Corylin Ameliorates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Suppressing the MAPKs and IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Corylin Suppresses the Production of IL-6 by LPS-Induced Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells (HBEC3-KT Cells)
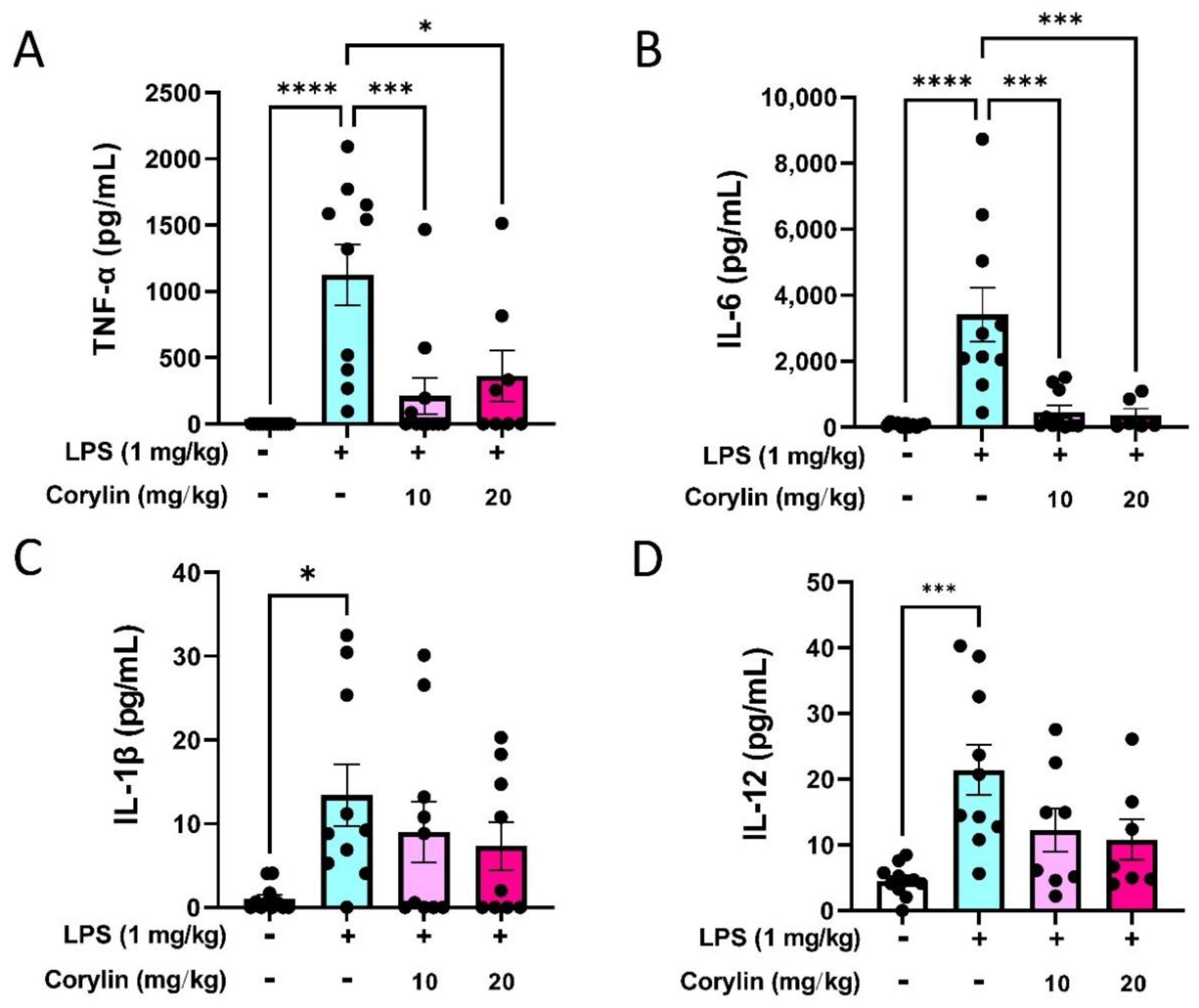
2.2. Corylin Attenuates the Production of Inflammatory Cytokines in LPS-Induced ALI Mice
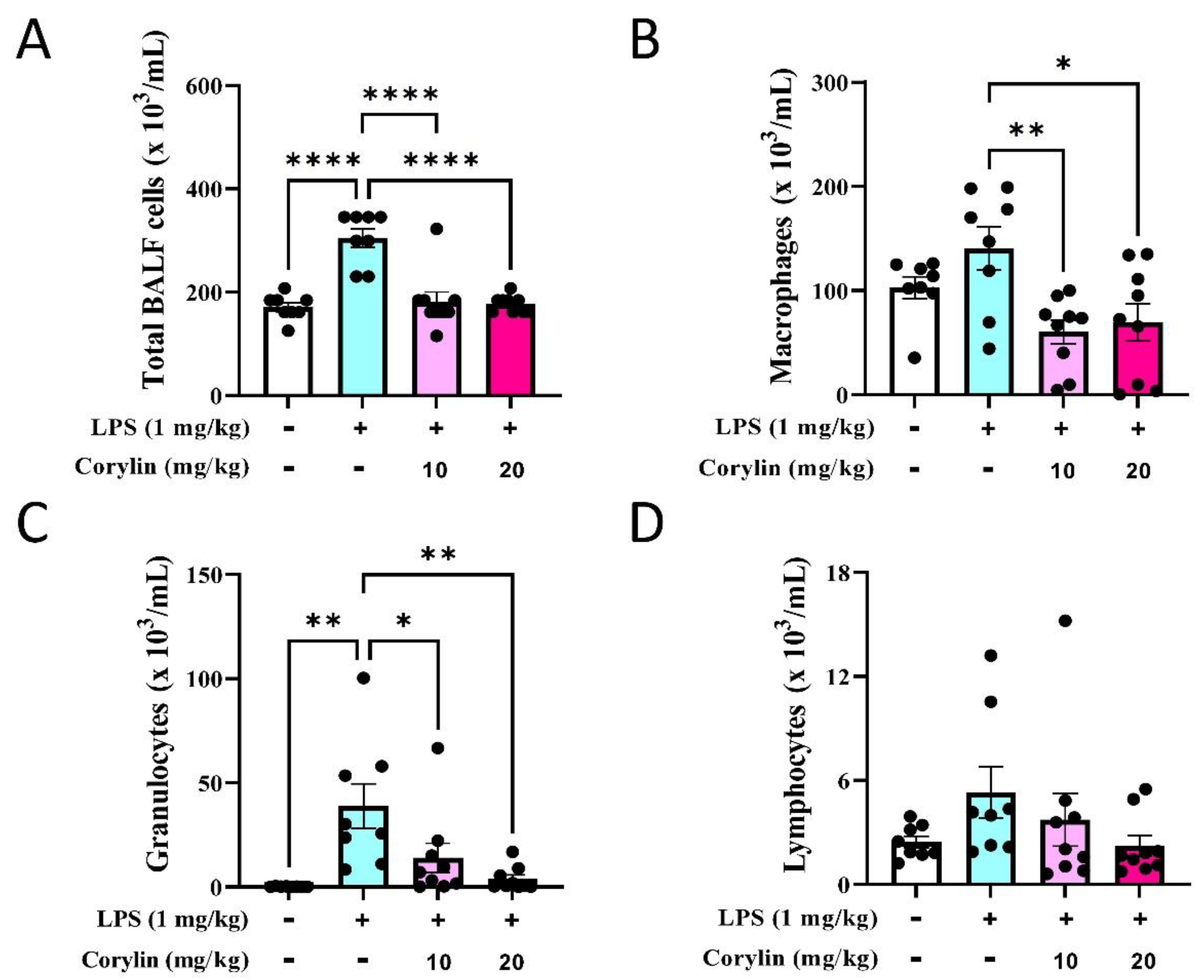
2.3. Corylin Reduces the Infiltration of Inflammatory Cells in Lung in LPS-Induced ALI Mice
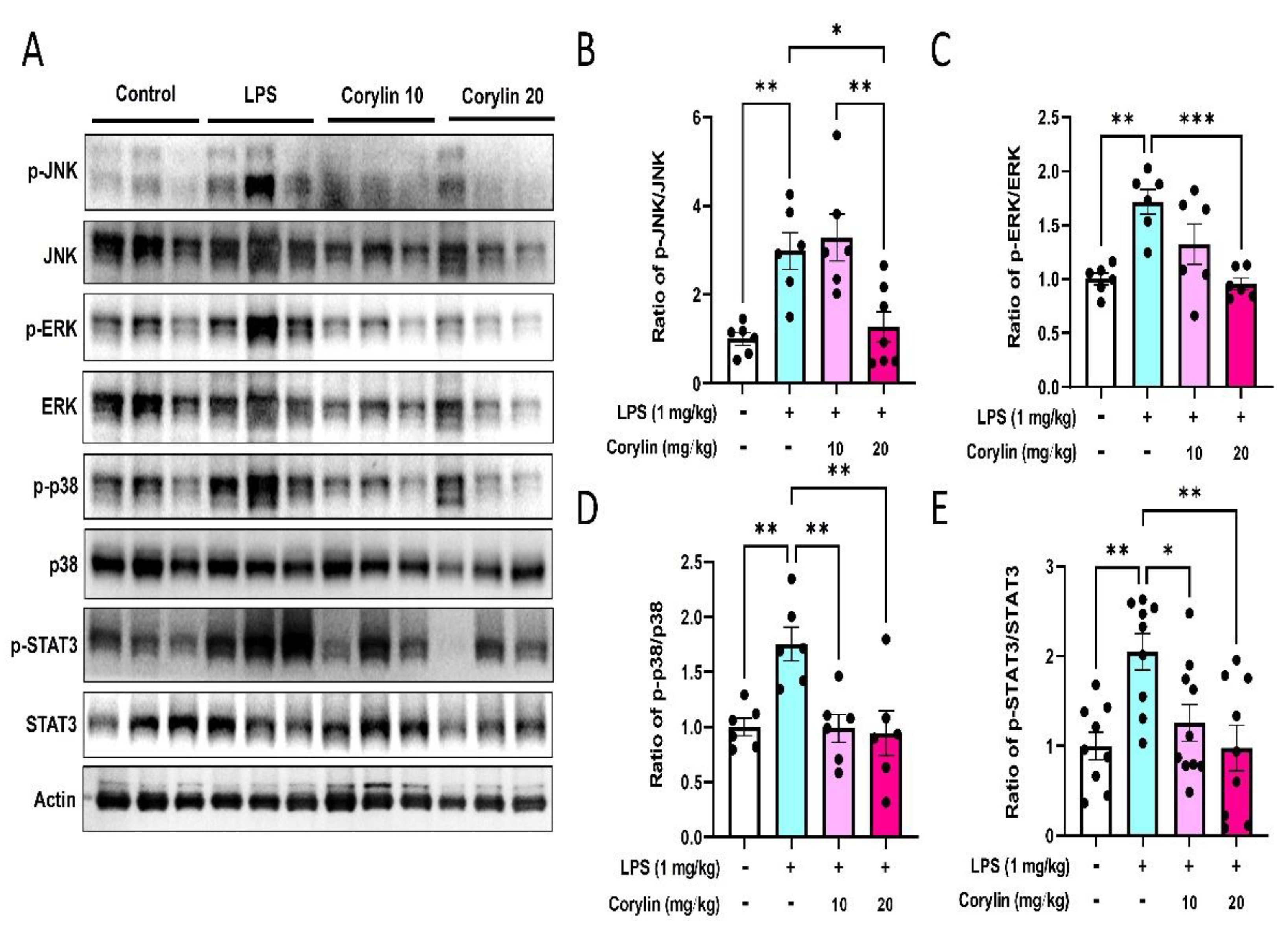
2.4. Corylin Decreases the Phosphorylation of MAPKs and STAT3 in Lung Tissues of LPS-Induced ALI Mice
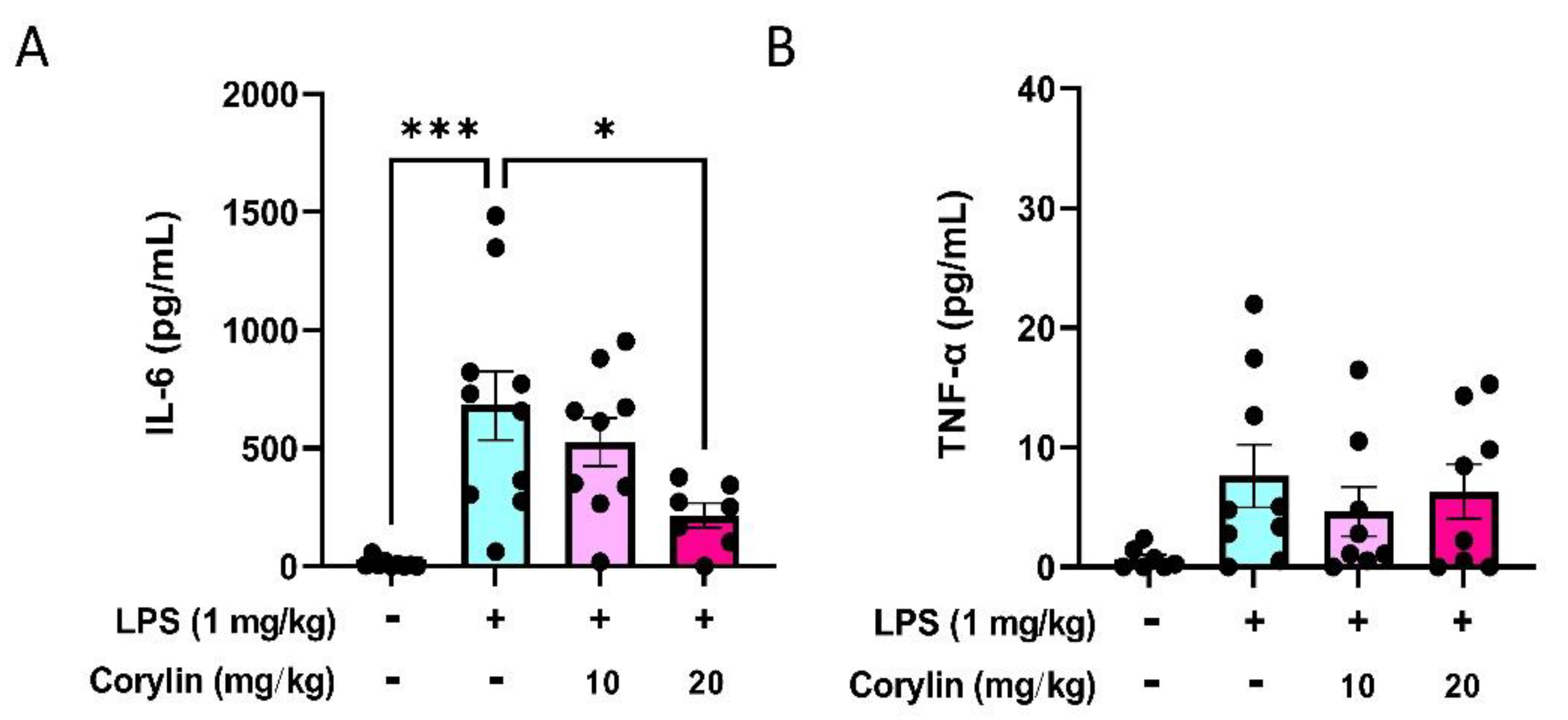
2.5. Corylin Reduces the Expression of IL-6 in Mouse Serum
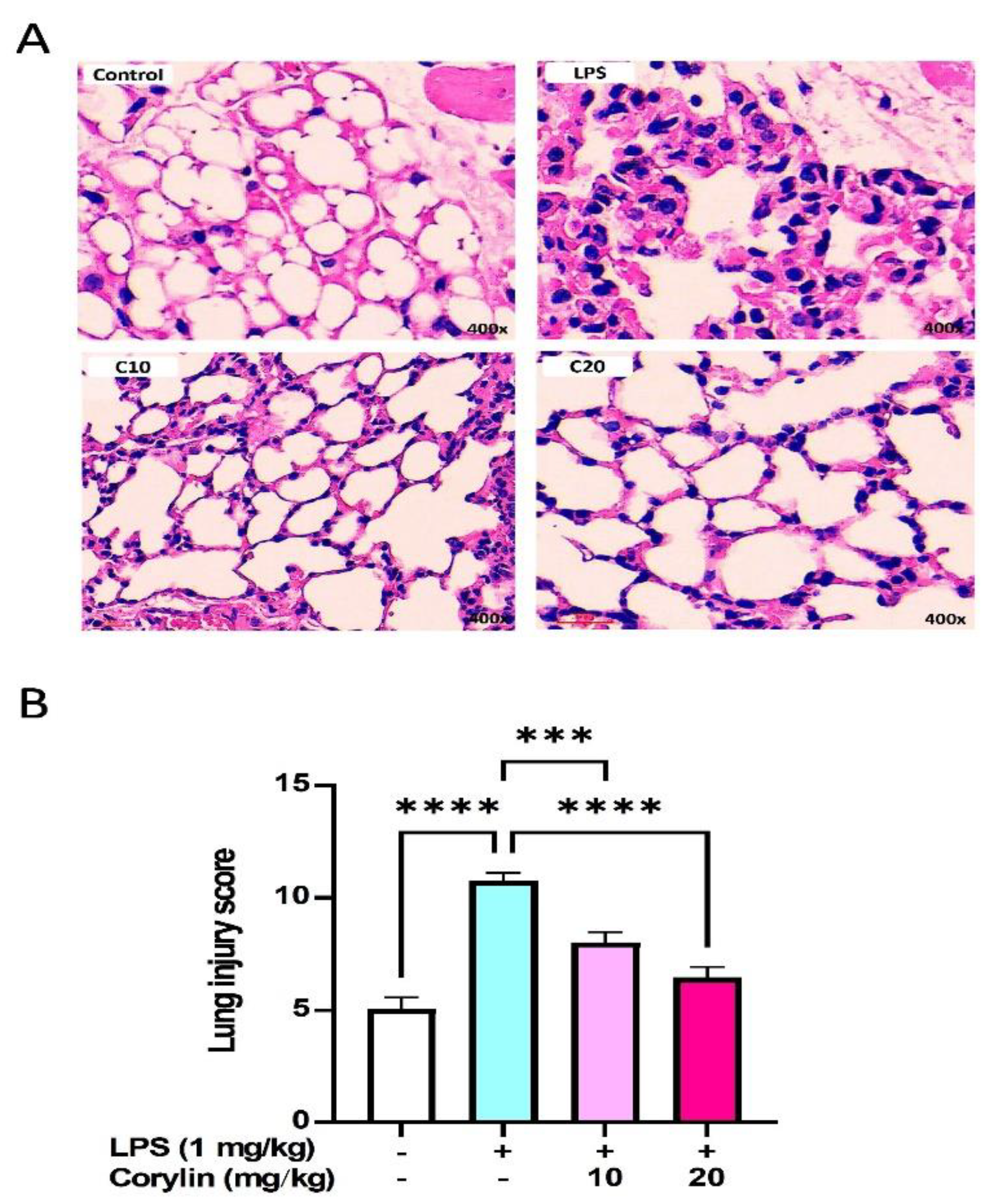
2.6. Corylin Decreases Lung Injury in LPS-Induced ALI Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. ALI Model
4.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.6. Multicolor Flow Cytometry
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Histopathological Assessment with Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
4.9. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phua, J.; Badia, J.R.; Adhikari, N.K.; Friedrich, J.O.; Fowler, R.A.; Singh, J.M.; Scales, D.C.; Stather, D.R.; Li, A.; Jones, A.; et al. Has mortality from acute respiratory distress syndrome decreased over time?: A systematic review. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubenfeld, G.D.; Caldwell, E.; Peabody, E.; Weaver, J.; Martin, D.P.; Neff, M.; Stern, E.J.; Hudson, L.D. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharp, C.; Millar, A.B.; Medford, A.R. Advances in understanding of the pathogenesis of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Respiration 2015, 89, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network; Brower, R.G.; Matthay, M.A.; Morris, A.; Schoenfeld, D.; Thompson, B.T.; Wheeler, A. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, L.J.; Matthay, M.A. Biomarkers in acute lung injury: Insights into the pathogenesis of acute lung injury. Crit. Care Clin. 2011, 27, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manicone, A.M. Role of the pulmonary epithelium and inflammatory signals in acute lung injury. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 5, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voiriot, G.; Razazi, K.; Amsellem, V.; Tran Van Nhieu, J.; Abid, S.; Adnot, S.; Mekontso Dessap, A.; Maitre, B. Interleukin-6 displays lung anti-inflammatory properties and exerts protective hemodynamic effects in a double-hit murine acute lung injury. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinton, L.J.; Jones, M.R.; Robson, B.E.; Simms, B.T.; Whitsett, J.A.; Mizgerd, J.P. Alveolar epithelial STAT3, IL-6 family cytokines, and host defense during Escherichia coli pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.R.; Quinton, L.J.; Simms, B.T.; Lupa, M.M.; Kogan, M.S.; Mizgerd, J.P. Roles of interleukin-6 in activation of STAT proteins and recruitment of neutrophils during Escherichia coli pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 193, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Gibson, S.A.; Yan, Z.; Xu, X.; Gaggar, A.; Li, P.K.; Li, C.; Wei, S.; et al. Protective effect of suppressing STAT3 activity in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2016, 311, L868–L880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaver, L.M.; Stemmy, E.J.; Schwartz, A.M.; Damsker, J.M.; Constant, S.L.; Ceryak, S.M.; Patierno, S.R. Lung inflammation, injury, and proliferative response after repetitive particulate hexavalent chromium exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1896–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, J.P.; Thompson, D.; Hamilton, E.; Debrue, M.; David, F.; Hickey, G. Effects of a MAPK p38 inhibitor on lung function and airway inflammation in equine recurrent airway obstruction. Equine Vet. J. 2008, 40, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Cai, S.X.; Wang, C.L.; Sun, X.X.; Li, K.; Yan, X.W.; Sun, Y.B.; Sun, X.Z.; Gu, C.K.; Dai, M.Y.; et al. Modulation of mitogenactivated protein kinase attenuates sepsisinduced acute lung injury in acute respiratory distress syndrome rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 9652–9658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, A.X.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, S.Z.; Kong, X.P.; Kwan, K.K.; Zheng, B.Z.; Wu, K.Q.; Dong, T.T.; Tsim, K.W. Biological Evaluation and Transcriptomic Analysis of Corylin as an Inhibitor of Osteoclast Differentiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Li, H.Y.; Leu, Y.L.; Chen, Y.J.; Wang, C.J.; Wang, S.H. Corylin Inhibits Vascular Cell Inflammation, Proliferation and Migration and Reduces Atherosclerosis in ApoE-Deficient Mice. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.Y.; Tu, C.E.; Wang, S.C.; Hung, Y.L.; Su, C.C.; Fang, S.H.; Chen, C.S.; Liu, P.L.; Cheng, W.C.; Huang, Y.W.; et al. Corylin inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response and attenuates the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.L.; Fang, S.H.; Wang, S.C.; Cheng, W.C.; Liu, P.L.; Su, C.C.; Chen, C.S.; Huang, M.Y.; Hua, K.F.; Shen, K.H.; et al. Corylin protects LPS-induced sepsis and attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory response. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Yao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, F.; Chen, L.; Hu, W.; Xiang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; et al. Effect of the isoflavone corylin from cullen corylifolium on colorectal cancer growth, by targeting the STAT3 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2021, 80, 153366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.X.; Xu, M.L.; Yao, P.; Kwan, K.K.; Liu, Y.X.; Duan, R.; Dong, T.T.; Ko, R.K.; Tsim, K.W. Corylin, a flavonoid derived from Psoralea Fructus, induces osteoblastic differentiation via estrogen and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 4311–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Kuo, C.H.; Leu, Y.L.; Wang, S.H. Corylin reduces obesity and insulin resistance and promotes adipose tissue browning through SIRT-1 and beta3-AR activation. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 164, 105291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.; Oh, Y.S.; Kim, D.; Lee, M.Y.; Chae, S.; Jun, H.S. Protective Role of Psoralea corylifolia L. Seed Extract against Hepatic Mitochondrial Dysfunction Induced by Oxidative Stress or Aging. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 678028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.W.; Yun, B.R.; Kim, M.H.; Park, C.S.; Lee, W.S.; Oh, H.M.; Rho, M.C. Phenolic compounds isolated from Psoralea corylifolia inhibit IL-6-induced STAT3 activation. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, A.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y. Role of p38 MAPK and STAT3 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated mouse alveolar macrophages. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 8, 1772–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arthur, J.S.C.; Ley, S.C. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, J.W.; Chen, B.J.; Brass, D.M.; Berman, K.; Gunn, M.D.; Cook, D.N.; Schwartz, D.A. The critical role of hematopoietic cells in lipopolysaccharide-induced airway inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beck-Schimmer, B.; Schwendener, R.; Pasch, T.; Reyes, L.; Booy, C.; Schimmer, R.C. Alveolar macrophages regulate neutrophil recruitment in endotoxin-induced lung injury. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Xiu, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G. The Role of Macrophages in the Pathogenesis of ALI/ARDS. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1264913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.E.; Chambers, R.C. The mercurial nature of neutrophils: Still an enigma in ARDS? Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L217–L230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakshmi, S.P.; Reddy, A.T.; Naik, M.U.; Naik, U.P.; Reddy, R.C. Effects of JAM-A deficiency or blocking antibodies on neutrophil migration and lung injury in a murine model of ALI. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 303, L758–L766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Feng, B.; Xu, Y.; Chen, W.; Sheng, X.; Feng, X.; Shi, X.; Liu, J.; Pan, Q.; Yu, J.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the proinflammatory function of Ly6C(+) CD8(+) T cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.; Zou, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, J. Ginsenoside Rg1 improves lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting inflammatory responses and modulating infiltration of M2 macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meduri, G.U.; Headley, S.; Kohler, G.; Stentz, F.; Tolley, E.; Umberger, R.; Leeper, K. Persistent elevation of inflammatory cytokines predicts a poor outcome in ARDS. Plasma IL-1 beta and IL-6 levels are consistent and efficient predictors of outcome over time. Chest 1995, 107, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Mizoguchi, I.; Chiba, Y.; Ohashi, M.; Xu, M.; Yoshimoto, T. Expanding Diversity in Molecular Structures and Functions of the IL-6/IL-12 Heterodimeric Cytokine Family. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zundler, S.; Neurath, M.F. Interleukin-12: Functional activities and implications for disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekman, W.; Amatngalim, G.D.; de Mooij-Eijk, Y.; Oostendorp, J.; Roelofs, H.; Taube, C.; Stolk, J.; Hiemstra, P.S. TNF-alpha and IL-1beta-activated human mesenchymal stromal cells increase airway epithelial wound healing in vitro via activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gierlikowska, B.; Filipek, A.; Gierlikowski, W.; Kania, D.; Stefanska, J.; Demkow, U.; Kiss, A.K. Grindelia squarrosa Extract and Grindelic Acid Modulate Pro-inflammatory Functions of Respiratory Epithelium and Human Macrophages. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 534111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorey, J.S.; Cooper, A.M. Macrophage signalling upon mycobacterial infection: The MAP kinases lead the way. Cell. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, S.K.; Schorey, J.S. Differential regulation of the mitogen-activated protein kinases by pathogenic and nonpathogenic mycobacteria. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3040–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guha, M.; Mackman, N. LPS induction of gene expression in human monocytes. Cell. Signal. 2001, 13, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samavati, L.; Rastogi, R.; Du, W.; Huttemann, M.; Fite, A.; Franchi, L. STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation is critical for interleukin 1 beta and interleukin-6 production in response to lipopolysaccharide and live bacteria. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 1867–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.L.; Flanagan, K.L. Sex differences in immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfinanda, L.; Ravindran, K.; Kohse, F.; Gallo, K.; Preissner, R.; Walther, T.; Kuebler, W.M. Oestrogen-mediated upregulation of the Mas receptor contributes to sex differences in acute lung injury and lung vascular barrier regulation. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2000921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misharin, A.V.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; Mutlu, G.M.; Budinger, G.R.; Perlman, H. Flow cytometric analysis of macrophages and dendritic cell subsets in the mouse lung. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suen, J.L.; Wu, T.T.; Li, Y.H.; Lee, C.L.; Kuo, F.C.; Yan, P.S.; Wu, C.F.; Tran, M.; Wang, C.J.; Hung, C.H.; et al. Environmental Factor-Mediated Transgenerational Inheritance of Igf2r Hypomethylation and Pulmonary Allergic Response via Targeting Dendritic Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 603831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrozek, J.D.; Smith, K.M.; Bing, D.R.; Meyers, P.A.; Simonton, S.C.; Connett, J.E.; Mammel, M.C. Exogenous surfactant and partial liquid ventilation: Physiologic and pathologic effects. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, I.-C.; Wang, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-T.; Tseng, H.-H.; Liu, P.-L.; Lin, T.-C.; Wu, H.-E.; Chen, Y.-R.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Hsu, J.-H.; et al. Corylin Ameliorates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Suppressing the MAPKs and IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Pathways. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14101046
Chen I-C, Wang S-C, Chen Y-T, Tseng H-H, Liu P-L, Lin T-C, Wu H-E, Chen Y-R, Tseng Y-H, Hsu J-H, et al. Corylin Ameliorates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Suppressing the MAPKs and IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Pathways. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(10):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14101046
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, I-Chen, Shu-Chi Wang, Yi-Ting Chen, Hsin-Han Tseng, Po-Len Liu, Tzu-Chieh Lin, Hsin-En Wu, Yuan-Ru Chen, Yu-Hsin Tseng, Jong-Hau Hsu, and et al. 2021. "Corylin Ameliorates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Suppressing the MAPKs and IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Pathways" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 10: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14101046
APA StyleChen, I.-C., Wang, S.-C., Chen, Y.-T., Tseng, H.-H., Liu, P.-L., Lin, T.-C., Wu, H.-E., Chen, Y.-R., Tseng, Y.-H., Hsu, J.-H., Dai, Z.-K., Suen, J.-L., & Li, C.-Y. (2021). Corylin Ameliorates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Suppressing the MAPKs and IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Pathways. Pharmaceuticals, 14(10), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14101046







