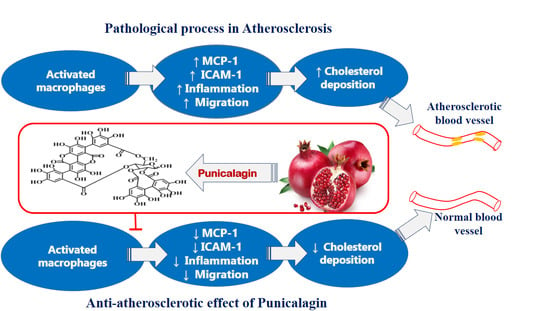
Punicalagin Regulates Key Processes Associated with Atherosclerosis in THP-1 Cellular Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Punicalagin Does Not Alter THP-1 Macrophages Viability
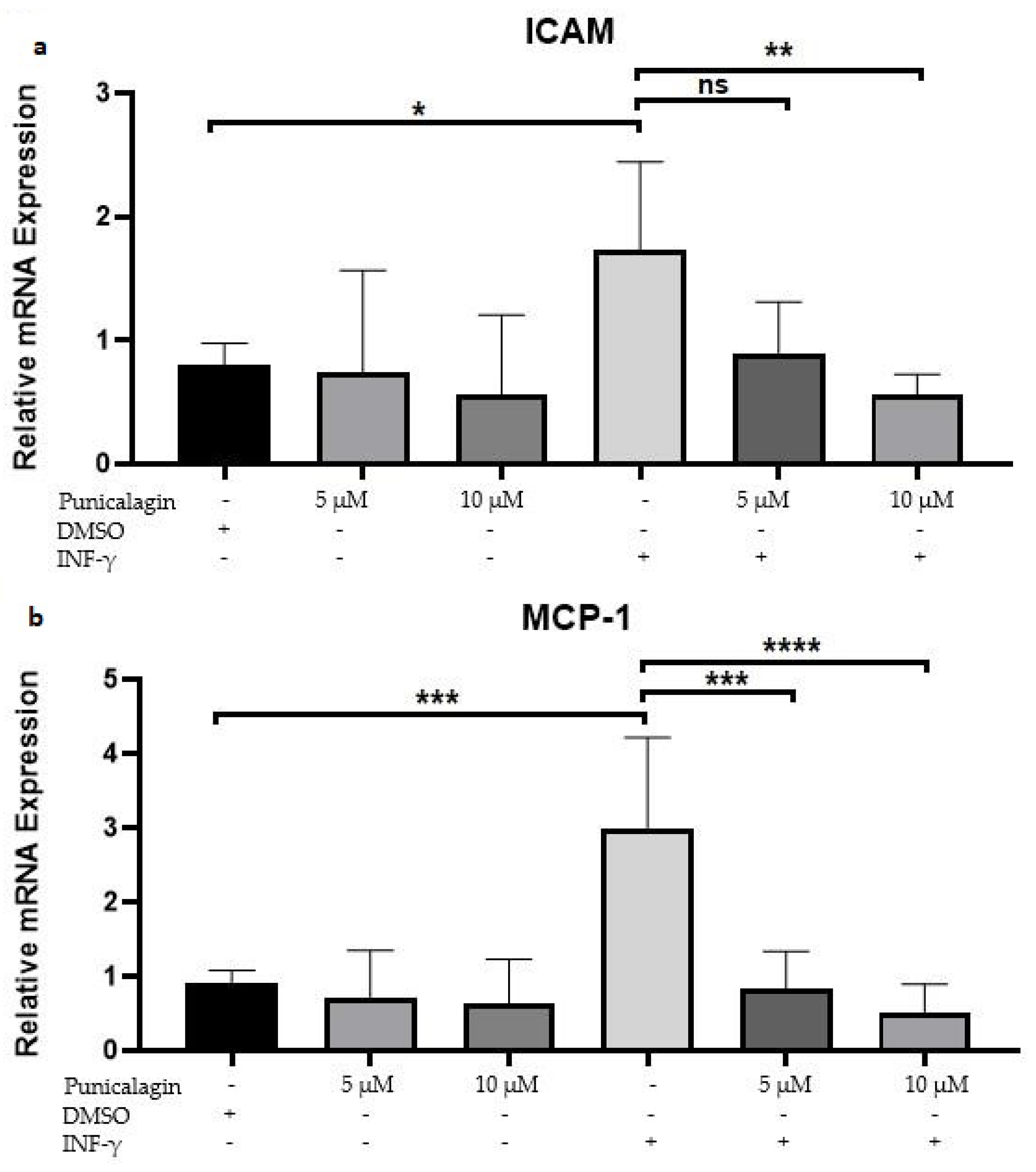
2.2. Punicalagin Reduces IFN-γ-Induced mRNA Overexpression of MCP-1 and ICAM-1 in THP-1 Macrophages
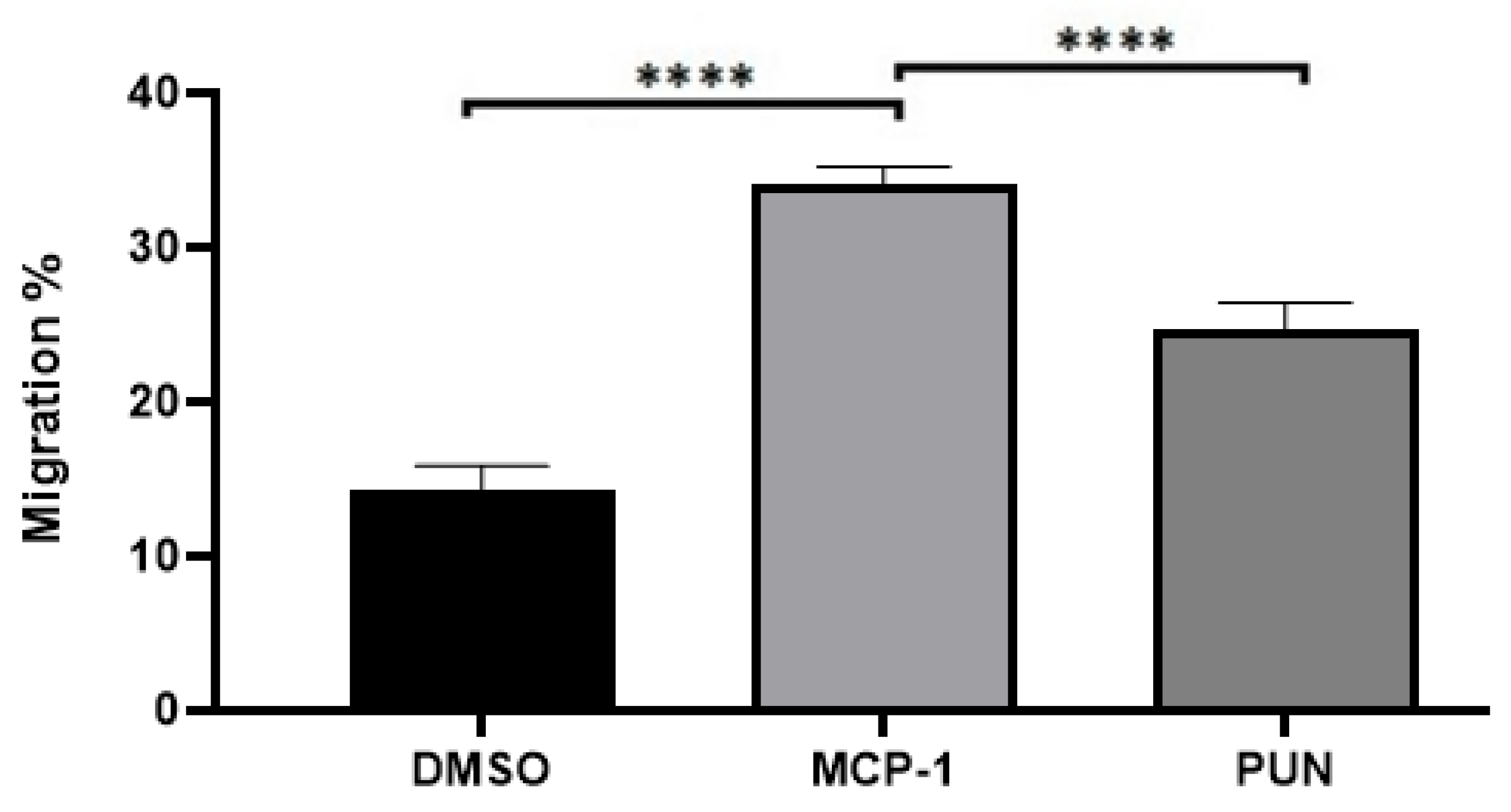
2.3. Punicalagin Inhibits MCP-1-Mediated Migration of THP-1 Monocytes
2.4. Punicalagin Enhances Cholesterol Efflux in IFN-γ-Induced THP-1 Macrophages
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Preparation of Punicalagin Treatment
4.3. THP-1 Cell Culture
4.4. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Assay
4.5. Crystal Violet Assay
4.6. RNA Extraction
4.7. Analysis of Gene Expression Using qRT-PCR
4.8. MCP-1-Induced Monocyte Migration Assay
4.9. Cholesterol Efflux Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buckley, M.L.; Ramji, D.P. The influence of dysfunctional signaling and lipid homeostasis in mediating the inflammatory responses during atherosclerosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2015, 1852, 1498–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldridge, N.B. Economic burden of physical inactivity: Healthcare costs associated with cardiovascular disease. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2008, 15, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirós-Fernández, R.; López-Plaza, B.; Bermejo, L.M.; Palma-Milla, S.; Gómez-Candela, C. Supplementation with hydroxytyrosol and punicalagin improves early atherosclerosis markers involved in the asymptomatic phase of atherosclerosis in the adult population: A randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusis, A.J. Genetics of atherosclerosis. Trends Genet. 2012, 28, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusis, A.J. Atherosclerosis—Insight Review Articles. Nature 2000, 407, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.; Swerdlow, D.I.; Preiss, D.; Fairhurst-Hunter, Z.; Keating, B.J.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Sattar, N.; Humphries, S.E.; Hingorani, A.D.; Holmes, M.V. Association of lipid fractions with risks for coronary artery disease and diabetes. JAMA Cardiol. 2016, 1, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, B.; Emberson, J.; Blackwell, L.; Keech, A.; Simes, J.; Barnes, E.H.; Voysey, M.; Gray, A.; Collins, R.; Baigent, C.; et al. The effects of lowering LDL cholesterol with statin therapy in people at low risk of vascular disease: Meta-analysis of individual data from 27 randomised trials. Lancet 2012, 380, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orekhov, A.N.; Ivanova, E.A. Cellular models of atherosclerosis and their implication for testing natural substances with anti-atherosclerotic potential. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanput, W.; Mes, J.J.; Wichers, H.J. THP-1 cell line: An in vitro cell model for immune modulation approach. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 23, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeram, N.; Lee, R.; Hardy, M.; Heber, D. Rapid large scale purification of ellagitannins from pomegranate husk, a by-product of the commercial juice industry. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 41, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollebeeck, S.; Winand, J.; Hérent, M.F.; During, A.; Leclercq, J.; Larondelle, Y.; Schneider, Y.J. Anti-inflammatory effects of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) husk ellagitannins in Caco-2 cells, an in vitro model of human intestine. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.T.; Fitschen, P.J.; Kistler, B.M.; Jeong, J.H.; Chung, H.R.; Aviram, M.; Phillips, S.A.; Fernhall, B.; Wilund, K.R. Effects of Pomegranate Extract Supplementation on Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Physical Function in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviram, M.; Rosenblat, M. Pomegranate protection against cardiovascular diseases. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Nigris, F.; Williams-Ignarro, S.; Sica, V.; Lerman, L.O.; D’Armiento, F.P.; Byrns, R.E.; Casamassimi, A.; Carpentiero, D.; Schiano, C.; Sumi, D.; et al. Effects of a Pomegranate Fruit Extract rich in punicalagin on oxidation-sensitive genes and eNOS activity at sites of perturbed shear stress and atherogenesis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 73, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansky, E.; Shubert, S.; Neeman, I. Pharmacological and therapeutic properties of pomegranate. Adv. Res. Technol. 2000, 235, 231–235. [Google Scholar]
- Calvo, C.F.; Yoshimura, T.; Gelman, M.; Mallat, M. Production of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 by rat brain macrophages. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wautier, J.; Setiadi, H.; Vilette, D. Leukocyte Adhesion to Endothelial Cells (Accepted by Editor G.W. Schmid-Schonbein). 1990, pp. 425–432. Available online: https://content.iospress.com/articles/biorheology/bir27-3-4-19 (accessed on 8 November 2020).
- Muller, W.A. Mechanisms of leukocyte transendothelial migration. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2011, 6, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Sasaki, T.; Hashimoto, H.; Kuwabara, K.; Ohtsuki, T.; Hori, M. Involvement of ICAM-1 in the progression of atherosclerosis in APOE-knockout mice. Atherosclerosis 2002, 160, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; McLaren, J.E.; Michael, D.R.; Clement, M.; Fielding, C.A.; Ramji, D.P. ERK Is Integral to the IFN-γ–Mediated Activation of STAT1, the Expression of Key Genes Implicated in Atherosclerosis, and the Uptake of Modified Lipoproteins by Human Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3041–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullenix, P.S.; Andersen, C.A.; Starnes, B.W. Atherosclerosis as inflammation. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2005, 19, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Luo, F.; Ruan, G.; Peng, R.; Li, X. Hypertriglyceridemia and atherosclerosis. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.A.; Ismael, N.M.; Bedewy, M. The Anti-inflammatory and Antiatherogenic In Vivo Effects of Pomegranate Peel Powder: From Waste to Medicinal Food. J. Med. Food 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Gilles, D.; Li, L.; Vaidyanathan, V.G.; King, R.; Cho, B.; Worthen, D.R.; Chichester, C.O.; Seeram, N.P. Inhibitory effects of polyphenol punicalagin on type-II collagen degradation in vitro and inflammation in vivo. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2013, 205, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.J.; Chen, L.G.; Liang, W.L.; Wang, C.C. Multiple activities of punica granatum linne against acne vulgaris. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrahimovich, D.; Samson, A.O.; Khattib, A.; Vaya, J.; Khatib, S. Punicalagin Decreases Serum Glucose Levels and Increases PON1 Activity and HDL Anti-Inflammatory Values in Balb/c Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaidikar, L.; Thakur, S. Punicalagin attenuated cerebral ischemia–reperfusion insult via inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines, up-regulation of Bcl-2, down-regulation of Bax, and caspase-3. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 402, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wei, D.; Fu, Z.; Li, D.; Tan, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, T. Punicalagin Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Mice. Inflammation 2015, 38, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimbach, G.; Valacchi, G.; Canali, R.; Virgili, F. Macrophages stimulated with IFN-γ activate NF-κb and induce MCP-1 gene expression in primary human endothelial cells. Mol. Cell Biol. Res. Commun. 2000, 3, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.J.; Holtzman, M.J.; Chen, C.C. Interferon-γ-induced epithelial ICAM-1 expression and monocyte adhesion. Involvement of protein kinase c-dependent c-Src tyrosine kinase activation pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 7118–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Tall, A.R.; Schindler, C. IFN-gamma potentiates atherosclerosis in ApoE knock-out mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2752–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, V.; Patil, A.; Phatak, A.; Chandra, N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulselvan, P.; Fard, M.T.; Tan, W.S.; Gothai, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Kumar, S.S. Role of Antioxidants and Natural Products in Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.I.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Hess-Pierce, B.; Holcroft, D.M.; Kader, A.A. Antioxidant activity of pomegranate juice and its relationship with phenolic composition and processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4581–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestas, J.; Ley, K. Monocyte-Endothelial Cell Interactions in the Development of Atherosclerosis. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2008, 18, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boring, L.; Gosling, J.; Cleary, M.; Charo, I.F. Decreased lesion formation in CCR2(-/-) mice reveals a role for chemokines in the initiation of atherosclerosis. Nature 1998, 394, 894–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, A.V.; Cuchel, M.; de la Llera-Moya, M.; Rodrigues, A.; Burke, M.F.; Jafri, K.; French, B.C.; Phillips, J.A.; Mucksavage, M.L.; Wilensky, R.L.; et al. Cholesterol Efflux Capacity, High-Density Lipoprotein Function, and Atherosclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 2012, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.J.; Sheedy, F.J.; Fisher, E.A. Macrophages in atherosclerosis: A dynamic balance. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volobueva, A.; Zhang, D.; Grechko, A.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Foam cell formation and cholesterol trafficking and metabolism disturbances in atherosclerosis. Cor Vasa 2019, 61, E48–E54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.H.; Fu, Y.C.; Zhang, D.W.; Yin, K.; Tang, C.K. Foam cells in atherosclerosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 424, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, J.W.E.; Davies, T.S.; Garaiova, I.; Plummer, S.F.; Michael, D.R.; Ramji, D.P. A unique combination of nutritionally active ingredients can prevent several key processes associated with atherosclerosis in vitro. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosling, J.; Slaymaker, S.; Gu, L.; Tseng, S.; Zlot, C.H.; Young, S.G.; Rollins, B.J.; Charo, I.F. MCP-1 deficiency reduces susceptibility to atherosclerosis in mice that overexpress human apolipoprotein B. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Genes | Forward Sequence (5′-3′) | Reverse Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| H-GAPDH | CTTTTGCGTCGCCAGCCGAG | GCCCAATACGACCAAATCCGTTGACT |
| H-MCP-1 | CGCTCAGCCAGATGCAATCAATG | ATGGTCTTGAAGATCACAGCTTCTTTGG |
| H-ICAM-1 | GACCAGAGGTTGAACCCCAC | GCGCCGGAAAGCTGTAGAT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almowallad, S.; Huwait, E.; Al-Massabi, R.; Saddeek, S.; Gauthaman, K.; Prola, A. Punicalagin Regulates Key Processes Associated with Atherosclerosis in THP-1 Cellular Model. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110372
Almowallad S, Huwait E, Al-Massabi R, Saddeek S, Gauthaman K, Prola A. Punicalagin Regulates Key Processes Associated with Atherosclerosis in THP-1 Cellular Model. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(11):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110372
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmowallad, Sanaa, Etimad Huwait, Rehab Al-Massabi, Salma Saddeek, Kalamegam Gauthaman, and Alexandre Prola. 2020. "Punicalagin Regulates Key Processes Associated with Atherosclerosis in THP-1 Cellular Model" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 11: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110372
APA StyleAlmowallad, S., Huwait, E., Al-Massabi, R., Saddeek, S., Gauthaman, K., & Prola, A. (2020). Punicalagin Regulates Key Processes Associated with Atherosclerosis in THP-1 Cellular Model. Pharmaceuticals, 13(11), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13110372