Gaze Estimation Network Based on Multi-Head Attention, Fusion, and Interaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
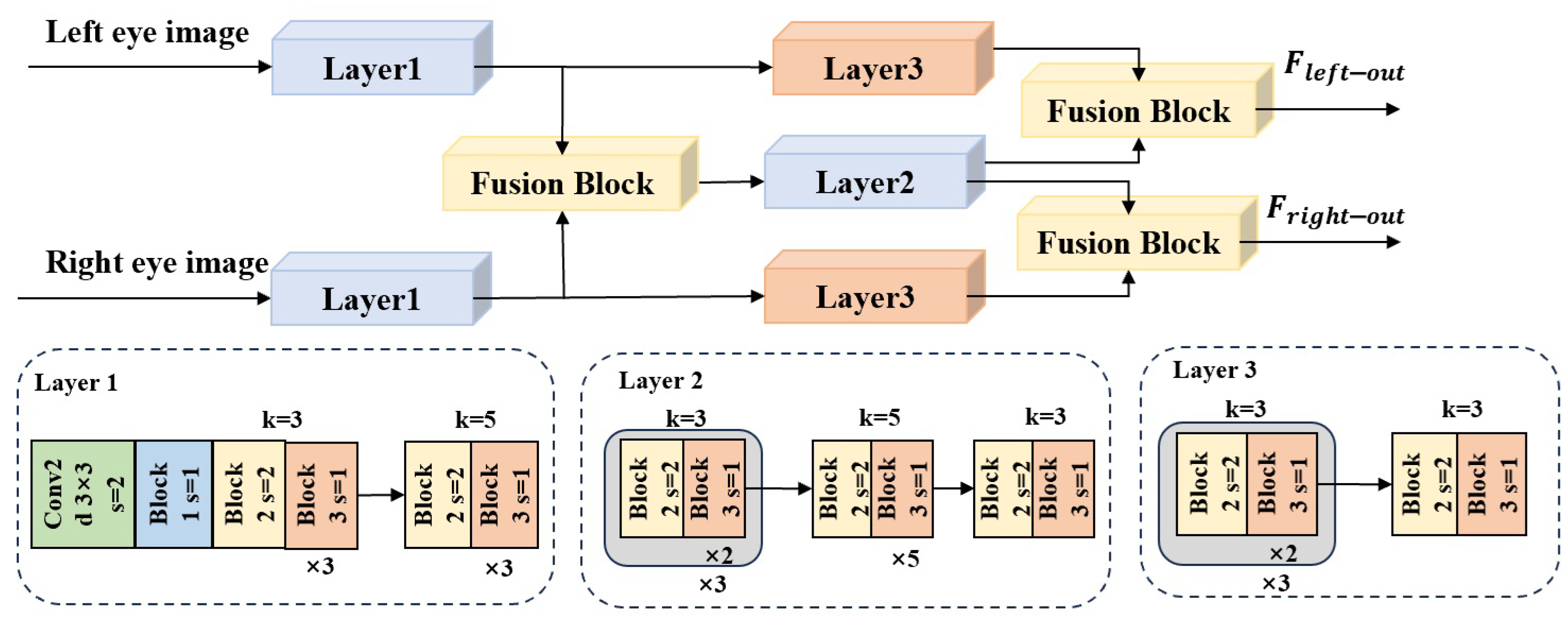
- An eye feature fusion module (EFFM) is designed, which uses cross-attention mechanisms multiple times to hierarchically fuse features from both eyes using fusion blocks, thereby greatly enriching the extracted eye features.
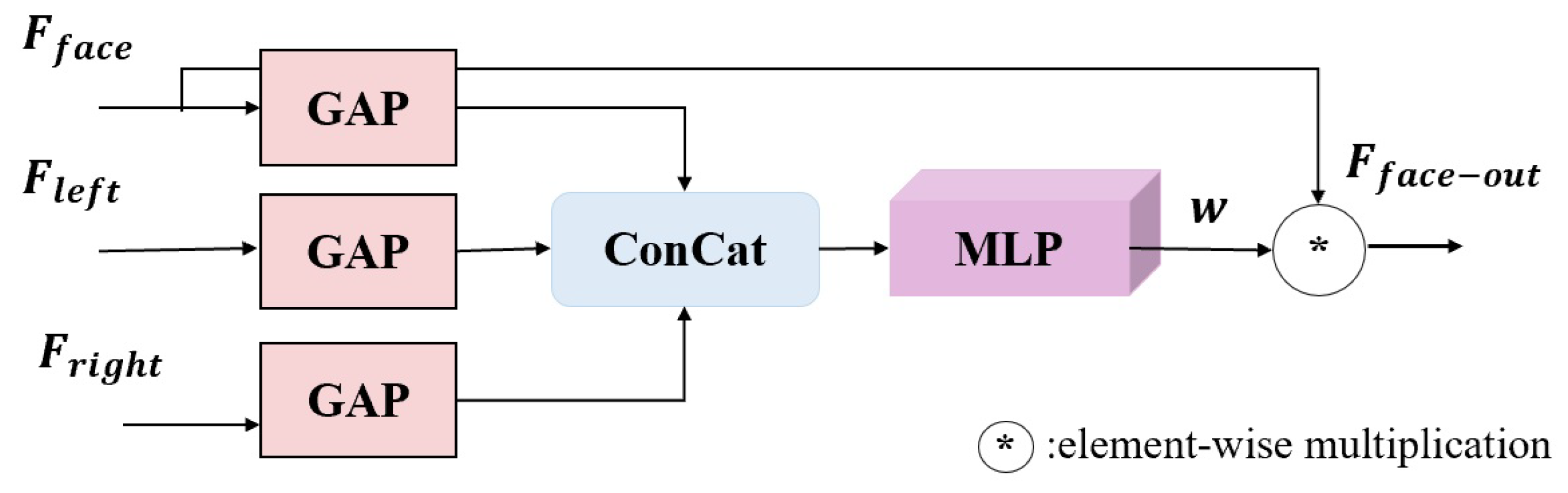
- A face and eye interaction module (FEIM) is designed. The facial features are weighted by the enhanced features in the binocular neighborhood to focus on eye position information, which helps in gaze estimation.
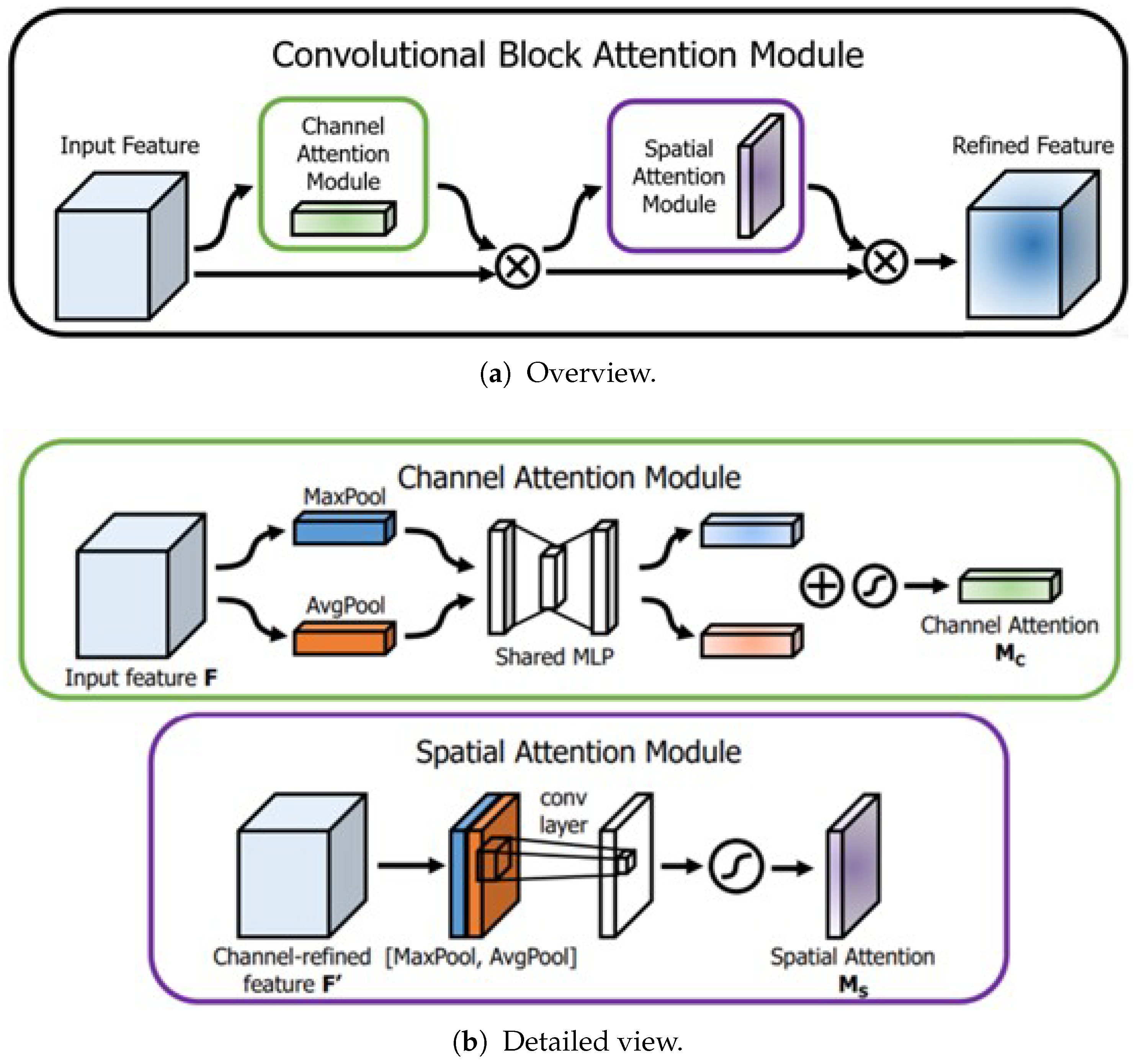
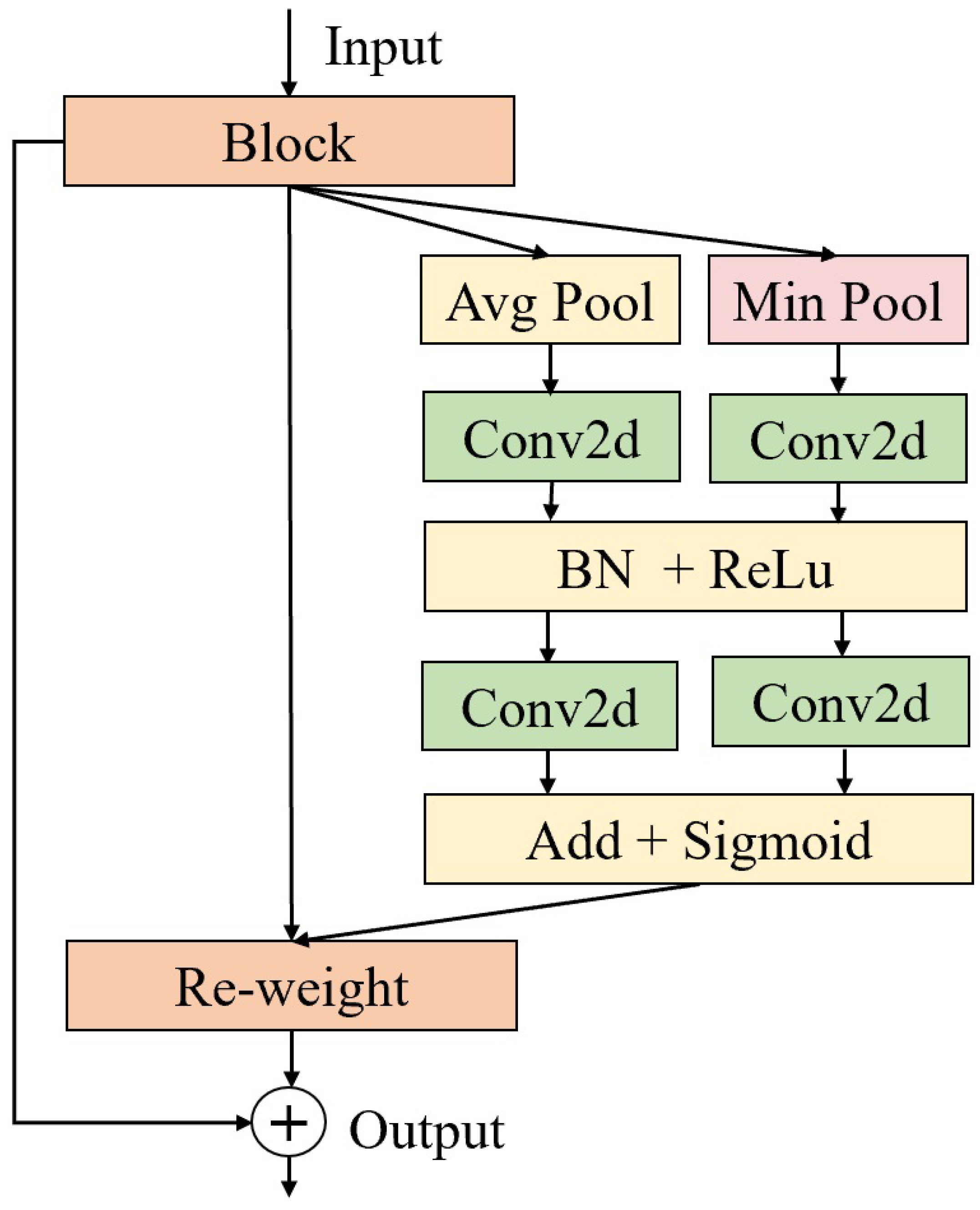
- In the channel attention module of CBAM, minimum pooling is utilized instead of maximum pooling, and a shortcut connection is introduced to help capture facial details.
2. Related Work
2.1. Three-Dimensional Geometric Modeling Stage
2.2. Deep Learning Stage
3. Method
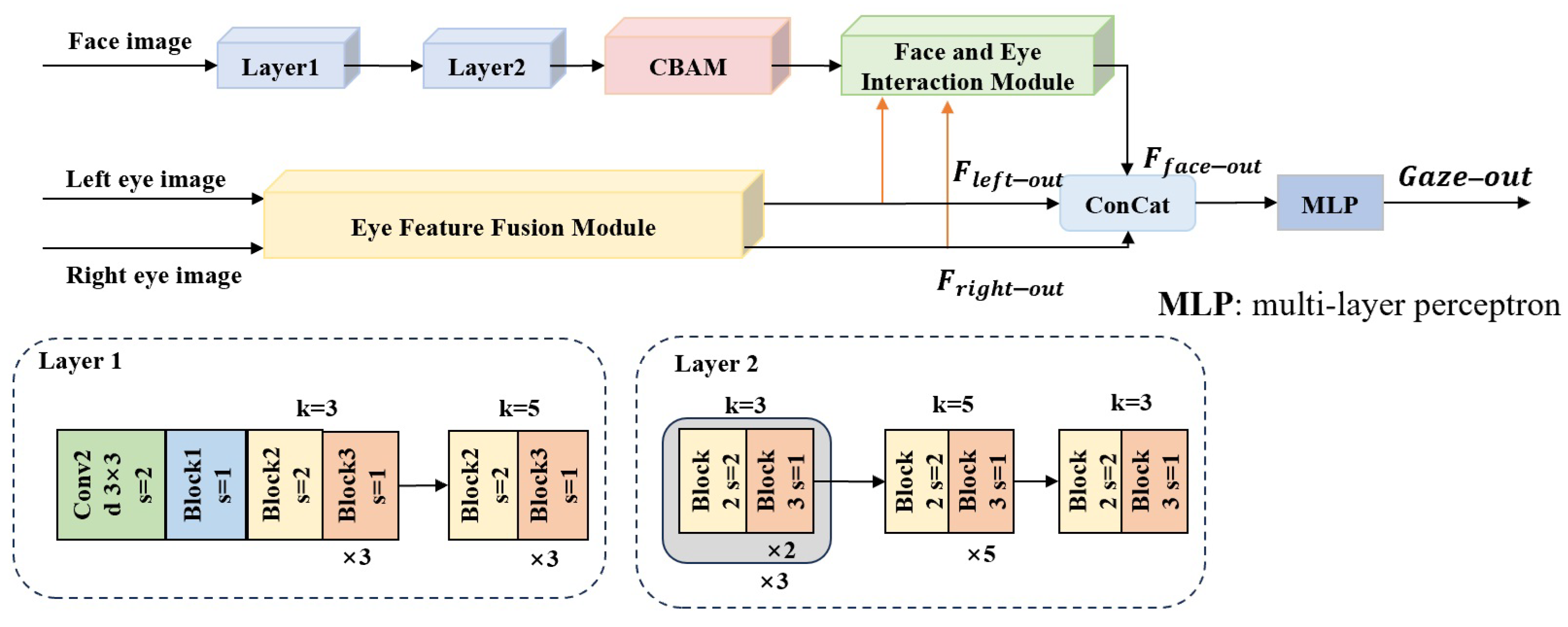
3.1. Network Structure
3.1.1. Facial Feature Extraction Branch
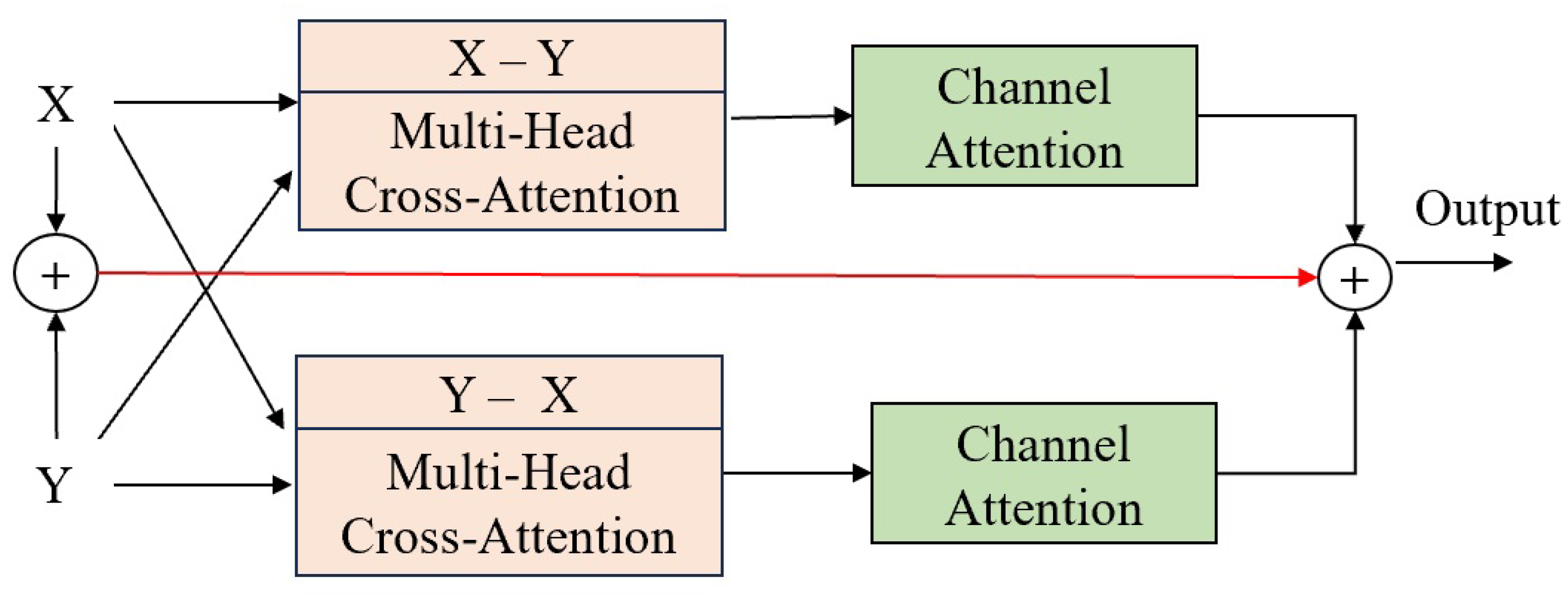
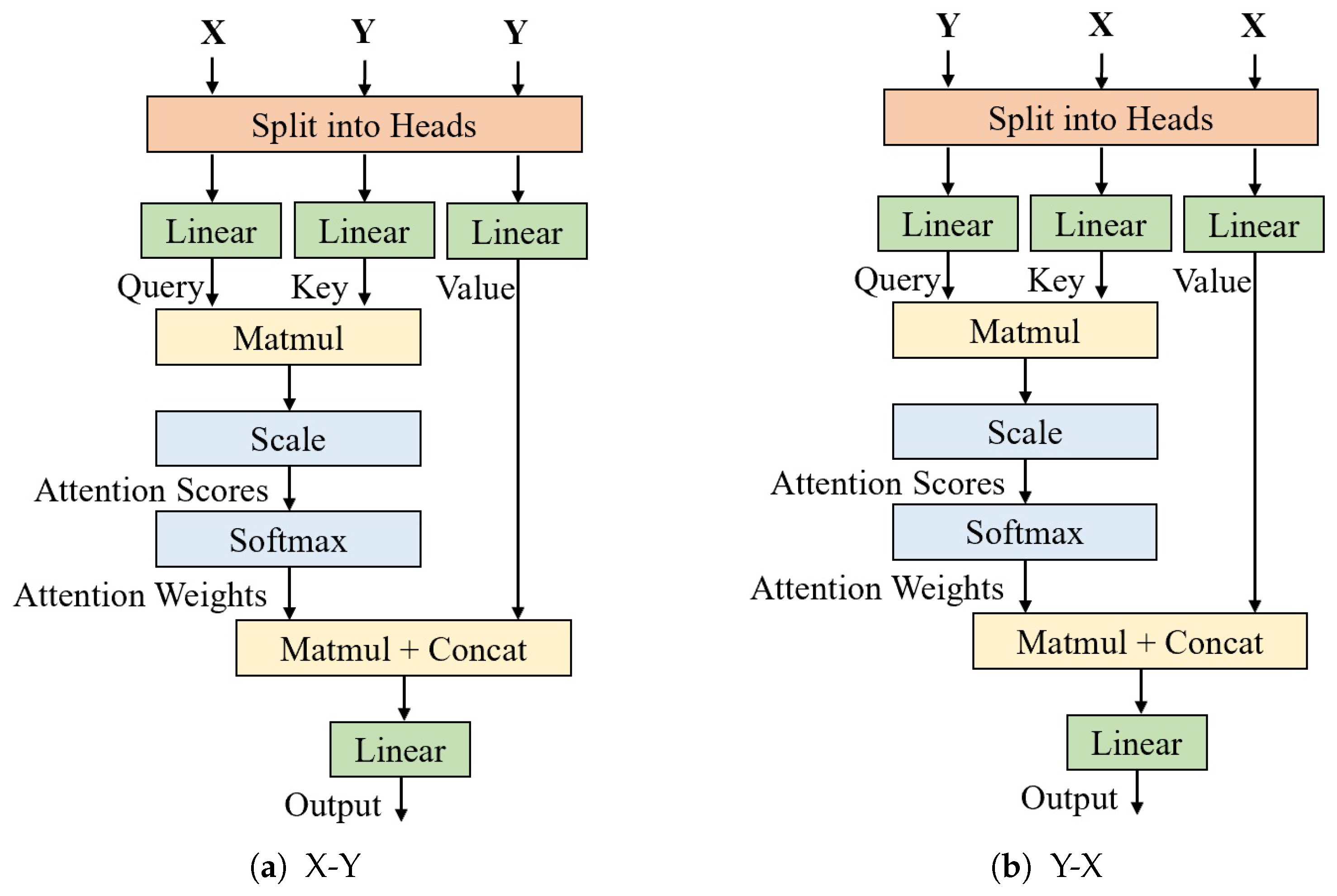
3.1.2. Eye Feature Extraction and Fusion Branch
3.1.3. Face and Eye Interaction Module
3.1.4. Gaze Estimation Result
3.2. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Evaluation Indicator
4.3. Implementation Details
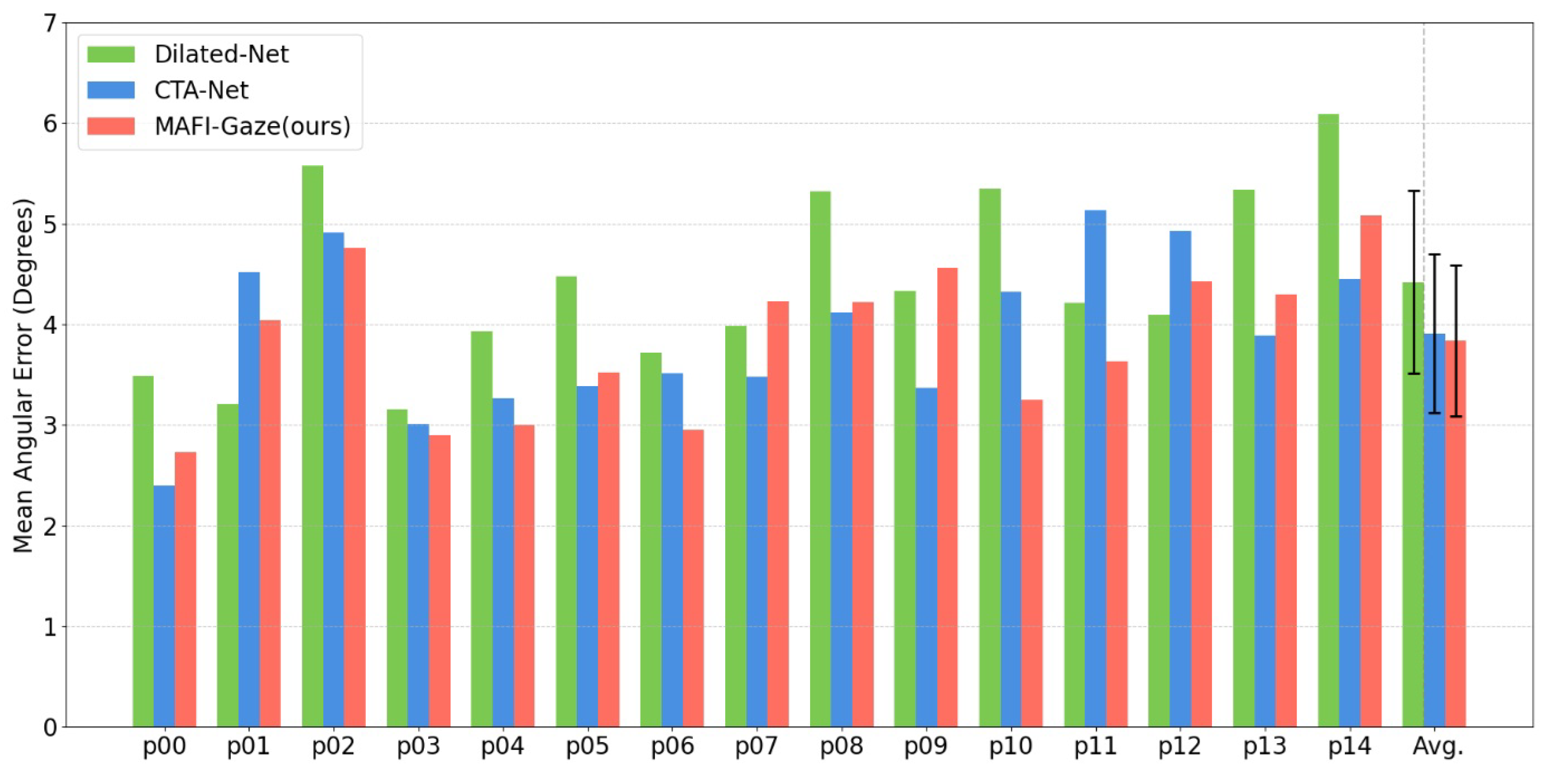
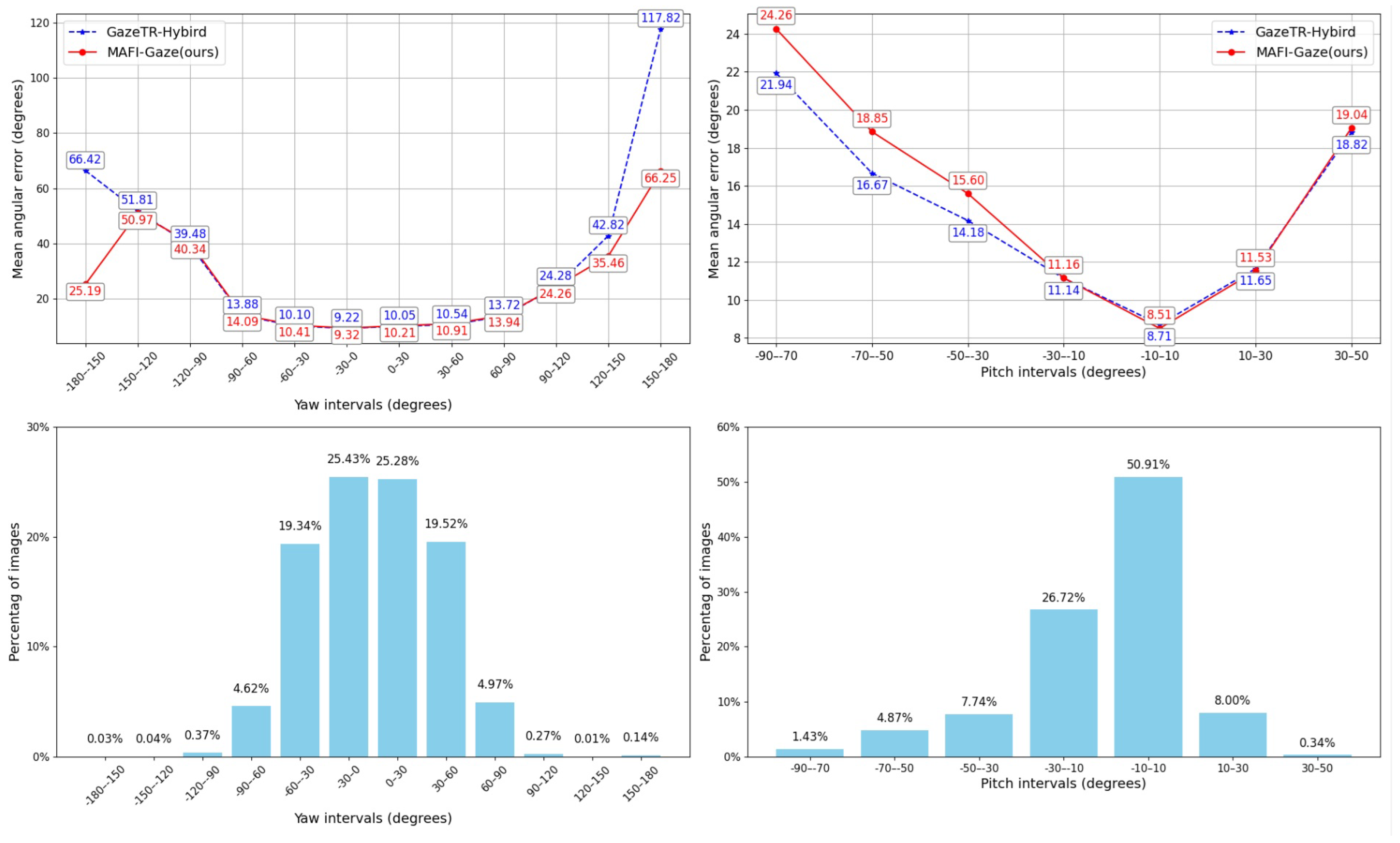
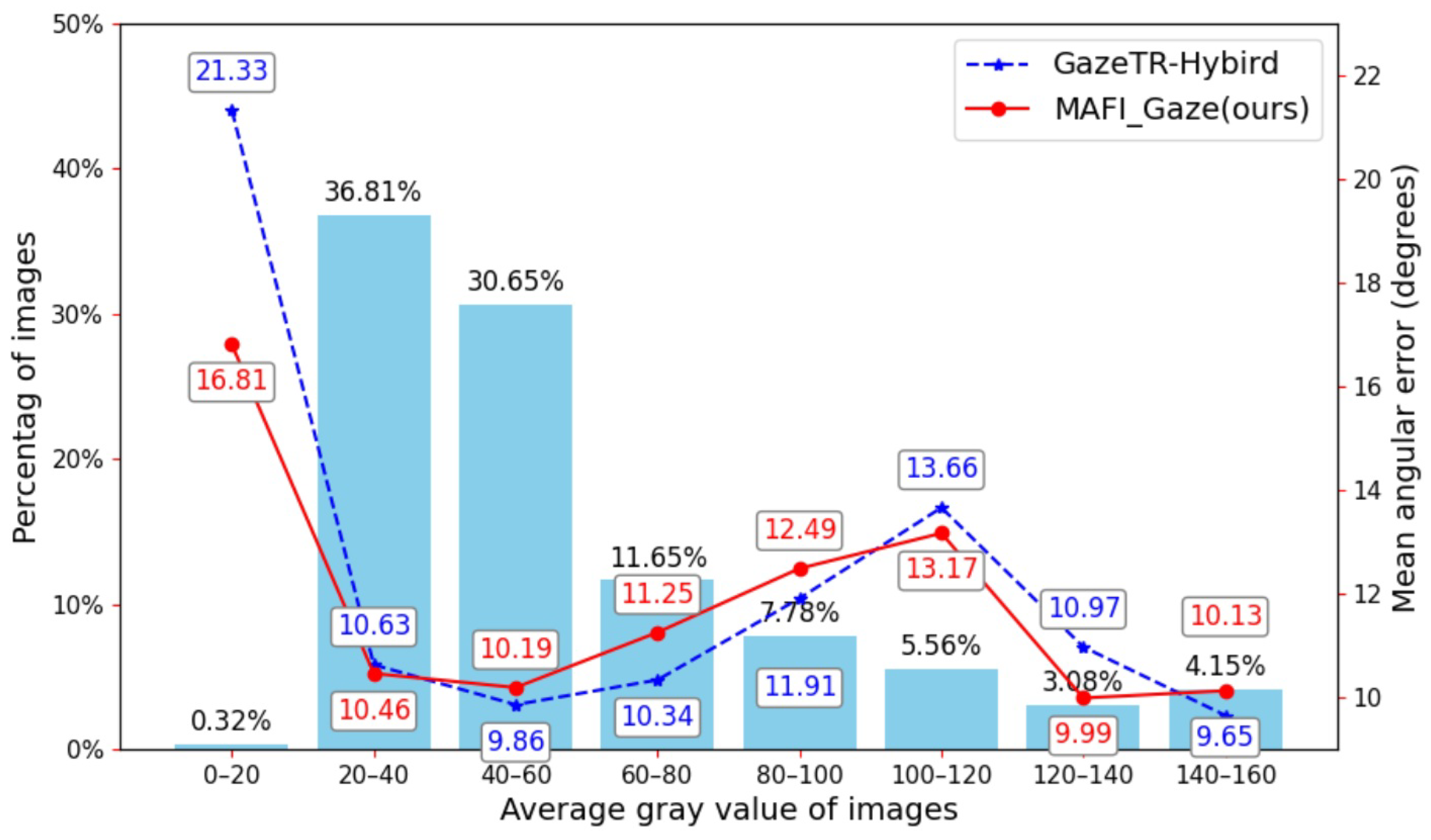
4.4. Experimental Results
4.5. Ablation Experiments
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Q.; Cui, H.; Liang, Z.; Feng, S.; Zhao, Y. Application and analysis of human computer interaction based on eye tracking technology. Electron. World 2022, 2, 86–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, Y.; Zhang, X.; Bulling, A. AggreGaze: Collective Estimation of Audience Attention on Public Displays. In Proceedings of the Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology (UIST), Tokyo Japan, 16–19 October 2016; pp. 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Lam, H.K.; Han, J.; Ouyang, G.; Li, X.; Liu, H. Appearance-Based Gaze Estimation for ASD Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 6504–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Dhall, A.; Hayat, M.; Knibbe, J.; Ji, Q. Automatic Gaze Analysis: A Survey of Deep Learning Based Approaches. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, K.J.; Zannoli, M.; Xiao, L.; Warren, J.; Talathi, S.S. Estimating Gaze From Head and Hand Pose and Scene Images for Open-Ended Exploration in VR Environments. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (VRW), Lisbon, Portugal, 27 March–1 April 2021; pp. 554–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Healey, J.; Manocha, D. VRDoc: Gaze-based Interactions for VR Reading Experience. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Singapore, 17–21 October 2022; pp. 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, F.; Song, D.; Lu, Y.; Liu, J. GazMon: Eye Gazing Enabled Driving Behavior Monitoring and Prediction. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2021, 20, 1420–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lv, C.; Hang, P.; Huang, C.; Xing, Y. Data-Driven Estimation of Driver Attention Using Calibration-Free Eye Gaze and Scene Features. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 1800–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krafka, K.; Khosla, A.; Kellnhofer, P.; Kannan, H.; Bhandarkar, S.; Matusik, W.; Torralba, A. Eye Tracking for Everyone. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2176–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Chang, H.J.; Demiris, Y. RT-GENE: Real-Time Eye Gaze Estimation in Natural Environments. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Cham, Switzerland, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sugano, Y.; Fritz, M.; Bulling, A. It’s Written All Over Your Face: Full-Face Appearance-Based Gaze Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, A.A.; Hempel, T.; Khalifa, A.; Al-Hamadi, A.; Dinges, L. L2CS-Net: Fine-Grained Gaze Estimation in Unconstrained Environments. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th International Conference on Frontiers of Signal Processing (ICFSP), Corfu, Greece, 23–25 October 2023; pp. 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellnhofer, P.; Recasens, A.; Stent, S.; Matusik, W.; Torralba, A. Gaze360: Physically Unconstrained Gaze Estimation in the Wild. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6911–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sugano, Y.; Fritz, M.; Bulling, A. Appearance-based gaze estimation in the wild. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4511–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sugano, Y.; Fritz, M.; Bulling, A. MPIIGaze: Real-World Dataset and Deep Appearance-Based Gaze Estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, B.E. Appearance-Based Gaze Estimation Using Dilated-Convolutions. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), Cham, Switzerland, 2–6 December 2018; pp. 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, N.; Ni, B.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Gao, W. MUGGLE: MUlti-Stream Group Gaze Learning and Estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 3637–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, B.E. Towards High Performance Low Complexity Calibration in Appearance Based Gaze Estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 1174–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, Z.; Hungler, P.; Etemad, A. Multistream Gaze Estimation With Anatomical Eye Region Isolation by Synthetic to Real Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2024, 5, 4232–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, K.A.F.; Monay, F.; Odobez, J.M. EYEDIAP: A Database for the Development and Evaluation of Gaze Estimation Algorithms from RGB and RGB-D Cameras. In EYEDIAP: A Database for the Development and Evaluation of Gaze Estimation Algorithms from RGB and RGB-D Cameras; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; Si, J.; Liu, H.; Shen, D.; Li, J. Gaze estimation methods based on deep learning: Research status, challenge and future. In Proceedings of the 2023 8th International Conference on Information Systems Engineering (ICISE), Dalian, China, 23–25 June 2023; pp. 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukada, A.; Shino, M.; Devyver, M.; Kanade, T. Illumination-free gaze estimation method for first-person vision wearable device. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2084–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, E.; Baltruaitis, T.; Zhang, X.; Sugano, Y.; Robinson, P.; Bulling, A. Rendering of Eyes for Eye-Shape Registration and Gaze Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3756–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Xiong, C.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H. Robust and accurate pupil detection for head-mounted eye tracking. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 93, 107193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chi, J.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z. 3D Model-Based Gaze Tracking Via Iris Features With a Single Camera and a Single Light Source. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2021, 51, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhu, W. Monocular Free-Head 3D Gaze Tracking with Deep Learning and Geometry Constraints. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3162–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; He, C.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, T.; Gu, N. A High-Frame-Rate Eye-Tracking Framework for Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Research and Application of Eye Tracking Method Based on Deep Learning. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Petroleum, Xi’an, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, F.; Qian, C.; Lu, F. A Coarse-to-Fine Adaptive Network for Appearance-Based Gaze Estimation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Vienna, Austria, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Lu, F. Gaze Estimation using Transformer. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–25 August 2022; pp. 3341–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.O.; Chang, H.J.; Choi, S.I. Self-Attention with Convolution and Deconvolution for Efficient Eye Gaze Estimation from a Full Face Image. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 4988–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Huang, K. GFNet: Gaze Focus Network using Attention for Gaze Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Brisbane, Australia, 10–14 July 2023; pp. 2399–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Hu, H.; Lin, K.; Wang, Q.; Liu, T.; Chen, G. Attention-guided and fine-grained feature extraction from face images for gaze estimation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 106994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Tao, Z. CTA-Net: A Gaze Estimation network based on Dual Feature Aggregation and Attention Cross Fusion. Comput. Sci. Inf. Syst. 2024, 21, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, S.; Yadav, M. Spatio-Temporal Attention and Gaussian Processes for Personalized Video Gaze Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–18 June 2024; pp. 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Bao, Y.; Lu, F. Appearance-Based Gaze Estimation with Deep Learning: A Review and Benchmark. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 7509–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

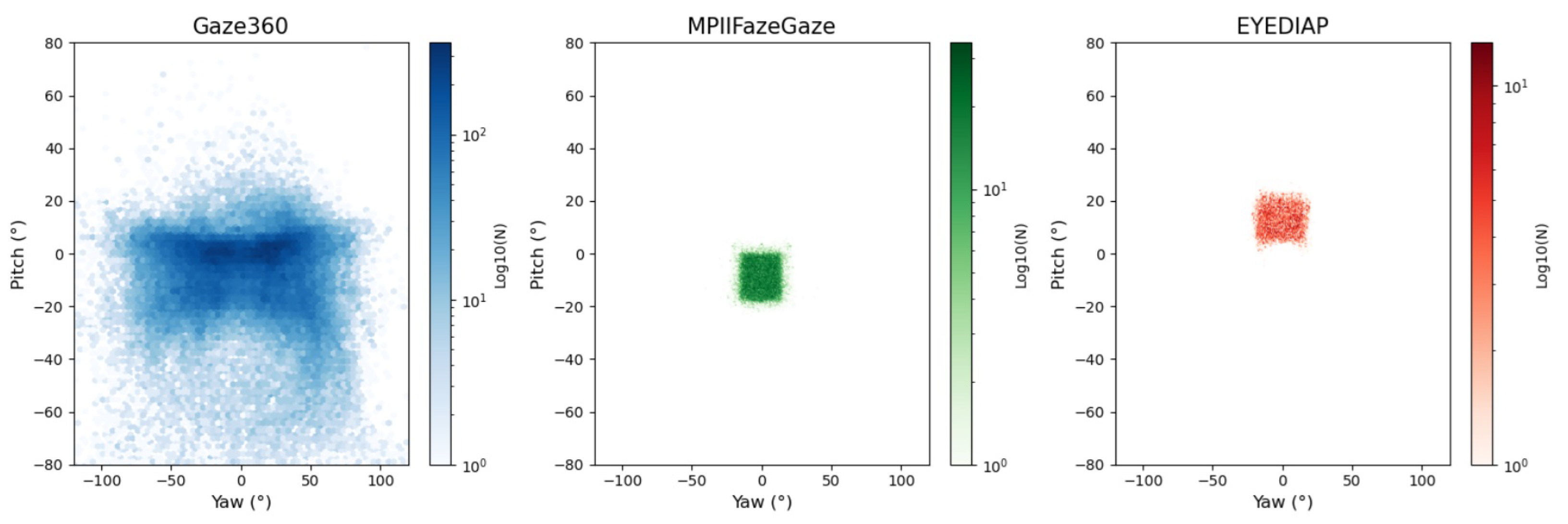
| Feature Dimension | Gaze360 | MPIIFaceGaze | EYEDIAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data collection environment | Complex outdoor | Lab-controlled | Dynamic interaction |
| Head pose range | ±70° | ±30° | ±45° |
| Illumination variation | Strong light/shadow | Artificial light | Indoor natural light |
| Sample diversity | 238 participants | 15 participants | 16 scenarios |
| Method | Input | Angular Error | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Face image | Eye Images | Head Pose | Gaze360 | MPIIFaceGaze | EYEDIAP | |
| FullFace [11] | √ | 14.99° | 4.93° | 6.53° | ||
| RT-Gene [10] | √ | 12.26° | 4.66° | 6.02° | ||
| GazeNet [15] | √ | √ | - | 5.76° | 6.79° | |
| Dilated-Net [16] | √ | √ | √ | 13.37 | 4.42° | 6.19° |
| Gaze360 [13] | √ | 11.04° | 4.06° | 5.36° | ||
| CA-Net [29] | √ | √ | 11.20° | 4.27° | 5.27° | |
| GazeTR-Pure [32] | √ | 13.58° | 4.74° | 5.72° | ||
| GazeTR-Hybird [32] | √ | 10.62° | 4.00° | 5.17° | ||
| SCD-Net [33] | √ | 10.70° | 4.04° | 5.25° | ||
| GFNet [34] | √ | √ | - | 3.96° | 5.40° | |
| GTiT-Hybrid [35] | √ | 11.20° | 4.11° | 5.35° | ||
| CTA-Net [36] | √ | √ | 10.44° | 3.91° | - | |
| MSGazeNet [19] | √ | - | 4.64° | 5.86° | ||
| Hybrid-SAM [37] | √ | 10.05° | - | 6.54° | ||
| MAFI-Gaze (ours) | √ | √ | 10.78° | 3.84° | 5.01° | |
| Pooling | Shortcut | Gaze360 | MPIIFaceGaze | EYEDIAP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Average | Maximum | ||||
| √ | √ | 11.47° | 4.26° | 5.04° | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 11.41° | 4.22° | 5.21° | |
| √ | √ | 11.31° | 4.01° | 5.13° | ||
| √ | 11.09° | 3.94° | 5.28° | |||
| √ | √ | 11.02° | 3.92° | 5.14° | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 10.78° | 3.84° | 5.01° | |
| Method | Gaze360 | MPIIFaceGaze | EYEDIAP | FLOPs (G) | Params (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAFI-Gaze w/o face | 13.12° | 4.60° | 5.53° | 0.21 | 6.21 |
| MAFI-Gaze w/o eyes | 11.07° | 4.14° | 5.25° | 1.34 | 6.67 |
| MAFI-Gaze w/o FEI | 10.91° | 4.08° | 5.13° | 1.56 | 12.89 |
| MAFI-Gaze w/o EFF | 10.85° | 3.92° | 5.06° | 1.50 | 12.88 |
| MAFI-Gaze | 10.78° | 3.84° | 5.01° | 1.56 | 12.90 |
| Gaze360 | MPIIFaceGaze | EYEDIAP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 1 | 11.07° | 4.17° | 5.24° |
| 100 | 1 | 10.78° | 3.84° | 5.01° |
| 150 | 1 | 10.90° | 3.88° | 4.97° |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Li, F.; Zhang, K.; Chen, N.; Pan, Z. Gaze Estimation Network Based on Multi-Head Attention, Fusion, and Interaction. Sensors 2025, 25, 1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061893
Li C, Li F, Zhang K, Chen N, Pan Z. Gaze Estimation Network Based on Multi-Head Attention, Fusion, and Interaction. Sensors. 2025; 25(6):1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061893
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Changli, Fangfang Li, Kao Zhang, Nenglun Chen, and Zhigeng Pan. 2025. "Gaze Estimation Network Based on Multi-Head Attention, Fusion, and Interaction" Sensors 25, no. 6: 1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061893
APA StyleLi, C., Li, F., Zhang, K., Chen, N., & Pan, Z. (2025). Gaze Estimation Network Based on Multi-Head Attention, Fusion, and Interaction. Sensors, 25(6), 1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061893







