Detection and Pattern Recognition of Chemical Warfare Agents by MOS-Based MEMS Gas Sensor Array
Abstract
Highlights
- A sensor array consisting of 24 MOS-based MEMS sensors with good sensing performance in relation to chemical warfare agents (CWAs), a simple device structure, small size, and low power consumption was developed.
- Pattern recognition methods, such as principal component analysis and machine learning algorithms, were applied and accurately classified five CWAs based on features extracted from the initial kinetic characteristics and dynamic change characteristics of sensing response in testing data.
- The developed sensor array can meet the needs for qualitatively detecting and providing an early warning regarding low concentrations of CWAs.
- The sensor array can be integrated into portable devices and is driven by algorithms to realize the rapid, in situ, and on-site detection and identification of CWAs.
Abstract
1. Introduction
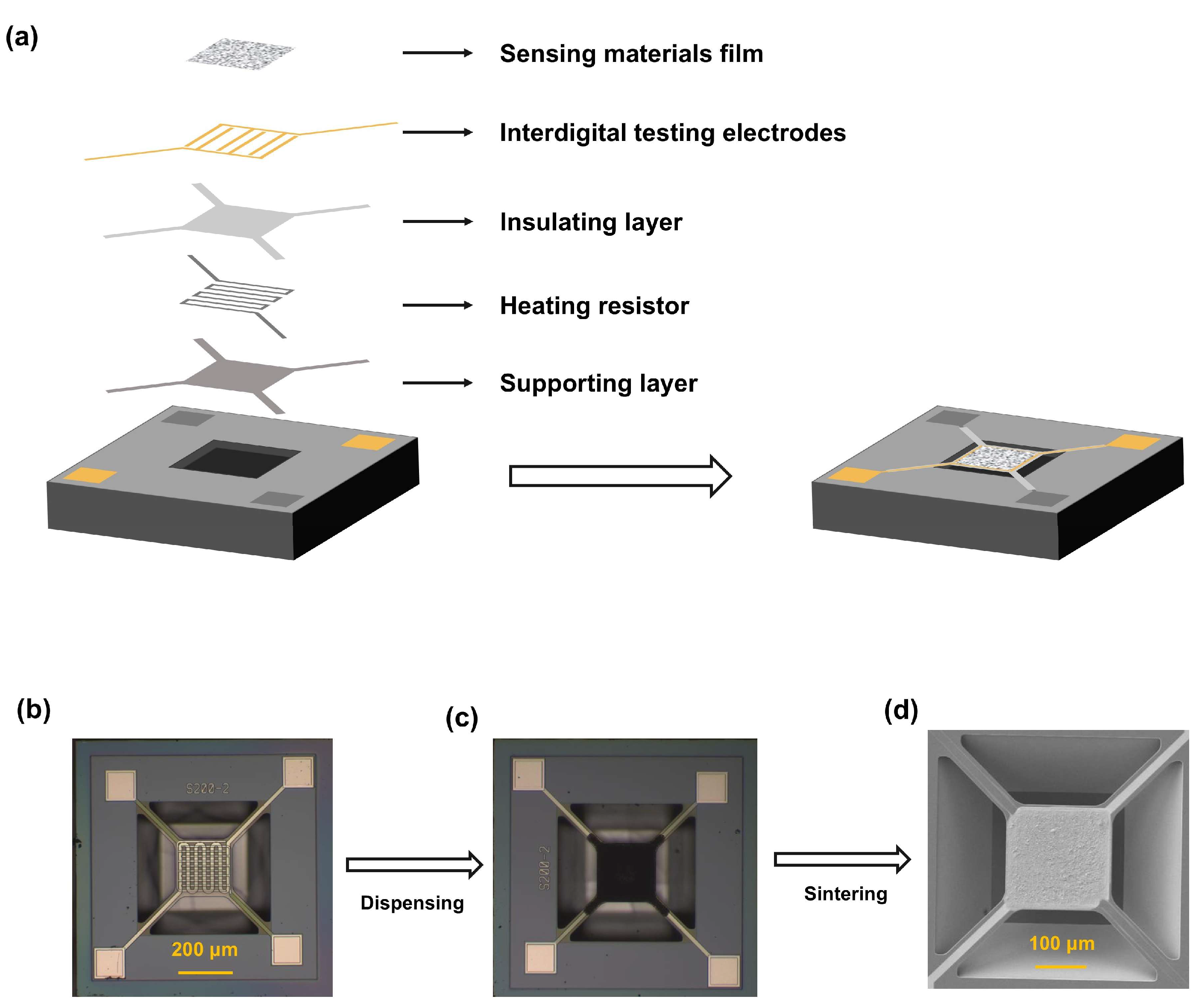
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Devices
2.2. Gas Sensing Tests
3. Results and Discussion
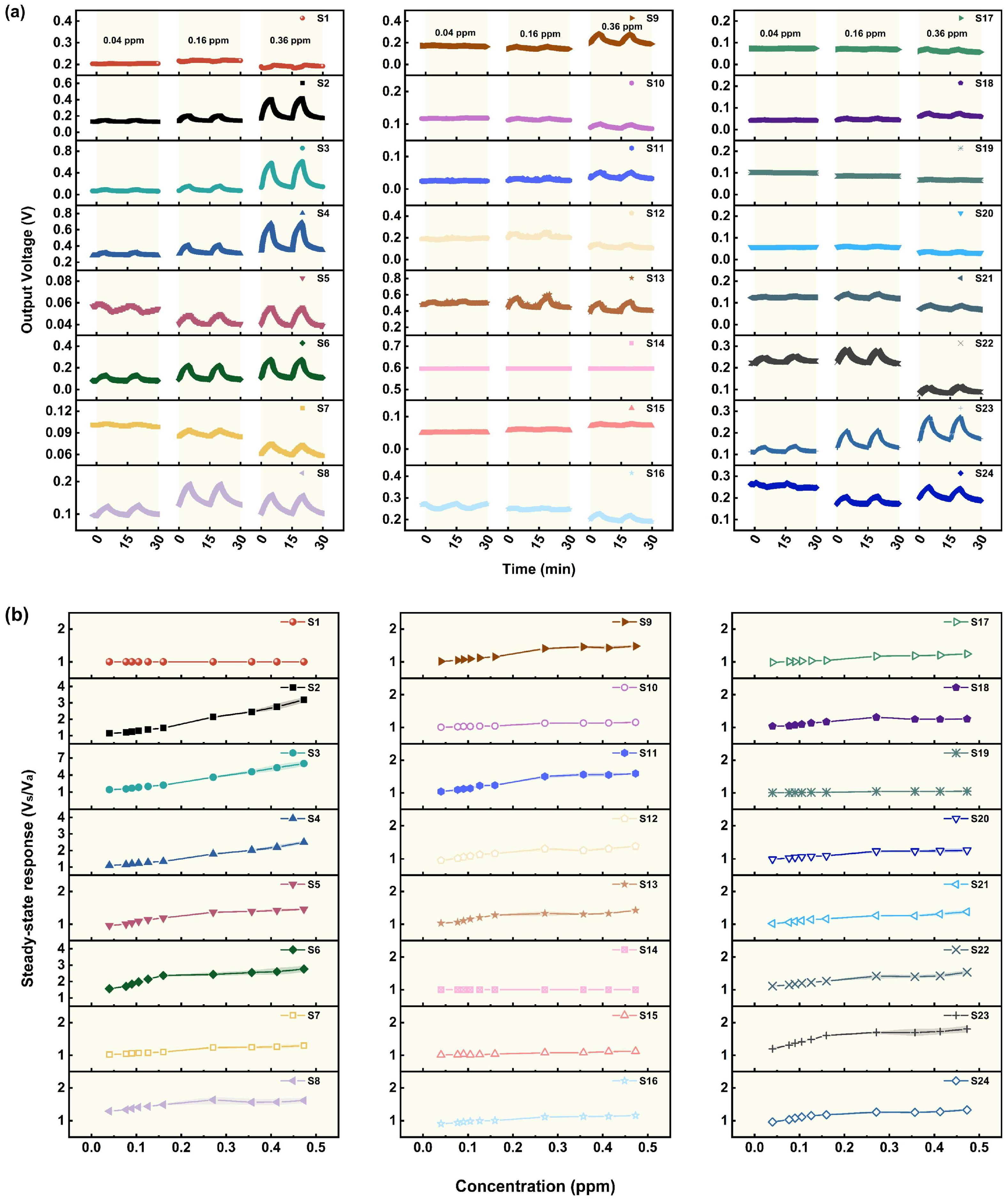
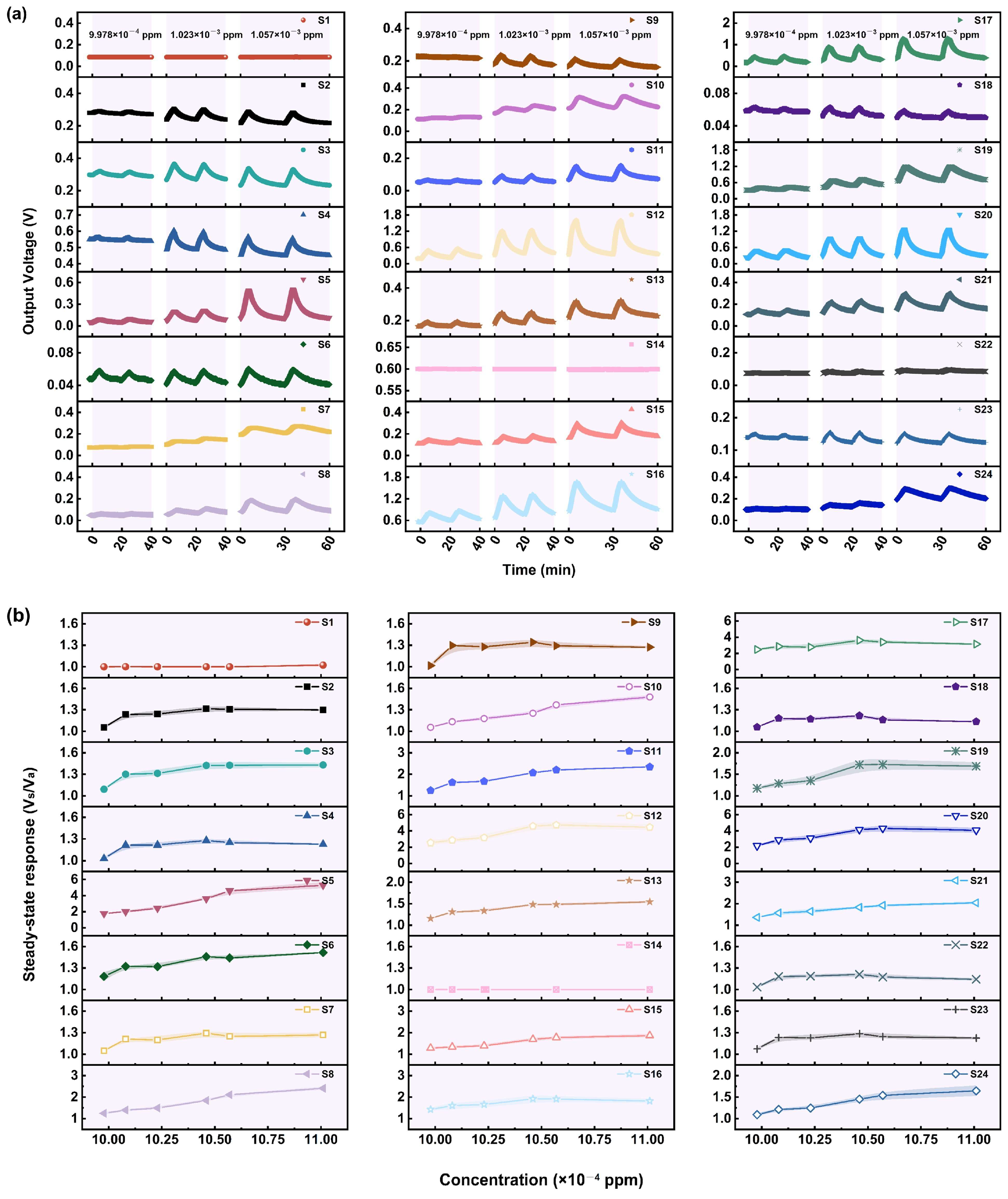
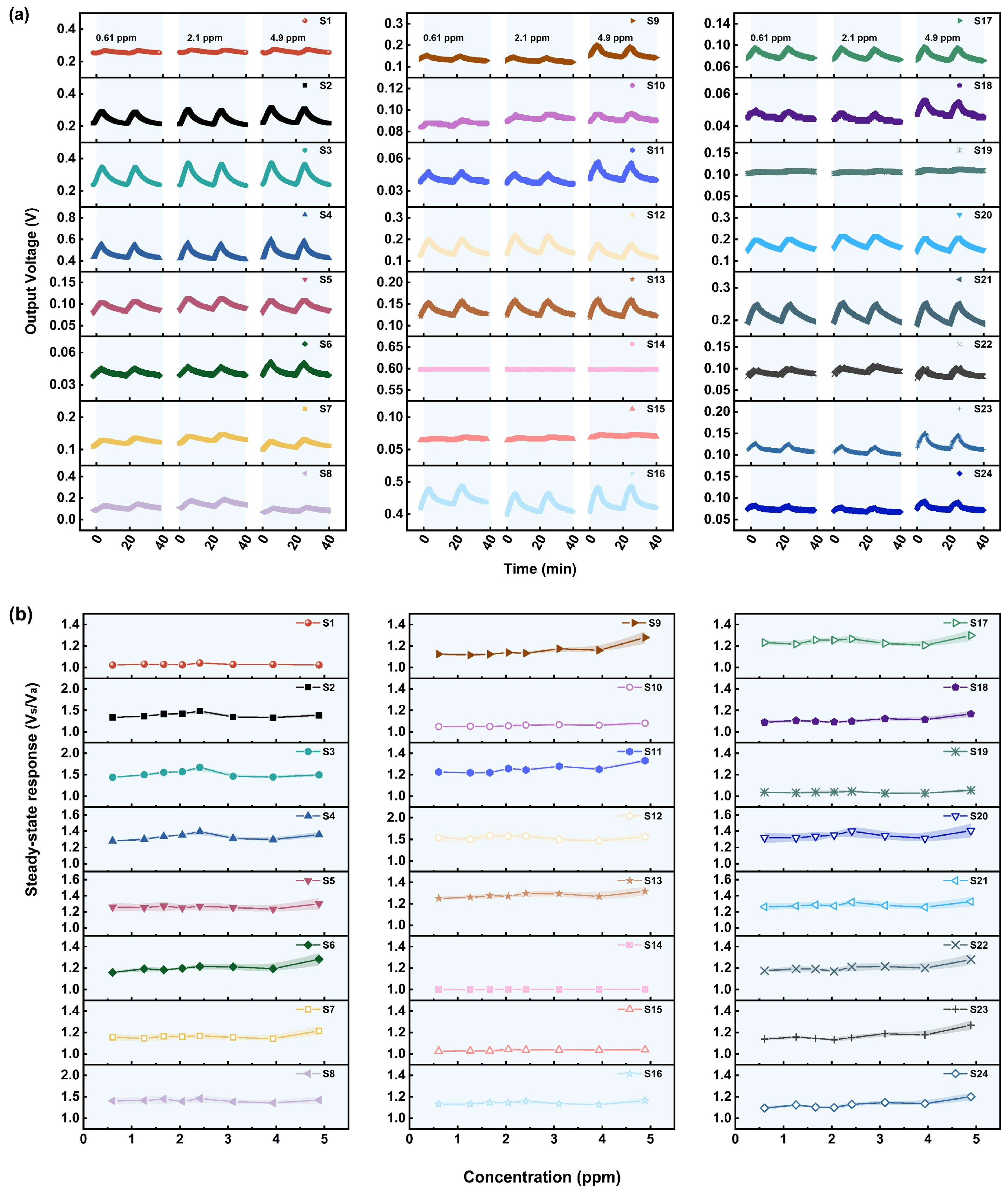
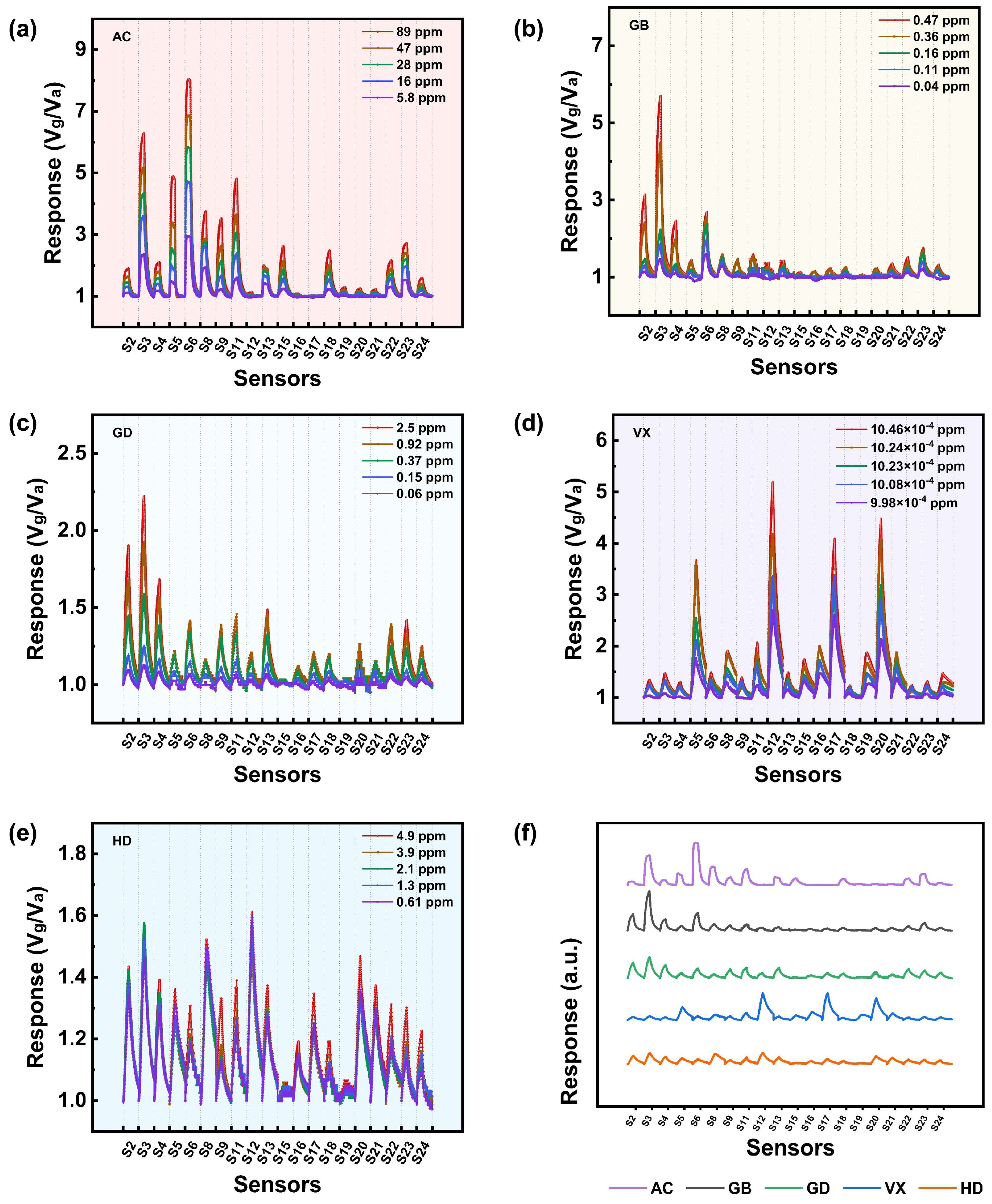
3.1. Gas Sensing Performances
3.1.1. Performance of the Sensors in Relation to AC
3.1.2. Performance of the Sensors in Relation to GB
3.1.3. Performance of the Sensors in Relation to GD
3.1.4. Performance of the Sensors in Relation to VX
3.1.5. Performance of the Sensors in Relation to HD
3.1.6. Potential Applications and Limitations of the Sensors
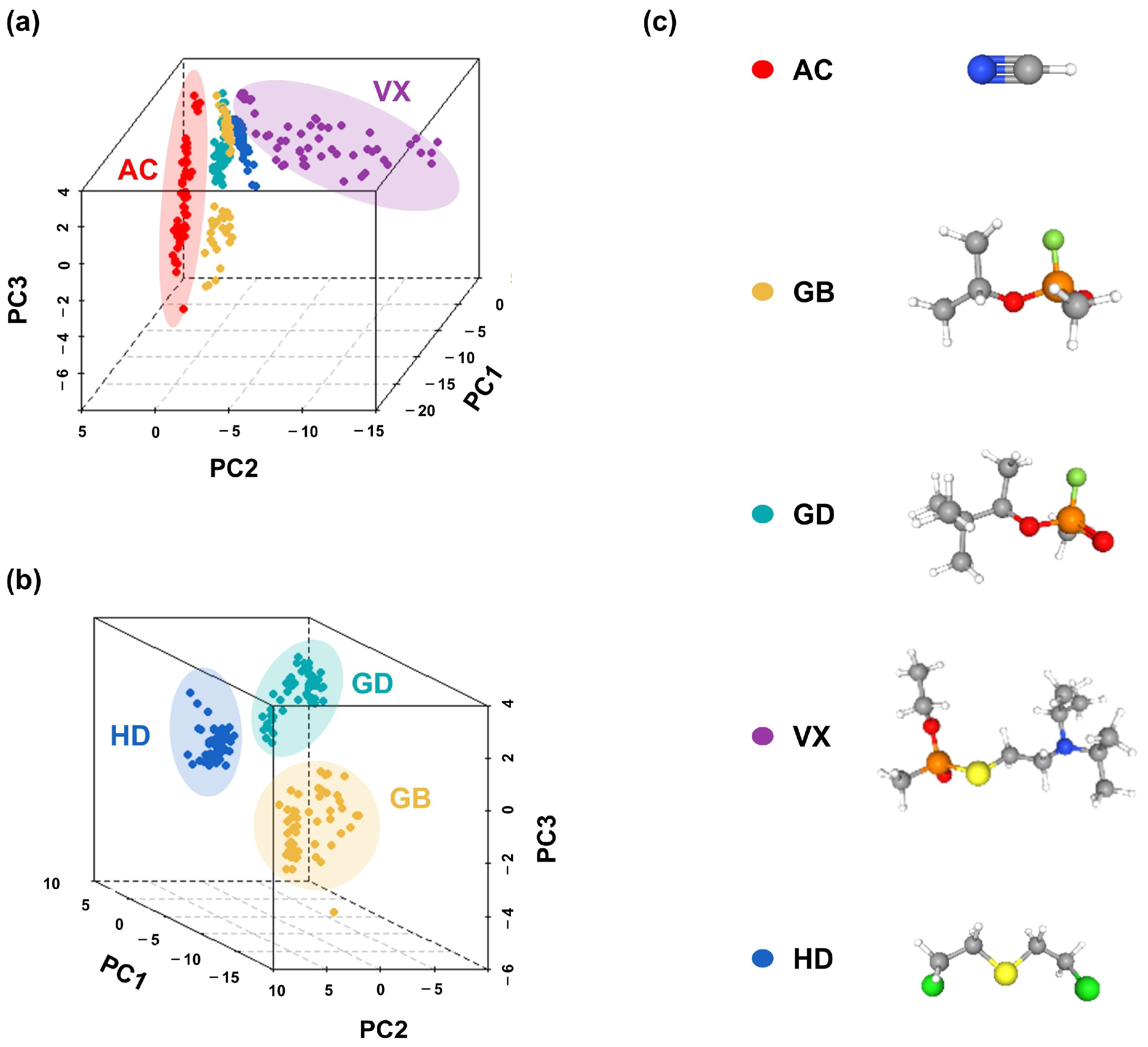
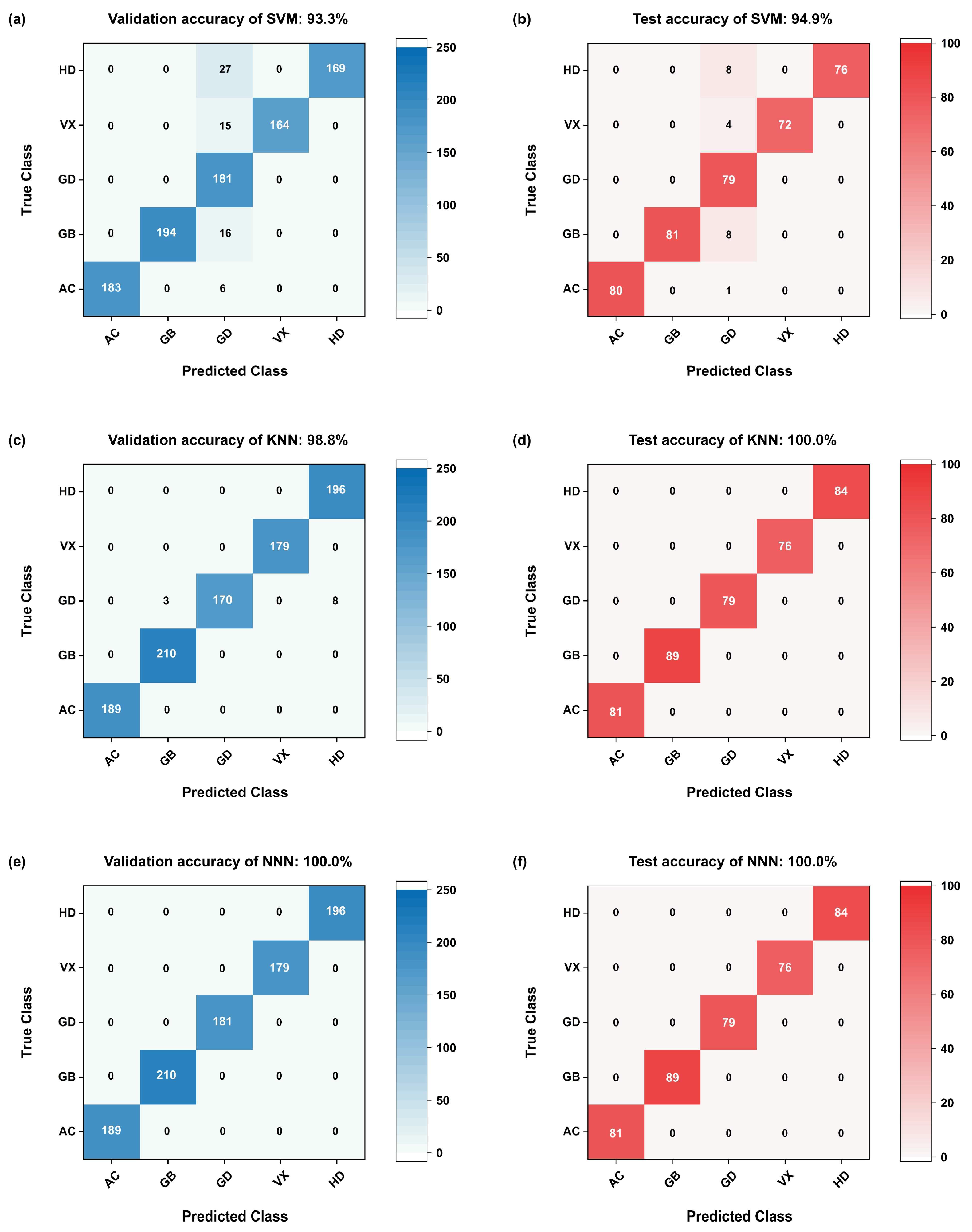
3.2. Pattern Recognition
3.2.1. Kinetic Characteristics and Principal Component Analysis
3.2.2. Dynamic Change Characteristics and Machine Learning Algorithms
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CWAs | Chemical warfare agents |
| MOS | Metal oxide semiconductor |
| MEMS | Micro-Electro-Mechanical System |
| AC | Hydrogen cyanide |
| GB | 2-[fluoro(methyl)phosphoryl]oxypropane |
| GD | 3-[fluoro(methyl)phosphoryl]oxy-2,2-dimethylbutane |
| VX | Ethyl S-(2-diisopropylaminoethyl) methylphosphonothioate |
| HD | Di-2-chloroethyl sulfide |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| LOD | Low limit of detection |
| R | Response |
| SR | Steady-state response |
| MR | Maximum response |
| IDLH | Immediately dangerous for life and health |
| SVM | Support vector machines |
| KNN | K-nearest neighbor algorithm |
| NNN | Narrow neural networks |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
References
- Pacsial-Ong, E.J. Chemical warfare agent detection a review of current trends and future perspective. Front. Biosci. 2013, S5, 516–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diauudin, F.N.; Rashid, J.I.A.; Knight, V.F.; Wan Yunus, W.M.Z.; Ong, K.K.; Kasim, N.A.M.; Abdul Halim, N.; Noor, S.A.M. A review of current advances in the detection of organophosphorus chemical warfare agents based biosensor approaches. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2019, 26, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, G.; Dai, L.; Yang, M.; Su, Y. Rapid and highly selective dopamine sensing with CuInSe2-modified nanocomposite. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, D.; Maccato, C.; Gasparotto, A. Metal oxide nanosystems as chemoresistive gas sensors for chemical warfare agents: A focused review. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2102525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Cheong, H.W.; Son, L.D.N.; Yoon, Y.S. Surface reaction mechanism of acetonitrile on doped SnO2 sensor element and its response behavior. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 2119–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Fei, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T. The synergistic effects of oxygen vacancy engineering and surface gold decoration on commercial SnO2 for ppb-level DMMP sensing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 2703–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, L.A.; Bari, A.R.; Shinde, M.D.; Deo, V.; Kaushik, M.P. Detection of dimethyl methyl phosphonate—A simulant of sarin: The highly toxic chemical warfare—Using platinum activated nanocrystalline ZnO thick films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, R.; Cho, S.; Song, M.J.; Lee, W. Highly sensitive gas sensor based on Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles for detection of dimethyl methylphosphonate as a chemical warfare agent simulant. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, R.; Yoo, S.; Lee, D.; Kim, J.; Cho, S.; Lee, W. Highly selective detection of dimethyl methylphosphonate (DMMP) using CuO nanoparticles /ZnO flowers heterojunction. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alali, K.T.; Liu, J.; Moharram, D.; Liu, Q.; Yu, J.; Chen, R.; Li, R.; Wang, J. Fabrication of electrospun Co3O4/CuO p-p heterojunctions nanotubes functionalized with HFIP for detecting chemical nerve agent under visible light irradiation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 314, 128076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigiani, L.; Zappa, D.; Barreca, D.; Gasparotto, A.; Sada, C.; Tabacchi, G.; Fois, E.; Comini, E.; Maccato, C. Sensing nitrogen mustard gas simulant at the ppb scale via selective dual-site activation at Au/Mn3O4 interfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 23692–23700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Li, T. Trace level analysis of nerve agent simulant DMMP with silicon nanowire FET sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 12096–12101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Z.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Cheng, Z. Silicon nanowire array sensor for highly sensitive and selective detection of nerve agent simulant vapor via surface hydroxyl groups. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 16th International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems (NEMS), Xiamen, China, 25–29 April 2021; pp. 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Xu, P.; Yu, H.; Cheng, Z.; Li, X. Synergistic improvement of gas sensing performance by micro-gravimetrically extracted kinetic/thermodynamic parameters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 863, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; He, J.; Hu, X.; Yan, C.; Cheng, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zuo, G. Copper oxide nanoparticle sensors for hydrogen cyanide detection: Unprecedented selectivity and sensitivity. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 155, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; He, J.; Hu, X.; Yan, C.; Cheng, Z. CuO nanostructures as quartz crystal microbalance sensing layers for detection of trace hydrogen cyanide gas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6088–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asri, M.I.A.; Hasan, M.N.; Fuaad, M.R.A.; Yunos, Y.M.; Ali, M.S.M. MEMS gas sensors: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 18381–18397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollé, E.P.; Farré-Lladós, J.; Casals-Terré, J. Advancements in microfabricated gas sensors and microanalytical tools for the sensitive and selective detection of odors. Sensors 2020, 20, 5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazemi, H.; Joseph, A.; Park, J.; Emadi, A. Advanced micro- and nano-gas sensor technology: A review. Sensors 2019, 19, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, F.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Yu, H.; Dong, X.; Wang, T. Polyoxometalates/metal–organic frameworks-derived ZnO/ZnWO4 nanoparticles for highly sensitive and selective ppb-level NO2 detection. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sun, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, P.; Wu, Z. Highly selective room-temperature formaldehyde gas sensor based on SnO2 nanoparticle-modified In2O3 microspheres. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 695, 162856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomchenko, A.A.; Harmer, G.P.; Marquis, B.T. Detection of chemical warfare agents using nanostructured metal oxide sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.R.; Park, H.D.; Lee, D.D. Acetonitrile sensing characteristics and infrared study of SnO2-based gas sensors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2000, 161, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, D.D.; Huh, J.S.; Jun, H.K.; Kim, J.C. The sensing behavior of SnO2-based thick-film gas sensors at a low concentration of chemical agent simulants. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sberveglieri, G.; Baratto, C.; Comini, E.; Faglia, G.; Ferroni, M.; Pardo, M.; Ponzoni, A.; Vomiero, A. Semiconducting tin oxide nanowires and thin films for chemical warfare agents detection. Thin Solid. Film. 2009, 517, 6156–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alali, K.T.; Liu, J.; Aljebawi, K.; Liu, P.; Chen, R.; Li, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J. Electrospun n-p WO3/CuO heterostructure nanofibers as an efficient sarin nerve agent sensing material at room temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 793, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguín, C.; Laguarda Miró, N.; Pascual, L.; García Breijo, E.; Martínez Mañez, R.; Soto, J. An electronic nose for the detection of Sarin, Soman and Tabun mimics and interfering agents. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.J.; Kwak, J.H.; Lim, Y.T.; Bahn, T.H.; Yun, K.Y.; Kim, J.C.; Huh, J.S.; Lee, D.D. Classification of chemical warfare agents using thick film gas sensor array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, S.M.; Mirzaei, A.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, T.W. Recent advances in energy-saving chemiresistive gas sensors: A review. Nano Energy 2021, 79, 105369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Brewster Ii, J.T.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Challenges and opportunities of chemiresistors based on microelectromechanical systems for chemical olfaction. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 17778–17801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Wang, F. A review of MEMS-based metal oxide semiconductors gas sensor in Mainland China. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2022, 32, 054003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Chen, D.; Peng, S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Wu, F. A low power cantilever-based metal oxide semiconductor gas sensor. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 2019, 40, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patial, P.; Deshwal, M. Selectivity and sensitivity property of metal oxide semiconductor based gas sensor with dopants variation: A review. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 2022, 23, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenk, M. Chemical warfare agents. Classes and targets. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 293, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, W.; Lee, W. Chemiresistive gas sensors for detection of chemical warfare agent simulants. J. Sens. Sci. Technol. 2019, 28, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Aliha, H.M.; Khodadadi, A.A.; Mortazavi, Y. The sensing behaviour of metal oxides (ZnO, CuO and Sm2O3) doped-SnO2 for detection of low concentrations of chlorinated volatile organic compounds. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 181, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.; Hu, X.; Zhang, H.; Miao, T.; Ma, L.; Liang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Cheng, Z.; Sun, X. Detection and Pattern Recognition of Chemical Warfare Agents by MOS-Based MEMS Gas Sensor Array. Sensors 2025, 25, 2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082633
Xu M, Hu X, Zhang H, Miao T, Ma L, Liang J, Zhu Y, Zhu H, Cheng Z, Sun X. Detection and Pattern Recognition of Chemical Warfare Agents by MOS-Based MEMS Gas Sensor Array. Sensors. 2025; 25(8):2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082633
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Mengxue, Xiaochun Hu, Hongpeng Zhang, Ting Miao, Lan Ma, Jing Liang, Yuefeng Zhu, Haiyan Zhu, Zhenxing Cheng, and Xuhui Sun. 2025. "Detection and Pattern Recognition of Chemical Warfare Agents by MOS-Based MEMS Gas Sensor Array" Sensors 25, no. 8: 2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082633
APA StyleXu, M., Hu, X., Zhang, H., Miao, T., Ma, L., Liang, J., Zhu, Y., Zhu, H., Cheng, Z., & Sun, X. (2025). Detection and Pattern Recognition of Chemical Warfare Agents by MOS-Based MEMS Gas Sensor Array. Sensors, 25(8), 2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082633



