PARP Inhibition by Flavonoids Induced Selective Cell Killing to BRCA2-Deficient Cells
Abstract
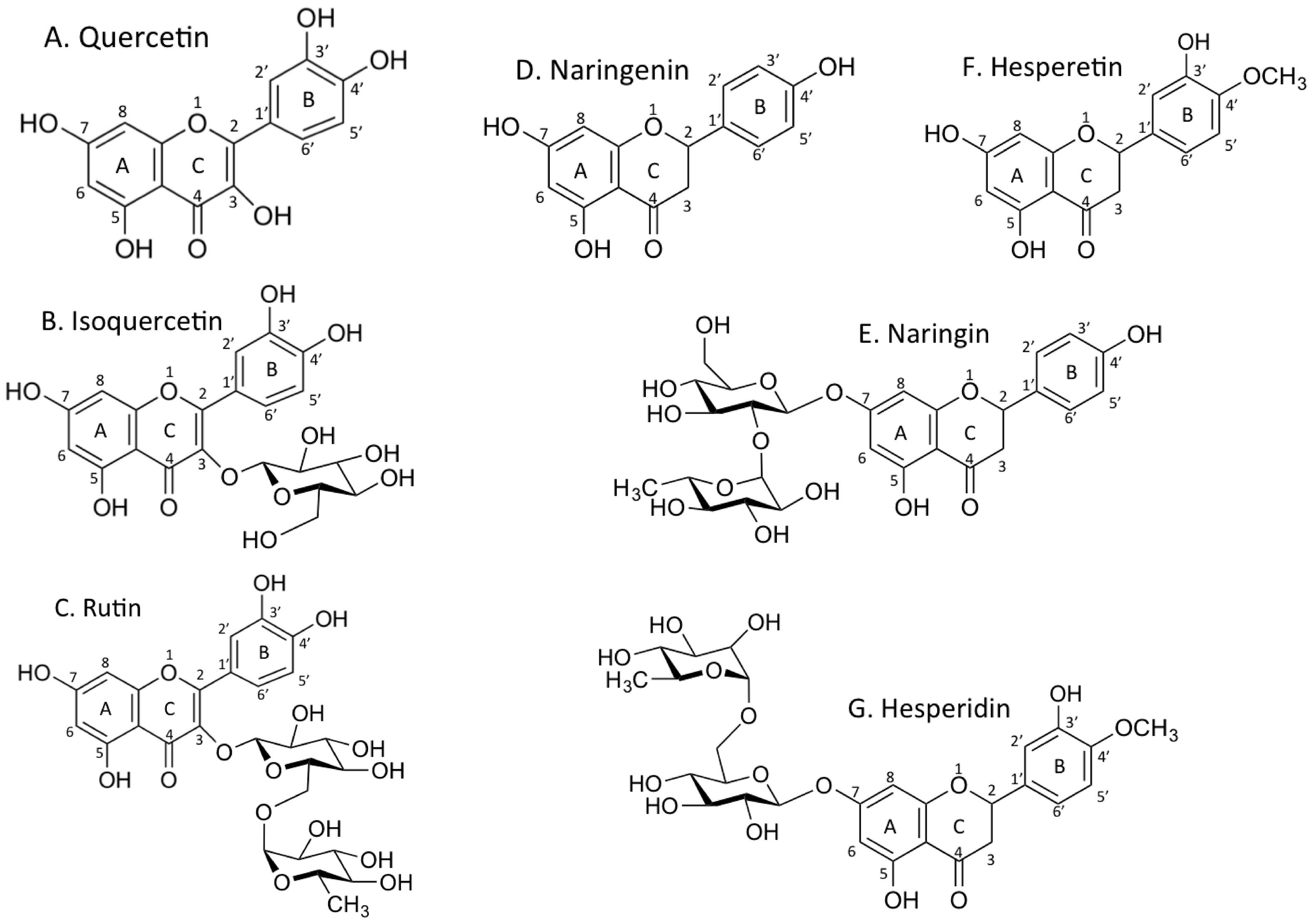
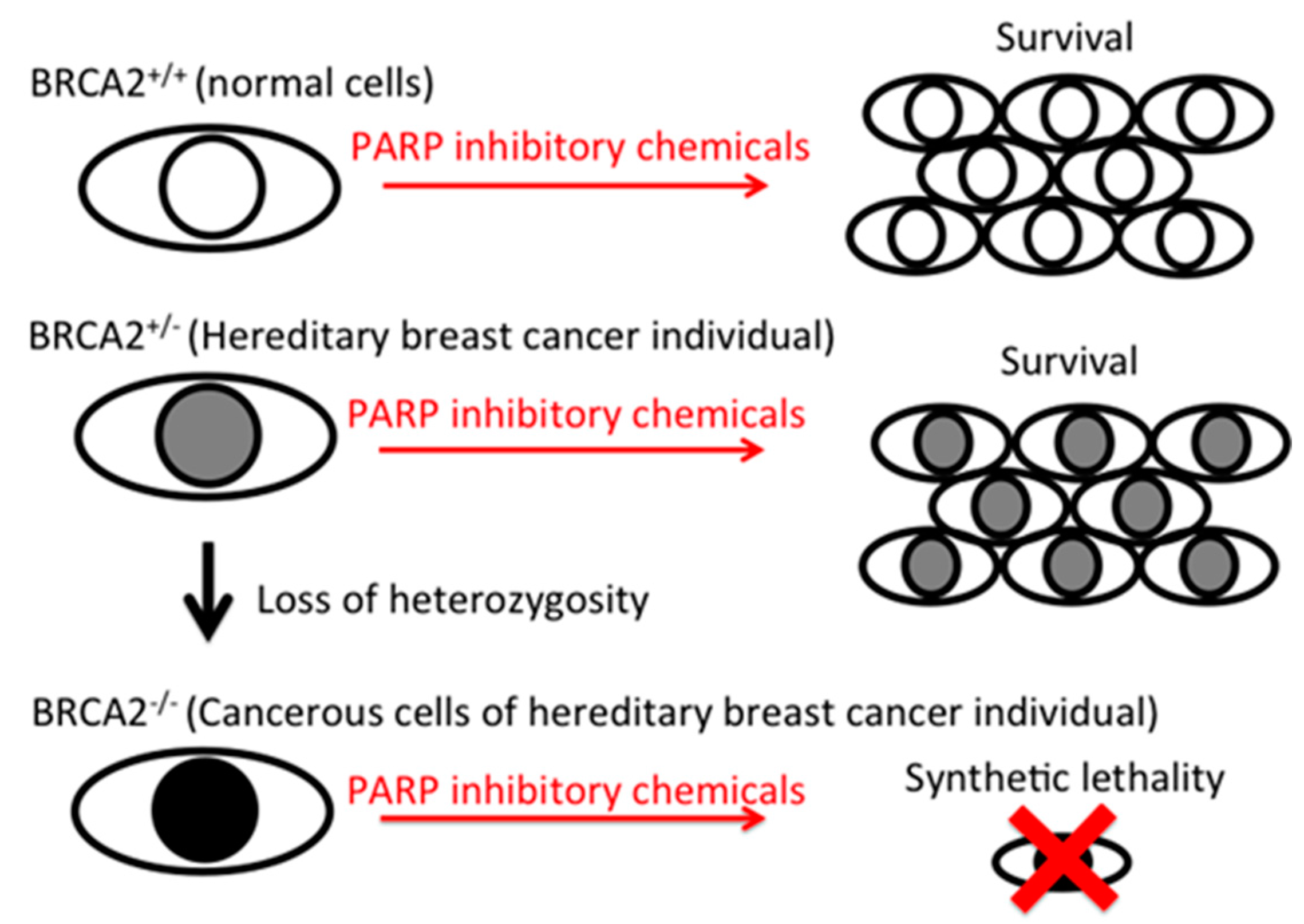
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. In Vitro PARP Inhibition Assay
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Cell Survival Asssay
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
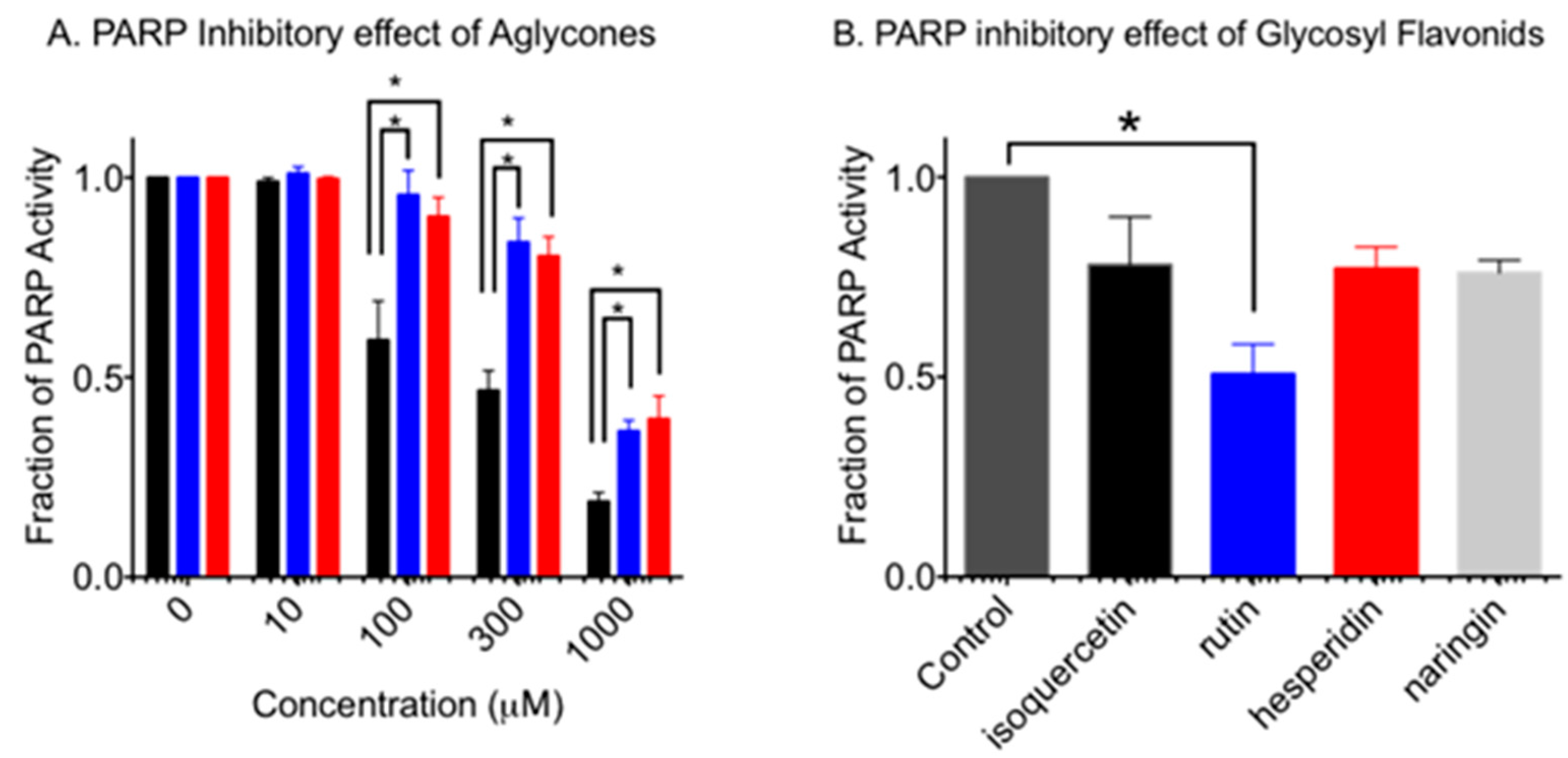
3.1. Inhibition of PARP Activity
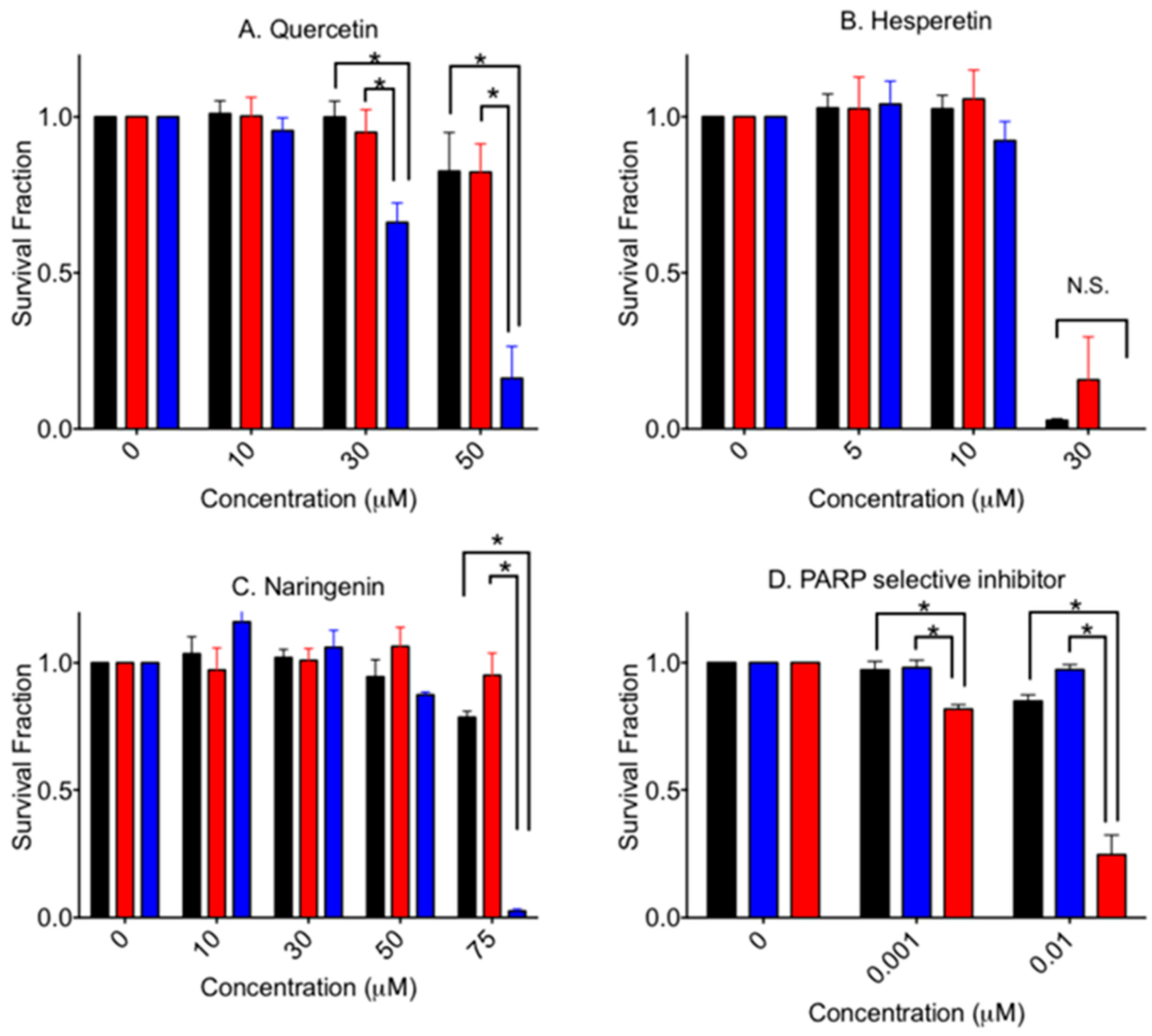
3.2. Cytotoxicity to Aglycone Form Flavonoids
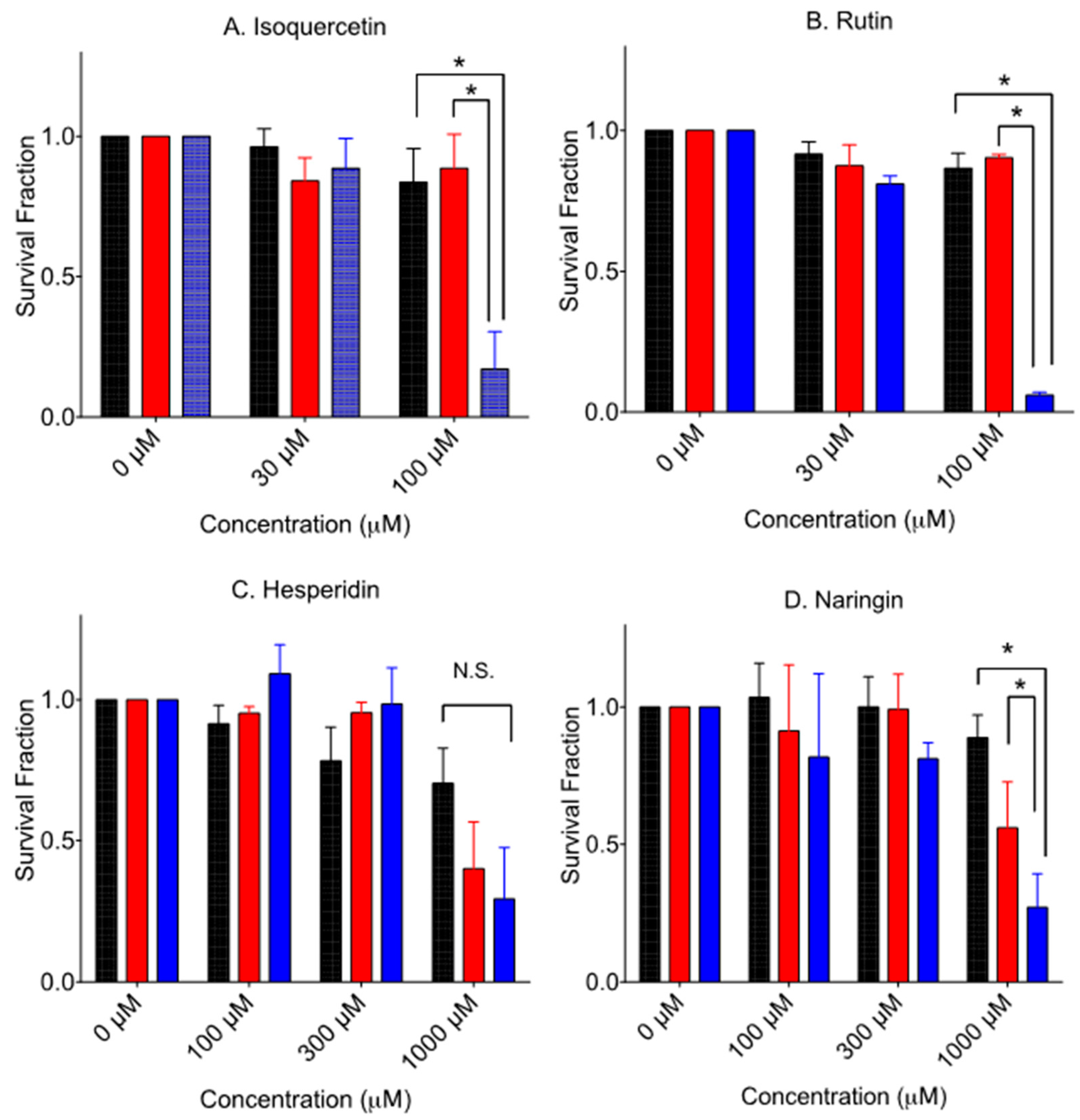
3.3. Cytotoxicity to Glycosyl Form Flavonids
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harwood, M.; Danielewska-Nikiel, B.; Borzelleca, J.F.; Flamm, G.W.; Williams, G.M.; Lines, T.C. A critical review of the data related to the safety of quercetin and lack of evidence of in vivo toxicity, including lack of genotoxic/carcinogenic properties. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 2179–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, A.J.; Williamson, G. Biomarkers for exposure to dietary flavonoids: A review of the current evidence for identification of quercetin glycosides in plasma. Br. J. Nutr. 2001, 86 (Suppl. 1), S105–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boots, A.W.; Haenen, G.R.; Bast, A. Health effects of quercetin: From antioxidant to nutraceutical. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 585, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.A.; Subhan, N.; Rahman, M.M.; Uddin, S.J.; Reza, H.M.; Sarker, S.D. Effect of citrus flavonoids, naringin and naringenin, on metabolic syndrome and their mechanisms of action. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banjerdpongchai, R.; Wudtiwai, B.; Khaw-on, P.; Rachakhom, W.; Duangnil, N.; Kongtawelert, P. Hesperidin from citrus seed induces human hepatocellular carcinoma hepg2 cell apoptosis via both mitochondrial and death receptor pathways. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aruoma, O.I. Antioxidant actions of plant foods: Use of oxidative DNA damage as a tool for studying antioxidant efficacy. Free Radic. Res. 1999, 30, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Hsu, F.L.; Lee, W.R. Differential apoptosis-inducing effect of quercetin and its glycosides in human promyeloleukemic hl-60 cells by alternative activation of the caspase 3 cascade. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 89, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, A.K. Chemistry and biological activities of flavonoids: An overview. Sci. World. J. 2013, 2013, 162750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Haskins, J.S.; Su, C.; Allum, A.; Haskins, A.H.; Salinas, V.A.; Sunada, S.; Inoue, T.; Aizawa, Y.; Uesaka, M.; et al. In vitro screening of radioprotective properties in the novel glucosylated flavonoids. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, J.; Roybal, E.J.; Brents, C.A.; Uesaka, M.; Aizawa, Y.; Kato, T.A. Natural and glucosyl flavonoids inhibit poly(adp-ribose) polymerase activity and induce synthetic lethality in brca mutant cells. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engen, A.; Maeda, J.; Wozniak, D.E.; Brents, C.A.; Bell, J.J.; Uesaka, M.; Aizawa, Y.; Kato, T.A. Induction of cytotoxic and genotoxic responses by natural and novel quercetin glycosides. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2015, 784–785, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, H.E.; Schultz, N.; Thomas, H.D.; Parker, K.M.; Flower, D.; Lopez, E.; Kyle, S.; Meuth, M.; Curtin, N.J.; Helleday, T. Specific killing of brca2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(adp-ribose) polymerase. Nature 2005, 434, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, P.C.; Yap, T.A.; Boss, D.S.; Carden, C.P.; Mergui-Roelvink, M.; Gourley, C.; De Greve, J.; Lubinski, J.; Shanley, S.; Messiou, C.; et al. Poly(adp)-ribose polymerase inhibition: Frequent durable responses in brca carrier ovarian cancer correlating with platinum-free interval. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2512–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferla, R.; Calo, V.; Cascio, S.; Rinaldi, G.; Badalamenti, G.; Carreca, I.; Surmacz, E.; Colucci, G.; Bazan, V.; Russo, A. Founder mutations in brca1 and brca2 genes. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18 (Suppl. 6), vi93–vi98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fackenthal, J.D.; Olopade, O.I. Breast cancer risk associated with brca1 and brca2 in diverse populations. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drost, R.; Jonkers, J. Opportunities and hurdles in the treatment of brca1-related breast cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3753–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mersch, J.; Jackson, M.A.; Park, M.; Nebgen, D.; Peterson, S.K.; Singletary, C.; Arun, B.K.; Litton, J.K. Cancers associated with brca1 and brca2 mutations other than breast and ovarian. Cancer 2015, 121, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, C.; Kim, E.H.; Royce, D.B.; Williams, C.R.; Collins, R.M.; Risingsong, R.; Sporn, M.B.; Liby, K.T. The parp inhibitors, veliparib and olaparib, are effective chemopreventive agents for delaying mammary tumor development in brca1-deficient mice. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.N.; Yu, X.M.; Jaskula-Sztul, R.; Chen, H. Hesperetin activates the notch1 signaling cascade, causes apoptosis, and induces cellular differentiation in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21 (Suppl. 4), S497–S504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menear, K.A.; Adcock, C.; Boulter, R.; Cockcroft, X.L.; Copsey, L.; Cranston, A.; Dillon, K.J.; Drzewiecki, J.; Garman, S.; Gomez, S.; et al. 4-[3-(4-cyclopropanecarbonylpiperazine-1-carbonyl)-4-fluorobenzyl]-2h-phthalazin-1-one: A novel bioavailable inhibitor of poly(adp-ribose) polymerase-1. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 6581–6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaegh, G.W.; Jongmans, W.; Morolli, B.; Jaspers, N.G.; van der Schans, G.P.; Lohman, P.H.; Zdzienicka, M.Z. A novel type of X-ray-sensitive chinese hamster cell mutant with radioresistant DNA synthesis and hampered DNA double-strand break repair. Mutat. Res. 1995, 337, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdzienicka, M.Z.; Simons, J.W. Mutagen-sensitive cell lines are obtained with a high frequency in v79 chinese hamster cells. Mutat. Res. 1987, 178, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, C.; Manach, C.; Crespy, V.; Remesy, C. Respective bioavailability of quercetin aglycone and its glycosides in a rat model. BioFactors 2000, 12, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarebczan, B.; Pinchot, S.N.; Kunnimalaiyaan, M.; Chen, H. Hesperetin, a potential therapy for carcinoid cancer. Am. J. Surg. 2011, 201, 329–332, discussion 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, C.; Haskins, A.H.; Omata, C.; Aizawa, Y.; Kato, T.A. PARP Inhibition by Flavonoids Induced Selective Cell Killing to BRCA2-Deficient Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10040080
Su C, Haskins AH, Omata C, Aizawa Y, Kato TA. PARP Inhibition by Flavonoids Induced Selective Cell Killing to BRCA2-Deficient Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2017; 10(4):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10040080
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Cathy, Alexis H. Haskins, Chisato Omata, Yasushi Aizawa, and Takamitsu A. Kato. 2017. "PARP Inhibition by Flavonoids Induced Selective Cell Killing to BRCA2-Deficient Cells" Pharmaceuticals 10, no. 4: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10040080
APA StyleSu, C., Haskins, A. H., Omata, C., Aizawa, Y., & Kato, T. A. (2017). PARP Inhibition by Flavonoids Induced Selective Cell Killing to BRCA2-Deficient Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 10(4), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10040080



