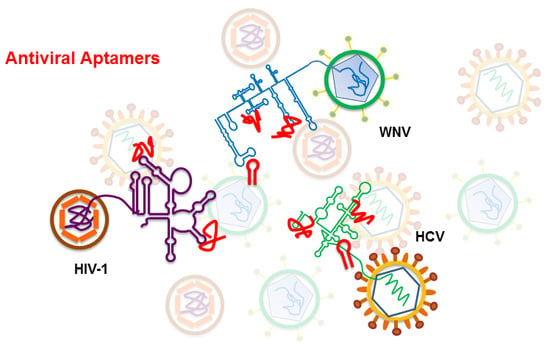
Two Examples of RNA Aptamers with Antiviral Activity. Are Aptamers the Wished Antiviral Drugs?
Abstract
1. Introduction
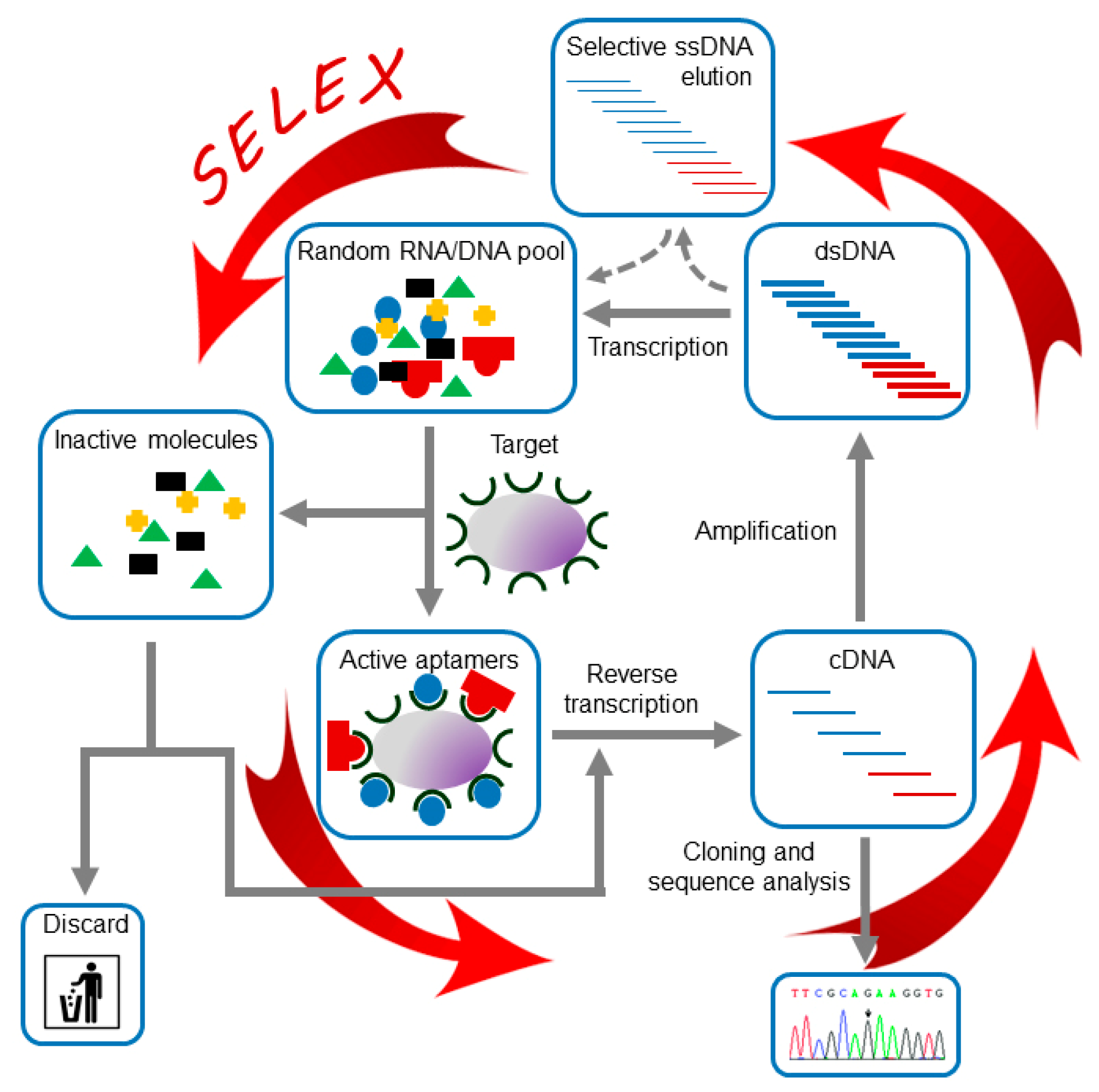
2. Aptamers, Selection Procedure, and Features
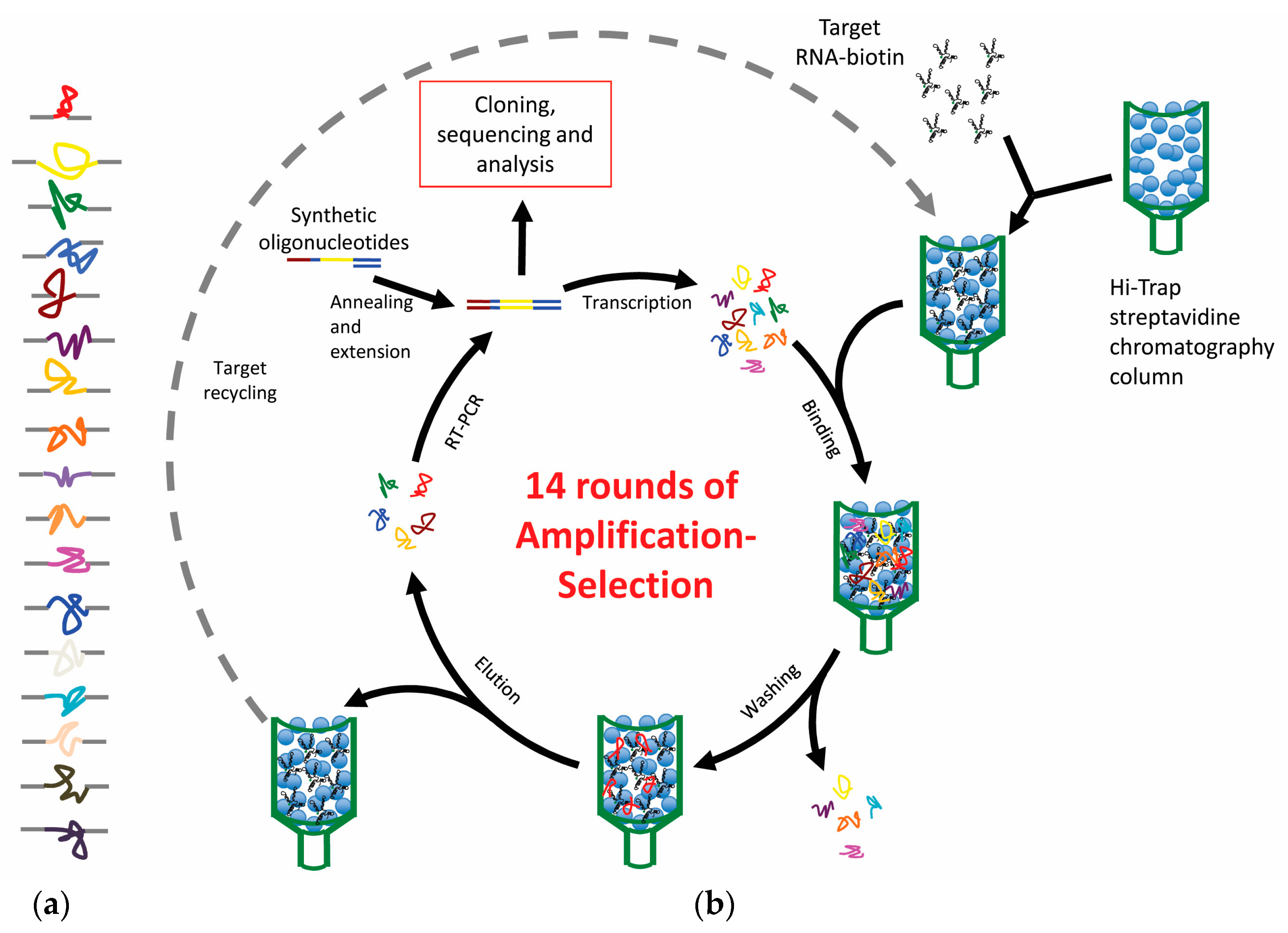
2.1. SELEX
2.2. Aptamer Features
3. Antiviral Aptamers
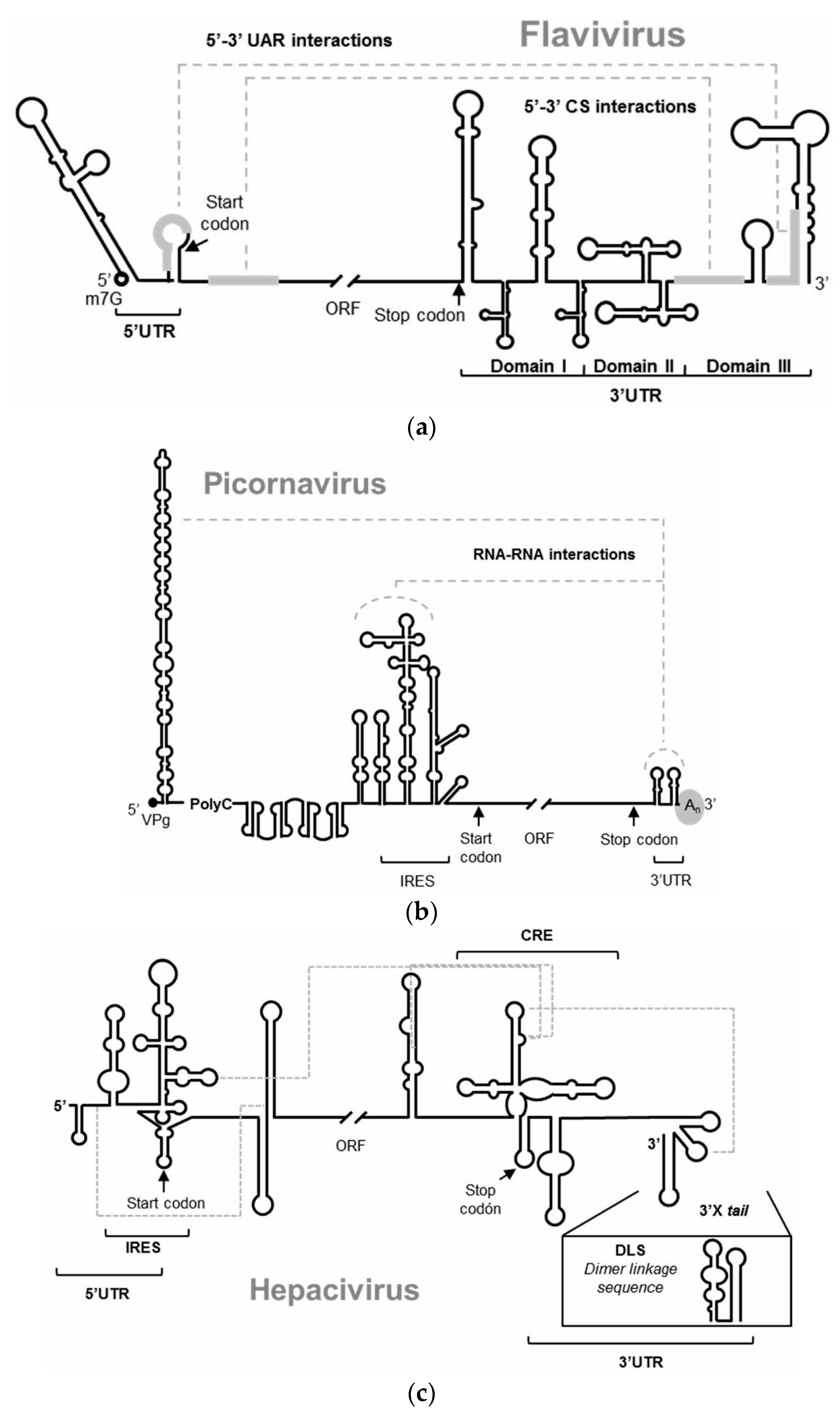
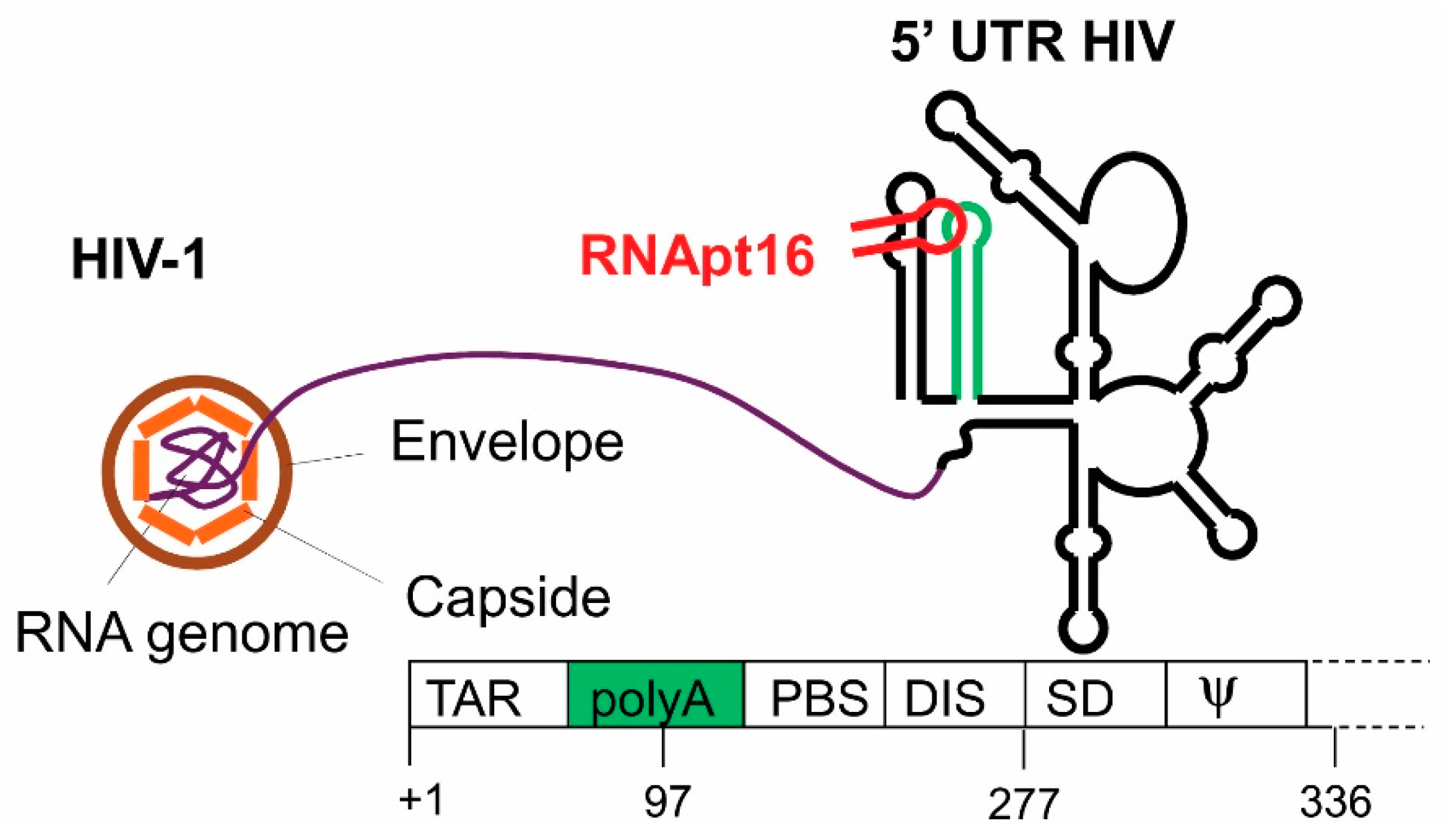
3.1. Anti HIV-1 RNA Aptamers
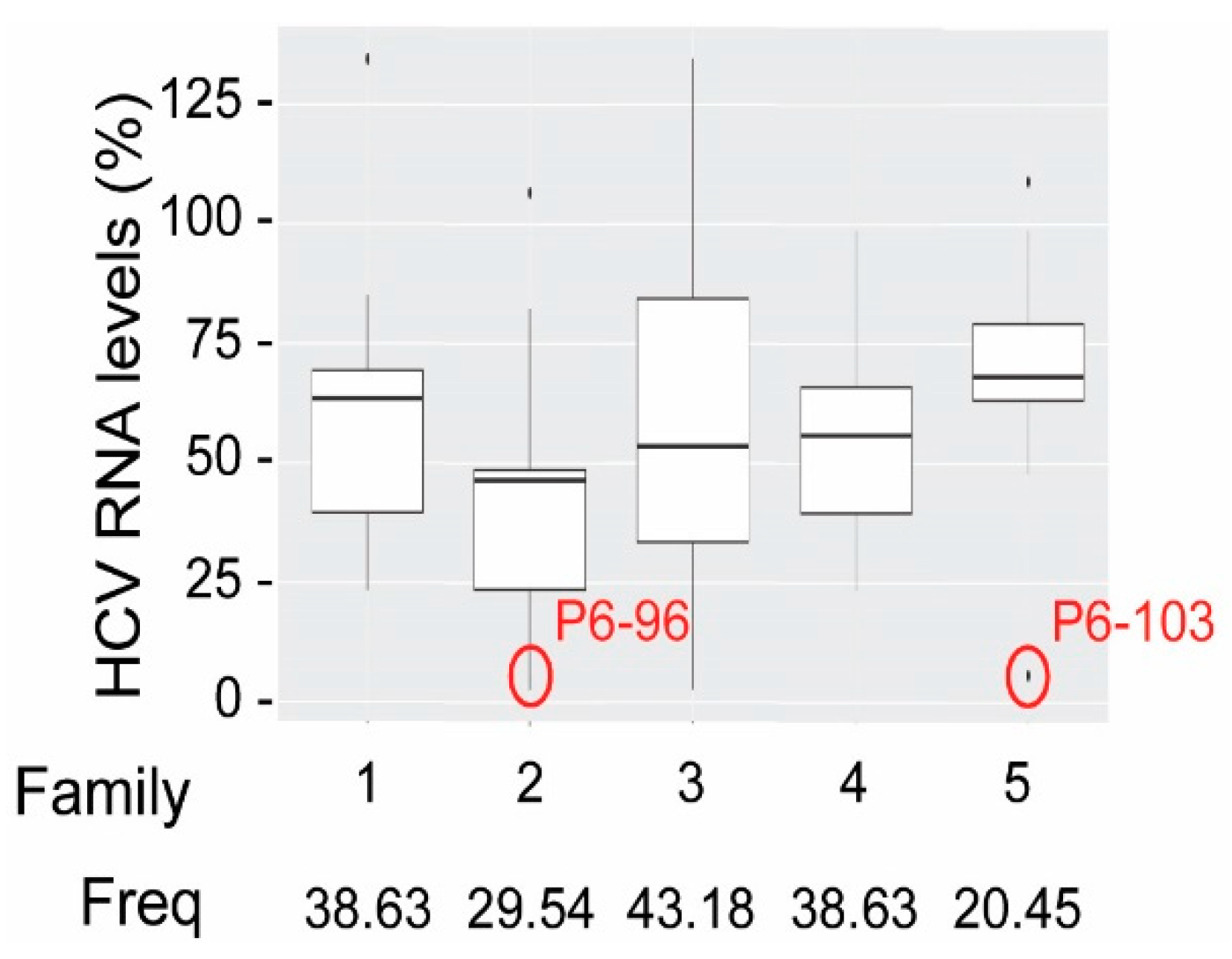
3.2. Anti HCV RNA Aptamers
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Romero-López, C.; Berzal-Herranz, A. Unmasking the information encoded as structural motifs of viral RNA genomes: A potential antiviral target. Rev. Med. Virol. 2013, 23, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moomau, C.; Musalgaonkar, S.; Khan, Y.A.; Jones, J.E.; Dinman, J.D. Structural and functional characterization of programmed ribosomal frameshift signals in west nile virus strains reveals high structural plasticity among cis-acting RNA elements. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 15788–15795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendra, J.A.; Advani, V.M.; Chen, B.; Briggs, J.W.; Zhu, J.; Bress, H.J.; Pathy, S.M.; Dinman, J.D. Functional and structural characterization of the chikungunya virus translational recoding signals. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 17536–17545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. Selection in vitro of single-stranded DNA molecules that fold into specific ligand-binding structures. Nature 1992, 355, 850–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.; Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Selection of high affinity RNA ligands to the bacteriophage R17 coat protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 228, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.S.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of functional nucleic acids. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999, 68, 611–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, M.; Ellington, A.D. Selection of fluorescent aptamer beacons that light up in the presence of zinc. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 390, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raddatz, M.S.; Dolf, A.; Endl, E.; Knolle, P.; Famulok, M.; Mayer, G. Enrichment of cell-targeting and population-specific aptamers by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 5190–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Chavolla, E.; Alocilja, E.C. Aptasensors for detection of microbial and viral pathogens. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3175–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marton, S.; Reyes-Darias, J.A.; Sánchez-Luque, F.J.; Romero-Lopez, C.; Berzal-Herranz, A. In vitro and ex vivo selection procedures for identifying potentially therapeutic DNA and RNA molecules. Molecules 2010, 15, 4610–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, T.H.; Zhang, T.; Luo, H.; Yen, T.M.; Chen, P.W.; Han, Y.; Lo, Y.H. Nucleic acid aptamers: An emerging tool for biotechnology and biomedical sensing. Sensors 2015, 15, 16281–16313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.K. Monitoring intact viruses using aptamers. Biosensors 2016, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, E.W.; Adamis, A.P. Anti-VEGF aptamer (pegaptanib) therapy for ocular vascular diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1082, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, E.W.; Shima, D.T.; Calias, P.; Cunningham, E.T., Jr.; Guyer, D.R.; Adamis, A.P. Pegaptanib, a targeted anti-VEGF aptamer for ocular vascular disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciulla, T.A.; Rosenfeld, P.J. Antivascular endothelial growth factor therapy for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2009, 20, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, S.C. Methods developed for SELEX. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombelli, S.; Minunni, M.; Mascini, M. Analytical applications of aptamers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 2424–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeh, F.; Nsairat, H.; Alshaer, W.; Ismail, M.A.; Esawi, E.; Qaqish, B.; Bawab, A.A.; Ismail, S.I. Aptamers chemistry: Chemical modifications and conjugation strategies. Molecules 2019, 25, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzal-Herranz, A.; Romero-Lopez, C. RNA Aptamers: Antiviral Drugs of the Future. In Proceedings of the 5th International Electronic Conference in Medicinal Chemistry, MDPI AG: Sciforum. 12 November 2019. Available online: https://ecmc2019.sciforum.net/ (accessed on 22 July 2020). [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Theissen, G.; Richter, A.; Lukacs, N. Degree of biotinylation in nucleic acids estimated by a gel retardation assay. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 179, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-López, C.; Barroso-delJesus, A.; Puerta-Fernández, E.; Berzal-Herranz, A. Interfering with hepatitis C virus IRES activity using RNA molecules identified by a novel in vitro selection method. Biol. Chem. 2005, 386, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marton, S.; Berzal-Herranz, B.; Garmendia, E.; Cueto, F.J.; Berzal-Herranz, A. Anti-HCV RNA aptamers targeting the genomic cis-acting replication element. Pharmaceuticals 2012, 5, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Luque, F.J.; Stich, M.; Manrubia, S.; Briones, C.; Berzal-Herranz, A. Efficient HIV-1 inhibition by a 16 nt-long RNA aptamer designed by combining in vitro selection and in silico optimisation strategies. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkhout, B. HIV-1 as RNA evolution machine. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berzal-Herranz, A.; Romero-López, C.; Berzal-Herranz, B.; Ramos-Lorente, S. Potential of the other genetic information coded by the viral RNA genomes as antiviral target. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-López, C.; Berzal-Herranz, A. The role of the RNA-RNA interactome in the hepatitis C virus life cycle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-López, C.; Berzal-Herranz, A. The 5BSL3.2 functional RNA domain connects distant regions in the hepatitis C virus genome. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Sanlés, A.; Berzal-Herranz, B.; González-Matamala, R.; Ríos-Marco, P.; Romero-López, C.; Berzal-Herranz, A. RNA aptamers as molecular tools to study the functionality of the hepatitis C virus CRE region. Molecules 2015, 20, 16030–16047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marton, S.; Romero-López, C.; Berzal-Herranz, A. RNA aptamer-mediated interference of HCV replication by targeting the CRE-5BSL3.2 domain. J. Viral Hepat. 2013, 20, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-López, C.; Díaz-González, R.; Berzal-Herranz, A. Inhibition of hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation by an RNA targeting the conserved IIIf domain. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 2994–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-López, C.; Díaz-González, R.; Barroso-delJesus, A.; Berzal-Herranz, A. Inhibition of hepatitis C virus replication and internal ribosome entry site-dependent translation by an RNA molecule. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-López, C.; Berzal-Herranz, B.; Gómez, J.; Berzal-Herranz, A. An engineered inhibitor RNA that efficiently interferes with hepatitis C virus translation and replication. Antivir. Res. 2012, 94, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-López, C.; Lahlali, T.; Berzal-Herranz, B.; Berzal-Herranz, A. Development of optimized inhibitor RNAs allowing multisite-targeting of the HCV genome. Molecules 2017, 22, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Nº Repetitions | Aptamer 1 |
|---|---|
| 23 | CACCACUAUUGUUGGCAAGGAAGCA |
| 6 | GUACGGCAAGGAGUACAUCGUAGCA |
| 2 | CACAACCUGGGUGGCAAGGAACCCA |
| 1 | CACCGCUAUUGUUGGCAAGGAAGCA |
| 1 | CACCACUAUUGUUGGCAAGGAAGCA |
| 1 | GUACGGCAAGGAGUACAUCGCAGCA |
| 1 | CACUACUCUACGGCUCGAAGCCCCA |
| 1 | AACCACAACGGCUAACCACUGCCCA |
| 1 | CACUACCGACCGUCCACACCAGCCA |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berzal-Herranz, A.; Romero-López, C. Two Examples of RNA Aptamers with Antiviral Activity. Are Aptamers the Wished Antiviral Drugs? Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080157
Berzal-Herranz A, Romero-López C. Two Examples of RNA Aptamers with Antiviral Activity. Are Aptamers the Wished Antiviral Drugs? Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(8):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080157
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerzal-Herranz, Alfredo, and Cristina Romero-López. 2020. "Two Examples of RNA Aptamers with Antiviral Activity. Are Aptamers the Wished Antiviral Drugs?" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 8: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080157
APA StyleBerzal-Herranz, A., & Romero-López, C. (2020). Two Examples of RNA Aptamers with Antiviral Activity. Are Aptamers the Wished Antiviral Drugs? Pharmaceuticals, 13(8), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080157