Development of Pharmacophore Model for Indeno[1,2-b]indoles as Human Protein Kinase CK2 Inhibitors and Database Mining
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The Chemical Compounds
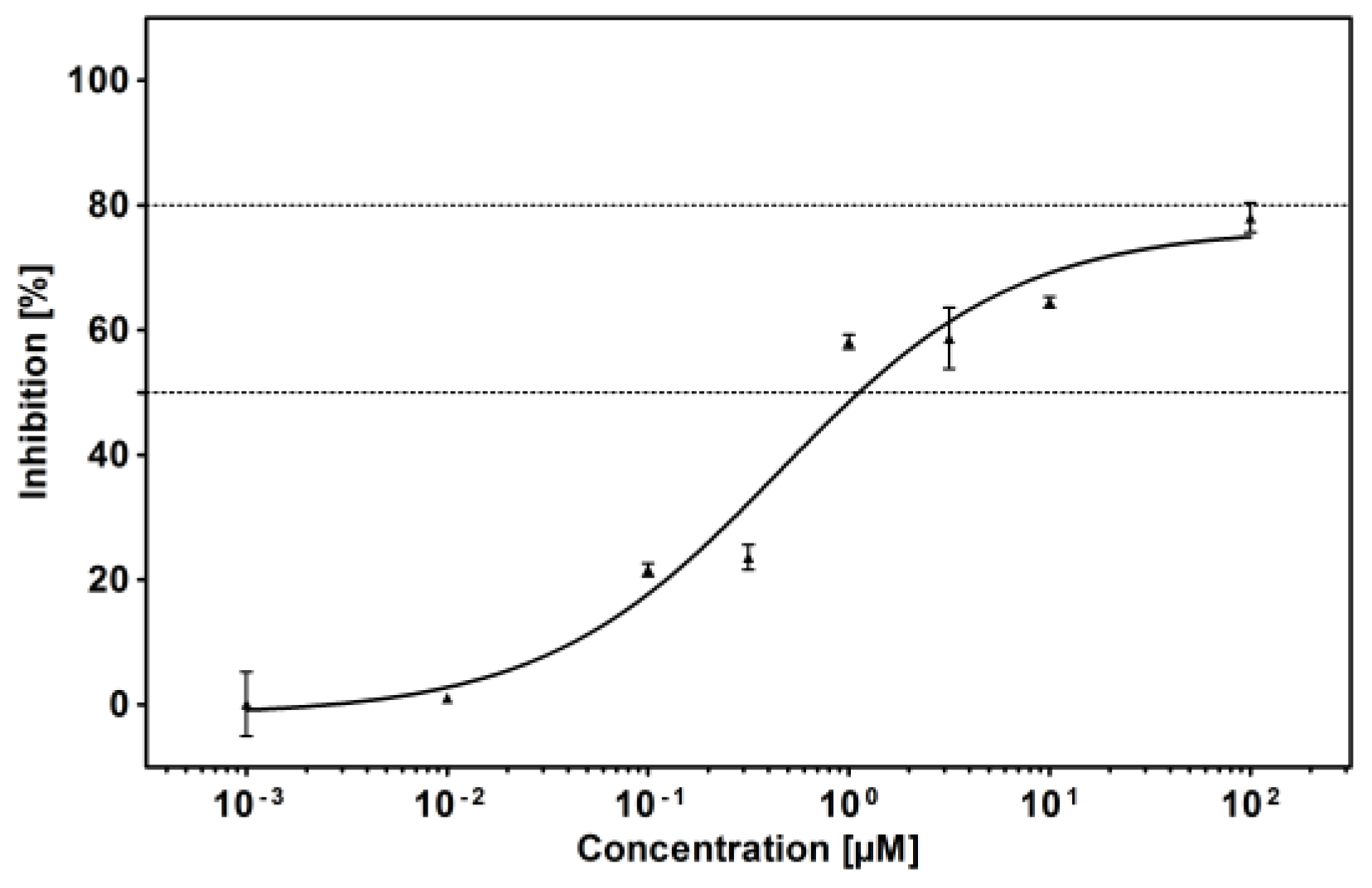
4.2. In Vitro Assay
4.3. Computational Methods
4.3.1. Pharmacophore Generation
4.3.2. Database Search
4.3.3. Receptor Refinement
4.3.4. Database Generation
4.3.5. Molecular Docking
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO: Cancer Fact Sheet N°297. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/ (accessed on 4 January 2017).
- Ahmad, K.A.; Wang, G.; Slaton, J.; Unger, G.; Ahmed, K. Targeting CK2 for cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs 2005, 16, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozza, G.; Pinna, L.A. Casein kinases as potential therapeutic targets. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozza, G.; Pinna, L.A.; Moro, S. Protein kinase CK2 inhibitors: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2012, 22, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druker, B.J.; Sawyers, C.L.; Kantarjian, H.; Resta, D.J.; Reese, S.F.; Ford, J.M.; Capdeville, R.; Talpaz, M. Activity of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in the blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the philadelphia chromosome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1038–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbro, D.; Cowan-Jacob, S.W.; Mobitz, H.; Martiny-Baron, G. Targeting cancer with small-molecular-weight kinase inhibitors. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 795, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Faust, R.A.; Gapany, M.; Tristani, P.; Davis, A.; Adams, G.L.; Ahmed, K. Elevated protein kinase CK2 activity in chromatin of head and neck tumors: Association with malignant transformation. Cancer Lett. 1996, 101, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongved, P.; Kirsch, G.; Bouaziz, Z.; Jose, J.; le Borgne, M. Indenoindoles and cyclopentacarbazoles as bioactive compounds: Synthesis and biological applications. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 69, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alchab, F.; Ettouati, L.; Bouaziz, Z.; Bollacke, A.; Delcros, J.G.; Gertzen, C.G.; Gohlke, H.; Pinaud, N.; Marchivie, M.; Guillon, J.; et al. Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modeling of substituted indeno[1,2-b]indoles as inhibitors of human protein kinase CK2. Pharmaceuticals 2015, 8, 279–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hundsdorfer, C.; Hemmerling, H.J.; Gotz, C.; Totzke, F.; Bednarski, P.; Le Borgne, M.; Jose, J. Indeno[1,2-b]indole derivatives as a novel class of potent human protein kinase CK2 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 2282–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hundsdorfer, C.; Hemmerling, H.J.; Hamberger, J.; le Borgne, M.; Bednarski, P.; Gotz, C.; Totzke, F.; Jose, J. Novel indeno[1,2-b]indoloquinones as inhibitors of the human protein kinase CK2 with antiproliferative activity towards a broad panel of cancer cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 424, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozzi, G.J.; Bouaziz, Z.; Winter, E.; Daflon-Yunes, N.; Honorat, M.; Guragossian, N.; Marminon, C.; Valdameri, G.; Bollacke, A.; Guillon, J.; et al. Phenolic indeno[1,2-b]indoles as ABCG2-selective potent and non-toxic inhibitors stimulating basal atpase activity. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 3481–3495. [Google Scholar]
- Jabor Gozzi, G.; Bouaziz, Z.; Winter, E.; Daflon-Yunes, N.; Aichele, D.; Nacereddine, A.; Marminon, C.; Valdameri, G.; Zeinyeh, W.; Bollacke, A.; et al. Converting potent indeno[1,2-b]indole inhibitors of protein kinase CK2 into selective inhibitors of the breast cancer resistance protein ABCG2. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuccinardi, T.; Poli, G.; Corchia, I.; Granchi, C.; Lapillo, M.; Macchia, M.; Minutolo, F.; Ortore, G.; Martinelli, A. A virtual screening study for lactate dehydrogenase 5 inhibitors by using a pharmacophore-based approach. Mol. Inform. 2016, 35, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.; Singh, A.; Patel, V.; Jain, D.K.; Veerasamy, R.; Rajak, H. Pharmacophore based 3D-qsar, virtual screening and docking studies on novel series of HDAC inhibitors with thiophen linker as anticancer agents. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2016, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meetei, P.A.; Rathore, R.S.; Prabhu, N.P.; Vindal, V. In silico screening for identification of novel β-1,3-glucan synthase inhibitors using pharmacophore and 3D-QSAR methodologies. Springerplus 2016, 5, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berinyuy, E.; Soliman, M.E. Identification of novel potential GP120 of HIV-1 antagonist using per-residue energy contribution-based pharmacophore modelling. Interdiscip. Sci. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugale, V.G.; Bari, S.B. Identification of potential GLY/NMDA receptor antagonists by cheminformatics approach: A combination of pharmacophore modelling, virtual screening and molecular docking studies. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2016, 27, 125–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozza, G.; Bonvini, P.; Zorzi, E.; Poletto, G.; Pagano, M.A.; Sarno, S.; Donella-Deana, A.; Zagotto, G.; Rosolen, A.; Pinna, L.A.; et al. Identification of ellagic acid as potent inhibitor of protein kinase CK2: A successful example of a virtual screening application. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 2363–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, J.J.; Sterling, T.; Mysinger, M.M.; Bolstad, E.S.; Coleman, R.G. Zinc: A free tool to discover chemistry for biology. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 1757–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molecular Operating Environment (MOE), C.C.G.I., 1010 Sherbooke St. West, Suite #910, Montreal, QC, Canada, H3A 2R7, 2013. Available online: https://www.chemcomp.com/MOE-Molecular_Operating_Environment.htm (accessed on 4 January 2017).
- Sanders, M.P.; Barbosa, A.J.; Zarzycka, B.; Nicolaes, G.A.; Klomp, J.P.; de Vlieg, J.; del Rio, A. Comparative analysis of pharmacophore screening tools. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 1607–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Congreve, M.; Chessari, G.; Tisi, D.; Woodhead, A.J. Recent developments in fragment-based drug discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 3661–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RCSB PDB-3C13: Low pH-Value Crystal Structure of Emodin in Complex with the Catalytic Subunit of Protein Kinase CK2. Available online: http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=3C13 (accessed on 4 January 2017).
- Pauli, I.; dos Santos, R.N.; Rostirolla, D.C.; Martinelli, L.K.; Ducati, R.G.; Timmers, L.F.; Basso, L.A.; Santos, D.S.; Guido, R.V.; Andricopulo, A.D.; et al. Discovery of new inhibitors of mycobacterium tuberculosis inha enzyme using virtual screening and a 3D-pharmacophore-based approach. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 2390–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budman, D.R.; Berry, D.A.; Cirrincione, C.T.; Henderson, I.C.; Wood, W.C.; Weiss, R.B.; Ferree, C.R.; Muss, H.B.; Green, M.R.; Norton, L.; et al. Dose and dose intensity as determinants of outcome in the adjuvant treatment of breast cancer. The cancer and leukemia group B. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1998, 90, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limon, M.C.; Rodriguez-Ortiz, R.; Avalos, J. Bikaverin production and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreitman, G.; Nord, F.F. Lycopersin, a pigment from fusarium lycopersici. Arch. Biochem. 1949, 21, 457. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olgen, S.; Gotz, C.; Jose, J. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 3-(substituted-benzylidene)-1,3-dihydro-indolin derivatives as human protein kinase CK2 and p60(c-SRC) tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratz, A.; Gotz, C.; Jose, J. A ce-based assay for human protein kinase CK2 activity measurement and inhibitor screening. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brase, S.; Encinas, A.; Keck, J.; Nising, C.F. Chemistry and biology of mycotoxins and related fungal metabolites. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3903–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuska, J.; Proksa, B.; Fuskova, A. New potential cytotoxic and antitumor substances I. In vitro effect of bikaverin and its derivatives on cells of certain tumors. Neoplasma 1975, 22, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
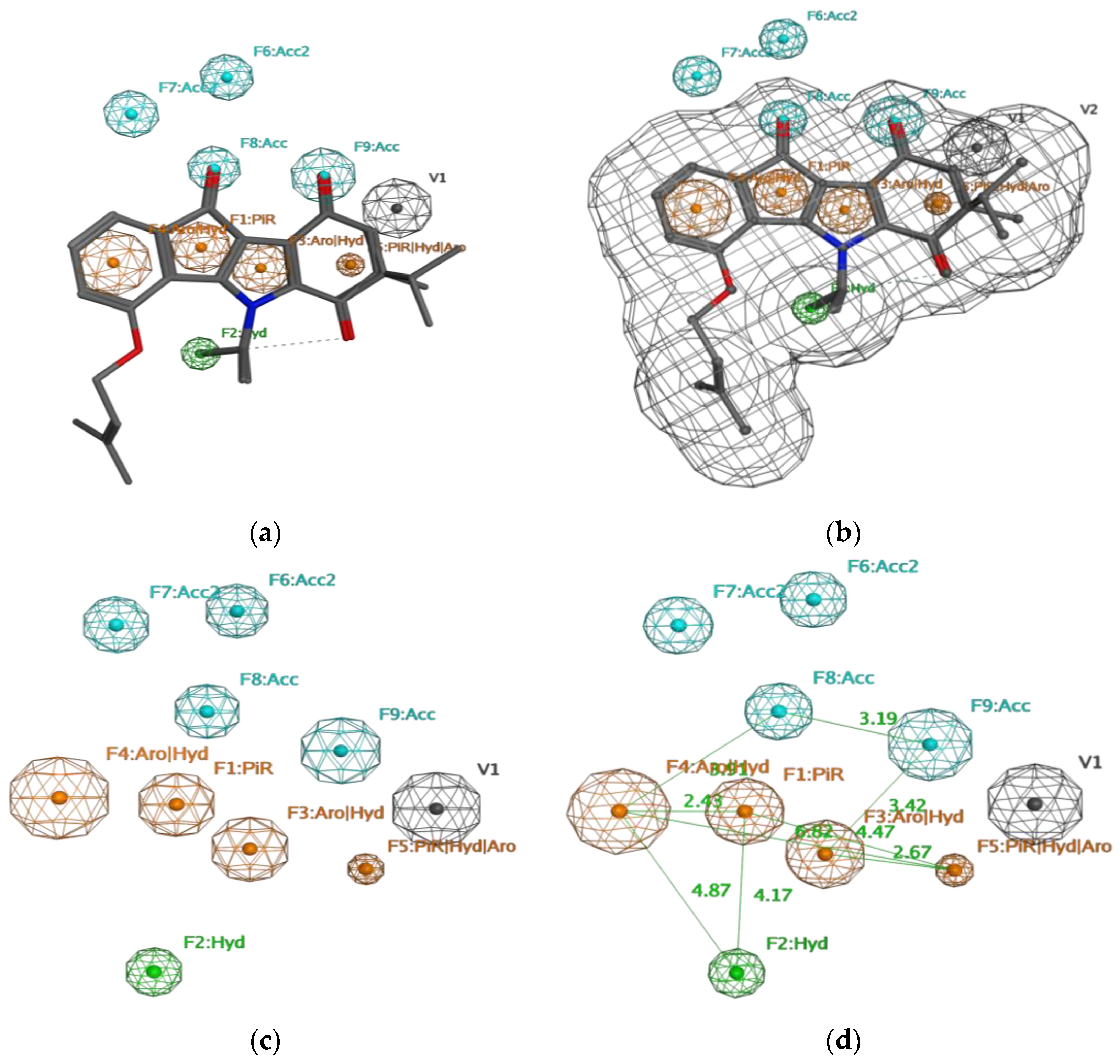
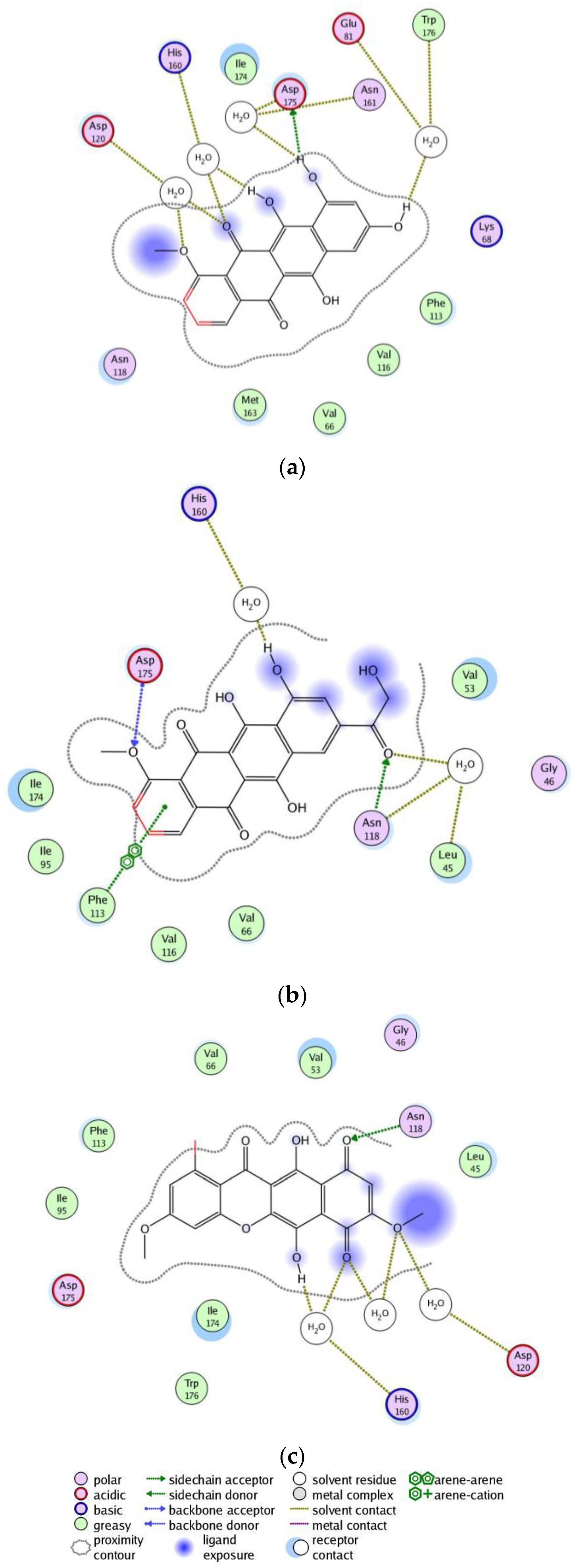
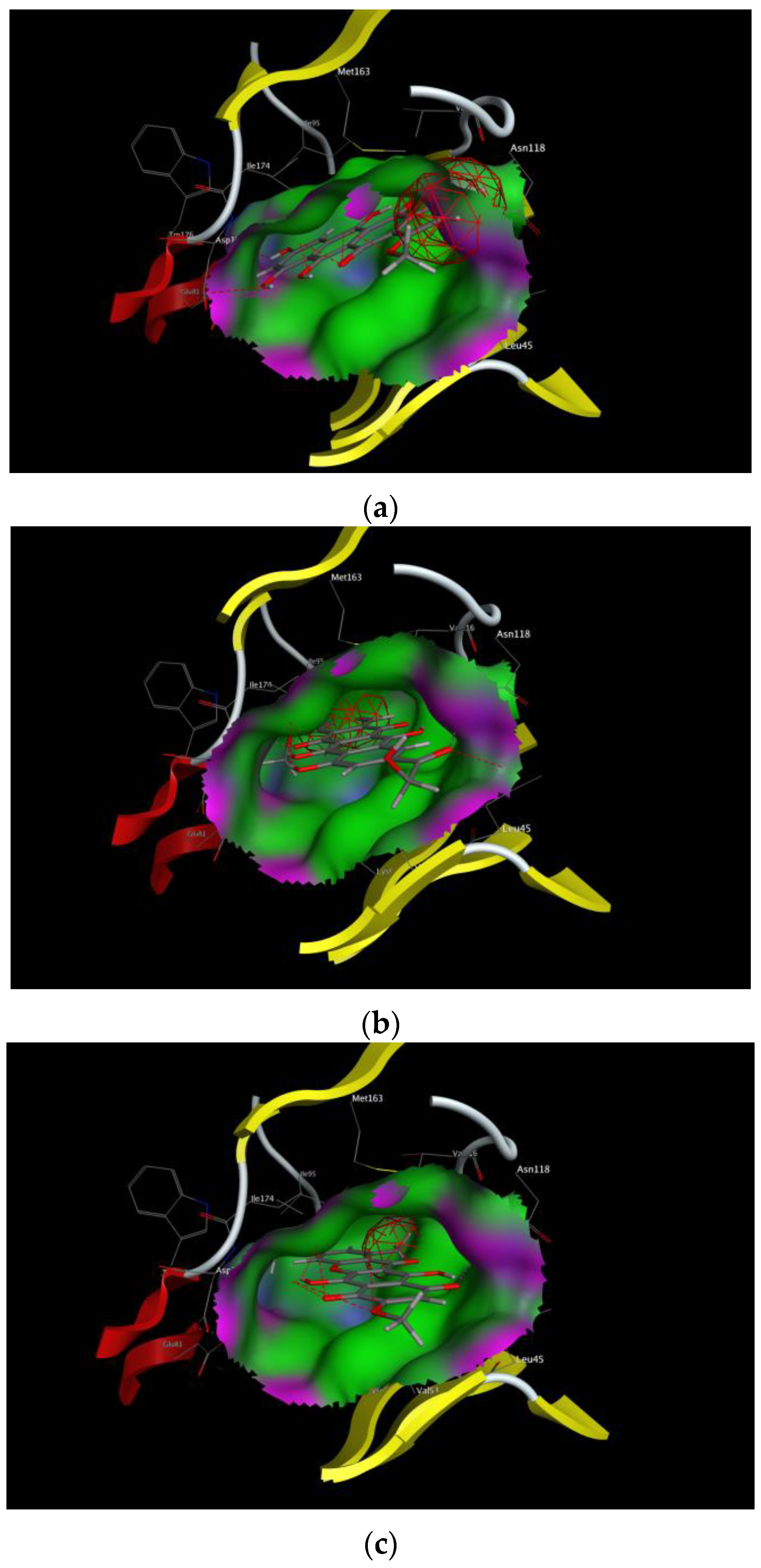
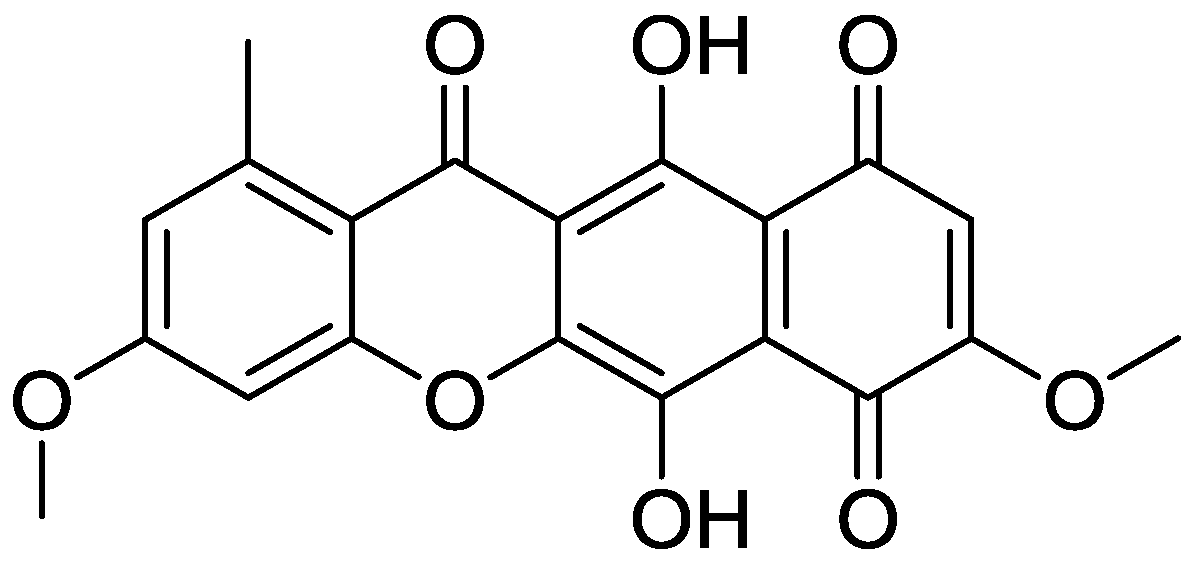
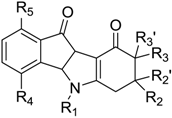
| Code | R1 | R2 | R2′ | R3 | R3′ | R4 | R5 | IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
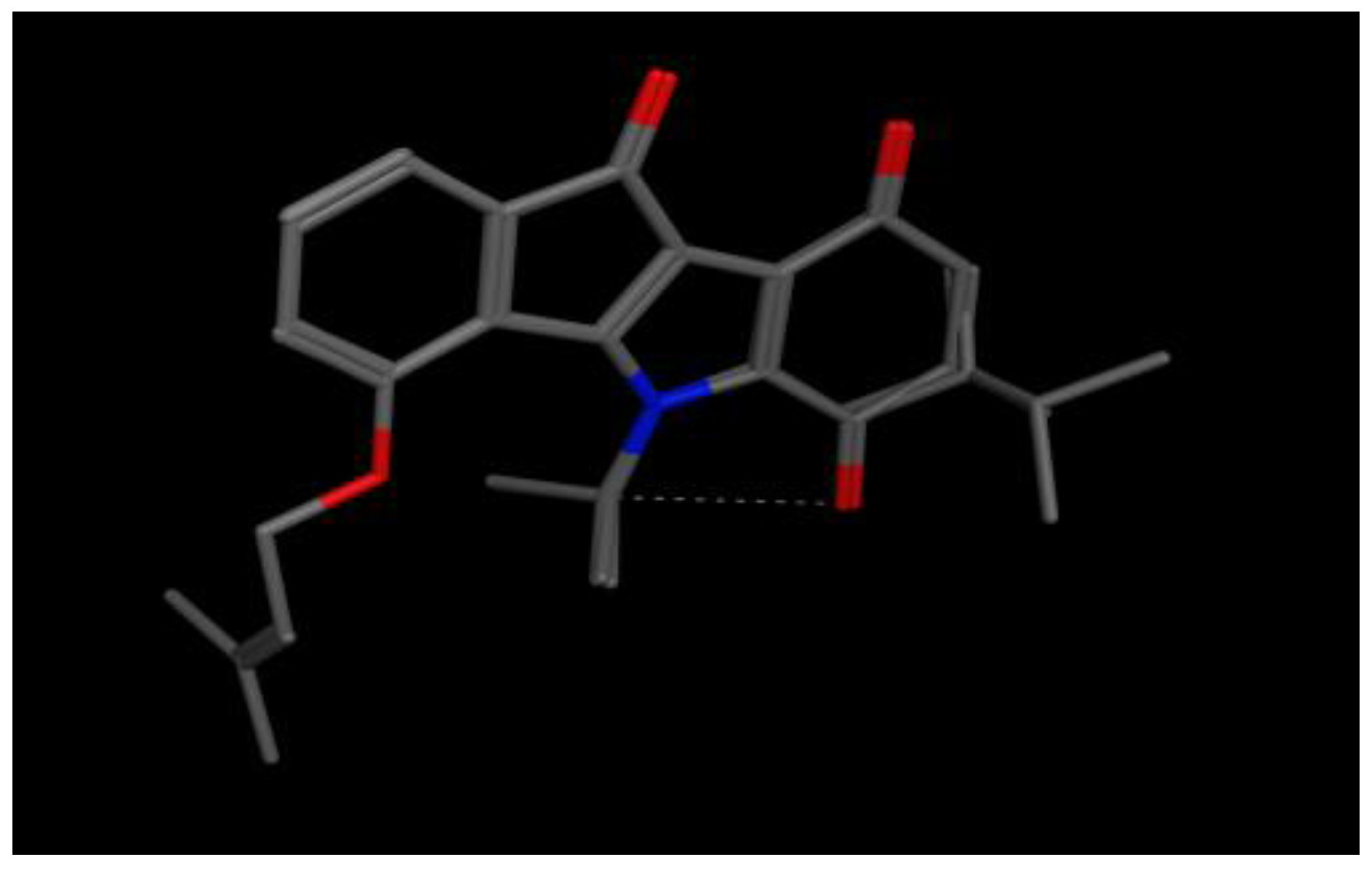
| 1 | CH(CH3)2 | H | H | H | H | O–CH2CH=C(CH3)2 | H | 0.025 |
| 2 | CH(CH3)2 | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | 0.17 |
| 3 | CH(CH3)2 | H | H | H | H | H | H | 0.36 |
| 5 | CH(CH3)2 | CH(CH3)2 | H | H | H | H | H | 0.61 |
| 8 | CH2CH2(ortho-OMe)Ph | H | H | H | H | H | H | 1.40 |
| 9 | H | H | H | H | H | H | 1.44 | |
| 14 | CH2CH2C6H5 | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | 2.50 |
| 18 | CH2CH2(para-OMe)Ph | H | H | H | H | H | H | 4.10 |
| 22 | CH2CH2(meta-OMe)Ph | H | H | H | H | H | H | 5.10 |
| 23 | CH2CH2 CH2C6H5 | H | H | H | H | H | H | 6.00 |
| 24 | CH2CH2C6H5 | H | H | H | H | H | H | 7.00 |
| 26 | CH(CH3)2 | H | H | CH3 | H | H | H | 9.20 |
| 28 | CH(CH3)2 | H | H | (CH2Ph)2 | CH2Ph | H | H | >10 |
| 29 | CH2(para-OMe)Ph | H | H | H | H | H | H | >10 |
| 32 | CH(CH3)2 | H | H | H | H | H | O–CH2CH=C(CH3)2 | >10 |
| 37 | CH(CH3)2 | (para-F)Ph | H | H | H | H | H | >10 |
| 39 | CH(CH3)2 | furan-2-yl | H | H | H | H | H | >10 |
| 40 | CH2Ph | H | H | H | H | H | H | >10 |
| 41 | CH2CH2Ph | Ph | H | H | H | H | H | >10 |
| 43 | H | CH3 | H | COOCH3 | H | H | H | >10 |
| 44 | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | >10 |
| 45 | CH2Ph | CH3 | H | COOCH3 | H | H | H | >10 |
| 46 | CH(CH3)2 | H | H | CH(CH3)2 | H | H | H | >10 |
| 47 | CH2Ph | CH3 | CH3 | H | H | H | H | >10 |
| 48 | CH2Ph | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | >10 |
| 49 | CH(CH3)2 | Ph | H | H | H | H | H | >10 |
| 50 | CH2Ph | Ph | H | H | H | H | H | >10 |
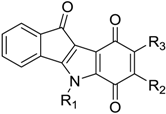
| Code | R1 | R2 | R3 | IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | CH(CH3)2 | CH3 | H | 1.27 |
| 7 | CH2CH2(ortho-OMe)Ph | H | H | 1.30 |
| 10 | CH(CH3)2 | CH(CH3)2 | H | 1.65 |
| 12 | CH(CH3)2 | H | H | 2.00 |
| 15 | CH(CH3)2 | (para-F)Ph | H | 2.77 |
| 16 | CH(CH3)2 | furan-2-yl | H | 3.63 |
| 25 | CH2CH2C6H5 | H | H | 7.50 |
| 27 | CH2Ph | Ph | H | >10 |
| 30 | CH2CH2C6H5 | CH3 | H | >10 |
| 33 | CH(CH3)2 | H | CH3 | >10 |
| 38 | CH(CH3)2 | H | CH(CH3)2 | >10 |
| 42 | CH2Ph | H | H | >10 |
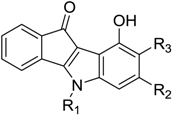
| Code | R1 | R2 | R3 | IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | CH(CH3)2 | CH3 | H | 0.43 |
| 11 | CH(CH3)2 | furan-2-yl | H | 1.65 |
| 13 | CH2C6H5 | H | H | 2.20 |
| 17 | CH2CH2C6H5 | CH3, | H | 4.10 |
| 19 | CH(CH3)2 | CH(CH3)2 | H | 4.76 |
| 20 | CH(CH3)2 | H | CH3 | 4.90 |
| 21 | CH(CH3)2 | H | H | 5.50 |
| 31 | CH(CH3)2 | H | CH(CH3)2 | >10 |
| 34 | CH(CH3)2 | (para-F)Ph | H | >10 |
| 35 | CH(CH3)2 | Ph | H | >10 |
| 36 | CH2CH2Ph | H | H | >10 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haidar, S.; Bouaziz, Z.; Marminon, C.; Laitinen, T.; Poso, A.; Le Borgne, M.; Jose, J. Development of Pharmacophore Model for Indeno[1,2-b]indoles as Human Protein Kinase CK2 Inhibitors and Database Mining. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10010008
Haidar S, Bouaziz Z, Marminon C, Laitinen T, Poso A, Le Borgne M, Jose J. Development of Pharmacophore Model for Indeno[1,2-b]indoles as Human Protein Kinase CK2 Inhibitors and Database Mining. Pharmaceuticals. 2017; 10(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaidar, Samer, Zouhair Bouaziz, Christelle Marminon, Tuomo Laitinen, Antti Poso, Marc Le Borgne, and Joachim Jose. 2017. "Development of Pharmacophore Model for Indeno[1,2-b]indoles as Human Protein Kinase CK2 Inhibitors and Database Mining" Pharmaceuticals 10, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10010008
APA StyleHaidar, S., Bouaziz, Z., Marminon, C., Laitinen, T., Poso, A., Le Borgne, M., & Jose, J. (2017). Development of Pharmacophore Model for Indeno[1,2-b]indoles as Human Protein Kinase CK2 Inhibitors and Database Mining. Pharmaceuticals, 10(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10010008