Dual-Mode Visual System for Brain–Computer Interfaces: Integrating SSVEP and P300 Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
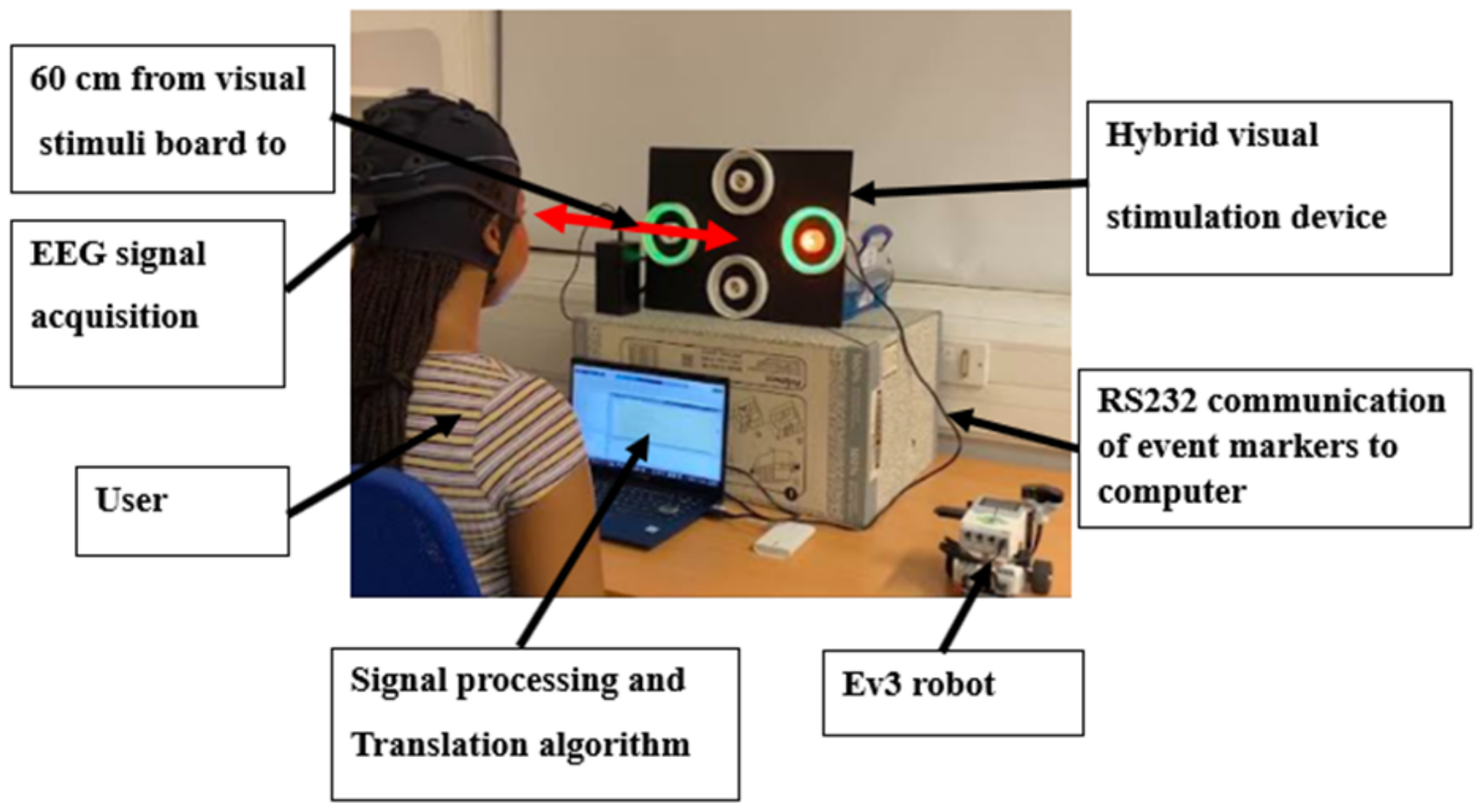
2.1. Hardware Design
2.2. Signal Acquisition and Processing
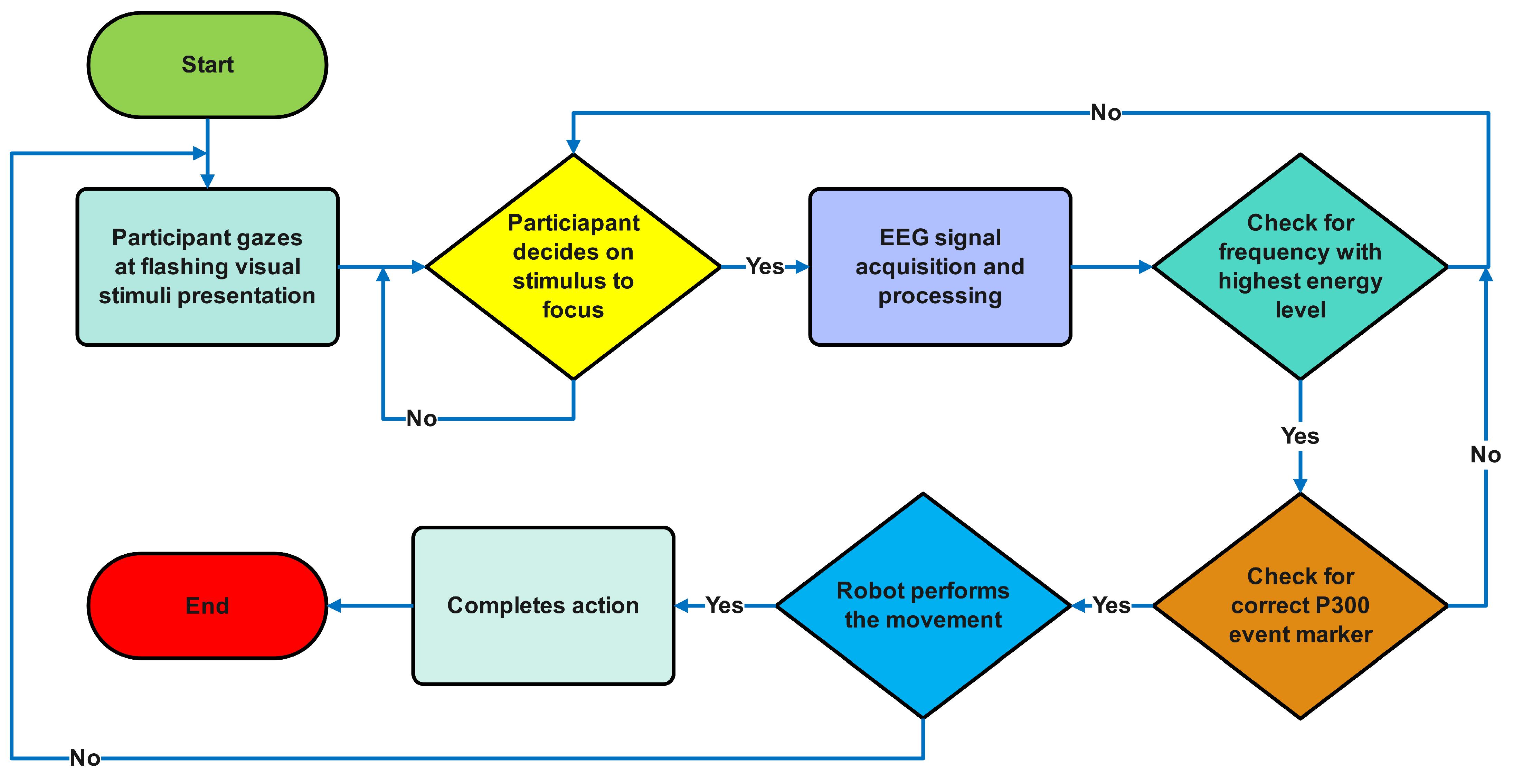
2.3. Methodological Validation of Experimental Design
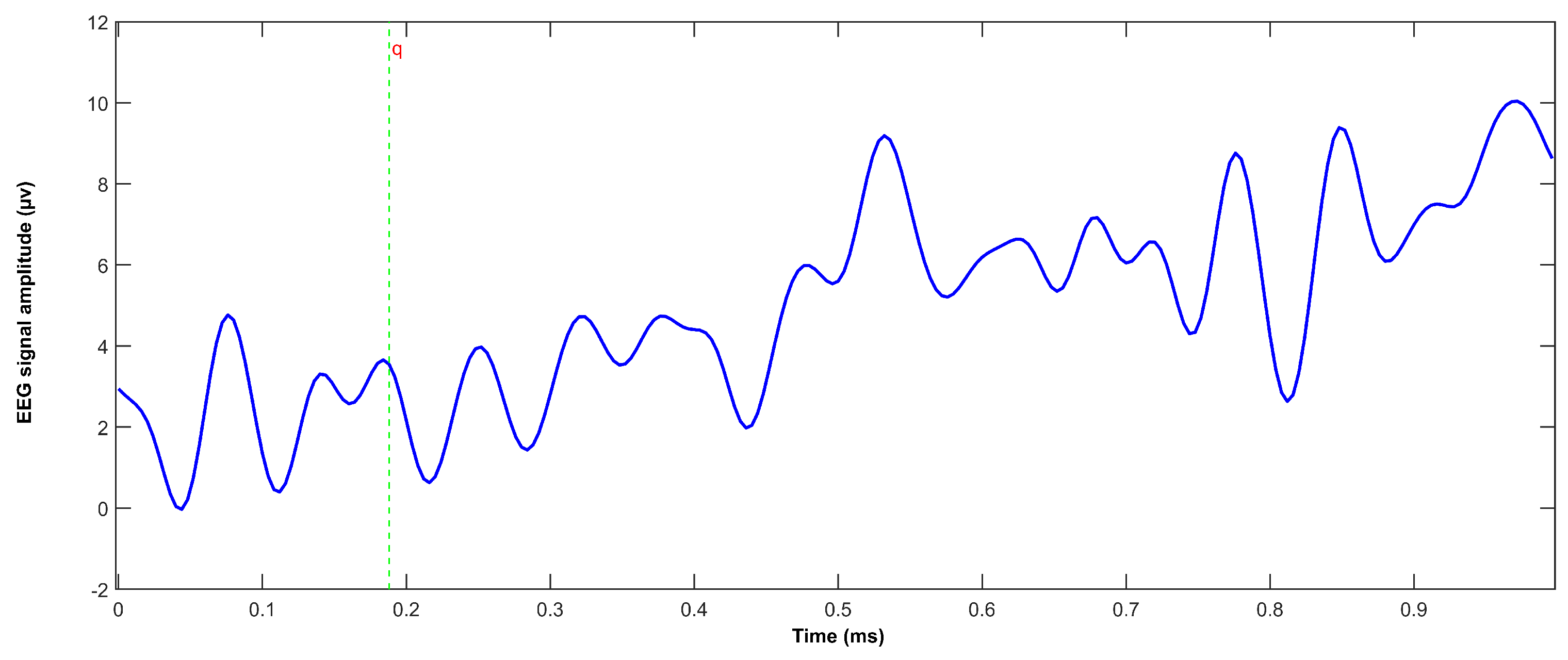
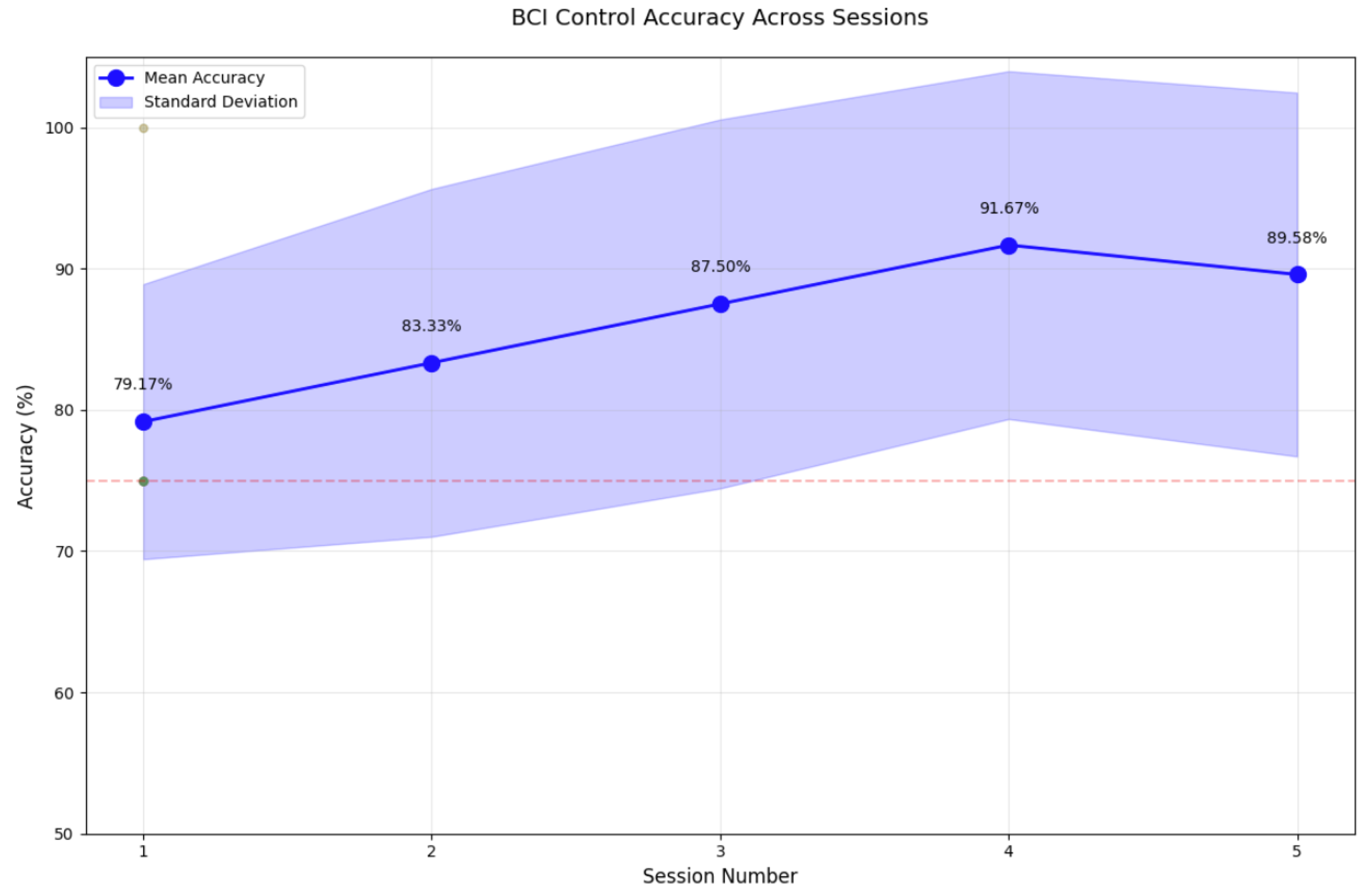
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Huang, Z.; Huang, D.; Yu, H.; Li, Z. Recent Progress in Wearable Brain–Computer Interface (BCI) Devices Based on Electroencephalogram (EEG) for Medical Applications: A Review. Health Data Sci. 2023, 3, 0096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, R.; Chouhan, T.; Guan, C. BCI for stroke rehabilitation: Motor and beyond. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 041001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterniuk, A.; Browarska, N.; Al-Bakri, A.; Pelc, M.; Zygarlicki, J.; Sidikova, M.; Martinek, R.; Gorzelanczyk, E.J. Summary of over Fifty Years with Brain-Computer Interfaces—A Review. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, H.; Maini, S. Electroencephalogram based brain-computer interface: Applications, challenges, and opportunities. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 47003–47047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouli, S.; Palaniappan, R.; Molefi, E.; McLoughlin, I. In-Ear Electrode EEG for Practical SSVEP BCI. Technologies 2020, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljalal, M.; Ibrahim, S.; Djemal, R.; Ko, W. Comprehensive review on brain-controlled mobile robots and robotic arms based on electroencephalography signals. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2020, 13, 539–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janapati, R.; Dalal, V.; Sengupta, R. Advances in modern EEG-BCI signal processing: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 80, 2563–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondini, V.; Mangia, A.L.; Cappello, A. EEG-Based BCI System Using Adaptive Features Extraction and Classification Procedures. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 2016, 4562601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Putz, G.; Schwarz, A.; Pereira, J.; Ofner, P.; Hessing, B.; Schneiders, M.; Stein, S.; Ramsay, A.; Williamson, J.H.; Murray-Smith, R.; et al. Non-invasive Brain–Computer Interfaces for Control of Grasp Neuroprosthesis: The European MoreGrasp Initiative. In Neuroprosthetics and Brain-Computer Interfaces in Spinal Cord Injury: A Guide for Clinicians and End Users; Müller-Putz, G., Rupp, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 307–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezeika, A.; Benda, M.; Stawicki, P.; Gembler, F.; Saboor, A.; Volosyak, I. Brain–Computer Interface Spellers: A Review. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, X.; Ai, J.; Ji, M.; Zhu, X.; Meng, J. A hybrid BCI combining SSVEP and EOG and its application for continuous wheelchair control. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 88, 105530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapgate, D.D. Application of hybrid SSVEP + P300 brain computer interface to control avatar movement in mobile virtual reality gaming environment. Behav. Brain Res. 2024, 472, 115154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Daly, I.; Allison, B.Z.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, X. A new hybrid BCI paradigm based on P300 and SSVEP. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 244, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Xiao, J.; Wang, F.; Liang, Q.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Xie, Q. A Hybrid Brain–Computer Interface Combining P300 Potentials and Emotion Patterns for Detecting Awareness in Patients with Disorders of Consciousness. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2023, 15, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, C.; Chao, F.; Liu, C.; Jiao, X.; An, Y.; Nwachukwu, S.E.; Jiang, M. Towards portable SSVEP-based brain-computer interface using Emotiv EPOC and mobile phone. In Proceedings of the 2018 Tenth International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence (ICACI), Xiamen, China, 29–31 March 2018; pp. 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kancaoğlu, M.; Kuntalp, M. Low-cost, mobile EEG hardware for SSVEP applications. HardwareX 2024, 19, e00567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.X. Analyzing Neural Time Series Data; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladouce, S.; Darmet, L.; Torre Tresols, J.J.; Velut, S.; Ferraro, G.; Dehais, F. Improving user experience of SSVEP BCI through low amplitude depth and high frequency stimuli design. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siribunyaphat, N.; Punsawad, Y. Steady-State visual-evoked Potential-Based Brain–Computer Interface Using a Novel Visual Stimulus with Quick Response (QR) Code Pattern. Sensors 2022, 22, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guger, C.; Allison, B.Z.; Großwindhager, B.; Prückl, R.; Hintermüller, C.; Kapeller, C.; Bruckner, M.; Krausz, G.; Edlinger, G. How Many People Could Use an SSVEP BCI? Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.S.; Mah, W.L.; Mok, S.Y.; Ng, D.W.K.; Tan, L.F.; Tan, Y.Q.; Ramli, N.; Goh, K.J.; Goh, S.Y. Age-dependent changes in steady-state visual-evoked potentials. Neurol. Asia 2022, 27, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, K.; Ai, Q.; Xie, S. Review: Recent Development of Signal Processing Algorithms for SSVEP-based Brain Computer Interfaces. J. Med Biol. Eng. 2014, 34, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ji, B.; Shao, D.; Chen, W.; Gao, K. A Methodology for Enhancing SSVEP Features Using Adaptive Filtering Based on the Spatial Distribution of EEG Signals. Micromachines 2023, 14, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ravi, A.; Jiang, N. Does Inter-Stimulus Distance Influence the Decoding Performance of SSVEP and SSMVEP BCI? In Proceedings of the 10th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), Virtual, 4–6 May 2021; pp. 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duart, X.; Quiles, E.; Suay, F.; Chio, N.; García, E.; Morant, F. Evaluating the Effect of Stimuli Color and Frequency on SSVEP. Sensors 2020, 21, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havaei, P.; Zekri, M.; Mahmoudzadeh, E.; Rabbani, H. An efficient deep learning framework for P300 evoked related potential detection in EEG signal. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023, 229, 107324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, L.; Liti, C.; Liuzzi, G.; Piccialli, V.; Salvatore, C. Improving P300 Speller performance by means of optimization and machine learning. Ann. Oper. Res. 2021, 312, 1221–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delijorge, J.; Mendoza-Montoya, O.; Gordillo, J.L.; Caraza, R.; Martinez, H.R.; Antelis, J.M. Evaluation of a P300-Based Brain-Machine Interface for a Robotic Hand-Orthosis Control. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 589659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Jung, T.P.; Ming, D. A comparison of classification methods for recognizing single-trial P300 in brain-computer interfaces. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 3032–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.K.; S, M.K.; S, H.R.; Jayachandra, M.; Pandya, H.J. Design, Development and Validation of a Portable Visual P300 Event-Related Potential Extraction System. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Taipei, Taiwan, 13–15 October 2022; pp. 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.; Rhiu, I.; Lee, Y.; Yun, M.H.; Nam, C.S. A Systematic Review of Hybrid brain-computer interfaces: Taxonomy and Usability Perspectives. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Park, S.; Ha, J.; Kim, L. Hybrid approach of SSVEP and EEG-based eye-gaze tracking for enhancing BCI performance. In Proceedings of the 2023 11th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), Jeongseon, Republic of Korea, 20–22 February 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, S.D.T.; Das, R.; Olsson, M.D.; Khan, M.A.; Puthusserypady, S. Hybrid EEG-EOG-based BCI system for Vehicle Control. In Proceedings of the 2021 9th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), Jeongseon, Republic of Korea, 22–24 February 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Li, M.; Qi, S.; Ng, A.C.M.; Ng, T.; Qian, W. A Hybrid P300-SSVEP brain-computer Interface Speller with a Frequency Enhanced Row and Column Paradigm. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1133933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapgate, D.D. Hybrid SSVEP + P300 brain-computer Interface Can Deal with non-stationary Cerebral Responses with the Use of Adaptive Classification. J. Neurorestoratology 2024, 12, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantisatirapong, S.; Dechwechprasit, P.; Senavongse, W.; Phothisonothai, M. Time-frequency based coherence analysis of red and green flickering visual stimuli for EEG-controlled applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 9th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), Chonburi, Thailand, 1–4 February 2017; pp. 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouli, S.; Palaniappan, R.; Sillitoe, I.P.; Gan, J.Q. Performance analysis of multi-frequency SSVEP-BCI using clear and frosted colour LED stimuli. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE International Conference on BioInformatics and BioEngineering, Chania, Greece, 10–13 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambalde, E.P.; Borges, L.R.; Jablonski, G.; Barros de Almeida, M.; Naves, E.L.M. Influence of Stimuli Spatial Proximity on a SSVEP-Based BCI Performance. IRBM 2022, 43, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


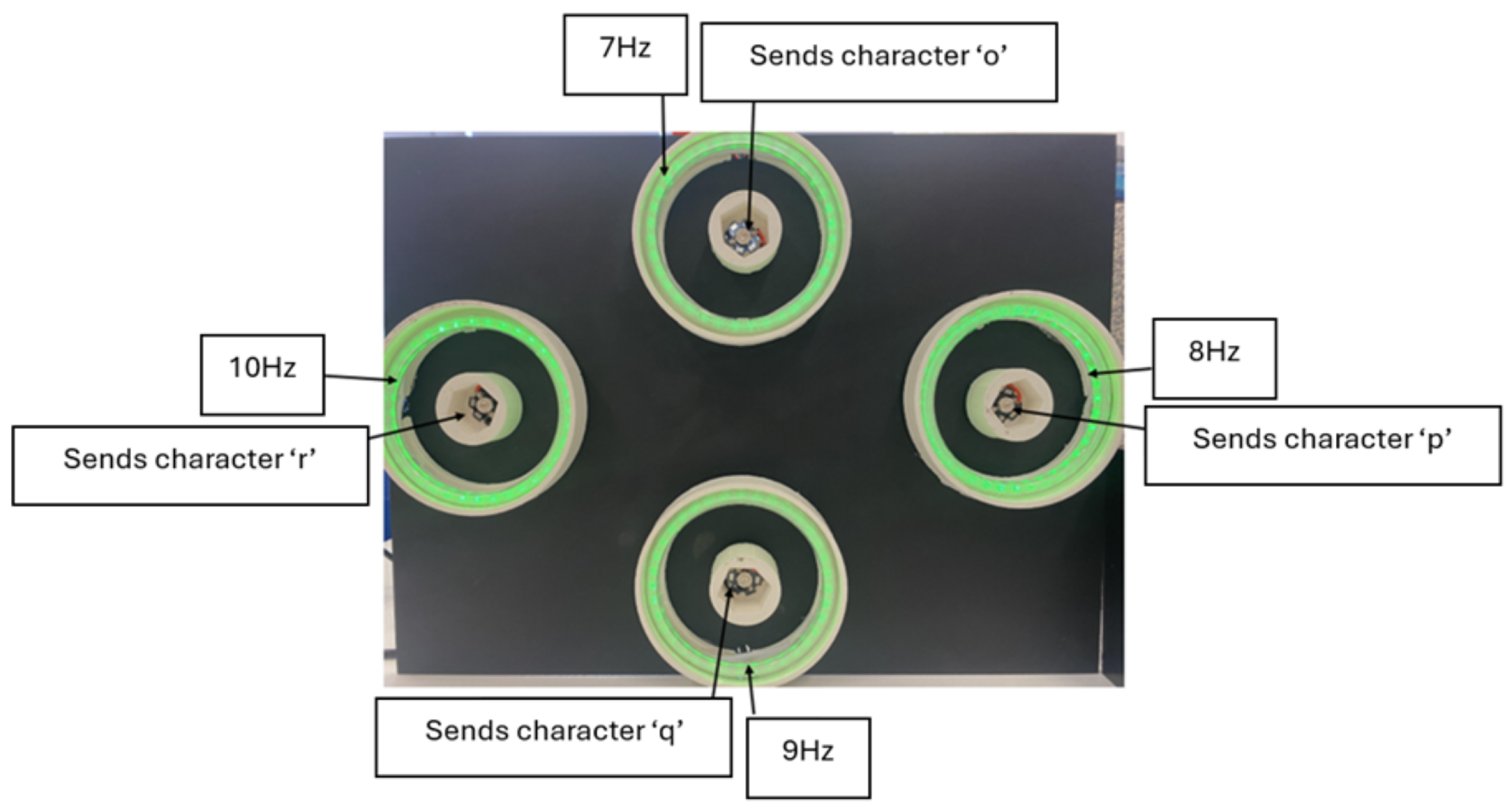




| SSVEP Frequency (Hz) | P300 Event Marker | Robot Navigation |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | o | Forward |
| 8 | p | Right |
| 9 | q | Backward |
| 10 | r | Left |
| Participant 1 | Participant 2 | ||||||||||
| Trial | F | B | L | R | A (%) | Trial | F | B | L | R | A (%) |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 75 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 75 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75 |
| Participant 3 | Participant 4 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 75 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 75 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 75 |
| Participant 5 | Participant 6 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 100 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 75 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 75 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 75 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| Participant 7 | Participant 8 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 75 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 75 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| Participant 9 | Participant 10 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 75 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 75 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 75 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75 |
| Participant 11 | Participant 12 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 75 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 75 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 75 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 100 |
| 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kasawala, E.; Mouli, S. Dual-Mode Visual System for Brain–Computer Interfaces: Integrating SSVEP and P300 Responses. Sensors 2025, 25, 1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061802
Kasawala E, Mouli S. Dual-Mode Visual System for Brain–Computer Interfaces: Integrating SSVEP and P300 Responses. Sensors. 2025; 25(6):1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061802
Chicago/Turabian StyleKasawala, Ekgari, and Surej Mouli. 2025. "Dual-Mode Visual System for Brain–Computer Interfaces: Integrating SSVEP and P300 Responses" Sensors 25, no. 6: 1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061802
APA StyleKasawala, E., & Mouli, S. (2025). Dual-Mode Visual System for Brain–Computer Interfaces: Integrating SSVEP and P300 Responses. Sensors, 25(6), 1802. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061802







