3D-Printed Insole for Measuring Ground Reaction Force and Center of Pressure During Walking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
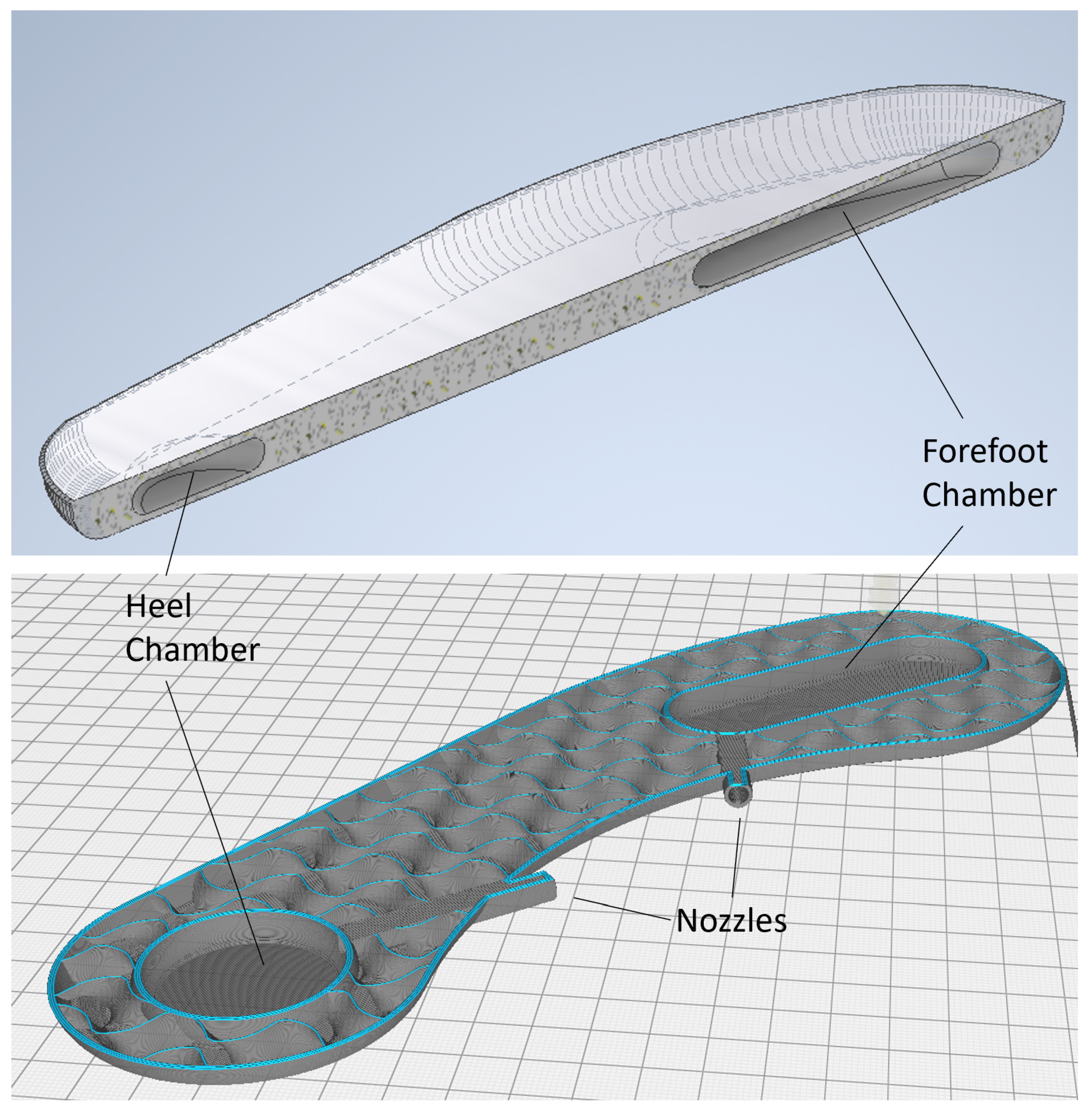
2.1. Insole Design
2.2. Material Choice and Fabrication
2.3. Measurement Range and Bandwidth
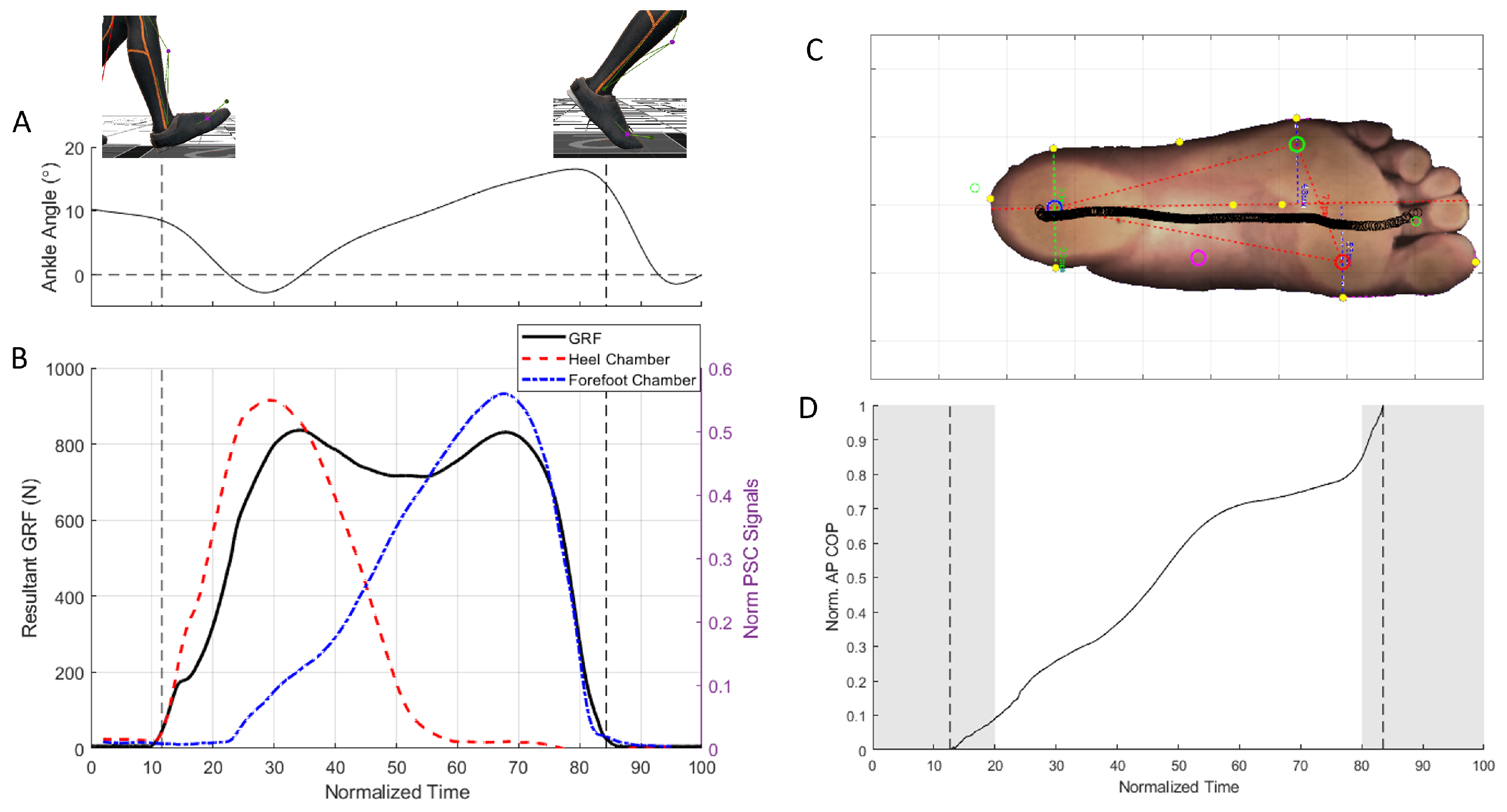
2.4. Characterization Experiments
2.4.1. GRF Model Parameter Identification
2.4.2. COP Model Parameter Identification
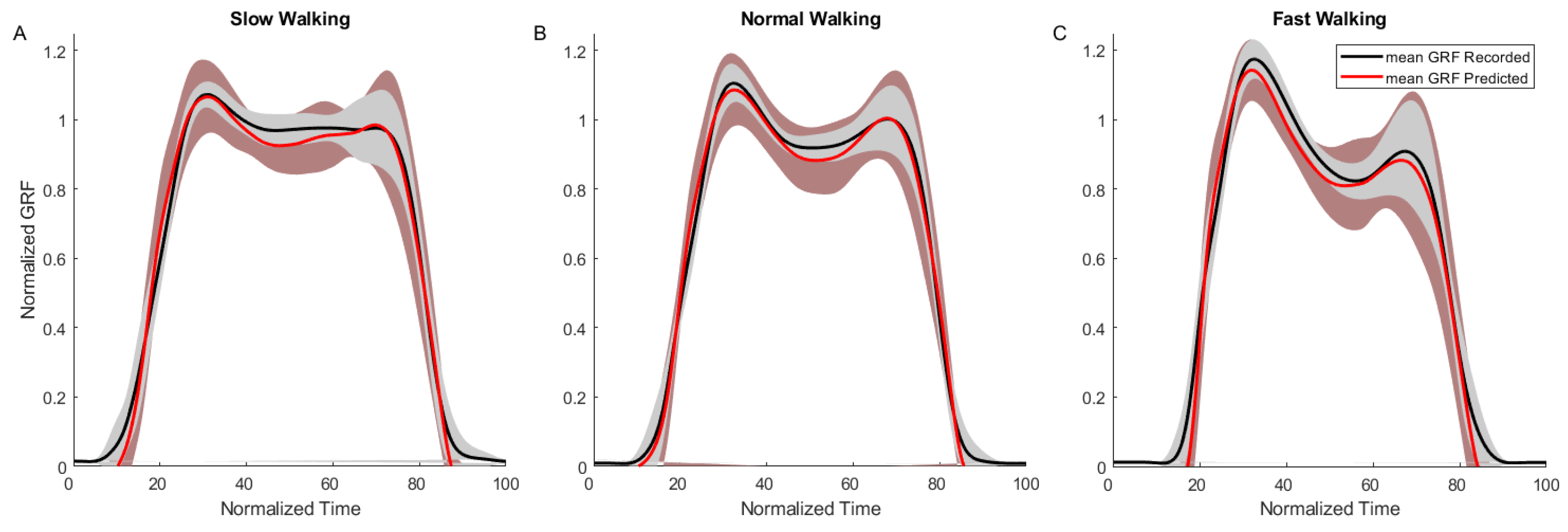
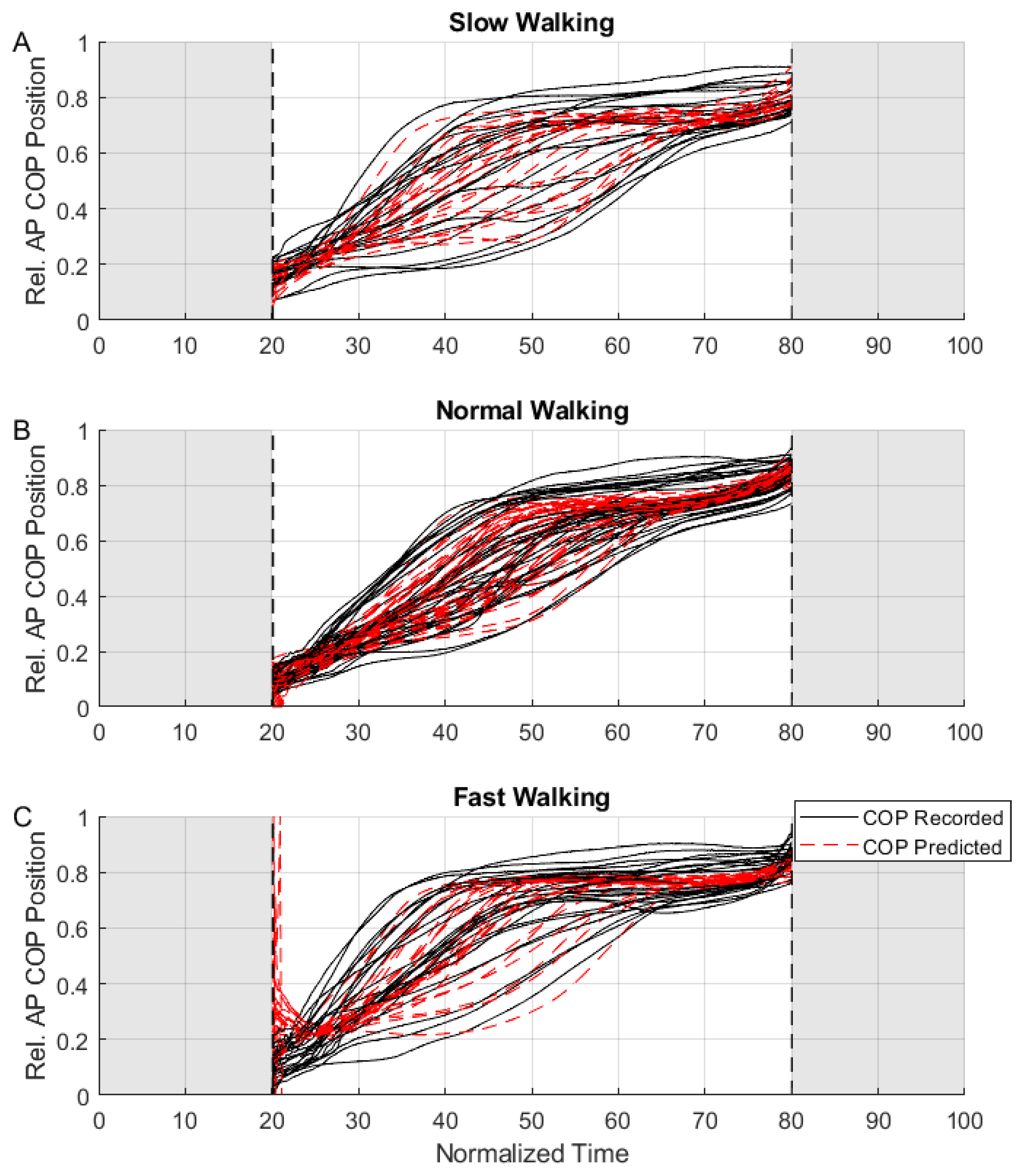
2.4.3. Validation and Comparison
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GRF | Ground Reaction Force |
| COP | Center of Pressure |
| PSC | Pneumatic Sensing Chamber |
| TPU | Thermoplastic Polyurethane |
| FDM | Fused Deposition Modelling |
| DAQ | Data Acquisition Hub |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
References
- van der Worp, H.; Vrielink, J.W.; Bredeweg, S.W. Do runners who suffer injuries have higher vertical ground reaction forces than those who remain injury-free? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sport. Med. 2016, 50, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willwacher, S.; Kurz, M.; Robbin, J.; Thelen, M.; Hamill, J.; Kelly, L.; Mai, P. Running-Related Biomechanical Risk Factors for Overuse Injuries in Distance Runners: A Systematic Review Considering Injury Specificity and the Potentials for Future Research. Sport. Med. 2022, 52, 1863–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Gao, Z.; Wang, A.; Shim, V.; Fekete, G.; Gu, Y.; Fernandez, J. Rethinking running biomechanics: A critical review of ground reaction forces, tibial bone loading, and the role of wearable sensors. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1377383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, F.; Allard, P.; Guelton, K.; Colobert, B.; Godillon-Maquinghen, A.P. Estimation of the 3-D center of mass excursion from force-plate data during standing. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2003, 11, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delp, S.L.; Anderson, F.C.; Arnold, A.S.; Loan, P.; Habib, A.; John, C.T.; Guendelman, E.; Thelen, D.G. OpenSim: Open-Source Software to Create and Analyze Dynamic Simulations of Movement. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 1940–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, A.; Hicks, J.L.; Uchida, T.K.; Habib, A.; Dembia, C.L.; Dunne, J.J.; Ong, C.F.; DeMers, M.S.; Rajagopal, A.; Millard, M.; et al. OpenSim: Simulating musculoskeletal dynamics and neuromuscular control to study human and animal movement. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, L.C.; Clermont, C.A.; Bošnjak, E.; Ferber, R. The use of wearable devices for walking and running gait analysis outside of the lab: A systematic review. Gait Posture 2018, 63, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutabarat, Y.; Owaki, D.; Hayashibe, M. Recent Advances in Quantitative Gait Analysis Using Wearable Sensors: A Review. IEEE Sensors J. 2021, 21, 26470–26487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lach, J.; Lo, B.; Yang, G.Z. Toward Pervasive Gait Analysis With Wearable Sensors: A Systematic Review. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 1521–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.; Kim, W.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Shin, K.; Park, T.; Lee, J.; Han, C. Development of a lower extremity Exoskeleton Robot with a quasi-anthropomorphic design approach for load carriage. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 5345–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvade, P.S.; Joshi, A.K.; Madhe, S.P. IoT based monitoring of foot pressure using FSR sensor. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Chennai, India, 6–8 April 2017; pp. 0635–0639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqueveque, P.; Osorio, R.; Pastene, F.; Saavedra, F.; Pino, E. Capacitive Sensors Array for Plantar Pressure Measurement Insole fabricated with Flexible PCB. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 4393–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Martí, F.; Martínez-García, M.S.; García-Díaz, S.G.; García-Jiménez, J.; Palma, A.J.; Carvajal, M.A. Embedded sensor insole for wireless measurement of gait parameters. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2014, 37, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.Y.; Youn, J.H.; Lim, S.H.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, U.; Kyung, K.U. Development of a Three-Axis Monolithic Flexure-Based Ground Reaction Force Sensor for Various Gait Analysis. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 4118–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drăgulinescu, A.; Drăgulinescu, A.M.; Zincă, G.; Bucur, D.; Feies, V.; Neagu, D.M. Smart Socks and In-Shoe Systems: State-of-the-Art for Two Popular Technologies for Foot Motion Analysis, Sports, and Medical Applications. Sensors 2020, 20, 4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawk, C.; in het Panhuis, M.; Spinks, G.M.; Alici, G. Soft Pneumatic Sensing Chambers for Generic and Interactive Human–Machine Interfaces. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2019, 1, 1900002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottin-Noonan, J.; Sreenivasa, M.; Alici, G. Development and Characterization of a 3D Printed Soft Sensor to Identify Physiological Joint Forces. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, AIM, Sapporo, Japan, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soames, R. Foot pressure patterns during gait. J. Biomed. Eng. 1985, 7, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, J.R.R.; Hutton, W.C.; Stokes, I.A.F. Forces under the foot. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 1973, 55-B, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessert, M.J.; Vyas, M.; Leach, J.; Hu, K.; Lipsitz, L.A.; Novak, V. Foot pressure distribution during walking in young and old adults. BMC Geriatr. 2005, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alici, G.; Spinks, G.M.; Madden, J.D.; Wu, Y.; Wallace, G.G. Response characterization of electroactive polymers as mechanical sensors. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2008, 13, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, D.A. Kinematic and kinetic patterns in human gait: Variability and compensating effects. Hum. Mov. Sci. 1984, 3, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Optitrack Baseline Lower (20) Skeleton Marker Set. Available online: https://docs.optitrack.com/markersets/lower/baseline-lower-20 (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Tahir, A.M.; Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Khandakar, A.; Al-Hamouz, S.; Abdalla, M.; Awadallah, S.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Al-Emadi, N. A Systematic Approach to the Design and Characterization of a Smart Insole for Detecting Vertical Ground Reaction Force (vGRF) in Gait Analysis. Sensors 2020, 20, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, A.M.; Kobayashi, T.; Hayes, H.A.; Foreman, K.B.; Bamberg, S.J.M. Kinetic Gait Analysis Using a Low-Cost Insole. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 3284–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binelli, M.R.; van Dommelen, R.; Nagel, Y.; Kim, J.; Haque, R.I.; Coulter, F.B.; Siqueira, G.; Studart, A.R.; Briand, D. Digital manufacturing of personalised footwear with embedded sensors. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, R.T.; Davis, I.S. Landing Pattern Modification to Improve Patellofemoral Pain in Runners: A Case Series. J. Orthop. Sport. Phys. Ther. 2011, 41, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seong, M.; Kim, G.; Yeo, D.; Kang, Y.; Yang, H.; Delpreto, J.; Matusik, W.; Rus, D.; Kim, S. MultiSenseBadminton: Wearable Sensor–Based Biomechanical Dataset for Evaluation of Badminton Performance. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawk, C.; Alici, G. A Review of 3D-Printable Soft Pneumatic Actuators and Sensors: Research Challenges and Opportunities. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiberl, W.; Jensen, E.; Merker, J.; Leitel, M.; Schwirtz, A. Accuracy and precision of loadsol® insole force-sensors for the quantification of ground reaction force-based biomechanical running parameters. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weizman, Y.; Tan, A.M.; Fuss, F.K. Accuracy of Centre of Pressure Gait Measurements from Two Pressure-Sensitive Insoles. Proceedings 2018, 2, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zanotto, D.; Agrawal, S.K. Estimating CoP Trajectories and Kinematic Gait Parameters in Walking and Running Using Instrumented Insoles. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 2159–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijoux, F.; Nicolaï, A.; Chairi, I.; Bargiotas, I.; Ricard, D.; Yelnik, A.; Oudre, L.; Bertin-Hugault, F.; Vidal, P.P.; Vayatis, N.; et al. A review of center of pressure (COP) variables to quantify standing balance in elderly people: Algorithms and open-access code. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e15067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, I.; Okada, K.; Nishi, T.; Wakasa, M.; Saito, A.; Sugawara, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Kinoshita, K. Foot Pressure Pattern and its Correlation With Knee Range of Motion Limitations for Individuals With Medial Knee Osteoarthritis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 2502–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Kong, K. A Soft Three-Axis Force Sensor Based on Radially Symmetric Pneumatic Chambers. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 5229–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Slow | Normal | Fast | Combined | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRF | 1.5746 | 1.4319 | 1.67 | 1.529 | |
| 1.9876 | 1.906 | 2.0363 | 1.9663 | ||
| −1.1669 | −3.3699 | 4.0188 | 0.02 | ||
| 24.8631 | 24.232 | 25.1783 | 25.3092 | ||
| COP | 0.2407 | 0.199 | 0.257 | 0.2193 | |
| 0.7317 | 0.7528 | 0.7573 | 0.7585 | ||
| −4.1693 | −3.2918 | 1.4174 | 1.5132 | ||
| −5.5972 | −5.2196 | −1.8396 | −2.5901 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vu, L.T.; Bottin-Noonan, J.; Armitage, L.; Alici, G.; Sreenivasa, M. 3D-Printed Insole for Measuring Ground Reaction Force and Center of Pressure During Walking. Sensors 2025, 25, 2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082524
Vu LT, Bottin-Noonan J, Armitage L, Alici G, Sreenivasa M. 3D-Printed Insole for Measuring Ground Reaction Force and Center of Pressure During Walking. Sensors. 2025; 25(8):2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082524
Chicago/Turabian StyleVu, Le Tung, Joel Bottin-Noonan, Lucy Armitage, Gursel Alici, and Manish Sreenivasa. 2025. "3D-Printed Insole for Measuring Ground Reaction Force and Center of Pressure During Walking" Sensors 25, no. 8: 2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082524
APA StyleVu, L. T., Bottin-Noonan, J., Armitage, L., Alici, G., & Sreenivasa, M. (2025). 3D-Printed Insole for Measuring Ground Reaction Force and Center of Pressure During Walking. Sensors, 25(8), 2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25082524







