Synthesis of Curcumin Derivatives and Analysis of Their Antitumor Effects in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
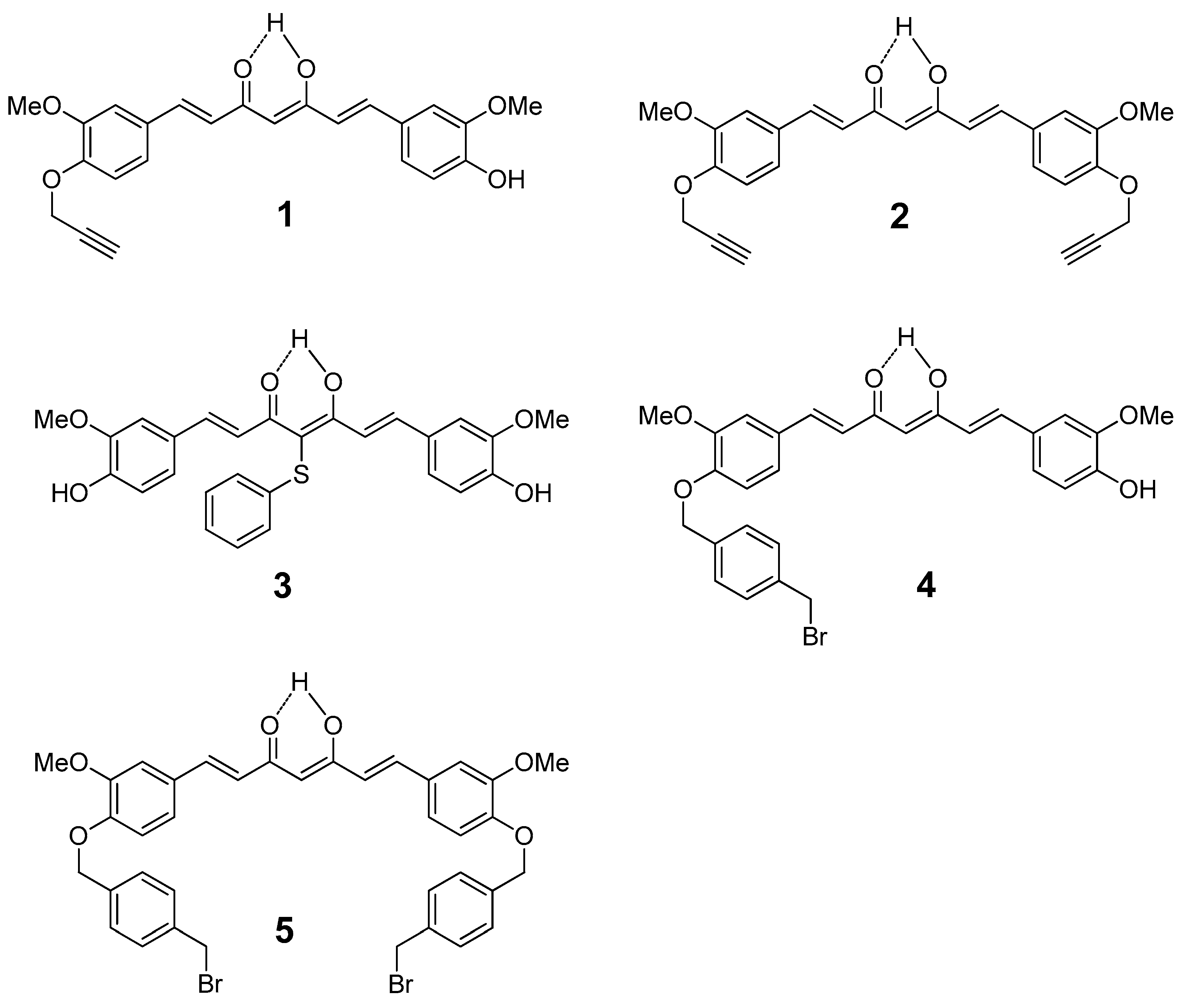
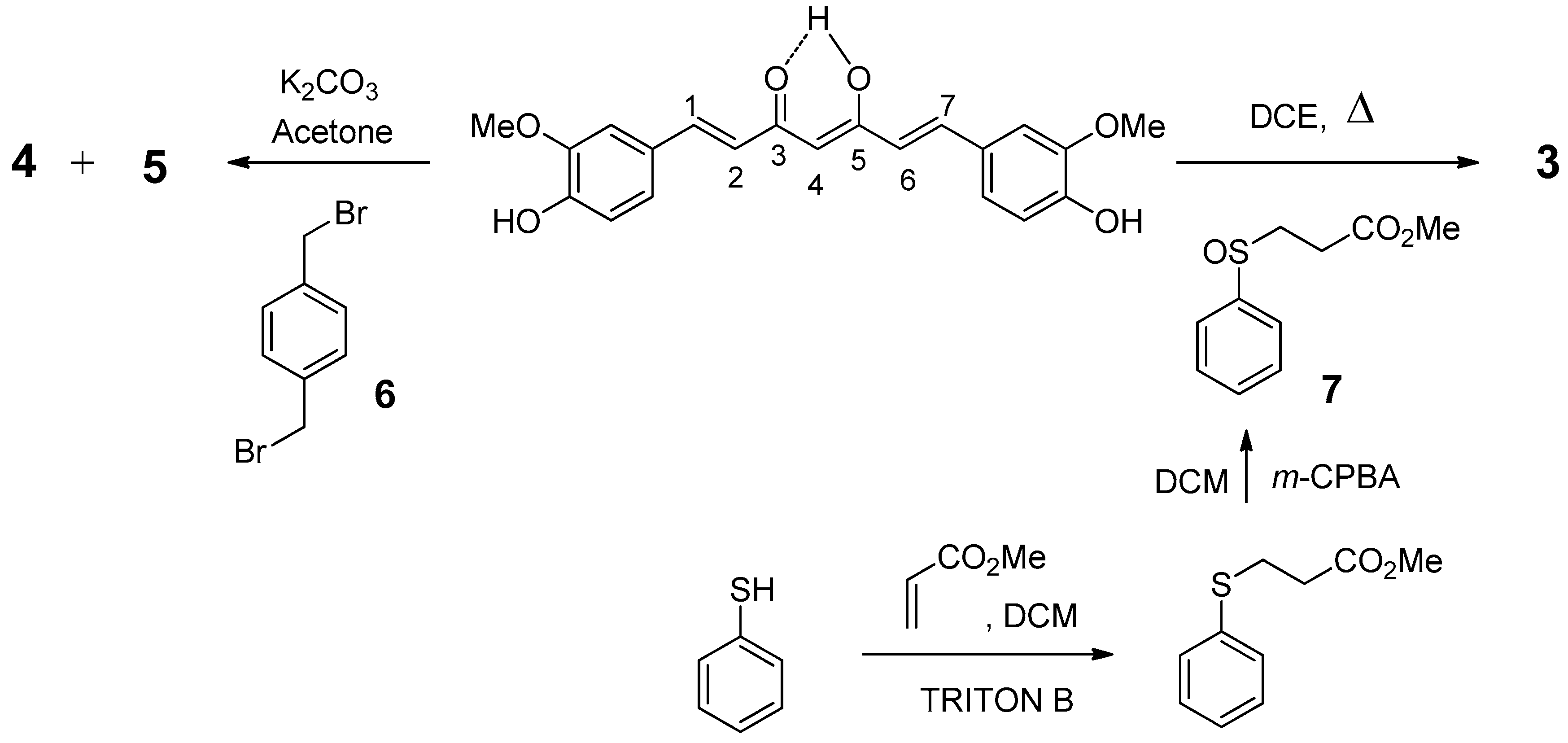
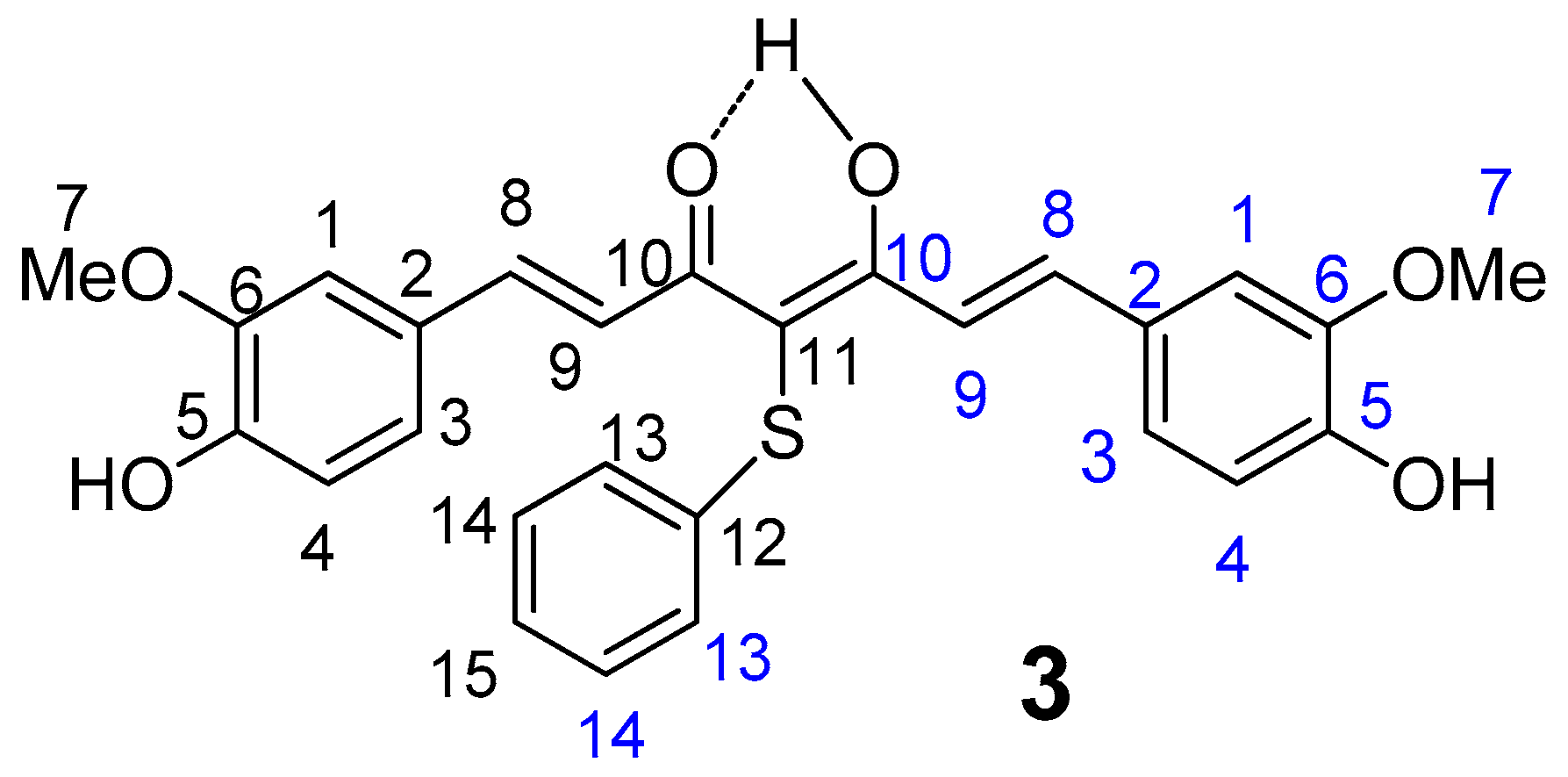
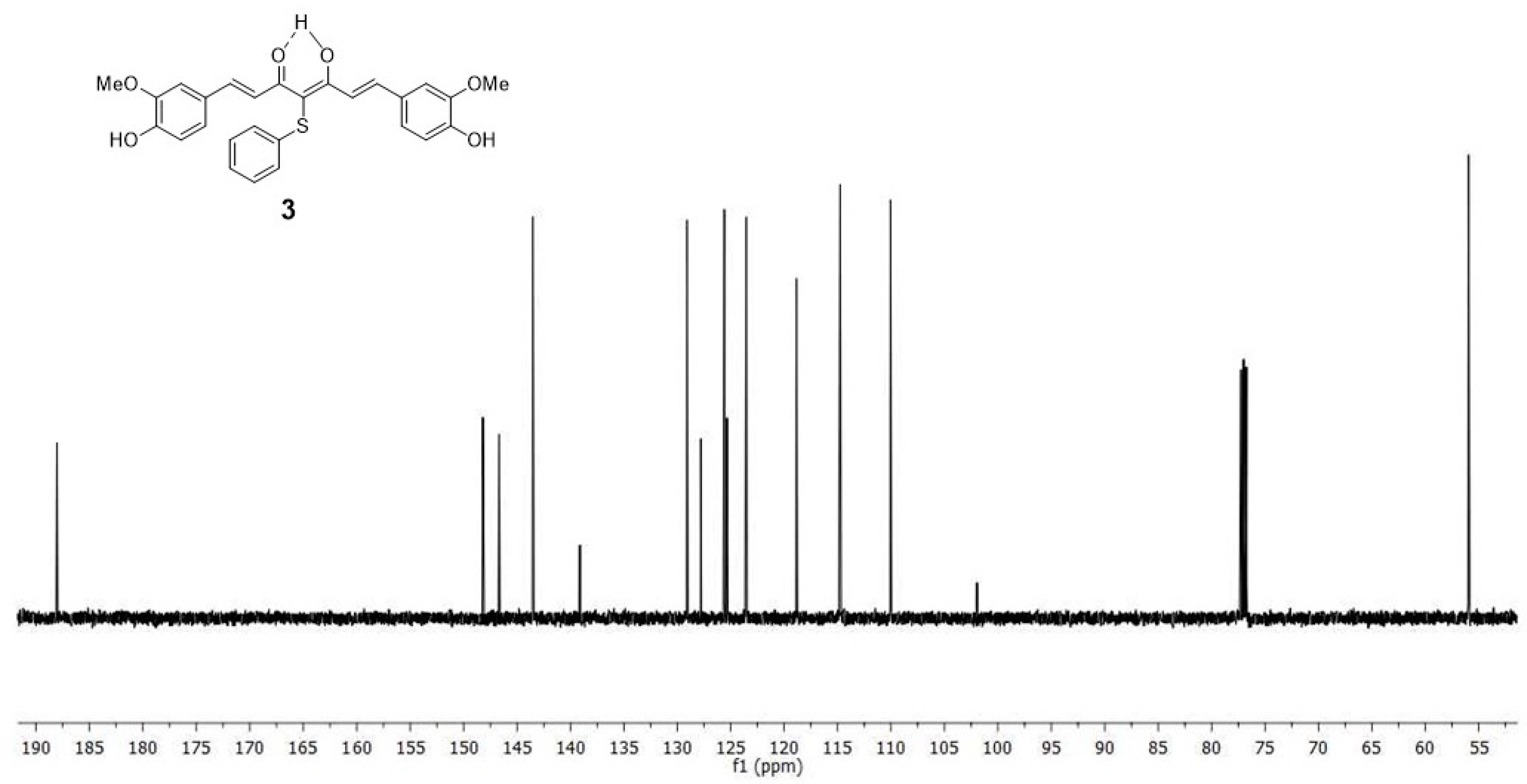
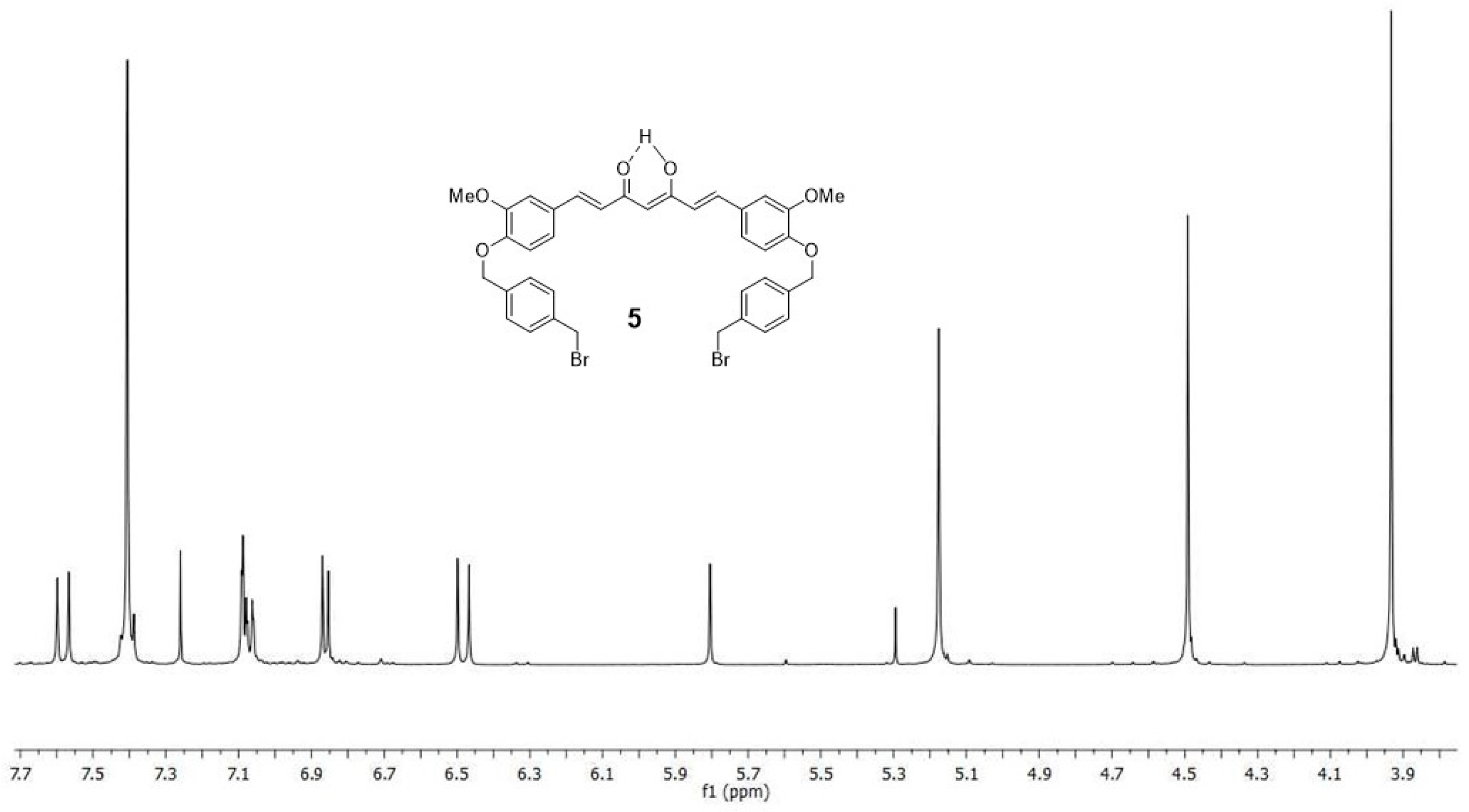
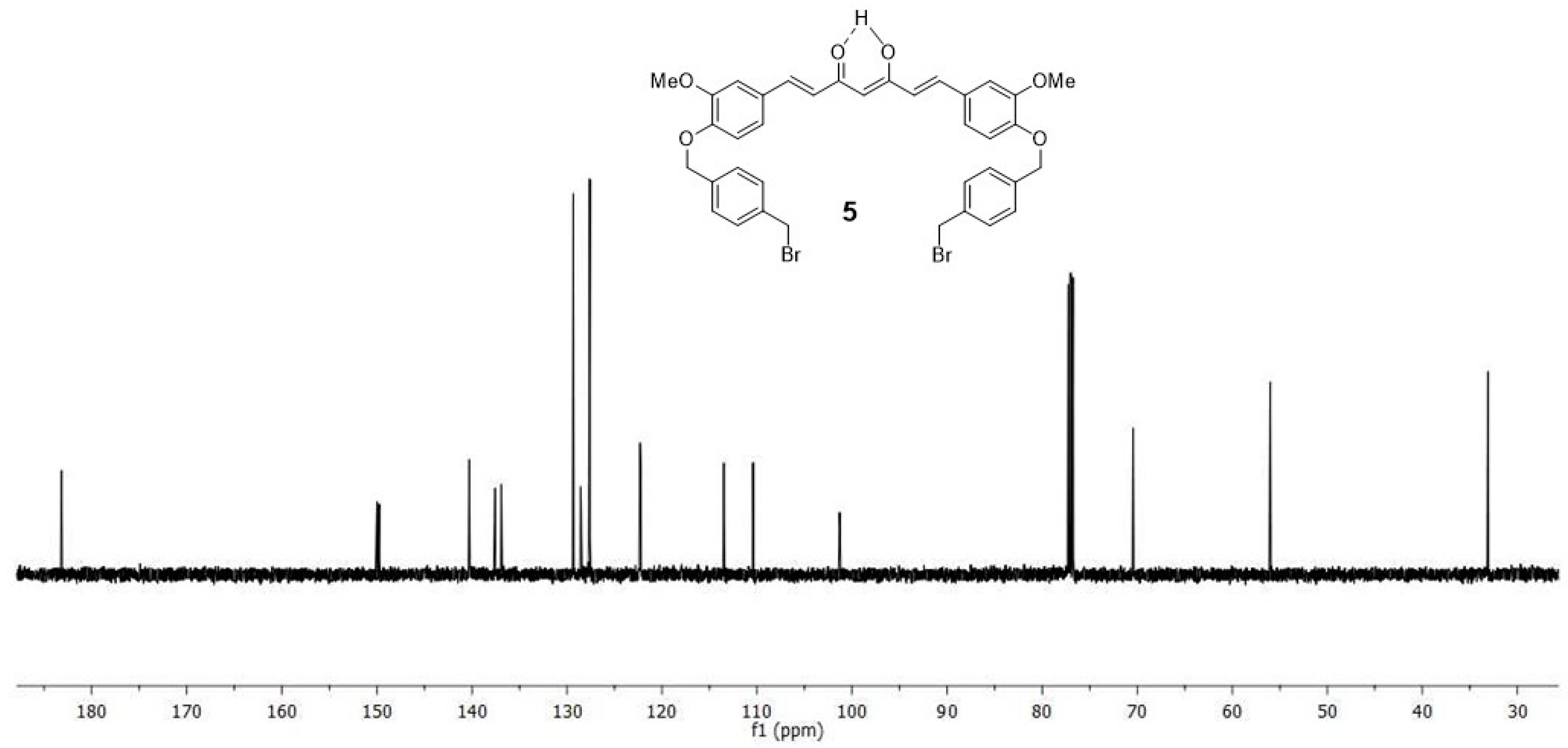
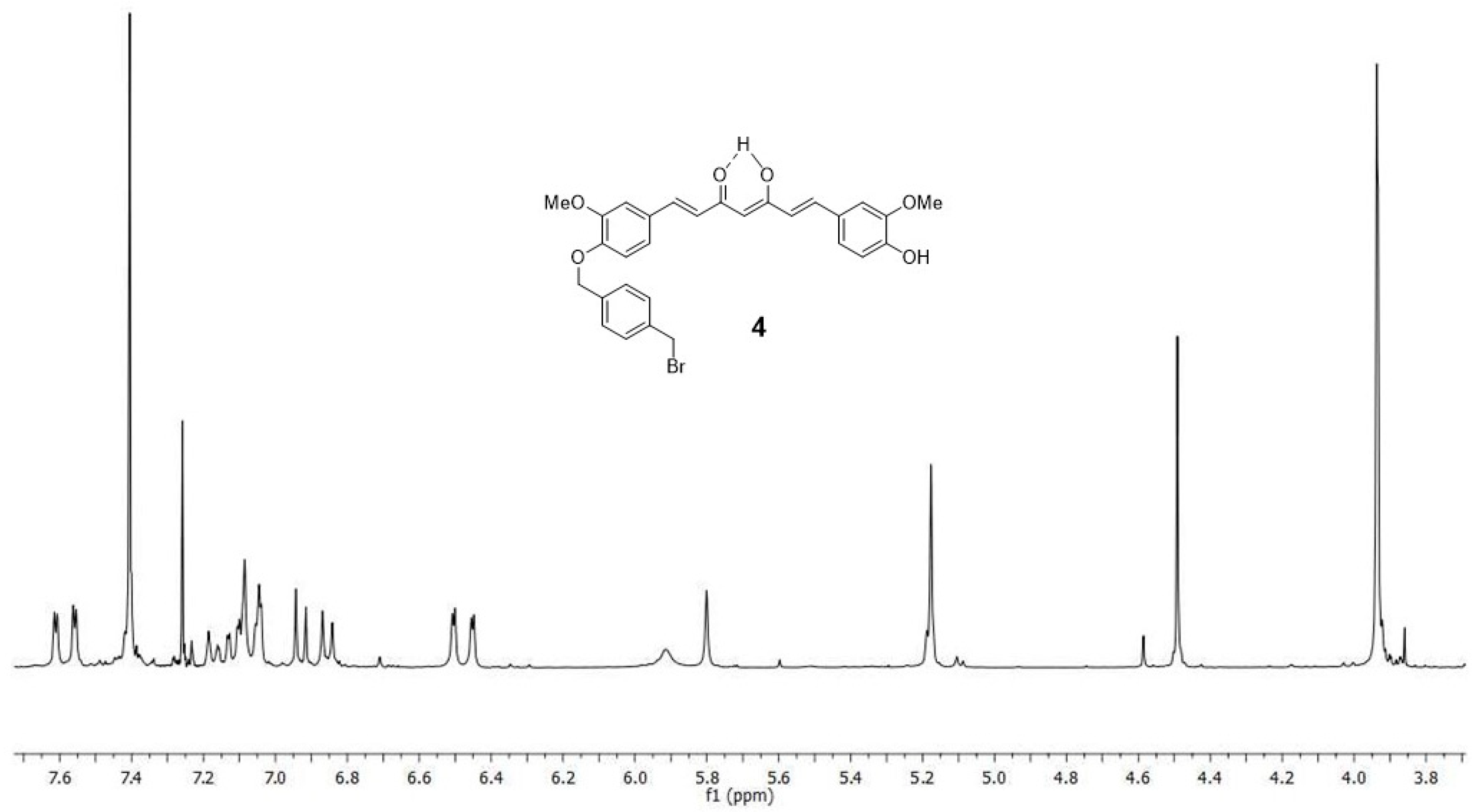
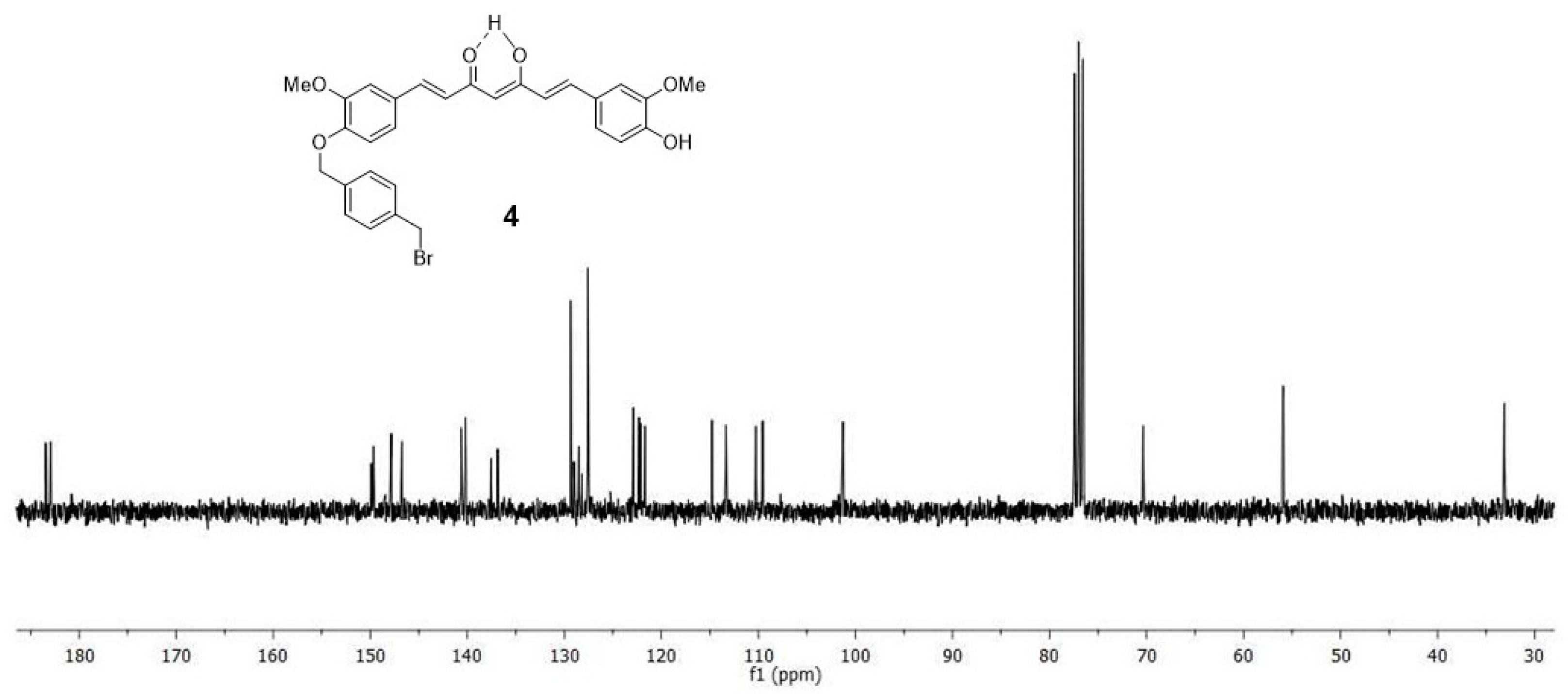
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Studies
2.2.1. Antiproliferative Activity
2.2.2. Pro- and Antioxidant Activity
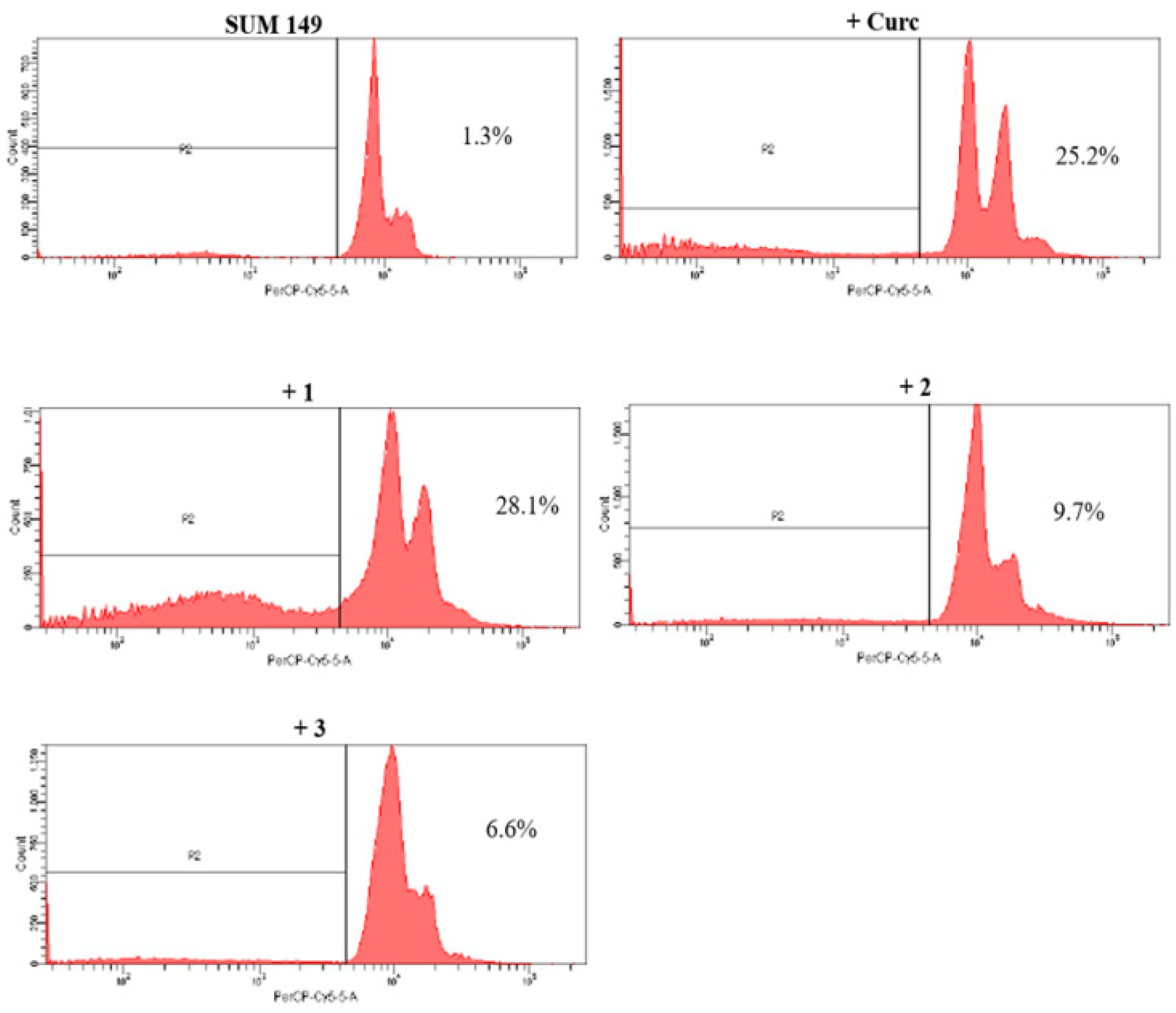
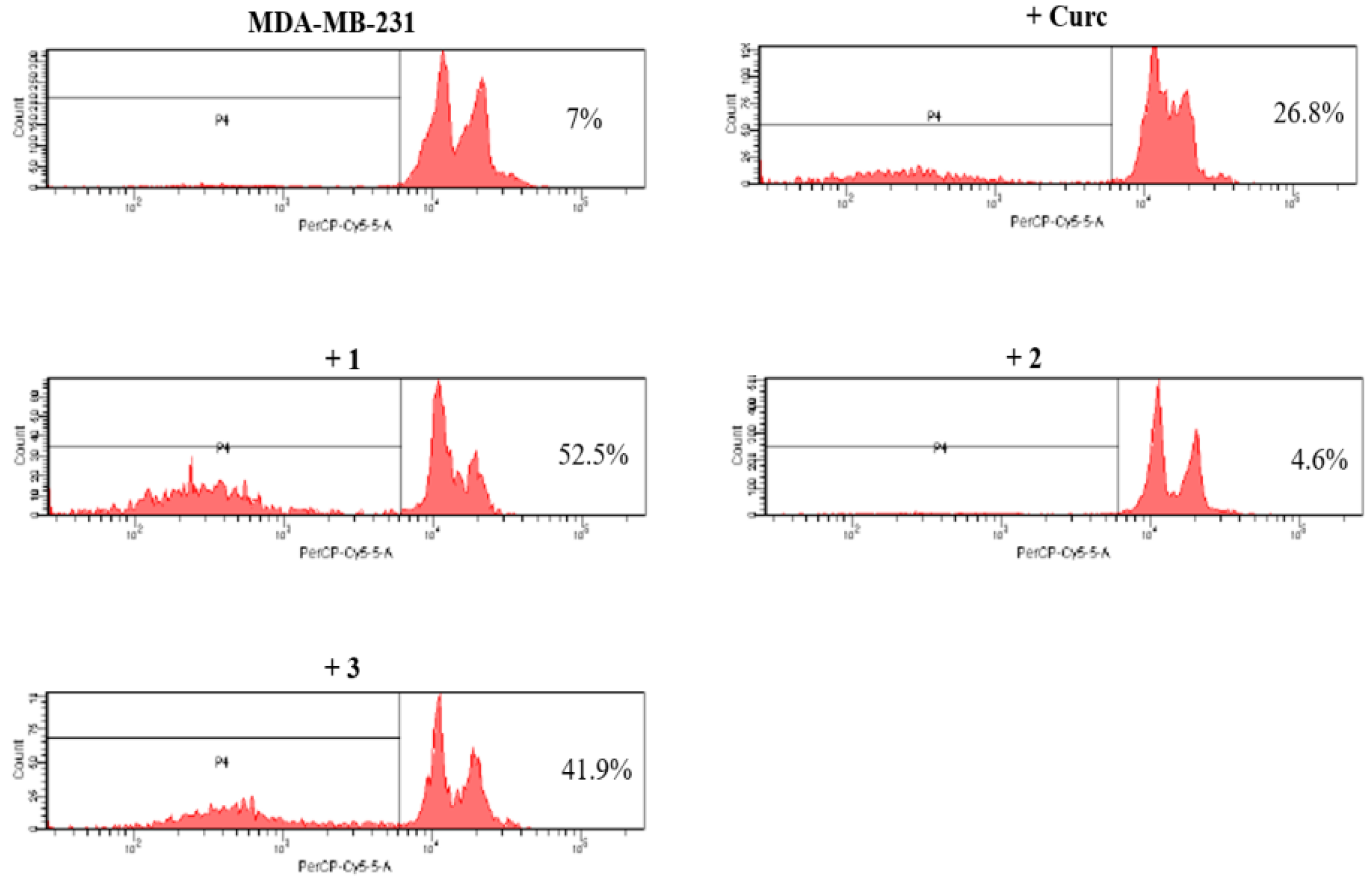
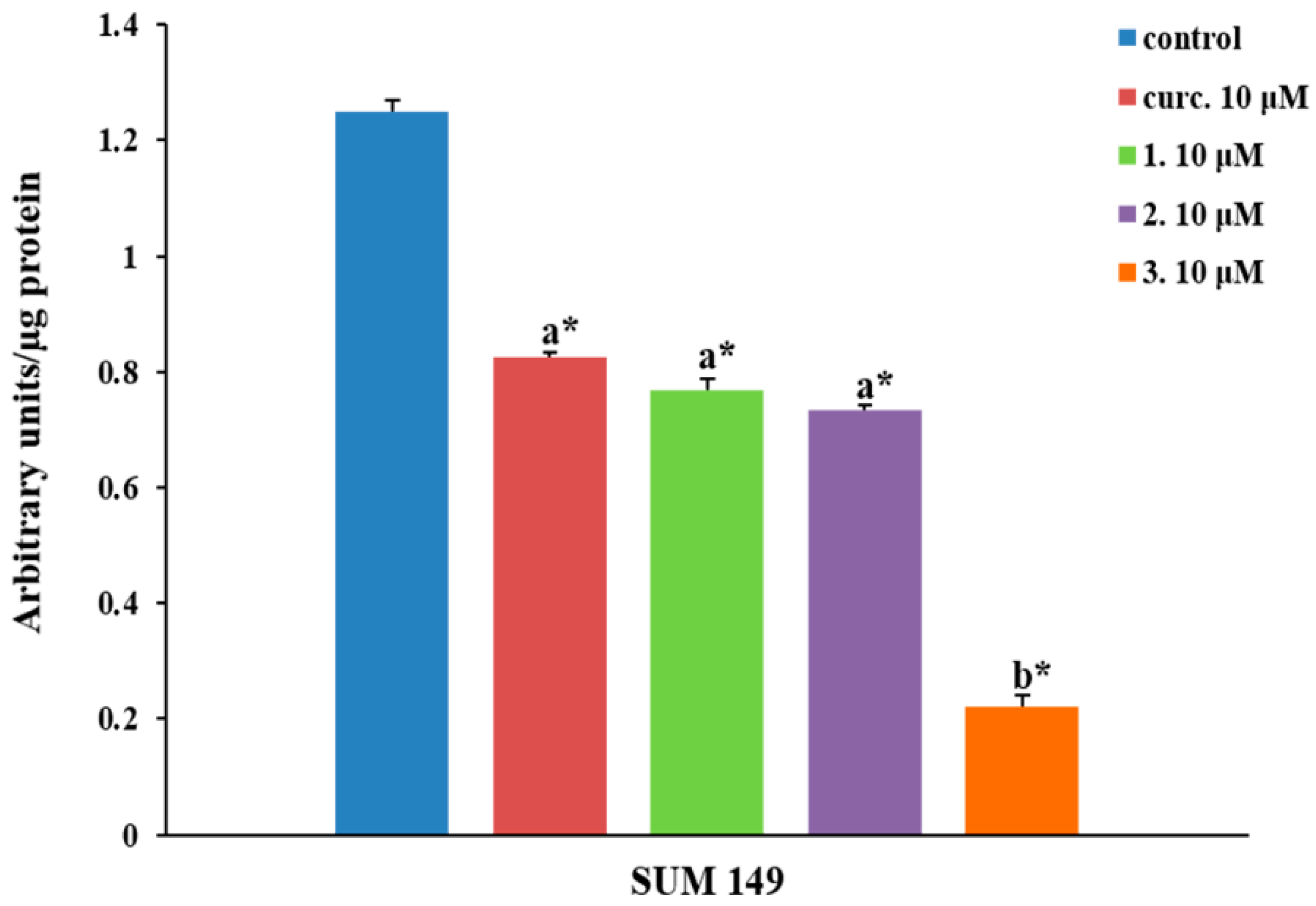
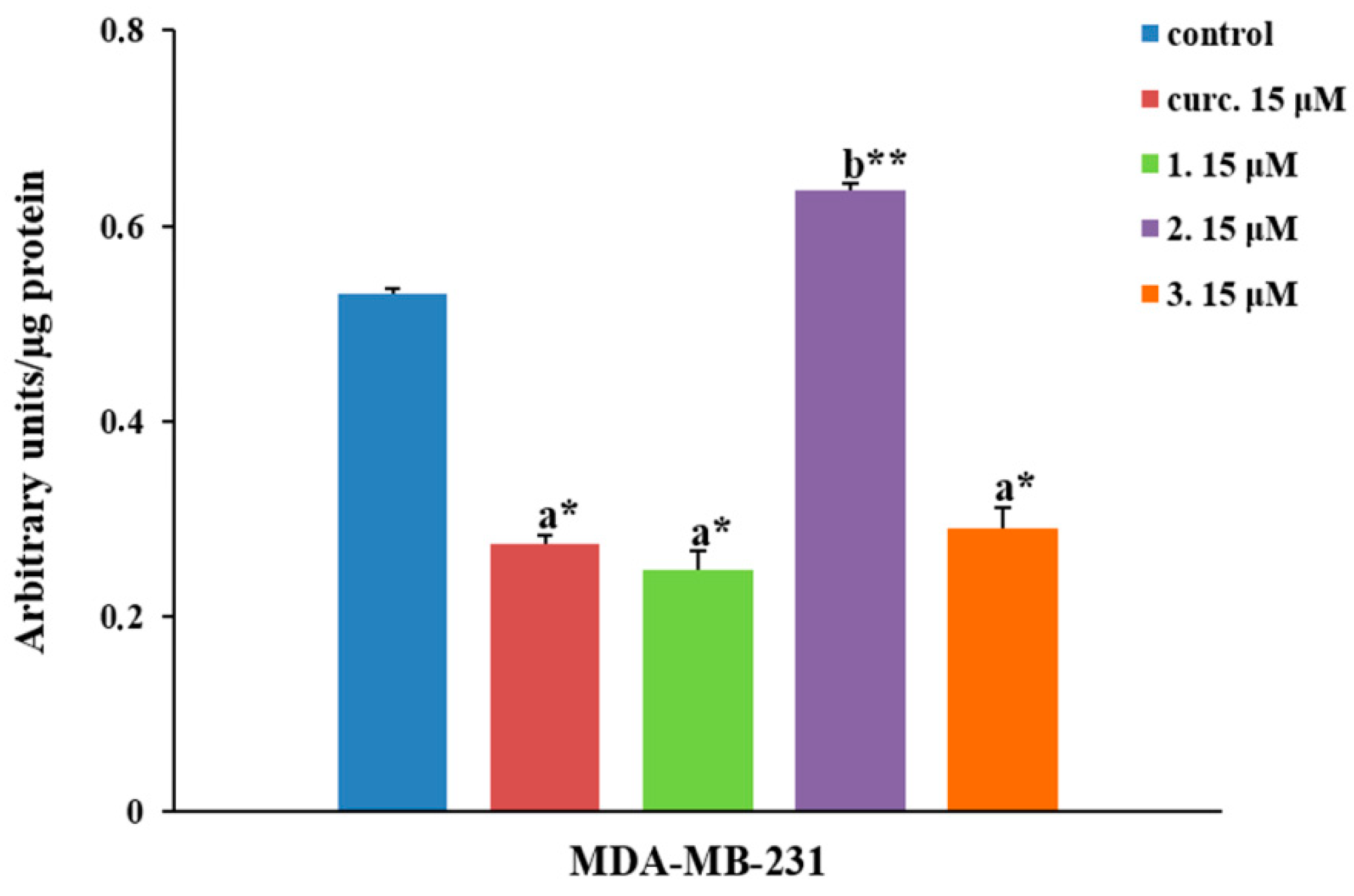
2.2.3. Pro-Apoptotic Activity
2.2.4. NF-κB Inhibition
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis
4.1.1. (1E,6E)-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-(3-methoxy-4-propargyloxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene -3,5-dione (1) and (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(3-methoxy-4-propargyloxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione (2)
4.1.2. 4-phenylsulfanyl-(1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione (3)
4.1.3. (1E,6E)-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-[3-methoxy-4(4-methylbromobenzyl)oxyphenyl] hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione (4) and (1E,6E)-1,7-bis [3-methoxy-4(4-methylbromobenzyl) oxyphenyl]hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione (5)
4.2. Cell Lines
4.3. Cell Growth Aassays
4.4. Anti- and Pro-oxidant Activity
4.5. Evaluation of Cell Death by Flow Cytometry
4.6. NF-κB Activation
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Alessandro, N.; Poma, P.; Montalto, G. Multifactorial nature of hepatocellular carcinoma drug resistance: Could plant polyphenols be helpful? World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asensi, M.; Ortega, A.; Mena, S.; Feddi, F.; Estrela, J.M. Natural polyphenols in cancer therapy. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2011, 48, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsiades, C.S.; Davies, F.E.; Laubach, J.P.; Joshua, D.; San Miguel, J.; Anderson, K.C.; Richardson, P.G. Future directions of next-generation novel therapies, combination approaches, and the development of personalized medicine in myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1916–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, P.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Newman, R.A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Bioavailability of curcumin: Problems and promises. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomeh, M.A.; Hadianamrei, R.; Zhao, X. A Review of Curcumin and Its Derivatives as Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbozzetta, M.; Notarbartolo, M.; Poma, P.; Maurici, A.; Inguglia, L.; Marchetti, P.; Rizzi, M.; Baruchello, R.; Simoni, D.; D’Alessandro, N. Curcumin as a possible lead compound against hormone-independent, multidrug-resistant breast cancer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1155, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, G.; Gul, H.I.; Yamali, C.; Mohamed, A.A.M.; Badr, B.M.; Gul, M.; Abo Markeb, A.; Abo El-Maali, N. Curcumin analogue 1,5-bis(4-hydroxy-3-((4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl)phenyl) penta-1,4-dien-3-one mediates growth arrest and apoptosis by targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and PKC-theta signaling pathways in human breast carcinoma cells. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 78, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C.; Hsieh, M.T.; Yang, J.S.; Lu, C.C.; Tsai, F.J.; Tsao, J.W.; Chiu, Y.J.; Kuo, S.C.; Lee, K.H. Effect of bis (hydroxymethyl) alkanoate curcuminoid derivative MTH-3 on cell cycle arrest, apoptotic and autophagic pathway in triple-negative breast adenocarcinoma MDA-MB-231 cells: An in vitro study. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, K.; Utsumi, T.; Kumano, T.; Maekawa, S.; Oyama, N.; Kawakami, J. Discovery of a new function of curcumin which enhances its anticancer therapeutic potency. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willenbacher, E.; Khan, S.Z.; Mujica, S.C.A.; Trapani, D.; Hussain, S.; Wolf, D.; Willenbacher, W.; Spizzo, G.; Seeber, A. Curcumin: New Insights into an Ancient Ingredient against Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Sundaram, C.; Jhurani, S.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin and cancer: An “old-age” disease with an “age-old” solution. Cancer Lett. 2008, 267, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Zhang, M.; Dai, E.; Luo, Y. Molecular targets of curcumin in breast cancer (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notarbartolo, M.; Poma, P.; Perri, D.; Dusonchet, L.; Cervello, M.; D’Alessandro, N. Antitumor effects of curcumin, alone or in combination with cisplatin or doxorubicin, on human hepatic cancer cells. Analysis of their possible relationship to changes in NF-kB activation levels and in IAP gene expression. Cancer Lett. 2005, 224, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouhpeikar, H.; Butler, A.E.; Bamian, F.; Barreto, G.E.; Majeed, M.; Sahebkar, A. Curcumin as a therapeutic agent in leukemia. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 12404–12414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Bougie, P.; Halliez, M.; Maïga, S.; Godon, C.; Kervoëlen, C.; Pellat-Deceunynck, C.; Moreau, P.; Amiot, M. Curcumin induces cell death of the main molecular myeloma subtypes, particularly the poor prognosis subgroups. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.J.; Zheng, B.Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liang, B. Curcumin inhibits the growth via Wnt/β-catenin pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 22, 7492–7499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hao, Y.; Wu, L.; Dong, X.; Jiang, N.; Cong, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Tang, D.; De Perrot, M.; et al. Curcumin induces apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis in murine malignant mesothelioma. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 2531–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, A.R.; Moore-Medlin, T.; Ekshyyan, O.; Gu, X.; Abreo, F.; Nathan, C.O. Local and systemic Curcumin C3 complex inhibits 4NQO-induced oral tumorigenesis via modulating FGF-2/FGFR-2 activation. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 2538–2547. [Google Scholar]
- Mahammedi, H.; Planchat, E.; Pouget, M.; Durando, X.; Curé, H.; Guy, L.; Van-Praagh, I.; Savareux, L.; Atger, M.; Bayet-Robert, M.; et al. The New Combination Docetaxel, Prednisone and Curcumin in Patients with Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Phase II Study. Oncology 2016, 90, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killian, P.H.; Kronski, E.; Michalik, K.M.; Barbieri, O.; Astigiano, S.; Sommerhoff, C.P.; Pfeffer, U.; Nerlich, A.G.; Bachmeier, B.E. Curcumin inhibits prostate cancer metastasis in vivo by targeting the inflammatory cytokines CXCL1 and -2. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 2507–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahcheraghi, S.H.; Zangui, M.; Lotfi, M.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Ghorbani, A.; Jaliani, H.Z.; Sadeghnia, H.R.; Sahebkar, A. Therapeutic Potential of Curcumin in the Treatment of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gersey, Z.C.; Rodriguez, G.A.; Barbarite, E.; Sanchez, A.; Walters, W.M.; Ohaeto, K.C.; Komotar, R.J.; Graham, R.M. Curcumin decreases malignant characteristics of glioblastoma stem cells via induction of reactive oxygen species. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poma, P.; Notarbartolo, M.; Labbozzetta, M.; Maurici, A.; Carina, V.; Alaimo, A.; Rizzi, M.; Simoni, D.; D’Alessandro, N. The antitumor activities of curcumin and of its isoxazole analogue are not affected by multiple gene expression changes in an MDR model of the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line: Analysis of the possible molecular basis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 20, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoni, D.; Rizzi, M.; Rondanin, R.; Baruchello, R.; Marchetti, P.; Invidiata, F.P.; Labbozzetta, M.; Poma, P.; Carina, V.; Notarbartolo, M.; et al. Antitumor effects of curcumin and structurally beta-diketone modified analogs on multidrug resistant cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbozzetta, M.; Baruchello, R.; Marchetti, P.; Gueli, M.C.; Poma, P.; Notarbartolo, M.; Simoni, D.; D’Alessandro, N. Lack of nucleophilic addition in the isoxazole and pyrazole diketone modified analogs of curcumin; implications for their antitumor and chemosensitizing activities. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 181, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riela, S.; Massaro, M.; Colletti, C.G.; Bommarito, A.; Giordano, C.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Poma, P.; Lazzara, G. Development and characterization of co-loaded curcumin/triazole-halloysite systems and evaluation of their potential anticancer activity. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, M.; Amorati, R.; Cavallaro, G.; Guernelli, S.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Noto, R.; Poma, P.; Riela, S. Direct chemical grafted curcumin on halloysite nanotubes as dual-responsive prodrug for pharmacological applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 140, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Lin, Y.J.; Huang, W.T.; Hung, C.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Tu, Y.C.; Liu, D.M.; Lan, S.J.; Sheu, M.J. Demethoxycurcumin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticle Downregulates DNA Repair Pathway to Improve Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Molecules 2018, 23, 3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, W.J.; Shi, J.B.; Liu, X.H. Novel curcumin analogue hybrids: Synthesis and anticancer activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 156, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.S.; M Dos Santos, D.; Almeida, A.; Marchiori, L.; Campana-Filho, S.P.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Sarmento, B. N-(2-Hydroxy)-propyl-3-trimethylammonium, O-Mysristoyl Chitosan Enhances the Solubility and Intestinal Permeability of Anticancer Curcumin. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Liao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xi, K.; Huang, W.; Jia, X. Water-dispersible PEG-curcumin/amine-functionalized covalent organic framework nanocomposites as smart carriers for in vivo drug delivery. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansalone, L.; Veliz, E.A.; Myrthil, N.G.; Stathias, V.; Walters, W.; Torrens, I.; Schürer, S.C.; Vanni, S.; Leblanc, R.M.; Graham, R.M. Novel Curcumin Inspired Bis-Chalcone Promotes Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Glioblastoma Neurosphere Cell Death. Cancers 2019, 11, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Rauf Khan, A.; Fu, M.; Zhai, Y.; Ji, J.; Bobrovskaya, L.; Zhai, G. Advances in curcumin-loaded nanopreparations: Improving bioavailability and overcoming inherent drawbacks. Drug Target 2019, 23, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B is suppressed by curcumin (diferuloylmethane) [corrected]. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 24995–25000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poma, P.; Labbozzetta, M.; D’Alessandro, N.; Notarbartolo, M. NF-κB Is a Potential Molecular Drug Target in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. OMICS 2017, 21, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vreese, R.; Grootaert, C.; D’hoore, S.; Theppawong, A.; Van Damme, S.; Van Bogaert, M.; Van Camp, J.; D’hooghe, M. Synthesis of novel curcuminoids accommodating a central β-enaminone motif and their impact on cell growth and oxidative stress. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 123, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.M.; Hunsaker, L.A.; Abcouwer, S.F.; Deck, L.M.; Vander Jagt, D.L. Anti-oxidant activities of curcumin and related enones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 3811–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolai, S.; Shi, W.; Corbo, C.; Sun, C.; Averick, S.; Obeysekera, D.; Farid, M.; Alonso, A.; Banerjee, P.; Raja, K. “Clicked” sugar-curcumin conjugate: Modulator of amyloid-β and tau peptide aggregation at ultralow concentrations. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, L.V.; Allison, W.S. The inactivation of the acyl phosphatase activity catalyzed by the sulfenic acid form of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase by dimedone and olefins. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 6234–6243. [Google Scholar]
- Barattucci, A.; Aversa, M.C.; Mancuso, A.; Salerno, T.M.G.; Bonaccorsi, P. Transient Sulfenic Acids in the Synthesis of Biologically Relevant Products. Molecules 2018, 23, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aversa, M.C.; Barattucci, A.; Bonaccorsi, P.; Temperini, A. Regio- and Stereocontrolled Synthesis of (Z)-α-(Phenylseleno) sulfinyl and-sulfonyl Alkenes via Sulfenic Acids, and a Study of their Reactivity. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 28, 5668–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aversa, M.C.; Bonaccorsi, P.; Faggi, C.; Lamanna, G.; Menichetti, S. Enantiopure arenesulfenic acids as intermediates in stereoselective synthesis. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 11902–11909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorsi, P.; Marino-Merlo, F.; Barattucci, A.; Battaglia, G.; Papaianni, E.; Papalia, T.; Aversa, M.C.; Mastino, A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a new class of glycoconjugated disulfides that exhibit potential anticancer properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 3186–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez-Arroyo, I.J.; Rios-Fuller, T.J.; Feliz-Mosquea, Y.R.; Lacourt-Ventura, M.; Leal-Alviarez, D.J.; Maldonado-Martinez, G.; Cubano, L.A.; Martínez-Montemayor, M.M. Ganoderma lucidum Combined with the EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Erlotinib Synergize to Reduce Inflammatory Breast Cancer Progression. J. Cancer. 2016, 7, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, D.; Gilkes, D.M.; Chaturvedi, P.; Xiang, L.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factors are required for chemotherapy resistance of breast cancer stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5429–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poma, P.; Labbozzetta, M.; Notarbartolo, M.; Bruno, M.; Maggio, A.; Rosselli, S.; Sajeva, M.; Zito, P. Chemical composition, in vitro antitumor and pro-oxidant activities of Glandora rosmarinifolia (Boraginaceae) essential oil. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
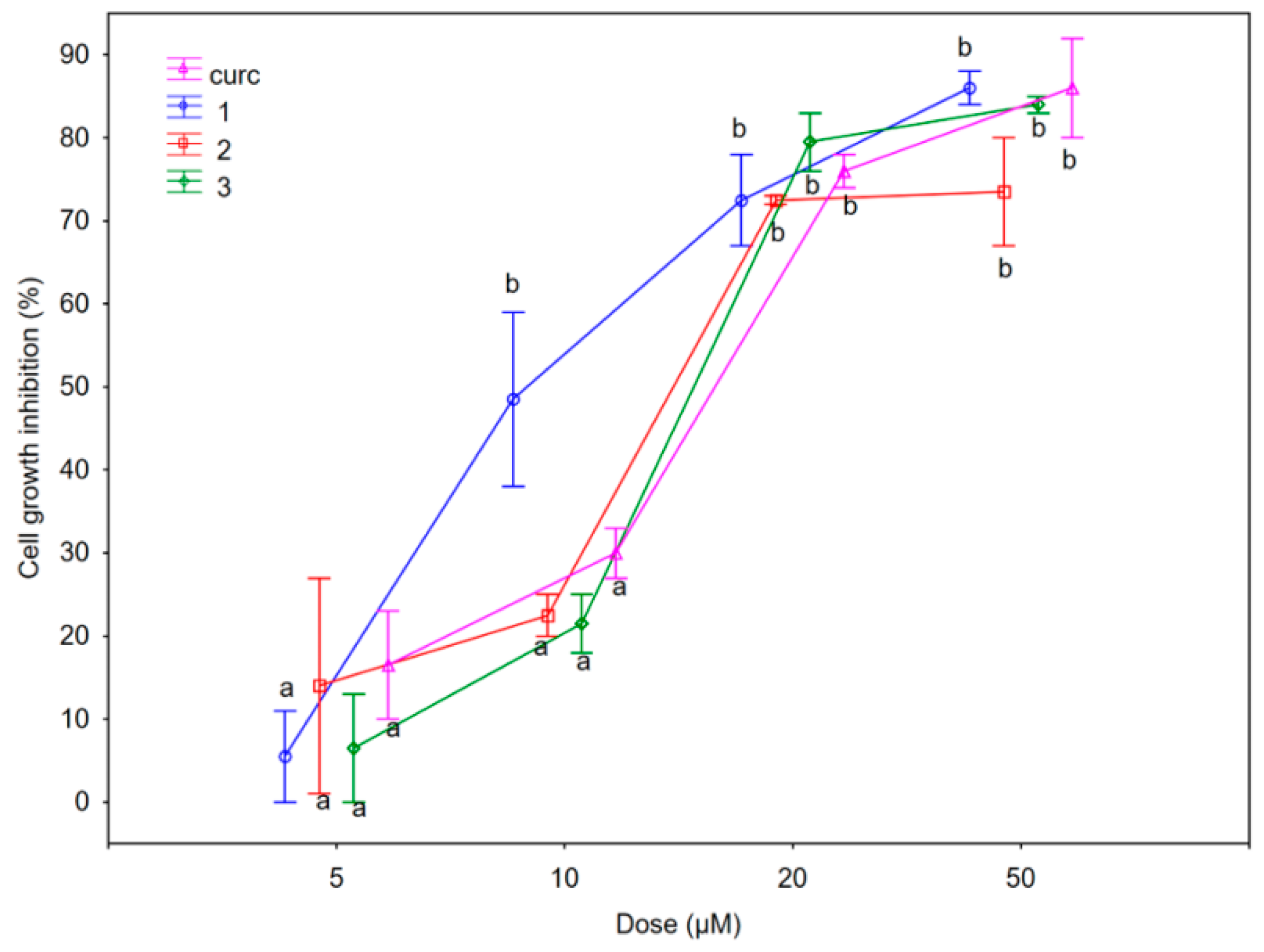
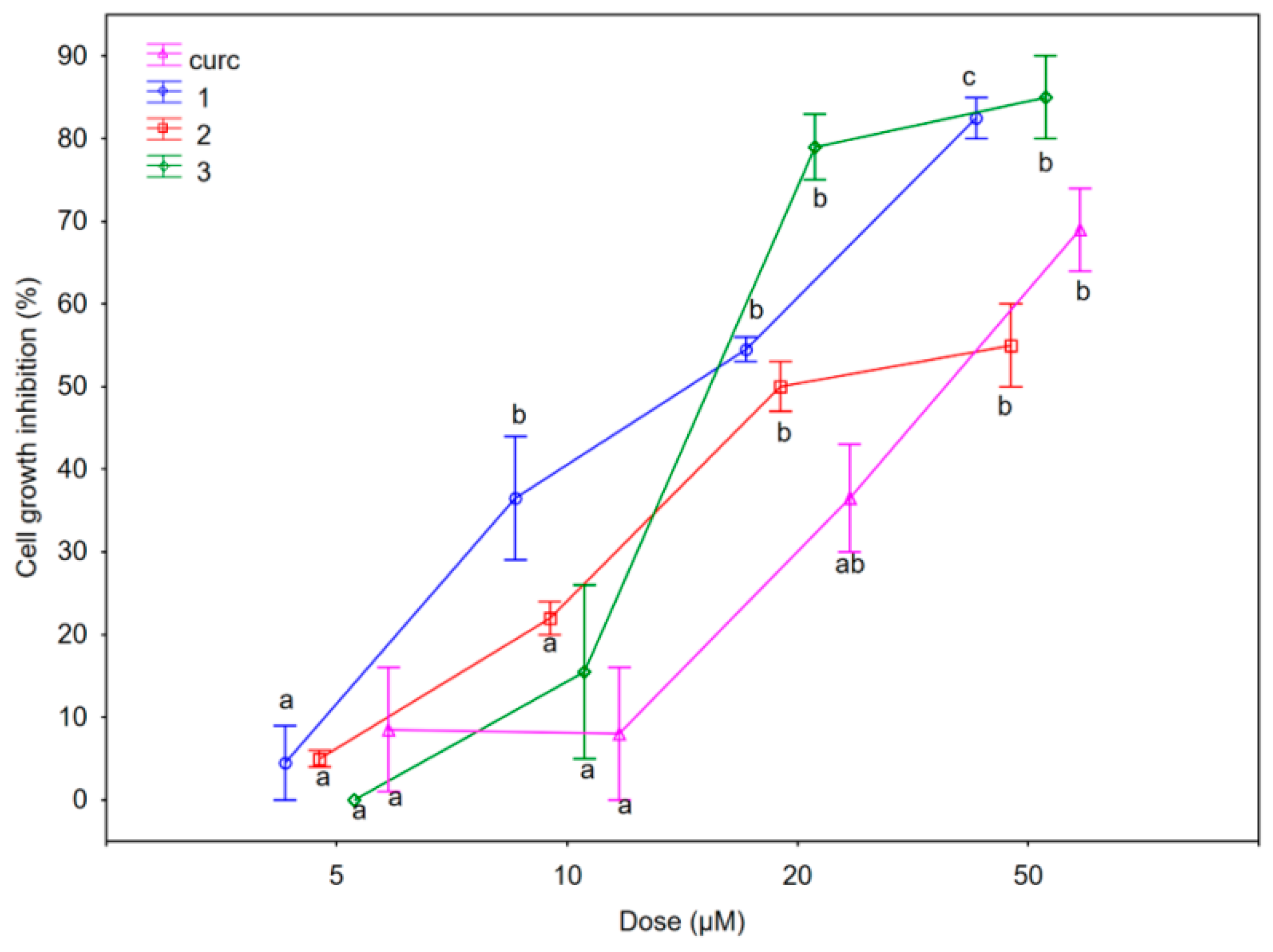
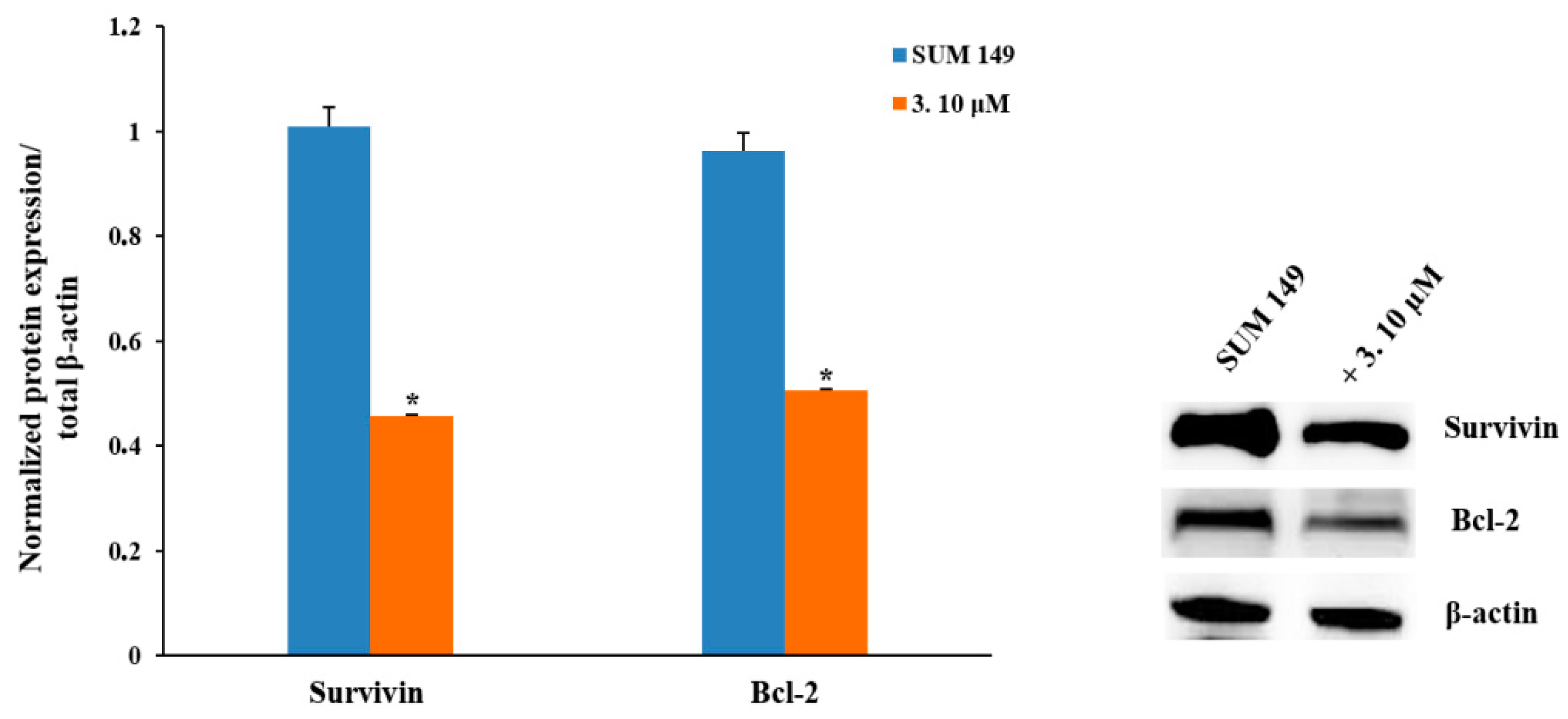
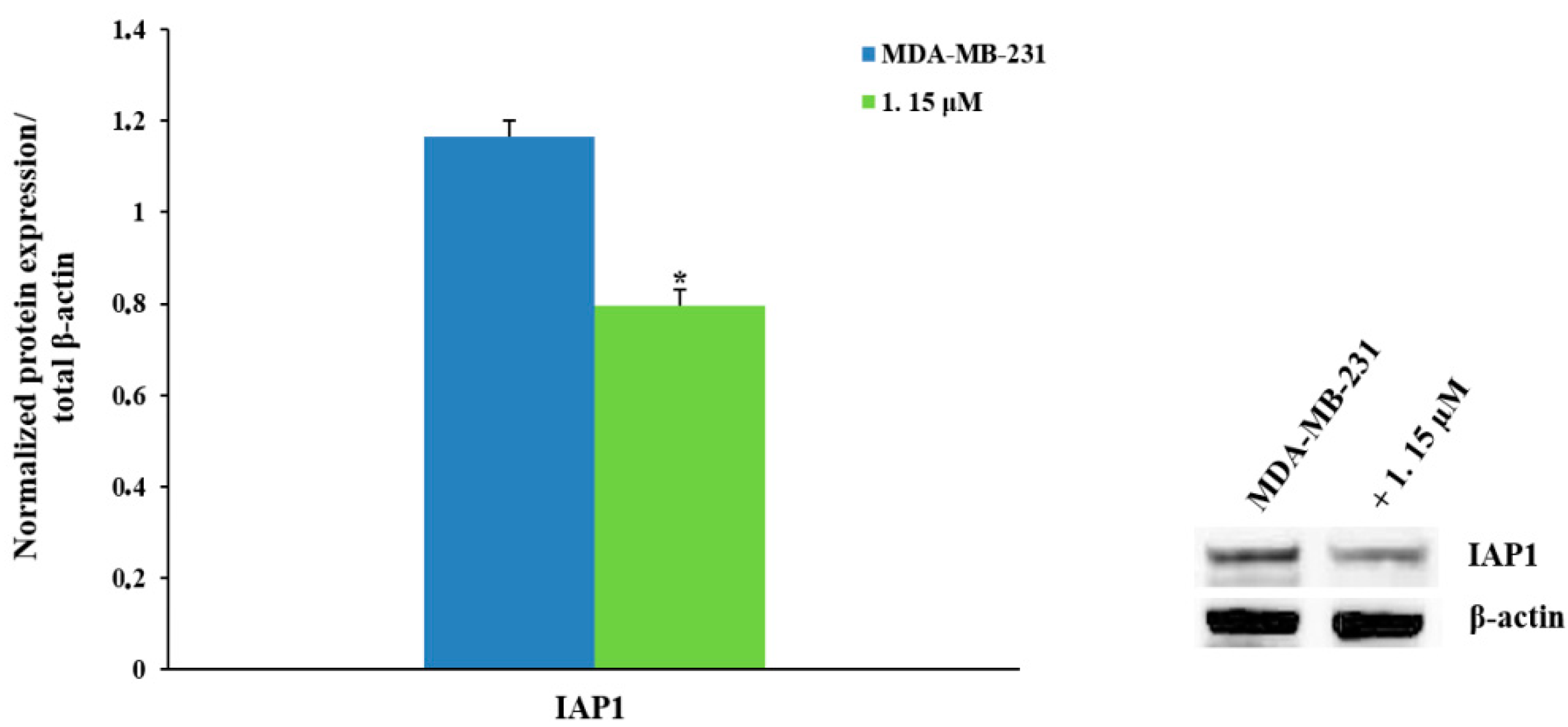

| Compounds | SUM149 IC50 (μM) | MDA-MB-231 IC50 (μM) | 1-7HB2 IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Curcumin (curc) 1 | 14.0 ± 0.29 11.2 ± 1.30 | 25.5 ± 0.35 18.0 ± 0.41 | 37.5 ± 0.51 20.0 ± 0.22 |
| 2 | 13.2 ± 1.59 | 20.0 ± 0.00 | not reached |
| 3 | 13.5 ± 0.88 | 15.0 ± 0.85 | 12.5 ± 0.43 |
| 4 | not reached | not reached | not reached |
| 5 | not reached | not reached | not reached |
| A | Cell Lines and Treatments | Cell Viability (%) |
| SUM 149 | ||
| + NAC 2 mM a,* | 100.0 ± 9.5 | |
| + curc. 14 μM bc,* + 1. 11 μM bc,* | 32.0 ± 2.1 28.0 ± 3.2 | |
| + 2. 13 μM bd,* | 36.6 ± 1.8 | |
| + 3. 14 μM bc,* | 34.0 ± 2.1 | |
| + NAC + curc de,* | 74.5 ± 0.0 | |
| + NAC + 1 ae,* | 100.0 ± 20.5 | |
| + NAC + 2 ae,* | 74.4 ± 1.4 | |
| + NAC + 3 c,* | 14.0 ± 4.6 | |
| B | MDA-MB-231 | |
| + NAC 2 mM a,* | 87.0 ± 3.9 | |
| + curc. 25μM ab,* + 1. 18μM b,* | 45.0 ± 4.6 23.0 ± 1.4 | |
| + 2. 20μM ab,* | 44.0 ± 4.9 | |
| + 3. 15μM b,* | 25.6 ± 0.7 | |
| + NAC + curc abc,* | 60.0 ± 2.1 | |
| + NAC + 1 ab,* | 53.5 ± 0.7 | |
| + NAC + 2 ac,* | 78.0 ± 1.8 |
| ED50 | ARC (1/ED50) | |
|---|---|---|
| Trolox | 12.0 µM | 5 |
| Curcumin 1 | 7.5 µM >100 µM | 8 - |
| 2 | >100 µM | - |
| 3 | 19.2 µM | 3.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonaccorsi, P.M.; Labbozzetta, M.; Barattucci, A.; Salerno, T.M.G.; Poma, P.; Notarbartolo, M. Synthesis of Curcumin Derivatives and Analysis of Their Antitumor Effects in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cell Lines. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040161
Bonaccorsi PM, Labbozzetta M, Barattucci A, Salerno TMG, Poma P, Notarbartolo M. Synthesis of Curcumin Derivatives and Analysis of Their Antitumor Effects in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cell Lines. Pharmaceuticals. 2019; 12(4):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040161
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonaccorsi, Paola Maria, Manuela Labbozzetta, Anna Barattucci, Tania Maria Grazia Salerno, Paola Poma, and Monica Notarbartolo. 2019. "Synthesis of Curcumin Derivatives and Analysis of Their Antitumor Effects in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cell Lines" Pharmaceuticals 12, no. 4: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040161
APA StyleBonaccorsi, P. M., Labbozzetta, M., Barattucci, A., Salerno, T. M. G., Poma, P., & Notarbartolo, M. (2019). Synthesis of Curcumin Derivatives and Analysis of Their Antitumor Effects in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Cell Lines. Pharmaceuticals, 12(4), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12040161









