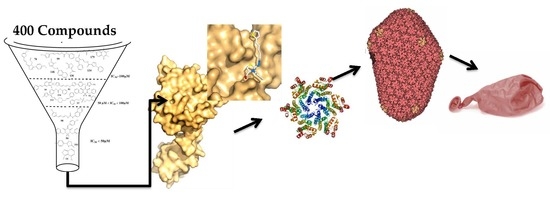
Looking for Novel Capsid Protein Multimerization Inhibitors of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
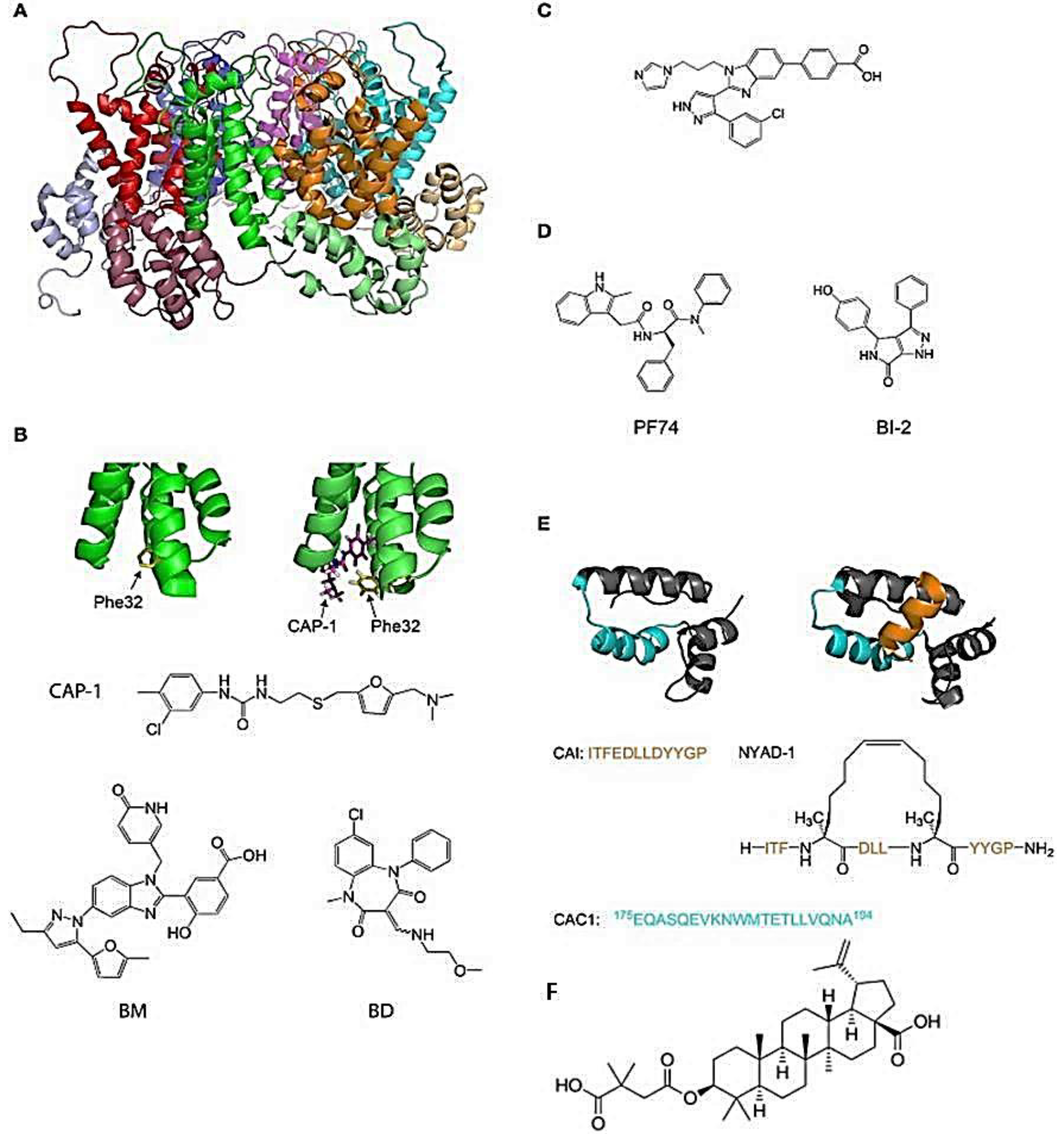
2. Results and Discussion
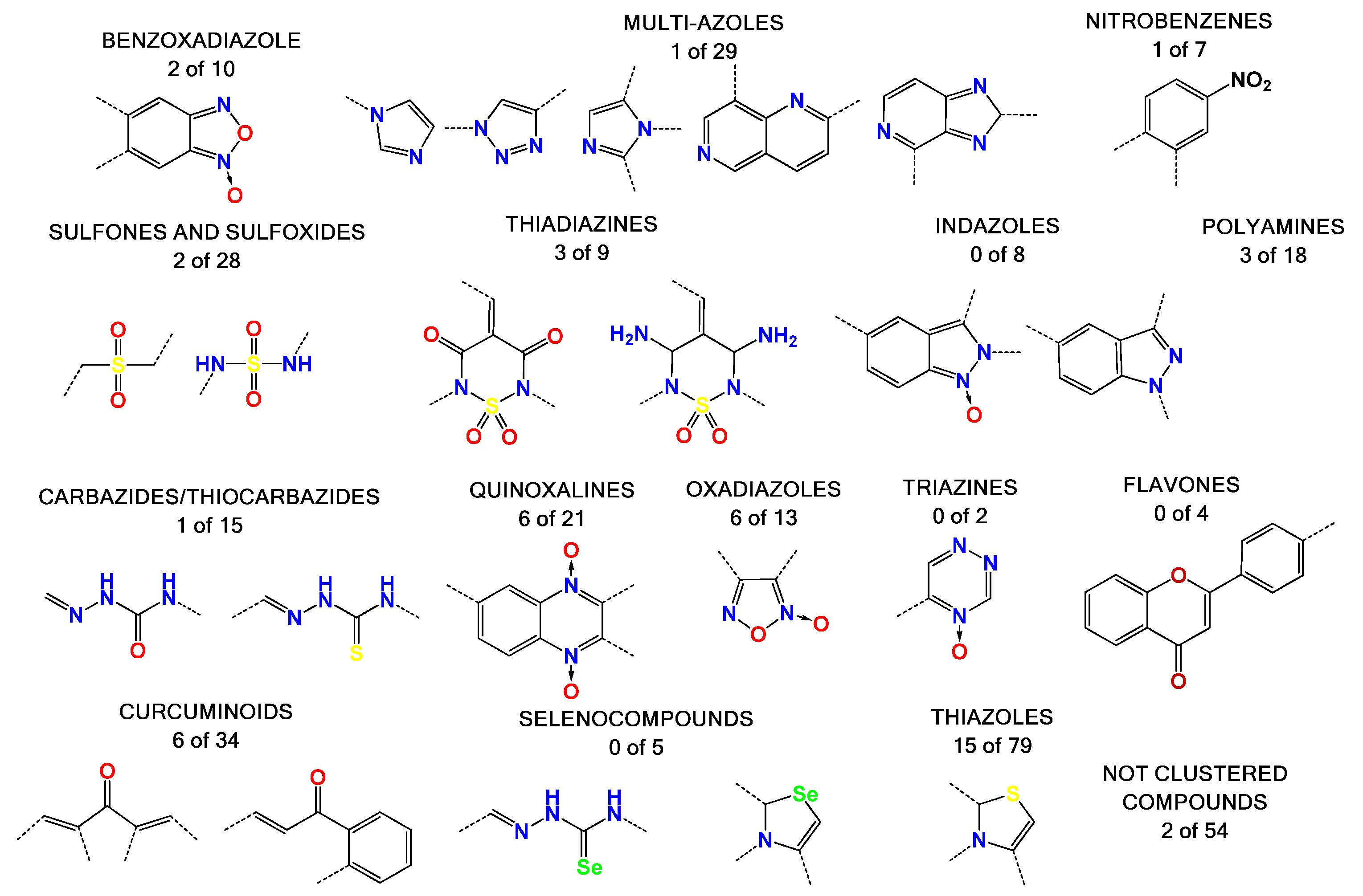
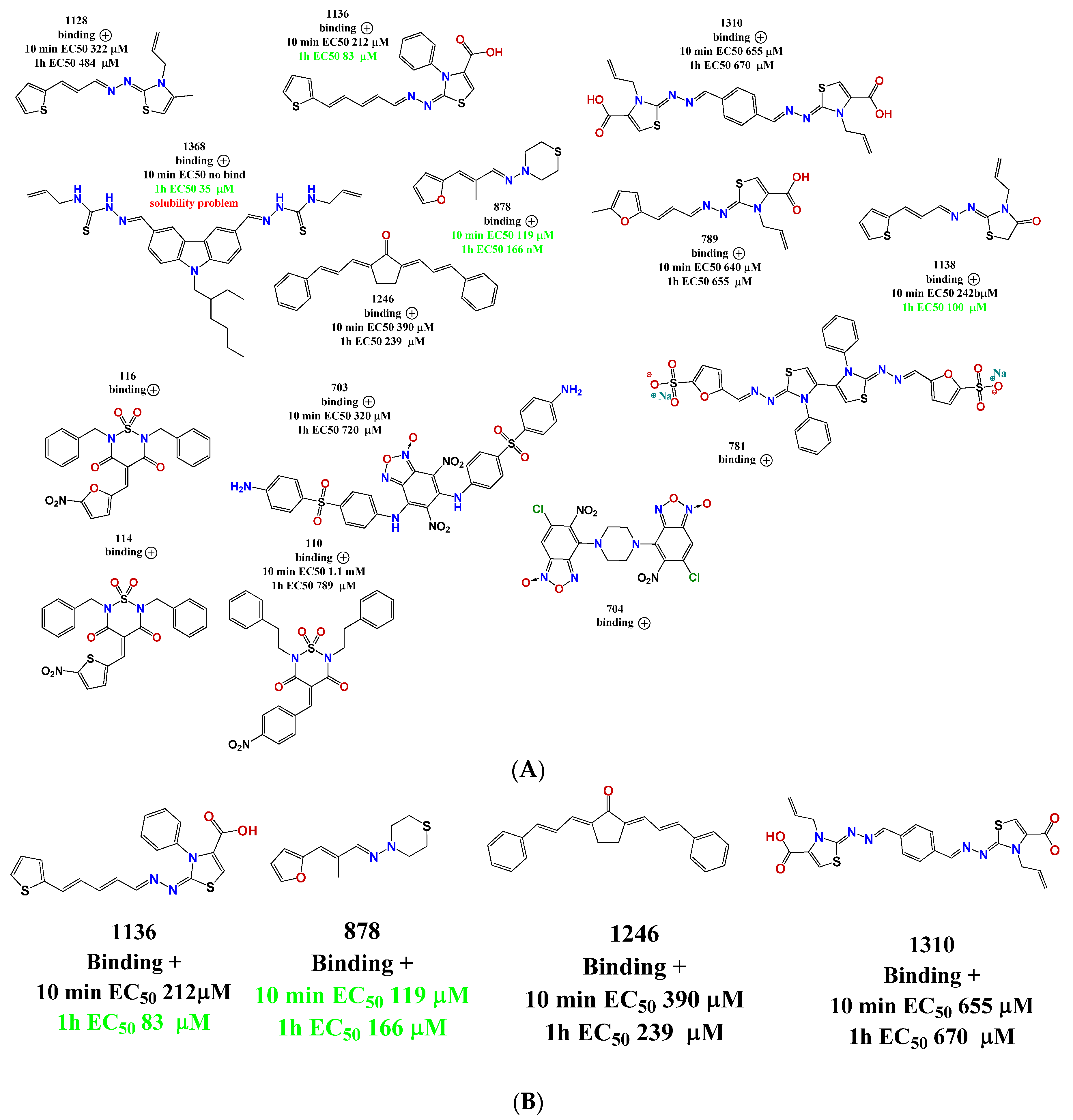
2.1. Our In-House Library
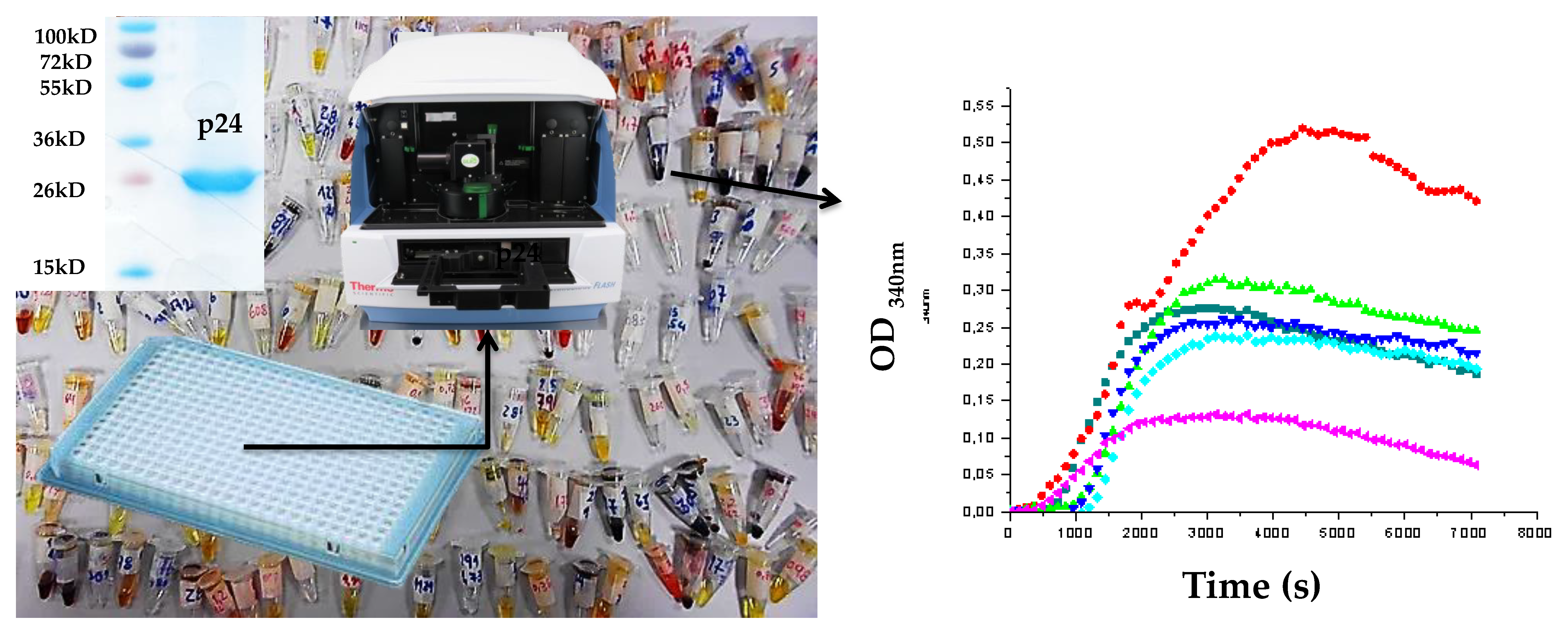
2.2. In Vitro Assembly Studies
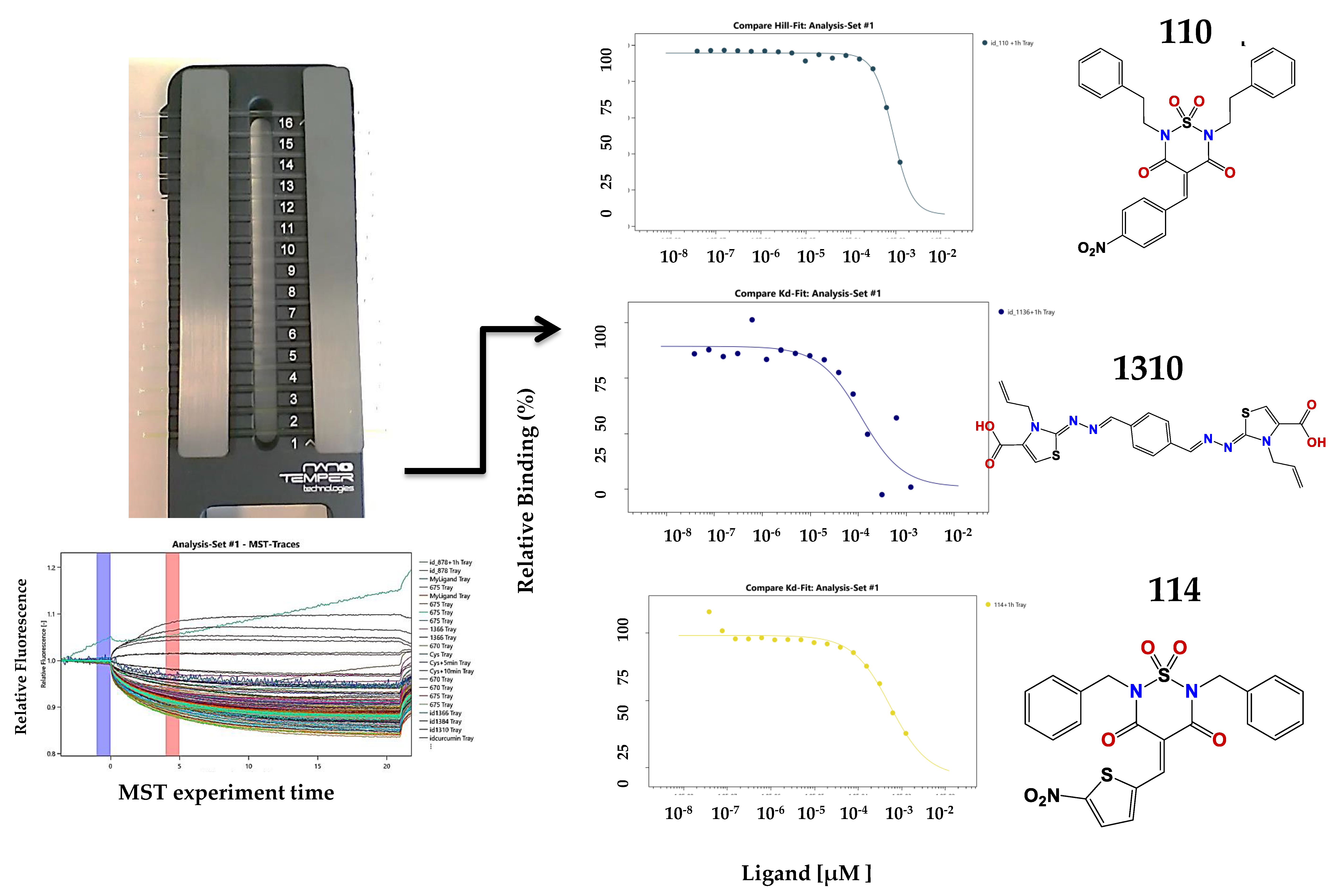
2.3. Microscale Thermophoresis Studies
2.4. Docking Analysis
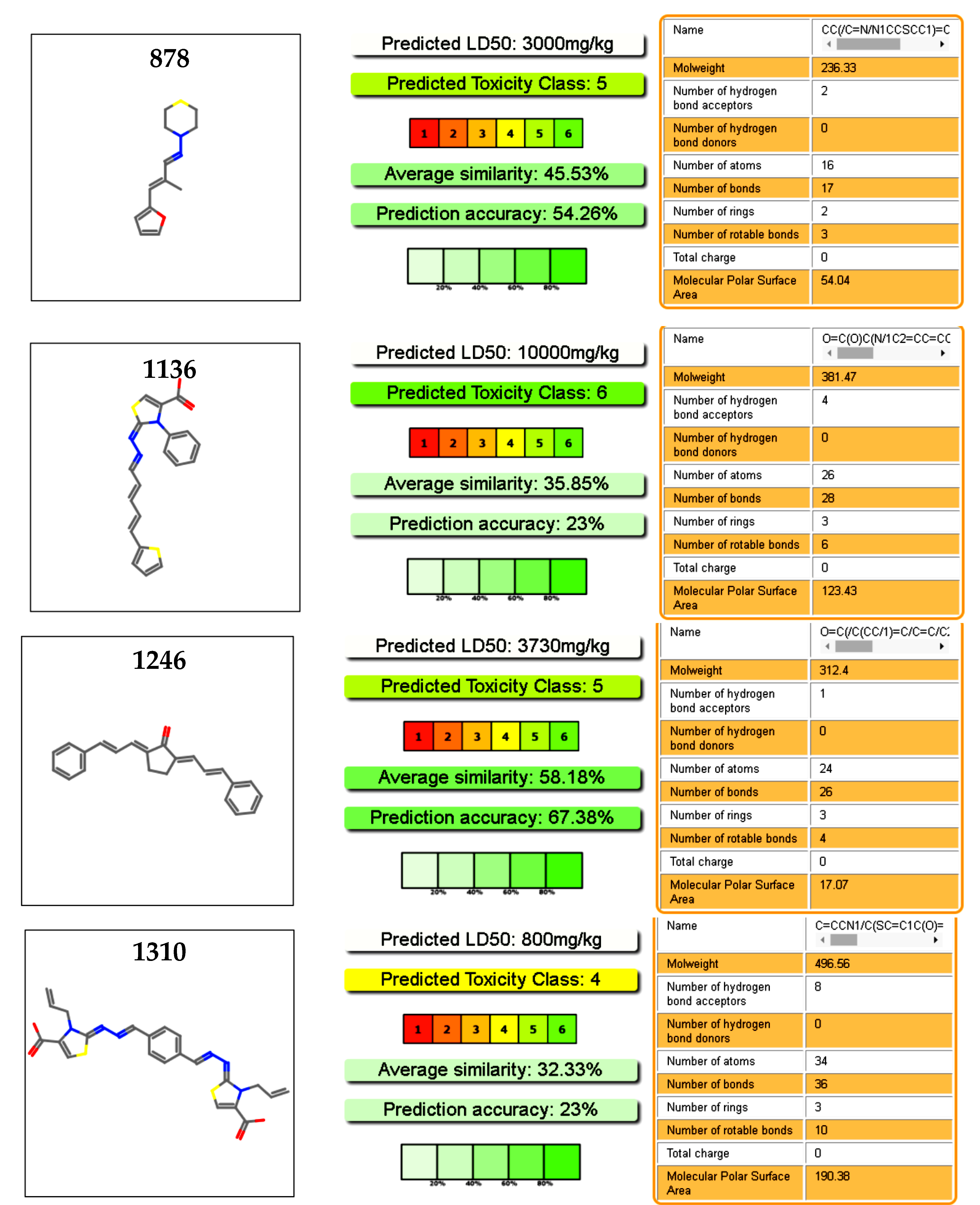
2.5. Toxicology Data
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Expression and Purification of CA
3.2. Assembly Assay by Spectrophotometry [24]
3.3. Microscale Thermophoresis [41]
3.4. Docking
3.5. Cytotoxicity Assay in Mammalian Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwartz, A.M.; McCrackin, M.A.; Schinazi, R.F.; Hill, P.B.; Vahlenkamp, T.W.; Tompkins, M.B.; Hartmann, K. Antiviral efficacy of nine nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors against feline immunodeficiency virus in feline peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 75, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, H.; Bienzle, D. Pharmacological inhibition of feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV). Viruses 2012, 4, 708–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, J.K.; Sanou, M.P.; Abbott, J.R.; Coleman, J.K. Feline immunodeficiency virus model for designing HIV/AIDS vaccines. Curr. HIV Res. 2010, 8, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luttge, B.G.; Freed, E.O. FIV Gag: Virus assembly and host-cell interactions. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 134, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, S.; Nolte, I. Long-Term Treatment of Diseased, FIV-Seropositive Field Cats with Azidothymidine (AZT). J. Vet. Med. Ser. A 1995, 42, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, N.R.; McCracken, C.; Gaskell, R.M.; Cameron, J.M.; Coates, J.A.; Gaskell, C.J.; Hart, C.A.; Bennett, M. Susceptibility in Cell Culture of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus to Eighteen Antiviral Agents. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1994, 34, 589–594. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7532645 (accessed on 17 May 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosie, M.; Techakriengkrai, N.; Bęczkowski, P.; Harris, M.; Logan, N.; Willett, B. The Comparative Value of Feline Virology Research: Can Findings from the Feline Lentiviral Vaccine Be Translated to Humans? Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwase, H.; Katsube, T.; Iida, K.; Komai, T.; Nishigaki, T. Investigation into the mode of action of R-91650, an arylpiperazinyl fluoroquinolone, on feline immunodeficiency virus replication inhibitory activity. Arch. Virol. 2000, 145, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timilsina, U.; Ghimire, D.; Timalsina, B.; Nitz, T.J.; Wild, C.T.; Freed, E.O.; Gaur, R. Identification of potent maturation inhibitors against HIV-1 clade C. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinsztejn, B.; Hosseinipour, M.C.; Ribaudo, H.J.; Swindells, S.; Eron, J.; Chen, Y.Q.; Wang, L.; Ou, S.S.; Anderson, M.; McCauley, M.; et al. Effects of early versus delayed initiation of antiretroviral treatment on clinical outcomes of HIV-1 infection: Results from the phase 3 HPTN 052 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, K.A.; Wilkinson, J.G.; Frick, R.; Francke, S.; Mathes, L.E. Early suppression of viremia by ZDV does not alter the spread of feline immunodeficiency virus infection in cats. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. Hum. Retrovirol. 1995, 9, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Morris, G.M.; Lee, T.; Laco, G.S.; Wong, C.H.; Olson, A.J.; Elder, J.H.; Wlodawer, A.; Gustchina, A. Structural studies of FIV and HIV-1 proteases complexed with an efficient inhibitor of FIV protease. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 2000, 38, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka-sans, B.; Protack, T.; Lin, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Y.; Samanta, H.; Terry, B. Identification and Characterization of BMS-955176, a Second-Generation HIV-1 Maturation Inhibitor with Improved Potency, Antiviral Spectrum, and Gag Polymorphic Coverage. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 3956–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, M.; Bonneau, P.; Bousquet, Y.; DeRoy, P.; Duan, J.; Duplessis, M.; Gagnon, A.; Garneau, M.; Goudreau, N.; Guse, I.; et al. Inhibition of HIV-1 capsid assembly: Optimization of the antiviral potency by site selective modifications at N1, C2 and C16 of a 5-(5-furan-2-yl-pyrazol-1-yl)-1H-benzimidazole scaffold. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 7512–7517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundquist, W.I.; Kräusslich, H.G. HIV-1 assembly, budding, and maturation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabizon, R.; Friedler, A.; Jahnke, W. Allosteric modulation of protein oligomerization: An emerging approach to drug design. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, J.; Halambage, U.D.; Jurado, K.A.; Jamin, A.V.; Wang, Y.; Engelman, A.N.; Aiken, C. Inhibition of HIV-1 Maturation via Small Molecule Targeting of the Amino-Terminal Domain in the Viral Capsid Protein. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02155-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Ambrose, Z.; Martin, T.D.; Oztop, I.; Julias, J.G.; Vandegraaff, N.; Baumann, J.G.; Wang, R.; Takemura, T.; Shelton, K.; et al. Flexible Use of Nuclear Import Pathways by HIV-1. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 7, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, A.J.; Fletcher, A.J.; Schaller, T.; Elliott, T.; Lee, K.E.; KewalRamani, V.N.; Chin, J.W.; Towers, G.J.; James, L.C. CPSF6 Defines a Conserved Capsid Interface that Modulates HIV-1 Replication. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, A.J.; Jacques, D.A.; Mcewan, W.A.; Fletcher, A.J.; Essig, S.; Chin, J.W.; Halambage, U.D.; Aiken, C.; James, L.C. Host Cofactors and Pharmacologic Ligands Share an Essential Interface in HIV-1 Capsid That Is Lost upon Disassembly. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zhou, J.; Shah, V.B.; Aiken, C.; Whitby, K. Small-molecule inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection by virus capsid destabilization. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thenin-houssier, S.; Valente, S.T.; Sciences, M. HIV-1 capsid inhibitors as antiretroviral agents Suzie. Curr. HIV Res. 2017, 14, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamorte, L.; Titolo, S.; Lemke, C.T.; Goudreau, N.; Mercier, J.F.; Wardrop, E.; Shah, V.B.; Von Schwedler, U.K.; Langelier, C.; Banik, S.S.R.; et al. Discovery of novel small-molecule HIV-1 replication inhibitors that stabilize capsid complexes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4622–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Loeliger, E.; Kinde, I.; Kyere, S.; Mayo, K.; Barklis, E.; Sun, Y.; Huang, M.; Summers, M.F. Antiviral Inhibition of the HIV-1 Capsid Protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 327, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortagere, S.; Madani, N.; Mankowski, M.K.; Schön, A.; Zentner, I.; Swaminathan, G.; Princiotto, A.; Anthony, K.; Oza, A.; Sierra, L.-J.; et al. Inhibiting Early-Stage Events in HIV-1 Replication by Small-Molecule Targeting of the HIV-1 Capsid. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 8472–8481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemke, C.T.; Faucher, A.; Mason, S.W.; Bonneau, P. A novel inhibitor-binding site on the HIV-1 capsid N-terminal domain leads to improved crystallization via compound-mediated dimerization research papers. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2013, 69, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rihn, S.J.; Wilson, S.J.; Loman, N.J.; Alim, M.; Bakker, S.E.; Bhella, D.; Gifford, R.J.; Rixon, F.J.; Bieniasz, P.D. Extreme Genetic Fragility of the HIV-1 Capsid. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, E.; Varela, J.; Birriel, E.; Serna, E.; Torres, S.; Yaluff, G.; DeBilbao, N.V.; Aguirre-López, B.; Cabrera, N.; DíazMazariegos, S.; et al. Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Trypanosoma cruzi Triosephosphate Isomerase with Concomitant Inhibition of Cruzipain: Inhibition of Parasite Growth through Multitarget Activity. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, G.; Varela, J.; Márquez, P.; Gabay, M.; Arias Rivas, C.E.; Cuchilla, K.; Echeverría, G.A.; Piro, O.E.; Chorilli, M.; Leal, S.M.; et al. Optimization of antitrypanosomatid agents: Identification of nonmutagenic drug candidates with in vivo activity. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3984–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, G.; Martínez, J.; Varela, J.; Birriel, E.; Cruces, E.; Gabay, M.; Leal, S.M.; Escobar, P.; Aguirre-lópez, B.; De Gómez-puyou, M.T.; et al. Development of bis-thiazoles as inhibitors of triosephosphate isomerase from Trypanosoma cruzi. Identification of new non-mutagenic agents that are active in vivo. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 100, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fader, L.D.; Landry, S.; Goulet, S.; Morin, S.; Kawai, S.H.; Bousquet, Y.; Dion, I.; Hucke, O.; Goudreau, N.; Lemke, C.T.; et al. Optimization of a 1,5-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4]diazepine-2,4-dione series of HIV capsid assembly inhibitors 2: Structure-activity relationships (SAR) of the C3-phenyl moiety. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3401–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemke, C.T.; Titolo, S.; von Schwedler, U.; Goudreau, N.; Mercier, J.-F.; Wardrop, E.; Faucher, A.-M.; Coulombe, R.; Banik, S.S.R.; Fader, L.; et al. Distinct effects of two HIV-1 capsid assembly inhibitor families that bind the same site within the N-terminal domain of the viral CA protein. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6643–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thenin-houssier, S.; De Vera, M.S.; Pedro-Rosa, L.; Brady, A.; Richard, A.; Konnick, B.; Opp, S.; Buffone, C.; Fuhrmann, J.; Kota, S.; et al. Ebselen, a Small-Molecule Capsid Inhibitor of HIV-1 Replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2195–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obal, G.; Trajtenberg, F.; Carrion, F.; Tome, L.; Larrieux, N.; Zhang, X.; Pritsch, O.; Buschiazzo, A. Conformational plasticity of a native retroviral capsid revealed by X-ray crystallography. Science 2015, 349, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrière, J.; Fenel, D.; Schoehn, G.; Gouet, P.; Guillon, C. Biophysical characterization of the feline immunodeficiency virus p24 capsid protein conformation and in vitro capsid assembly. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, G.; Aguirre-Lopez, B.; Varela, J.; Cabrera, M.; Merlino, A.; Lopez, G.V.; Lavaggi, M.L.; Porcal, W.; Di Maio, R.; Gonzalez, M.; et al. Massive screening yields novel and selective Trypanosoma cruzi triosephosphate isomerase dimer-interface-irreversible inhibitors with anti-trypanosomal activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 5767–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, G.; Perdomo, C.; Coronel, C.; Aguilera, E.; Varela, J.; Aparicio, G.; Zolessi, F.R.; Cabrera, N.; Vega, C.; Rolón, M.; et al. Multi-anti-parasitic activity of arylidene ketones and thiazolidene hydrazines against Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania spp. Molecules 2017, 22, E709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacques, D.A.; McEwan, W.A.; Hilditch, L.; Price, A.J.; Towers, G.J.; James, L.C. HIV-1 uses dynamic capsid pores to import nucleotides and fuel encapsidated DNA synthesis. Nature 2016, 536, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folio, C.; Sierra, N.; Dujardin, M.; Alvarez, G.; Guillon, C. Crystal structure of the full-length feline immunodeficiency virus capsid protein shows an N-terminal β-hairpin in the absence of N-terminal proline. Viruses 2017, 9, E335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drwal, M.N.; Banerjee, P.; Dunkel, M.; Wettig, M.R.; Preissner, R. ProTox: A web server for the in silico prediction of rodent oral toxicity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Bonete, M.J.; Jensen, M.; Recktenwald, C.V.; Rocha, S.; Stadler, V.; Bokarewa, M.; Katona, G. Bayesian Analysis of MicroScale Thermophoresis Data to Quantify Affinity of Protein:Protein Interactions with Human Survivin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.; Huey, R. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fort, R.S.; Mathó, C.; Geraldo, M.V.; Ottati, M.C.; Yamashita, A.S.; Saito, K.C.; Leite, K.R.M.; Méndez, M.; Maedo, N.; Méndez, L.; et al. Nc886 is epigenetically repressed in prostate cancer and acts as a tumor suppressor through the inhibition of cell growth. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
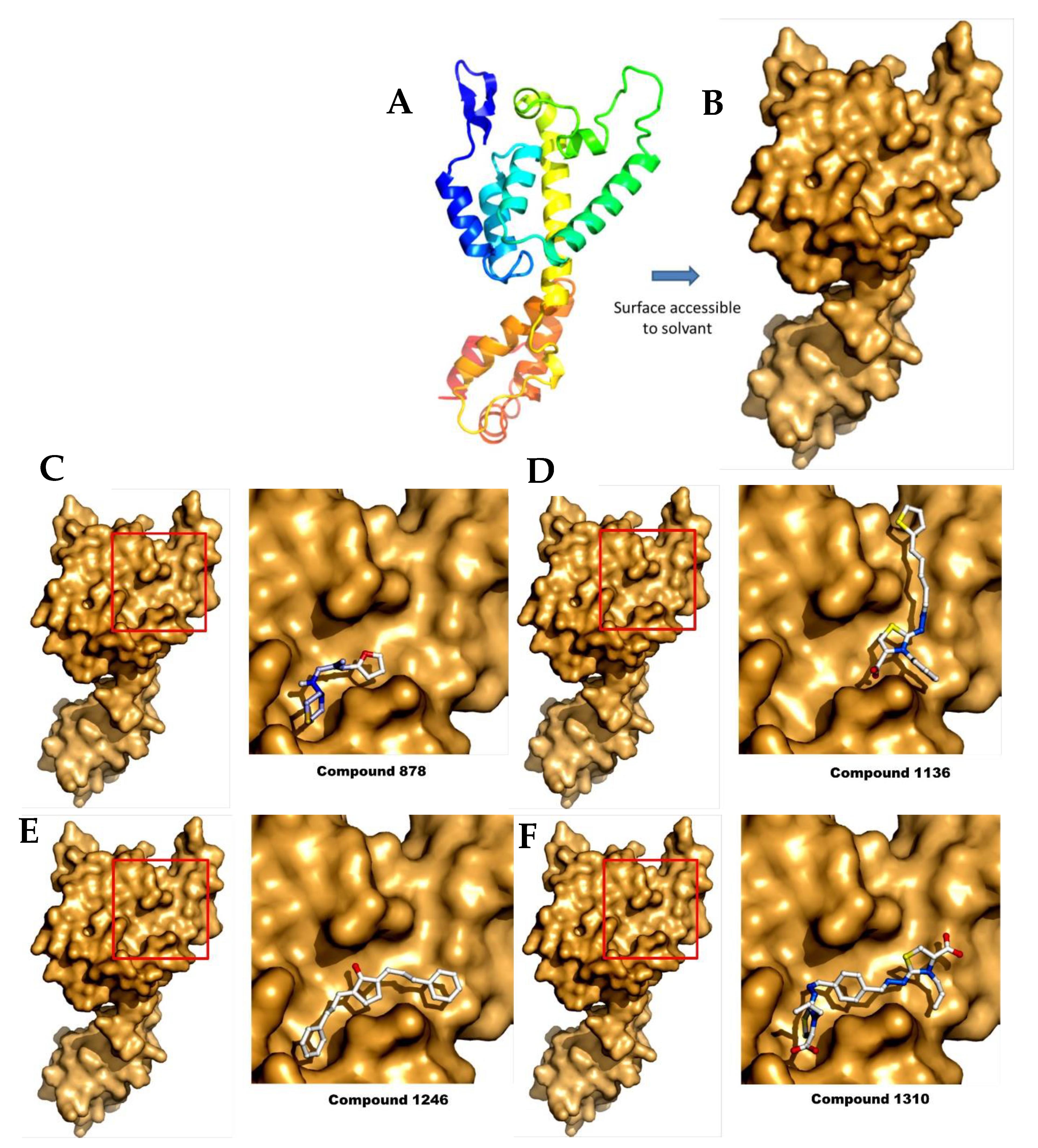
| Compounds | Predicted Binding ΔG (kcal·mol−1) Range Values | Predicted KD (µM) Range Values |
|---|---|---|
| 878 | −5.2/−4.9 | 163/269 |
| 1136 | −6.6/−6.1 | 17/36 |
| 1246 | −7.4/−7.0 | 4/8 |
| 1310 | −6.3/−6.0 | 26/43 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sierra, N.; Folio, C.; Robert, X.; Long, M.; Guillon, C.; Álvarez, G. Looking for Novel Capsid Protein Multimerization Inhibitors of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030067
Sierra N, Folio C, Robert X, Long M, Guillon C, Álvarez G. Looking for Novel Capsid Protein Multimerization Inhibitors of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus. Pharmaceuticals. 2018; 11(3):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030067
Chicago/Turabian StyleSierra, Natalia, Christelle Folio, Xavier Robert, Mathieu Long, Christophe Guillon, and Guzmán Álvarez. 2018. "Looking for Novel Capsid Protein Multimerization Inhibitors of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus" Pharmaceuticals 11, no. 3: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030067
APA StyleSierra, N., Folio, C., Robert, X., Long, M., Guillon, C., & Álvarez, G. (2018). Looking for Novel Capsid Protein Multimerization Inhibitors of Feline Immunodeficiency Virus. Pharmaceuticals, 11(3), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030067