Insights into Macrophage Heterogeneity and Cytokine-Induced Neuroinflammation in Major Depressive Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
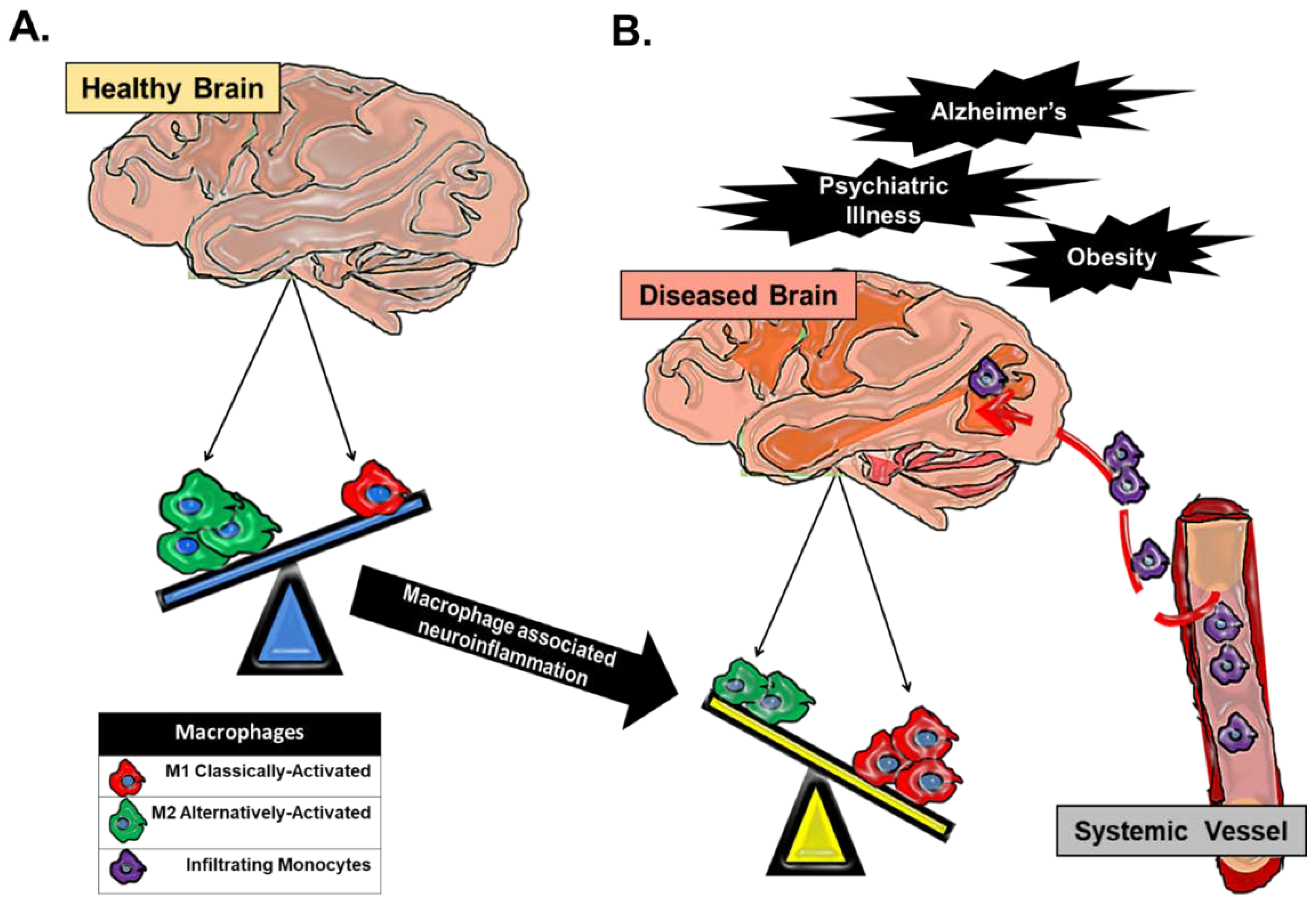
2. Macrophage Heterogeneity in Neuroinflammation and Major Depressive Disorder
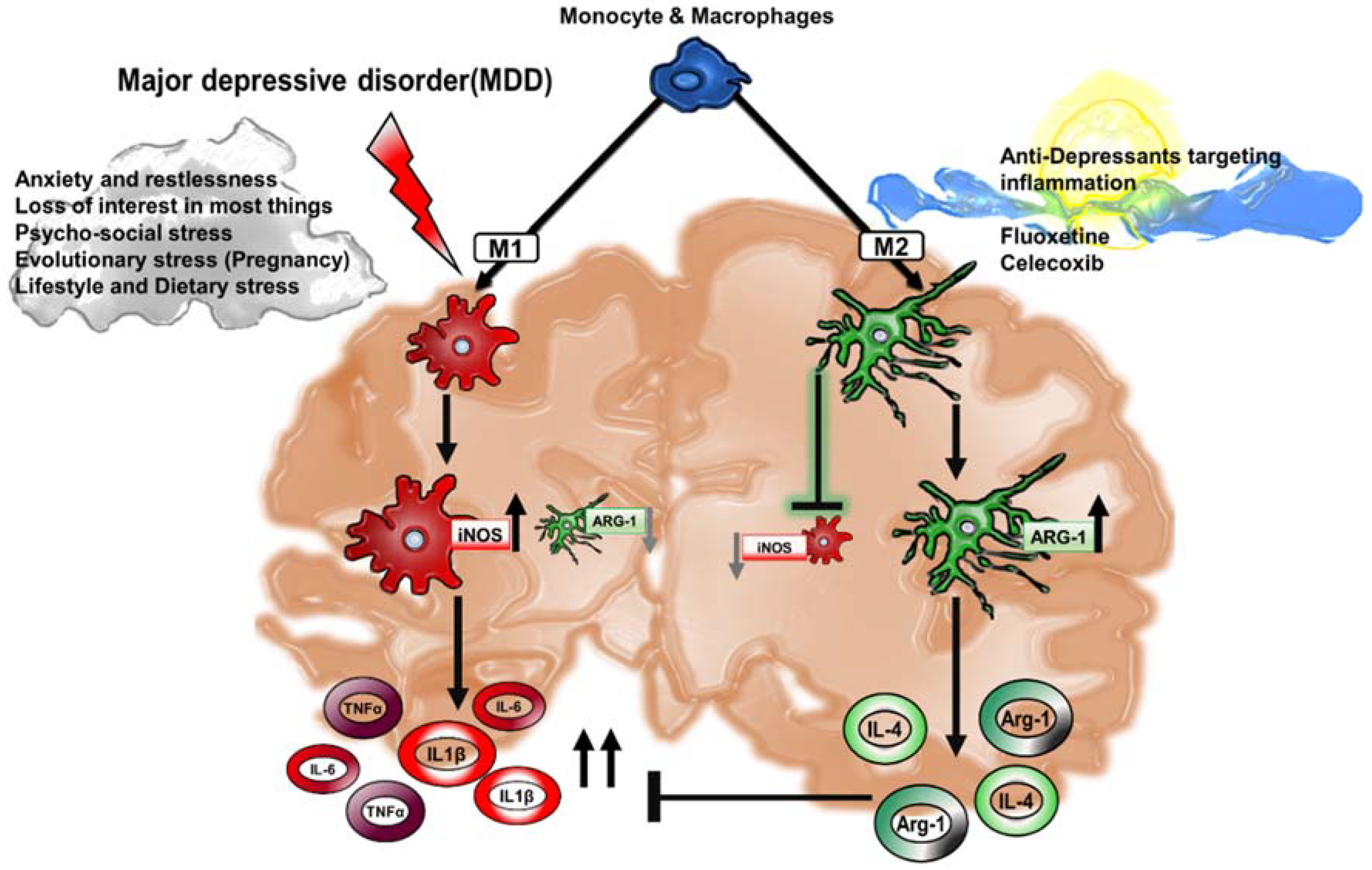
3. Cytokines and Their Role in Major Depressive Disorder
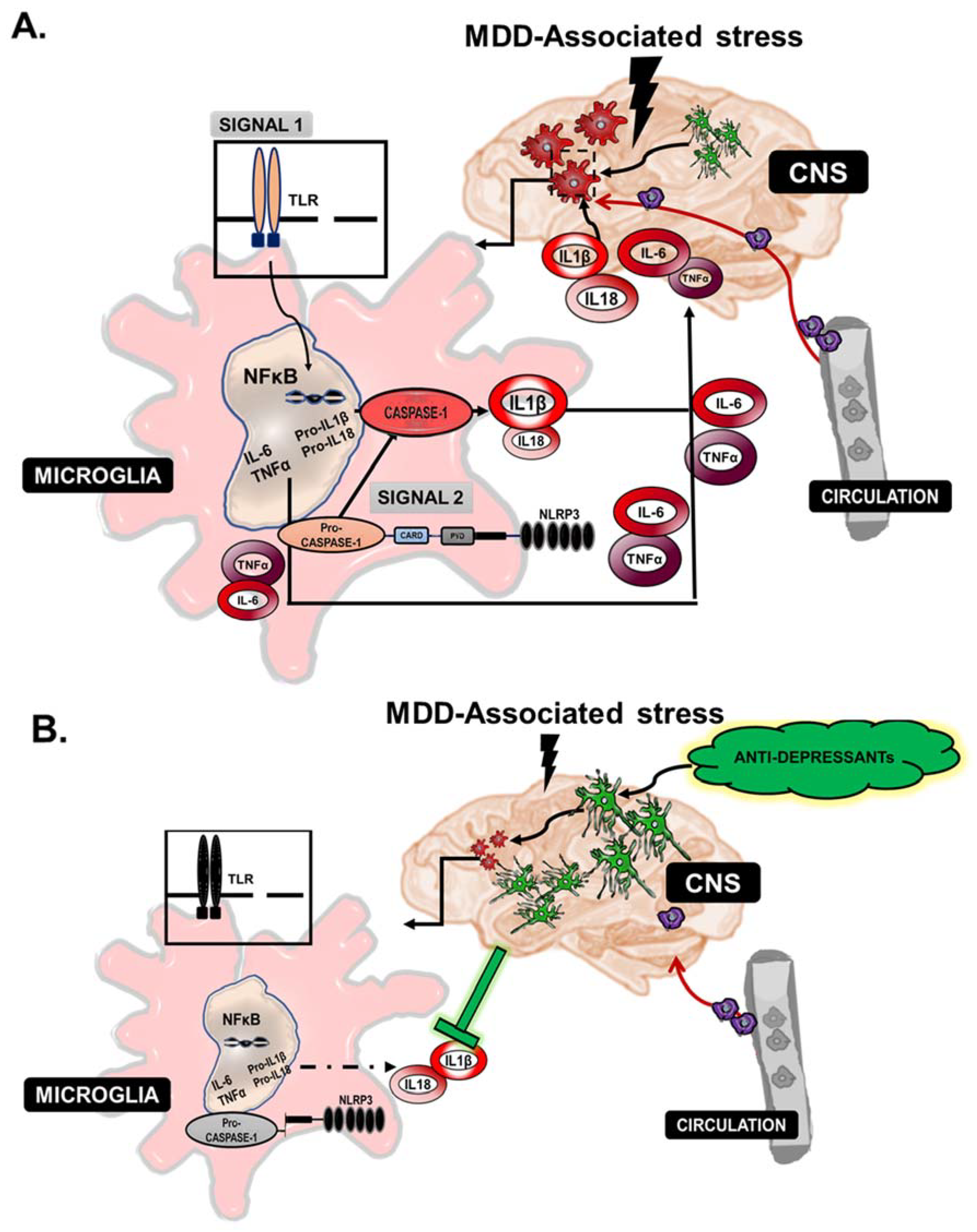
4. The Inflammasome
5. Chronic Inflammation and Links to Depression
6. Drug Therapeutics Targeting Macrophage Polarization
7. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Depression-Fact Sheet. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs369/en/ (accessed on 4 January 2018).
- Bebbington, P. The World Health Report 2001. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2001, 36, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, J.L.; Murray, L.; Lopez, A.D. Evidence-Based Health Policy-Lessons from the Global Burden of Disease Study Published by: American Association for the Advancement of Science Evidence-Based Health Policy-Lessons from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Science 1996, 274, 740–743. [Google Scholar]
- Kessler, R.C. The costs of depression. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lépine, J.P.; Briley, M. The increasing burden of depression. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2011, 7, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najjar, S.; Pearlman, D.M.; Alper, K.; Najjar, A.; Devinsky, O. Neuroinflammation and psychiatric illness. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haapakoski, R.; Ebmeier, K.P.; Alenius, H.; Kivimäki, M. Innate and adaptive immunity in the development of depression: An update on current knowledge and technological advances. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 66, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.W.; Zhang, X.; Huang, W.J. Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3391–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, C.K.; Saijo, K.; Winner, B.; Marchetto, M.C.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms Underlying Inflammation in Neurodegeneration. Cell 2010, 140, 918–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, A.; De Vito, F.; Fresegna, D.; Musella, A.; Buttari, F.; Bullitta, S.; Mandolesi, G.; Centonze, D. Exploring the role of microglia in mood disorders associated with experimental multiple sclerosis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.S. The macrophage theory of depression. Med. Hypotheses 1991, 35, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, M.; Priller, J. Microglia and brain macrophages in the molecular age: From origin to neuropsychiatric disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz, M.; Tay, T.L.; Wolf, Y.; Jung, S. Microglia: Unique and common features with other tissue macrophages. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colton, C.A. Heterogeneity of microglial activation in the innate immune response in the brain. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009, 4, 399–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Pamer, E.G. Monocyte Recruitment during Infection and Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 11, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeway, C.A., Jr. Pillars article: Approaching the asymptote? Evolution and revolution in immunology. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1989. 54: 1-13. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4475–4487. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Italiani, P.; Boraschi, D. From monocytes to M1/M2 macrophages: Phenotypical vs. functional differentiation. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, C.D.; Ley, K. M1 and M2 Macrophages: The Chicken and the Egg of Immunity. J. Innate Immun. 2014, 6, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munder, M.; Eichmann, K.; Morán, J.M.; Centeno, F.; Soler, G.; Modolell, M. Th1/Th2-regulated expression of arginase isoforms in murine macrophages and dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 3771–3777. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mills, C.D.; Kincaid, K.; Alt, J.M.; Heilman, M.J.; Hill, A.M. M-1/M-2 Macrophages and the Th1/Th2 Paradigm. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 6166–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosser, D.M.; Edwards, J.P. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Valin, K.L.; Dixon, M.L.; Leavenworth, J.W. The Role of Microglia and Macrophages in CNS Homeostasis, Autoimmunity, and Cancer. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 5150687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colin, S.; Chinetti-Gbaguidi, G.; Staels, B. Macrophage phenotypes in atherosclerosis. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 262, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, A.; Allen, J.; Hankey-giblin, P.A. Ontogeny and polarization of macrophages in inflammation: Blood monocytes versus tissue macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2015, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, V.H.; Teeling, J. Microglia and macrophages of the central nervous system: The contribution of microglia priming and systemic inflammation to chronic neurodegeneration. Semin. Immunopathol. 2013, 35, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz, M.; Erny, D.; Hagemeyer, N. Ontogeny and homeostasis of CNS myeloid cells. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olah, M.; Biber, K.; Vinet, J.; Boddeke, H.W. Microglia phenotype diversity. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2011, 10, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, C.; Gomez Perdiguero, E.; Chorro, L.; Szabo-Rogers, H.; Cagnard, N.; Kierdorf, K.; Prinz, M.; Wu, B.; Jacobsen, S.E.W.; Pollard, J.W.; et al. A lineage of myeloid cells independent of Myb and hematopoietic stem cells. Science 2012, 336, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggen, B.J.L.; Raj, D.; Hanisch, U.K.; Boddeke, H.W. Microglial phenotype and adaptation. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 807–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajami, B.; Bennett, J.L.; Krieger, C.; McNagny, K.M.; Rossi, F.M. Infiltrating monocytes trigger EAE progression, but do not contribute to the resident microglia pool. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldmann, T.; Wieghofer, P.; Prutek, F.; Hagemeyer, N.; Frenzel, K.; Staszewski, O.; Kierdorf, K.; Amann, L.; Krueger, M.; Locatelli, G.; et al. Origin, fate and dynamics of macrophages at CNS interfaces. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biber, K.; Vinet, J.; Boddeke, H.W. Neuron-microglia signaling: Chemokines as versatile messengers. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 198, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, Y.; Yona, S.; Kim, K.-W.; Jung, S. Microglia, seen from the CX3CR1 angle. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linnartz, B.; Neumann, H. Microglial activatory (immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif)- and inhibitory (immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif)-signaling receptors for recognition of the neuronal glycocalyx. Glia 2013, 61, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koning, N.; Van Eijk, M.; Pouwels, W.; Brouwer, M.S.M.; Voehringer, D.; Huitinga, I.; Hoek, R.M.; Raes, G.; Hamann, J. Expression of the inhibitory CD200 receptor is associated with alternative macrophage activation. J. Innate Immun. 2010, 2, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crain, J.M.; Nikodemova, M.; Watters, J.J. Microglia express distinct M1 and M2 phenotypic markers in the postnatal and adult central nervous system in male and female mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 2013, 91, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varnum, M.M.; Ikezu, T. The classification of microglial activation phenotypes on neurodegeneration and regeneration in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz.) 2012, 60, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezai-Zadeh, K.; Gate, D.; Town, T. CNS infiltration of peripheral immune cells: D-Day for neurodegenerative disease? J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009, 4, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raedler, T.J. Inflammatory mechanisms in major depressive disorder. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2011, 24, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Leonard, B.E.; Myint, A.M.; Kubera, M.; Verkerk, R. The new “5-HT” hypothesis of depression: Cell-mediated immune activation induces indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, which leads to lower plasma tryptophan and an increased synthesis of detrimental tryptophan catabolites (TRYCATs), both of which contribute to the onset of depression. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 702–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichers, M.C.; Koek, G.H.; Robaeys, G.; Verkerk, R.; Scharpé, S.; Maes, M. IDO and interferon-α-induced depressive symptoms: A shift in hypothesis from tryptophan depletion to neurotoxicity. Mol. Psychiatry 2005, 10, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Platas, S.G.; Cruceanu, C.; Chen, G.G.; Turecki, G.; Mechawar, N. Evidence for increased microglial priming and macrophage recruitment in the dorsal anterior cingulate white matter of depressed suicides. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2014, 42, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, T.W.W.; Mletzko, T.C.; Alagbe, O.; Musselman, D.L.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Miller, A.H.; Heim, C.M. Increased Stress-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Male Patients with Major Depression and Increased Early Life Stress. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 1630–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toben, C.; Baune, B.T. An Act of Balance Between Adaptive and Maladaptive Immunity in Depression: A Role for T Lymphocytes. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2015, 10, 595–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Réus, G.Z.; Fries, G.R.; Stertz, L.; Badawy, M.; Passos, I.C.; Barichello, T.; Kapczinski, F.; Quevedo, J. The role of inflammation and microglial activation in the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders. Neuroscience 2015, 300, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corwin, E.J. Understanding Cytokines Part I: Physiology and Mechanism of Action. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2000, 2, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.D.; Nedjai, B.; Hurst, T.; Pennington, D.J. Cytokines and chemokines: At the crossroads of cell signalling and inflammatory disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 2563–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Liang, H.; Zen, K. Molecular mechanisms that influence the macrophage M1-M2 polarization balance. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felger, J.C.; Lotrich, F.E. Inflammatory Cytokines in Depression: Neruobiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Neuroscience 2013, 246, 199–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Chen, L.; Lim, G.; Sung, B.; Wang, S.; Mccabe, M.F. Brain indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase contributes to the comorbidity of pain and depression Hyangin. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2940–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, S.W.; Arevalo, J.M.G.; Takahashi, R.; Sloan, E.K.; Lutgendorf, S.K.; Sood, A.K.; Sheridan, J.F.; Seeman, T.E. Computational identification of gene-social environment interaction at the human IL6 locus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5681–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monje, F.J.; Cabatic, M.; Divisch, I.; Kim, E.-J.; Herkner, K.R.; Binder, B.R.; Pollak, D.D. Constant Darkness Induces IL-6-Dependent Depression-Like Behavior through the NF-B Signaling Pathway. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 9075–9083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodes, G.E.; Ménard, C.; Russo, S.J. Integrating Interleukin-6 into depression diagnosis and treatment. Neurobiol. Stress 2016, 4, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, L.; Zhang, X.D.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.W.; Yang, C.C.; Rao, C.L.; Zhou, C.J.; Zeng, L.; Zhao, L.B.; Fang, L.; et al. Pioglitazone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behaviors, modulates NF-κB/IL-6/STAT3, CREB/BDNF pathways and central serotonergic neurotransmission in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 49, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postal, M.; Lapa, A.T.; Sinicato, N.A.; de Oliveira Peliçari, K.; Peres, F.A.; Costallat, L.T.L.; Fernandes, P.T.; Marini, R.; Appenzeller, S. Depressive symptoms are associated with tumor necrosis factor alpha in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Probert, L.; Akassoglou, K.; Kassiotis, G.; Pasparakis, M.; Alexopoulou, L.; Kollias, G. TNF-α transgenic and knockout models of CNS inflammation and degeneration. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997, 72, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, A.J. Cytokine Activation of the HPA Axis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 917, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christmas, D.M.; Potokar, J.P.; Davies, S.J.C. A biological pathway linking inflammation and depression: Activation of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2011, 7, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myint, A.M.; Kim, Y.K. Cytokine-serotonin interaction through IDO: A neurodegeneration hypothesis of depression. Med. Hypotheses 2003, 61, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.M.; Scully, P.; Fitzgerald, P.; Scott, L.V.; Dinan, T.G. Plasma cytokine profiles in depressed patients who fail to respond to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor therapy. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2007, 41, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roumestan, C.; Michel, A.; Bichon, F.; Portet, K.; Detoc, M.; Henriquet, C.; Jaffuel, D.; Mathieu, M. Anti-inflammatory properties of desipramine and fluoxetine. Respir. Res. 2007, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmerich, H.; Fischer, J.; Bauer, K.; Kirkby, K.C.; Sack, U.; Krügel, U. Stress-induced cytokine changes in rats. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2013, 24, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettencourt, A.; Leal, B.; Ferreira, M.; Carvalho, C.; Moreira, I.; Santos, E.; Pinho, P.; Silva, B.; Cavaco, S.; Silva, A.M. Depression symptoms in multiple sclerosis patients- The role of IL1B. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 381, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porterfield, V.M.; Zimomra, Z.R.; Caldwell, E.A.; Camp, R.M.; Gabella, K.M.; Johnson, J.D. Rat strain differences in restraint stress induced brain cytokines. Neuroscience 2011, 188, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laumet, G.; Zhou, W.; Dantzer, R.; Edralin, J.D.; Huo, X.J.; Budac, D.P.; O’Connor, J.C.; Lee, A.W.; Heijnen, C.J.; Kavelaars, A. Upregulation of neuronal kynurenine 3-monooxygenase mediates depression-like behavior in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxenkrug, G.F. Tryptophan-kynurenine metabolism as a common mediator of genetic and environmental impacts in major depressive disorder: The serotonin hypothesis revisited 40 years later. Isr. J. Psychiatry Relat. Sci. 2010, 47, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, J.C.; Lawson, M.A.; André, C.; Moreau, M.; Lestage, J.; Castanon, N.; Kelley, K.W.; Dantzer, R. Lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior is mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activation in mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. The history of fever, leukocytic pyrogen and interleukin-1. Temperature 2015, 2, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, M.H.; Reimer, T.; Kim, Y.; Nuñez, G. NOD-like Receptors (NLRs): Bona Fide Intracellular Microbial Sensors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009, 20, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Hara, H.; Núñez, G. Mechanism and Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liston, A.; Masters, S.L. Homeostasis-altering molecular processes as mechanisms of inflammasome activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilig, R.; Broz, P. Function and mechanism of the pyrin inflammasome. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 48, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, T.T.; Forni, M.F.; Correa-Costa, M.; Ramos, R.N.; Barbuto, J.A.; Branco, P.; Castoldi, A.; Hiyane, M.I.; Davanso, M.R.; Latz, E.; et al. Soluble Uric Acid Activates the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duewell, P.; Kono, H.; Rayner, K.J.; Sirois, C.M.; Bauernfeind, F.G.; Abela, G.S.; Franchi, L.; Nuñez, G.; Espevik, T.; Lien, E.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature 2010, 464, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsbury, S.R.; Conaghan, P.G.; McDermott, M.F. The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in gout. J. Inflamm. Res. 2011, 4, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajamäki, K.; Lappalainen, J.; Öörni, K.; Välimäki, E.; Matikainen, S.; Kovanen, P.T.; Kari, E.K. Cholesterol crystals activate the NLRP3 inflammasome in human macrophages: A novel link between cholesterol metabolism and inflammation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.G.; Muruve, D.A.; Power, C. Inflammasomes in the CNS. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latz, E.; Xiao, T.S.; Stutz, A. Activation and regulation of the inflammasomes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasco, J.A.; Nicholson, G.C.; Williams, L.J.; Jacka, F.N.; Henry, M.J.; Kotowicz, M.A.; Schneider, H.G.; Leonard, B.E.; Berk, M. Association of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein with de novo major depression. Br. J. Psychiatry 2010, 197, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantaratnotai, N.; Mosikanon, K.; Lee, Y.; McIntyre, R.S. The interface of depression and obesity. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira-Miranda, E.; Costa, P.R.F.; Queiroz, V.A.O.; Pereira-Santos, M.; Santana, M.L.P. Overweight and Obesity Associated with Higher Depression Prevalence in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2017, 36, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Xiao, L. Obesity and depression in US women: Results from the 2005-2006 national health and nutritional examination survey. Obesity 2010, 18, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvahill, J.S.; Nicol, G.E.; Dixon, D.; Lenze, E.J.; Karp, J.F.; Reynolds, C.F.; Blumberger, D.M.; Mulsant, B.H. Effect of Metabolic Syndrome on Late-Life Depression: Associations with Disease Severity and Treatment Resistance. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 2651–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amano, S.U.; Cohen, J.L.; Vangala, P.; Tencerova, M.; Sarah, M.; Yawe, J.C.; Shen, Y.; Czech, M.P.; Aouadi, M. Local proliferation of macrophages contributes to obesity- associated adipose tissue inflammation. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Santibañez, G.; Nien-Kai Lumeng, C. Macrophages and the Regulation of Adipose Tissue Remodeling. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2014, 34, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity induces a phenotipic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanthier, N.; Molendi-Coste, O.; Horsmans, Y.; van Rooijen, N.; Cani, P.D.; Leclercq, I.A. Kupffer cell activation is a causal factor for hepatic insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G107–G116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Allen, J.N.; Dey, A.; Zhang, L.; Balandaram, G.; Kennett, M.J.; Xia, M.; Peters, J.M.; Patterson, A.; Hankey-Giblin, P.A. The Ron Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Regulates Macrophage Heterogeneity and Plays a Protective Role in Diet-Induced Obesity, Atherosclerosis, and Hepatosteatosis. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, A.; Allen, J.N.; Fraser, J.W.; Snyder, L.M.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Paulson, R.F.; Patterson, A.; Cantorna, M.T.; Hankey-Giblin, P.A. Neuroprotective Role of the Ron Receptor Tyrosine kinase underlying CNS Inflammation in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, C.D.; Lenz, L.L.; Ley, K. Macrophages at the fork in the road to health or disease. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikita, J.; Dubourdieu-Cassagno, N.; Deloire, M.S.; Vekris, A.; Biran, M.; Raffard, G.; Brochet, B.; Canron, M.H.; Franconi, J.M.; Boiziau, C.; et al. Altered M1/M2 activation patterns of monocytes in severe relapsing experimental rat model of multiple sclerosis. Amelioration of clinical status by M2 activated monocyte administration. Mult. Scler. J. 2011, 17, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horikawa, H.; Kato, T.A.; Mizoguchi, Y.; Monji, A.; Seki, Y.; Ohkuri, T.; Gotoh, L.; Yonaha, M.; Ueda, T.; Hashioka, S.; et al. Inhibitory effects of SSRIs on IFN-γ induced microglial activation through the regulation of intracellular calcium. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 34, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durairaj, H.; Steury, M.D.; Parameswaran, N. Paroxetine differentially modulates LPS-induced TNFα and IL-6 production in mouse macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 25, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talmon, M.; Rossi, S.; Pastore, A.; Cattaneo, C.I.; Brunelleschi, S.; Fresu, L.G. Vortioxetine exerts anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects on human monocytes/macrophages. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, O.; Krogh, J.; Mors, O.; Eriksen Benros, M. Inflammation in Depression and the Potential for Anti-Inflammatory Treatment. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, O.; Benros, M.E.; Nordentoft, M.; Farkouh, M.E.; Iyengar, R.L.; Mors, O.; Krogh, J. Effect of anti-inflammatory treatment on depression, depressive symptoms, and adverse effects a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. JAMA Psychiatry 2014, 71, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilici, M.; Efe, H.; Köroğlu, M.A.; Uydu, H.A.; Bekaroğlu, M.; Değer, O. Antioxidative enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in major depression: Alterations by antidepressant treatments. J. Affect. Disord. 2001, 64, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Chiba, K. Role of microglial M1/M2 polarization in relapse and remission of psychiatric disorders and diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2014, 7, 1028–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyama, S.; Ishikawa, Y.; Yoshikawa, K.; Shimoda, K.; Ide, S.; Satoh, M.; Minami, M. Resolvin D1 and D2 Reverse Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Depression-Like Behaviors Through the mTORC1 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, B.; Yoon, Y.-S.; Le Lay, J.; Kaestner, K.H.; Hedrick, S.; Montminy, M. CREB pathway links PGE2 signaling with macrophage polarization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15642–15647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.; Vaidya, V.A. Cyclic AMP response element binding protein and brain-derived neurotrophic factor: Molecules that modulate our mood? J. Biosci. 2006, 31, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dey, A.; Hankey Giblin, P.A. Insights into Macrophage Heterogeneity and Cytokine-Induced Neuroinflammation in Major Depressive Disorder. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030064
Dey A, Hankey Giblin PA. Insights into Macrophage Heterogeneity and Cytokine-Induced Neuroinflammation in Major Depressive Disorder. Pharmaceuticals. 2018; 11(3):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030064
Chicago/Turabian StyleDey, Adwitia, and Pamela A. Hankey Giblin. 2018. "Insights into Macrophage Heterogeneity and Cytokine-Induced Neuroinflammation in Major Depressive Disorder" Pharmaceuticals 11, no. 3: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030064
APA StyleDey, A., & Hankey Giblin, P. A. (2018). Insights into Macrophage Heterogeneity and Cytokine-Induced Neuroinflammation in Major Depressive Disorder. Pharmaceuticals, 11(3), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030064




