Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method for Stochastic Degrading Devices Considering Predictive Maintenance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Motivation and Degradation Modeling
2.1. Motivation
- (1)
- The assumption is made that the same batch of degrading devices consists of M components, with each component functioning independently and exhibiting individual variability in the degradation process. denotes the detection interval, which is usually considered negligible.
- (2)
- The preventive maintenance activities for devices are imperfect maintenance activities, and the number of such activities is limited.
- (3)
- The lifetime and RUL discussed in this study are mainly concerned with the working time of the devices, without taking into account the downtime resulting from preventive maintenance activities.
- (4)
- The degradation processes of components, both prior to and following preventive maintenance activities, are assumed to be statistically independent.
2.2. Degradation Model Incorporating Imperfect Maintenance
3. RUL Prediction Incorporating Imperfect Maintenance
4. Model Parameter Identification and Updating
4.1. Parameter Estimation of Residual Degradation State
4.2. Parameter Estimation of Degradation Model
5. Case Study
5.1. Numerical Simulation
5.2. A Case Study of the Gyroscope
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Acronyms, Abbreviations and Nomenclatures
| Acronyms and Abbreviations | |
| PdM | predictive maintenance |
| RUL | remaining useful life |
| probability density function | |
| CDF | cumulative density function |
| AR(1) | autoregressive model of order 1 |
| FHT | first hitting time |
| CM | condition monitoring |
| MLE | maximum likelihood estimation |
| RE | relative error |
| MSE | mean squared error |
| INS | inertial navigation system |
| Nomenclatures | |
| failure threshold | |
| preventive maintenance threshold | |
| degradation state | |
| drift term | |
| diffusion coefficient | |
| standard Brownian motion | |
| residual degradation state | |
| change coefficient | |
References
- Patrizi, G.; Martiri, L.; Pievatolo, A.; Magrini, A.; Meccariello, G.; Cristaldi, L.; Nikiforova, N.D. A review of degradation models and remaining useful life prediction for testing design and predictive maintenance of lithium-ion batteries. Sensors 2024, 24, 3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, N.; Huang, S.; Su, C. Elevating smart manufacturing with a unified predictive maintenance platform: The synergy between data warehousing, apache spark, and machine learning. Sensors 2024, 24, 4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, K.T.P.; Medjaher, K.; Tran, D.T. A review of artificial intelligence methods for engineering prognostics and health management with implementation guidelines. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 3659–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weikun, D.E.N.G.; Nguyen, K.T.; Medjaher, K.; Christian, G.O.G.U.; Morio, J. Physics-informed machine learning in prognostics and health management: State of the art and challenges. Appl. Math. Model. 2023, 124, 325–352. [Google Scholar]
- Shaheen, B.; Német, I. Data-driven failure prediction and RUL estimation of mechanical components using accumulative artificial neural networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 119, 105749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Dai, Z.; Jiang, L.; Song, C.; Zhong, C.; Chen, Y. Prediction of the remaining useful life of bearings through cnn-bi-lstm-based domain adaptation model. Sensors 2024, 24, 6906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonta, T.; Da Costa, C.A.; da Rosa Righi, R.; de Lima, M.J.; da Trindade, E.S.; Li, G.P. Predictive maintenance in the Industry 4.0: A systematic literature review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 150, 106889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.; Santos, J.; Rocha, E. Challenges in predictive maintenance—A review. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2023, 40, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serradilla, O.; Zugasti, E.; Rodriguez, J.; Zurutuza, U. Deep learning models for predictive maintenance: A survey, comparison, challenges and prospects. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 10934–10964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.T.P.; Medjaher, K. A new dynamic predictive maintenance framework using deep learning for failure prognostics. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2019, 188, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Xu, A.; Wang, X.L. A prognostic driven predictive maintenance framework based on Bayesian deep learning. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 234, 109181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Li, N.; Lin, J. A new method based on stochastic process models for machine remaining useful life prediction. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2016, 65, 2671–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakib, N.; Wuest, T. Challenges and opportunities of condition-based predictive maintenance: A review. Procedia Cirp 2018, 78, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Si, X.; Hu, C.; Lei, Y. Degradation data analysis and remaining useful life estimation: A review on Wiener-process-based methods. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 271, 775–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lei, Y.; Yan, T.; Li, N.; Han, T. A Wiener-process-model-based method for remaining useful life prediction considering unit-to-unit variability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 2092–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Yin, H.; Chen, M.; Lin, Z. Remaining useful life prediction for multi-phase deteriorating process based on Wiener process. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 207, 107361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoorkand, H.D.; Nourelfath, M.; Hajji, A. A hybrid CNN-LSTM model for joint optimization of production and imperfect predictive maintenance planning. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 241, 109707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijima, M. Some results for repairable systems with general repair. J. Appl. Probab. 1989, 26, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T. Sequential imperfect preventive maintenance policies. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 1988, 37, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xi, L.; Lee, J. Reliability-centered predictive maintenance scheduling for a continuously monitored system subject to degradation. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2007, 92, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Wang, W.; Guo, B.; Si, X. A maintenance optimization model for mission-oriented systems based on Wiener degradation. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2013, 111, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Gaudoin, O.; Xie, M. Degradation-based maintenance decision using stochastic filtering for systems under imperfect maintenance. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 245, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Hu, C.H.; Si, X.S.; Zio, E. Remaining useful life prediction of degrading systems subjected to imperfect maintenance: Application to draught fans. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 100, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Pei, H.; Wang, Z. Remaining useful lifetime estimation for equipment subjected to intervention of imperfect maintenance activities. J. Chin. Inert. Technol. 2016, 24, 688–695. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Pei, H.; Wang, Z.; Si, X.; Zhang, Z. A new remaining useful life estimation method for equipment subjected to intervention of imperfect maintenance activities. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2018, 31, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Cai, L.; Liao, G.; Yin, H.; Si, X.; Zhang, P. A multi-phase Wiener process-based degradation model with imperfect maintenance activities. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 232, 109075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Pei, H.; Li, T.; Hu, C.; Si, X. Remaining useful lifetime prognostic approach for stochastic degradation equipment considering imperfect maintenance activities. J. Mech. Eng. 2023, 59, 14–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Q.; Ye, Z. RUL prediction of deteriorating products using an adaptive Wiener process model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 2911–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.S.; Wang, W.; Hu, C.H.; Chen, M.Y.; Zhou, D.H. A Wiener process based degradation model with a recursive filter algorithm for remaining useful life estimation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 35, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Lu, J.; Han, Y. Remaining useful life prediction for two-phase nonlinear degrading systems with three-source variability. Sensors 2024, 24, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Chai, Y.; Fan, L.; Zhang, K. Remaining useful life prediction using nonlinear multi-phase Wiener process and variational Bayesian approach. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 242, 109800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.S.; Wang, W.B.; Chen, M.Y.; Hu, C.H.; Zhou, D.H. A degradation path-dependent approach for remaining useful life estimation with an exact and closed form solution. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 226, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, B.; Cheng, Z. Residual life estimation based on bivariate Wiener degradation process with time-scale transformations. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2014, 84, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Hu, M.; Zhao, Y. Consensus control with a constant gain for discrete-time binary-valued multi-agent systems based on a projected empirical measure method. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2019, 6, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


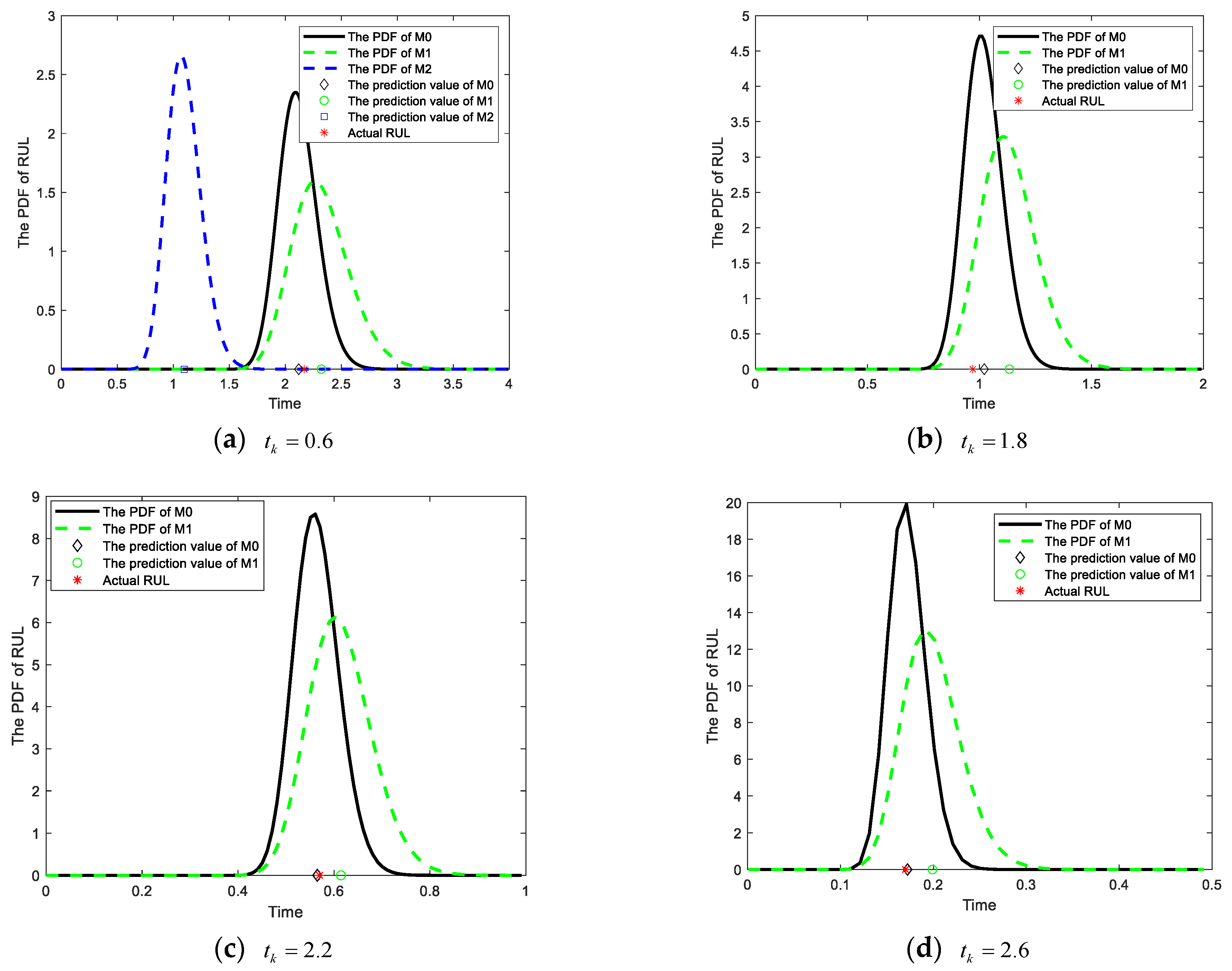
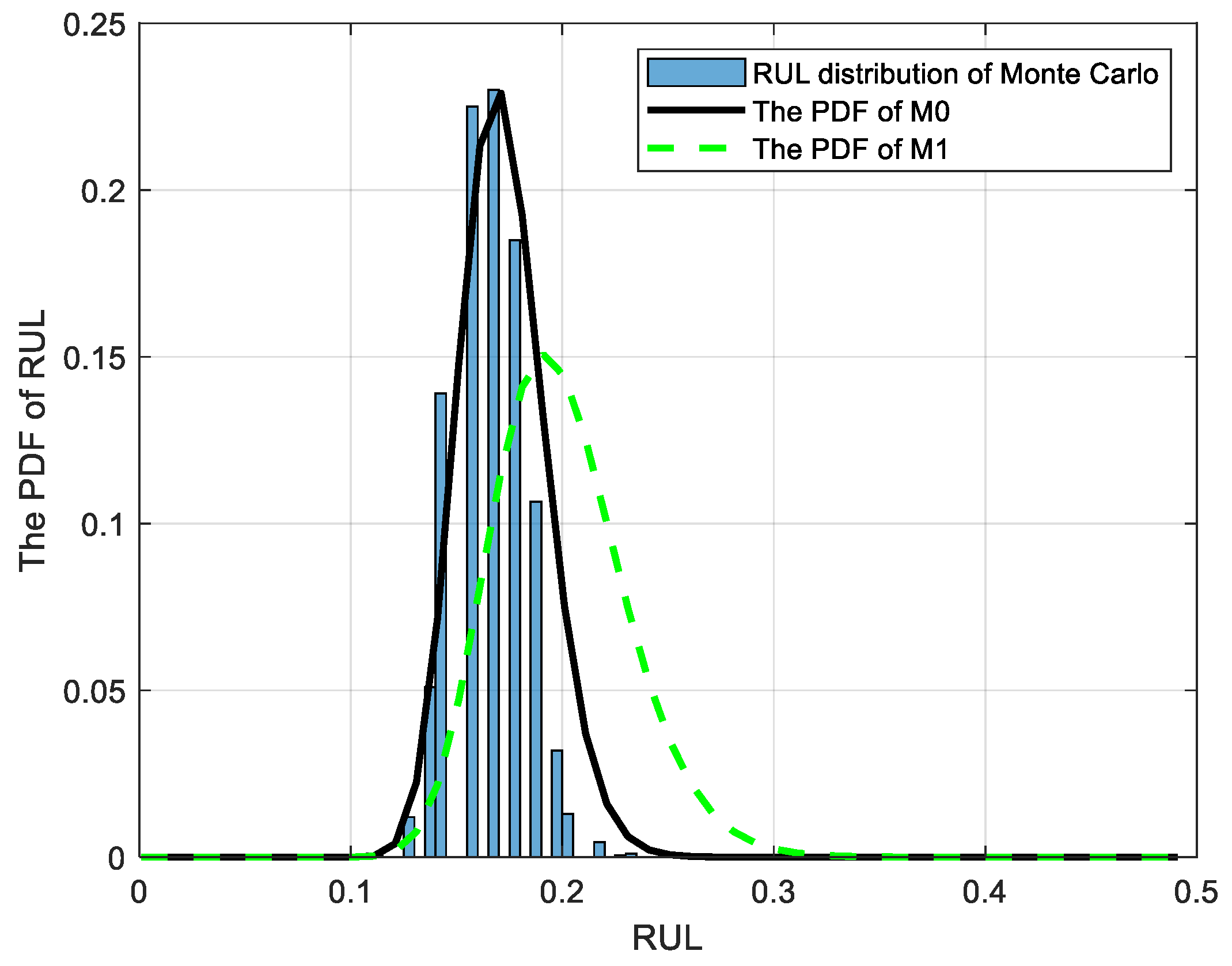



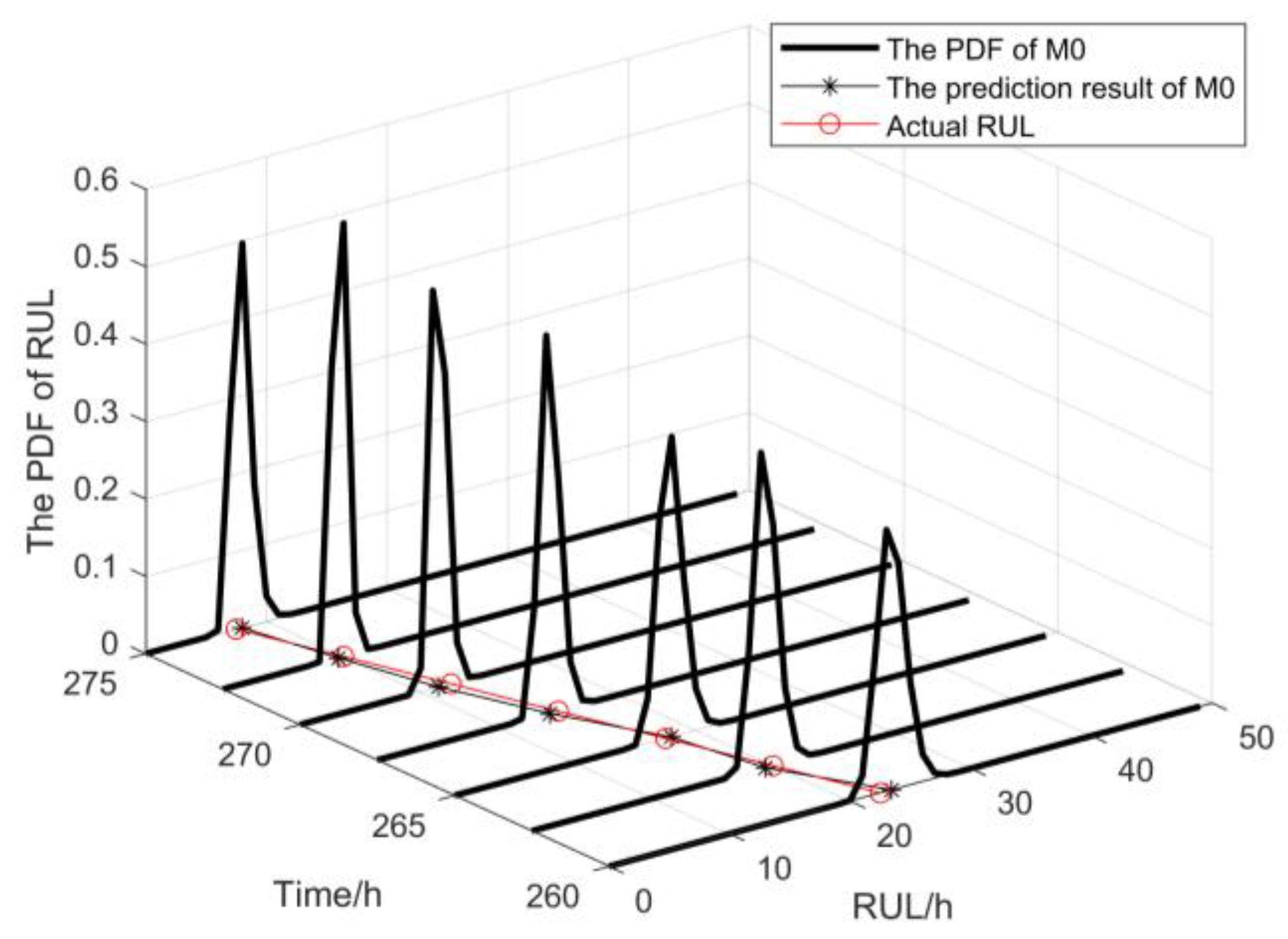
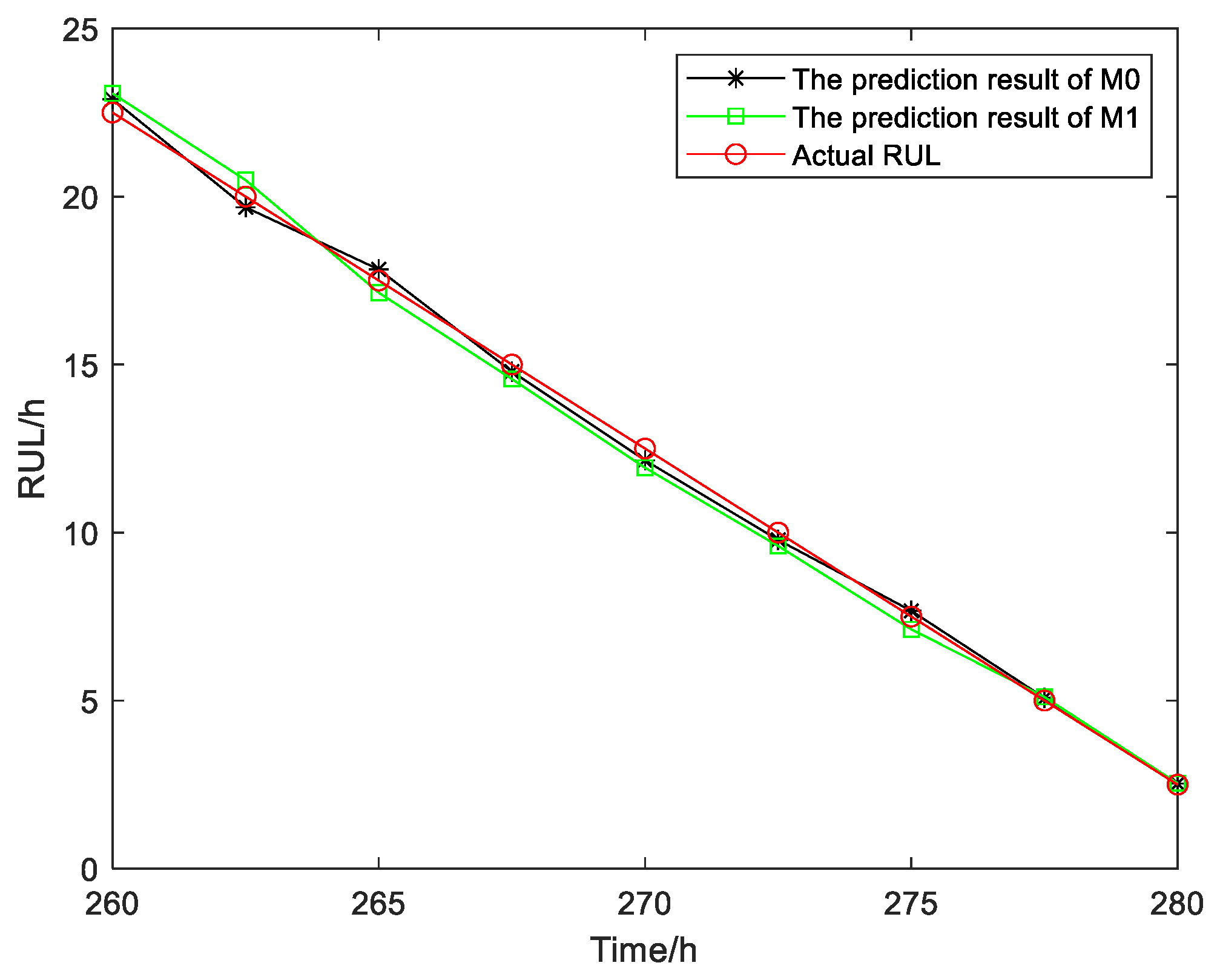
| Parameter | Values | Parameter | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial drift term | 1.8 | Residual degradation hyperparameter | 2 |
| Diffusion coefficient of drift term | 0.1 | Residual degradation hyperparameter | 5 |
| Change coefficient means | 1.2 | Maintenance frequency | 3 |
| Standard deviation of coefficient change | 0.3 | Failure threshold | 3.5 |
| Diffusion coefficient | 0.35 | Preventive maintenance threshold | 3 |
| Time interval | 0.01 | Nonlinear parameter | 1.2 |
| Time | RE of RUL Prediction | MSE of RUL Prediction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | M1 | M2 | M0 | M1 | M2 | |
| 0.6 | 2.30% | 11.62% | 44.74% | 0.0025 | 0.0626 | 0.9424 |
| 1.8 | 5.31% | 16.87% | \ | 0.0026 | 0.0268 | \ |
| 2.2 | 0.85% | 7.82% | \ | 2.34 × 10−5 | 0.002 | \ |
| 2.6 | 1.27% | 17.05% | \ | 4.67 × 10−6 | 8.40 × 10−4 | \ |
| Monitoring Point/h | M0 | M1 | Actual RUL/h |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSE | MSE | ||
| 260 | 0.1600 | 0.3260 | 22.5 |
| 262.5 | 0.1024 | 0.2401 | 20 |
| 265 | 0.1089 | 0.1296 | 17.5 |
| 267.5 | 0.0441 | 0.1849 | 15 |
| 270 | 0.1225 | 0.3249 | 12.5 |
| 272.5 | 0.0484 | 0.1600 | 10 |
| 275 | 0.0289 | 0.1444 | 7.5 |
| 277.5 | 0.0062 | 0.0115 | 5 |
| 280 | 0.00089 | 0.0014 | 2.5 |
| Score | 5.2228 | 5.6447 | \ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Q.; Pei, H.; Hu, C.; Zheng, J.; Du, D. Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method for Stochastic Degrading Devices Considering Predictive Maintenance. Sensors 2025, 25, 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25041218
Dong Q, Pei H, Hu C, Zheng J, Du D. Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method for Stochastic Degrading Devices Considering Predictive Maintenance. Sensors. 2025; 25(4):1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25041218
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Qing, Hong Pei, Changhua Hu, Jianfei Zheng, and Dangbo Du. 2025. "Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method for Stochastic Degrading Devices Considering Predictive Maintenance" Sensors 25, no. 4: 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25041218
APA StyleDong, Q., Pei, H., Hu, C., Zheng, J., & Du, D. (2025). Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method for Stochastic Degrading Devices Considering Predictive Maintenance. Sensors, 25(4), 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25041218






