A Systematic Review of Molecular Imaging Agents Targeting Bradykinin B1 and B2 Receptors
Abstract
1. Introduction
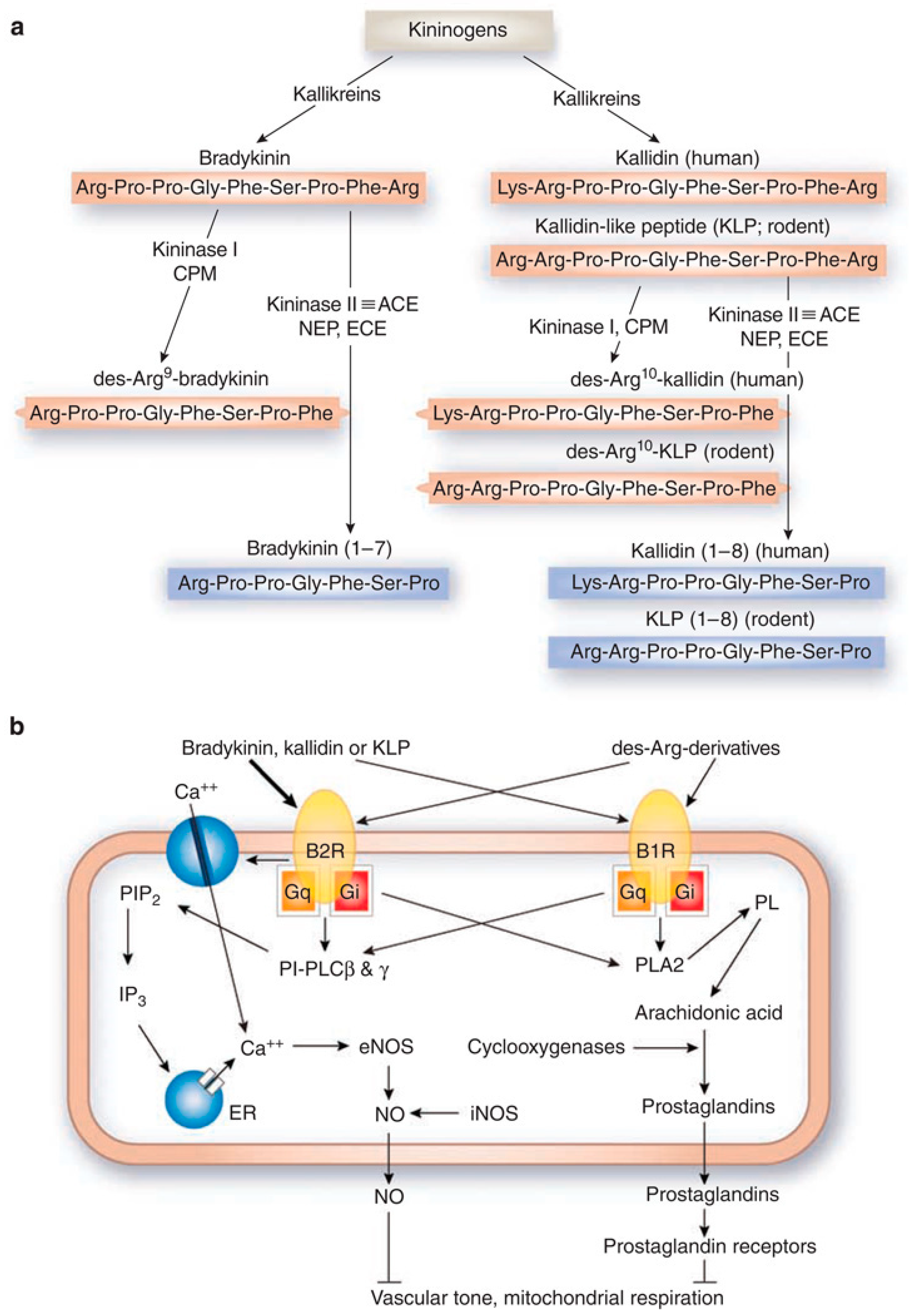
2. Kinin Receptors, Signaling, and Ligands
| Drug | Target | Clinical Phase | Indications | Comments | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
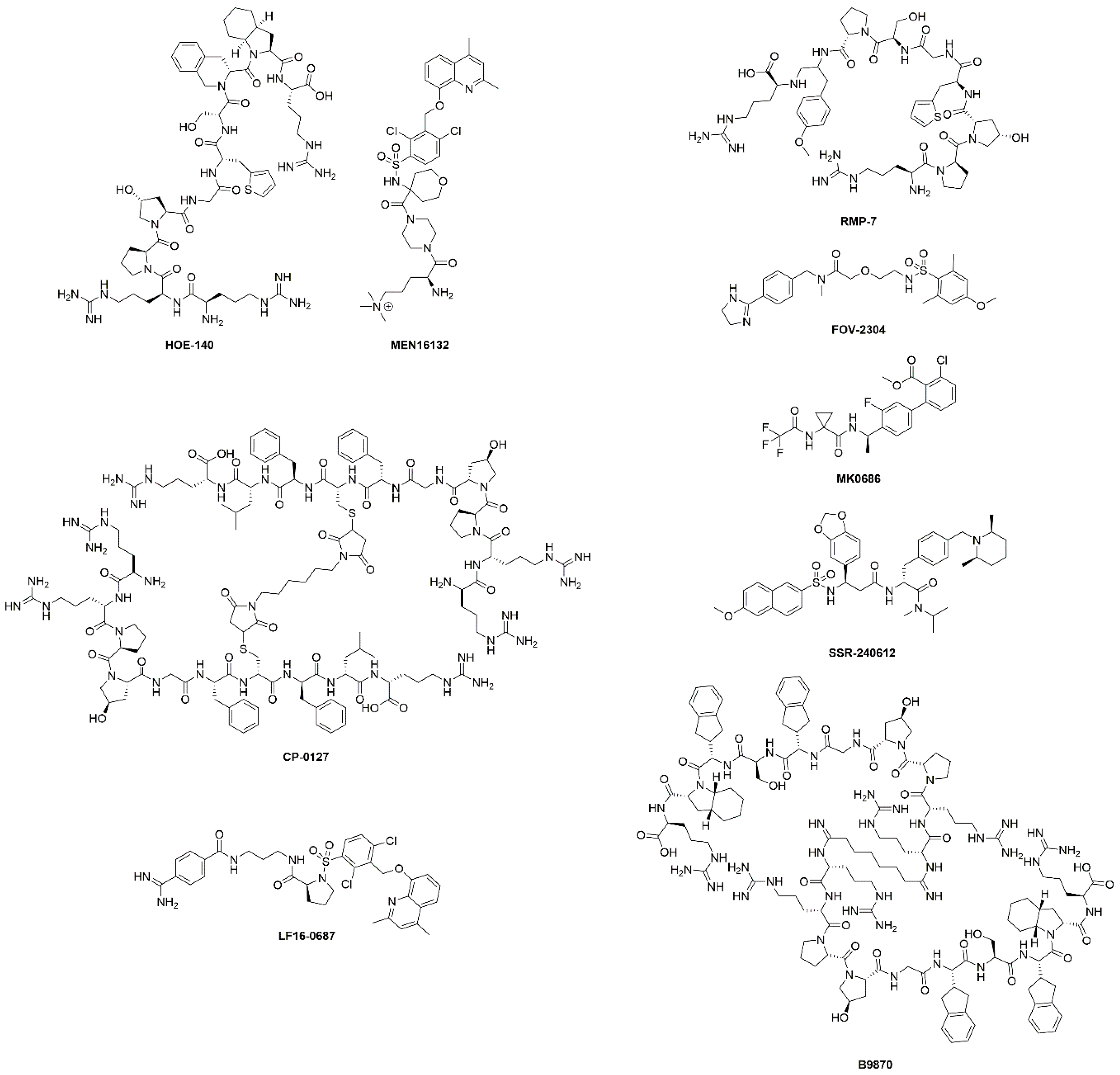
| HOE-140 (Icatibant) | B2R antagonist | Approved | Hereditary angioedema | Shortened the duration of acute attacks. | [26] |
| Phases I-IV | Cardiopulmonary bypass, inflammation, fibrinolysis, surgery, ischaemic heart diseases, ischaemic reperfusion, heart failure, ACE inhibitor associated angioedema, angioneurotic edema | Many completed and ongoing studies. Decreased intraoperative fibrinolytic capacity in cardiopulmonary bypass. No efficacy demonstrated for angioedema and ischemia-reperfusion injury. | [34,35,36] | ||
| Phase II | Mitochondria and chronic kidney disease | Completed, no evidence of efficacy. | NCT03177798 | ||
| Phase II | Knee pain in osteoarthritis | Completed, results not available. | NCT00303056 | ||
| MEN16132 (Fasitibant) | B2R antagonist | Phase II | Knee pain in osteoarthritis | Two studies completed. No direct evidence of efficacy, treated patients used less rescue medication. | NCT01091116 NCT02205814 |
| CP-0127 (Deltibant) | B2R antagonist | Phase II | Severe traumatic brain injury sepsis | Ineffective for sepsis. Discontinued due to unexpected preclinical findings. | [37] |
| LF16-0687 (Anatibant) | B2R antagonist | Phase II | Severe traumatic brain injury | Inconclusive results and possible safety issues. Trial halted. | [32] |
| RMP-7 (Lobradimil) | B2R agonist | Phase II | Childhood brain tumors | Completed. No improved efficacy. | [38] |
| Phase I | HIV infection and cryptococcal meningitis | Completed, results not available. | NCT00002316 | ||
| FOV-2304 (Safotibant) | B1R antagonist | Phase II | Diabetic macular edema | Discontinued, results not available. | [17,39] |
| MK-0686 | B1R antagonist | Phase II | Postherpetic neuralgia, postoperative dental pain, osteoarthritis | Terminated for postherpetic neuralgia, completed for dental pain and osteoarthritis. No results disclosed. | [17] |
| BI-113823 | B1R antagonist | Phase I | Osteoarthritis | Terminated. | NCT01207973 |
| SSR-240612 | B1R antagonist | Phase II | Inflammation and neuropathic pain | Halted for undisclosed reasons. | [40] |
| B9870 (Breceptin) | Dual B1R and B2R antagonist | Phase I | Small cell lung cancer | No information available. | [17] |
3. Kinin Receptors in Disease
3.1. Pain
3.2. Cardiovascular Diseases
3.3. Renal Diseases
3.4. Neurological Disorders
3.5. Cancers
3.6. Other Indications
4. Imaging of Kinin Receptors
4.1. B1R Imaging Agents
| Peptide Name | Peptide Sequence | Ki (nM) | Average Tissue Uptake (1 h p.i., %ID/g) | Average B1R+ Tumor-to-Background Contrast Ratio (1 h p.i.) | Ref | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1R+ Tumor | Kidney | To Blood | To Muscle | ||||
| Bradykinin | Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg | 5.7 a | [99] | ||||
| Kallidin | Lys-Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg | 7.4 a | [99] | ||||
| [Leu9,desArg10]kallidin | Lys-Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Leu | 8.9 b | [99] | ||||
| 68Ga-P03083 | 68Ga-DOTA-Ahx-[Leu9,desArg10]kallidin | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 0.79 ± 0.22 | 4.95 ± 0.86 | 10.4 ± 3.78 | 8.18 ± 1.69 | [77] |
| 68Ga-SH01078 | 68Ga-DOTA-Ahx-[Hyp4,Cha6,Leu9,desArg10]kallidin | 27.8 ± 4.9 | 2.06 ± 0.52 | 3.14 ± 0.62 | 7.78 ± 2.20 | 30.2 ± 7.42 | [77] |
| 68Ga-P03034 | 68Ga-DOTA-dPEG2-[Hyp4,Cha6,Leu9,desArg10]kallidin | 16 ± 1.9 | 2.17 ± 0.49 | 4.50 ± 2.17 | 5.72 ± 2.20 | 25.5 ± 13.1 | [77] |
| 68Ga-P04115 | 68Ga-DOTA-Gly-Gly-[Hyp4,Cha6,Leu9,desArg10]kallidin | 11 ± 2.5 | 1.96 ± 0.83 | 4.02 ± 2.40 | 6.37 ± 3.82 | 26.1 ± 8.91 | [78] |
| 68Ga-P04168 | 68Ga-DOTA-Pip-[Hyp4,Cha6,Leu9,desArg10]kallidin | 3.6 ± 0.2 | 4.15 ± 1.13 | 4.02 ± 1.22 | 15.9 ± 6.84 | 78.1 ± 28.5 | [78] |
| 68 Ga-Z01115 | 68Ga-DOTA-Ahx-[Hyp4,Cha6,D-Phe9,desArg10]kallidin | 25.4 ± 5.1 | 5.65 ± 0.59 | 4.63 ± 1.27 | 24.4 ± 12.9 | 82.9 ± 35.0 | [79] |
| B9858 | Lys-Lys-Arg-Pro-Hyp-Gly-Igl-Ser-D-Igl-Oic | 10.1 b | [89] | ||||
| 68Ga-P04158 | 68Ga-DOTA-dPEG2-B9858 | 1.5 ± 1.9 | 19.6 ± 4.50 | 69.2 ± 7.39 | 19.2 ± 8.21 | 66.1 ± 17.0 | [80] |
| 18F-L08064 | 18F-AmBF3-Mta-Pip-B9858 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 3.94 ± 1.24 | 36.2 ± 5.78 | 6.69 ± 3.60 | 21.3 ± 4.33 | [81] |
| B9958 | Lys-Lys-Arg-Pro-Hyp-Gly-Cpg-Ser-D-Tic-Cpg | 0.089 | [100] | ||||
| 68Ga-Z02090 | 68Ga-DOTA-dPEG2-B9958 | 1.1 ± 0.8 | 14.1 ± 1.63 | 50.1 ± 9.68 | 29.9 ± 5.58 | 124 ± 28.1 | [80] |
| 68Ga-Z02176 | 68Ga-DOTA-Pip-B9958 | 2.5 ± 0.8 | 28.9 ± 6.21 | 90.9 ± 22.8 | 56.1 ± 17.3 | 167 ± 57.6 | [82] |
| 68Ga-Z02137 | 68Ga-NODA-Mpaa-Pip-B9958 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 14.0 ± 4.86 | 85.2 ± 12.1 | 34.3 ± 15.2 | 103 ± 30.2 | [82] |
| 18F-L08060 | 18F-AmBF3-Mta-Pip-B9958 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 4.20 ± 0.98 | 30.9 ± 6.74 | 14.7 ± 3.56 | 48.6 ± 10.7 | [81] |
| 18F-Z04139 | Al18F-NODA-Mpaa-Pip-B9958 | 1.4 ± 0.7 | 22.6 ± 3.41 | 101 ± 14.4 | 58.0 ± 20.9 | 173 ± 42.9 | [82] |
| R954 | Ac-Orn-Arg-Oic-Pro-Gly-αMePhe-Ser-D-2Nal-Ile | 10.0 ± 3.1 | [83] | ||||
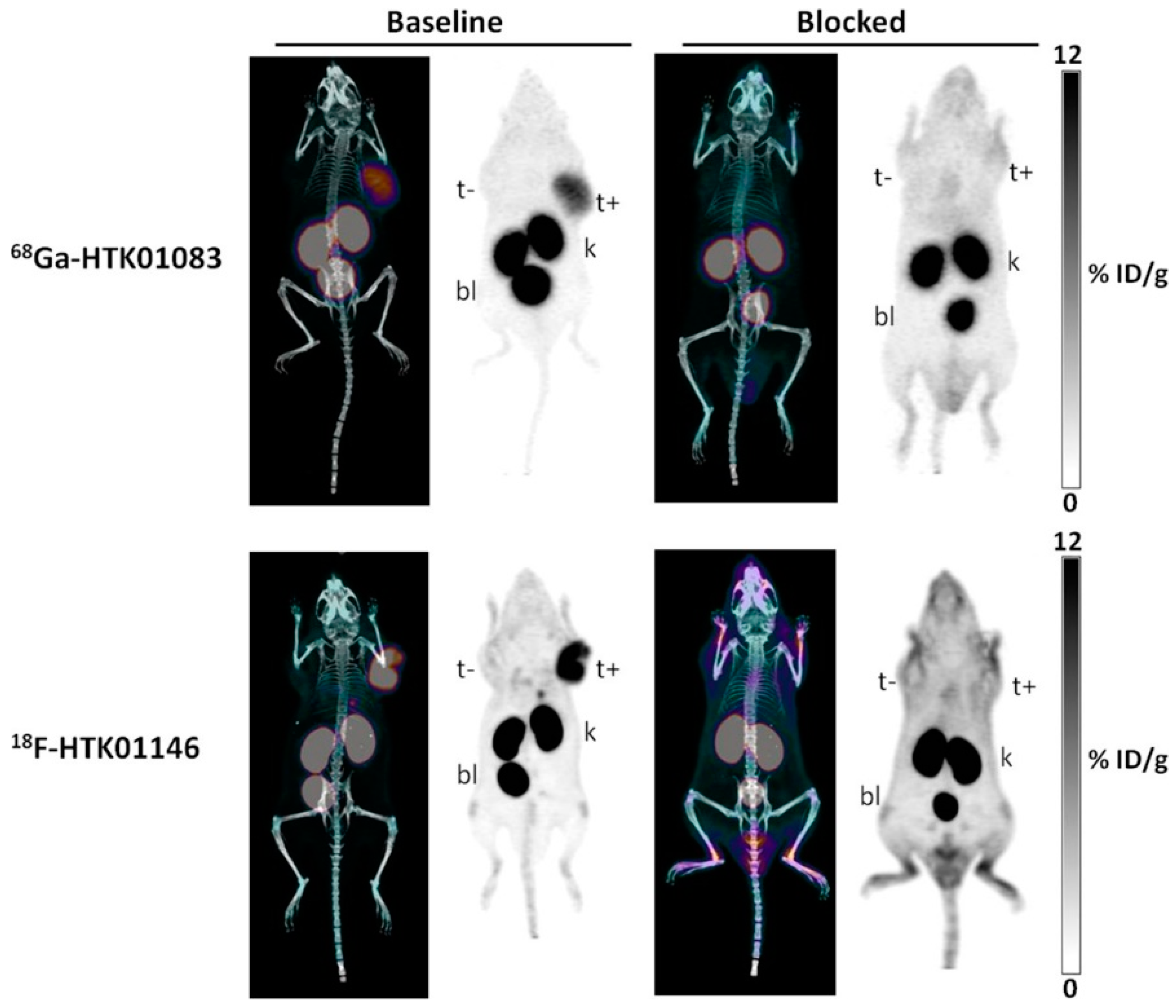
| 68Ga-HTK01083 | 68Ga-DOTA-dPEG2-R954 | 30.5 ± 7.6 | 8.46 ± 1.44 | 66.1 ± 9.70 | 6.32 ± 1.44 | 20.7 ± 3.58 | [83] |
| 18F-HTK01146 | 18F-AmBF3-Mta-dPEG2-R954 | 24.8 ± 2.8 | 9.25 ± 0.69 | 77.0 ± 19.5 | 7.24 ± 2.56 | 19.5 ± 4.29 | [83] |
4.2. B2R Imaging Agents
5. Perspective and Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leeb-Lundberg, L.M.F.; Marceau, F.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Pettibone, D.J.; Zuraw, B.L. International union of pharmacology. XLV. Classification of the kinin receptor family: From molecular mechanisms to pathophysiological consequences. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 27–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, F.; Bachelard, H.; Bouthillier, J.; Fortin, J.P.; Morissette, G.; Bawolak, M.T.; Charest-Morin, X.; Gera, L. Bradykinin receptors: Agonists, antagonists, expression, signaling, and adaptation to sustained stimulation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regoli, D.; Barabe, J.; Park, W.K. Receptors for bradykinin in rabbit aortae. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1977, 55, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regoli, D.; Marceau, F.; Barabe, J. De novo formation of vascular receptors for bradykinin. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1978, 56, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouin, J.N.; St-Pierre, S.A.; Regoli, D. Receptors for bradykinin and kallidin. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1979, 57, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couture, R.; Harrisson, M.; Vianna, R.M.; Cloutier, F. Kinin receptors in pain and inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 429, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, F.; Bader, M. Kinin B1 receptors as a therapeutic target for inflammation. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, F.; Regoli, D. Bradykinin receptor ligands: Therapeutic perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, T.F.; Gambhir, S.S. Molecular imaging in living subjects: Seeing fundamental biological processes in a new light. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 545–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruemmer, K.J.; Crossley, S.W.M.; Chang, C.J. Activity-Based Sensing: A Synthetic Methods Approach for Selective Molecular Imaging and Beyond. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Xu, Z.; De Geest, B.G.; Xu, H.; Yu, H. Molecular Imaging for Cancer Immunotherapy: Seeing Is Believing. Bioconjug. Chem. 2020, 31, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirovano, G.; Roberts, S.; Kossatz, S.; Reiner, T. Optical imaging modalities: Principles and applications in preclinical research and clinical settings. J. Nucl. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, D.; Singhal, S.; Selmic, L.E. Near-infrared imaging and optical coherence tomography for intraoperative visualization of tumors. Vet. Surg. 2020, 49, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz, S.C.; Oliveira, F.; Herrmann, K.; Veit-Haibach, P. Nuclear medicine and molecular imaging advances in the 21st century. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20200095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, V.P.B.; Tognarelli, J.M.; Crossey, M.M.E.; Cox, I.J.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; McPhail, M.J.W. Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Principles and Techniques: Lessons for Clinicians. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2015, 5, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha E Silva, M.; Beraldo, W.T.; Rosenfeld, G. Bradykinin, a hypotensive and smooth muscle stimulating factor released from plasma globulin by snake venoms and by trypsin. Am. J. Physiol. 1949, 156, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, P.L.N.; Sirois, P.; Tannock, I.F.; Chammas, R. The role of kinin receptors in cancer and therapeutic opportunities. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoki, M.; Smithies, O. The kallikreinkinin system in health and in diseases of the kidney. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regoli, D.; Barabé, J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol. Rev. 1980, 32, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Duka, A.; Kintsurashvili, E.; Duka, I.; Ona, D.; Hopkins, T.A.; Bader, M.; Gavras, I.; Gavras, H. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition After Experimental Myocardial Infarct. Hypertension 2008, 51, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savard, M.; Labonté, J.; Dubuc, C.; Neugebauer, W.; D’orléans-Juste, P.; Gobeil, F. Further pharmacological evaluation of a novel synthetic peptide bradykinin B2 receptor agonist. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duka, A.; Duka, I.; Gao, G.; Shenouda, S.; Gavras, I.; Gavras, H. Role of bradykinin B1 and B2 receptors in normal blood pressure regulation. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrifield, R.B. Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis. III. An Improved Synthesis of Bradykinin. Biochemistry 1964, 3, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeGruyter, J.N.; Malins, L.R.; Baran, P.S. Residue-Specific Peptide Modification: A Chemist’s Guide. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 3863–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marceau, F.; Bawolak, M.T.; Fortin, J.P.; Morissette, G.; Roy, C.; Bachelard, H.; Gera, L.; Charest-Morin, X. Bifunctional ligands of the bradykinin B 2 and B 1 receptors: An exercise in peptide hormone plasticity. Peptides 2018, 105, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicardi, M.; Banerji, A.; Bracho, F.; Malbrán, A.; Rosenkranz, B.; Riedl, M.; Bork, K.; Lumry, W.; Aberer, W.; Bier, H.; et al. Icatibant, a New Bradykinin-Receptor Antagonist, in Hereditary Angioedema. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, A.; Gibson, C.; Marceau, F.; Ambrosi, H.-D.; Saupe, J.; Katzer, W.; Loenders, B.; Charest-Morin, X.; Knolle, J. In Vitro Pharmacological Profile of a New Small Molecule Bradykinin B2 Receptor Antagonist. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurusamy, M.; Nasseri, S.; Lee, H.; Jung, B.; Lee, D.; Khang, G.; Abraham, W.M.; Doods, H.; Wu, D. Kinin B1 receptor antagonist BI113823 reduces allergen-induced airway inflammation and mucus secretion in mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 104, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Junior, V.S.; Pail, P.B.; Villela, A.D.; Falcão, V.C.A.; Dadda, A.S.; Abbadi, B.L.; Pesquero, J.B.; Santos, D.S.; Basso, L.A.; Campos, M.M. Effect of the bradykinin 1 receptor antagonist SSR240612 after oral administration in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected mice. Tuberculosis 2018, 109, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasaeifar, B.; Lupala, C.S.; Gomez-Gutierrez, P.; Perez, J.J. Molecular features characterizing non-peptide selectivity to the human B1 and B2 bradykinin receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, G.M.; Perkins, M.N.; Rang, H.P.; Campbell, E.A.; Brown, M.C.; McIntyre, P.; Urban, L.; Dziadulewicz, E.K.; Ritchie, T.J.; Hallett, A.; et al. Bradyzide, a potent non-peptide B2 bradykinin receptor antagonist with long-lasting oral activity in animal models of inflammatory hyperalgesia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 129, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakur, H.; Andrews, P.; Asser, T.; Balica, L.; Boeriu, C.; Quintero, J.D.C.; Dewan, Y.; Druwé, P.; Fletcher, O.; Frost, C.; et al. The BRAIN TRIAL: A randomised, placebo controlled trial of a Bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist (Anatibant) in patients with traumatic brain injury. Trials 2009, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenti, S.; Pascarelli, N.A.; Cheleschi, S.; Guidelli, G.M.; Fioravanti, A. The Emerging Role of Bradykinin in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis and its Possible Clinical Implications. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2016, 12, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaguer, J.M.; Yu, C.; Byrne, J.G.; Ball, S.K.; Petracek, M.R.; Brown, N.J.; Pretorius, M. Contribution of endogenous bradykinin to fibrinolysis, inflammation, and blood product transfusion following cardiac surgery: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 93, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straka, B.T.; Ramirez, C.E.; Byrd, J.B.; Stone, E.; Woodard-Grice, A.; Nian, H.; Yu, C.; Banerji, A.; Brown, N.J. Effect of bradykinin receptor antagonism on ACE inhibitor-associated angioedema. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, C.M.; Schmidt, M.R.; Barnes, G.; Bøtker, H.E.; Kharbanda, R.K.; Newby, D.E.; Cruden, N.L. Bradykinin does not mediate remote ischaemic preconditioning or ischaemia-reperfusion injury in vivo in man. Heart 2011, 97, 1857–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalley, E.T.; Figueroa, C.D.; Gera, L.; Bhoola, K.D. Discovery and therapeutic potential of kinin receptor antagonists. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 1129–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, K.; Jakacki, R.; Widemann, B.; Aikin, A.; Libucha, M.; Packer, R.; Vezina, G.; Reaman, G.; Shaw, D.; Krailo, M.; et al. Phase II trial of intravenous lobradimil and carboplatin in childhood brain tumors: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruneau, D.; Bélichard, P.; Sahel, J.A.; Combal, J.P. Targeting the kallikrein-kinin system as a new therapeutic approach to diabetic retinopathy. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2010, 11, 507–514. [Google Scholar]
- Bozó, É.; Éles, J.; Keser, G.M. Bradykinin B1 receptor antagonists: A patent update 2009–2012. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2012, 22, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaes, N.; Girolami, J.P. Targeting the “Janus face” of the B2-bradykinin receptor. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 1145–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; He, F.; Ma, L.; Liu, P.; Wang, J.; Zhu, X. Bradykinin Receptors in Ischemic Injury. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2018, 15, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.I.; Hwang, S.W. Depolarizing effectors of bradykinin signaling in nociceptor excitation in pain perception. Biomol. Ther. 2018, 26, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernit, V.; Sénécal, J.; Othman, R.; Couture, R. Reciprocal regulatory interaction between TRPV1 and kinin B1 receptor in a rat neuropathic pain model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo Su, J. Kinins and Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 3423–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitsch, H. The therapeutic potential of bradykinin B2 receptor agonists in the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2003, 12, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolis, A.J.; Marketou, M.E.; Gavras, I.; Gavras, H. Cardioprotective properties of bradykinin: Role of the B2 receptor. Hypertens. Res. 2010, 33, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchene, J.; Ahluwalia, A. The kinin B1 receptor and inflammation: New therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriramula, S. Kinin B1 receptor: A target for neuroinflammation in hypertension. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhenc-Gelas, F.; Bouby, N.; Girolami, J.-P. Kallikrein/K1, Kinins, and ACE/Kininase II in Homeostasis and in Disease Insight From Human and Experimental Genetic Studies, Therapeutic Implication. Front. Med. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.C.W.; Yiu, W.H.; Lin, M.; Lai, K.N. Diabetic nephropathy and proximal tubular damage. J. Ren. Nutr. 2015, 25, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Stanton, R.C.; Zhang, Z. The kallikrein-kinin system in diabetic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2017, 26, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nokkari, A.; Abou-El-Hassan, H.; Mechref, Y.; Mondello, S.; Kindy, M.S.; Jaffa, A.A.; Kobeissy, F. Implication of the Kallikrein-Kinin system in neurological disorders: Quest for potential biomarkers and mechanisms. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 165–167, 26–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodi, D.; Couture, R.; Ongali, B.; Simonato, M. Targeting Kinin Receptors for the Treatment of Neurological Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandadi, S.; Leduc-Pessah, H.; Hong, P.; Ejdrygiewicz, J.; Sharples, S.A.; Trang, T.; Whelan, P.J. Modulatory and plastic effects of kinins on spinal cord networks. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 1017–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, A.L.; Dong-Creste, K.E.; Amaral, F.A.; Monteiro-Silva, K.C.; Pesquero, J.B.; Araujo, M.S.; Montor, W.R.; Viel, T.A.; Buck, H.S. Kinin B2 receptor can play a neuroprotective role in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropeptides 2015, 53, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, J.; Savard, M.; Neugebauer, W.; Fortin, D.; Lepage, M.; Gobeil, F. Dual kinin B1 and B2 receptor activation provides enhanced blood-brain barrier permeability and anticancer drug delivery into brain tumors. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, C.D.; Ehrenfeld, P.; Bhoola, K.D. Kinin receptors as targets for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Hsu, J.W.; Lin, H.Y.; Lai, S.W.; Huang, B.R.; Tsai, C.F.; Lu, D.Y. Bradykinin B1 receptor contributes to interleukin-8 production and glioblastoma migration through interaction of STAT3 and SP-1. Neuropharmacology 2019, 144, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubuc, C.; Savard, M.; Bovenzi, V.; Lessard, A.; Côté, J.; Neugebauer, W.; Geha, S.; Chemtob, S.; Gobeil, F. Antitumor activity of cell-penetrant kinin B1 receptor antagonists in human triple-negative breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 2851–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Wei, R.; Jiang, G.; Li, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Long, S.; Ma, D.; Xi, L. Serum bradykinin levels as a diagnostic marker in cervical cancer with a potential mechanism to promote VEGF expression via BDKRB2. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.N.; Pillat, M.M.; Motaln, H.; Ulrich, H.; Lah, T.T. Kinin-B1 Receptor Stimulation Promotes Invasion and is Involved in Cell-Cell Interaction of Co-Cultured Glioblastoma and Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, P.L.N.; Wynne, D.; Fifis, T.; Nguyen, L.; Perini, M.; Christophi, C. The kallikrein-Kinin system modulates the progression of colorectal liver metastases in a mouse model. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.D.; Gomes, N.D.M.; Sirois, P. The bradykinin B1 receptor antagonist R-954 inhibits Ehrlich tumor growth in rodents. Peptides 2011, 32, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutra, R.C. Kinin receptors: Key regulators of autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oehmcke, S.; Herwald, H. Contact system activation in severe infectious diseases. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 88, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, Z.L.M.; Relan, A.; Zeerleder, S.; Drouet, C.; Zuraw, B.; Hack, C.E. Angioedema attacks in patients with hereditary angioedema: Local manifestations of a systemic activation process. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine, S.A.; Budsberg, S.C. Synovial membrane receptors as therapeutic targets: A review of receptor localization, structure, and function. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 35, 1589–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
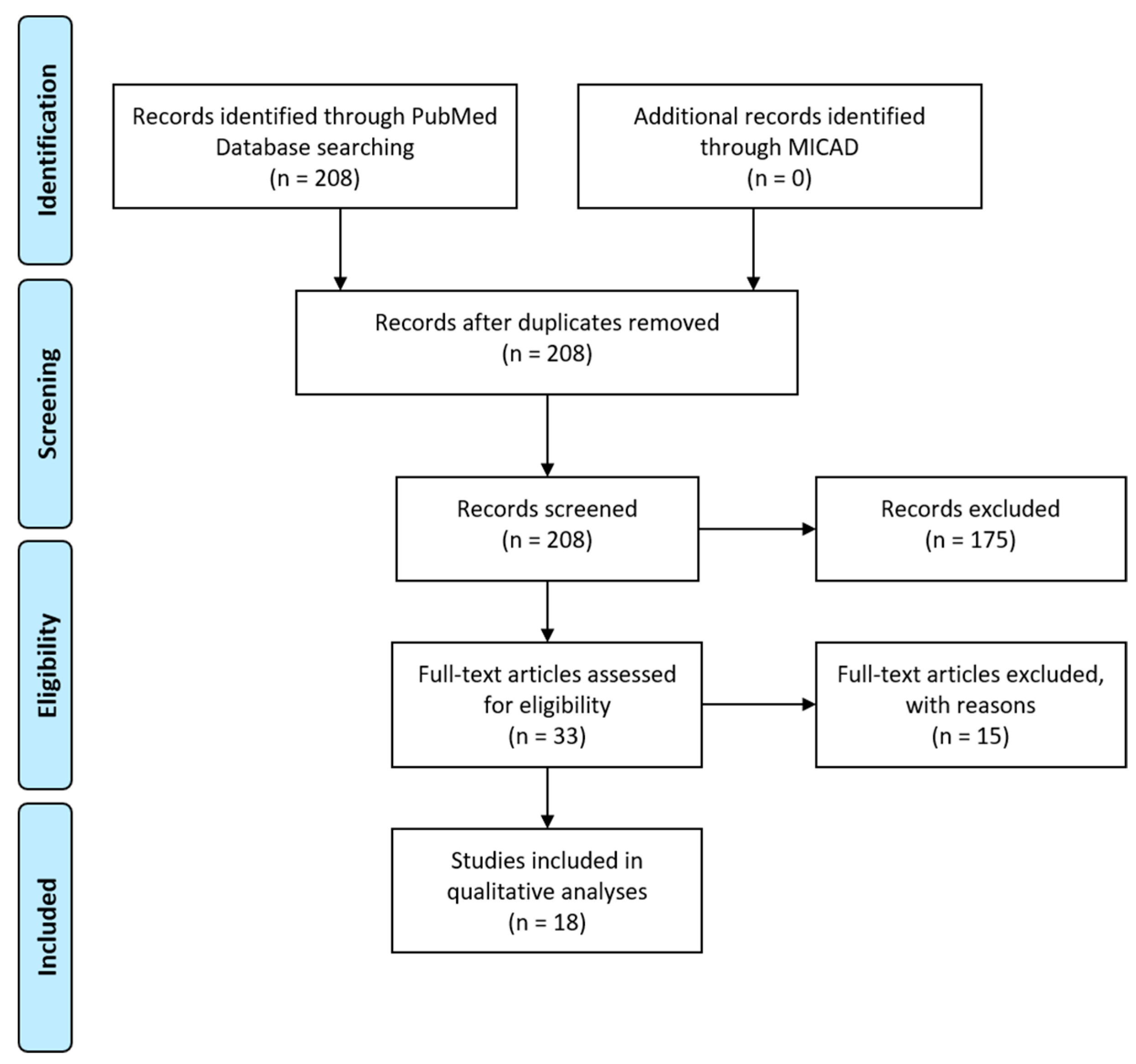
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schottelius, M.; Wester, H.J. Molecular imaging targeting peptide receptors. Methods 2009, 48, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawolak, M.T.; Gera, L.; Bouthillier, J.; Stewart, J.M.; Adam, A.; Marceau, F. A fluorescent version of the bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist B-9430: Pharmacological characterization and use in live cell imaging. Peptides 2008, 29, 1626–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bawolak, M.T.; Gera, L.; Morissette, G.; Bouthillier, J.; Stewart, J.M.; Gobeil, L.A.; Lodge, R.; Adam, A.; Marceau, F. Fluorescent ligands of the bradykinin B receptors: Pharmacologic characterization and application to the study of agonist-induced receptor translocation and cell surface receptor expression. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 329, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gera, L.; Stewart, J.M.; Whalley, E.T.; Burkard, M.; Zuzack, J.S. New bradykinin antagonists having very high potency at B1 receptors. Immunopharmacology 1996, 33, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, S.; Théberge-Turmel, P.; Liazoghli, D.; Sénécal, J.; Gaudreau, P.; Couture, R. Cellular localization of kinin B1 receptor in the spinal cord of streptozotocin-diabetic rats with a fluorescent [Nα- Bodipy]-des-Arg9-bradykinin. J. Neuroinflamm. 2009, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
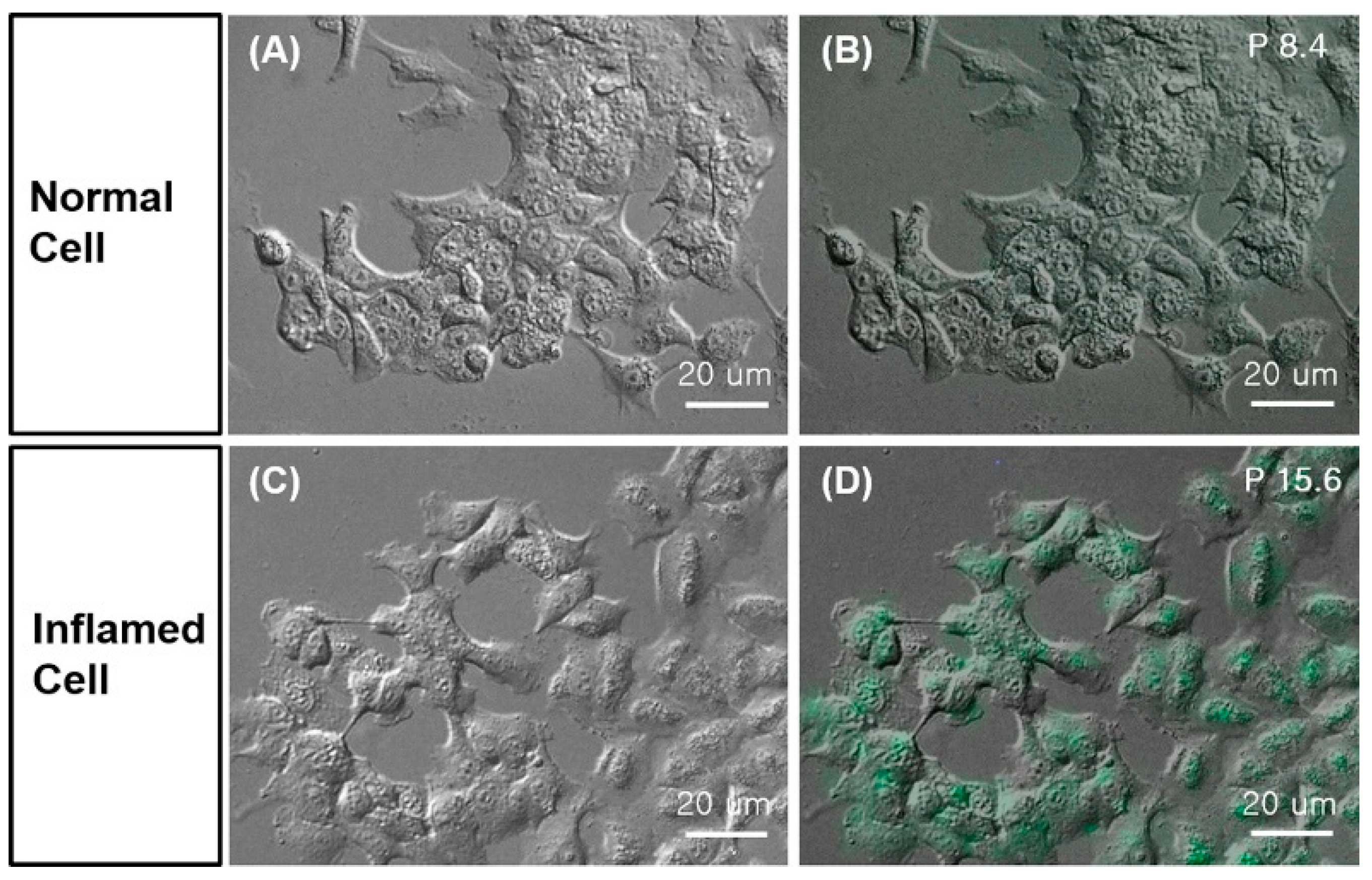
- Yeo, K.B.; Kim, H.B.; Choi, Y.S.; Pack, S.P. Highly effective detection of inflamed cells using a modified bradykinin ligand labeled with FITC fluorescence. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2016, 82, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charest-Morin, X.; Marceau, F. Biotechnological Fluorescent Ligands of the Bradykinin B1 Receptor: Protein Ligands for a Peptide Receptor. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.S.; Pan, J.; Amouroux, G.; Turashvili, G.; Mesak, F.; Hundal-Jabal, N.; Pourghiasian, M.; Lau, J.; Jenni, S.; Aparicio, S.; et al. In vivo radioimaging of bradykinin receptor B1, a widely overexpressed molecule in human cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouroux, G.; Pan, J.; Jenni, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Hundal-Jabal, N.; Colpo, N.; Liu, Z.; Bénard, F.; Lin, K.S. Imaging Bradykinin B1 Receptor with 68Ga-Labeled [des-Arg10]Kallidin Derivatives: Effect of the Linker on Biodistribution and Tumor Uptake. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouroux, G.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, J.; Jenni, S.; Zhang, C.; Hundal-Jabal, N.; Colpo, N.; Zeisler, J.; Lin, K.S.; Bénard, F.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of a 68Ga-labeled bradykinin B1 receptor agonist for imaging with positron emission tomography. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.S.; Amouroux, G.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jenni, S.; Lau, J.; Liu, Z.; Hundal-Jabal, N.; Colpo, N.; Bénard, F. Comparative studies of three 68Ga-labeled [Des-Arg10] kallidin derivatives for imaging bradykinin B1 receptor expression with PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Amouroux, G.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, J.; Hundal-Jabal, N.; Colpo, N.; Lau, J.; Perrin, D.M.; Bénard, F.; Lin, K.S. 18F-trifluoroborate derivatives of [Des-Arg10] kallidin for imaging bradykinin B1 receptor expression with positron emission tomography. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Amouroux, G.; Pan, J.; Jenni, S.; Zeisler, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Perrin, D.M.; Bénard, F.; Lin, K.S. Radiolabeled B9958 Derivatives for Imaging Bradykinin B1 Receptor Expression with Positron Emission Tomography: Effect of the Radiolabel-Chelator Complex on Biodistribution and Tumor Uptake. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.T.; Pan, J.; Lau, J.; Zhang, C.; Zeisler, J.; Colpo, N.; Bénard, F.; Lin, K.S. Radiolabeled R954 Derivatives for Imaging Bradykinin B1 Receptor Expression with Positron Emission Tomography. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Kuo, H.T.; Lau, J.; Jenni, S.; Zhang, C.; Zeisler, J.; Bénard, F.; Lin, K.S. Design, synthesis and evaluation of 18F-labeled bradykinin B1 receptor-targeting small molecules for PET imaging. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 4095–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiniova, L.; De Palatis, L.; Etchebehere, E.; Ravizzini, G. Gallium-68 in Medical Imaging. Curr. Radiopharm. 2016, 9, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talip, Z.; Favaretto, C.; Geistlich, S.; van der Meulen, N.P. A Step-by-Step Guide for the Novel Radiometal Production for Medical Applications: Case Studies with 68Ga, 44Sc, 177Lu and 161Tb. Molecules 2020, 25, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, J.; Savard, M.; Bovenzi, V.; Bélanger, S.; Morin, J.; Neugebauer, W.; Larouche, A.; Dubuc, C.; Gobeil, F. Novel kinin B1 receptor agonists with improved pharmacological profiles. Peptides 2009, 30, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.; Rousseau, E.; Kwon, D.; Lin, K.-S.; Bénard, F.; Chen, X. Insight into the Development of PET Radiopharmaceuticals for Oncology. Cancers 2020, 12, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.M.; Gera, L.; Chan, D.C.; Whalley, E.T.; Hanson, W.L.; Zuzack, J.S. Potent, long-acting, orally-active bradykinin antagonists for a wide range of applications. Immunopharmacology 1997, 36, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, C.A.; McBride, W.J.; Sharkey, R.M.; Todaro, L.J.; Goldenberg, D.M. High-yielding aqueous 18F-labeling of peptides via Al 18F chelation. Bioconjug. Chem. 2011, 22, 1793–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, K.S.; Bénard, F.; Pourghiasian, M.; Kiesewetter, D.O.; Perrin, D.M.; Chen, X. One-step 18 F labeling of biomolecules using organotrifluoroborates. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.T.; Lepage, M.L.; Lin, K.S.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Pryyma, A.; Zhang, C.; Merkens, H.; Roxin, A.; et al. One-step 18F-labeling and preclinical evaluation of prostate-specific membrane antigen trifluoroborate probes for cancer imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepage, M.L.; Kuo, H.T.; Roxin, Á.; Huh, S.; Zhang, Z.; Kandasamy, R.; Merkens, H.; Kumlin, J.O.; Limoges, A.; Zeisler, S.K.; et al. Toward 18F-Labeled Theranostics: A Single Agent that Can Be Labeled with 18F, 64Cu, or 177Lu. ChemBioChem 2020, 21, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varlow, C.; Szames, D.; Dahl, K.; Bernard-Gauthier, V.; Vasdev, N. Fluorine-18: An untapped resource in inorganic chemistry. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 11835–11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, N.S.; Joshi, R.K.; Bharath, R.D.; Kumar, P. Fluorine-18: A radionuclide with diverse range of radiochemistry and synthesis strategies for target based PET diagnosis. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 187, 111979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, W.; Blais, P.A.; Hallé, S.; Filteau, C.; Regoli, D.; Gobeil, F. Kinin B1 receptor antagonists with multi-enzymatic resistance properties. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2002, 80, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobeil, F.; Sirois, P.; Regoli, D. Preclinical pharmacology, metabolic stability, pharmacokinetics and toxicology of the peptidic kinin B1 receptor antagonist R-954. Peptides 2014, 52, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, M.; Bondoux, M.; Luccarini, J.M.; Peyrou, V.; Dodey, P.; Pruneau, D.; Massardier, C.; Paquet, J.L. From bradykinin B2 receptor antagonists to orally active and selective bradykinin B1 receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 2574–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regoli, D.; Nsa Allogho, S.; Rizzi, A.; Gobeil, F.J. Bradykinin receptors and their antagonists. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 348, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gera, L.; Stewart, J.M.; Fortin, J.P.; Morissette, G.; Marceau, F. Structural modification of the highly potent peptide bradykinin B1 receptor antagonist B9958. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
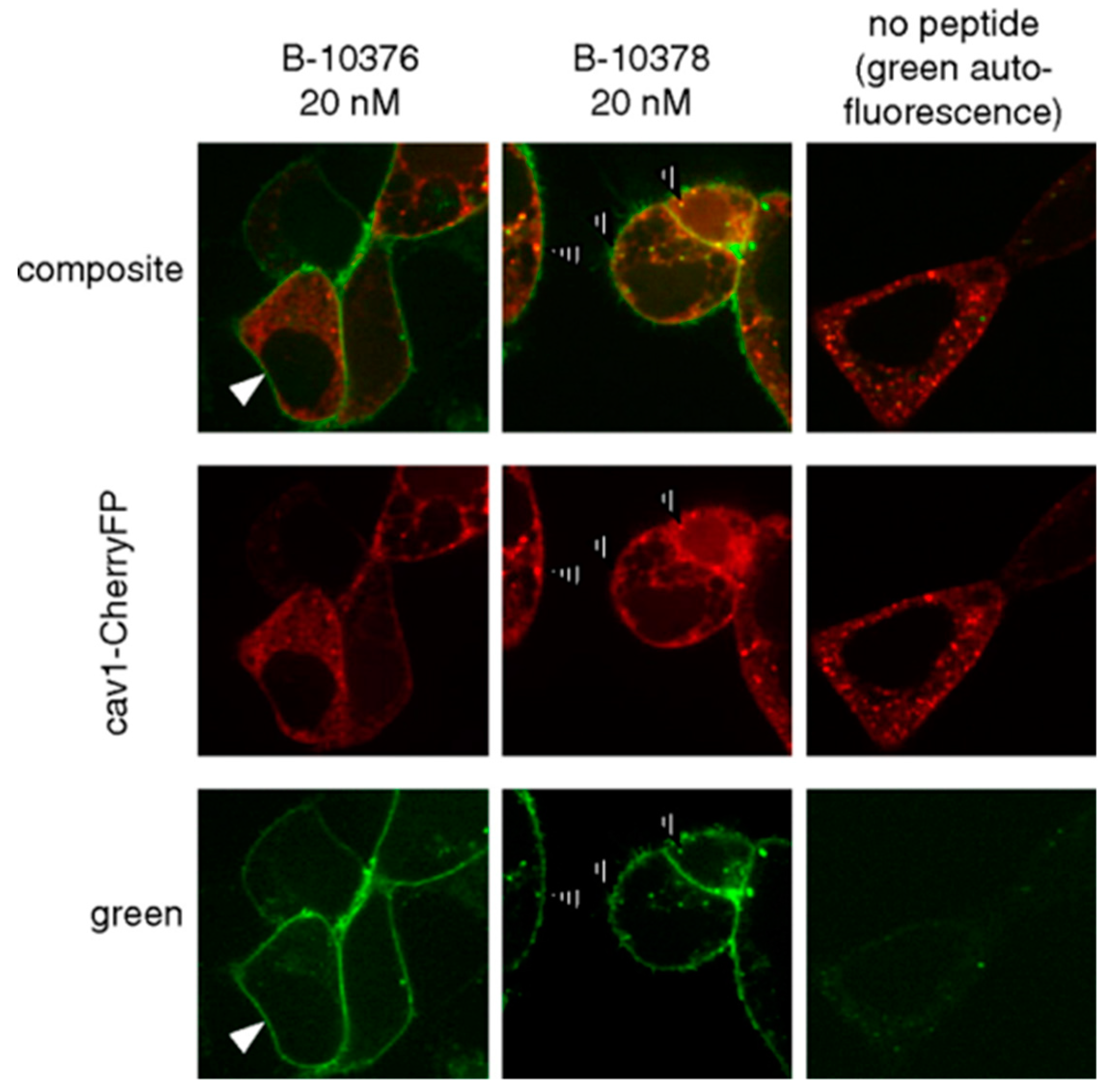
- Gera, L.; Bawolak, M.T.; Roy, C.; Lodge, R.; Marceau, F. Design of fluorescent bradykinin analogs: Application to imaging of B2 receptor-mediated agonist endocytosis and trafficking and angiotensin-converting enzyme. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 337, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gera, L.; Roy, C.; Bawolak, M.T.; Charest-Morin, X.; Marceau, F. N-terminal extended conjugates of the agonists and antagonists of both bradykinin receptor subtypes: Structure-activity relationship, cell imaging using ligands conjugated with fluorophores and prospect for functionally active cargoes. Peptides 2012, 34, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
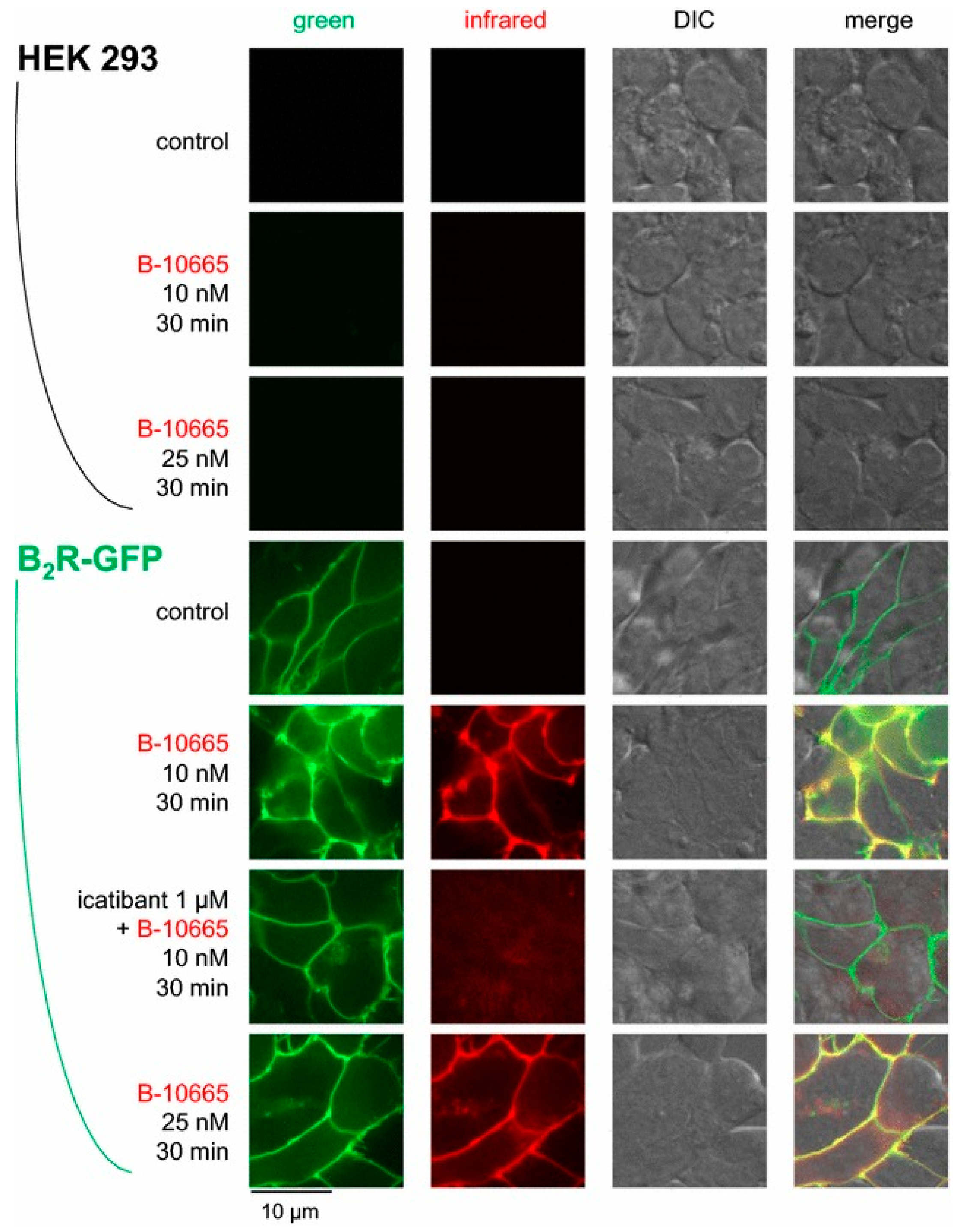
- Charest-Morin, X.; Fortin, J.P.; Bawolak, M.T.; Lodge, R.; Marceau, F. Green fluorescent protein fused to peptide agonists of two dissimilar G protein-coupled receptors: Novel ligands of the bradykinin B2 (rhodopsin family) receptor and parathyroid hormone PTH1 (secretin family) receptor. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gera, L.; Charest-Morin, X.; Jean, M.; Bachelard, H.; Marceau, F. Infrared-emitting, peptidase-resistant fluorescent ligands of the bradykinin B2 receptor: Application to cytofluorometry and imaging. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
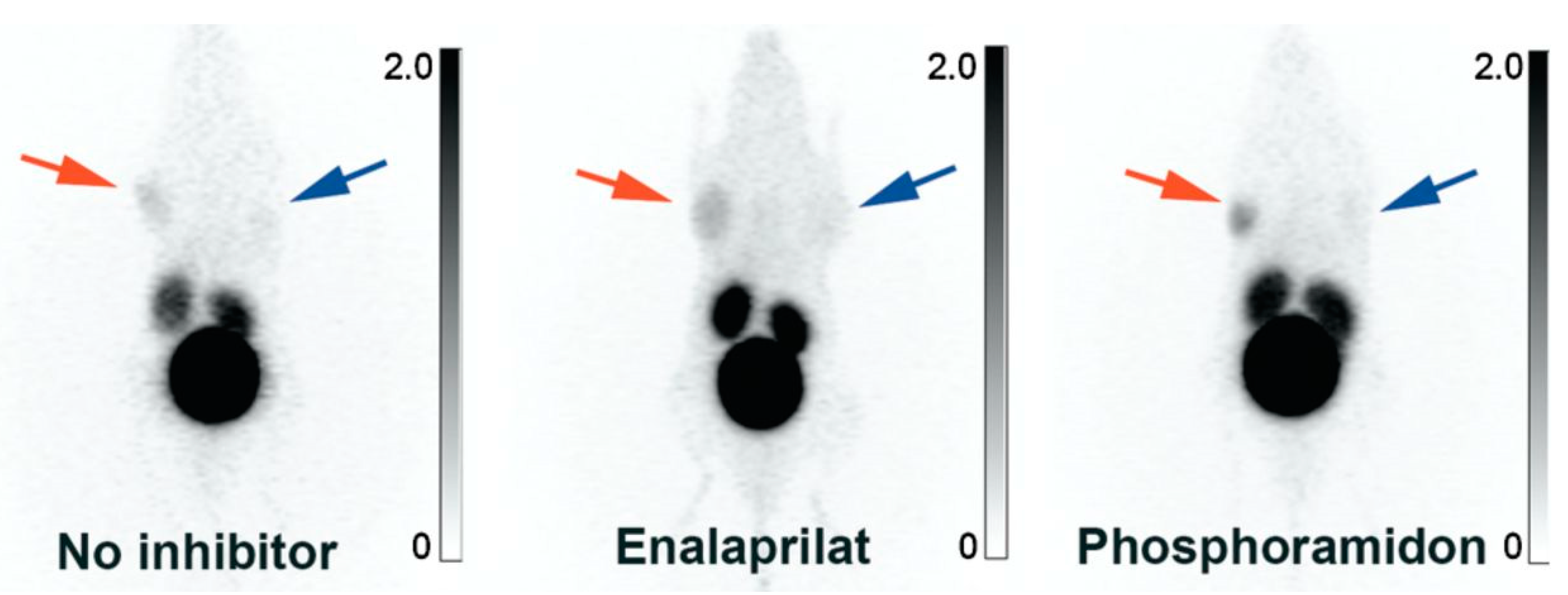
- Stahl, W.; Breipohl, G.; Gerhards, H.J.; Kuhlmann, L.; Steinsträsser, A.; Schölkens, B.A. Technetium-99m-Labeled HOE 140: A Potential Bradykinin B2 Receptor Imaging Agent. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 2799–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lau, J.; Rousseau, J.; Kwon, D.; Bénard, F.; Lin, K.-S. A Systematic Review of Molecular Imaging Agents Targeting Bradykinin B1 and B2 Receptors. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080199
Lau J, Rousseau J, Kwon D, Bénard F, Lin K-S. A Systematic Review of Molecular Imaging Agents Targeting Bradykinin B1 and B2 Receptors. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(8):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080199
Chicago/Turabian StyleLau, Joseph, Julie Rousseau, Daniel Kwon, François Bénard, and Kuo-Shyan Lin. 2020. "A Systematic Review of Molecular Imaging Agents Targeting Bradykinin B1 and B2 Receptors" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 8: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080199
APA StyleLau, J., Rousseau, J., Kwon, D., Bénard, F., & Lin, K.-S. (2020). A Systematic Review of Molecular Imaging Agents Targeting Bradykinin B1 and B2 Receptors. Pharmaceuticals, 13(8), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080199





