Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Changes in Ecological Environment Quality on Changxing Island Using an Optimized Remote Sensing Ecological Index
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
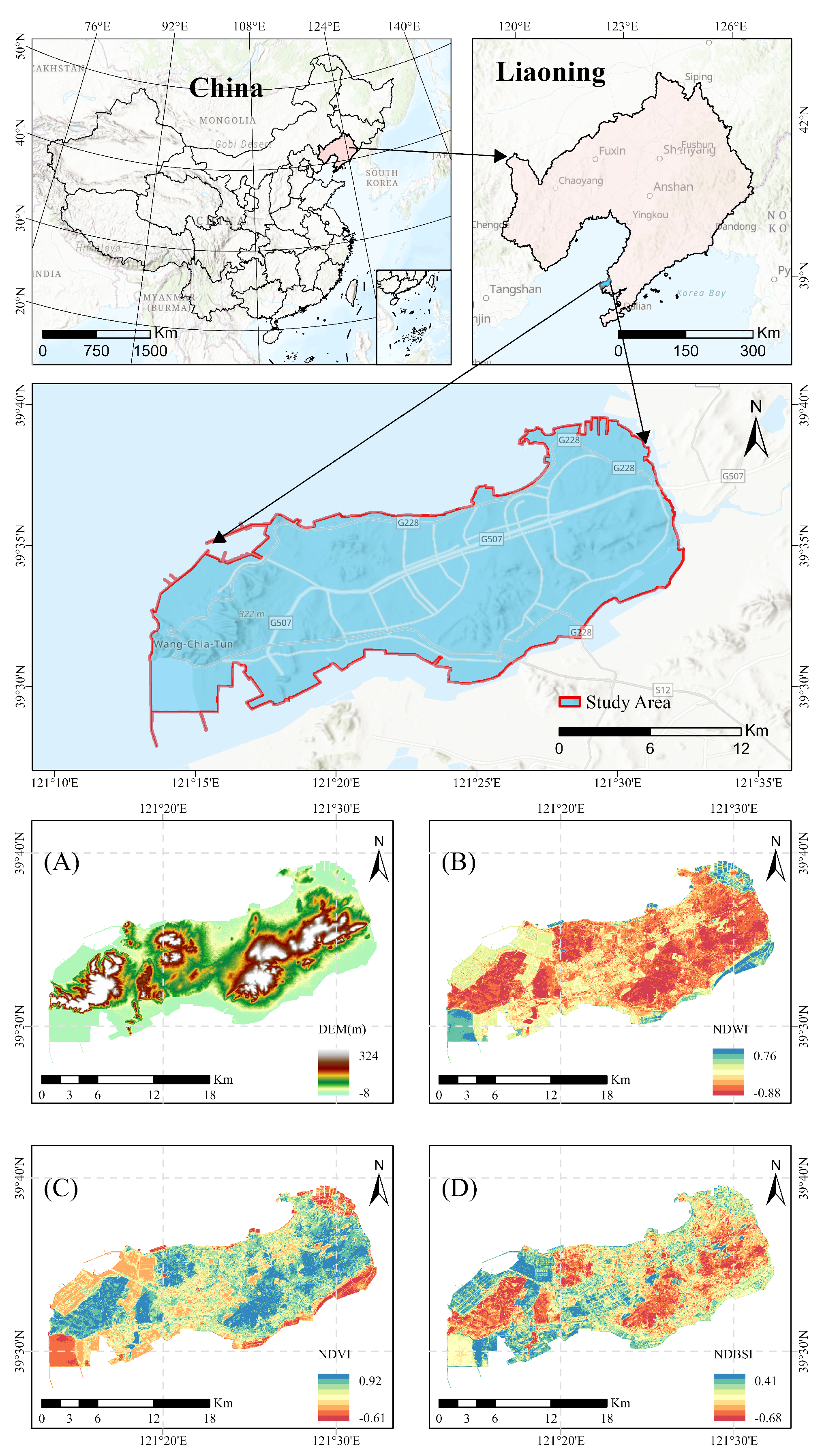
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Preprocessing
2.3. Land Use Change Analysis
Land Cover Classification and Accuracy Assessment
2.4. Shoreline Extraction and Change Analysis
2.5. Method for Evaluating Island Ecological Quality
3. Results
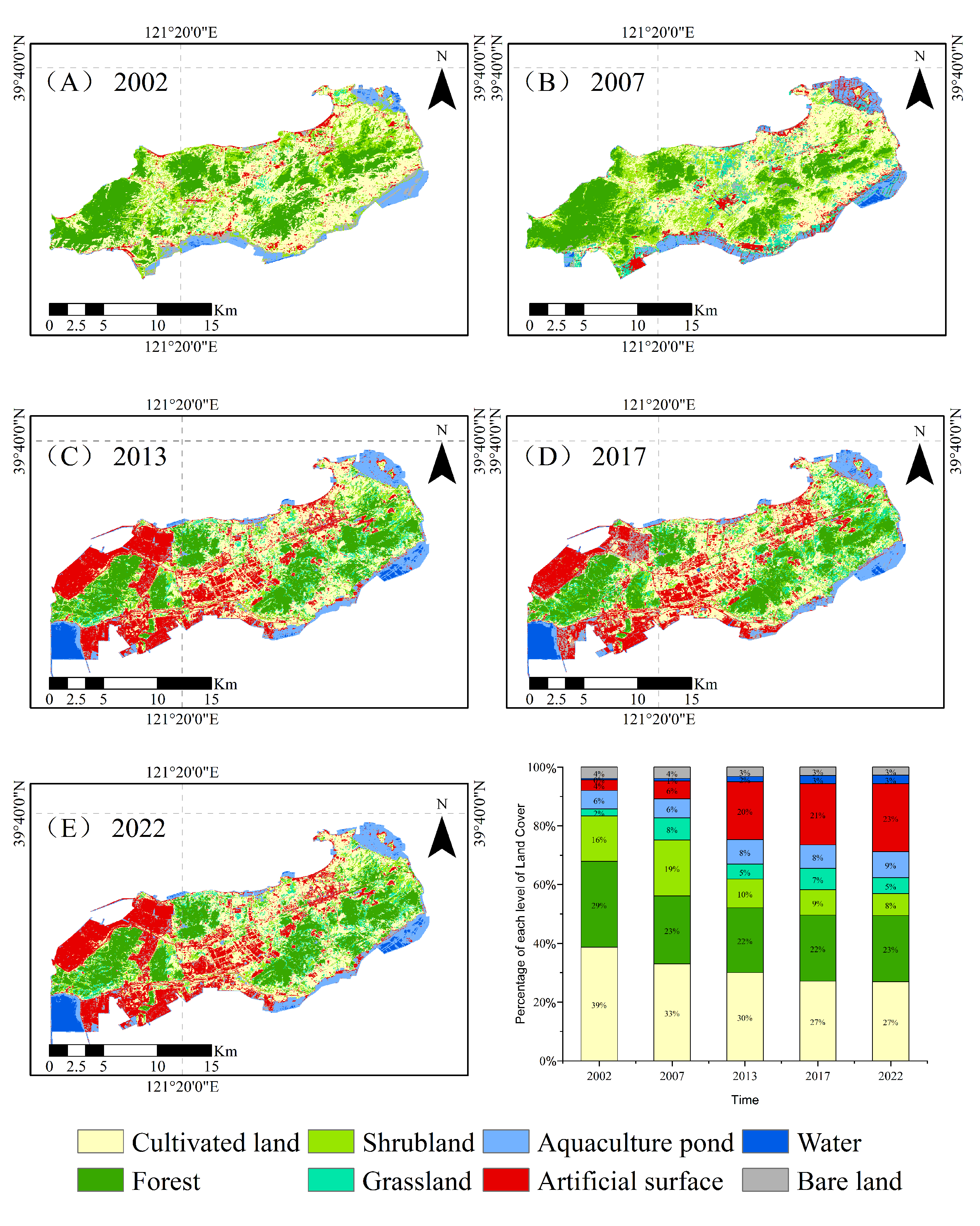
3.1. Overview of Land Use Changes on Changxing Island
3.1.1. Evaluation of the Land Use Classification Accuracy
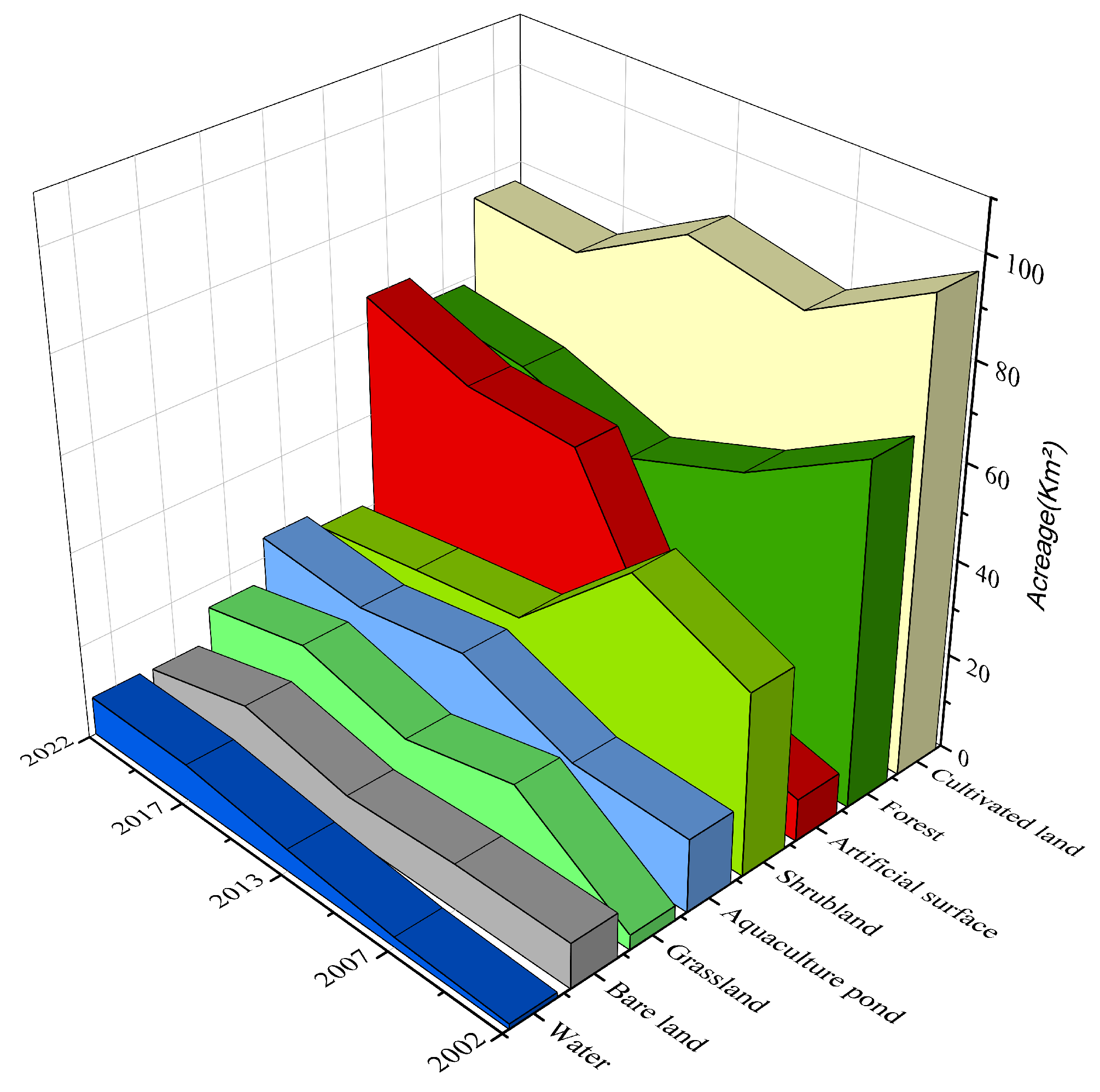
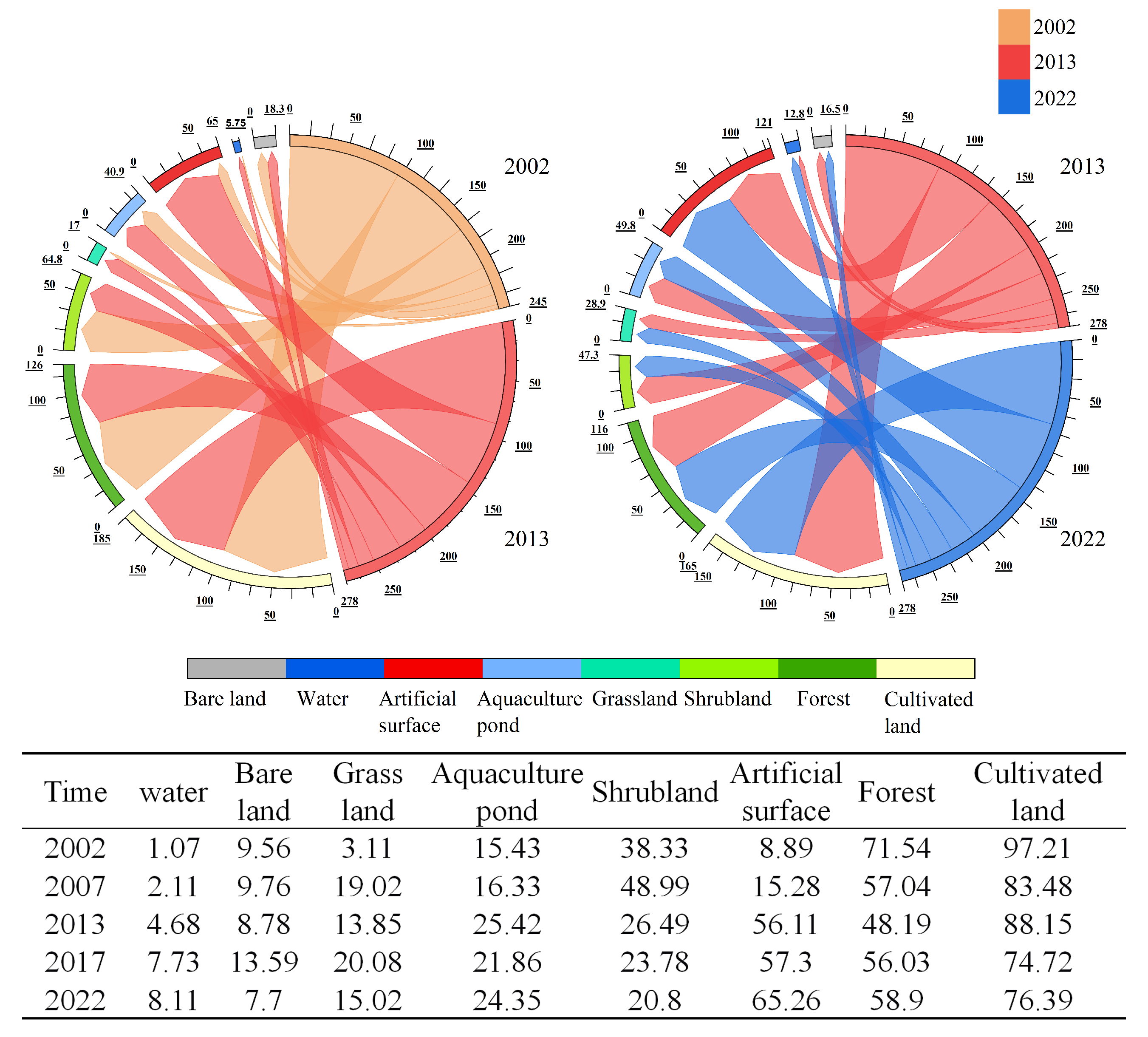
3.1.2. Area Changes in Land Use Types
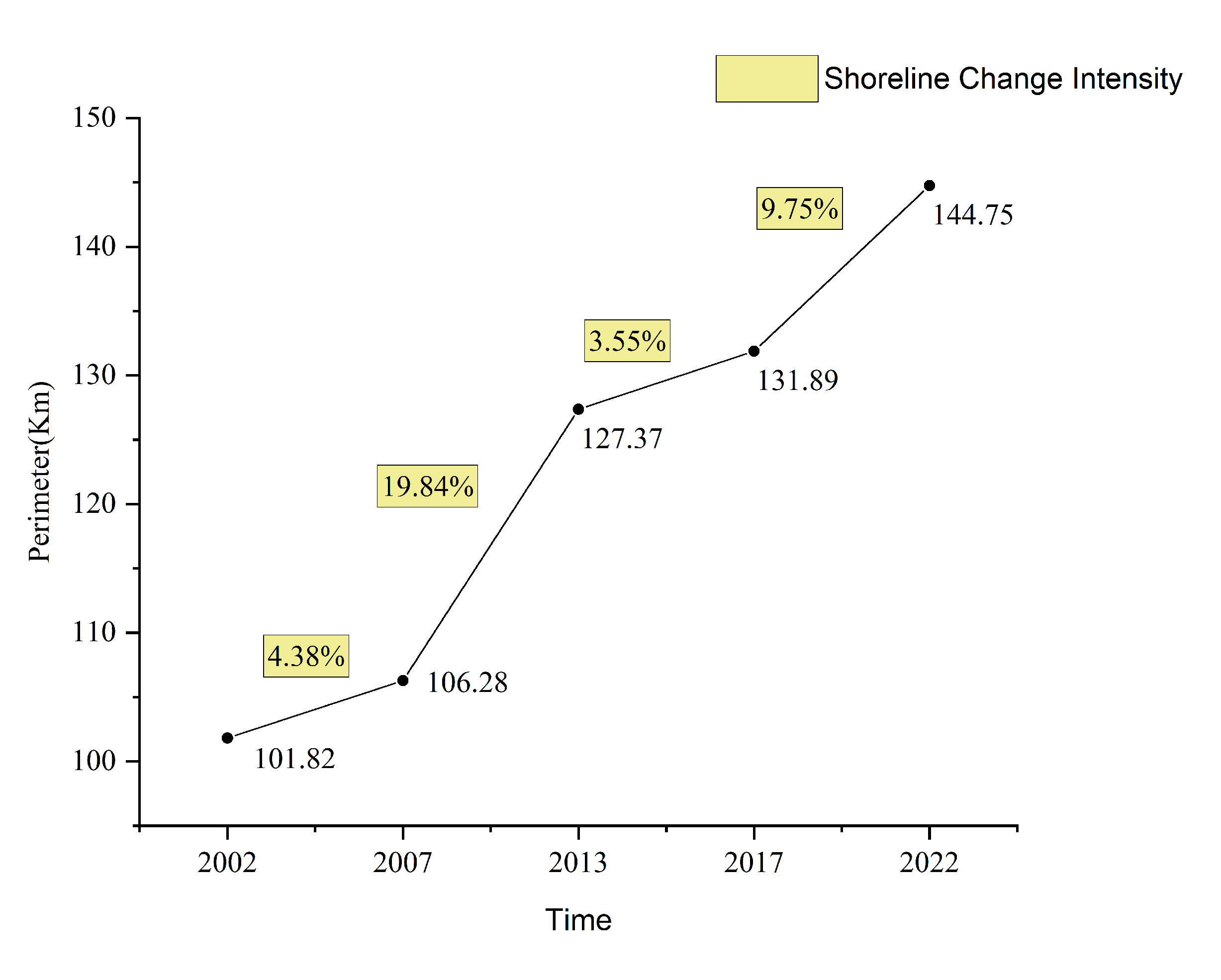
3.2. Overview of Shoreline Changes on Changxing Island
Shoreline Extraction and Accuracy Assessment
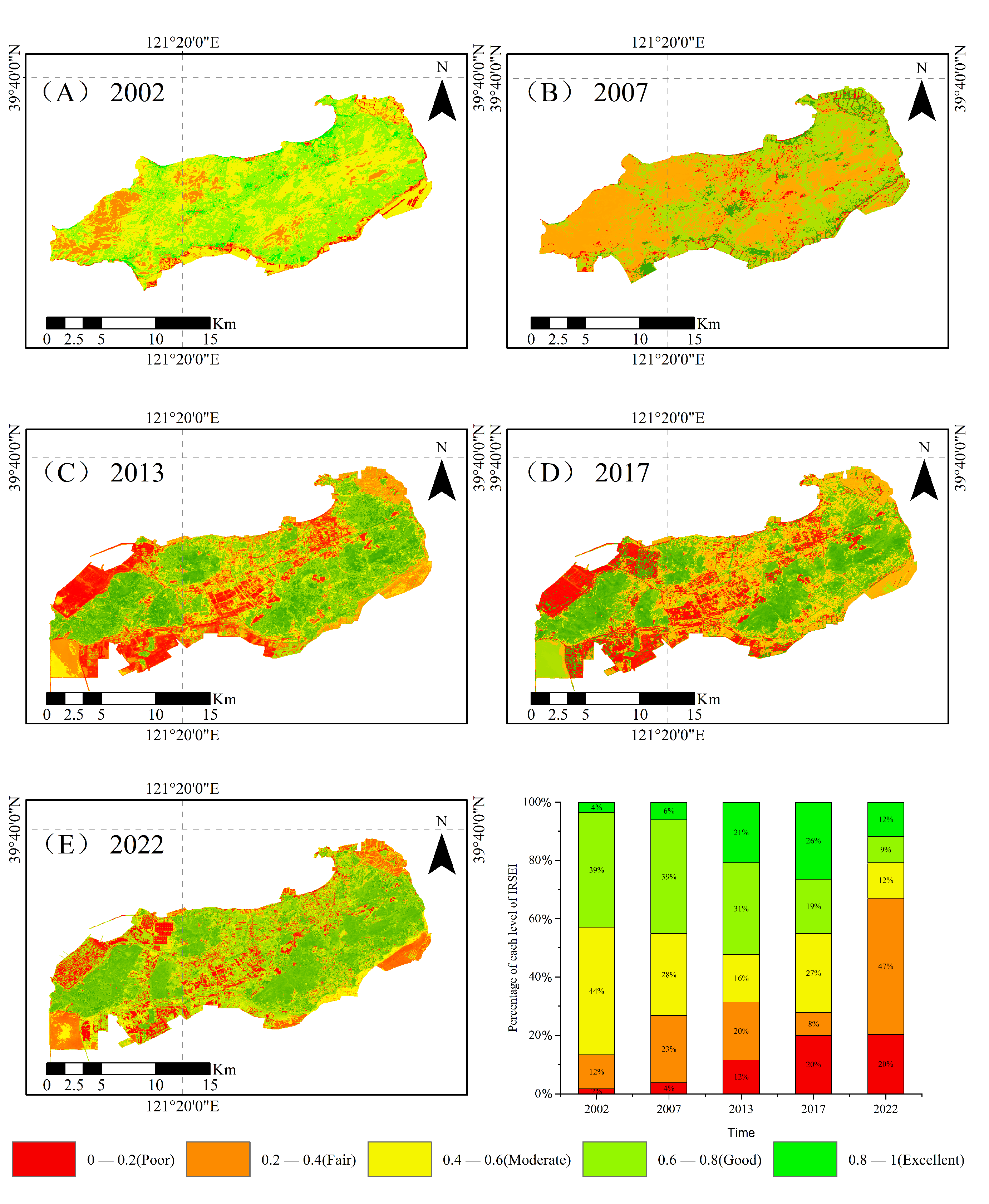
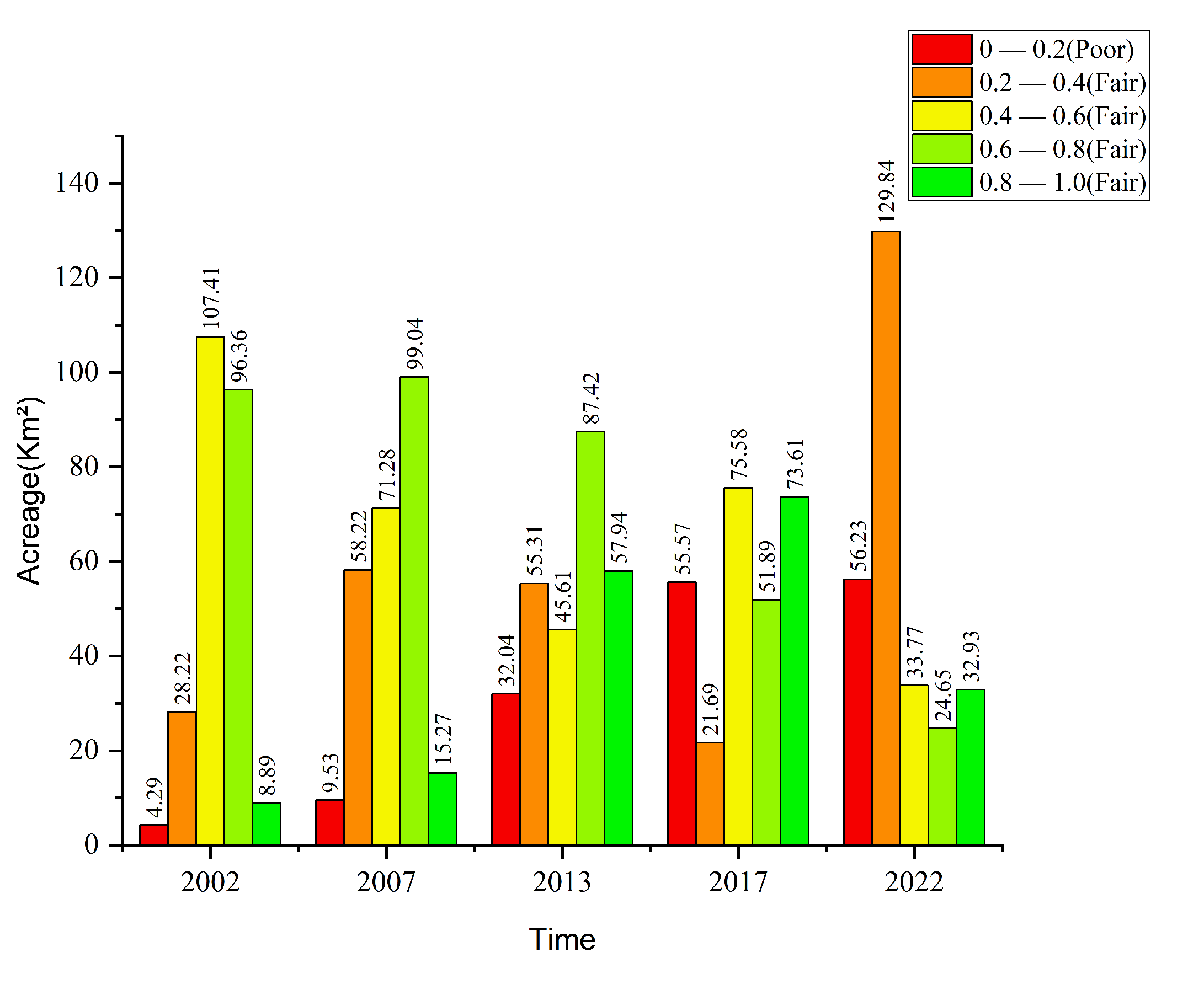
3.3. Overview of Ecological Index Changes on Changxing Island
Temporally Dynamic Analysis of Ecological Index Changes
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Land Cover on the Island Remote Sensing Ecological Index (IRSEI)
4.2. Effects of Shoreline Changes on the Island Remote Sensing Ecological Index (IRSEI)
4.3. Limitations and Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
- Changxing Island experienced significant changes in land use and shoreline expansion from 2002 to 2022. Farmland decreased substantially, while construction land increased notably, indicating rapid urbanization. The total shoreline length increased continuously over the 20−year period, with an average annual increase of 2.15 km, primarily driven by reclamation and coastal development. The quality of the ecological environment declined significantly, with high−quality areas decreasing annually, while areas classified as poor and very poor expanded continuously, indicating that the health of the ecosystem is facing serious degradation issues.
- The use of multisource data and cloud computing platforms enabled an in−depth analysis of the dynamic characteristics of the ecological environment on Changxing Island. The advantages of large−scale remote sensing data processing methods were highlighted, providing scientific support for local governments in developing ecological protection and sustainable development strategies. However, it is essential to integrate socioeconomic factors further to fully understand the multidimensional impacts of human activities on the ecological environment.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Liao, J.; Chen, J.; Sun, S. Long Time-Series Mapping and Change Detection of Coastal Zone Land Use Based on Google Earth Engine and Multi-Source Data Fusion. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Lou, Z.P.; Sun, C.C.; Sun, S. Ecological environment changes in Daya Bay, China, from 1982 to 2004. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Du, S.; Scussolini, P.; Wen, J.; He, C.; Huang, Q.; Gao, J. Rapid Population Growth in Chinese Floodplains from 1990 to 2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, A.; Zulfiqar, S.; Tabassum, N.; Khan, A.S.; Abid, M.A.; Akhtar, M.S.; Al-Misned, F.; Aljuwayid, A.M.; Zahmatkesh, S.; Asif, S. Biocompatible cellulose acetate supported ammonium based ionic liquid membranes; way forward to remediate water pollution. Chemosphere 2023, 322, 138151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadigov, R. Rapid Growth of the World Population and Its Socioeconomic Results. Sci. World J. 2022, 2022, 8110229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Guo, H.; Nor, D.D.M.M.; Song, A.; Dai, L. Mineral resources depletion, environmental degradation, and exploitation of natural resources: COVID-19 aftereffects. Resour. Policy 2023, 85, 103907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Hou, L.; Qi, Z.; Wan, L. Impacts of climate change and human activities on vegetation NDVI in China’s Mu Us Sandy Land during 2000–2019. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akomolafe, G.F.; Rosazlina, R. Land use and land cover changes influence the land surface temperature and vegetation in Penang Island, Peninsular Malaysia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, S.B.; Van Der Sleen, P.; Siddiqui, S.F.; Bogotá-Gregory, J.D.; Arantes, C.C.; Barnett, A.A.; Couto, T.B.A.; Goulding, M.; Anderson, E.P. Biotic Indicators for Ecological State Change in Amazonian Floodplains. BioScience 2022, 72, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddik, M.S.; Tulip, S.S.; Rahman, A.; Islam, M.N.; Haghighi, A.T.; Mustafa, S.M.T. The impact of land use and land cover change on groundwater recharge in northwestern Bangladesh. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Harmay, N.S.; Kim, D.; Choi, M. Urban Heat Island associated with Land Use/Land Cover and climate variations in Melbourne, Australia. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, F.; Su, F. Changes in coastline and coastal reclamation in the three most developed areas of China, 1980–2018. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2021, 204, 105542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normand, J.C.L.; Heggy, E.; Castellazzi, P. Nationwide Subsidence in Bahrain Island: Drivers and Implications for Relative Sea-Level Rise. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 9286–9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yu, K.; Liu, J. Dynamic Landscape Fragmentation and the Driving Forces on Haitan Island, China. Land 2022, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Li, X.; Jiang, D.; Lin, S.; Yang, B.; Chen, S. Threshold of island anthropogenic disturbance based on ecological vulnerability Assessment—A case study of Zhujiajian Island. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 167, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Cui, W.; Cai, L.; Chen, M.; Xu, C. Spatiotemporal Evolution Characteristics of Ecosystem Service Values Based on NDVI Changes in Island Cities. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 12922–12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z. Spatial–Temporal Evolution Monitoring and Ecological Risk Assessment of Coastal Wetlands on Hainan Island, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S.; Gui, F.; Le, Q. Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment of Zhoushan Island Based on LULC Change. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Ma, X.; De Jong, M.; Bao, X. Assessment on Island Ecological Vulnerability to Urbanization: A Tale of Chongming Island, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xu, W.; Lu, N.; Huang, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Dai, F.; Kou, W. Assessment of spatial–temporal changes of ecological environment quality based on RSEI and GEE: A case study in Erhai Lake Basin, Yunnan province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizizi, Y.; Kasimu, A.; Liang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, B. Evaluation of ecological space and ecological quality changes in urban agglomeration on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Yang, B.; Li, M. An improved framework for assessing the impact of different urban development strategies on land cover and ecological quality changes—A case study from Nanjing Jiangbei New Area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xifeng, J.; Junling, H.; Qi, Z.; Saitiniyazi, A. Evolution pattern and driving mechanism of eco-environmental quality in arid oasis belt—A case study of oasis core area in Kashgar Delta. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, R.; Li, X. Mapping changes in coastlines and tidal flats in developing islands using the full time series of Landsat images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Dong, X.; Liu, Z.; Gao, W.; Hu, Z.; Wu, G. Mapping Tidal Flats with Landsat 8 Images and Google Earth Engine: A Case Study of the China’s Eastern Coastal Zone circa 2015. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parracciani, C.; Gigante, D.; Bonini, F.; Grassi, A.; Morbidini, L.; Pauselli, M.; Valenti, B.; Lilli, E.; Antonielli, F.; Vizzari, M. Leveraging Google Earth Engine for a More Effective Grassland Management: A Decision Support Application Perspective. Sensors 2024, 24, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapiou, A. Multi-Temporal Change Detection Analysis of Vertical Sprawl over Limassol City Centre and Amathus Archaeological Site in Cyprus during 2015–2020 Using the Sentinel-1 Sensor and the Google Earth Engine Platform. Sensors 2021, 21, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khachoo, Y.H.; Cutugno, M.; Robustelli, U.; Pugliano, G. Impact of Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) Changes on Carbon Stocks and Economic Implications in Calabria Using Google Earth Engine (GEE). Sensors 2024, 24, 5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Nawaz, Z. Testing Accuracy of Land Cover Classification Algorithms in the Qilian Mountains Based on GEE Cloud Platform. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, K.; Khanal, N.; Chaudhary, S.; Maharjan, S.; Thapa, R.B. Coastal morphological changes: Assessing long-term ecological transformations across the northern Bay of Bengal. Environ. Chall. 2020, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jia, A.; Song, X.; Bai, Y. Extraction and spatiotemporal evolution analysis of tidal flats in the Bohai Rim during 1984–2019 based on remote sensing. J. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 76–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, B. Quality Assessment of Ecological Environment Based on Google Earth Engine: A Case Study of the Zhoushan Islands. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 918756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida Pereira, G.H.; Fusioka, A.M.; Nassu, B.T.; Minetto, R. Active fire detection in Landsat-8 imagery: A large-scale dataset and a deep-learning study. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 178, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinnert, J.C.; Via, S.M.; Nettleton, B.P.; Tuley, P.A.; Moore, L.J.; Stallins, J.A. Connectivity in coastal systems: Barrier island vegetation influences upland migration in a changing climate. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 2419–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Main-Knorn, M.; Pflug, B.; Louis, J.; Debaecker, V.; Müller-Wilm, U.; Gascon, F. Sen2Cor for Senti-2. In Proceedings of the Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXIII, Warsaw, Poland, 11–13 September 2017; p. 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, L.; Van Deventer, H.; Ramoelo, A.; Mathieu, R.; Nondlazi, B.; Gangat, R. Estimating above ground biomass as an indicator of carbon storage in vegetated wetlands of the grassland biome of South Africa. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 78, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pech-May, F.; Aquino-Santos, R.; Rios-Toledo, G.; Posadas-Durán, J.P.F. Mapping of Land Cover with Optical Images, Supervised Algorithms, and Google Earth Engine. Sensors 2022, 22, 4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, D.H.; Mucsi, L. From Land Cover Map to Land Use Map: A Combined Pixel-Based and Object-Based Approach Using Multi-Temporal Landsat Data, a Random Forest Classifier, and Decision Rules. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Explaining the unsuitability of the kappa coefficient in the assessment and comparison of the accuracy of thematic maps obtained by image classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Research on temporal and spatial evolution of land use and landscape pattern in Anshan City based on GEE. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 988346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodato, F.; Colonna, N.; Pennazza, G.; Praticò, S.; Santonico, M.; Vollero, L.; Pollino, M. Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Urban Expansion of the Rome Coastline through GEE and RF Algorithm, Using Landsat Imagery. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Sahebi, M.; Shokri, M. MODIFIED OPTIMIZATION WATER INDEX (MOWI) FOR LANDSAT-8 OLI/TIRS. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, XLII-4/W4, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.P.; Efraim De Oliveira, I.; Lyra, R.; Scaranto Dazzi, R.L.; Martins, V.G.; Henrique Da Fontoura Klein, A. Coastal Analyst System from Space Imagery Engine (CASSIE): Shoreline management module. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 140, 105033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Q.; Liu, J.; Sang, H.; Yang, D.; Zhai, L.; Li, N.; Yuan, X. Coastline changes in mainland China from 2000 to 2015. Int. J. Image Data Fusion 2022, 13, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, X. Characteristics of Coastline Changes on Southeast Asia Islands from 2000 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, M.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z. Analysis of Ecological Environment in the Shanxi Section of the Yellow River Basin and Coal Mining Area Based on Improved Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Sensors 2024, 24, 6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Xi, X. Ecological environment evaluation based on remote sensing ecological index: A case study in East China over the past 20 years. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, E.; Shi, F.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Hai, H. Evaluating environmental quality and its driving force in northeastern China using the remote sensing ecological index. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hou, Q.; Duan, Y.; Ma, S. Spatial and Temporal Heterogeneity of Eco-Environmental Quality in Yanhe Watershed (China) Using the Remote-Sensing-Based Ecological Index (RSEI). Land 2024, 13, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, M. Vulnerability analysis of island ecological environment and regulating measures. Coast. Eng. 2008, 27, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhan, C.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y. Evolution and reconstruction of settlement space in tourist islands: A case study of Dachangshan Island, Changhai County. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 24, 9777–9808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; She, J.; Zhang, Y. Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Land Use Change and Eco-Environmental Effects in the Chang-Zhu-Tan Core Area. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Shi, T.; Guan, H.; Fang, C.; Lin, Z. Prediction of ecological effects of potential population and impervious surface increases using a remote sensing based ecological index (RSEI). Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Yue, X.; Liao, H.; Ma, Y. A humidity-based exposure index representing ozone damage effects on vegetation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 044030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, Y. Eco-Environmental Quality Assessment in China’s 35 Major Cities Based On Remote Sensing Ecological Index. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 51295–51311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahooni, A.; Kakroodi, A.; Kiavarz, M. Monitoring of land surface albedo and its impact on land surface temperature (LST) using time series of remote sensing data. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 75, 102118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Zhou, J.; Yang, R.; Jiang, S.; Yang, L.; Tang, B. Lower land use intensity promoted soil macrofaunal biodiversity on a reclaimed coast after land use conversion. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 306, 107208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Chen, S.; Liu, K.; Wang, W.; Hou, H.; Gao, L.; Zhang, F.; Su, H. Spatiotemporal variation in sensitivity of urban vegetation growth and greenness to vegetation water content: Evidence from Chinese megacities. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wu, C. NDBSI: A normalized difference bare soil index for remote sensing to improve bare soil mapping accuracy in urban and rural areas. CATENA 2022, 214, 106265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Zhao, H.; Deng, L.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, R.; Che, Y. Characterizing the warming effect of increasing temperatures on land surface: Temperature change, heat pattern dynamics and thermal sensitivity. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 70, 102904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sargent, I.; Pan, X.; Li, H.; Gardiner, A.; Hare, J.; Atkinson, P.M. Joint Deep Learning for land cover and land use classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewers, F.L.; Ferreira, G.R.; Arruda, H.F.D.; Silva, F.N.; Comin, C.H.; Amancio, D.R.; Costa, L.D.F. Principal Component Analysis: A Natural Approach to Data Exploration. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 54, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, J.; Krzywinski, M.; Altman, N. Principal component analysis. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 641–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharani, M.; Sreenivasulu, G. Land use and land cover change detection by using principal component analysis and morphological operations in remote sensing applications. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2021, 43, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, T.; Bang, E. Investigation of odor pollution by utilizing selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry (SIFT-MS) and principal component analysis (PCA). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Pang, X.; Jiang, F.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Wu, G.; Li, C.; Xu, T.; et al. Movable oil content evaluation of lacustrine organic-rich shales: Methods and a novel quantitative evaluation model. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 214, 103545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Xue, X.; Shi, L.; Gao, L. Urban spatial expansion and its impacts on island ecosystem services and landscape pattern: A case study of the island city of Xiamen, Southeast China. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2013, 81, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Hao, Z.; Post, C.J.; Mikhailova, E.A. Monitoring Ecological Changes on a Rapidly Urbanizing Island Using a Remote Sensing-Based Ecological Index Produced Time Series. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Shan, X.; Chen, Y.; Jin, X.; Muhammed, F.R. Dynamics of shoreline and land reclamation from 1985 to 2015 in the Bohai Sea, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 2031–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, D.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Wei, X.; Sang, M.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Hu, B. Monitoring and analysis of coastal reclamation from 1995–2015 in Tianjin Binhai New Area, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Duan, Z.; Yu, T.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of coastline changes under the impact of human activities during 1985–2020 in Tianjin, China. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0289969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xue, X. Construction and Application of a Coastline Ecological Index: A Case Study of Fujian Province, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claverie, M.; Vermote, E.F.; Franch, B.; Masek, J.G. Evaluation of the Landsat-5 TM and Landsat-7 ETM+ surface reflectance products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Im, J.; Lee, J.; Gong, H.; Ryu, Y. Characteristics of Landsat 8 OLI-derived NDVI by comparison with multiple satellite sensors and in-situ observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 164, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.; Zhang, H.K.; Liu, J. Making Landsat 5, 7 and 8 reflectance consistent using MODIS nadir-BRDF adjusted reflectance as reference. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 262, 112517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Feng, R.; Gong, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Guan, X.; Li, S. Combing remote sensing information entropy and machine learning for ecological environment assessment of Hefei-Nanjing-Hangzhou region, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapucci, C.; Antonini, A.; Böhm, E.; Organelli, E.; Massi, L.; Ortolani, A.; Brandini, C.; Maselli, F. Use of Sentinel-3 OLCI Images and Machine Learning to Assess the Ecological Quality of Italian Coastal Waters. Sensors 2023, 23, 9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sensors | Data | Spatial Resolution | Acquisition Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landsat/LT05 | LANDSAT/LT05/ C02/T1_TOA | 30 m | May 2002/May 2007 |
| Landsat/LC08 | LANDSAT/LC08/ C02/T1_L2 | 30 m | May 2013/May 2017 |
| Sentinel−2A | COPERNICUS/ S2_SR_HARMONIZED | 30 m | May 2022 |
| Land Class | Definition |
|---|---|
| Cultivated land | Land used for agricultural planting, such as the cultivation of grains, cash crops, and vegetables, as a fundamental resource for agricultural production. |
| Forest | Land typically found in mountainous, hilly, and similar regions. |
| Water | Land covered by water, primarily consisting of rivers, lakes, seas, and other water bodies. |
| Grassland | Grassland refers to vegetated areas mainly composed of herbaceous plants, encompassing both natural and cultivated grasslands. |
| Shrubland | Vegetated areas typically found in arid regions, mainly composed of mountain shrubs, evergreen shrubs, and similar vegetation types. |
| Bare land | Includes natural lands like sandy beaches, gravel areas, and bare rock−covered land, with minimal vegetation cover. |
| Aquaculture pond | Artificial or naturally constructed ponds used for aquaculture. |
| Artificial surface | Land characterized by human development activities, such as urban residential areas and infrastructure land. |
| Index | Formula | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| NDVI | and correspond to the near−infrared and red bands of Landsat imagery, respectively [36] | |
| NDBI | and represent the red and green bands of Landsat imagery, respectively [37] | |
| NDWI | and correspond to the near−infrared and green bands of Landsat imagery, respectively [38] |
| Index | Formula | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| AWEI | corresponds to Band 3 in Landsat imagery and Band 3 in Sentinel−2 imagery. corresponds to Band 6 in Landsat imagery and Band 11 in Sentinel-2 imagery. corresponds to Band 5 in Landsat imagery and Band 8 in Sentinel−2 imagery. corresponds to Band 7 in Landsat imagery and Band 12 in Sentinel−2 imagery. | |
| CCI | and represent the shoreline lengths at times and (in km), respectively, and T represents the time interval (in years). |
| Time | Overall Classification Accuracy/% | Kappa Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| 2002 | 91.0714% | 0.8952 |
| 2007 | 90.4255% | 0.8877 |
| 2013 | 89.7540% | 0.8805 |
| 2017 | 90.2255% | 0.8815 |
| 2022 | 94.3625% | 0.9271 |
| Time | LST | LUI | M−NDBSI | GNDVI | WET | Total Eigenvalue Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 0.0405 | 0.7762 | 0.4498 | −0.4316 | −0.0848 | 0.1840 |
| 2017 | 0.0548 | 0.8833 | 0.3138 | −0.3349 | −0.0781 | 0.1544 |
| 2013 | 0.1777 | 0.6530 | 0.5002 | −0.5278 | −0.1136 | 0.1878 |
| 2007 | −0.0046 | −0.9981 | −0.0262 | 0.0538 | −0.0121 | 0.0682 |
| 2002 | −0.1138 | −0.8327 | −0.3884 | 0.0359 | 0.3752 | 0.1012 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Wang, F.; Yu, H.; Liao, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, J. Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Changes in Ecological Environment Quality on Changxing Island Using an Optimized Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Sensors 2025, 25, 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061791
Zhu Y, Hou Y, Wang F, Yu H, Liao Z, Yu Q, Zhu J. Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Changes in Ecological Environment Quality on Changxing Island Using an Optimized Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Sensors. 2025; 25(6):1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061791
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yuanyi, Yingzi Hou, Fangxiong Wang, Haomiao Yu, Zhiying Liao, Qiao Yu, and Jianfeng Zhu. 2025. "Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Changes in Ecological Environment Quality on Changxing Island Using an Optimized Remote Sensing Ecological Index" Sensors 25, no. 6: 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061791
APA StyleZhu, Y., Hou, Y., Wang, F., Yu, H., Liao, Z., Yu, Q., & Zhu, J. (2025). Analysis of Temporal and Spatial Changes in Ecological Environment Quality on Changxing Island Using an Optimized Remote Sensing Ecological Index. Sensors, 25(6), 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061791








