An Explanation for the Adiponectin Paradox
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Adiponectin Levels in Metabolic Syndrome
3. Adiponectin Signaling
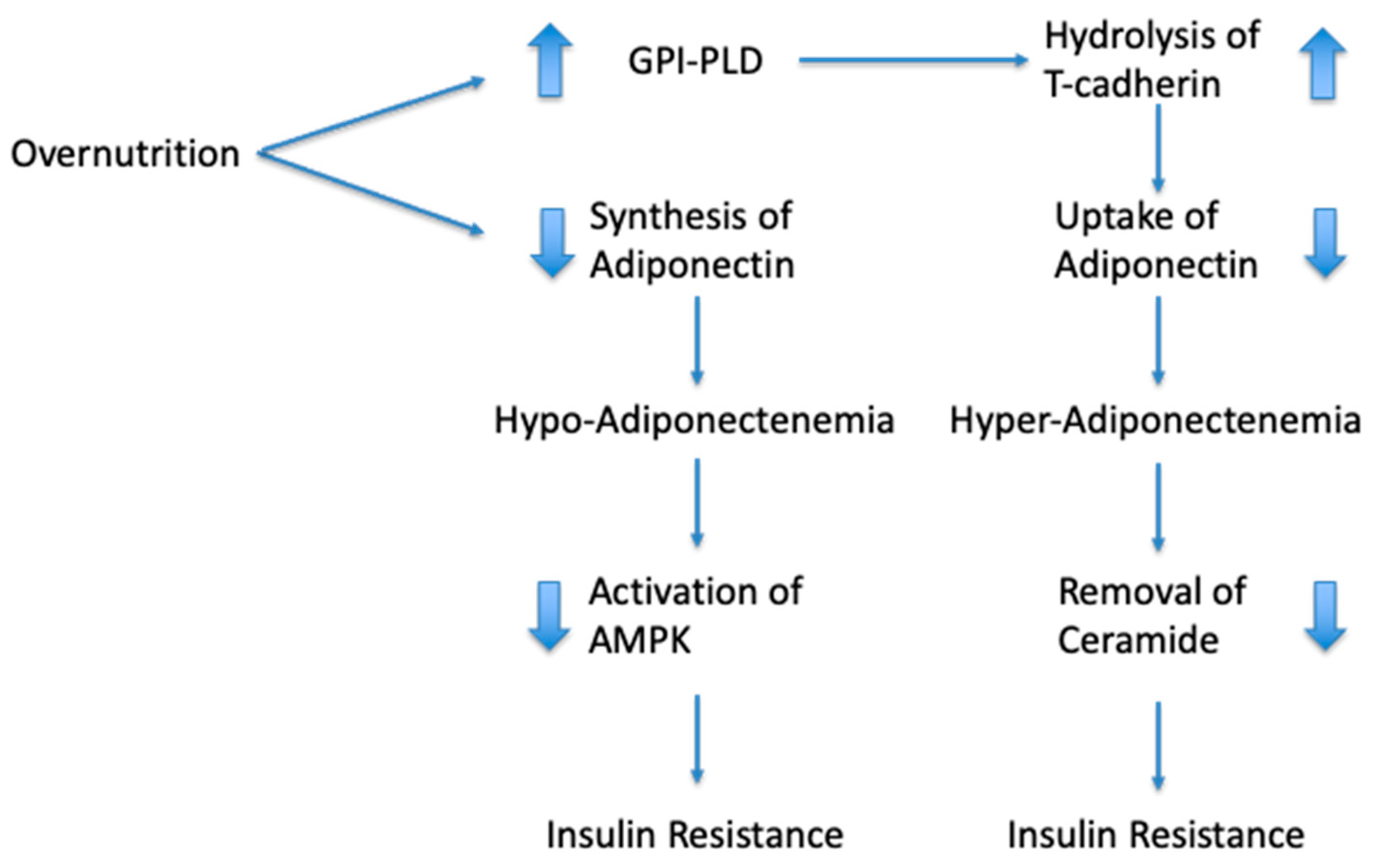
4. Mechanistic Explanation for the “Adiponectin Paradox”
5. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, P.H.; Huang, H.; McMullen, M.R.; Mandal, P.; Sun, L.; Nagy, L.E. Suppression of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by adiponectin is mediated by transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 26850–26858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, P.; Pratt, B.T.; Barnes, M.; McMullen, M.R.; Nagy, L.E. Molecular mechanism for adiponectin-dependent M2 macrophage polarization: Link between the metabolic and innate immune activity of full-length adiponectin. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 13460–13469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Stijn, C.M.; Kim, J.; Lusis, A.J.; Barish, G.D.; Tangirala, R.K. Macrophage polarization phenotype regulates adiponectin receptor expression and adiponectin anti-inflammatory response. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Mao, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, M.; Wetzel, M.D.; Guan, K.L.; Dong, L.Q.; Liu, F. Adiponectin sensitizes insulin signaling by reducing p70 S6 kinase-mediated serine phosphorylation of IRS-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7991–7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.J.; Wu, X. Imbalanced insulin action in chronic over nutrition: Clinical harm, molecular mechanisms, and a way forward. Atherosclerosis 2016, 247, 225–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Gao, Z.; Yin, J.; He, Q. Hypoxia is a potential risk factor for chronic inflammation and adiponectin reduction in adipose tissue of ob/ob and dietary obese mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E1118–E1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Kim, J.H.; Li, F.; Qu, A.; Gavrilova, O.; Shah, Y.M.; Gonzalez, F.J. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha regulates a SOCS3-STAT3-adiponectin signal transduction pathway in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 3844–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancello, R.; Henegar, C.; Viguerie, N.; Taleb, S.; Poitou, C.; Rouault, C.; Coupaye, M.; Pelloux, V.; Hugol, D.; Bouillot, J.L.; et al. Reduction of macrophage infiltration and chemoattractant gene expression changes in white adipose tissue of morbidly obese subjects after surgery-induced weight loss. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J. Emerging role of adipose tissue hypoxia in obesity and insulin resistance. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, J.M.; Lihn, A.S.; Verdich, C.; Pedersen, S.B.; Toubro, S.; Astrup, A.; Richelsen, B. Regulation of adiponectin by adipose tissue-derived cytokines: In vivo and in vitro investigations in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 285, E527–E533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, H.P.; Krzyzanowska, K.; Mohlig, M.; Spranger, J.; Pfeiffer, A.F.; Schernthaner, G. Effects of marked weight loss on plasma levels of adiponectin, markers of chronic subclinical inflammation and insulin resistance in morbidly obese women. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2005, 29, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilarrasa, N.; Vendrell, J.; Sanchez-Santos, R.; Broch, M.; Megia, A.; Masdevall, C.; Gomez, N.; Soler, J.; Pujol, J.; Bettonica, C.; et al. Effect of weight loss induced by gastric bypass on proinflammatory interleukin-18, soluble tumour necrosis factor-alpha receptors, C-reactive protein and adiponectin in morbidly obese patients. Clin. Endocrinol. 2007, 67, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illan-Gomez, F.; Gonzalvez-Ortega, M.; Orea-Soler, I.; Alcaraz-Tafalla, M.S.; Aragon-Alonso, A.; Pascual-Diaz, M.; Perez-Paredes, M.; Lozano-Almela, M.L. Obesity and inflammation: Change in adiponectin, C-reactive protein, tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 after bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2012, 22, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal-Calderon, J.R.; Cuellar-Tamez, R.; Castillo, E.C.; Luna-Ceron, E.; Garcia-Rivas, G.; Elizondo-Montemayor, L. Metabolic shift precedes the resolution of inflammation in a cohort of patients undergoing bariatric and metabolic surgery. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K.; Tobe, K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, L.G.; Scherer, P.E. Metabolic Messengers: Adiponectin. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuhisa, M.; Yamasaki, Y.; Emoto, M.; Shimabukuro, M.; Ueda, S.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y. A novel index of insulin resistance determined from the homeostasis model assessment index and adiponectin levels in Japanese subjects. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 77, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.C.; Okeke, E.; Cheung, S.; Keenan, H.; Tsui, T.; Cheng, K.; King, G.L. A cross-sectional characterization of insulin resistance by phenotype and insulin clamp in East Asian Americans with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkura, T.; Shiochi, H.; Fujioka, Y.; Sumi, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Matsuzawa, K.; Izawa, S.; Kinoshita, H.; Ohkura, H.; Kato, M.; et al. 20/(fasting C-peptide x fasting plasma glucose) is a simple and effective index of insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A preliminary report. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2013, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, R.W.; Kunutsor, S.K.; Chowdhury, R.; Yuan, J.M.; Koh, W.P.; Pan, A. Plasma adiponectin levels and type 2 diabetes risk: A nested case-control study in a Chinese population and an updated meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.M.; Weschenfelder, J.; Sander, C.; Minkwitz, J.; Thormann, J.; Chittka, T.; Mergl, R.; Kirkby, K.C.; Fasshauer, M.; Stumvoll, M.; et al. Inflammatory cytokines in general and central obesity and modulating effects of physical activity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caer, C.; Rouault, C.; Le Roy, T.; Poitou, C.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Torcivia, A.; Bichet, J.C.; Clement, K.; Guerre-Millo, M.; Andre, S. Immune cell-derived cytokines contribute to obesity-related inflammation, fibrogenesis and metabolic deregulation in human adipose tissue. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, B.V.; Ruotolo, G.; Robbins, D.C. Obesity and dyslipidemia. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 32, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klop, B.; Elte, J.W.; Cabezas, M.C. Dyslipidemia in obesity: Mechanisms and potential targets. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1218–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.V.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin, the past two decades. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 8, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehzad, A.; Iqbal, W.; Shehzad, O.; Lee, Y.S. Adiponectin: Regulation of its production and its role in human diseases. Hormones (Athens) 2012, 11, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liang, S.; Que, S.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S.; Mardinoglu, A. Meta-Analysis of Adiponectin as a Biomarker for the Detection of Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, R.K.; Halberg, N.H.; Burling, K.; Soos, M.A.; Schraw, T.; Luan, J.; Cochran, E.K.; Dunger, D.B.; Wareham, N.J.; Scherer, P.E.; et al. Paradoxical elevation of high-molecular weight adiponectin in acquired extreme insulin resistance due to insulin receptor antibodies. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1712–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pereira, R.I.; Snell-Bergeon, J.K.; Erickson, C.; Schauer, I.E.; Bergman, B.C.; Rewers, M.; Maahs, D.M. Adiponectin dysregulation and insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E642–E647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzaghi, C.; Trischitta, V. The Adiponectin Paradox for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality. Diabetes 2018, 67, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloemer, J.; Bhattacharya, S.; Amin, R.; Suppiramaniam, V. Impaired insulin signaling and mechanisms of memory loss. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2014, 121, 413–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, R.J.; Diehl, T.C.; Chia, C.W.; Kapogiannis, D. Insulin Resistance as a Link between Amyloid-Beta and Tau Pathologies in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.E.; Arvanitakis, Z.; Macauley-Rambach, S.L.; Koenig, A.M.; Wang, H.Y.; Ahima, R.S.; Craft, S.; Gandy, S.; Buettner, C.; Stoeckel, L.E.; et al. Brain insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer disease: Concepts and conundrums. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Une, K.; Takei, Y.A.; Tomita, N.; Asamura, T.; Ohrui, T.; Furukawa, K.; Arai, H. Adiponectin in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid in MCI and Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2011, 18, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemka, V.K.; Bagchi, D.; Bandyopadhyay, K.; Bir, A.; Chattopadhyay, M.; Biswas, A.; Basu, D.; Chakrabarti, S. Altered serum levels of adipokines and insulin in probable Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 41, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.F.; Wang, Z.X.; Jiang, T.; Tan, M.S.; Yu, J.T.; Tan, L. Peripheral Blood Adipokines and Insulin Levels in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: A Replication Study and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2016, 13, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letra, L.; Matafome, P.; Rodrigues, T.; Duro, D.; Lemos, R.; Baldeiras, I.; Patricio, M.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Caetano, G.; Seica, R.; et al. Association between Adipokines and Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 67, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letra, L.; Rodrigues, T.; Matafome, P.; Santana, I.; Seica, R. Adiponectin and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: Clinical and molecular links. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2019, 52, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, C.; Silva, N.; Golden, S.H.; Rajala, U.; Timonen, M.; Stahl, D.; Ismail, K. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between depression and insulin resistance. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.G.; Min, B.J.; Lim, S.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, J.J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.B.; Han, J.W.; Choi, S.H.; Park, Y.J.; et al. Plasma adiponectin elevation in elderly individuals with subsyndromal depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012, 37, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Huang, W.Y.; Kor, C.T.; Liu, K.H.; Chen, T.Y.; Lin, P.T.; Wu, H.M. Relationships between depression and anxiety symptoms and adipocyte-derived proteins in postmenopausal women. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, J.E.; Jamieson, N.; Greer, I.A.; Sattar, N. Paradoxical elevation in adiponectin concentrations in women with preeclampsia. Hypertension 2003, 42, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, L.; Akoumianakis, I.; Antoniades, C. Unravelling the adiponectin paradox: Novel roles of adiponectin in the regulation of cardiovascular disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 4007–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waragai, M.; Ho, G.; Takamatsu, Y.; Wada, R.; Sugama, S.; Takenouchi, T.; Masliah, E.; Hashimoto, M. Adiponectin Paradox in Alzheimer’s Disease; Relevance to Amyloidogenic Evolvability? Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, N.; Nelson, S.M. Adiponectin, diabetes, and coronary heart disease in older persons: Unraveling the paradox. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 3299–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uetani, E.; Tabara, Y.; Kawamoto, R.; Onuma, H.; Kohara, K.; Osawa, H.; Miki, T. CDH13 genotype-dependent association of high-molecular weight adiponectin with all-cause mortality: The J-SHIPP study. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yau, S.Y.; Li, A.; Hoo, R.L.; Ching, Y.P.; Christie, B.R.; Lee, T.M.; Xu, A.; So, K.F. Physical exercise-induced hippocampal neurogenesis and antidepressant effects are mediated by the adipocyte hormone adiponectin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15810–15815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowka, A.; Dobrzyn, P. Role of Perivascular Adipose Tissue-Derived Adiponectin in Vascular Homeostasis. Cells 2021, 10, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, C.; Wang, J.; Ahmad, N.S.; Bogan, J.S.; Tsao, T.S.; Lodish, H.F. T-cadherin is a receptor for hexameric and high-molecular-weight forms of Acrp30/adiponectin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10308–10313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denzel, M.S.; Scimia, M.C.; Zumstein, P.M.; Walsh, K.; Ruiz-Lozano, P.; Ranscht, B. T-cadherin is critical for adiponectin-mediated cardioprotection in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 4342–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, K.; Fujishima, Y.; Maeda, N.; Mori, T.; Hirata, A.; Sekimoto, R.; Tsushima, Y.; Masuda, S.; Yamaoka, M.; Inoue, K.; et al. Positive feedback regulation between adiponectin and T-cadherin impacts adiponectin levels in tissue and plasma of male mice. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, Y.; Kita, S.; Koyama, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Takeda, H.; Takahashi, M.; Fujishima, Y.; Nagao, H.; Masuda, S.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Adiponectin/T-cadherin system enhances exosome biogenesis and decreases cellular ceramides by exosomal release. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e99680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, J.M.; Ottenhoff, R.; Powlson, A.S.; Grefhorst, A.; van Eijk, M.; Dubbelhuis, P.F.; Aten, J.; Kuipers, F.; Serlie, M.J.; Wennekes, T.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of glucosylceramide synthase enhances insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, W.L.; Brozinick, J.T.; Wang, L.P.; Hawkins, E.D.; Sargent, K.M.; Liu, Y.; Narra, K.; Hoehn, K.L.; Knotts, T.A.; Siesky, A.; et al. Inhibition of ceramide synthesis ameliorates glucocorticoid-, saturated-fat-, and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Przybylska, M.; Wu, I.H.; Zhang, J.; Siegel, C.; Komarnitsky, S.; Yew, N.S.; Cheng, S.H. Inhibiting glycosphingolipid synthesis improves glycemic control and insulin sensitivity in animal models of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Park, C.W. Mechanisms of Adiponectin Action: Implication of Adiponectin Receptor Agonism in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, K.J.; Hepworth, M.R.; Raikwar, N.S.; Deeg, M.A.; Sevlever, D. Effect of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-phospholipase D overexpression on GPI metabolism. Biochem. J. 2004, 378, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, S.; Fujishima, Y.; Maeda, N.; Tsugawa-Shimizu, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Obata, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Nagao, H.; Kita, S.; et al. Impact of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D on hepatic diacylglycerol accumulation, steatosis, and insulin resistance in diet-induced obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 316, E239–E250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, M.S.; Hsu, L.A.; Wu, S.; Sun, Y.C.; Juan, S.H.; Ko, Y.L. Association of CDH13 genotypes/haplotypes with circulating adiponectin levels, metabolic syndrome, and related metabolic phenotypes: The role of the suppression effect. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; Kita, S.; Miyashita, K.; Iioka, M.; Murai, J.; Nakamura, T.; Nishizawa, H.; Fujishima, Y.; Morinaga, J.; Oike, Y.; et al. Identification and Clinical Associations of 3 Forms of Circulating T-cadherin in Human Serum. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, T.A.; Fineberg, N.S.; Considine, R.V.; Deeg, M.A. Insulin resistance is associated with increased serum levels of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D. Metabolism 2004, 53, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Raikwar, N.S.; Deeg, M.A. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase d in nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease: A preliminary study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 2279–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G.A.; Tschop, M.H.; Muller, T.D. Upregulated phospholipase D activity toward glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins in micelle-like serum complexes in metabolically deranged rats and humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 318, E462–E479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBoeuf, R.C.; Caldwell, M.; Guo, Y.; Metz, C.; Davitz, M.A.; Olson, L.K.; Deeg, M.A. Mouse glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D (Gpld1) characterization. Mamm. Genome 1998, 9, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, W.; Huang, J.; Zhu, M.; Liu, X.; Tao, J. Association between elevated adiponectin level and adverse outcomes in patients with heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, e8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.M.; Doss, H.M.; Kim, K.S. Multifaceted Physiological Roles of Adiponectin in Inflammation and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brezovec, N.; Perdan-Pirkmajer, K.; Cucnik, S.; Sodin-Semrl, S.; Varga, J.; Lakota, K. Adiponectin Deregulation in Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.I.; Lee, A.H.; Shin, H.Y.; Song, H.R.; Park, J.H.; Kang, T.B.; Lee, S.R.; Yang, S.H. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-alpha) in Autoimmune Disease and Current TNF-alpha Inhibitors in Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hector, J.; Schwarzloh, B.; Goehring, J.; Strate, T.G.; Hess, U.F.; Deuretzbacher, G.; Hansen-Algenstaedt, N.; Beil, F.U.; Algenstaedt, P. TNF-alpha alters visfatin and adiponectin levels in human fat. Horm. Metab. Res. 2007, 39, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajri, T.; Tao, H.; Wattacheril, J.; Marks-Shulman, P.; Abumrad, N.N. Regulation of adiponectin production by insulin: Interactions with tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 300, E350–E360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Feng, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Hua, M. Adiponectin, TNF-alpha and inflammatory cytokines and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine 2016, 86, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J. Role of obesity-induced inflammation in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: History of the research and remaining questions. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 26, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, O.; Fujita, M.; Kato, M.; Yamazaki, S.; Asano, Y.; Ogai, A.; Okazaki, H.; Asai, M.; Nagamachi, Y.; Maeda, N.; et al. Natriuretic peptides enhance the production of adiponectin in human adipocytes and in patients with chronic heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, T.; Hashimura, K.; Asakura, M.; Ogai, A.; Amaki, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Kanzaki, H.; Sonoda, M.; Nishizawa, H.; Funahashi, T.; et al. Dynamic changes in plasma total and high molecular weight adiponectin levels in acute heart failure. J. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, M.M.; Melo, A.L.; Damasceno, N.R. The benefits of omega-3 supplementation depend on adiponectin basal level and adiponectin increase after the supplementation: A randomized clinical trial. Nutrition 2017, 34, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farimani, A.R.; Hariri, M.; Azimi-Nezhad, M.; Borji, A.; Zarei, S.; Hooshmand, E. The effect of n-3 PUFAs on circulating adiponectin and leptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matouk, A.I.; Taye, A.; El-Moselhy, M.A.; Heeba, G.H.; Abdel-Rahman, A.A. The Effect of Chronic Activation of the Novel Endocannabinoid Receptor GPR18 on Myocardial Function and Blood Pressure in Conscious Rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 69, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, F. Up- and down-regulation of adiponectin expression and multimerization: Mechanisms and therapeutic implication. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2126–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada-Iwabu, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Iwabu, M.; Honma, T.; Hamagami, K.; Matsuda, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Tanabe, H.; Kimura-Someya, T.; Shirouzu, M.; et al. A small-molecule AdipoR agonist for type 2 diabetes and short life in obesity. Nature 2013, 503, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otvos, L., Jr. Potential Adiponectin Receptor Response Modifier Therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2019, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Ahadullah; Christie, B.R.; Lin, K.; Siu, P.M.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, T.F.; Komal, P.; Xu, A.; So, K.F.; et al. Chronic AdipoRon Treatment Mimics the Effects of Physical Exercise on Restoring Hippocampal Neuroplasticity in Diabetic Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 4666–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Deepa, S.S.; Etzler, J.C.; Ryu, J.; Mao, X.; Fang, Q.; Liu, D.D.; Torres, J.M.; Jia, W.; Lechleiter, J.D.; et al. Adiponectin activates AMP-activated protein kinase in muscle cells via APPL1/LKB1-dependent and phospholipase C/Ca2+/Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-dependent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 22426–22435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Yang, G.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Ha, J. AMPK activators: Mechanisms of action and physiological activities. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, M.C.; Cheng, Y.C.; Chen, S.J.; Yen, C.H.; Huang, R.N. Metformin activation of AMPK-dependent pathways is neuroprotective in human neural stem cells against Amyloid-beta-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 347, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.R.; Lu, Z.H.; Su, Y.; Zhao, N.; Dong, C.L.; Sun, L.; Zhao, S.F.; Li, Y. Relationship of Serum Adiponectin Levels and Metformin Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Horm. Metab. Res. 2016, 48, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalkman, H.O. An Explanation for the Adiponectin Paradox. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121266
Kalkman HO. An Explanation for the Adiponectin Paradox. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(12):1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121266
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalkman, Hans O. 2021. "An Explanation for the Adiponectin Paradox" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 12: 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121266
APA StyleKalkman, H. O. (2021). An Explanation for the Adiponectin Paradox. Pharmaceuticals, 14(12), 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121266




