epilepsies in Clinical Practice. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020165
Stefanatou M, Vasileiadou Kapetanou E, Kimiskidis VK, Papaliagkas V, Polychronopoulos P, Markoula S, Charisiou K, Kazis D, Verentzioti A, Patrikelis P, et al. Α Multicenter Retrospective Study Evaluating Brivaracetam in the Treatment of Epilepsies in Clinical Practice. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(2):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020165
Chicago/Turabian StyleStefanatou, Maria, Eirini Vasileiadou Kapetanou, Vasilios K. Kimiskidis, Vasileios Papaliagkas, Panagiotis Polychronopoulos, Sofia Markoula, Kleoniki Charisiou, Dimitrios Kazis, Anastasia Verentzioti, Panayiotis Patrikelis, and et al. 2021. "Α Multicenter Retrospective Study Evaluating Brivaracetam in the Treatment of Epilepsies in Clinical Practice" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 2: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020165
APA StyleStefanatou, M., Vasileiadou Kapetanou, E., Kimiskidis, V. K., Papaliagkas, V., Polychronopoulos, P., Markoula, S., Charisiou, K., Kazis, D., Verentzioti, A., Patrikelis, P., Alexoudi, A., & Gatzonis, S. (2021). Α Multicenter Retrospective Study Evaluating Brivaracetam in the Treatment of Epilepsies in Clinical Practice. Pharmaceuticals, 14(2), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020165










