Regenerative Injections Including 5% Dextrose and Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
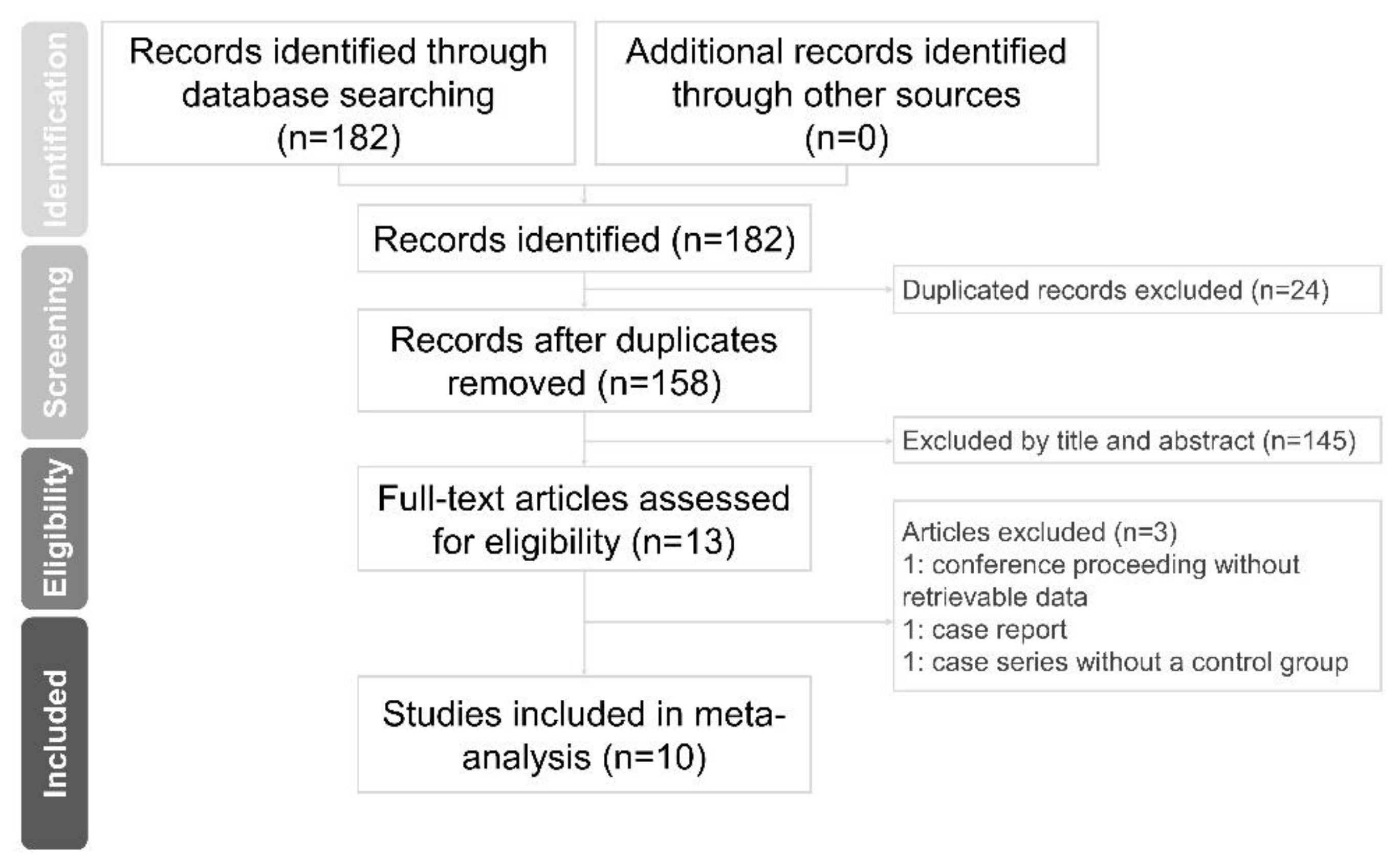
2.1. Study Selection and Characteristics of the Included Studies
2.2. Assessment of the Quality of the Included Studies
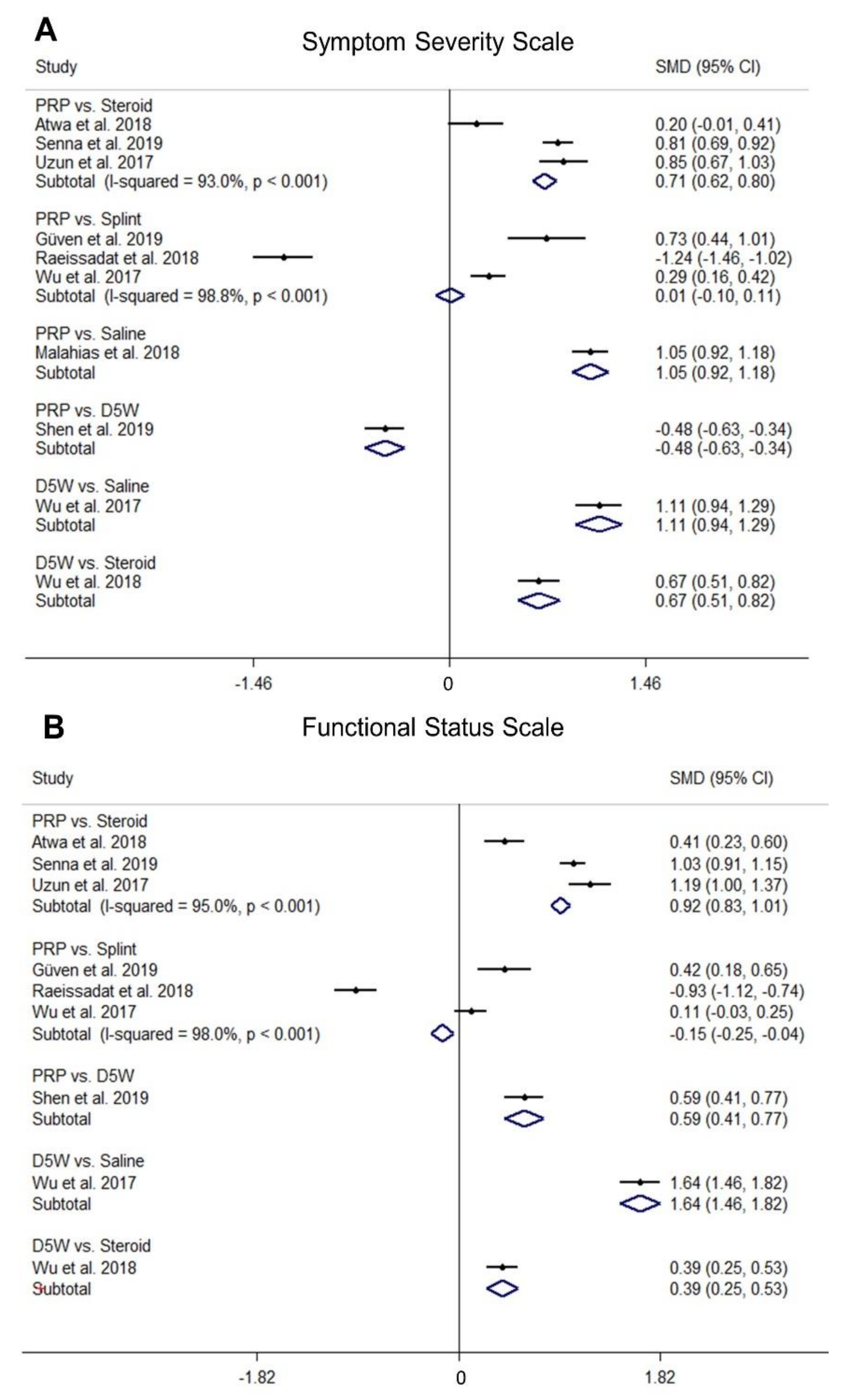
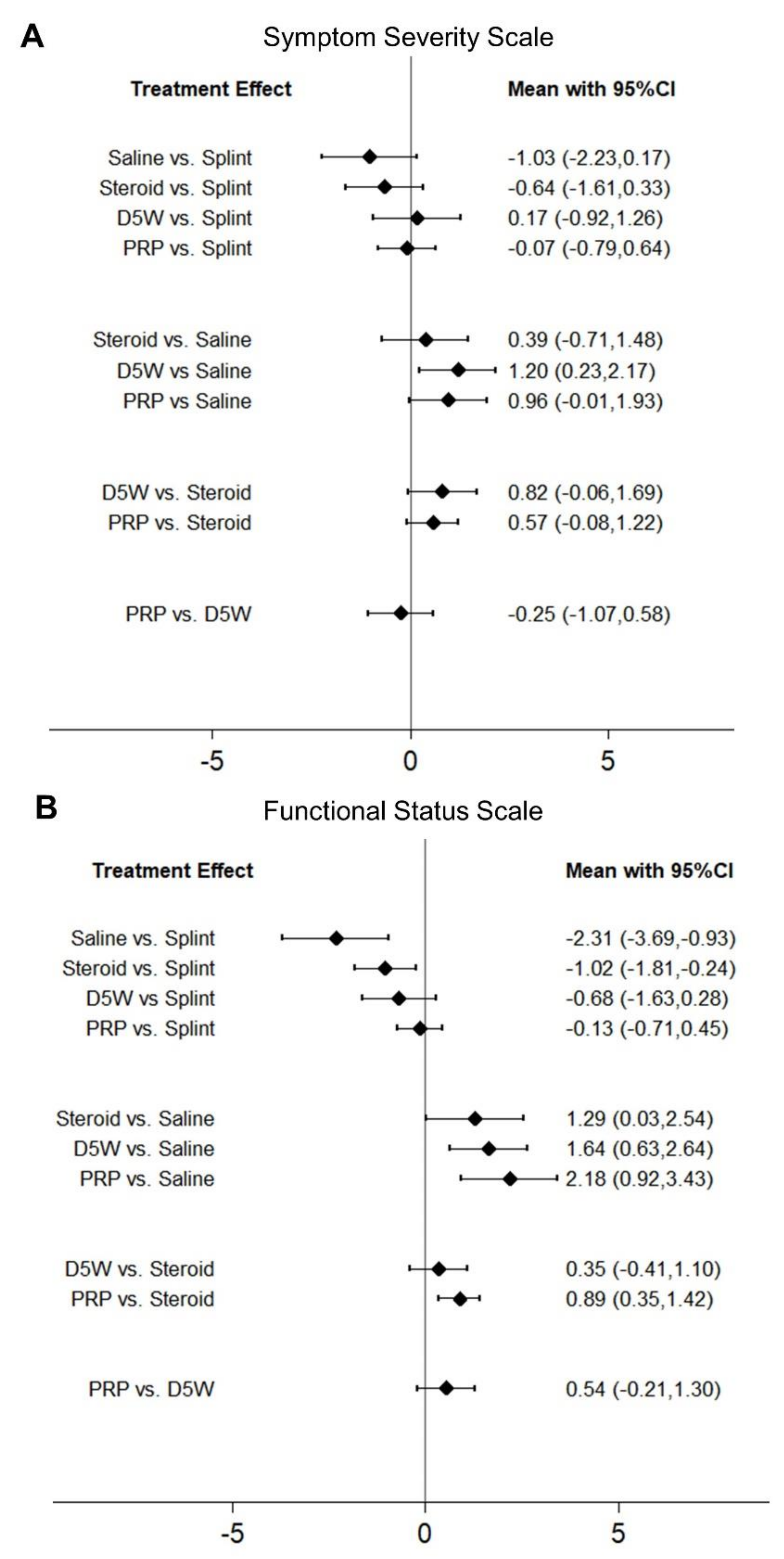
2.3. Comparison of Standardized Mean Differences (SMDs) of SSS among Different Treatments
2.4. Comparison of SMDs of FSS among Different Treatments
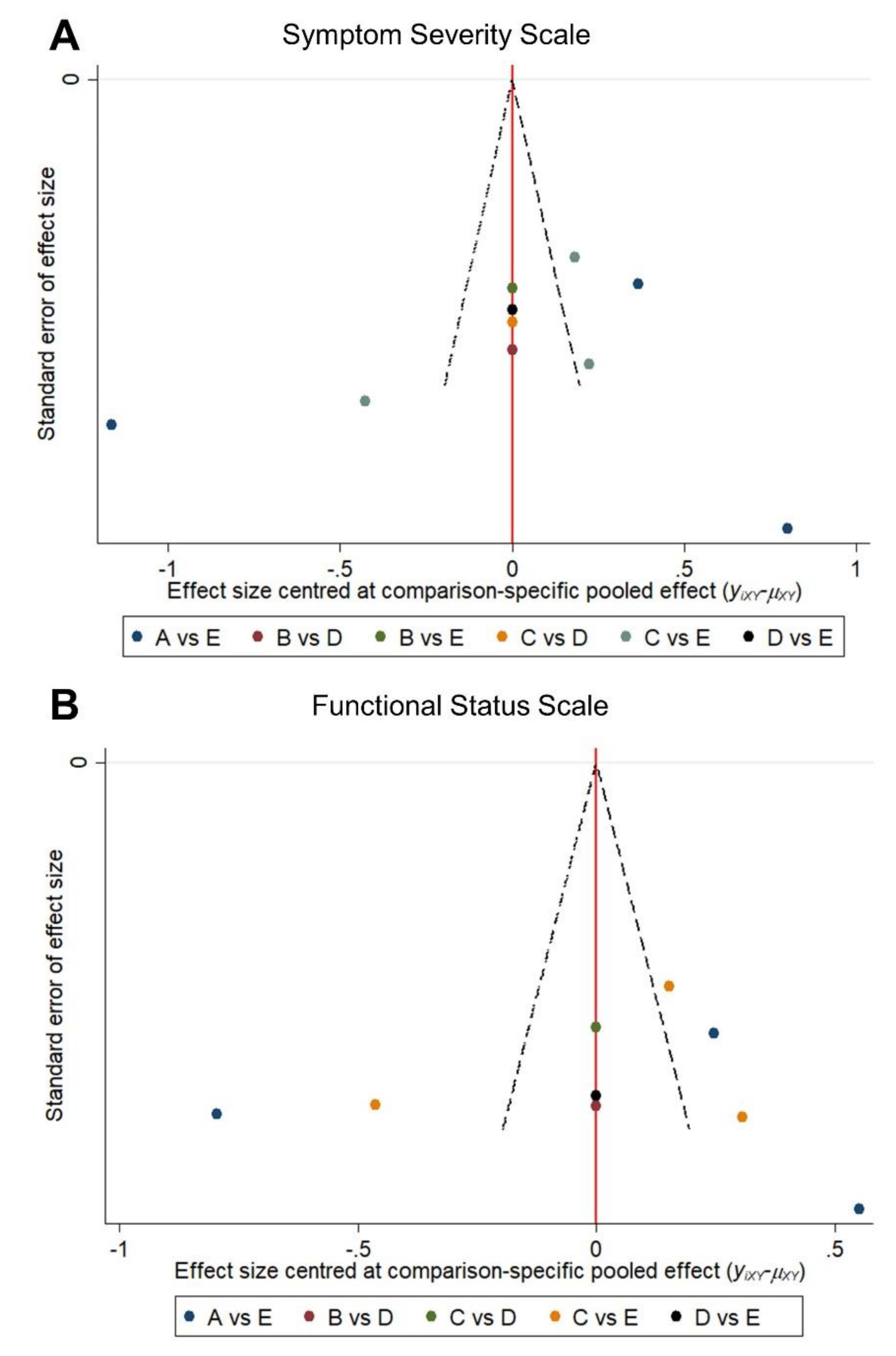
2.5. Publication Bias
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Methods
5.1. Literature Search
5.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
5.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
5.4. Data Synthesis and Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A: Search Strategy
- (carpal tunnel syndrome[Title/Abstract]) AND dextrose[Title/Abstract]
- (carpal tunnel syndrome[Title/Abstract]) AND platelet rich plasma[Title/Abstract]
- 1 OR 2
- (carpal tunnel syndrome[Title/Abstract]) AND dextrose[Title/Abstract]
- (carpal tunnel syndrome[Title/Abstract]) AND platelet rich plasma[Title/Abstract]
- 1 OR 2
Ethical Approval
References
- Atroshi, I.; Gummesson, C.; Johnsson, R.; Ornstein, E.; Ranstam, J.; Rosen, I. Prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome in a general population. JAMA 1999, 282, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondelli, M.; Giannini, F.; Giacchi, M. Carpal tunnel syndrome incidence in a general population. Neurology 2002, 58, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, J.T.; Gauger, M.R.; Whaley, J.D.; Zinberg, E.M. Patient-reported symptom-mapping in carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 2019, 59, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geoghegan, J.M.; Clark, D.I.; Bainbridge, L.C.; Smith, C.; Hubbard, R. Risk factors in carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Hand Surg. Br. 2004, 29, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.H.; Katz, J.N.; Bohn, R.; Mogun, H.; Avorn, J. Nonoccupational risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 1999, 14, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Costoso, A.; Martinez-Vizcaino, V.; Alvarez-Bueno, C.; Ferri-Morales, A.; Cavero-Redondo, I. Accuracy of Ultrasonography for the Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 758–765.e710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Guiding Treatment for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. 2018, 29, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Massy-Westropp, N.; O’Connor, D.; Pitt, V. Splinting for carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, CD010003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; O’Connor, D.; Pitt, V.; Massy-Westropp, N. Exercise and mobilisation interventions for carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, CD009899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; O’Connor, D.; Pitt, V.; Massy-Westropp, N. Therapeutic ultrasound for carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, CD009601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggard, M.A.; Harness, N.G.; Chang, W.T.; Parikh, J.A.; Asch, S.M.; Nuckols, T.K.; Carpal Tunnel Quality, G. Indications for performing carpal tunnel surgery: Clinical quality measures. Plast Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 126, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauder, A.; Mithani, S.; Leversedge, F.J. Management of Recalcitrant Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 27, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesterton, L.S.; Blagojevic-Bucknall, M.; Burton, C.; Dziedzic, K.S.; Davenport, G.; Jowett, S.M.; Myers, H.L.; Oppong, R.; Rathod-Mistry, T.; van der Windt, D.A.; et al. The clinical and cost-effectiveness of corticosteroid injection versus night splints for carpal tunnel syndrome (INSTINCTS trial): An open-label, parallel group, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, S.; Tardif, G.; Ashworth, N. Local corticosteroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, CD001554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.C.; Chang, K.V.; Wu, W.T.; Han, D.S.; Ozcakar, L. Ultrasound-Guided Standard vs Dual-Target Subacromial Corticosteroid Injections for Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, L.F.; Wolf, E.J.; Brindle, T.; Cernich, A.; Dean, W.K.; Dearth, C.L.; Grimm, M.; Kusiak, A.; Nitkin, R.; Potter, K.; et al. The convergence of regenerative medicine and rehabilitation: Federal perspectives. NPJ Regen. Med. 2018, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Woodall, J., Jr.; Vieira, A. Treatment of tendon and muscle using platelet-rich plasma. Clin. Sports Med. 2009, 28, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, R.A.; Lackner, J.B.; Steilen-Matias, D.; Harris, D.K. A Systematic Review of Dextrose Prolotherapy for Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain. Clin. Med. Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 9, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, R.A.; Andary, M. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Pathophysiology and clinical neurophysiology. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Nassiri, N.; Hazel, A.; Bathen, M.; Mozaffar, T. Chronic nerve compression alters Schwann cell myelin architecture in a murine model. Muscle Nerve 2012, 45, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboonq, M.S. Pathophysiology of carpal tunnel syndrome. Neurosciences 2015, 20, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Ke, M.J.; Ho, T.Y.; Li, T.Y.; Shen, Y.P.; Chen, L.C. Randomized double-blinded clinical trial of 5% dextrose versus triamcinolone injection for carpal tunnel syndrome patients. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 84, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guven, S.C.; Ozcakar, L.; Kaymak, B.; Kara, M.; Akinci, A. Short-term effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma in carpal tunnel syndrome: A controlled study. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, M.J.; Wu, Y.T.; Ho, T.Y.; Li, T.Y.; Chen, C.F. Platelet-rich plasma versus 5% dextrose for mild-to-moderate carpal tunnel syndrome. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, S184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.C.; Lee, C.C.; Hsieh, L.F. Ultrasound-guided perineural injection with platelet-rich plasma improved the neurophysiological parameters of carpal tunnel syndrome: A case report. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 44, 234–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malahias, M.A.; Johnson, E.O.; Babis, G.C.; Nikolaou, V.S. Single injection of platelet-rich plasma as a novel treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 1856–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwa, E.T.; Esh, A.M.; Al, I.T.A.E.; Awad, Y.M. Platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injections for carpal tunnel syndrome: Clinical and electrophysiological study. Egypt. Rheumatol. 2019, 41, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malahias, M.A.; Nikolaou, V.S.; Johnson, E.O.; Kaseta, M.K.; Kazas, S.T.; Babis, G.C. Platelet-rich plasma ultrasound-guided injection in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: A placebo-controlled clinical study. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, e1480–e1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeissadat, S.A.; Karimzadeh, A.; Hashemi, M.; Bagherzadeh, L. Safety and efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome; a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senna, M.K.; Shaat, R.M.; Ali, A.A.A. Platelet-rich plasma in treatment of patients with idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.P.; Li, T.Y.; Chou, Y.C.; Ho, T.Y.; Ke, M.J.; Chen, L.C.; Wu, Y.T. Comparison of perineural platelet-rich plasma and dextrose injections for moderate carpal tunnel syndrome: A prospective randomized, single-blind, head-to-head comparative trial. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13, 2009–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzun, H.; Bitik, O.; Uzun, O.; Ersoy, U.S.; Aktas, E. Platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injections for carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2017, 51, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Ho, T.Y.; Chou, Y.C.; Ke, M.J.; Li, T.Y.; Huang, G.S.; Chen, L.C. Six-month efficacy of platelet-rich plasma for carpal tunnel syndrome: A prospective randomized, single-blind controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Ho, T.Y.; Chou, Y.C.; Ke, M.J.; Li, T.Y.; Tsai, C.K.; Chen, L.C. Six-month Efficacy of Perineural Dextrose for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.C.; Chuang, C.H.; Tu, Y.K.; Bai, C.H.; Chen, C.F.; Liaw, M. A Bayesian network meta-analysis: Comparing the clinical effectiveness of local corticosteroid injections using different treatment strategies for carpal tunnel syndrome. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei-Ghazani, A.; Roomizadeh, P.; Forogh, B.; Moeini-Taba, S.M.; Abedini, A.; Kadkhodaie, M.; Jahanjoo, F.; Eftekharsadat, B. Ultrasound-Guided Versus Landmark-Guided Local Corticosteroid Injection for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malahias, M.A.; Chytas, D.; Mavrogenis, A.F.; Nikolaou, V.S.; Johnson, E.O.; Babis, G.C. Platelet-rich plasma injections for carpal tunnel syndrome: A systematic and comprehensive review. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2019, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, E.; Donat, N.; Jaziri, S.; Kurdi, O.; Couturier, C.; Dreyfus, J.F.; Fischler, M. Ultrasound-guided perineural circumferential median nerve block with and without prior dextrose 5% hydrodissection: A prospective randomized double-blinded noninferiority trial. Anesth Analg. 2012, 115, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.V.; Hung, C.Y.; Ozcakar, L. Snapping Thumb and Superficial Radial Nerve Entrapment in De Quervain Disease: Ultrasound Imaging/Guidance Revisited. Pain Med. 2015, 16, 2214–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.V.; Wu, W.T.; Ozcakar, L. Ultrasound Imaging for a Rare Cause of Postpartum Forearm Pain: Diffuse Enlargement Rather than Focal Swelling of the Deep Branch of the Radial Nerve. Pain Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premkumar, L.S.; Sikand, P. TRPV1: A target for next generation analgesics. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2008, 6, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.V.; Hung, C.Y.; Aliwarga, F.; Wang, T.G.; Han, D.S.; Chen, W.S. Comparative effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma injections for treating knee joint cartilage degenerative pathology: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, M.Y.; Hung, C.Y.; Chang, K.V.; Chien, K.L.; Tu, Y.K.; Wang, T.G. Comparative effectiveness of autologous blood-derived products, shock-wave therapy and corticosteroids for treatment of plantar fasciitis: A network meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgetti, M.; Siciliano, G. Platelet-rich plasma: The role in neural repair. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 1920–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettema, A.M.; Amadio, P.C.; Zhao, C.; Wold, L.E.; An, K.N. A histological and immunohistochemical study of the subsynovial connective tissue in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2004, 86, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, S.; Thoreson, A.R.; Smith, J.; Zhao, C.; Geske, J.R.; Amadio, P.C. Ultrasound-guided hydrodissection decreases gliding resistance of the median nerve within the carpal tunnel. Muscle Nerve 2018, 57, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Chen, S.R.; Li, T.Y.; Ho, T.Y.; Shen, Y.P.; Tsai, C.K.; Chen, L.C. Nerve hydrodissection for carpal tunnel syndrome: A prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Muscle Nerve 2019, 59, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Liao, K.K.; Lin, K.P.; Chou, C.L.; Yang, T.F.; Huang, Y.F.; Wang, K.A.; Chiu, J.W. Efficacy of Combined Ultrasound-Guided Steroid Injection and Splinting in Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Juni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, J.C.; Jerosch-Herold, C.; Song, F. A systematic review of the psychometric properties of the Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2006, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaimani, A.; Higgins, J.P.; Mavridis, D.; Spyridonos, P.; Salanti, G. Graphical tools for network meta-analysis in STATA. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Author, Year | Study Design | Inclusion Criteria | Treatment Allocation | Participant Characteristics | Symptom Duration (Months) | Disease Severity | Randomization | Blinding | Outcome Measure | Follow-Up (Week) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Participants (Wrists) | Mean Age (Year) | Female (%) | ||||||||||
| Uzun et al. 2017 | Prospective quasi-experimental | Clinical + EDS | PRP | 20 (20) | 48.8 ± 5.8 | 80 | NA | Minimal to mild | No | No | BCTQ, EDS | 12,24 |
| Triamcinolone | 20 (20) | 48.5 ± 6.1 | 80 | |||||||||
| Wu et al. 2017(Mayo Clin Proc) | RCT | Clinical + EDS | D5W | 25 (30) | 58.4 ± 2.3 * | 86.7 | 44.5 ± 7.5 * | Mild to moderate | Computer-generated randomization | Blinded participants and outcome assessors | VAS, BCTQ, EDS, CSA of MN, Global assessment of treatment results | 4,12,24 |
| Normal saline | 24 (30) | 58.1 ± 1.9 * | 80 | 44.4 ± 5.5 * | ||||||||
| Wu et al. 2017(Sci Rep) | RCT | Clinical + EDS | PRP | 30 (30) | 57.87 ± 1.5 * | 90 | 34.43 ± 5.6 * | Mild to moderate | Computer-generated randomization | Blinded outcome assessors | VAS, BCTQ, EDS, CSA of MN, Finger pinch strength | 4,12,24 |
| Splinting | 30 (30) | 54.27 ± 1.3 * | 83.3 | 30.70 ± 6.0 * | ||||||||
| Malahias et al. 2018 | RCT | Clinical | PRP | 26 (26) | 60.4 ± 14.3 | NA | NA | Mild to moderate | Closed envelope method | Blinded outcome assessors | VAS, Q-DASH, Delta- CSA of MN | 4,12 |
| Normal saline | 24 (24) | 57.1 ± 16.1 | ||||||||||
| Raeissadat et al. 2018 | RCT | Clinical + EDS | PRP + splinting | 21 (21) | 51.2 ± 9.8 | 100 | 13.7 ± 11.5 | Mild to moderate | Online randomization website | No | VAS, BCTQ, EDS | 10 |
| Splinting | 20 (20) | 47.2 ± 7.1 | 100 | 14.1 ± 8.5 | ||||||||
| Wu et al. 2018 | RCT | Clinical + EDS | D5W | 27 (27) | 58.6 ± 2.2 * | 81.4 | 46.8 ± 8.9 * | Mild to moderate | Computer-generated randomization | Blinded outcome assessors | VAS, BCTQ, EDS, CSA of MN, global assessment of treatment results | 4,12,16,24 |
| Triamcinolone | 27 (27) | 54.3 ± 2.0 * | 77.7 | 45.6 ± 9.4 * | ||||||||
| Güven et al. 2019 | Prospective quasi-experimental | Clinical + EDS | PRP + Splinting | 18 (20) | 47.5 | 94.4 | 72 | Mild to moderate | No | No | BCTQ, EDS, CSA of MN, monofilament testing score, static 2PD testing score, dynamic 2PD testing score | 4 |
| Splinting | 12 (20) | 50.0 | 91.6 | 60 | ||||||||
| Atwa et al. 2019 | Prospective quasi-experimental | Clinical + EDS | PRP | 18 (18) | 38.5 ± 8.0 | 88.8 | 14 ± 9 | Mild to moderate | No | No | VAS, BCTQ, EDS | 4,12 |
| Methylprednisolone | 18 (18) | 36.6 ± 8.8 | 88.8 | 19 ± 11 | ||||||||
| Shen et al. 2019 | RCT | Clinical + EDS | PRP | 26 (26) | 56.8 ± 1.7 * | 96.2 | 58.3 ± 16.2 * | Moderate | Computer-generated randomization | Blinded outcome assessors | BCTQ, EDS, CSA of MN | 4,12,24 |
| D5W | 26 (26) | 58.5 ± 2.1 * | 84.6 | 37.5 ± 8.0 * | ||||||||
| Senna et al. 2019 | RCT | Clinical + EDS | PRP | 43 (43) | 38.3 ± 6.4 | 81.4 | NA | Mild to moderate | Block randomization | Blinded participants and outcome assessors | VAS, BCTQ, EDS, CSA of MN, Paresthesia, Phalen’s maneuver, and Tinel’s sign | 4,12 |
| Methylprednisolone | 42 (42) | 40.7 ± 9.4 | 85.7 | |||||||||
| Author, Year | Intervention | Intervention Regiment | Guidance Method | Injection Site | Adverse Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uzun et al. 2017 | PRP vs. Corticosteroid | PRP:2 mL PRP * Corticosteroid:40 mg/1 ml triamcinolone | Palpation-guided | 1 cm proximal to the distal wrist-flexion crease | No complication |
| Wu et al. 2017(Mayo Clin Proc) | Prolotherapy vs. Placebo | Prolotherapy:5 mL of 5% dextrose Placebo:5 mL normal saline | US-guided | Carpal tunnel inlet | No complication |
| Wu et al. 2017(Sci Rep) | PRP vs. Splinting | PRP:3 mL RegenKit-THT-1 Splinting:overnight ≥ 8 h daily | US-guided | Carpal tunnel inlet | No complication |
| Malahias et al. 2018 | PRP vs. Placebo | PRP:2 mL PRP * Placebo:2 mL 0.9% normal saline | US-guided | Carpal tunnel inlet | No complication |
| Raeissadat et al. 2018 | PRP vs. Splinting | PRP:0.8–1 mL Rooyagen kit, 0.5 mL lidocaine, night splint Splinting:overnight for 8 weeks | Palpation-guided | Distal carpal skin crease | 4 with pruritus, 1 with post-injection pain and 1 with burning sensation |
| Wu et al. 2018 | Prolotherapy vs. Corticosteroid | Prolotherapy:5 mL of 5% dextrose Corticosteroid:3 ml of triamcinolone (10 mg/mL), 2 mL normal saline | US-guided | Carpal tunnel inlet | No complication |
| Güven et al. 2019 | PRP vs. Splinting | PRP:1 mL PRP*, night splinting, activity modification for 4 weeks Splint:night splinting, activity modification for 4 weeks | US-guided | Not specified | No complication |
| Atwa et al. 2019 | PRP vs. Corticosteroid | PRP:2 mL PRP * Corticosteroid:40 mg/1 ml methylprednisolone | Palpation-guided | 1 cm proximal to the distal wrist-flexion crease | Not mentioned |
| Shen et al. 2019 | PRP vs. Prolotherapy | PRP:3 mL RegenKit-THT-1 Prolotherapy:3 mL of 5% dextrose | US-guided | Carpal tunnel inlet | No severe complication |
| Senna et al. 2019 | PRP vs. Corticosteroid | PRP:2 mL GD medical pharma Corticosteroid:40 mg/1 ml methylprednisolone | US-guided | Carpal tunnel inlet | No complication |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-P.; Chang, K.-V.; Huang, Y.-K.; Wu, W.-T.; Özçakar, L. Regenerative Injections Including 5% Dextrose and Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13030049
Lin C-P, Chang K-V, Huang Y-K, Wu W-T, Özçakar L. Regenerative Injections Including 5% Dextrose and Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(3):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13030049
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chih-Peng, Ke-Vin Chang, Yi-Kai Huang, Wei-Ting Wu, and Levent Özçakar. 2020. "Regenerative Injections Including 5% Dextrose and Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 3: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13030049
APA StyleLin, C.-P., Chang, K.-V., Huang, Y.-K., Wu, W.-T., & Özçakar, L. (2020). Regenerative Injections Including 5% Dextrose and Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 13(3), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13030049







