Libidibia ferrea (jucá), a Traditional Anti-Inflammatory: A Study of Acute Toxicity in Adult and Embryos Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
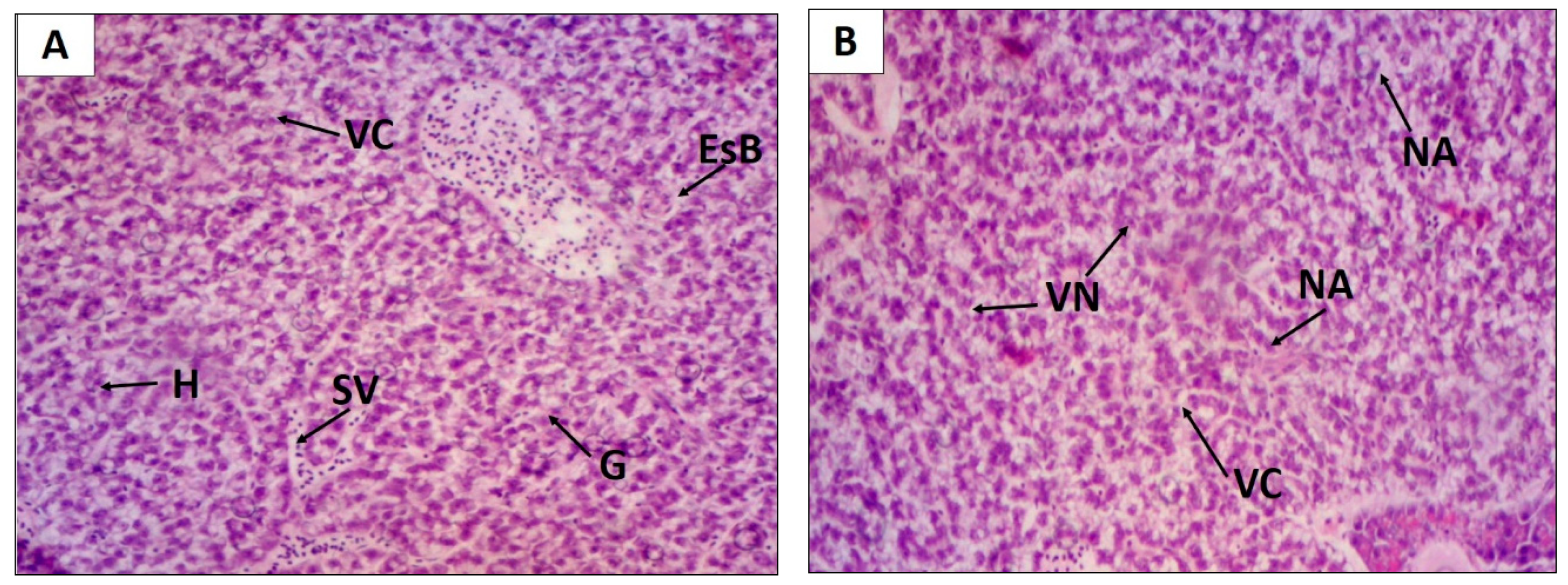
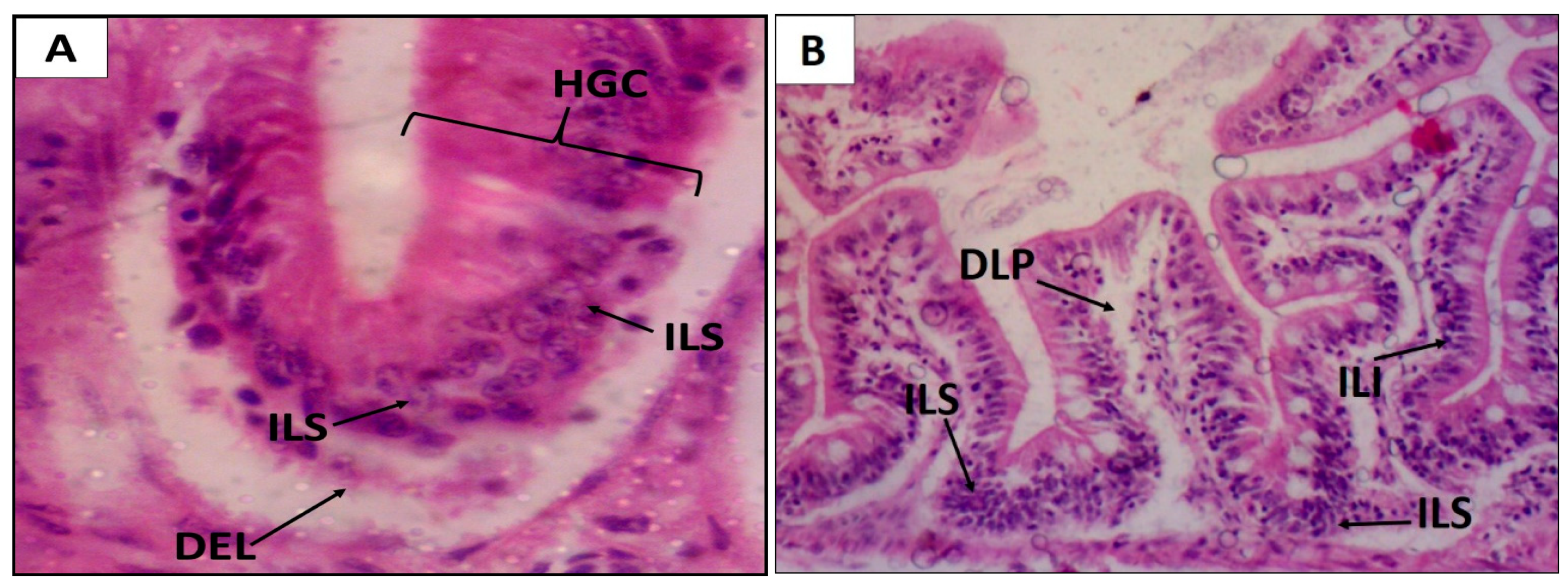
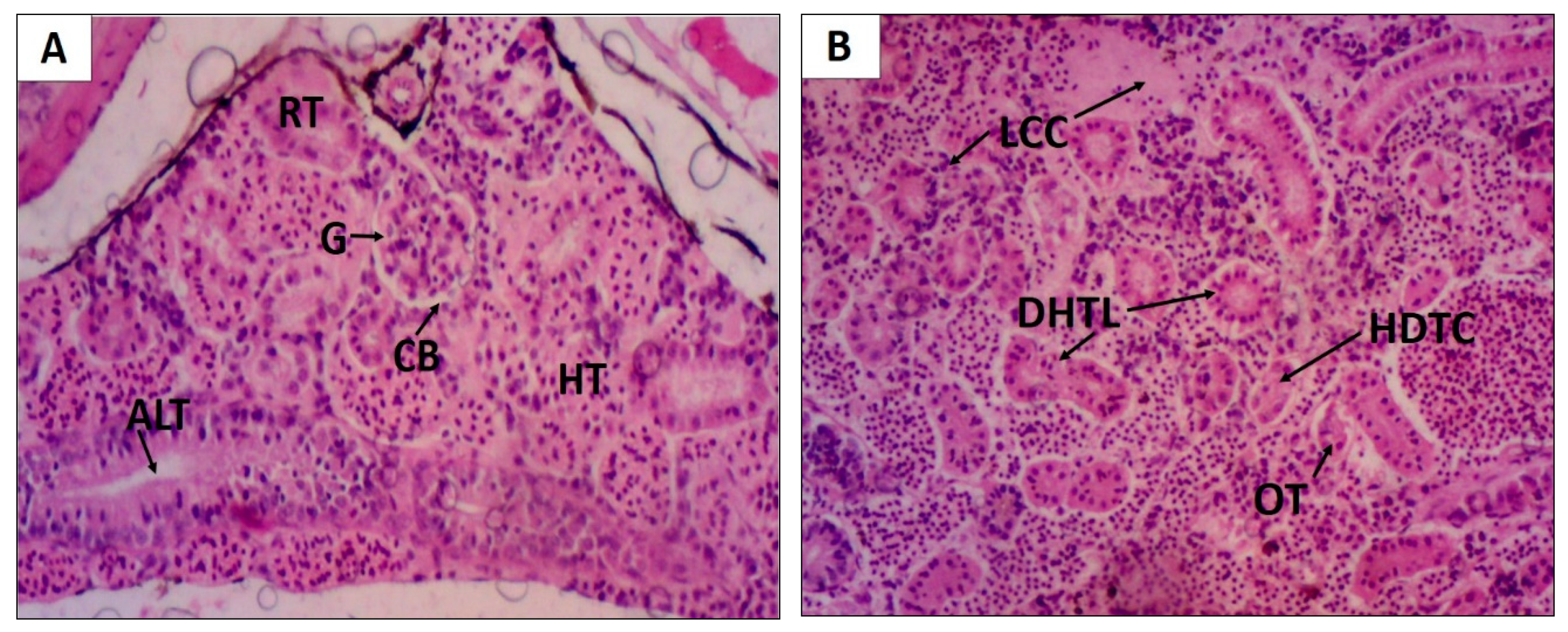
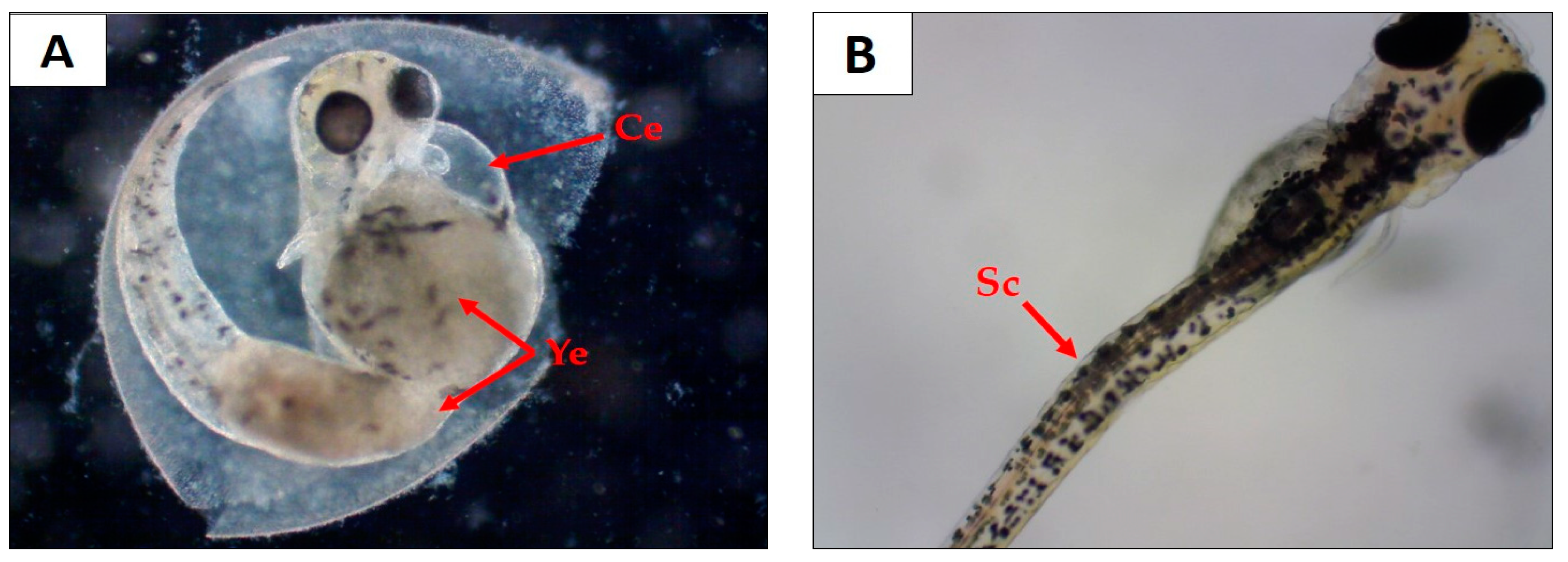
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Botanical Material
4.2. Obtaining EHEFLf
4.3. EHEFLf Analysis by Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-HRMS/MS)
4.4. Acute Toxicity Study in Zebrafish
4.4.1. Animals
4.4.2. Adult Zebrafish Study
4.4.3. Behavioral Assessment
4.4.4. Study on Zebrafish Embryos
4.4.5. Histopathological Study
- a = first stage;
- b = second stage;
- c = third stage;
- na = total number of changes considered to be first stage;
- nb = total number of changes considered to be second stage;
- nc = total number of changes considered to be third stage; and
- N = number of fish analyzed per treatment.
4.4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vásquez, S.P.F.; Mendonça, M.S.; Noda, S.N. Etnobotânica de plantas medicinais em comunidades ribeirinhas do Município de Manacapuru, Amazonas. Acta Amaz. 2014, 44, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, H. Ávores Brasileiras: Manual de Identificação e Cultivo de Plantas Arbóreas Nativas do Brasil, 6ª ed.; Ipsis Gráfica e Editora: São Paulo, Brasil, 2014; pp. 135–136. [Google Scholar]
- Fabaceae in Flora do Brasil 2020 em Construção. Available online: http://floradobrasil.jbrj.gov.br/reflora/listaBrasil/FichaPublicaTaxonUC/FichaPublicaTaxonUC.do?id=FB109828 (accessed on 26 September 2019).
- USDA. Serviço de Pesquisa Agrícola, Sistema Nacional de Germoplasma Vegetal. 2019. Rede de Informações sobre Recursos de Germoplasma (GRIN-Taxonomia). Available online: https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=465144 (accessed on 26 September 2019).
- Cavalheiro, M.G.; Farias, D.F.; Fernandes, G.S.; Nunes, E.P.; Cavalcanti, F.S.; Vasconcelos, I.M.; Melo, V.M.M.; Carvalho, A.F.U. Atividades biológicas e enzimáticas do extrato aquoso de sementes de Caesalpinia ferrea Mart., Leguminosa. Rev. Bras. Farmagn. 2009, 19, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.C.T.; Teixeira, J.R.M.; Souza, P.J.C.; Bastos, J.K.; Filho, D.S.; Santos, S.J. Preliminary studies of analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties of Caesalpinia ferrea crude extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1996, 53, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachi, E.M.; Sertie, J.A. Antiulcer action of Styrax camporum and Caesalpinia ferrea in rats. Planta Med. 1994, 60, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, H.; Tachibana, Y.; Moriyasu, M.; Kawanishi, K.; Alves, S.M. Aldose reductase inhibitors from the fruits of Caesalpinia ferrea Mart. Phytomedicine 2001, 5, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.F.; Batista, J.S.; Paiva, E.S.; Silva, A.E.; Farias, Y.J.M.D.; Damasceno, C.A.R.; Brito, P.D.; Queiroz, S.A.C.; Rodrigues, C.M.F.; Freitas, C.I.A. Avaliacao da atividade cicatrizante do juca (Caesalpinia ferrea Mart. ex Tul. var. ferrea) em lesoes cutneas de caprinos. Rev. Bras. Plantas Med. 2010, 12, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, E.S.; Kurosaki, F.; Arisawa, M.; Mukainaka, T.; Okuda, M.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H.; Junior, F.P. Cancer chemopreventive effects of constituents of Caesalpinia ferrea and related compounds. Cancer Lett. 2002, 177, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, A.C.V.A.; Soares, L.A.L.; Ferreira, M.R.A.; Araújo, A.A.; Rocha, H.A.O.R.; Medeiros, J.S.; Cavalcante, R.S.C.; Júnior, R.F.A. Libidibia ferrea presents antiproliferative, apoptotic and antioxidant effects in a colorectal cancer cell line. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, A.L.; Souza, R.S.; Aranha, E.S.P.; Costa, L.M.; De Souza, T.P.; Vasconcellos, M.C. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activies of Libidibia férrea bark and fruits extracts. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio, F.C.; Pereira, M.S.V.; Dias, C.S.; Costa, V.C.O.; Conde, N.C.O.; Buzalaf, M.A.R. In vitro antimicrobial acivity of Caesalpinia ferrea Martius fruits against oral pathogens. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 124, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comandolli-Wyrepkowski, C.D.; Jensen, B.B.; Grafova, I.; Santos, P.A.; Barros, A.M.C.; Soares, F.V.; Barcellos, J.F.M.; Silva, A.F.; Grafov, A.; Franco, A.M.R. Atividade antileishmanial de extratos de Libidibia ferrea: Desenvolvimento de testes in vitro e in vivo. Acta Amaz. 2017, 47, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.T.S.; Almeida, V.T.; Bandeira, T.; Alcântara, B.N.; Silva, W.L.R.; Silva, P.B.; Monteiro, M.V.B.; Almeida, M.B. Avaliação fitoquímica e potencial cicatrizante do extrato etanólico dos frutos de Jucá (Libidibia ferrea) em ratos Wistar. Braz. J. Vet. Res. 2015, 52, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Reboredo, M.M.; Lucinda, L.M.F.; Rocha, C.M.; Queiroz, G.T.; Faria, V.C.; Vieira, V.A.; Sá, R.C.S.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Avaliação da toxicidade do extrato aquoso de Caesalpinia ferrea em Organs vitais, no sistema reprodutor e na produção de espermatozóides de ratos Wistar submetidos a tratamento subagudo. Bol. Cent. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 26, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, C.S.V. Avaliação da Atividade Antiobesidade do Extrato Aquoso dos Frutos de Libidibia Ferrea(Mart.) L.P. Queiroz em Ratos Wistar. 89f. Master’s Thesis, Programa de Pós Graduação em Patologia da Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Recife, Brasil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M.R.A.; Soares, L.A.L. Libidibia ferrea (Mart. ex Tul.) LP Queiroz: A review of the biological activities and phytochemical composition. J. Med. Plants Res. 2015, 9, 140–150. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, L.M.; Simplicio, F.G.; Souza, T.P. Libidibia ferrea (março. extul) lp queiro z var. ferrea: Farmacológico, aspecto fitoquímico e botânicos. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, S.M.A.; Araújo, L.C.C.; Sitônio, M.M.; Freitas, A.C.C.; Moura, S.L.; Correia, M.T.S.; Malta, D.J.N.; Silva, T.G. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic potential of Caesalpinia ferrea. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2012, 22, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.P.; Silva, R.O.; Bringel, P.H.; Silva, K.E.; Assreuv, A.M.; Pereira, M.G. Polysaccharide fractions of Caesalpinia ferrea pods: Potential anti-inflammatory usage. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, T.R.; Araújo, A.A.; Soares, L.A.L.; Farias, I.B.; Silva, W.A.V.; Ferreira, M.R.A.; Araújo, R.F., Jr.; Medeiros, J.S.; Lopes, M.L.D.S.; Guerra, G.C.B. Libidibia ferrea Crude Extract and Fractions Show Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Antinociceptive Effect in Vivo and Increase Cell Viability in Vitro. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, A.A.; Soares, L.A.L.; Ferreira, M.R.A.; Souza Neto, M.A.; Silva, G.R.; Araújo, R.F., Jr.; Guerra, G.C.B.; Melo, M.C.N. Quantification of polyphenols and evaluation of antimicrobial, analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of aqueous and acetone–water extracts of Libidibia ferrea, Parapiptadenia rigida and Psidium guajava. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 156, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.R.A.; Fernandes, M.T.M.; Silva, W.A.V.; Bezerra, I.C.F.; Souza, T.P.; Pimentel, M.F.; Soares, L.A.L. Chromatographic and Spectrophotometric Analysis of Phenolic Compounds from Fruits of Libidibia ferrea Martius. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12, 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, J.S.; França, C.L.; Fernandes, J.F.F.; Silva, J.S.; Carvalho-Neta, R.N.F.; Teixeira, E.G. Biomarcadores histológicos em brânquias de Sciades herzbergii (Siluriformes, Ariidae) capturados no complexo Estuarino de São Marcos, Maranhão. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2018, 70, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.S. Estudo da Atividade Anti-inflamatória de Nanoemulsões a Base do óleo Essencial de Rosmarinus Officinalis L. 215f. Ph.D. Thesis, Programa de Pós-graduação em Inovação Farmacêutica da Universidade Federal do Amapá, Macapá, Brasil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Honorato, C.A.; Cruz, C.; Carneiro, D.J.; Machado, M.R.F.; Nascimento, C.A.; Saturnino, K.S. Histologia do Liver de tilápia do Nilo (Oreochromis niloticus) alimentados com dietas contendo silagem biológica de pescado. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2014, 34, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novaes, G.H.C.F.; Aureliano, B.C.; Fragoso-Moura, E.N.; Cavalcante, W.; Fracácio, R. Toxicidade dos metais níquel e cobre e sua possível atuação como interferentes endócrinos em ambientes aquáticos. Revista Brasileira de Ciências Ambientais 2018, 48, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkimin, G.D. Toxicidade de Cádmio e Zinco em Danio rerio: Comparação entre valores permitidos em legislação para proteção da vida aquática e a potencial atuação como interferentes endócrinos, 100f. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Estadual Paulista, Sorocaba, Brasil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.D.; Sheng, Z.; Wang, Y.F.; Han, Y.L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, J.Q. Glutathione peroxidase 1 expression, malondialdehyde levels and histological alterations in liver of Acrossocheilus fasciatus exposed to cadmium chlorid. Gene 2016, 578, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayao, A.L.B.A.; Buzollo, H.; Fávero, G.C.; Junior, A.A.S.; Portella, M.C.; Cruz, C.; CARNEIRO, D.J. Histologia hepática e produção em tanques-rede de tilápia-do-nilo masculinizada hormonalmente ou não masculinizada. Pesq. Agropec. Bras. 2013, 48, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarck, M.A.; Finkel, R.; Rey, J.A.; Whalen, K. Farmacologia Ilustrada; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil, 2013; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Golan, D.E.; Junior, T.; Armen, H.; Armstgrong, E.J.; Armstronge, A.W. Princípios de Farmacológia: A base Fisiopatológica da Farmacologia; Guanabara Koogan: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2014; pp. 95–156. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, J.C.T.; Keita, H.; Santana, G.R.; Souza, G.C.; Santos, I.V.F.; Amado, J.R.R.; Kourouma, A.; Prada, A.L.; Carvalho, H.O.; Silva, M.L. Effects of Bothrops alternatus venom in zebrafish: A histopathological study. Inflammopharmacol 2017, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, G.J.B. Efeitos do acetate na inflamação e proteção contra lesão renal aguda induzida por cisplatina em Zebrafh. 62f. Master’s Thesis, Programa de Pós-graduação em imunologia da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brasil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, G.C.; Duarte, J.L.; Fernandes, C.P.; Moyado, J.A.V.; Navarrete, A.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Obtainment and Study of the Toxicity of Perillyl Alcohol Nanoemulsion on Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Nanomed. Res. J. 2016, 5, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Takashima, F.; Hibiya, T. (Eds.) An Atlas of Fish Histology: Normal and Pathological Features, 2nd ed.; Kodansha Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pickler, T.B.; Lopes, K.P.; Magalhães, S.A.; Krueger, C.M.A.; Martins, M.M.; Filho, V.C.; Jozala, A.F.; Grotto, D.; Gerenutti, M. Effect of Libidibia ferrea bark and seed in maternal reproductive and biochemical outcomes and fetal anomaly in rats. Birth Defects Res. 2019, 111, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcão, T.R.; Rodrigues, C.A.O.; Araújo, A.A.; Medeiros, C.A.C.X.; Soares, L.A.L.; Ferreira, M.R.A.; Vasconcelos, R.C.; Júnior, R.F.A.; Lopes, M.L.D.S.; Guerra, G.C.B. Crude extract from Libidibia ferrea (Mart. ex. Tul.) L.P. Queiroz leaves decreased intra articular inflammation induced by zymosan in rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, G.C.; Muller, V.; Góes, L.D.; Sanchez-Ortiz, B.L.; da Silva, G.; de Souza, W.P.; Santos, C.B.R.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Reproductive toxicity of the hydroethanolic extract of the flowers of Acmella oleracea and spillanthol in zebrafish: In vivo and in silico evaluation. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2019, 2019, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Bittencourt, T.Q.M.; Santos, A.R.; Silva, M.C.G.; Silva, J.F.; Silva, N.P.C.; Silva, W.E.; Cadena, P.G.; Amorim, M.J.A.A.L. Efeitos tóxicos de compostos de vanádio sobre os parâmetros biológicos de embriões e adultos de zebrafish (Danio rerio)/Toxic effects of vanadium compounds on biological parameters of embryos and adults of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2018, 70, 1877–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Liu, K. Developmental toxicity and cardiac effects of butyl benzyl phthalate in zebrafish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 192, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD: Guideline for Testing of Chemicals. Acute Oral Toxicity—Up and Down Procedure (UDP). Test Guideline 425; OECD: Paris, French, 2008.
- OECD: Guideline for Testing of Chemicals. Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity Test—Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity Test. Test Guideline 236; OECD: Paris, French, 2013.
- Yang, L.; Ho, N.Y.; Alshut, R. Zebrafish embryos as models for embryotoxic and teratological effects of chemicals. Reprod. Toxicol. 2009, 28, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, G.C. Estudo da toxicidade da nanoemulsão de Álcool Perílico (NPOH) sobre Zebrafish (Danio rerio Hamiltoln 1822). 87f. Master’s Thesis, Programa de Pós-graduação em Ciências Farmacêuticas da Universidade Federal do Amapá, Macapá, Brasil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Favoretto, S.M.; Seabra, D.I.; Olivato, M.C.M. Guia de Eutanásia Para Animais de Ensino e Pesquisa; UNIFESP: São Paulo, Brazil, 2013; pp. 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Poleksic, V.; Mitrovic-Tutundzic, V. Fish gills as a monitor of sublethal and chronic effects of pollution. In Sublethal and Chronic Effects of Pollutants on Freshwater Fish; Müller, R., Lloyd, R., Eds.; Fishing News Books: Oxford, MS, USA, 1994; pp. 339–352. [Google Scholar]
- Takashima, F.; Hibiya, T. An Atlas of Fish Histology-Normal and Pathological Features. Kodansha Ltd.: Tóquio, Japan, 1984; Volume 69, p. 406. [Google Scholar]
- Rigolin-Sá, O. Toxicidade do herbicida Roundup (glifosato) e do acaricida omite (propargito) nas fases iniciais da otogenia do bagre Rhamidia hilarii (Valenciennes, 1840) (Pimelodidae, Siluriformes). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Federal de São Carlos, São Carlos, Brazil, 1999. [Google Scholar]
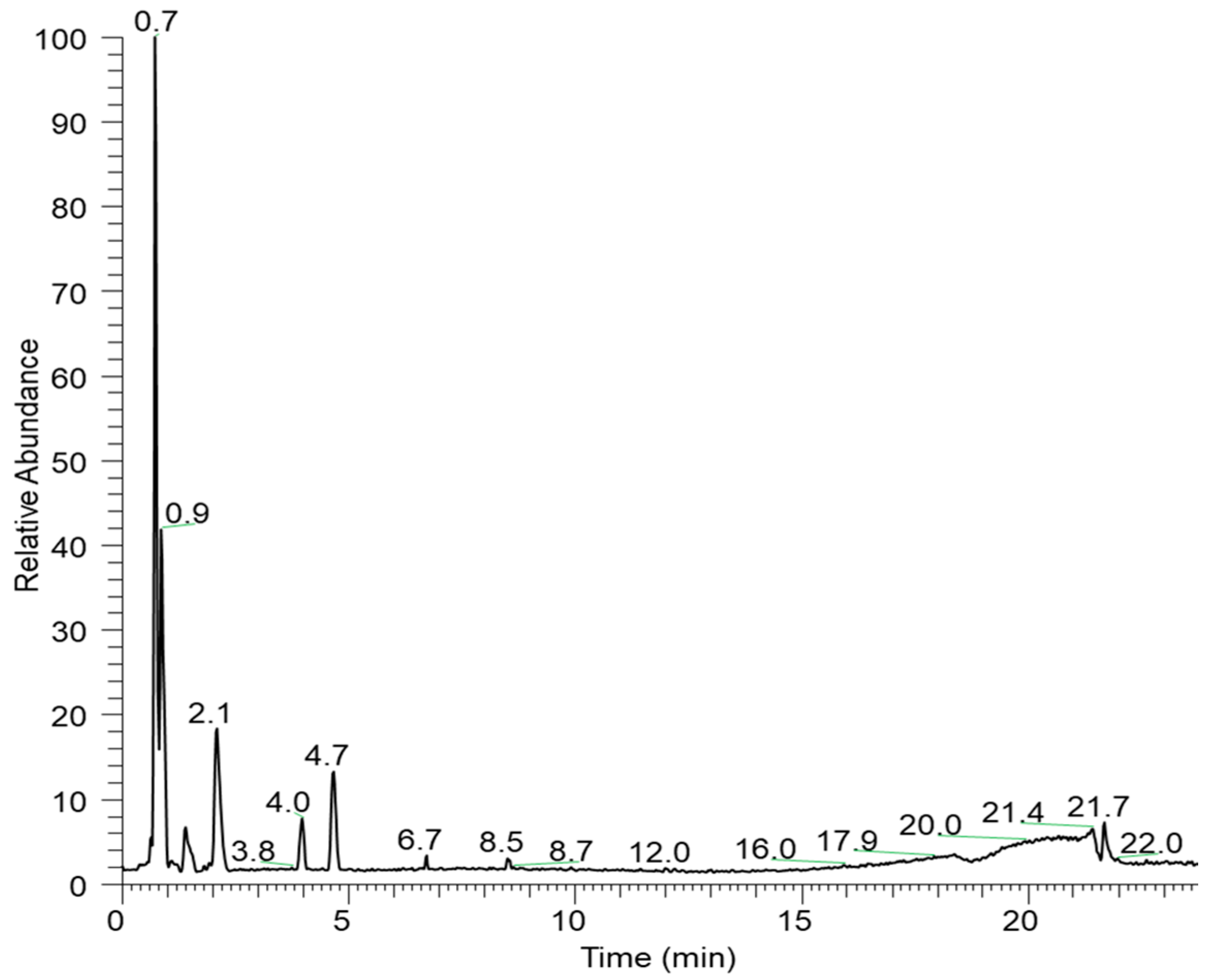
| RT (min) | [M-H]− | Molecular Formula | Error (ppm) | MS/MS | Substance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.89 | 169.01340 | C7H6O5 | 5.0 | 125.02324 | Gallic acid |
| 0.81 | 331.06729 | C13H16O10 | 0.7 | 271.04614 241.03496 211.02391 169.01331 125.02332 | Galloyl-glucose Ester |
| 0.86 | 345.08279 | C14H18O10 | 0.2 | 313.05731 169.01337 125.02334 | Gallic acid methoxy glycoside |
| 0.73 | 179.05540 | C6H12O6 | 0.9 | 161.04422 131.03365 113.02316 95.01269 | Hexose |
| 1.15 | 483.07861 | C20H20O14 | 1.2 | 331.0679 313.0551 271.0466 211.0238 169.0135 | di-O-galloyl-d-hexose |
| 1.94 | 633.07385 | C27H24O18 | 0.8 | 463.0479 300.997 | Corilagin |
| 2.1 | 469.00504 | C21H10O13 | 0.4 | 425.01523 299.99118 | Unknown |
| 3.98 | 197.04486 | C9H10O5 | 3.5 | 169.01332 152.89384 | Unknown |
| 4.68 | 300.99905 | C14H6O8 | 0.2 | - | Ellagic Acid |
| 6.25 | 449.10938 | C21H22O11 | 1.1 | 287.055 151.002 | Eriodictyol-O-hexoside |
| 6.32 | 433.11426 | C21H22O10 | 0.6 | 271.0593 | Naringenin-O-hexoside |
| Organ | Test Substance | Animal | Histological Changes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level I | Level II | Level III | |||
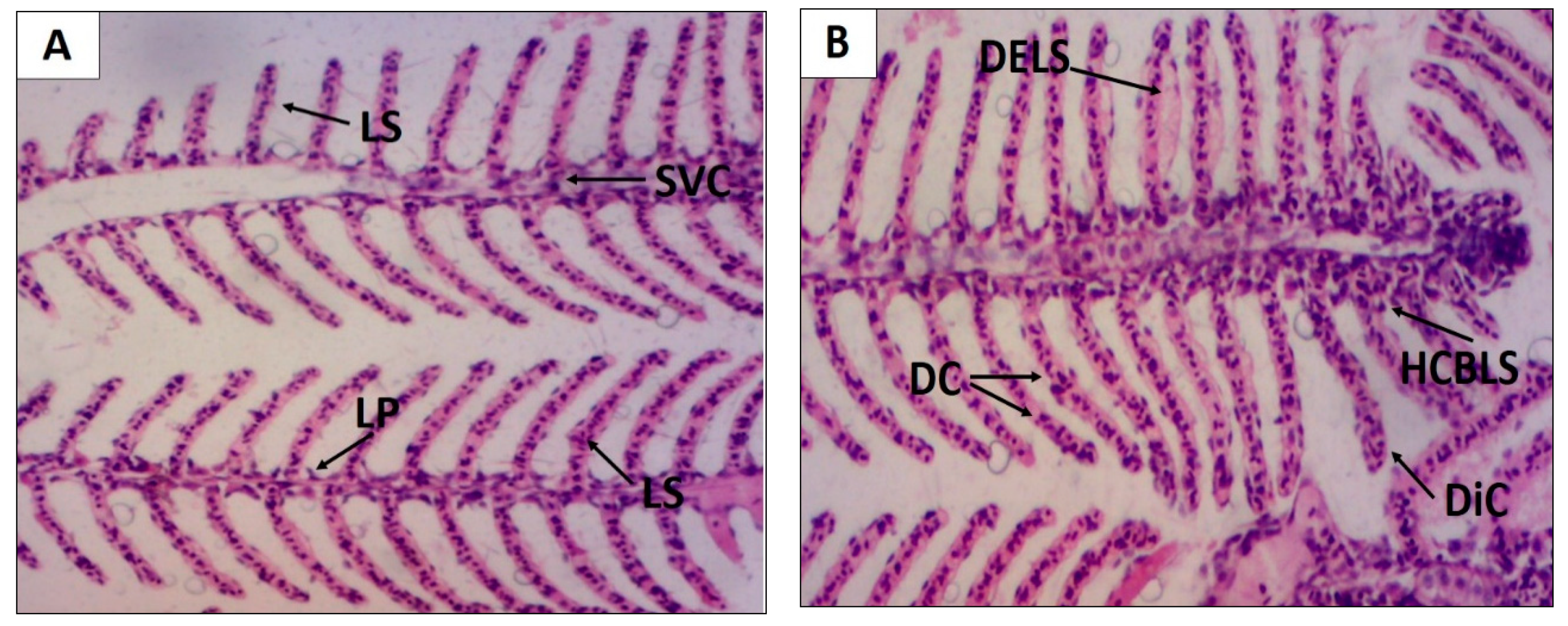
| Gill | EHEFLf | 01 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| 02 | 5 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 03 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 04 | 8 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 05 | 6 | 0 | 0 | ||
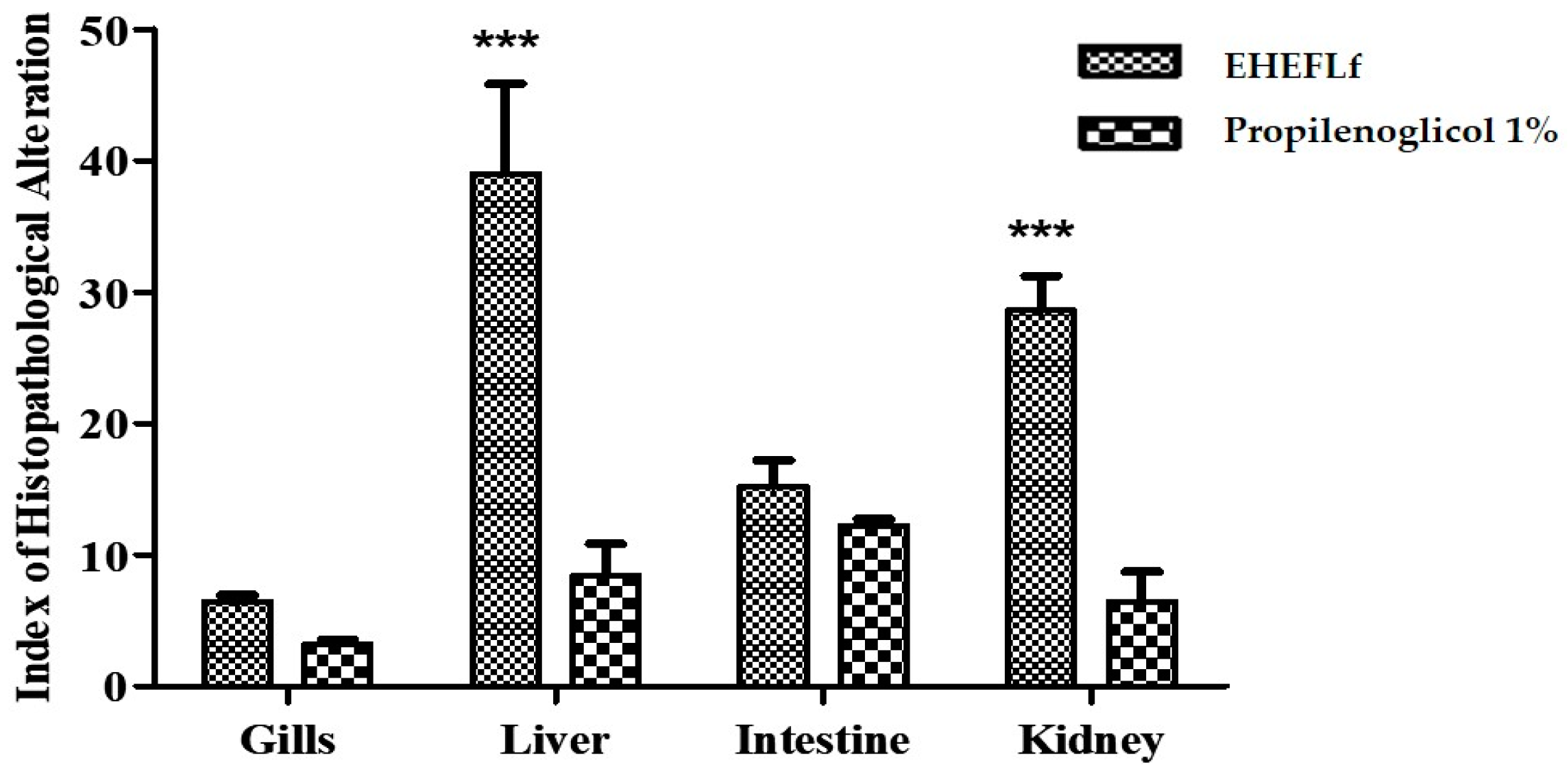
| Classification: | Normal | Mean: 6.4 ± 0.5 | |||
| Level I | Level II | Level III | |||
| Gill | (Control-vehicle) | 01 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 02 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 03 | 2 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 04 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 05 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Classification: | Normal | Mean: 3.2 ± 0.3 | |||
| Organ | Test Substance | Animal | Histological Changes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level I | Level II | Level III | |||
| Liver | EHELF | 01 | 5 | 3 | 0 |
| 02 | 7 | 4 | 0 | ||
| 03 | 7 | 5 | 0 | ||
| 04 | 6 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 05 | 10 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Classification: | Moderate to severe | Mean: 39.0 ± 6.8 | |||
| Level I | Level II | Level III | |||
| Liver | (Vehicle-control) | 01 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 02 | 8 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 03 | 2 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 04 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 05 | 3 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Classification: | Normal | Mean: 8.4 ± 2.4 | |||
| Organ | Test Substance | Animal | Histological Changes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level I | Level II | Level III | |||
| Intestine | EHELF | 01 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| 02 | 8 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 03 | 9 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 04 | 4 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 05 | 7 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Classification: | Mild to moderate | Mean: 15.2 ± 2.0 | |||
| Level I | Level II | Level III | |||
| Intestine | (Vehicle-control) | 01 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 02 | 3 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 03 | 3 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 04 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 05 | 3 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Classification: | Normal | Mean: 12.2 ± 0.5 | |||
| Organ | Test Substance | Animal | Histological Changes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level I | Level II | Level III | |||
| Kidneys | EHELF | 01 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| 02 | 8 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 03 | 9 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 04 | 4 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 05 | 7 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Classification: | Moderate to severe | Mean: 28.6 ± 2.6 | |||
| Level I | Level II | Level III | |||
| Kidneys | (Vehicle-control) | 01 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 02 | 2 | 1 | 0 | ||
| 03 | 3 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 04 | 2 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 05 | 2 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Classification: | Normal | Mean: 6.4 ± 2.3 | |||
| Teratogenic Changes | mg/L | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propyleneglycol 1% | 25 | 50 | 125 | 250 | 500 | Σt | % | |
| Cardiac edema | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 20 | 11.1 |
| Scoliosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 5.5 |
| Yolk sac edema | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 21 | 26 | 14.4 |
| Growth retardation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Lethal embryos | 8 | 9 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 3 | n/a | n/a |
| Σ Teratogenic embryos | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 21 | 36 | n/a |
| % Teratogenic embryos | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 70 | n/a | n/a |
| % Lethal embryos | 26.6 | 30 | 33.3 | 10 | 13,3 | 10 | n/a | n/a |
| Stages | Behavioral Changes |
|---|---|
| I |
|
| II |
|
| III |
|
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, D.Q.; Ferraz, T.O.; Araújo, R.S.; Cruz, R.A.S.; Fernandes, C.P.; Souza, G.C.; Ortiz, B.L.S.; Sarquis, R.S.F.R.; Miranda, J.C.M.M.; Garrett, R.; et al. Libidibia ferrea (jucá), a Traditional Anti-Inflammatory: A Study of Acute Toxicity in Adult and Embryos Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040175
Ferreira DQ, Ferraz TO, Araújo RS, Cruz RAS, Fernandes CP, Souza GC, Ortiz BLS, Sarquis RSFR, Miranda JCMM, Garrett R, et al. Libidibia ferrea (jucá), a Traditional Anti-Inflammatory: A Study of Acute Toxicity in Adult and Embryos Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Pharmaceuticals. 2019; 12(4):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040175
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Diego Q., Thamara O. Ferraz, Raquel S. Araújo, Rodrigo Alves Souza Cruz, Caio Pinho Fernandes, Gisele C. Souza, Brenda L. S. Ortiz, Rosangela S. F. R. Sarquis, Jemima C. M. M. Miranda, Rafael Garrett, and et al. 2019. "Libidibia ferrea (jucá), a Traditional Anti-Inflammatory: A Study of Acute Toxicity in Adult and Embryos Zebrafish (Danio rerio)" Pharmaceuticals 12, no. 4: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040175
APA StyleFerreira, D. Q., Ferraz, T. O., Araújo, R. S., Cruz, R. A. S., Fernandes, C. P., Souza, G. C., Ortiz, B. L. S., Sarquis, R. S. F. R., Miranda, J. C. M. M., Garrett, R., Carvalho, J. C. T., & Oliveira, A. E. M. d. F. M. (2019). Libidibia ferrea (jucá), a Traditional Anti-Inflammatory: A Study of Acute Toxicity in Adult and Embryos Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Pharmaceuticals, 12(4), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040175