A New Computational Method for Detecting Leak Flow and Tidal Volume Waveforms During Spontaneous or Mandatory Breathing Assisted with Nasopharyngeal Ventilation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
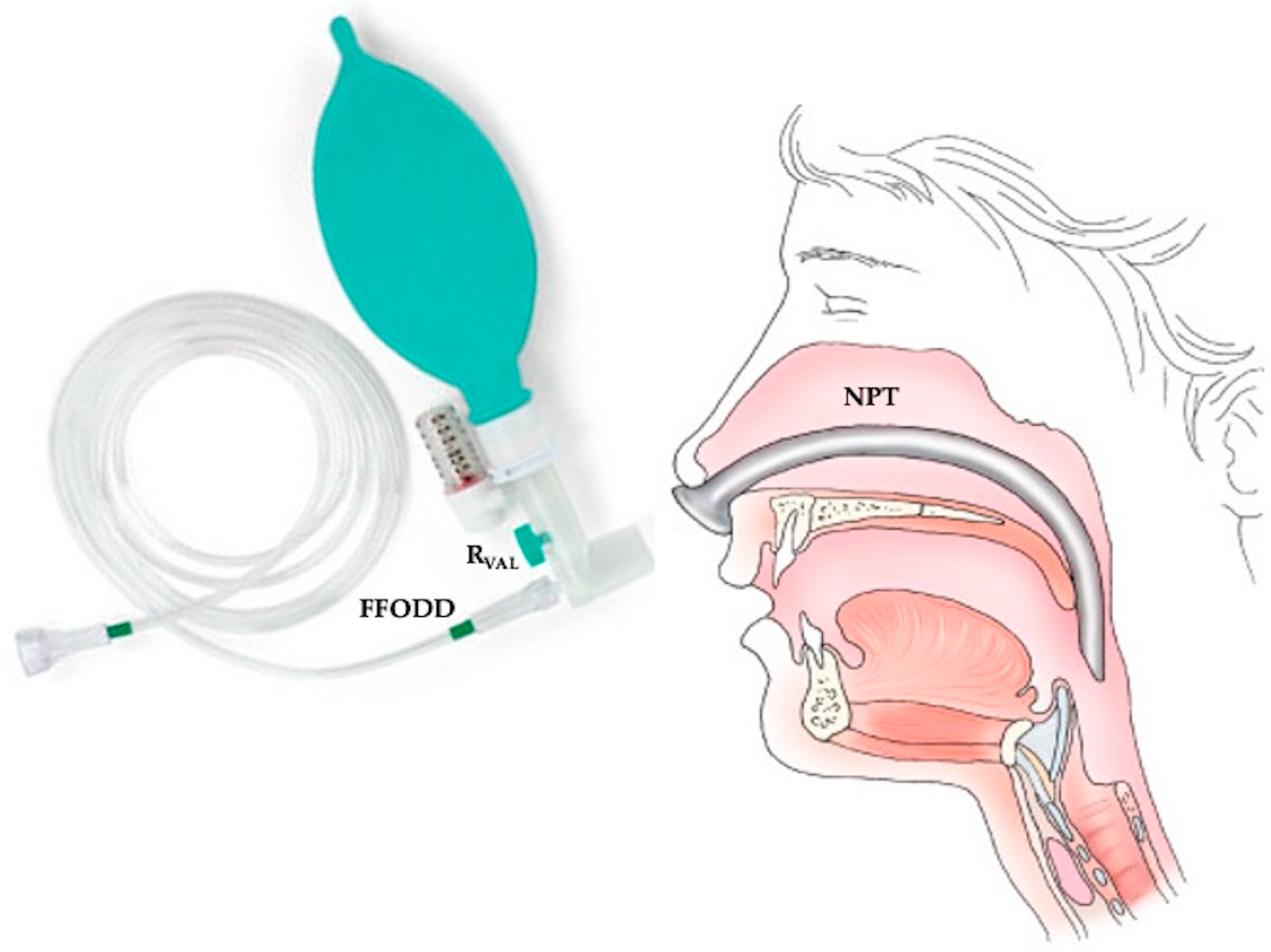
2.1. Description of the Ventilatory System (FFODD) Used with the NPT for NPV
2.2. Clinical Context and Experimental Setup Used to Measure and Calculate Leak Flow Waveform
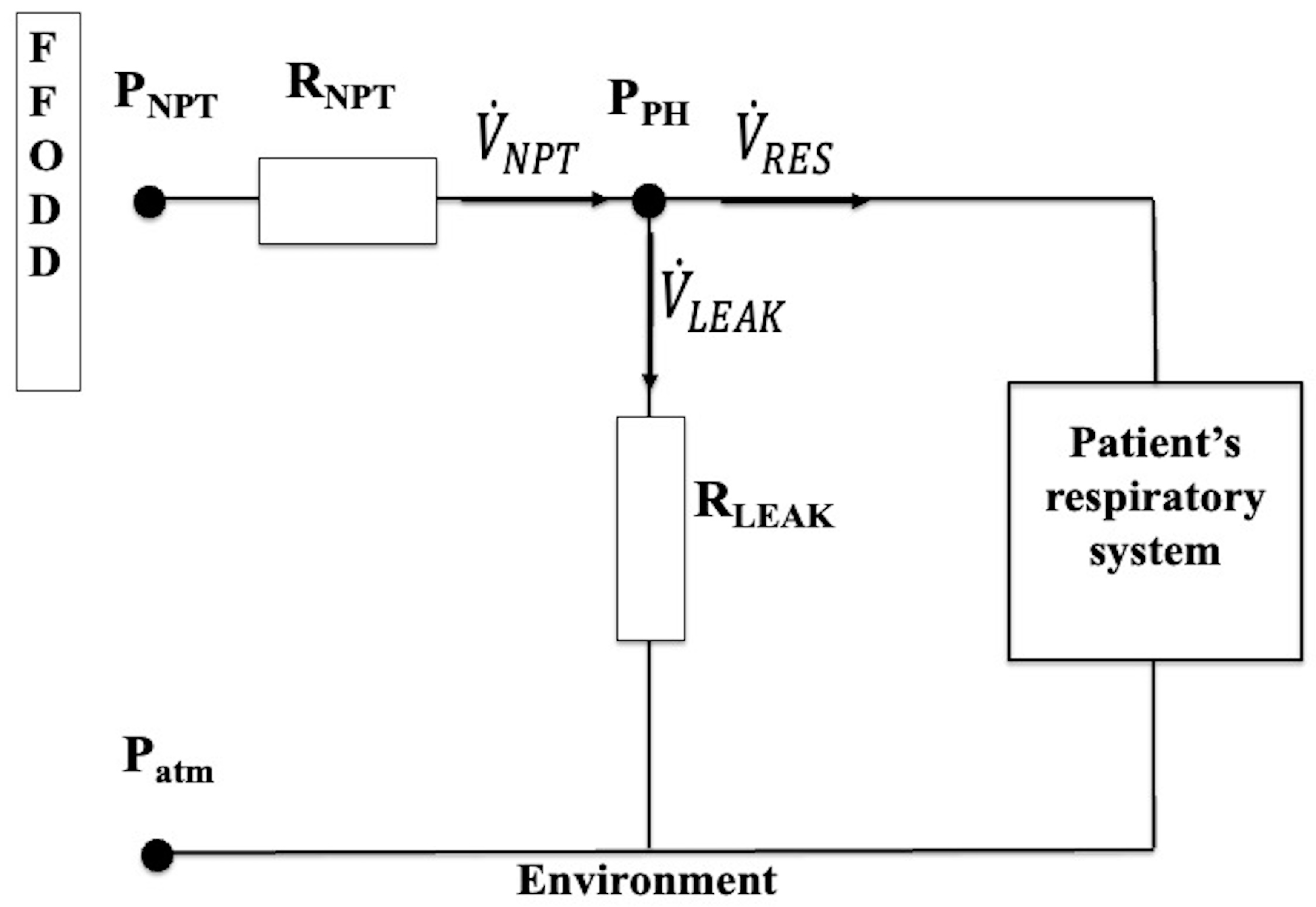
2.3. Physical Model of the Experimental Setup
- (1)
- Cinetic or Bernoulli component (ΔPK), which would exist if the fluid were ideal, since it only depends on the geometry;
- (2)
- Viscous or resistive component (ΔPR);
- (3)
- Elastic or capacitive component (ΔPC);
- (4)
- Inertial component (ΔPI).
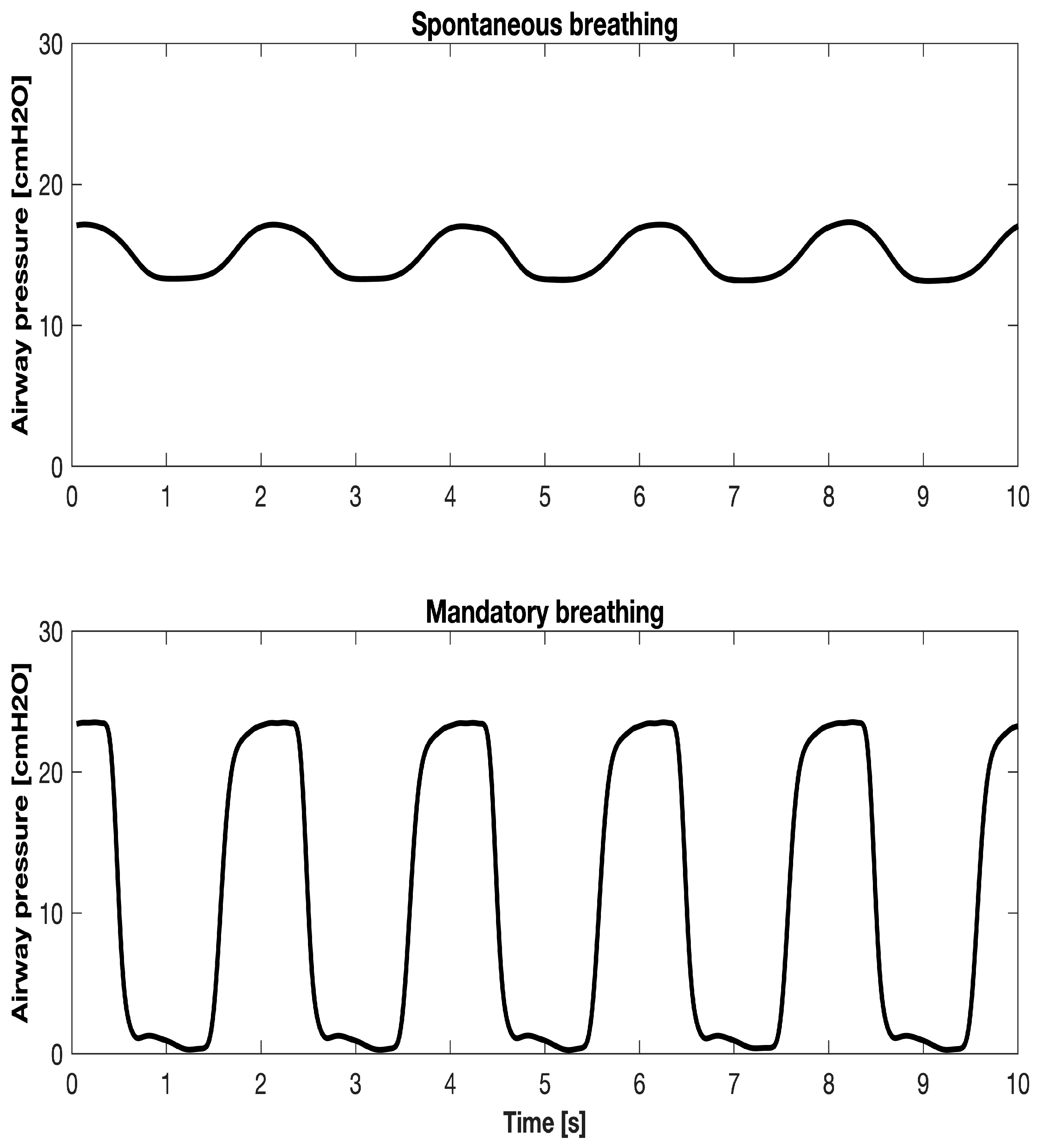
2.4. Calculation During Spontaneous or Mandatory Breathing
2.4.1. Method for kL_LEAK and kT_LEAK Calculation
2.4.2. Calculation During Spontaneous or Mandatory Breathing Once kL_LEAK and kT_LEAK Coefficients Have Been Calculated During the Apnea
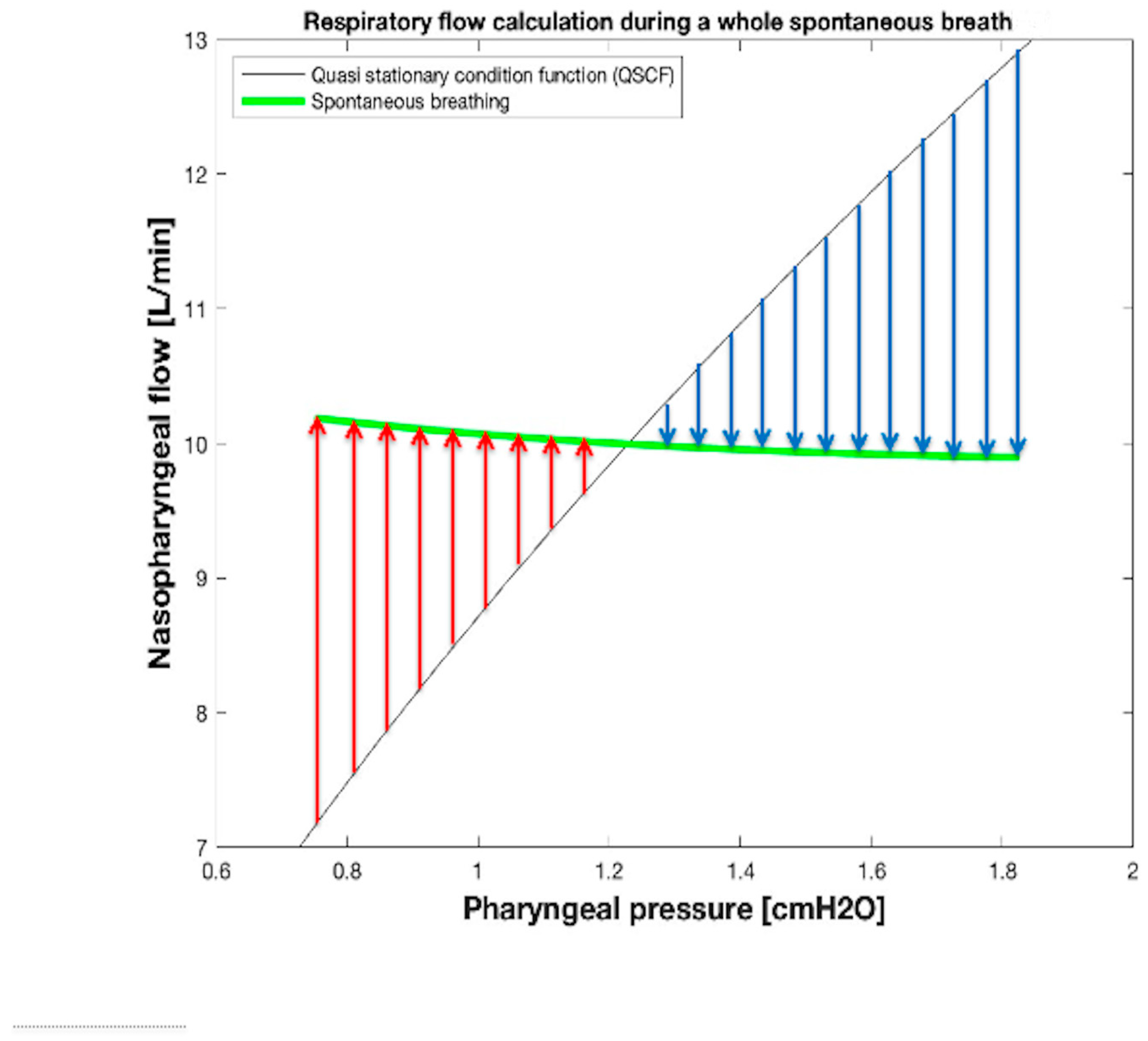
2.4.3. , , and Tidal Volume (VTID) Calculation During Spontaneous Breathing
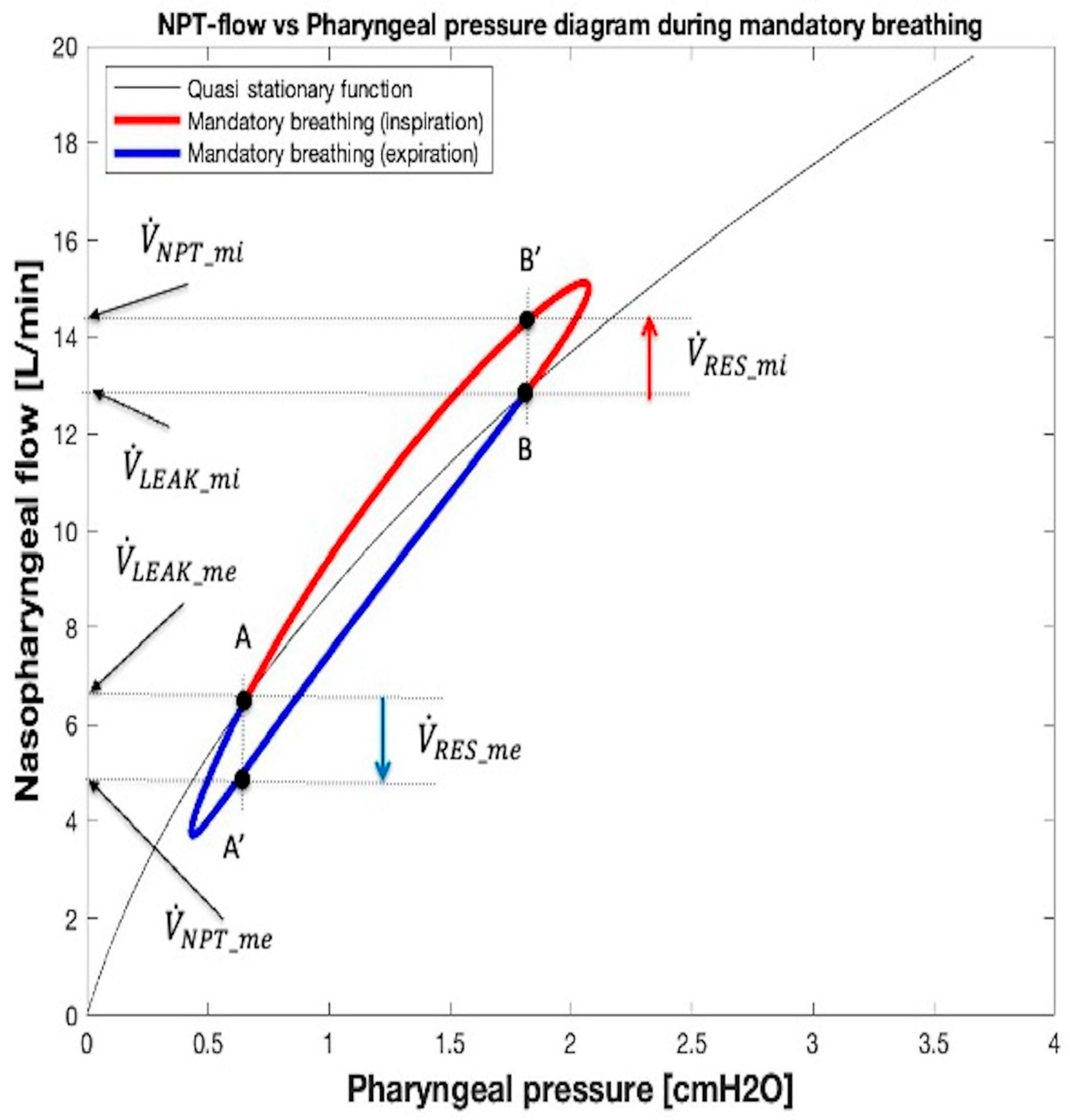
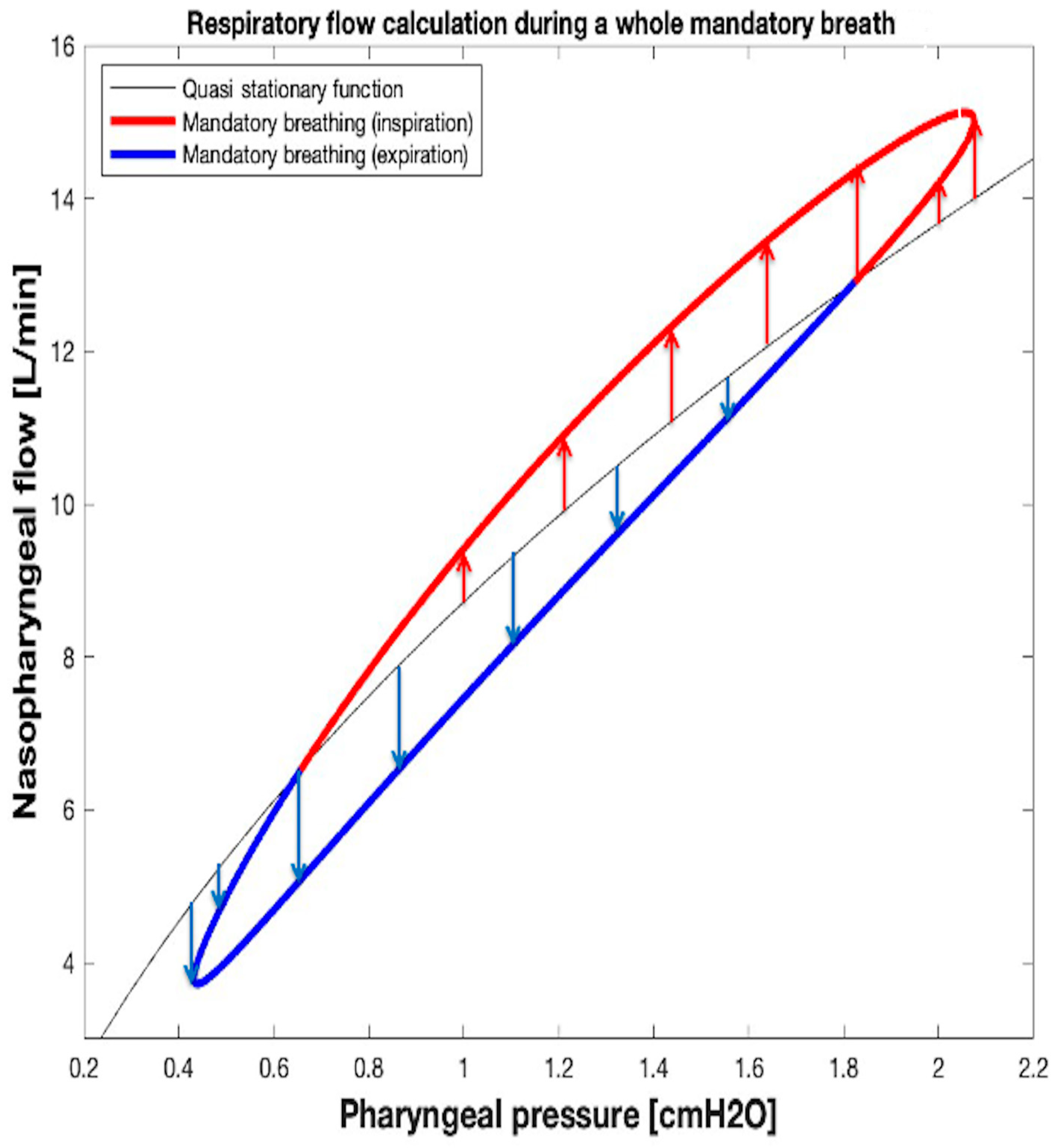
2.4.4. , , and VTID Calculation During Mandatory Breathing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
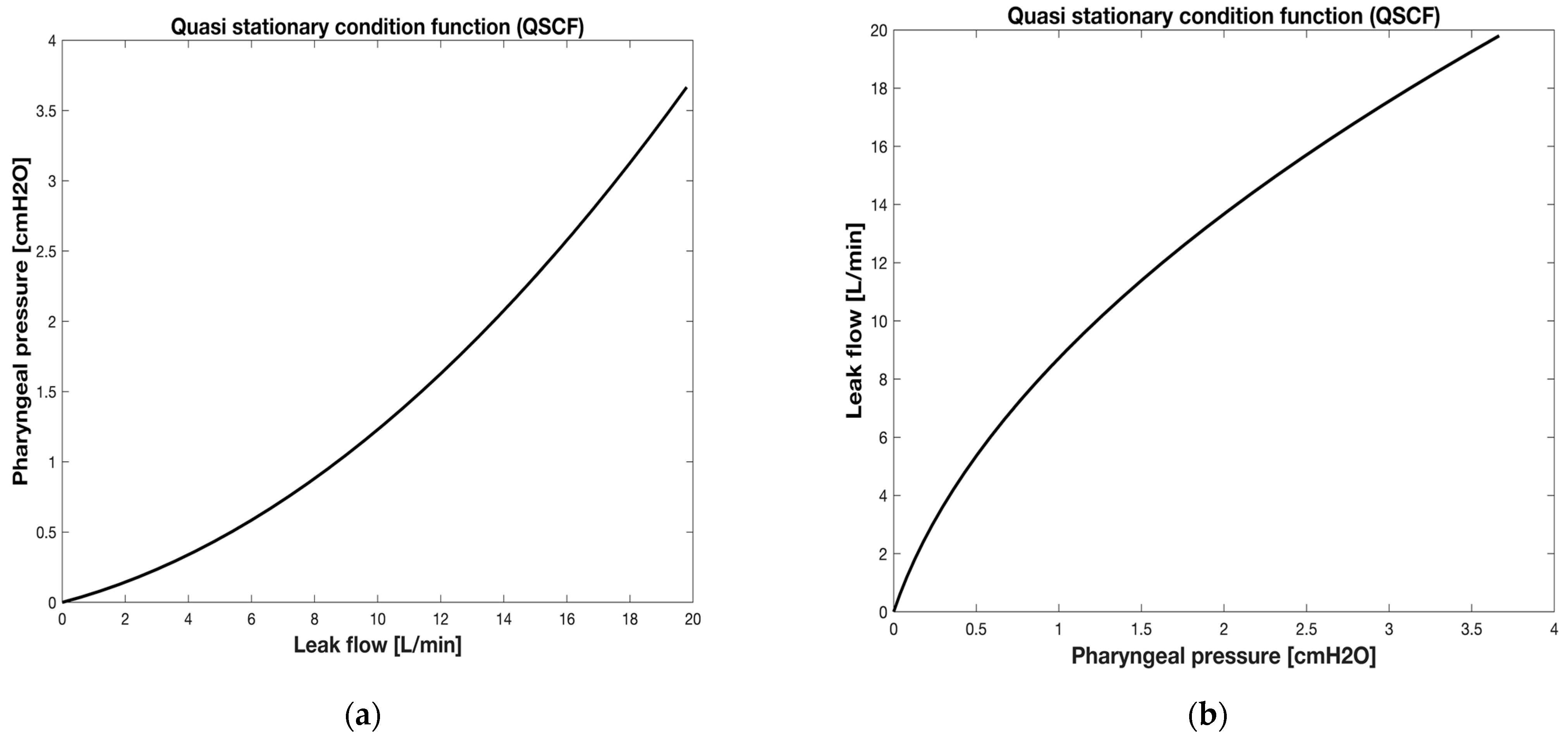
3.1. Results of Coefficient Determination (kL_LEAK and kT_LEAK)
3.2. Tidal Volume Computing and Validation
3.2.1. Validation of Tidal Volume Computation Using the Algorithm for of Spontaneous Breathing
3.2.2. Validation of Tidal Volume Computation Using the Algorithm for Mandatory Ventilation
4. Discussion
4.1. Other Methods to Measure Tidal Volume During Nasal Ventilation
4.2. Clinical Implications
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehta, S.; Hill, N.S. Noninvasive ventilation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 540–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criner, G.J.; Gayen, S.; Zantah, M.; Castillo, E.D.; Naranjo, M.; Lashari, B.; Pourshahid, S.; Gangemi, A. Clinical review of non-invasive ventilation. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 64, 2400396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenhardt, R.; Akca, O.; Obal, D.; Businger, J.; Cooke, E. Nasopharyngeal ventilation compared to facemask ventilation: A prospective, randomized, crossover trial in two different elective cohorts. Cureus 2023, 15, e39049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papoff, P.; Rosini, T.; Oliva, S.; Luciani, S.; Midulla, F.; Montecchia, F. Nasopharyngeal tubes in pediatric anesthesia: Is the flow-dependent pressure drop across the tube suitable for calculating oropharyngeal pressure ? Pediatr. Anaesth. 2021, 31, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, T.; Matsumoto, I.; Lanteri, C.J.; Sly, P.D. Respiratory mechanics during mechanical ventilation: A model study on the effect of leak around a tracheal tube. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1997, 24, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohmoud, R.A.; Fischer, H.S.; Proquittè, H.; Abudaif Shalaby, H.M.; Schmalish, G. Relationship between endotracheal tube leakage and under-reading of tidal volume in neonatal ventilators. Acta Pediatr. 2009, 98, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brochard, L. Mechanical ventilation: Invasive versus noninvasive. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22 (Suppl. S47), 31s–37s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabec, C.; Georges, M.; Kabeya, N.K.; Baudouin, N.; Massin, F.; Reybet-Degat, O.; Camus, P. Evaluating noninvasive ventilation using a monitoring system coupled to a ventilator: A bench-to-bedside study. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, H.S.; Roehr, C.C.; Proquitté, H.; Hammer, H.; Wauer, R.R.; Schmalisch, G. Is volume and leak monitoring feasible during nasopharyngeal continuous positive airway pressure in neonates? Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 1934–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storre, J.H.; Bhom, P.; Dreher, M.; Windisch, W. Clinical impact of leak compensation during non-invasive ventilation. Respir. Med. 2009, 103, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Montecchia, F.; Midulla, F.; Papoff, P. A flow-leak correction algorithm for pneumotachographic work-of-breathing measurements during high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy. Med. Eng. Phys. 2018, 54, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmalisch, G.; Fischer, H.; Roehr, C.C.; Proquittè, H. Comparison of different techniques to measure air leak during CPAP treatment in neonates. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicario, F.; Alkhairy, S.; Buizza, R.; Truschel, W.A. Two-parameters leak estimation in non-invasive ventilation. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual International Conference of IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 11–15 July 2017; pp. 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiao, H.; Liu, T.; Yin, J.; Zhang, Q.I. The detection and estimation of the air leakage in noninvasive ventilation: Platform study. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2020, 20, 2040043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foitzik, B.; Schmidt, M.; Windstetter, D.; Wauer, R.R.; Schmalish, G. Leak measurements in spontaneously breathing premature newborns by using the flow-through technique. J. App. Physiol. 1998, 85, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Oto, J.; Chenelle, C.T.; Marchese, A.D.; Kacmarek, R.M. Acomparison of leak compensation during pediatric noninvasive ventilation: A lung model study. Respir. Care 2014, 59, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banner, M.J.; Tams, C.G.; Euliano, N.R.; Stephan, P.J.; Leavitt, T.J.; Martin, A.D.; Al-Rawas, N.; Gabrielli, A. Real time noninvasive estimation of work of breathing using facemask leak-corrected tidal volume during noninvasive pressure support: Validation study. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2016, 30, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecchia, F.; Papoff, P. Real-Time Optimal Flow Setting and Respiratory Profile Evaluation in Infants Treated with High-Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC). Fluids 2024, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer, F. Flow resistance in human air passages and the effect of irregular branching of the bronchial system on the respiratory process in various regions of the lungs. Arch. Ges. Physiol. 1915, 162, 225–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlock, D.N.; Bai, S.; Weisner, M.D.; Comtois, N.; Beck, J.; Sinderby, C.; Courtney, S.E. Tidal volume transmission during non-synchronized nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation via RAM cannula. J. Perinatol. 2019, 39, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Janssen, M.L.; Jonkman, A.H.; Wennen, M.; Wils, E.-J.; Endeman, H.; Heunks, L. Diaphragm excursions as proxy for tidal volume during spontaneous breathing in invasively ventilated ICU patients. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2023, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Leak Size | kL_LEAK [cmH2O s/L] | kT_LEAK [cmH2O s2/L2] | GOF MSE; NRMSE; NMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small (SL) | 11.88 | 66.88 | 0.002; 0.988; 0.999 |
| Medium (ML) | 6.12 | 32.71 | 0.002; 0.981; 0.999 |
| Large (LL) | 3.66 | 17.34 | 0.003; 0.976; 0.999 |
| VTID_N/NPT ∅ | VTID_M/VTID_C M (SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric | Small Leak (SL) | Medium Leak (ML) | Large Leak (LL) |
| 10/3.0 mm | 9.92 (0.16)/9.90 (0.26) | 9.95 (0.11)/9.89 (0.26) | 9.94 (0.28)/9.89 (0.26) |
| 50/4.0 mm | 49.86 (1.33)/49.24 (1.31) | 49.85 (1.32)/49.22 (1.31) | 49.78 (1.33)/99.90 (1.31) |
| 100/5.0 mm | 99.87 (1.66)/98.43 (2.62) | 99.69 (1.86)/98.38 (2.62) | 99.34 (0.98)/98.33 (2.62) |
| Adult | |||
| 200/7.0 mm | 198.44 (2.88)/198.15 (5.28) | 198.87 (3.28)/198.05 (7.27) | 198.44 (3.88)/197.80 (5.27) |
| 300/8.0 mm | 298.62 (5.08)/302.14 (8.15) | 289.62 (6.08)/300.98 (8.56) | 301.62 (5.08)/305.60 (8.14) |
| 400/9.0 mm | 398.78 (8.94)/405.21 (10.78) | 410.78 (10.94)/405.01 (10.78) | 410.78 (10.94)/404.50 (10.77) |
| VTID_N/NPT ∅ | t | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric | Small Leak (SL) | Medium Leak (ML) | Large Leak (LL) |
| 10/3.0 mm | 0.3989 | 0.4788 | 0.5587 |
| 50/4.0 mm | 1.9925 | 2.0724 | 2.1523 |
| 100/5.0 mm | 2.3102 | 2.3901 | 2.4700 |
| Adult | |||
| 200/7.0 mm | 0.2392 | 0.3190 | 0.5188 |
| 300/8.0 mm | −1.3155 | −1.2357 | −1.0360 |
| 400/9.0 mm | 2.1755 | 2.2553 | 2.4550 |
| VTID_N/NPT ∅ | VTID_M/VTID_C M (SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric | Small Leak (SL) | Medium Leak (ML) | Large Leak (LL) |
| 10/3.0 mm | 10.3 (0.62)/9.89 (0.26) | 9.95 (0.51)/9.12 (0.37) | 9.89 (0.19)/9.34 (1.26) |
| 50/4.0 mm | 49.01 (2.31)/49.12 (1.31) | 50.13 (2.32)/49.22 (1.31) | 51.68 (5.13)/49.90 (2.38) |
| 100/5.0 mm | 102.45 (2.88)/97.35 (2.03) | 103.89 (4.86)/98.38 (3.25) | 100.44 (4.99)/98.56 (2.92) |
| Adult | |||
| 200/7.0 mm | 199.87 (3.78)/195.89 (5.28) | 200.87 (6.18)/198.10 (6.23) | 194.14 (3.67)/197.80 (5.27) |
| 300/8.0 mm | 300.90 (7.48)/304.14 (6.67) | 289.12 (6.89)/303.98 (8.90) | 305. 23 (4.16)/305.60 (8.14) |
| 400/9.0 mm | 397.10 (8.94)/406.23 (9.88) | 406.12 (5.84)/407.10 (10.88) | 410.18 (9.64)/404.50 (10.77) |
| VTID_N/NPT ∅ | t | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pediatric | Small Leak (SL) | Medium Leak (ML) | Large Leak (LL) |
| 10/3.0 mm | −1.2698 | −1.2698 | −1.4278 |
| 50/4.0 mm | −2.0529 | −2.0529 | −2.2109 |
| 100/5.0 mm | 1.7266 | 2.5058 | 2.3478 |
| Adult | |||
| 200/7.0 mm | −1.0325 | −1.1116 | −1.2303 |
| 300/8.0 mm | −1.8005 | −1.8796 | −1.9982 |
| 400/9.0 mm | 2.3484 | 2.2693 | 2.1506 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montecchia, F.; Papoff, P. A New Computational Method for Detecting Leak Flow and Tidal Volume Waveforms During Spontaneous or Mandatory Breathing Assisted with Nasopharyngeal Ventilation. Sensors 2025, 25, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072022
Montecchia F, Papoff P. A New Computational Method for Detecting Leak Flow and Tidal Volume Waveforms During Spontaneous or Mandatory Breathing Assisted with Nasopharyngeal Ventilation. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072022
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontecchia, Francesco, and Paola Papoff. 2025. "A New Computational Method for Detecting Leak Flow and Tidal Volume Waveforms During Spontaneous or Mandatory Breathing Assisted with Nasopharyngeal Ventilation" Sensors 25, no. 7: 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072022
APA StyleMontecchia, F., & Papoff, P. (2025). A New Computational Method for Detecting Leak Flow and Tidal Volume Waveforms During Spontaneous or Mandatory Breathing Assisted with Nasopharyngeal Ventilation. Sensors, 25(7), 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072022






