Interactions Between Epilepsy and Plasticity
Abstract
1. Introduction
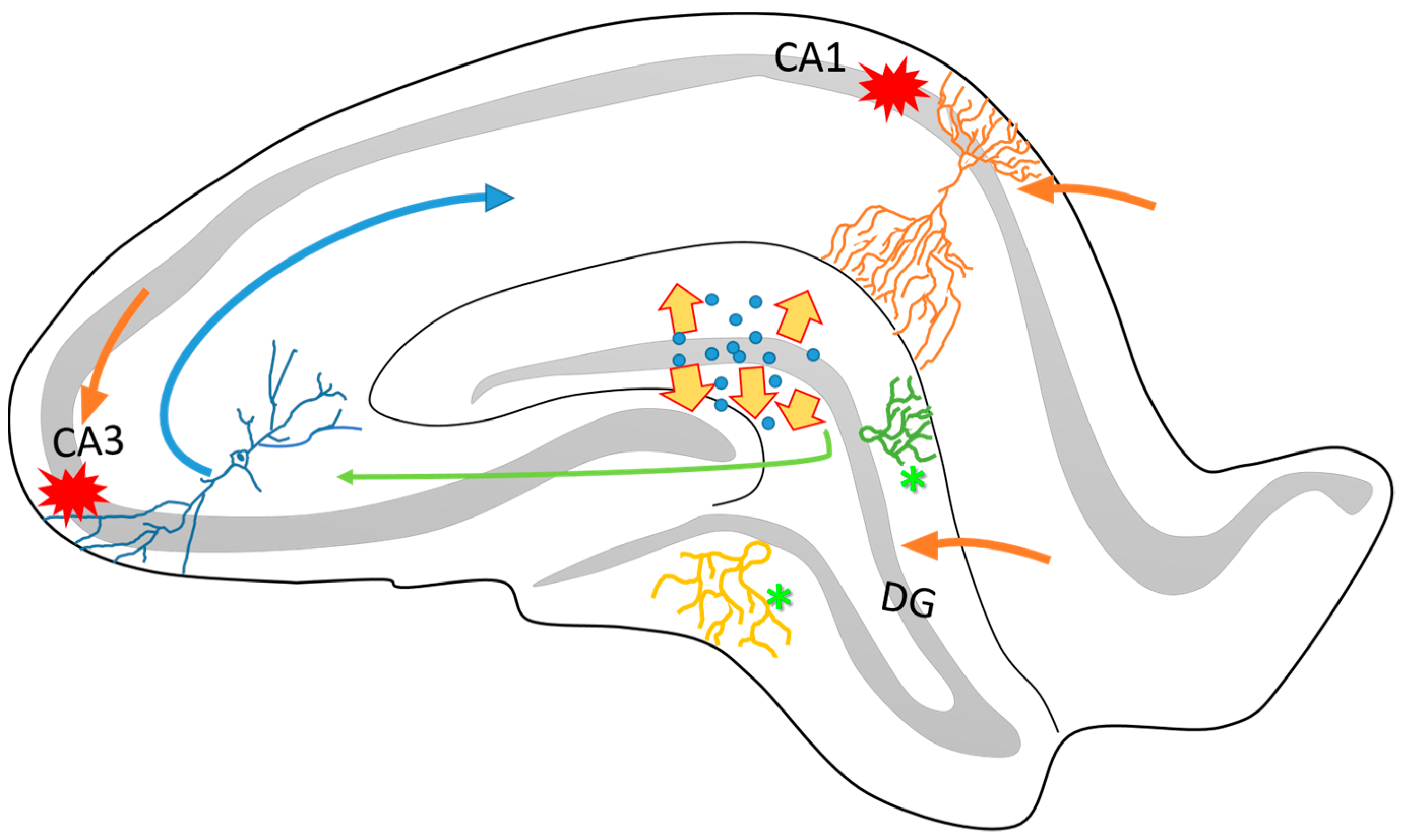
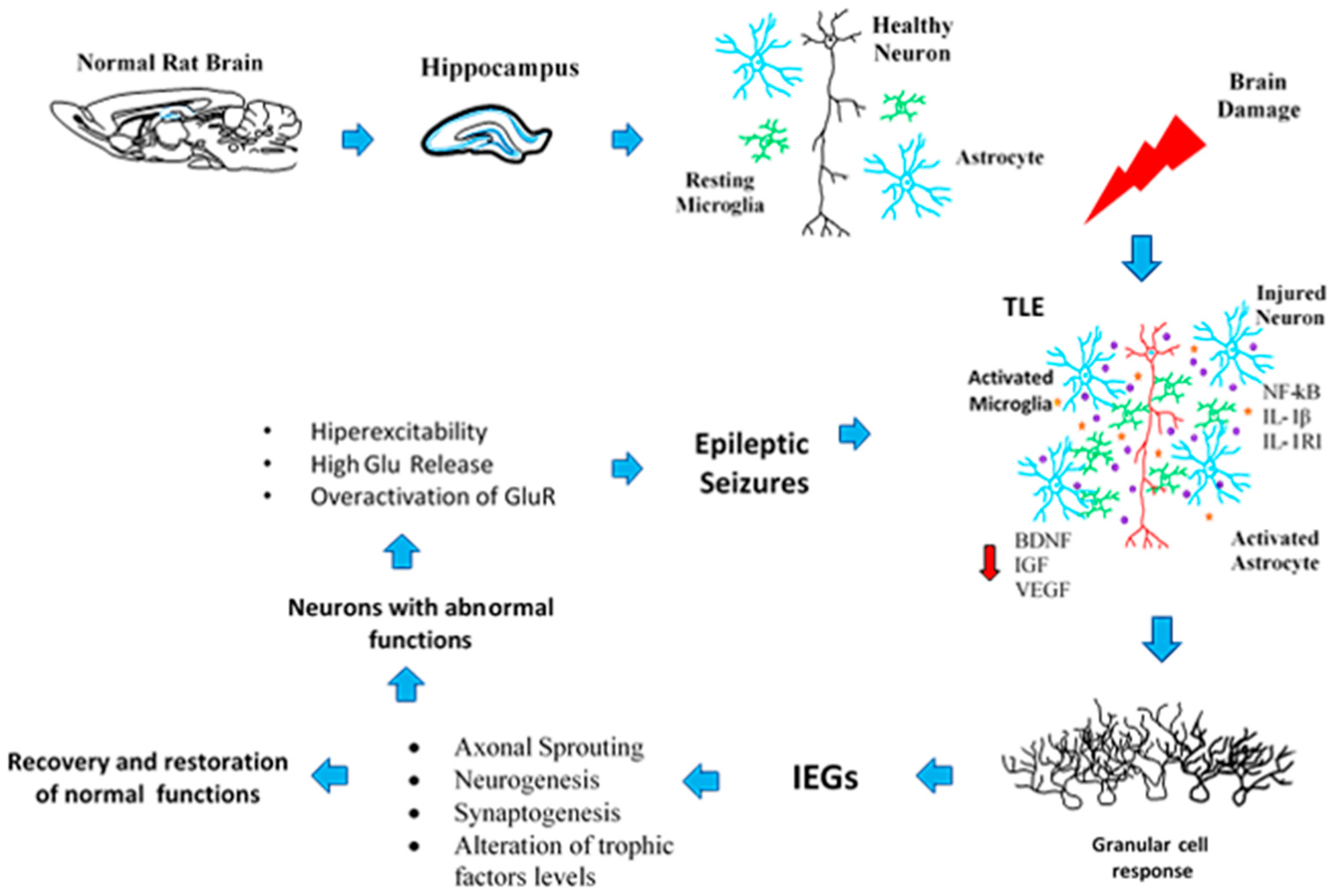
2. Neuroplasticity in the Epileptogenic Hippocampus
3. Axonal Sprouting: Hippocampal Cell Response to Epileptic Seizures
4. Transcriptional Changes Related to Seizures and the Neuroplasticity Process
5. Changes in the Neurotransmission Systems by Seizures Related to Neuroplasticity
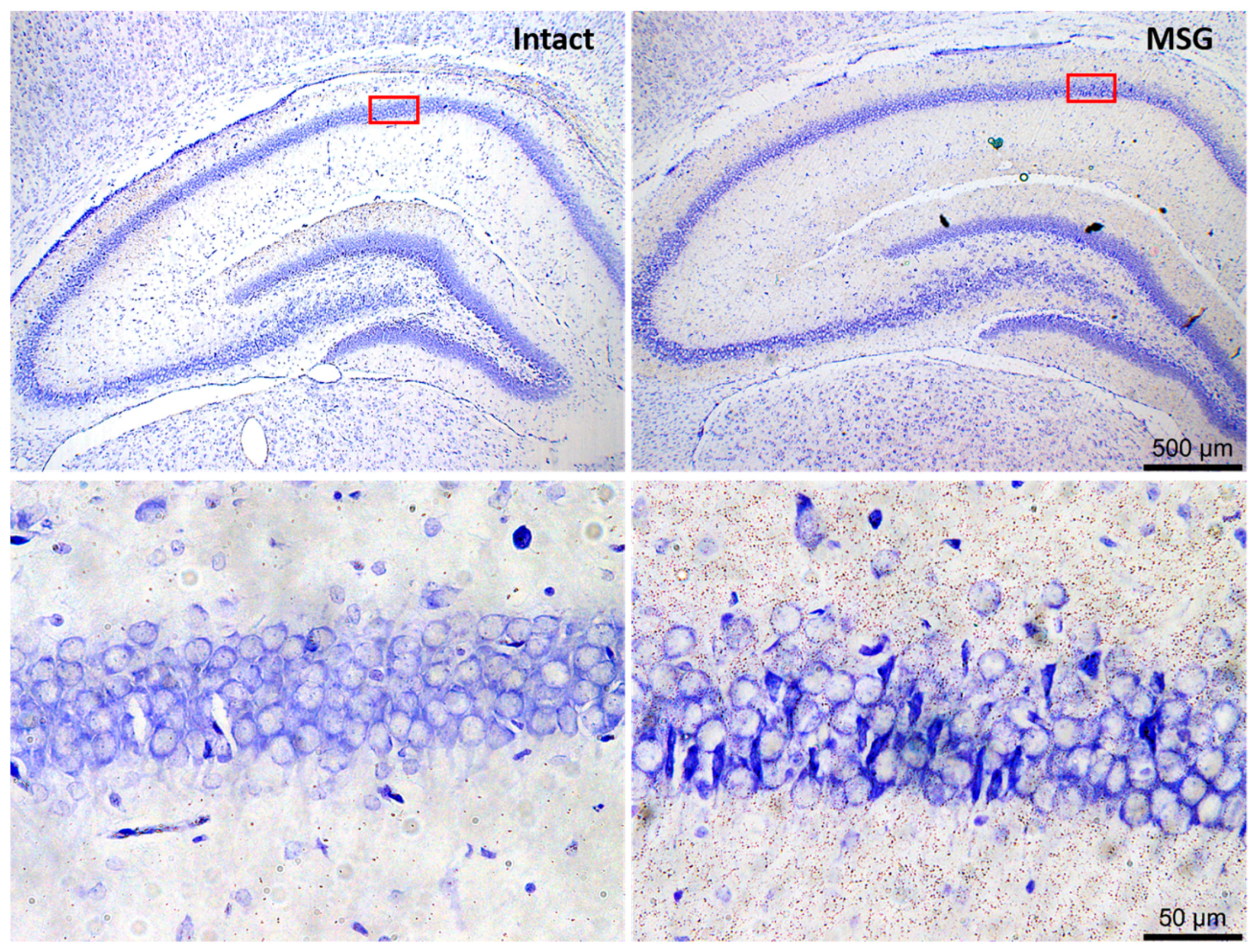
6. Neuronal and Glial Responses in the Hippocampus after Epileptic Seizures
7. Neurogenic and Synaptogenic Responses to Epileptic Seizures
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nieto-Sampedro, M.; Nieto-Diaz, M. Neural plasticity: Changes with age. J. Neural Transm. 2005, 112, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebb, D.O. Spontaneous neurosis in chimpanzees; theoretical relations with clinical and experimental phenomena. Psychosom. Med. 1947, 9, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnati, L.F.; Benfenati, F.; Solfrini, V.; Biagini, G.; Fuxe, K.; Guidolin, D.; Carani, C.; Zini, I. Brain aging and neuronal plasticity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1992, 673, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnati, L.F.; Zoli, M.; Biagini, G.; Fuxe, K. Neuronal plasticity and ageing processes in the frame of the ‘red queen theory’. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1992, 145, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach-y-Rita, P. Brain plasticity as a basis for recovery of function in humans. Neuropsychologia 1990, 28, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, J.H.; Merzenich, M.M.; Killackey, H.P. The reorganization of somatosensory cortex following peripheral nerve damage in adult and developing mammals. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1983, 6, 325–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, P.D.; Egger, M.D. Formation of new connexions in adult rat brains after partial deafferentation. Nature 1971, 232, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinow, R.; Malenka, R.C. Ampa receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 25, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, F.Y.; Fatemi, A.; Johnston, M.V. Cerebral plasticity: Windows of opportunity in the developing brain. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2017, 21, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, M.; Pozzo-Miller, L. Dendritic spine dysgenesis in autism related disorders. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 601, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glausier, J.R.; Lewis, D.A. Dendritic spine pathology in schizophrenia. Neuroscience 2013, 251, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekar, A.; Bialas, A.R.; de Rivera, H.; Davis, A.; Hammond, T.R.; Kamitaki, N.; Tooley, K.; Presumey, J.; Baum, M.; Van Doren, V.; et al. Schizophrenia risk from complex variation of complement component 4. Nature 2016, 530, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirtz, D.; Thurman, D.J.; Gwinn-Hardy, K.; Mohamed, M.; Chaudhuri, A.R.; Zalutsky, R. How common are the “common” neurologic disorders? Neurology 2007, 68, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonansco, C.; Fuenzalida, M. Plasticity of hippocampal excitatory-inhibitory balance: Missing the synaptic control in the epileptic brain. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 8607038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitkanen, A.; Sutula, T.P. Is epilepsy a progressive disorder? Prospects for new therapeutic approaches in temporal-lobe epilepsy. Lancet Neurol. 2002, 1, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.V. Losing neurons: Selective vulnerability and mesial temporal sclerosis. Epilepsia 2005, 46 (Suppl. 7), 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, S.; Okada, M.; Kaneko, S.; Mitsudome, A. Are some idiopathic epilepsies disorders of ion channels?: A working hypothesis. Epilepsy Res. 2000, 41, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkovic, S.F.; Scheffer, I.E. Genetics of the epilepsies. Epilepsia 2001, 42 (Suppl. 5), 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkum, J.M. Migraine triggers and oxidative stress: A narrative review and synthesis. Headache 2016, 56, 12–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathern, G.W.; Pretorius, J.K.; Babb, T.L. Influence of the type of initial precipitating injury and at what age it occurs on course and outcome in patients with temporal lobe seizures. J. Neurosurg. 1995, 82, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathern, G.W.; Babb, T.L.; Leite, J.P.; Pretorius, K.; Yeoman, K.M.; Kuhlman, P.A. The pathogenic and progressive features of chronic human hippocampal epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 1996, 26, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, J.A.; Williamson, P.D.; Thadani, V.M.; Darcey, T.M.; Mattson, R.H.; Spencer, S.S.; Spencer, D.D. Characteristics of medial temporal lobe epilepsy: I. Results of history and physical examination. Ann. Neurol. 1993, 34, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J., Jr. Ilae classification of epilepsy syndromes. Epilepsy Res. 2006, 70 (Suppl. 1), S5–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, D.G.; Witter, M.P. The three-dimensional organization of the hippocampal formation: A review of anatomical data. Neuroscience 1989, 31, 571–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennerici, M.G.; Szabo, K. Preface. Hippocampus from a neurologist’s point of view. Front. Neurol. Neurosci. 2014, 34, IX. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrone, D.F.; Petit, T.L. The role of synaptic morphology in neural plasticity: Structural interactions underlying synaptic power. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2002, 38, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drapeau, E.; Mayo, W.; Aurousseau, C.; Le Moal, M.; Piazza, P.V.; Abrous, D.N. Spatial memory performances of aged rats in the water maze predict levels of hippocampal neurogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14385–14390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.; Bassett, D.S.; Wisse, L.E.M.; Detre, J.A.; Stein, J.M.; Yushkevich, P.A.; Shinohara, R.T.; Pluta, J.B.; Valenciano, E.; Daffner, M.; et al. Mapping the structural and functional network architecture of the medial temporal lobe using 7t mri. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathern, G.W.; Adelson, P.D.; Cahan, L.D.; Leite, J.P. Hippocampal neuron damage in human epilepsy: Meyer’s hypothesis revisited. Prog. Brain Res. 2002, 135, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mathern, G.W.; Leiphart, J.L.; De Vera, A.; Adelson, P.D.; Seki, T.; Neder, L.; Leite, J.P. Seizures decrease postnatal neurogenesis and granule cell development in the human fascia dentata. Epilepsia 2002, 43 (Suppl. 5), 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J., Jr. Intractable epilepsy: Definition and neurobiology. Epilepsia 2001, 42 (Suppl. 6), 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, M.; Eriksson, S.; Martinian, L.; Caboclo, L.O.; McEvoy, A.W.; Duncan, J.S.; Sisodiya, S.M. Temporal lobe sclerosis associated with hippocampal sclerosis in temporal lobe epilepsy: Neuropathological features. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 68, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panayiotopoulos, C.P. Evidence-based epileptology, randomized controlled trials, and sanad: A critical clinical view. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, J.C.; Delanty, N. Epidemiology and classification of epilepsy: Gender comparisons. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2008, 83, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tellez-Zenteno, J.F.; Ladino, L.D. [Temporal epilepsy: Clinical, diagnostic and therapeutic aspects]. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 56, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, E.; Santos, N.F.; Torres, F.R.; Secolin, R.; Sardinha, L.A.; Lopez-Cendes, I.; Cendes, F. Magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities in familial temporal lobe epilepsy with auditory auras. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 1546–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodore, W.H.; Epstein, L.; Gaillard, W.D.; Shinnar, S.; Wainwright, M.S.; Jacobson, S. Human herpes virus 6b: A possible role in epilepsy? Epilepsia 2008, 49, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cendes, F.; Kobayashi, E.; Lopes-Cendes, I. Familial temporal lobe epilepsy with auditory features. Epilepsia 2005, 46 (Suppl. 10), 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmazer-Hanke, D.M.; Wolf, H.K.; Schramm, J.; Elger, C.E.; Wiestler, O.D.; Blumcke, I. Subregional pathology of the amygdala complex and entorhinal region in surgical specimens from patients with pharmacoresistant temporal lobe epilepsy. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 59, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloviter, R.S. Hippocampal epileptogenesis in animal models of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis: The importance of the “latent period” and other concepts. Epilepsia 2008, 49 (Suppl. 9), 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benbadis, S.; Helmers, S.; Hirsch, L.; Sirven, J.; Vale, F.L.; Wheless, J. Yes, neurostimulation has a role in the management of epilepsy. Neurology 2014, 83, 845–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartzkroin, P.A. Hippocampal slices in experimental and human epilepsy. Adv. Neurol. 1986, 44, 991–1010. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bercovici, E.; Kumar, B.S.; Mirsattari, S.M. Neocortical temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res Treat 2012, 2012, 103160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumcke, I.; Thom, M.; Aronica, E.; Armstrong, D.D.; Bartolomei, F.; Bernasconi, A.; Bernasconi, N.; Bien, C.G.; Cendes, F.; Coras, R.; et al. International consensus classification of hippocampal sclerosis in temporal lobe epilepsy: A task force report from the ilae commission on diagnostic methods. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Ari, Y.; Cossart, R. Kainate, a double agent that generates seizures: Two decades of progress. Trends Neurosci. 2000, 23, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, D.J.; Cavazos, J.E. Synaptic reorganization in subiculum and ca3 after early-life status epilepticus in the kainic acid rat model. Epilepsy Res. 2007, 73, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, D.D.; Spencer, S.S. Hippocampal resections and the use of human tissue in defining temporal lobe epilepsy syndromes. Hippocampus 1994, 4, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, S.S. Substrates of localization-related epilepsies: Biologic implications of localizing findings in humans. Epilepsia 1998, 39, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, S.S.; Spencer, D.D. Entorhinal-hippocampal interactions in medial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 1994, 35, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, I.; Bower, M.R.; Leyva, F.; Buckmaster, P.S. Early activation of ventral hippocampus and subiculum during spontaneous seizures in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 11100–11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkovic, S.F.; Andermann, F.; Olivier, A.; Ethier, R.; Melanson, D.; Robitaille, Y.; Kuzniecky, R.; Peters, T.; Feindel, W. Hippocampal sclerosis in temporal lobe epilepsy demonstrated by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann. Neurol. 1991, 29, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemori, T.; Toda, K.; Seki, T. Seizure severity-dependent selective vulnerability of the granule cell layer and aberrant neurogenesis in the rat hippocampus. Hippocampus 2017, 27, 1054–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavazos, J.E.; Zhang, P.; Qazi, R.; Sutula, T.P. Ultrastructural features of sprouted mossy fiber synapses in kindled and kainic acid-treated rats. J Comp. Neurol. 2003, 458, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckmaster, P.S. Mossy fiber sprouting in the dentate gyrus. In Jasper’s Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies, 4th ed.; Noebels, J.L., Avoli, M., Rogawski, M.A., Olsen, R.W., Delgado-Escueta, A.V., Eds.; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ribak, C.E.; Shapiro, L.A.; Yan, X.X.; Dashtipour, K.; Nadler, J.V.; Obenaus, A.; Spigelman, I.; Buckmaster, P.S. Seizure-induced formation of basal dendrites on granule cells of the rodent dentate gyrus. In Jasper’s Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies, 4th ed.; Noebels, J.L., Avoli, M., Rogawski, M.A., Olsen, R.W., Delgado-Escueta, A.V., Eds.; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Parent, J.M.; Kron, M.M. Neurogenesis and epilepsy. In Jasper’s Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies, 4th ed.; Noebels, J.L., Avoli, M., Rogawski, M.A., Olsen, R.W., Delgado-Escueta, A.V., Eds.; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cornejo, B.J.; Mesches, M.H.; Coultrap, S.; Browning, M.D.; Benke, T.A. A single episode of neonatal seizures permanently alters glutamatergic synapses. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, K.; Fahnestock, M.; Racine, R.J. Kindling and status epilepticus models of epilepsy: Rewiring the brain. Prog. Neurobiol. 2004, 73, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arellano, J.I.; Munoz, A.; Ballesteros-Yanez, I.; Sola, R.G.; DeFelipe, J. Histopathology and reorganization of chandelier cells in the human epileptic sclerotic hippocampus. Brain 2004, 127, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proper, E.A.; Oestreicher, A.B.; Jansen, G.H.; Veelen, C.W.; van Rijen, P.C.; Gispen, W.H.; de Graan, P.N. Immunohistochemical characterization of mossy fibre sprouting in the hippocampus of patients with pharmaco-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain J. Neurol. 2000, 123 Pt 1, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, J.O.; Huang, Y.Z.; Leonard, A.S. Molecular signaling mechanisms underlying epileptogenesis. Sci. STKE 2006, 2006, re12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Ari, Y. Cell death and synaptic reorganizations produced by seizures. Epilepsia 2001, 42 (Suppl. 3), 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuunanen, J.; Lukasiuk, K.; Halonen, T.; Pitkanen, A. Status epilepticus-induced neuronal damage in the rat amygdaloid complex: Distribution, time-course and mechanisms. Neuroscience 1999, 94, 473–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riba-Bosch, A.; Perez-Clausell, J. Response to kainic acid injections: Changes in staining for zinc, fos, cell death and glial response in the rat forebrain. Neuroscience 2004, 125, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfman, H.E. The neurobiology of epilepsy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2007, 7, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathern, G.W.; Babb, T.L.; Vickrey, B.G.; Melendez, M.; Pretorius, J.K. The clinical-pathogenic mechanisms of hippocampal neuron loss and surgical outcomes in temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain J. Neurol. 1995, 118 Pt 1, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steward, O. Cholinergic sprouting is blocked by repeated induction of electroconvulsive seizures, a manipulation that induces a persistent reactive state in astrocytes. Exp. Neurol. 1994, 129, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larner, A.J. Axonal sprouting and synaptogenesis in temporal lobe epilepsy: Possible pathogenetic and therapeutic roles of neurite growth inhibitory factors. Seizure 1995, 4, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloviter, R.S. The functional organization of the hippocampal dentate gyrus and its relevance to the pathogenesis of temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 1994, 35, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeiser, B.; Zentner, J.; Prinz, M.; Brandt, A.; Freiman, T.M. Extent of mossy fiber sprouting in patients with mesiotemporal lobe epilepsy correlates with neuronal cell loss and granule cell dispersion. Epilepsy Res. 2017, 129, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringer, J.L.; Agarwal, K.S.; Dure, L.S. Is cell death necessary for hippocampal mossy fiber sprouting? Epilepsy Res. 1997, 27, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althaus, A.L.; Zhang, H.; Parent, J.M. Axonal plasticity of age-defined dentate granule cells in a rat model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 86, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutula, T.P.; Dudek, F.E. Unmasking recurrent excitation generated by mossy fiber sprouting in the epileptic dentate gyrus: An emergent property of a complex system. Prog. Brain Res. 2007, 163, 541–563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sutula, T.; Cascino, G.; Cavazos, J.; Parada, I.; Ramirez, L. Mossy fiber synaptic reorganization in the epileptic human temporal lobe. Ann. Neurol. 1989, 26, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloviter, R.S. A simplified timm stain procedure compatible with formaldehyde fixation and routine paraffin embedding of rat brain. Brain Res. Bull. 1982, 8, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckmaster, P.S.; Zhang, G.F.; Yamawaki, R. Axon sprouting in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy creates a predominantly excitatory feedback circuit. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 6650–6658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Babb, T.L. Bilateral pathological damage in temporal lobe epilepsy. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 1991, 18, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendotti, C.; Pende, M.; Samanin, R. Expression of gap-43 in the granule cells of rat hippocampus after seizure-induced sprouting of mossy fibres: In situ hybridization and immunocytochemical studies. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1994, 6, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Represa, A.; Pollard, H.; Moreau, J.; Ghilini, G.; Khrestchatisky, M.; Ben-Ari, Y. Mossy fiber sprouting in epileptic rats is associated with a transient increased expression of alpha-tubulin. Neurosci. Lett. 1993, 156, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, E.Y.; Lai, Y.J. In vivo microdialysis study of excitatory and inhibitory amino acid levels in the hippocampus following penicillin-induced seizures in mature rats. Acta Paediatr. Taiwan 2002, 43, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tessier-Lavigne, M.; Goodman, C.S. The molecular biology of axon guidance. Science 1996, 274, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oestreicher, A.B.; De Graan, P.N.; Gispen, W.H.; Verhaagen, J.; Schrama, L.H. B-50, the growth associated protein-43: Modulation of cell morphology and communication in the nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 1997, 53, 627–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naffah-Mazzacoratti, M.G.; Funke, M.G.; Sanabria, E.R.; Cavalheiro, E.A. Growth-associated phosphoprotein expression is increased in the supragranular regions of the dentate gyrus following pilocarpine-induced seizures in rats. Neuroscience 1999, 91, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegg, M.H.; Savic, N.; Ehrengruber, M.U.; McKinney, R.A.; Gahwiler, B.H. Epileptiform activity in rat hippocampus strengthens excitatory synapses. J. Physiol. 2004, 554, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, L.; Tokay, T.; Porath, K.; Kohling, R.; Kirschstein, T. Enhanced nmda receptor-dependent ltp in the epileptic ca1 area via upregulation of nr2b. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 54, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.L.; Shatskikh, T.N.; Liu, X.; Holmes, G.L. Impaired single cell firing and long-term potentiation parallels memory impairment following recurrent seizures. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 3667–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.; Bozon, B.; Laroche, S. How necessary is the activation of the immediate early gene zif268 in synaptic plasticity and learning? Behav. Brain Res. 2003, 142, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhade, S.N.; Jensen, F.E. Epileptogenesis in the immature brain: Emerging mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2009, 5, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plath, N.; Ohana, O.; Dammermann, B.; Errington, M.L.; Schmitz, D.; Gross, C.; Mao, X.; Engelsberg, A.; Mahlke, C.; Welzl, H.; et al. Arc/arg3.1 is essential for the consolidation of synaptic plasticity and memories. Neuron 2006, 52, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gass, P.; Katsura, K.; Zuschratter, W.; Siesjo, B.; Kiessling, M. Hypoglycemia-elicited immediate early gene expression in neurons and glia of the hippocampus: Novel patterns of fos, jun, and krox expression following excitotoxic injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1995, 15, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, P.E.; Alexi, T.; Walton, M.; Williams, C.E.; Dragunow, M.; Clark, R.G.; Gluckman, P.D. Activity and injury-dependent expression of inducible transcription factors, growth factors and apoptosis-related genes within the central nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 1999, 57, 421–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapska, E.; Kaczmarek, L. A gene for neuronal plasticity in the mammalian brain: Zif268/egr-1/ngfi-a/krox-24/tis8/zenk? Prog. Neurobiol. 2004, 74, 183–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yutsudo, N.; Kamada, T.; Kajitani, K.; Nomaru, H.; Katogi, A.; Ohnishi, Y.H.; Ohnishi, Y.N.; Takase, K.; Sakumi, K.; Shigeto, H.; et al. Fosb-null mice display impaired adult hippocampal neurogenesis and spontaneous epilepsy with depressive behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013, 38, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sia, G.M.; Clem, R.L.; Huganir, R.L. The human language-associated gene srpx2 regulates synapse formation and vocalization in mice. Science 2013, 342, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, D.; Bonhoeffer, T.; Scheuss, V. Balance and stability of synaptic structures during synaptic plasticity. Neuron 2014, 82, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.P.; Gilley, J.A.; Zhang, G.; Kernie, S.G. Apoe is required for maintenance of the dentate gyrus neural progenitor pool. Development 2011, 138, 4351–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herdegen, T.; Leah, J.D. Inducible and constitutive transcription factors in the mammalian nervous system: Control of gene expression by jun, fos and krox, and creb/atf proteins. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 1998, 28, 370–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retchkiman, I.; Fischer, B.; Platt, D.; Wagner, A.P. Seizure induced c-fos mrna in the rat brain: Comparison between young and aging animals. Neurobiol. Aging 1996, 17, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhade, S.N.; Shah, A.K.; Agarwal, R.; Yao, B.; Asano, E.; Loeb, J.A. Activity-dependent gene expression correlates with interictal spiking in human neocortical epilepsy. Epilepsia 2007, 48 (Suppl. 5), 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakhade, S.N.; Yao, B.; Ahmed, S.; Asano, E.; Beaumont, T.L.; Shah, A.K.; Draghici, S.; Krauss, R.; Chugani, H.T.; Sood, S.; et al. A common pattern of persistent gene activation in human neocortical epileptic foci. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 58, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Fei, F.; Zhang, L.; Qu, Y.; Fei, Z. The role of glutamate receptors in traumatic brain injury: Implications for postsynaptic density in pathophysiology. Brain Res. Bull. 2011, 85, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, T.W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.T. Excitotoxicity and stroke: Identifying novel targets for neuroprotection. Prog. Neurobiol. 2014, 115, 157–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algattas, H.; Huang, J.H. Traumatic brain injury pathophysiology and treatments: Early, intermediate, and late phases post-injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 15, 309–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curia, G.; Gualtieri, F.; Bartolomeo, R.; Vezzali, R.; Biagini, G. Resilience to audiogenic seizures is associated with p-erk1/2 dephosphorylation in the subiculum of fmr1 knockout mice. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, C.; Costa, A.M.; Lucchi, C.; Leo, G.; Brunel, L.; Fehrentz, J.A.; Martinez, J.; Torsello, A.; Biagini, G. Progressive seizure aggravation in the repeated 6-hz corneal stimulation model is accompanied by marked increase in hippocampal p-erk1/2 immunoreactivity in neurons. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greer, P.L.; Greenberg, M.E. From synapse to nucleus: Calcium-dependent gene transcription in the control of synapse development and function. Neuron 2008, 59, 846–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa-Wagner, A.; Fischer, B.; Schmoll, H.; Platt, D.; Kessler, C. Increased expression of microtubule-associated protein 1b in the hippocampus, subiculum, and perforant path of rats treated with a high dose of pentylenetetrazole. Exp. Neurol. 1997, 148, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Levy, G.A.; Rocha, L.; Lubin, F.D.; Alonso-Vanegas, M.A.; Nani, A.; Buentello-Garcia, R.M.; Perez-Molina, R.; Briones-Velasco, M.; Recillas-Targa, F.; Perez-Molina, A.; et al. Increased expression of bdnf transcript with exon vi in hippocampi of patients with pharmaco-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience 2016, 314, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, E.; Naumann, T.; Deller, T.; Straube, A.; Nitsch, R.; Frotscher, M. Cholinergic sprouting in the rat fascia dentata after entorhinal lesion is not linked to early changes in neurotrophin messenger rna expression. Neuroscience 1997, 80, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa-Wagner, A.; Schroder, E.; Schmoll, H.; Walker, L.C.; Kessler, C. Upregulation of map1b and map2 in the rat brain after middle cerebral artery occlusion: Effect of age. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1999, 19, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmoll, H.; Badan, I.; Grecksch, G.; Walker, L.; Kessler, C.; Popa-Wagner, A. Kindling status in sprague-dawley rats induced by pentylenetetrazole: Involvement of a critical development period. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofler, N.; Kirchmair, E.; Schwarzer, C.; Sperk, G. Altered expression of npy-y1 receptors in kainic acid induced epilepsy in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 230, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzer, C.; Kofler, N.; Sperk, G. Up-regulation of neuropeptide y-y2 receptors in an animal model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 53, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzer, C.; Williamson, J.M.; Lothman, E.W.; Vezzani, A.; Sperk, G. Somatostatin, neuropeptide y, neurokinin b and cholecystokinin immunoreactivity in two chronic models of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience 1995, 69, 831–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, T.M.; Greisen, M.H.; Nielsen, S.M.; Bolwig, T.G.; Mikkelsen, J.D. Electroconvulsive stimuli enhance both neuropeptide y receptor y1 and y2 messenger rna expression and levels of binding in the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 2000, 98, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; Moneta, D.; Mule, F.; Ravizza, T.; Gobbi, M.; French-Mullen, J. Plastic changes in neuropeptide y receptor subtypes in experimental models of limbic seizures. Epilepsia 2000, 41 (Suppl. 6), S115–S121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A.; Sperk, G.; Colmers, W.F. Neuropeptide y: Emerging evidence for a functional role in seizure modulation. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.H.; Corbett, D. Plasticity during stroke recovery: From synapse to behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroff, O.A. Gaba and glutamate in the human brain. Neuroscientist 2002, 8, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Lozada, Z.; Ortega, A. Glutamatergic transmission: A matter of three. Neural Plast. 2015, 2015, 787396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, S.R. The role of glutamate in central nervous system health and disease—A review. Vet. J. 2007, 173, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, A.C.; Kemp, J.A. Glutamate- and gaba-based cns therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kann, O. The interneuron energy hypothesis: Implications for brain disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 90, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafstrom, C.E. Epilepsy comorbidities: How can animal models help? Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 813, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruediger, T.; Bolz, J. Neurotransmitters and the development of neuronal circuits. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 621, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perea, G.; Gomez, R.; Mederos, S.; Covelo, A.; Ballesteros, J.J.; Schlosser, L.; Hernandez-Vivanco, A.; Martin-Fernandez, M.; Quintana, R.; Rayan, A.; et al. Activity-dependent switch of gabaergic inhibition into glutamatergic excitation in astrocyte-neuron networks. eLife 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerriero, R.M.; Giza, C.C.; Rotenberg, A. Glutamate and gaba imbalance following traumatic brain injury. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2015, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Perez, S.J.; Urena-Guerrero, M.E.; Morales-Villagran, A. Monosodium glutamate neonatal treatment as a seizure and excitotoxic model. Brain Res. 2010, 1317, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struzynska, L. A glutamatergic component of lead toxicity in adult brain: The role of astrocytic glutamate transporters. Neurochem. Int. 2009, 55, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gareri, P.; Condorelli, D.; Belluardo, N.; Russo, E.; Loiacono, A.; Barresi, V.; Trovato-Salinaro, A.; Mirone, M.B.; Ferreri Ibbadu, G.; De Sarro, G. Anticonvulsant effects of carbenoxolone in genetically epilepsy prone rats (geprs). Neuropharmacology 2004, 47, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Carvantes, M.C.; Jarero-Basulto, J.J.; Feria-Velasco, A.I.; Beas-Zarate, C.; Navarro-Meza, M.; Gonzalez-Lopez, M.B.; Gudino-Cabrera, G.; Garcia-Rodriguez, J.C. Changes in the expression level of mapk pathway components induced by monosodium glutamate-administration produce neuronal death in the hippocampus from neonatal rats. Neuroscience 2017, 365, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker-Haliski, M.; White, H.S. Glutamatergic mechanisms associated with seizures and epilepsy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a022863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meldrum, B.S. The role of glutamate in epilepsy and other cns disorders. Neurology 1994, 44, S14–S23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murguia-Castillo, J.; Beas-Zarate, C.; Rivera-Cervantes, M.C.; Feria-Velasco, A.I.; Urena-Guerrero, M.E. Nkcc1 and kcc2 protein expression is sexually dimorphic in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex of neonatal rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 552, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaila, K.; Ruusuvuori, E.; Seja, P.; Voipio, J.; Puskarjov, M. Gaba actions and ionic plasticity in epilepsy. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2014, 26, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobolyi, A.; Kekesi, K.A.; Juhasz, G.; Szekely, A.D.; Lovas, G.; Kovacs, Z. Receptors of peptides as therapeutic targets in epilepsy research. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 764–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A.; Sperk, G. Overexpression of npy and y2 receptors in epileptic brain tissue: An endogenous neuroprotective mechanism in temporal lobe epilepsy? Neuropeptides 2004, 38, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfman, H.E. The enigmatic mossy cell of the dentate gyrus. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfman, H.E.; Smith, K.L.; Goodman, J.H.; Sollas, A.L. Survival of dentate hilar mossy cells after pilocarpine-induced seizures and their synchronized burst discharges with area ca3 pyramidal cells. Neuroscience 2001, 104, 741–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumcke, I.; Zuschratter, W.; Schewe, J.C.; Suter, B.; Lie, A.A.; Riederer, B.M.; Meyer, B.; Schramm, J.; Elger, C.E.; Wiestler, O.D. Cellular pathology of hilar neurons in ammon’s horn sclerosis. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 414, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curia, G.; Lucchi, C.; Vinet, J.; Gualtieri, F.; Marinelli, C.; Torsello, A.; Costantino, L.; Biagini, G. Pathophysiogenesis of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: Is prevention of damage antiepileptogenic? Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 663–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ambrosio, R. The role of glial membrane ion channels in seizures and epileptogenesis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 103, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinterkeuser, S.; Schroder, W.; Hager, G.; Seifert, G.; Blumcke, I.; Elger, C.E.; Schramm, J.; Steinhauser, C. Astrocytes in the hippocampus of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy display changes in potassium conductances. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 2087–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordey, A.; Spencer, D.D. Distinct electrophysiological alterations in dentate gyrus versus ca1 glial cells from epileptic humans with temporal lobe sclerosis. Epilepsy Res. 2004, 59, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowser, D.N.; Khakh, B.S. Atp excites interneurons and astrocytes to increase synaptic inhibition in neuronal networks. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 8606–8620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonansco, C.; Couve, A.; Perea, G.; Ferradas, C.A.; Roncagliolo, M.; Fuenzalida, M. Glutamate released spontaneously from astrocytes sets the threshold for synaptic plasticity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F.; Williamson, J.; Bertram, E.; Lothman, E.; Okuno, E.; Schwarcz, R. Kynurenine pathway enzymes in a rat model of chronic epilepsy: Immunohistochemical study of activated glial cells. Neuroscience 1993, 55, 975–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; Ravizza, T.; Moneta, D.; Conti, M.; Borroni, A.; Rizzi, M.; Samanin, R.; Maj, R. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor immunoreactivity in the limbic system of rats after acute seizures and during spontaneous convulsions: Temporal evolution of changes as compared to neuropeptide y. Neuroscience 1999, 90, 1445–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravizza, T.; Gagliardi, B.; Noe, F.; Boer, K.; Aronica, E.; Vezzani, A. Innate and adaptive immunity during epileptogenesis and spontaneous seizures: Evidence from experimental models and human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 29, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespel, A.; Coubes, P.; Rousset, M.C.; Brana, C.; Rougier, A.; Rondouin, G.; Bockaert, J.; Baldy-Moulinier, M.; Lerner-Natoli, M. Inflammatory reactions in human medial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis. Brain Res. 2002, 952, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepp, M.J.; Arstad, E.; Bankstahl, J.P.; Dedeurwaerdere, S.; Friedman, A.; Potschka, H.; Ravizza, T.; Theodore, W.H.; Baram, T.Z. Neuroinflammation imaging markers for epileptogenesis. Epilepsia 2017, 58 (Suppl. 3), 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivonkova, H.; Anderova, M. Altered homeostatic functions in reactive astrocytes and their potential as a therapeutic target after brain ischemic injury. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 5056–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, L.A.; Wang, L.; Ribak, C.E. Rapid astrocyte and microglial activation following pilocarpine-induced seizures in rats. Epilepsia 2008, 49 (Suppl. 2), 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turrin, N.P.; Rivest, S. Innate immune reaction in response to seizures: Implications for the neuropathology associated with epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004, 16, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simoni, M.G.; Perego, C.; Ravizza, T.; Moneta, D.; Conti, M.; Marchesi, F.; De Luigi, A.; Garattini, S.; Vezzani, A. Inflammatory cytokines and related genes are induced in the rat hippocampus by limbic status epilepticus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 2623–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plata-Salaman, C.R.; Ilyin, S.E.; Turrin, N.P.; Gayle, D.; Flynn, M.C.; Romanovitch, A.E.; Kelly, M.E.; Bureau, Y.; Anisman, H.; McIntyre, D.C. Kindling modulates the il-1beta system, tnf-alpha, tgf-beta1, and neuropeptide mrnas in specific brain regions. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2000, 75, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravizza, T.; Vezzani, A. Status epilepticus induces time-dependent neuronal and astrocytic expression of interleukin-1 receptor type i in the rat limbic system. Neuroscience 2006, 137, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arisi, G.M.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. Doublecortin-positive newly born granule cells of hippocampus have abnormal apical dendritic morphology in the pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain Res. 2007, 1165, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overstreet-Wadiche, L.S.; Bromberg, D.A.; Bensen, A.L.; Westbrook, G.L. Seizures accelerate functional integration of adult-generated granule cells. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 4095–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuruba, R.; Hattiangady, B.; Shetty, A.K. Hippocampal neurogenesis and neural stem cells in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2009, 14 (Suppl. 1), 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parent, J.M.; Yu, T.W.; Leibowitz, R.T.; Geschwind, D.H.; Sloviter, R.S.; Lowenstein, D.H. Dentate granule cell neurogenesis is increased by seizures and contributes to aberrant network reorganization in the adult rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 3727–3738. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scharfman, H.E.; Goodman, J.H.; Sollas, A.L. Granule-like neurons at the hilar/ca3 border after status epilepticus and their synchrony with area ca3 pyramidal cells: Functional implications of seizure-induced neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 6144–6158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scharfman, H.E.; Sollas, A.L.; Smith, K.L.; Jackson, M.B.; Goodman, J.H. Structural and functional asymmetry in the normal and epileptic rat dentate gyrus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2002, 454, 424–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfman, H.E.; Sollas, A.E.; Berger, R.E.; Goodman, J.H.; Pierce, J.P. Perforant path activation of ectopic granule cells that are born after pilocarpine-induced seizures. Neuroscience 2003, 121, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattiangady, B.; Rao, M.S.; Shetty, A.K. Chronic temporal lobe epilepsy is associated with severely declined dentate neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Neurobiol. Dis. 2004, 17, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirttila, T.J.; Lukasiuk, K.; Hakansson, K.; Grubb, A.; Abrahamson, M.; Pitkanen, A. Cystatin c modulates neurodegeneration and neurogenesis following status epilepticus in mouse. Neurobiol. Dis. 2005, 20, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, B.W.; Wang, S.; Burnham, W.M.; De Boni, U.; Wojtowicz, J.M. Kindling-induced neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 248, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, B.W.; Wojtowicz, J.M.; Burnham, W.M. Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the rat following electroconvulsive shock seizures. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 165, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, W.P.; Sundstrom, L.E. Kainic acid increases the proliferation of granule cell progenitors in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat. Brain Res. 1998, 790, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markakis, E.A.; Gage, F.H. Adult-generated neurons in the dentate gyrus send axonal projections to field ca3 and are surrounded by synaptic vesicles. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 406, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharfman, H.E. Epileptogenesis in the parahippocampal region. Parallels with the dentate gyrus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 911, 305–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, K.J. C-fos as a transcription factor: A stressful (re)view from a functional map. Neurochem. Int. 1998, 33, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, J.P.; Neder, L.; Arisi, G.M.; Carlotti, C.G., Jr.; Assirati, J.A.; Moreira, J.E. Plasticity, synaptic strength, and epilepsy: What can we learn from ultrastructural data? Epilepsia 2005, 46 (Suppl. 5), 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloviter, R.S. Permanently altered hippocampal structure, excitability, and inhibition after experimental status epilepticus in the rat: The “dormant basket cell” hypothesis and its possible relevance to temporal lobe epilepsy. Hippocampus 1991, 1, 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jarero-Basulto, J.J.; Gasca-Martínez, Y.; Rivera-Cervantes, M.C.; Ureña-Guerrero, M.E.; Feria-Velasco, A.I.; Beas-Zarate, C. Interactions Between Epilepsy and Plasticity. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11010017
Jarero-Basulto JJ, Gasca-Martínez Y, Rivera-Cervantes MC, Ureña-Guerrero ME, Feria-Velasco AI, Beas-Zarate C. Interactions Between Epilepsy and Plasticity. Pharmaceuticals. 2018; 11(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleJarero-Basulto, José J., Yadira Gasca-Martínez, Martha C. Rivera-Cervantes, Mónica E. Ureña-Guerrero, Alfredo I. Feria-Velasco, and Carlos Beas-Zarate. 2018. "Interactions Between Epilepsy and Plasticity" Pharmaceuticals 11, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11010017
APA StyleJarero-Basulto, J. J., Gasca-Martínez, Y., Rivera-Cervantes, M. C., Ureña-Guerrero, M. E., Feria-Velasco, A. I., & Beas-Zarate, C. (2018). Interactions Between Epilepsy and Plasticity. Pharmaceuticals, 11(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11010017



