Losartan Improves Memory, Neurogenesis and Cell Motility in Transgenic Alzheimer’s Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. ARB Improves the Spatial Memory Deficit in APP/PS 1 Mice Independent of Its BP-Lowering Effect
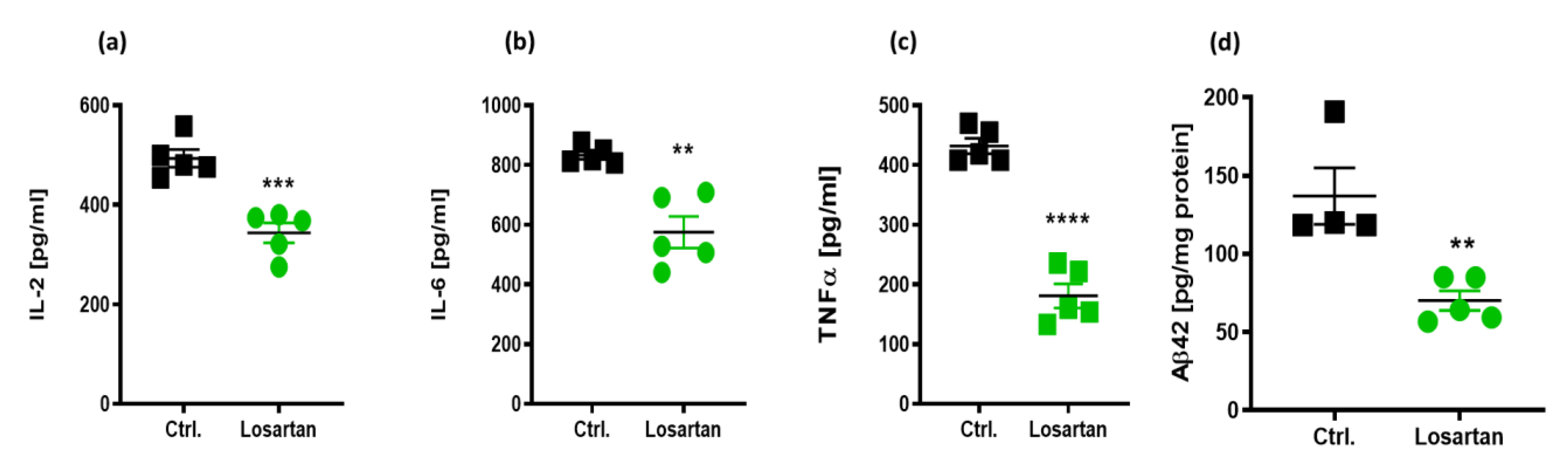
2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of ARB in APP/PS1 Mice
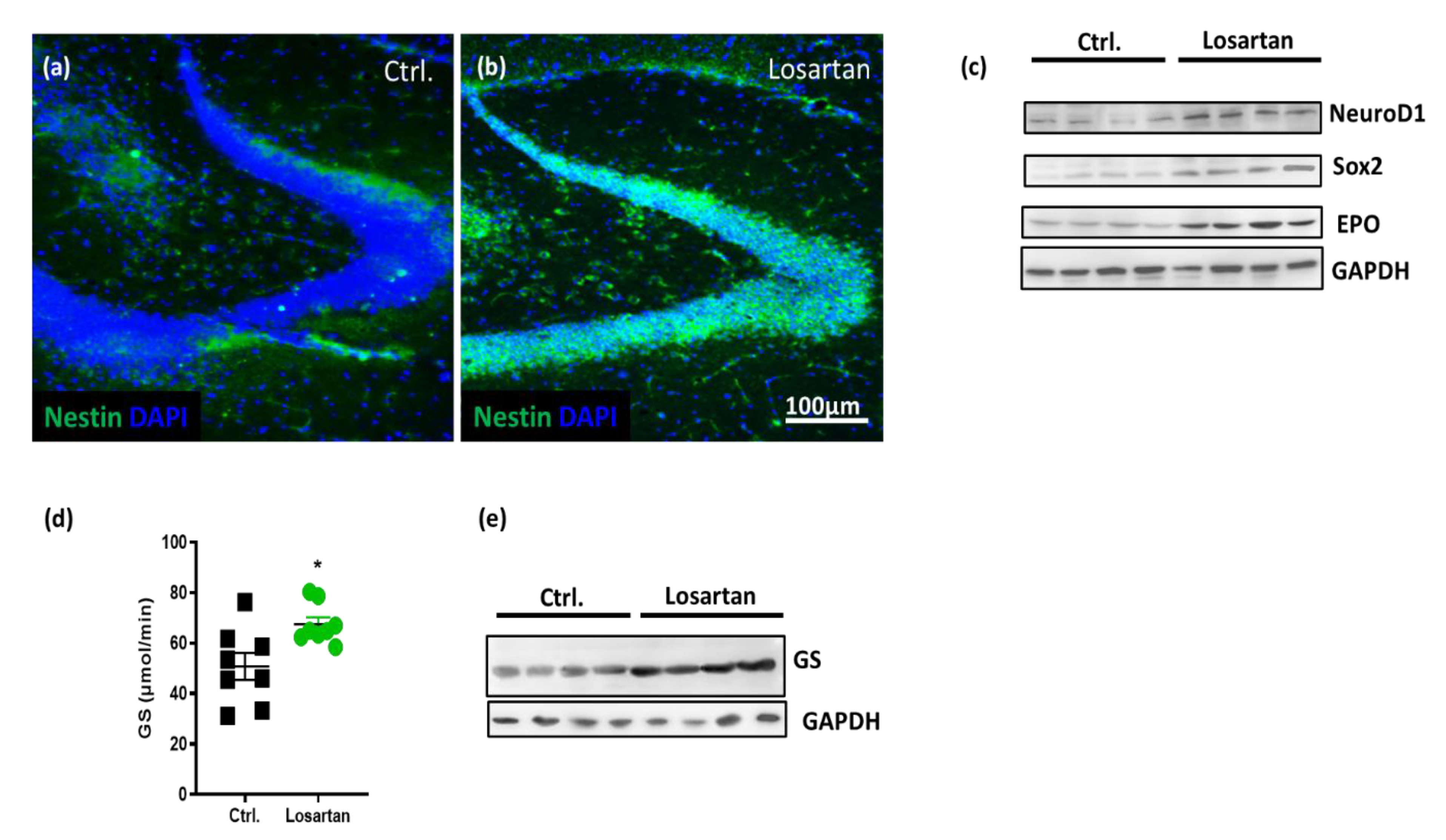
2.3. ARB Increases Neurogenesis Markers and EPO Production in APP/PS1 Mice
2.4. ARB Improves the Glutamate-Metabolizing Function in the CNS of APP/PS1 Mice
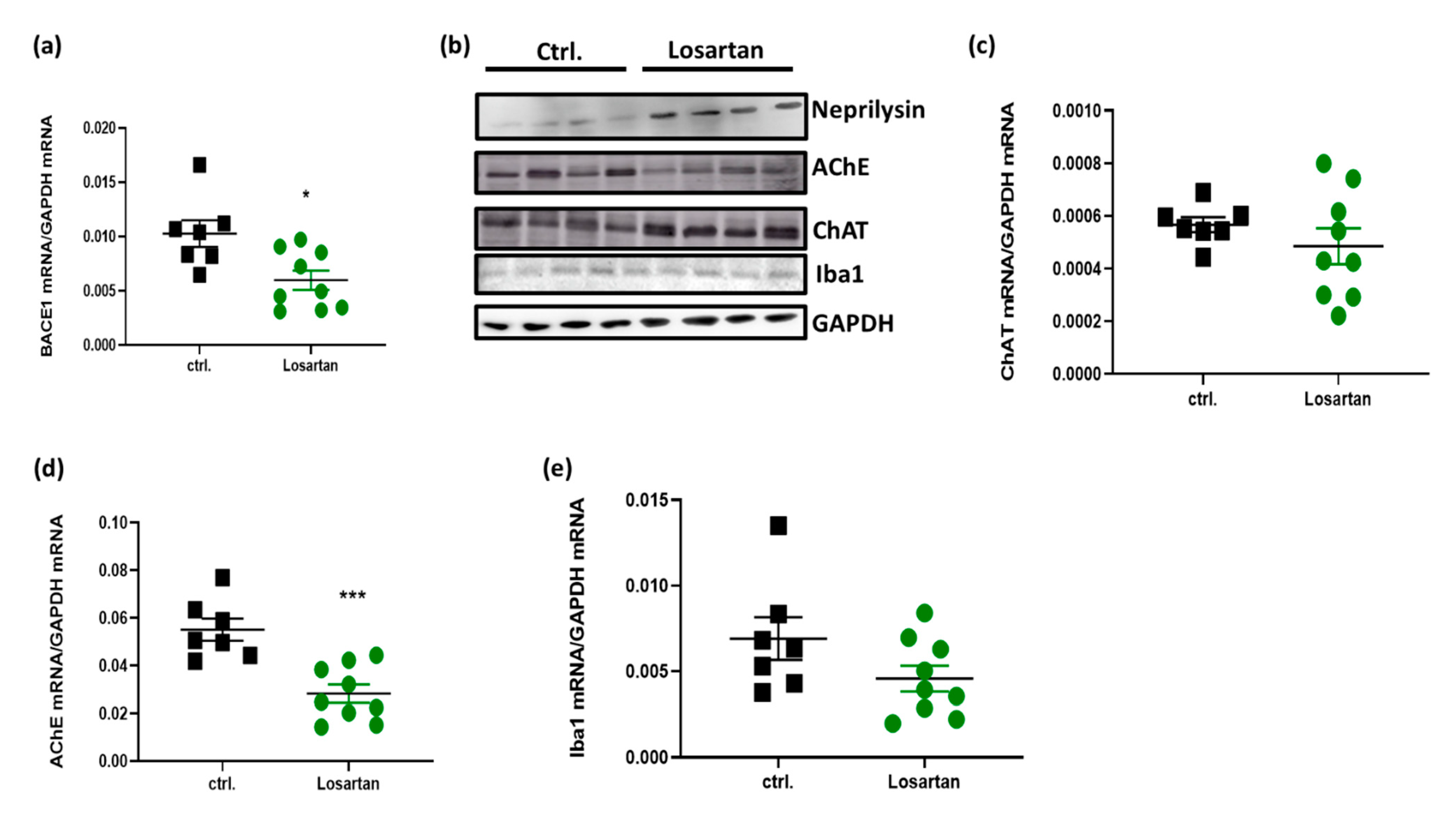
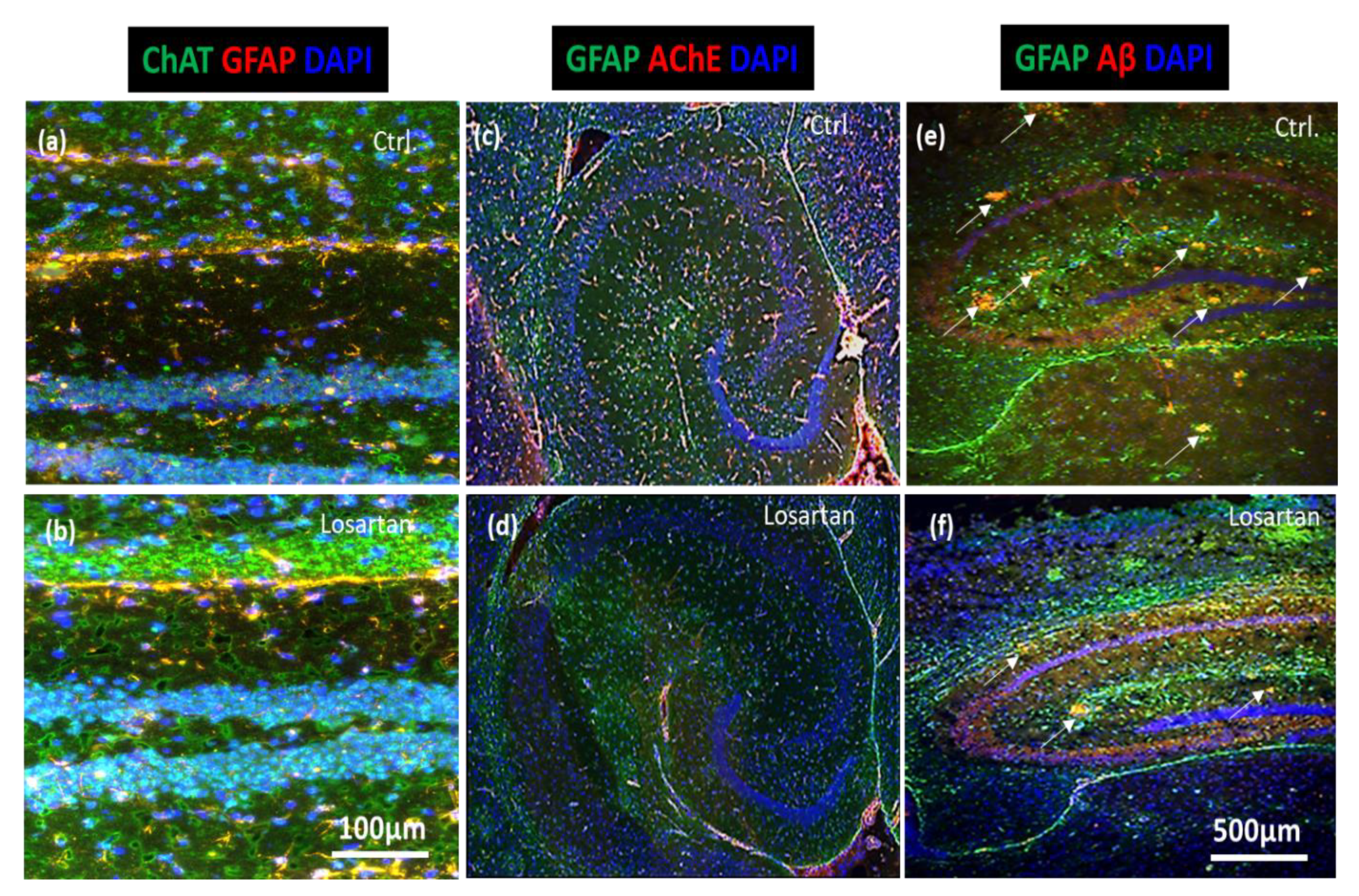
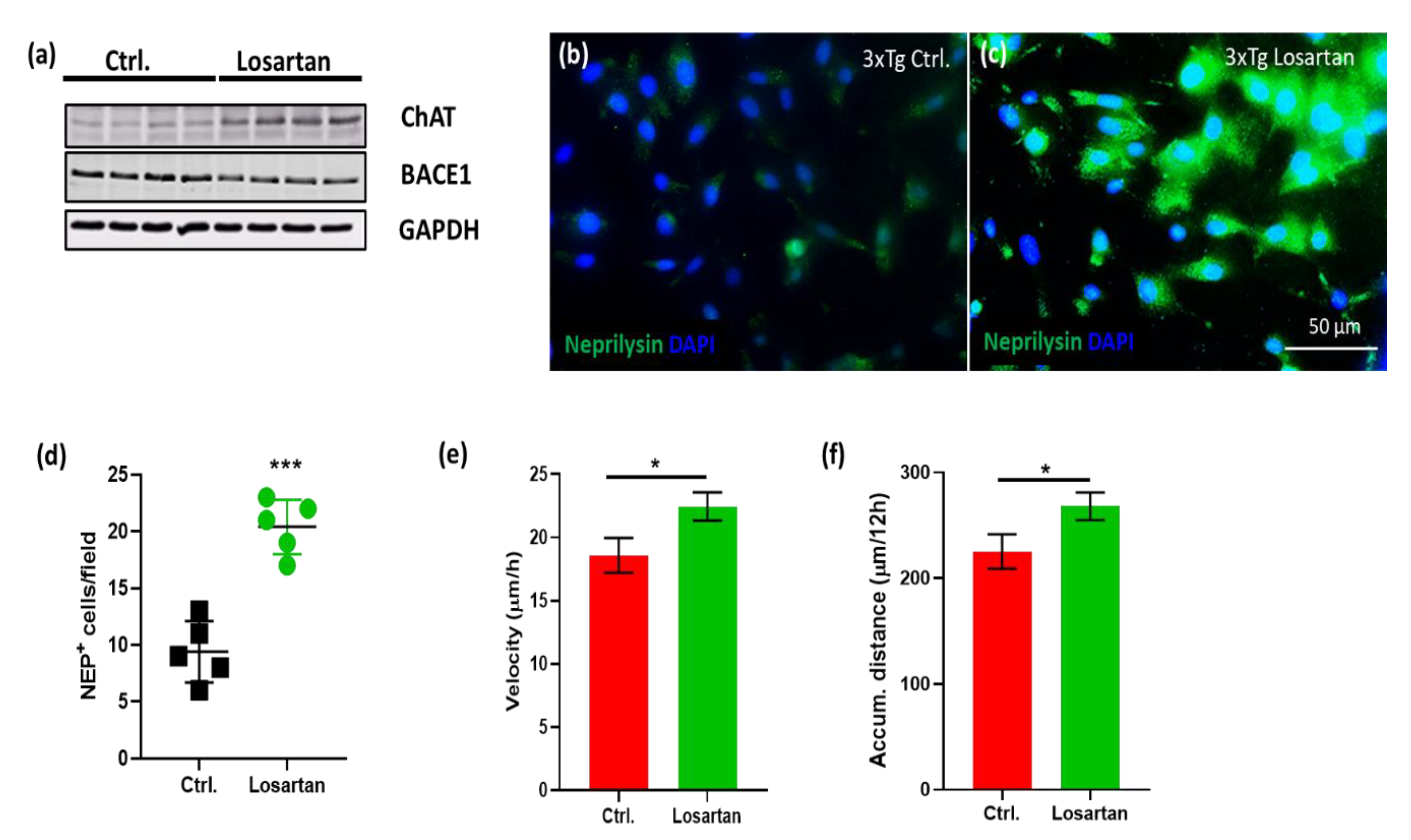
2.5. ARB Regulates the Expression of BACE1, AChE, ChAT and Neprilysin in the Brains of APP/PS1 Mice
2.6. ARB Enhances the Production of ACh, Neurogenesis and Cell Motility In Vitro
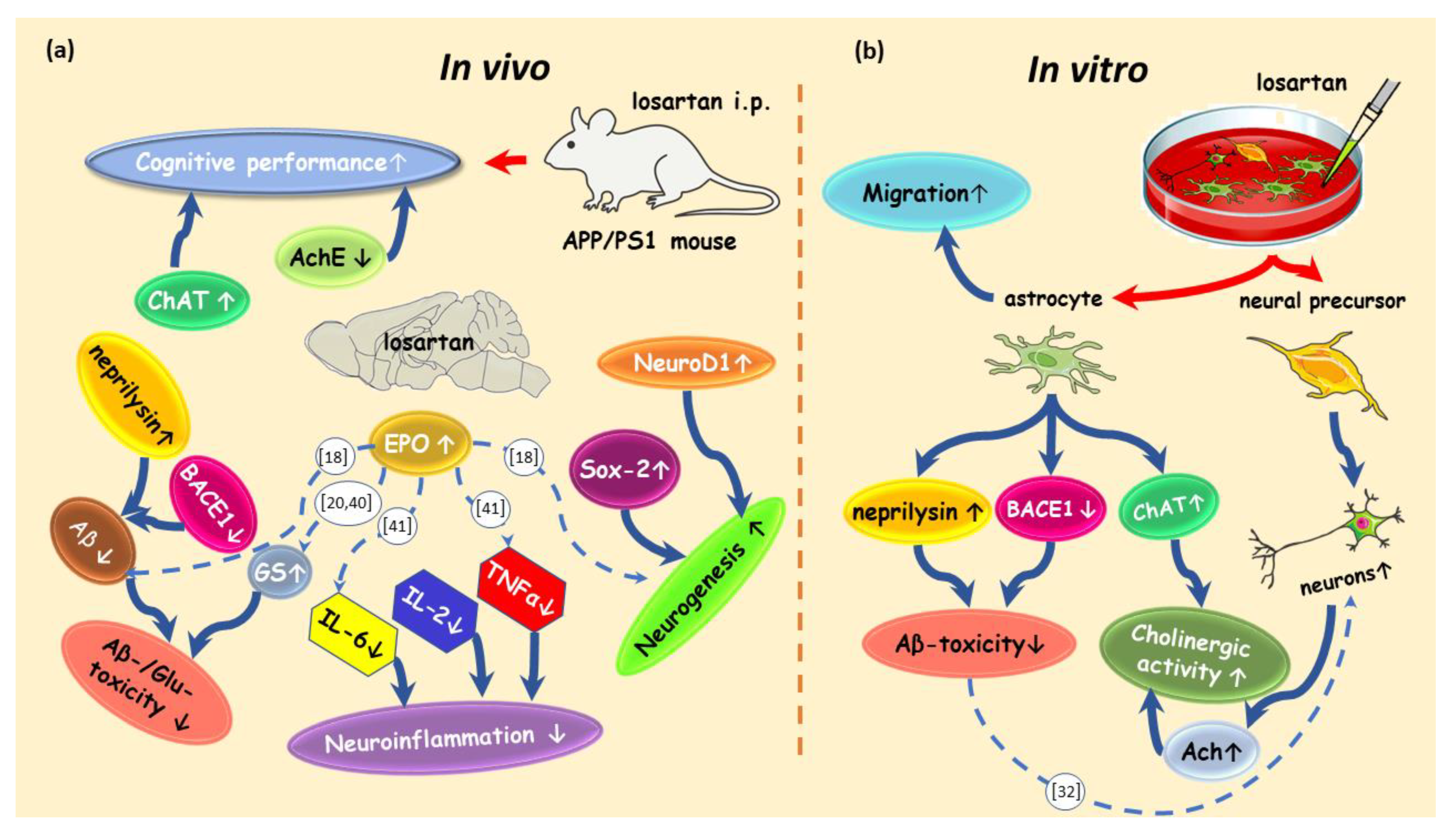
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. T Maze Testing
4.3. Cell Culture Experiments and Cell Migration Tracking
4.4. qPCR of APP/PS1 Mouse Brain Samples
4.5. Western Blot
4.6. Immunofluorescent Stainings
4.7. Aβ42 ELISA and Multiplex Analysis of Cytokines
4.8. Glutamine Synthetase Activity
4.9. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Savaskan, E. The Role of the Brain Renin-Angiotensin System in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2005, 2, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.; Eldahshan, W.; Fagan, S.C.; Ergul, A. Within the Brain: The Renin Angiotensin System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielyan, L.; Klein, R.; Hanson, L.R.; Buadze, M.; Schwab, M.; Gleiter, C.H.; Frey, W.H. Protective Effects of Intranasal Losartan in the APP/PS1 Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer Disease. Rejuvenation Res. 2010, 13, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torika, N.; Asraf, K.; Danon, A.; Apte, R.N.; Fleisher-Berkovich, S. Telmisartan Modulates Glial Activation: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royea, J.; Zhang, L.; Tong, X.-K.; Hamel, E. Angiotensin IV Receptors Mediate the Cognitive and Cerebrovascular Benefits of Losartan in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 5562–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, M.; Safar, M.M.; Abdelsalam, R.M.; Zaki, H.F. Telmisartan Protects Against Aluminum-Induced Alzheimer-like Pathological Changes in Rats. Neurotox. Res. 2019, 37, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drews, H.J.; Yenkoyan, K.; Lourhmati, A.; Buadze, M.; Kabisch, D.; Verleysdonk, S.; Petschak, S.; Beer-Hammer, S.; Davtyan, T.; Frey, W.H.; et al. Intranasal Losartan Decreases Perivascular Beta Amyloid, Inflammation, and the Decline of Neurogenesis in Hypertensive Rats. Neurotherapeutics 2019, 16, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torika, N.; Asraf, K.; Cohen, H.; Fleisher-Berkovich, S. Intranasal telmisartan ameliorates brain pathology in five familial Alzheimer’s disease mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 64, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigiani, L.J.; Royea, J.; Lacalle-Aurioles, M.; Tong, X.-K.; Hamel, E. Pleiotropic Benefits of the Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Candesartan in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer Disease. Hypertension 2018, 72, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, D.M.; Allen, S.J.; Benton, J.S.; Goodhardt, M.J.; Haan, E.A.; Palmer, A.M.; Sims, N.R.; Smith, C.C.T.; Spillane, J.A.; Esiri, M.M.; et al. Biochemical Assessment of Serotonergic and Cholinergic Dysfunction and Cerebral Atrophy in Alzheimer’s Dis-ease. J. Neurochem. 1983, 41, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, C.; Vargas-Lopes, C.; Brandão, C.O.; Reis, T.; Laks, J.; Panizzutti, R.; Ferreira, S.T. Elevated glutamate and glutamine levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with probable Alzheimer’s disease and depression. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinova, S.A.; Klodt, P.M.; Kudrin, V.S.; Narkevich, V.B.; Voronina, T.A. The behavior and neurotransmitter contents in brain structures of rats with Alzheimer’s disease modeled by administration of Aβ25–35. Neurochem. J. 2015, 9, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.-B.; Liu, M.-Y.; Chen, Z.-X.; Wei, M.-J. Schisandrin ameliorates cognitive impairment and attenuates Aβ deposition in APP/PS1 transgenic mice: Involvement of adjusting neurotransmitters and their metabolite changes in the brain. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, S.B.; Niewoehner, B.; Rawlins, J.N.P.; Bannerman, D.M. Dorsal hippocampal N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors un-derlie spatial working memory performance during non-matching to place testing on the T-maze. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 186, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pioli, E.Y.; Gaskill, B.N.; Gilmour, G.; Tricklebank, M.D.; Dix, S.L.; Bannerman, D.; Garner, J.P. An automated maze task for assessing hippocampus-sensitive memory in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 261, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-X.; Lai, Y.-H.; Mi, P.-Y.; Dai, X.-L.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Zhang, S.-J.; Zhang, X.-W.; Yang, B.-Y.; Cui, D.-M.; et al. Rescue of cognitive deficits in APP/PS1 mice by accelerating the aggregation of β-amyloid peptide. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2019, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.A.; Goel, R.; Shukla, S.; Shukla, R.; Hanif, K. Angiotensin Receptor Blockade by Inhibiting Glial Activation Promotes Hippocampal Neurogenesis Via Activation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Hypertension. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 55, 5282–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, Y.R.; Strehaiano, M.; Obaya, T.R.; Rodríguez, J.C.G.; Maurice, T. An Intranasal Formulation of Erythropoietin (Neuro-EPO) Prevents Memory Deficits and Amyloid Toxicity in the APPSwe Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 55, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, W.S.; Rex, T.S. Evidence That Erythropoietin Modulates Neuroinflammation through Differential Action on Neurons, Astrocytes, and Microglia. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourhmati, A.; Buniatian, G.H.; Paul, C.; Verleysdonk, S.; Buecheler, R.; Buadze, M.; Proksch, B.; Schwab, M.; Gleiter, C.H.; Danielyan, L. Age-Dependent Astroglial Vulnerability to Hypoxia and Glutamate: The Role for Erythropoietin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talantova, M.; Sanz-Blasco, S.; Zhang, X.; Xia, P.; Akhtar, M.W.; Okamoto, S.I.; Dziewczapolski, G.; Nakamura, T.; Cao, G.; Pratt, A.E.; et al. Aβ induces astrocytic glutamate release, extrasynaptic NMDA receptor activation, and synaptic loss. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2518–E2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armada-Moreira, A.; Gomes, J.I.; Pina, C.C.; Savchak, O.K.; Gonçalves-Ribeiro, J.; Rei, N.; Pinto, S.; Morais, T.P.; Martins, R.S.; Ribeiro, F.F.; et al. Going the Extra (Synaptic) Mile: Excitotoxicity as the Road Toward Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabarria, M.; Noristani, H.N.; Verkhratsky, A.; Rodríguez, J.J. Age-dependent decrease in glutamine synthetase expression in the hippocampal astroglia of the triple transgenic Alzheimer’s disease mouse model: Mechanism for deficient glutamatergic transmission? Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krabbe, G.; Halle, A.; Matyash, V.; Rinnenthal, J.L.; Eom, G.D.; Bernhardt, U.; Miller, K.R.; Prokop, S.; Kettenmann, H.; Heppner, F.L. Functional Impairment of Microglia Coincides with Beta-Amyloid Deposition in Mice with Alzheimer-Like Pathology. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsawa, K.; Imai, Y.; Kanazawa, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Kohsaka, S. Involvement of Iba1 in membrane ruffling and phagocytosis of macrophages/microglia. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 3073–3084. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Franco-Bocanegra, D.K.; George, B.; Lau, L.C.; Holmes, C.; Nicoll, J.A.R.; Boche, D. Microglial motility in Alzheimer’s disease and after Aβ42 immunotherapy: A human post-mortem study. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyss-Coray, T.; Loike, J.D.; Brionne, T.C.; Lu, E.; Anankov, R.; Yan, F.; Silverstein, S.C.; Husemann, J. Adult mouse astrocytes degrade amyloid-β in vitro and in situ. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, M.C.; Foster, C.; Brunner, H.R.; Liu, L. A Systematic Comparison of the Properties of Clinically Used Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Antagonists. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 809–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torika, N.; Asraf, K.; Apte, R.N.; Fleisher-Berkovich, S. Candesartan ameliorates brain inflammation associated with Alz-heimer’s disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2018, 24, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, J.; Song, K.; Abdelrahman, A.; Mendelsohn, F.A.O. Blockade by intravenous losartan of at1 angio-tensin II receptors in rat brain, kidney and adrenals demonstrated by in vitro autoradiog-raphy. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1994, 21, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezko, P.; Zufkova, V.; Remko, M. Modelling of absorption, distribution and physicochemical properties of AT1 receptor an-tagonists. Acta Fac. Pharm. Univ. Comenianae 2015, 62, 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre-Rueda, D.; Guerra-Ojeda, S.; Aldasoro, M.; Iradi, A.; Obrador, E.; Ortega, A.; Mauricio, M.D.; Vila, J.M.; Valles, S.L. Astrocytes Protect Neurons from Aβ1-42 Peptide-Induced Neurotoxicity Increasing TFAM and PGC-1 and Decreasing PPAR-γ and SIRT-1. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 12, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morey, T.M.; Albers, S.; Shilton, B.H.; Rylett, R.J. Enhanced ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of catalytically defi-cient human choline acetyltransferase mutants. J. Neurochem. 2016, 137, 630–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, A.N.; Smith, S.G.; Duke, L.M.; Pourquoi, A.; Vaz, S. Perturbations of Ubiquitin-Proteasome-Mediated Proteolysis in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccamo, A.; Oddo, S.; Billings, L.M.; Green, K.N.; Martinez-Coria, H.; Fisher, A.; LaFerla, F.M. M1 Receptors Play a Central Role in Modulating AD-like Pathology in Transgenic Mice. Neuron 2006, 49, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, D.; Nayak, V.; Kurady, L.B.; Rao, M. Ameliorative effects of angiotensin receptor blockers against scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2016, 9, 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- Itou, Y.; Nochi, R.; Kuribayashi, H.; Saito, Y.; Hisatsune, T. Cholinergic activation of hippocampal neural stem cells in aged dentate gyrus. Hippocampus 2010, 21, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.F.; Verkhratsky, A.; Parpura, V. Astrocyte glutamine synthetase: Pivotal in health and disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Xu, H.; Wang, F.; Xu, G.; Sinha, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.Y.; Tian, H.; Gao, F.; Li, W.; et al. Erythropoietin exerts a neuro-protective function against glutamate neurotoxicity in experimental diabetic retina. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 8208–8222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisi, P.; Arabpoor, Z.; Rashidi, B.; Alaei, H.; Salami, M.; Hamidi, G.; Shabrang, M.; Sharifi, M.R.; Dolatabadi, H.R.D. Erythropoietin improves neuronal proliferation in dentate gyrus of hippocampal formation in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2012, 1, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, L.; Zhang, N.; Dong, N.; Wang, D.-W.; Xu, D.-H.; Zhang, P.; Meng, X.-W. Erythropoietin Protects Rat Brain Injury from Carbon Monoxide Poisoning by Inhibiting Toll-Like Receptor 4/NF-kappa B-Dependent Inflammatory Responses. Inflammation 2015, 39, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ideguchi, M.; Shinoyama, M.; Gomi, M.; Hayashi, H.; Hashimoto, N.; Takahashi, J. Immune or inflammatory response by the host brain suppresses neuronal differentiation of transplanted ES cell–derived neural precursor cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 1936–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, E.; Vale, C.; Vieytes, M.R.; LaFerla, F.M.; Giménez-Llort, L.; Botana, L.M. 13-Desmethyl spirolide-C is neuroprotective and reduces intracellular Aβ and hyperphosphorylated tau in vitro. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 59, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Singh, N. Experimental hypertension induced vascular dementia: Pharmacological, biochemical and behavioral recuperation by angiotensin receptor blocker and acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 102, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, G.; Qian, W.; Song, G.; Zhaochun, S. Valsartan reverses depressive/anxiety-like behavior and induces hippocampal neurogenesis and expression of BDNF protein in unpredictable chronic mild stress mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 124, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buniatian, G.H.; Weiskirchen, R.; Weiss, T.S.; Schwinghammer, U.; Fritz, M.; Seferyan, T.; Proksch, B.; Glaser, M.; Lourhmati, A.; Buadze, M.; et al. Antifibrotic Effects of Amyloid-Beta and Its Loss in Cirrhotic Liver. Cells 2020, 9, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielyan, L.; Schwab, M.; Siegel, G.; Brawek, B.; Garaschuk, O.; Asavapanumas, N.; Buadze, M.; Lourhmati, A.; Wendel, H.-P.; Avci-Adali, M.; et al. Cell motility and migration as determinants of stem cell efficacy. EBioMedicine 2020, 60, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busche, M.A.; Eichhoff, G.; Adelsberger, H.; Abramowski, D.; Wiederhold, K.-H.; Haass, C.; Staufenbiel, M.; Konnerth, A.; Garaschuk, O. Clusters of Hyperactive Neurons Near Amyloid Plaques in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Science 2008, 321, 1686–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Zu, H. bing Microglial polarization: Novel therapeutic mechanism against Alzheimer’s disease. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Sagare, A.P.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood–brain barrier breakdown in Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.; Ottaway, J.H. Glutamine synthetase in muscle and kidney. Biochem. J. 1970, 119, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drews, H.J.; Klein, R.; Lourhmati, A.; Buadze, M.; Schaeffeler, E.; Lang, T.; Seferyan, T.; Hanson, L.R.; Frey II, W.H.; de Vries, T.C.G.M.; et al. Losartan Improves Memory, Neurogenesis and Cell Motility in Transgenic Alzheimer’s Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020166
Drews HJ, Klein R, Lourhmati A, Buadze M, Schaeffeler E, Lang T, Seferyan T, Hanson LR, Frey II WH, de Vries TCGM, et al. Losartan Improves Memory, Neurogenesis and Cell Motility in Transgenic Alzheimer’s Mice. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(2):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020166
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrews, Henning Johannes, Roman Klein, Ali Lourhmati, Marine Buadze, Elke Schaeffeler, Thomas Lang, Torgom Seferyan, Leah R. Hanson, William H. Frey II, Tom C.G.M. de Vries, and et al. 2021. "Losartan Improves Memory, Neurogenesis and Cell Motility in Transgenic Alzheimer’s Mice" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 2: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020166
APA StyleDrews, H. J., Klein, R., Lourhmati, A., Buadze, M., Schaeffeler, E., Lang, T., Seferyan, T., Hanson, L. R., Frey II, W. H., de Vries, T. C. G. M., Thijssen-van Loosdregt, I. A. E. W., Gleiter, C. H., Schwab, M., & Danielyan, L. (2021). Losartan Improves Memory, Neurogenesis and Cell Motility in Transgenic Alzheimer’s Mice. Pharmaceuticals, 14(2), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020166






