Distinct In Vitro Binding Profile of the Somatostatin Receptor Subtype 2 Antagonist [177Lu]Lu-OPS201 Compared to the Agonist [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
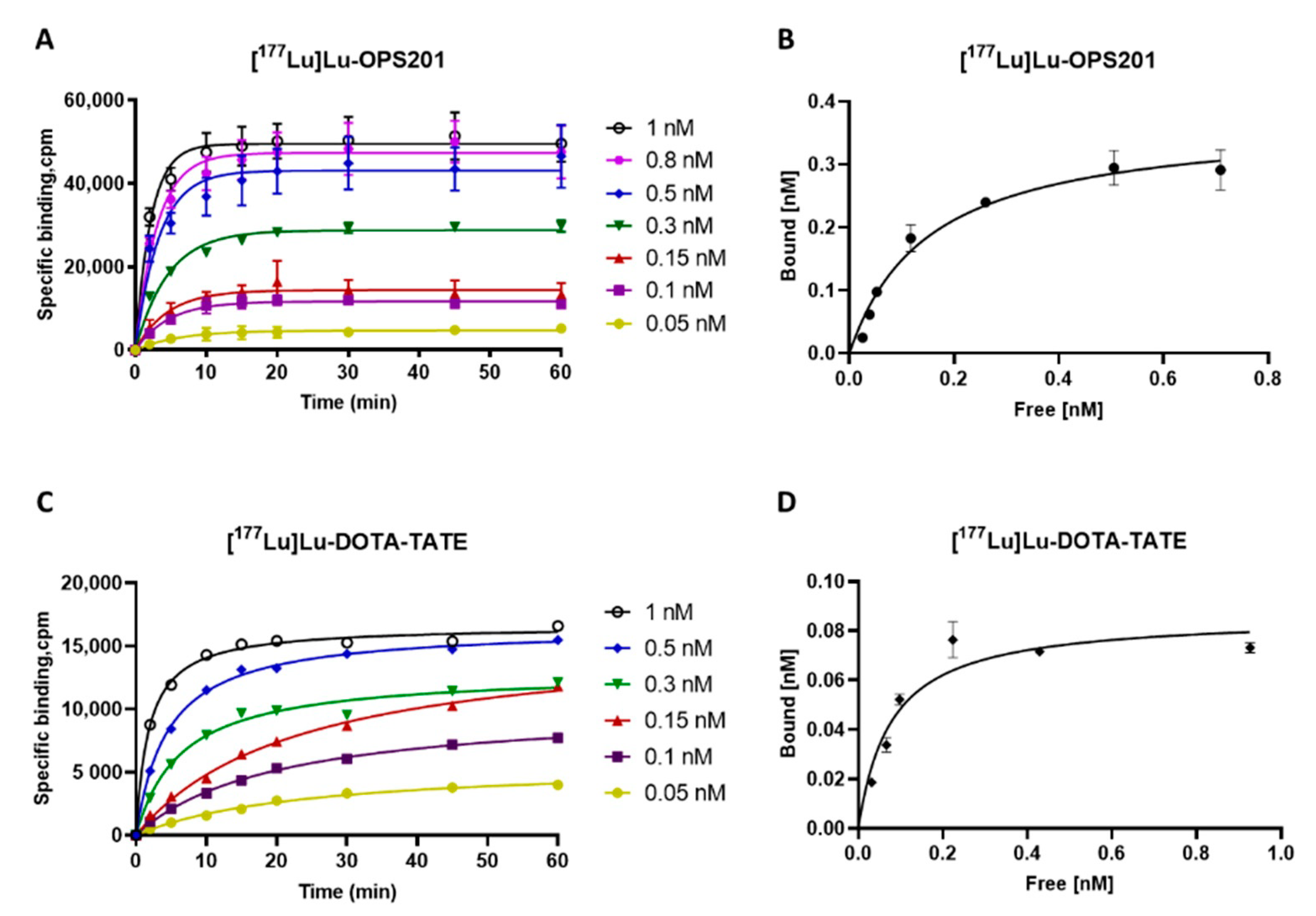
2.1. Association Kinetics and Saturation Binding on HEK-SST2 Cell Membranes
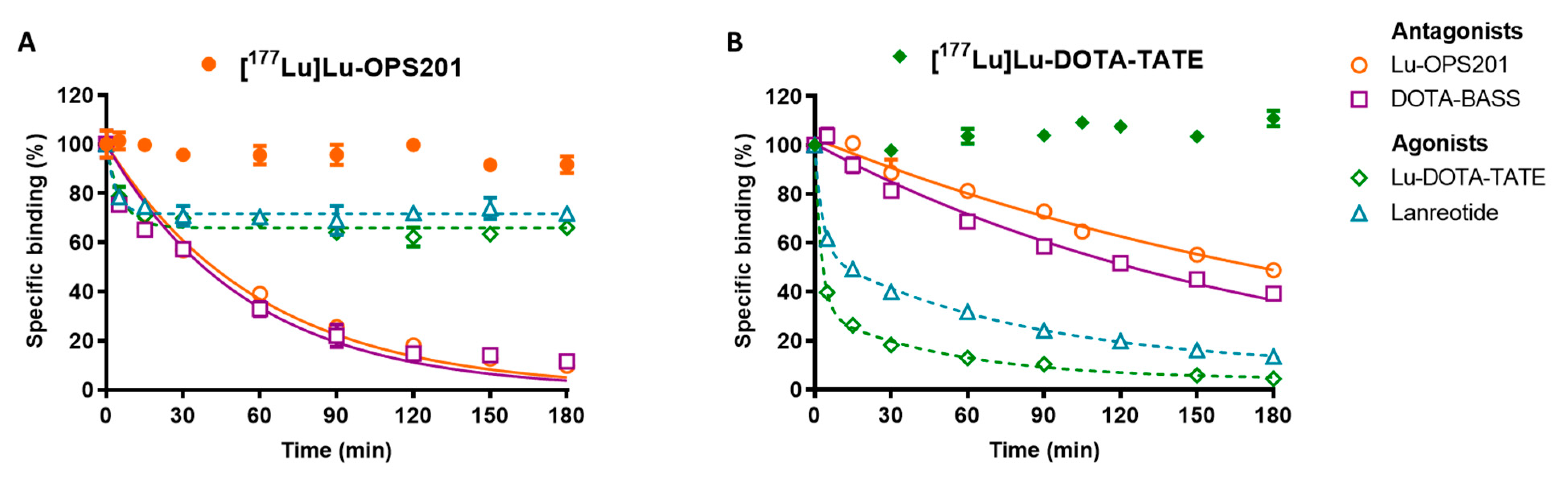
2.2. Dissociation Kinetics on Cell Membranes
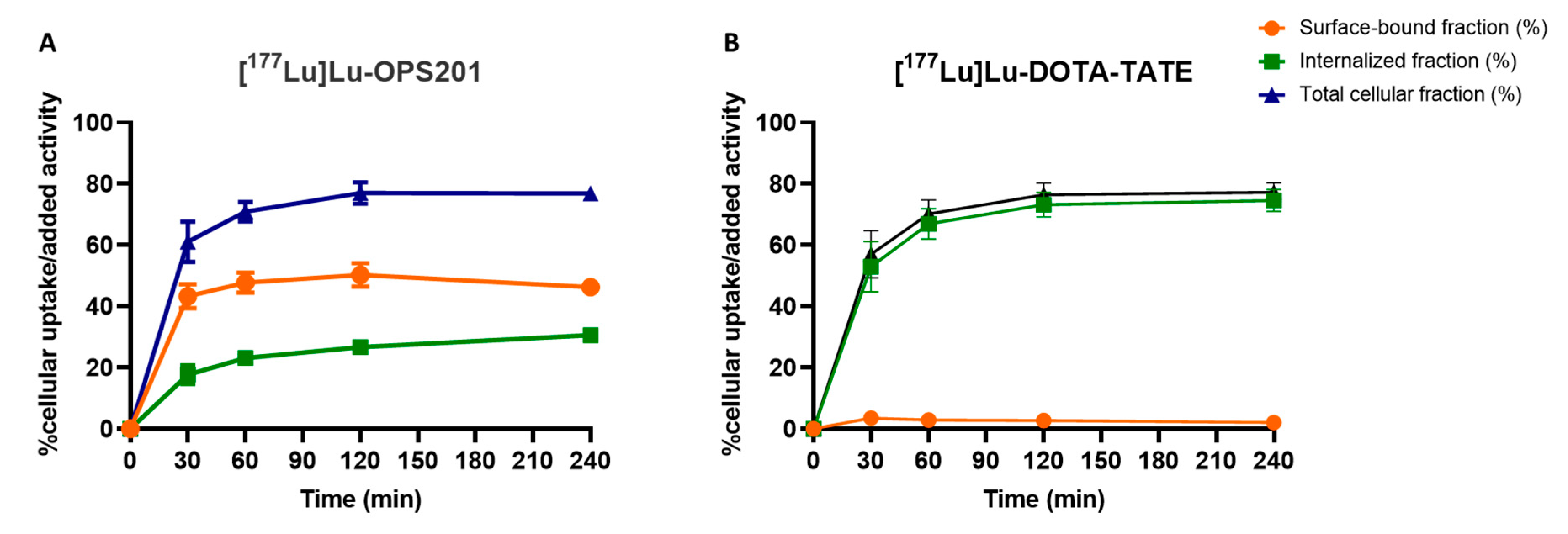
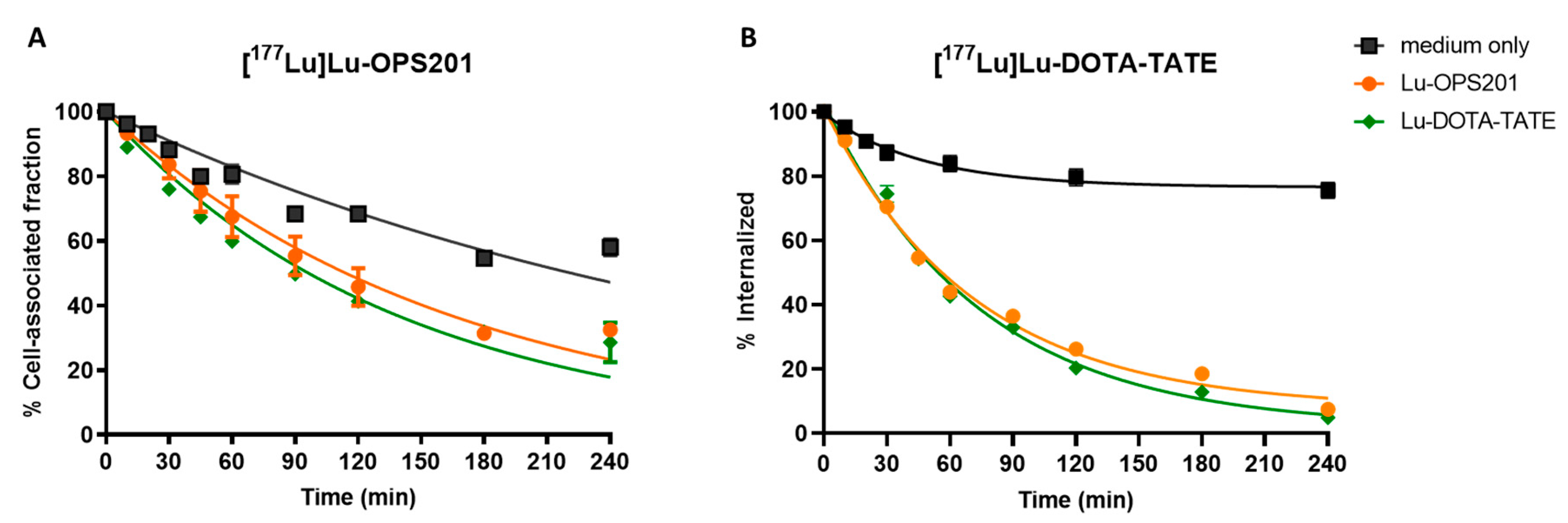
2.3. Cellular Uptake and Internalisation
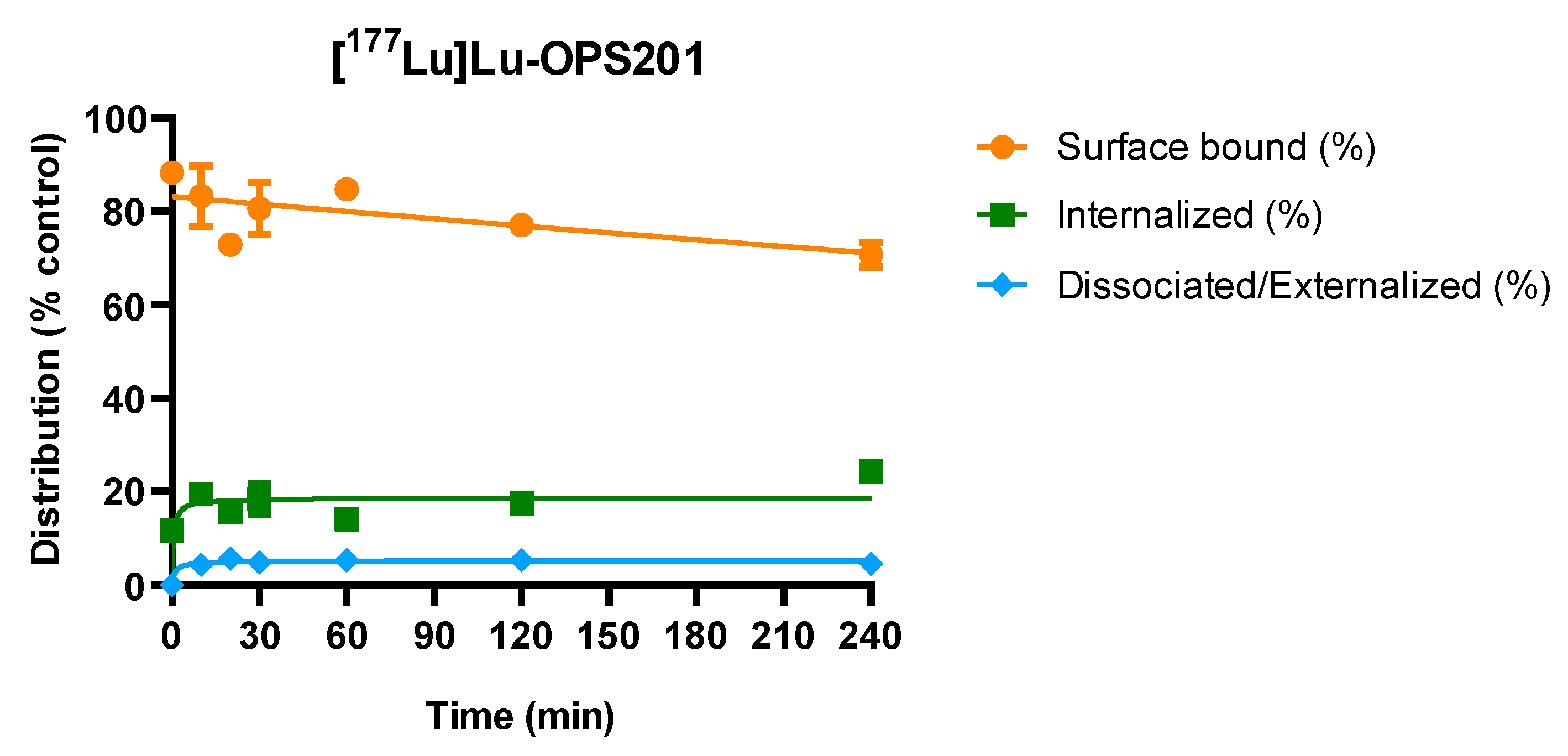
2.4. Redistribution of Cell Surface-Associated [177Lu]Lu-OPS201 at 37 °C
2.5. Release of Cell-Associated [177Lu]Lu-OPS201 with or without Unlabelled Competitors
2.6. Externalisation of [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE with or without Competitors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Radioligands
4.2. Cell Culture, Intact Cells, and Cell Membranes
4.3. Association Kinetics and Related Saturation Binding on Cell Membranes
4.4. Dissociation Kinetics on Cell Membranes
4.5. Radioligand Binding to and Internalisation by Intact Cells
4.6. Sub-Cellular Redistribution of Cell Surface-Bound [177Lu]Lu-OPS201 at 37 °C
4.7. Dissociation of Cell Surface-Bound [177Lu]Lu-OPS201 by Intact Cells
4.8. Externalisation of [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE by Intact Cells
4.9. Data and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gunther, T.; Tulipano, G.; Dournaud, P.; Bousquet, C.; Csaba, Z.; Kreienkamp, H.J.; Lupp, A.; Korbonits, M.; Castano, J.P.; Wester, H.J.; et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CV. Somatostatin Receptors: Structure, Function, Ligands, and New Nomenclature. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 763–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.H.; Goldner, W.S.; Benson, A.B., III; Bergsland, E.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Brock, P.; Chan, J.; Das, S.; Dickson, P.V.; Fanta, P.; et al. Neuroendocrine and Adrenal Tumors, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 839–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, R.J.; Kwekkeboom, D.J.; Krenning, E.; Bodei, L.; Grozinsky-Glasberg, S.; Arnold, R.; Borbath, I.; Cwikla, J.; Toumpanakis, C.; Kaltsas, G.; et al. ENETS Consensus Guidelines for the Standards of Care in Neuroendocrine Neoplasia: Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy with Radiolabeled Somatostatin Analogues. Neuroendocrinology 2017, 105, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fani, M.; Nicolas, G.P.; Wild, D. Somatostatin Receptor Antagonists for Imaging and Therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58 (Suppl. 2), 61S–66S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansi, R.; Fani, M. Design and development of the theranostic pair (177) Lu-OPS201/(68) Ga-OPS202 for targeting somatostatin receptor expressing tumors. J. Label. Comp. Radiopharm. 2019, 62, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidy-Lagunes, D.; Pandit-Taskar, N.; O’Donoghue, J.A.; Krebs, S.; Staton, K.D.; Lyashchenko, S.K.; Lewis, J.S.; Raj, N.; Gonen, M.; Lohrmann, C.; et al. Phase I Trial of Well-Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumors (NETs) with Radiolabeled Somatostatin Antagonist (177)Lu-Satoreotide Tetraxetan. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6939–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, D.; Fani, M.; Fischer, R.; Del Pozzo, L.; Kaul, F.; Krebs, S.; Fischer, R.; Rivier, J.E.; Reubi, J.C.; Maecke, H.R.; et al. Comparison of somatostatin receptor agonist and antagonist for peptide receptor radionuclide therapy: A pilot study. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1248–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginj, M.; Zhang, H.; Waser, B.; Cescato, R.; Wild, D.; Wang, X.; Erchegyi, J.; Rivier, J.; Macke, H.R.; Reubi, J.C. Radiolabeled somatostatin receptor antagonists are preferable to agonists for in vivo peptide receptor targeting of tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16436–16441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalm, S.U.; Nonnekens, J.; Doeswijk, G.N.; de Blois, E.; van Gent, D.C.; Konijnenberg, M.W.; de Jong, M. Comparison of the Therapeutic Response to Treatment with a 177Lu-Labeled Somatostatin Receptor Agonist and Antagonist in Preclinical Models. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, G.P.; Mansi, R.; McDougall, L.; Kaufmann, J.; Bouterfa, H.; Wild, D.; Fani, M. Biodistribution, Pharmacokinetics, and Dosimetry of (177)Lu-, (90)Y-, and (111)In-Labeled Somatostatin Receptor Antagonist OPS201 in Comparison to the Agonist (177)Lu-DOTATATE: The Mass Effect. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Peletier, L.A.; Bridge, L.; Keur, W.; de Vries, H.; Zweemer, A.; Heitman, L.H.; Ijzerman, A.P.I. A two-state model for the kinetics of competitive radioligand binding. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strange, P.G. Agonist binding, agonist affinity and agonist efficacy at G protein-coupled receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, C.; Grinde, E.; Dupre, A.; Roth, B.L.; Hake, M.; Teitler, M.; Herrick-Davis, K. Agonist high and low affinity state ratios predict drug intrinsic activity and a revised ternary complex mechanism at serotonin 5-HT(2A) and 5-HT(2C) receptors. Synapse 2000, 35, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkowitz, R.J.; Cotecchia, S.; Samama, P.; Costa, T. Constitutive activity of receptors coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1993, 14, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, L.J. Lipid rafts: Bringing order to chaos. J. Lipid Res. 2003, 44, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauquelin, G.; Bostoen, S.; Vanderheyden, P.; Seeman, P. Clozapine, atypical antipsychotics, and the benefits of fast-off D2 dopamine receptor antagonism. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2012, 385, 337–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, W.I.; Kobilka, B.K. The Molecular Basis of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Activation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 897–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel-Seifert, K.; Seifert, R. Molecular analysis of beta(2)-adrenoceptor coupling to G(s)-, G(i)-, and G(q)-proteins. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleight, A.J.; Stam, N.J.; Mutel, V.; Vanderheyden, P.M. Radiolabelling of the human 5-HT2A receptor with an agonist, a partial agonist and an antagonist: Effects on apparent agonist affinities. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 51, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauquelin, G.; Van Liefde, I.; Swinney, D.C. Radioligand binding to intact cells as a tool for extended drug screening in a representative physiological context. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2015, 17, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofland, L.J.; Lamberts, S.W. The pathophysiological consequences of somatostatin receptor internalization and resistance. Endocr. Rev. 2003, 24, 28–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadas, T.J.; Eiblmaier, M.; Zheleznyak, A.; Sherman, C.D.; Ferdani, R.; Liang, K.; Achilefu, S.; Anderson, C.J. Preparation and biological evaluation of 64Cu-CB-TE2A-sst2-ANT, a somatostatin antagonist for PET imaging of somatostatin receptor-positive tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, J.A.; Edwardson, J.M. Endocytosis and recycling of G protein-coupled receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1997, 18, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fani, M.; Del Pozzo, L.; Abiraj, K.; Mansi, R.; Tamma, M.L.; Cescato, R.; Waser, B.; Weber, W.A.; Reubi, J.C.; Maecke, H.R. PET of somatostatin receptor-positive tumors using 64Cu- and 68Ga-somatostatin antagonists: The chelate makes the difference. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylova, S.N.; Stoykow, C.; Del Pozzo, L.; Abiraj, K.; Tamma, M.L.; Kiefer, Y.; Fani, M.; Maecke, H.R. The somatostatin receptor 2 antagonist Cu-64-NODAGA-JR11 outperforms Cu-64-DOTA-TATE in a mouse xenograft model. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waser, B.; Tamma, M.L.; Cescato, R.; Maecke, H.R.; Reubi, J.C. Highly efficient in vivo agonist-induced internalization of sst2 receptors in somatostatin target tissues. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, P.; Tokmakoff, A. Time-resolved measurements of an ion channel conformational change driven by a membrane phase transition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10840–10845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauquelin, G.; Fierens, F.; Van Liefde, I. Long-lasting angiotensin type 1 receptor binding and protection by candesartan: Comparison with other biphenyl-tetrazole sartans. J. Hypertens. 2006, 24, S23–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierens, F.L.; Vanderheyden, P.M.; Roggeman, C.; Vande Gucht, P.; De Backer, J.P.; Vauquelin, G. Distinct binding properties of the AT(1) receptor antagonist [(3)H]candesartan to intact cells and membrane preparations. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 63, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, A.C.; Qian, H.; Pipolo, L.; Ziogas, J.; Miura, S.; Karnik, S.; Southwell, B.R.; Lew, M.J.; Thomas, W.G. Side-chain substitutions within angiotensin II reveal different requirements for signaling, internalization, and phosphorylation of type 1A angiotensin receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunyady, L.; Gaborik, Z.; Vauquelin, G.; Catt, K.J. Review: Structural requirements for signalling and regulation of AT1-receptors. J. Renin Angiotensin. Aldosterone Syst. 2001, 2 (Suppl. 1), S16–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cescato, R.; Schulz, S.; Waser, B.; Eltschinger, V.; Rivier, J.E.; Wester, H.J.; Culler, M.; Ginj, M.; Liu, Q.; Schonbrunn, A.; et al. Internalization of sst2, sst3, and sst5 receptors: Effects of somatostatin agonists and antagonists. J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pheng, L.H.; Dumont, Y.; Fournier, A.; Chabot, J.G.; Beaudet, A.; Quirion, R. Agonist- and antagonist-induced sequestration/internalization of neuropeptide Y Y1 receptors in HEK293 cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roettger, B.F.; Ghanekar, D.; Rao, R.; Toledo, C.; Yingling, J.; Pinon, D.; Miller, L.J. Antagonist-stimulated internalization of the G protein-coupled cholecystokinin receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 51, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin, T.; Miller, L.J. Seven transmembrane receptors as shapeshifting proteins: The impact of allosteric modulation and functional selectivity on new drug discovery. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 265–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Witte, W.E.A.; Danhof, M.; van der Graaf, P.H.; de Lange, E.C.M. In vivo Target Residence Time and Kinetic Selectivity: The Association Rate Constant as Determinant. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauquelin, G.; Charlton, S.J. Long-lasting target binding and rebinding as mechanisms to prolong in vivo drug action. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 488–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, J.A.; Kaur, R.; Dodgeon, I.; Edwardson, J.M.; Humphrey, P.P. Fates of endocytosed somatostatin sst2 receptors and associated agonists. Biochem. J. 1998, 336, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauquelin, G. Effects of target binding kinetics on in vivo drug efficacy: Koff, kon and rebinding. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 2319–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofland, L.J.; van Koetsveld, P.M.; Waaijers, M.; Zuyderwijk, J.; Breeman, W.A.; Lamberts, S.W. Internalization of the radioiodinated somatostatin analog [125I-Tyr3]octreotide by mouse and human pituitary tumor cells: Increase by unlabeled octreotide. Endocrinology 1995, 136, 3698–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Competitor | [177Lu]Lu-OPS201 | [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE |
|---|---|---|
| koff (min−1) in HEK-SST2 Membranes | ||
| Lu-OPS201 | 0.017 ± 0.002 | 0.004 ± 0.0002 |
| Lu-DOTA-TATE | n.a. | 0.019 ± 0.005 (k2) 0.38 ± 0.05 (k1) |
| DOTA-BASS | 0.018 ± 0.002 | 0.005 ± 0.0003 |
| Lanreotide | n.a. | 0.012 ± 0.002 (k2) 0.32 ± 0.03 (k1) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mansi, R.; Plas, P.; Vauquelin, G.; Fani, M. Distinct In Vitro Binding Profile of the Somatostatin Receptor Subtype 2 Antagonist [177Lu]Lu-OPS201 Compared to the Agonist [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121265
Mansi R, Plas P, Vauquelin G, Fani M. Distinct In Vitro Binding Profile of the Somatostatin Receptor Subtype 2 Antagonist [177Lu]Lu-OPS201 Compared to the Agonist [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(12):1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121265
Chicago/Turabian StyleMansi, Rosalba, Pascale Plas, Georges Vauquelin, and Melpomeni Fani. 2021. "Distinct In Vitro Binding Profile of the Somatostatin Receptor Subtype 2 Antagonist [177Lu]Lu-OPS201 Compared to the Agonist [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 12: 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121265
APA StyleMansi, R., Plas, P., Vauquelin, G., & Fani, M. (2021). Distinct In Vitro Binding Profile of the Somatostatin Receptor Subtype 2 Antagonist [177Lu]Lu-OPS201 Compared to the Agonist [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE. Pharmaceuticals, 14(12), 1265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121265








