Adaptive Steered Frequency–Wavenumber Analysis for High-Frequency Source Localization in Shallow Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Steered Frequency–Wavenumber Analysis
2.1. Bartlett SFK
2.2. MV+SFK Formula
2.3. WNC+SFK Formula
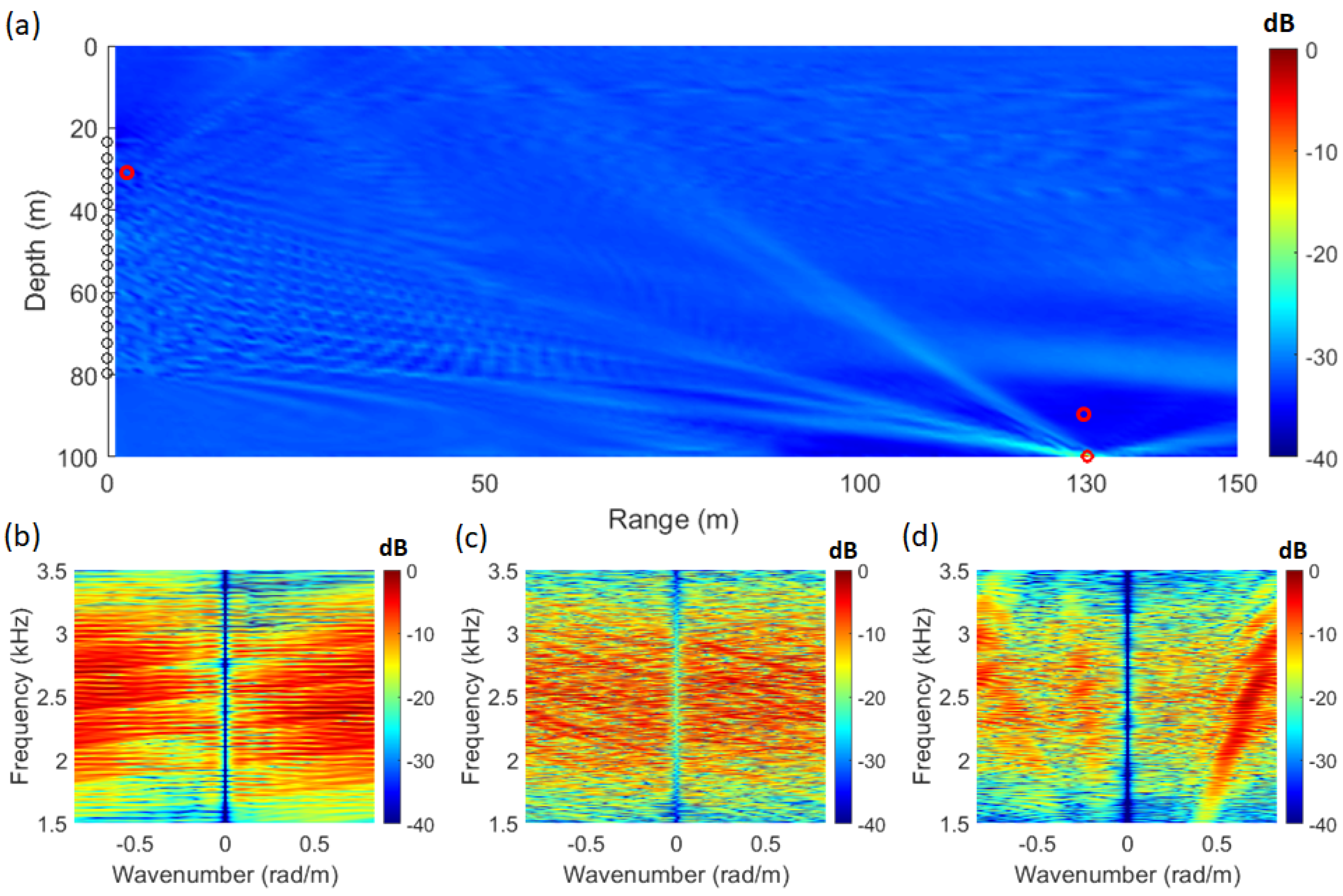
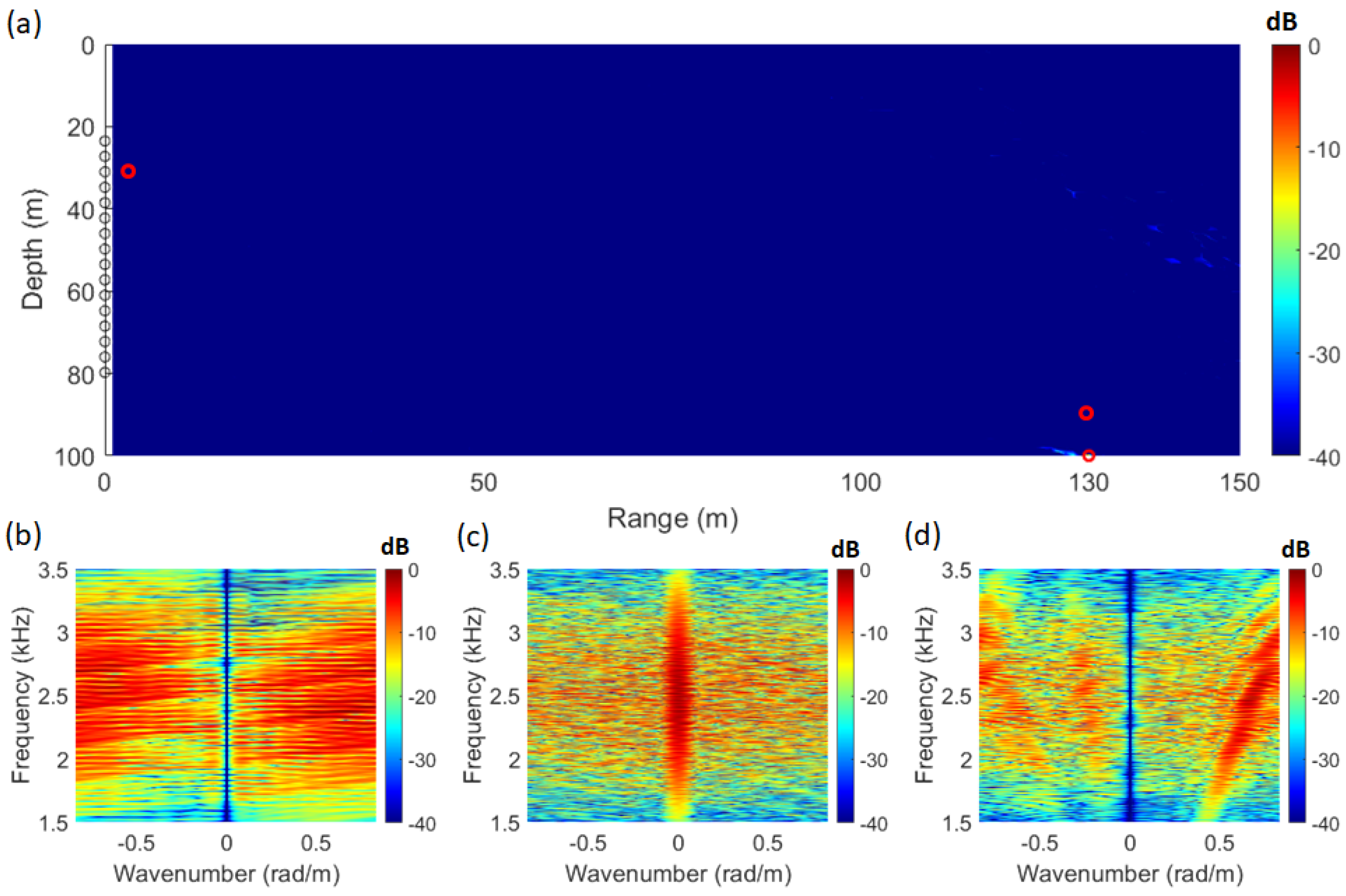
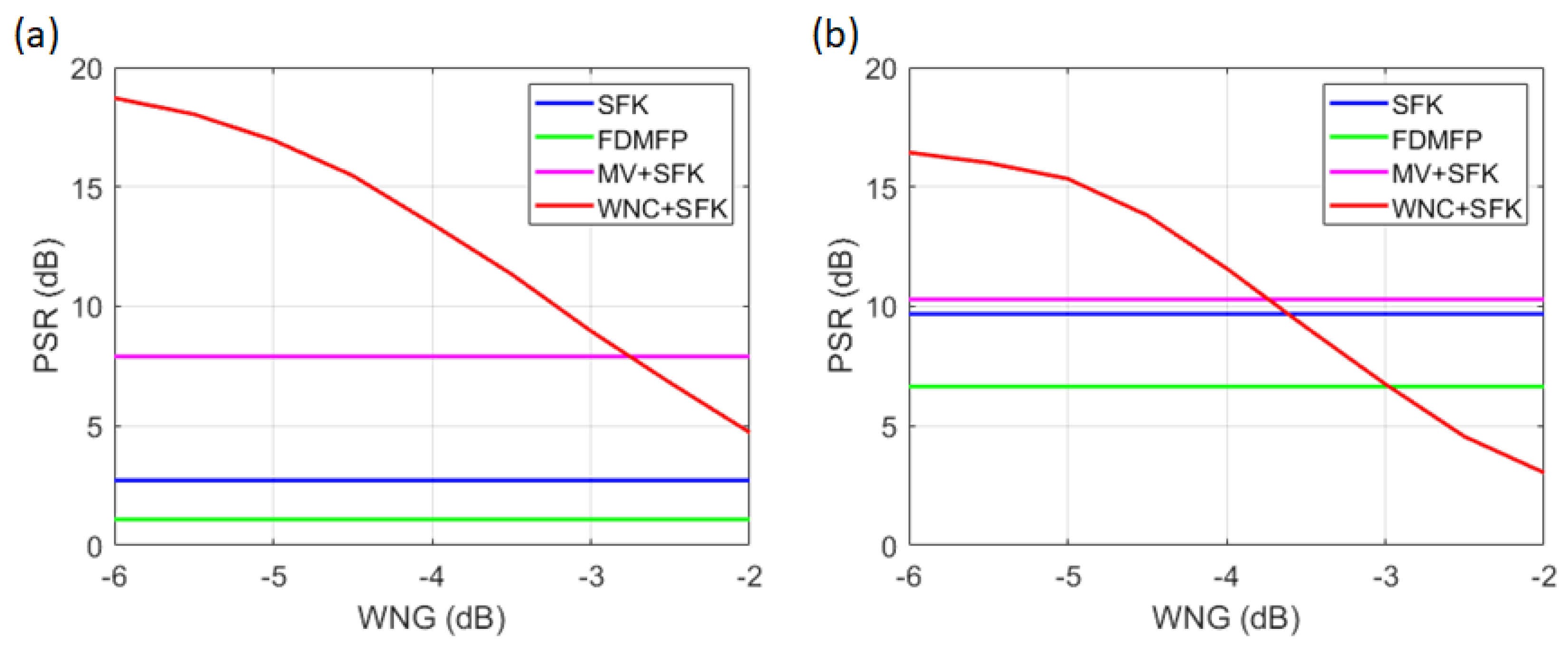
3. Simulation
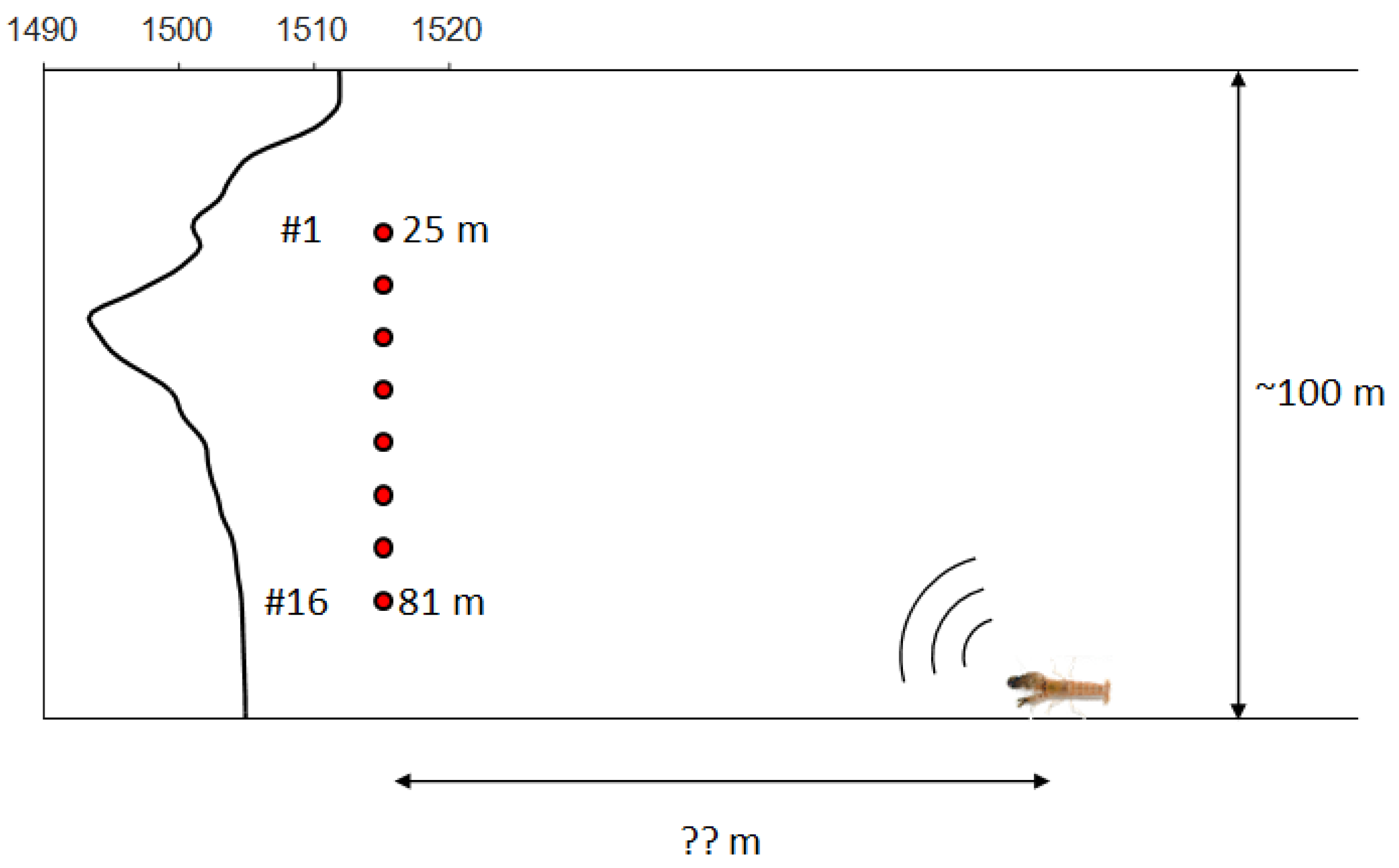
3.1. Geometry
3.2. Bartlett SFK
3.3. MV+SFK
3.4. WNC+SFK
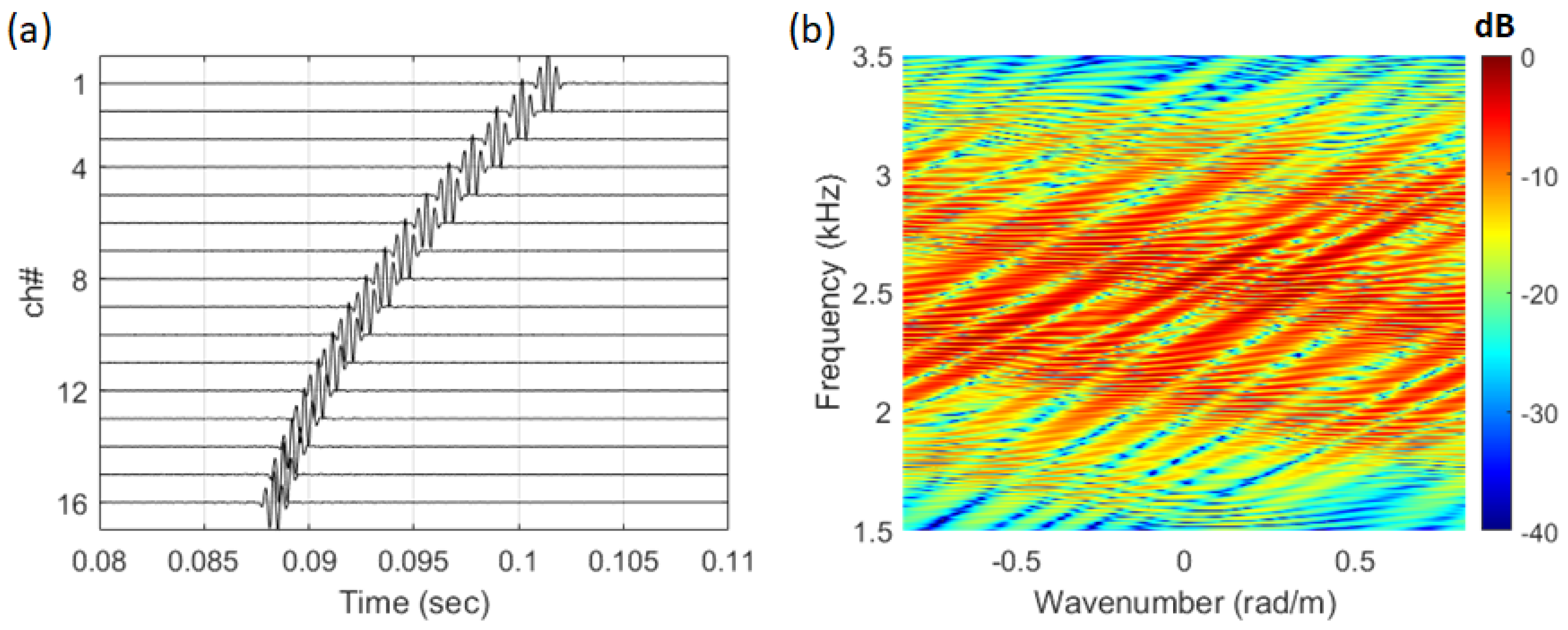
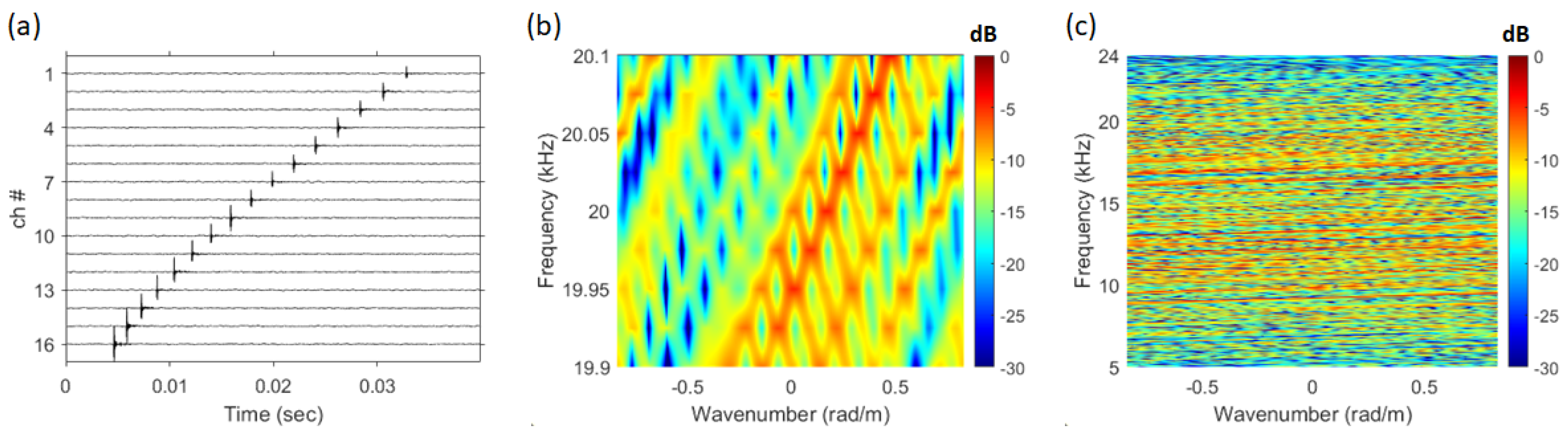
4. SAVEX15 Data Analysis
4.1. SAVEX15 Geometry
4.2. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuperman, W.A.; Jackson, D.R. Ocean acoustics, matched-field processing and phase conjugation. In Imaging of Complex Media with Acoustic and Seismic Waves; Kuperman, W.A., Jackson, D.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002; pp. 43–97. [Google Scholar]
- Dowling, D.R.; Sabra, K.G. Acoustic remote sensing. Am. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2015, 47, 221–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Sun, C.; Li, M. Multifrequency matched-field source localization based on Wasserstein metric for probability measures. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 154, 3062–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, W.F., II; Gerstoft, P.; Park, Y.S. Bayesian optimization with Gaussian process surrogate model for source localization. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 154, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.W.; Zhou, X.; Cao, R.; Huang, C.L.; Li, D.W.; Yin, J.R. Environmentally and statistically robust matched-field source localization based on information geometry principles. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2024, 156, 3893–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthmann, B.M.; Song, H.C.; Dowling, D.R. High frequency source localization in a shallow ocean sound channel using frequency difference matched field processing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, 3549–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Kim, J.S.; Byun, G. Source localization based on steered frequency-wavenumber analysis for sparse array. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 153, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Richards, E.L.; Song, H.C.; Hodgkiss, W.S.; Yan, S. Calibration of vertical array tilt using snapping shrimp sound. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 144, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.W.; Everest, F.A.; Young, R.W. The role of snapping shrimp (Cragon and Synalpheus) in the production of underwater noise in the sea. Biol. Bull. 1947, 93, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everest, F.A.; Young, R.W.; Johnson, M.W. Acoustical characteristics of noise produced by snapping shrimp. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1948, 20, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versluis, M.; Schmitz, B.; Von der Heydt, A.; Lohse, D. How snapping shrimp snap: Through cavitating bubbles. Sciences 2000, 289, 2114–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cato, D.H.; Bell, M.J. Ultrasonic ambient noise in Australian shallow waters at frequencies up to 200 kHz. In Material Research Laboratory Technical Report No. MRL-TR91-23; Material Research Laboratory: Victoria, BC, Canada, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Capon, J. High-Resolution Frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis. Proc. IEEE 1969, 57, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Hinich, M.J. Frequency-wavenumber array processing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1981, 69, 732–737. [Google Scholar]
- Masry, E. The estimation of the frequency-wavenumber spectrum using random acoustic arrays-Part. II. A class of consistent estimators. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1984, 76, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Dmochowski, J.; Benesty, J.; Affes, S. On spatial aliasing in microphone arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Cetinkaya, H.; Yarovoy, A. NUFFT based frequency-wavenumber domain focusing under MIMO array configurations. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 19–23 May 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Geoga, C.J.; Haley, C.L.; Siegel, A.R.; Anitescu, M. Frequency-wavenumber spectral analysis of spatio-temporal flows. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 848, 545–559. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas, B.; Mars, J.I.; Lacoume, J.L. Source depth estimation using a horizontal array by matched-mode processing in the frequency-wavenumber domain. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2006, 2006, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuge, X.; Yarovoy, A.G. Three-dimensional near-field MIMO array imaging using range migation techniques. IEEE. Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 3026–3033. [Google Scholar]
- Schissele, E.; Guilbert, J.; Gaffet, S.; Cansi, Y. Accurate time-frequency-wavenumber analysis to study coda waves. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 158, 577–591. [Google Scholar]
- Luu, K.; Liu, F.; Wei, S.; Wang, G. Target depth extraction based on the character of sound field vertical wavenumber spectrum. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/OES China Ocean Acoustics (COA), Harbin, China, 9–11 January 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Paviet-Salomon, T.; Bonnel, J.; Dorffer, C.; Nicolas, B.; Chonavel, T.; Tollefsen, D.; Knobles, D.P.; Wilson, P.; Dremeau, A. Estimation of frequency-wavenu mber diagrams using a physics-based grid-free compressed sensing method. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 47, 565–577. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.S. Direction finding based on Radon transform in frequency-wavenumber domain with a sparse array. J. Acoust. Soc. Korea 2019, 38, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Worthmann, B.M.; Song, H.C.; Dowling, D.R. Adaptive frequency-difference matched field processing for high frequency source localization in a noisy shallow ocean. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, F.B.; Kuperman, W.A.; Porter, M.B.; Schmidt, H. (Eds.) Computational Ocean Acoustics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Maksym, J. A robust formulation of an optimum cross spectral beamformer for line arrays. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1979, 65, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.C.; Hodgkiss, W.S.; Gerstoft, P.; Kim, J.S. Null broadening with snapshot-deficient covariance matrices. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2003, 28, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, G.; Akins, F.H.; Gemba, K.L.; Song, H.C.; Kuperman, W.A. Multiple constraint matched field processing tolerant to array tilt mismatch. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 147, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, H.; Zeskind, R.M.; Owen, M.M. Robust adaptive beamforming. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Sign. Process. 1987, 10, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Gemba, K.L.; Hodgkiss, W.S.; Gerstoft, P. Adaptive and compressive matched field processing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.G.; Lee, Y.R.; Seo, D.K. Target tracking based on kernelized correlation filter using MWIR and SWIR sensors. J. KIMST 2023, 26, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.C.; Cho, C.; Hodgkiss, W.A.; Nam, S.H.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, B.N. Underwater sound channel in the northeastern East China Sea. Ocean Eng. 2018, 147, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.B. The Bellhop Manual and User’s Guide: Preliminary Draft; Heat, Light, and Sound Research, Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.N.; Hahn, J.Y.; Choi, B.K.; Kim, B.C. Acoustic characteristics of pure snapping shrimp noise measured under laboratory conditions. Proc. Symp. Ultrason. Electron. 2009, 30, 167–168. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, Y.H.; Byun, G.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.S. Adaptive Steered Frequency–Wavenumber Analysis for High-Frequency Source Localization in Shallow Water. Sensors 2025, 25, 2036. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072036
Choi YH, Byun G, Kim D, Kim JS. Adaptive Steered Frequency–Wavenumber Analysis for High-Frequency Source Localization in Shallow Water. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):2036. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072036
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Y. H., Gihoon Byun, Donghyeon Kim, and J. S. Kim. 2025. "Adaptive Steered Frequency–Wavenumber Analysis for High-Frequency Source Localization in Shallow Water" Sensors 25, no. 7: 2036. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072036
APA StyleChoi, Y. H., Byun, G., Kim, D., & Kim, J. S. (2025). Adaptive Steered Frequency–Wavenumber Analysis for High-Frequency Source Localization in Shallow Water. Sensors, 25(7), 2036. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072036





