Numerical Investigation of Halbach-Array-Based Flexible Magnetic Sensors for Wide-Range Deformation Detection
Highlights
- Decoupled architecture for enhanced magnetic coupling. Separating the flexible PDMS-based Halbach magnetic array from the fixed Hall sensor preserves field uniformity under large deformation and enables mT-level detection at a sensing distance up to 15 mm.
- Dimensionality reduction of magnetic field distribution. The Halbach configuration transforms a complex 3D magnetic field into a near 1D directional field, enhancing sensitivity, simplifying signal processing, and supporting scalable high-resolution tactile sensing.
- The decoupled Halbach-array design provides a general strategy for achieving wide-range, high-sensitivity magnetic sensing in flexible systems, enabling more reliable tactile perception in wearable and robotic applications.
- The dimensionality reduction of magnetic fields offers a new approach to simplify signal processing and enhance real-time sensing speed in future intelligent tactile interfaces.
Abstract
1. Introduction
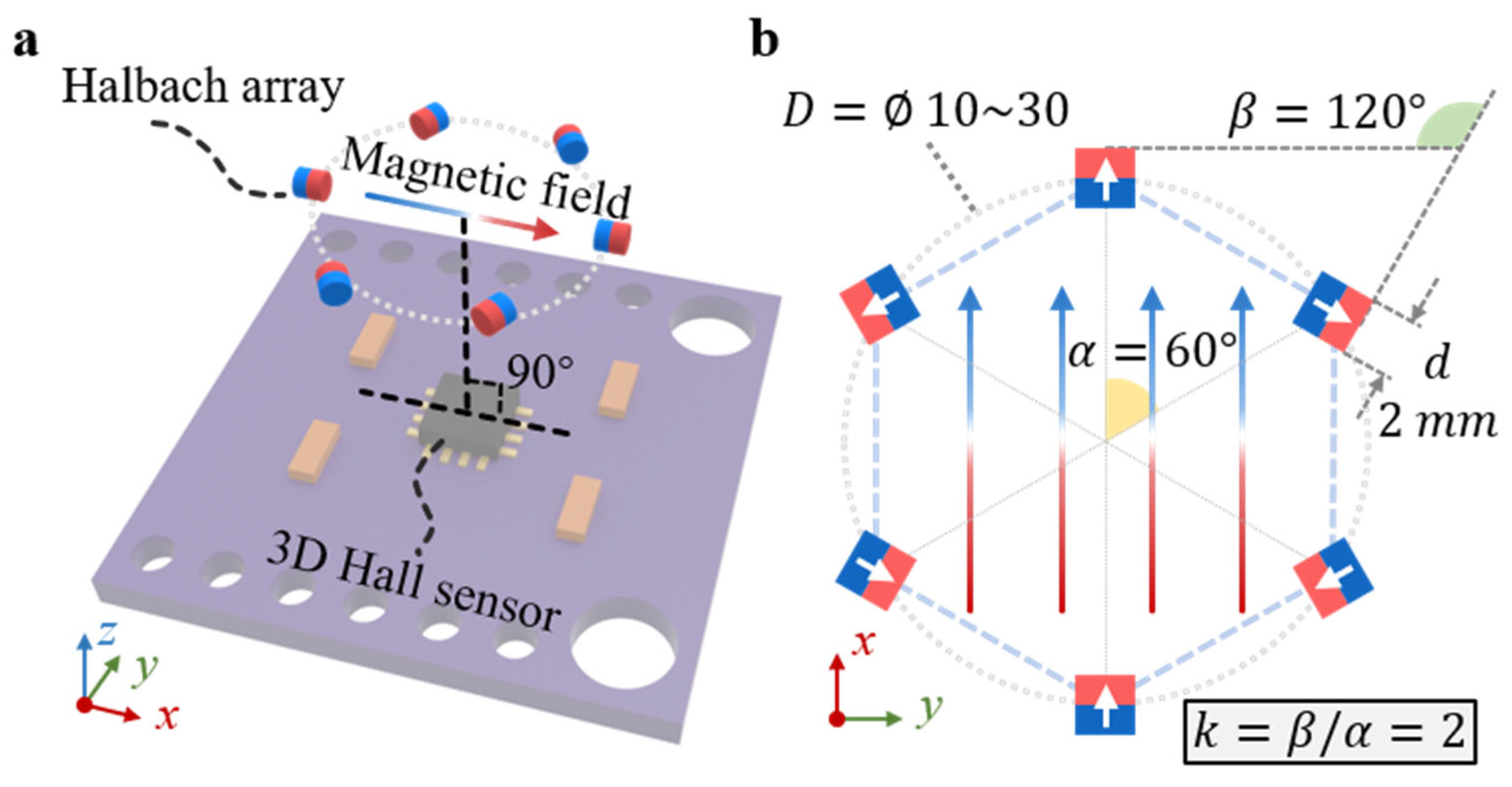
2. Proposed Flexible Magnetic Tactile Sensor
2.1. Halbach-Array-Based Magnetic Sensor Design and Working Principle
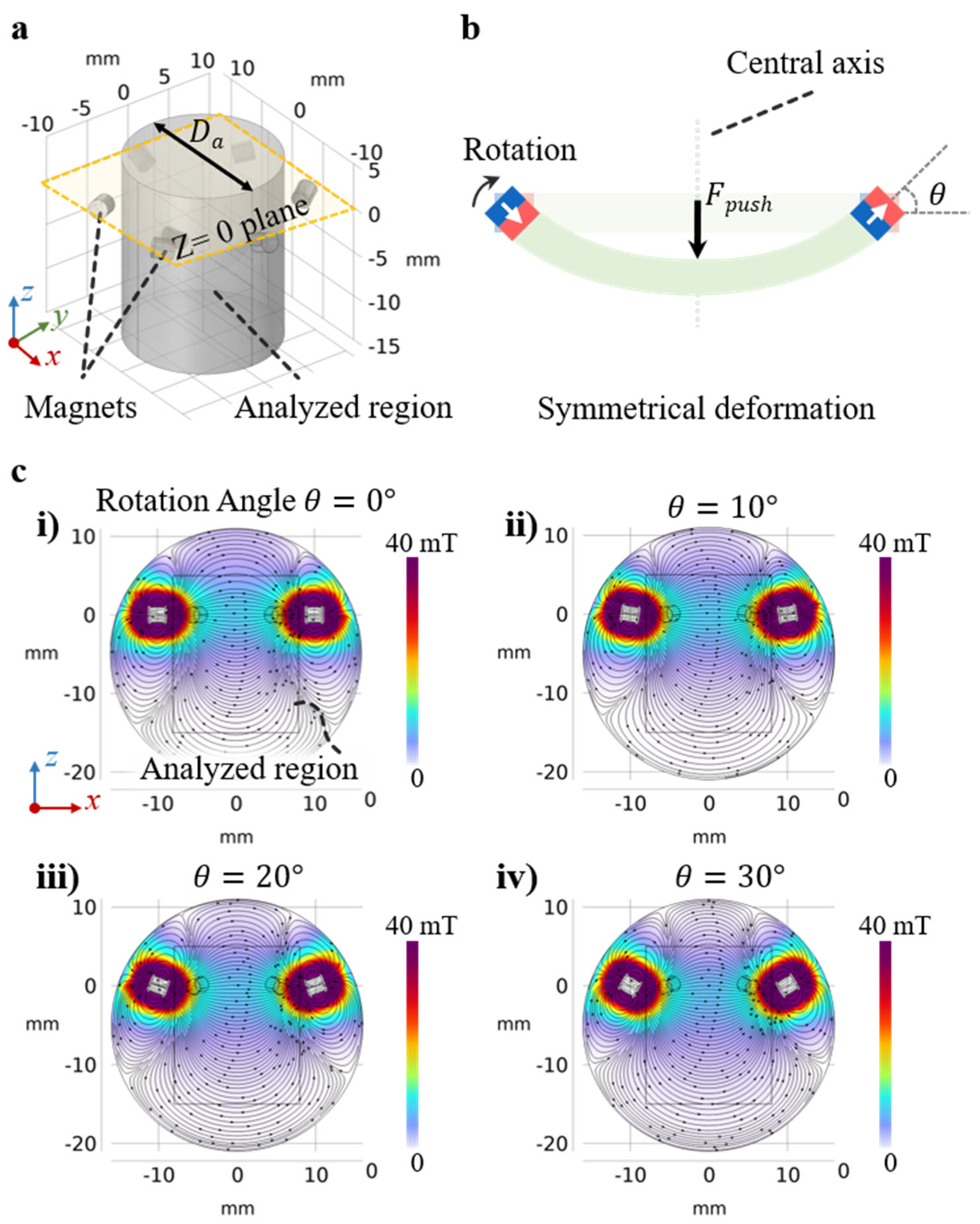
2.2. Finite Element Method for Sensor Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Magnetic Field Profile in the Central X–Z Plane During Rotation of the Halbach Array
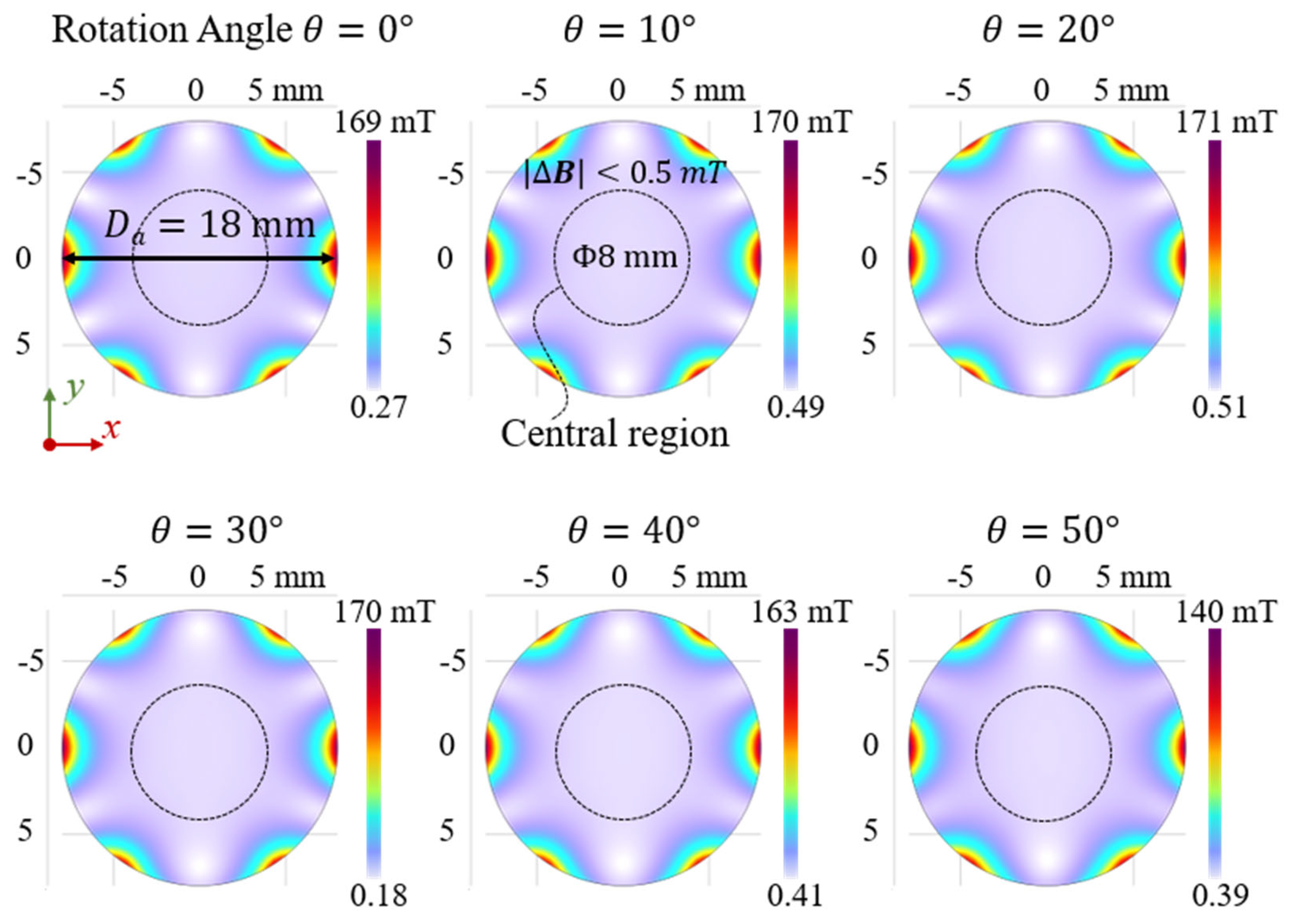
3.2. Magnetic Field Profile in X–Y Plane During Rotation of Halbach Array Units
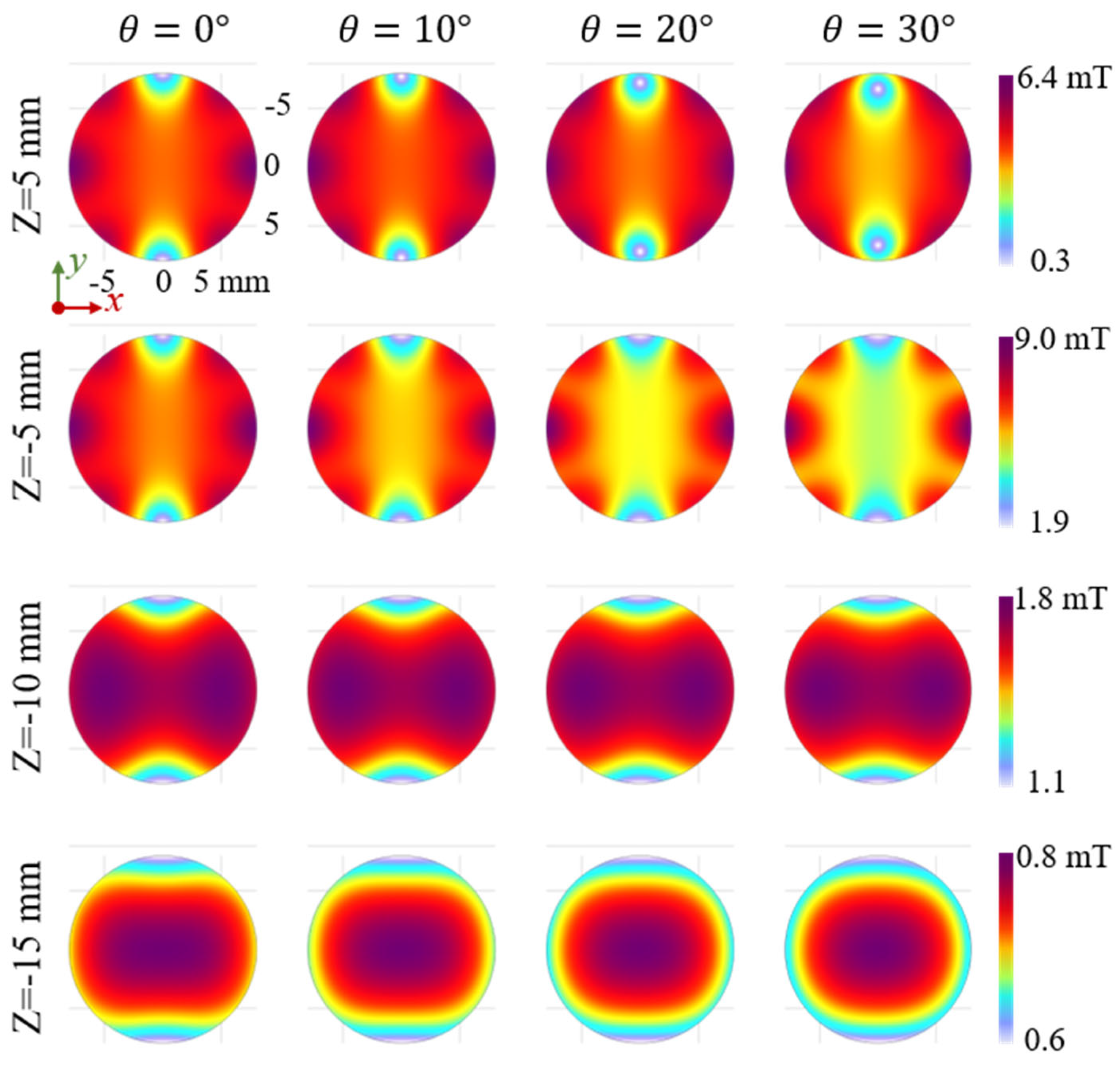
3.3. Magnetic Field Profile Along Central Z-Axis During Rotation of Halbach Array Units
3.4. Magnetic Field Profile When Adjusting Halbach Array Size
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bari, D.S.; Rammoo, M.N.S.; Aldosky, H.Y.Y.; Jaqsi, M.K.; Martinsen, Ø.G. The Five Basic Human Senses Evoke Electrodermal Activity. Sensors 2023, 23, 8181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.; Lee, Y.; Yoon, J.; Lee, B.; Oh, E.; Chung, S.; Lee, T.; Cho, K.-J.; Kim, J.; Hong, Y. Electronic skins for soft, compact, reversible assembly of wirelessly activated fully soft robots. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaas9020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wen, Z.; Sun, X. Recent progress in self-powered multifunctional e-skin for advanced applications. Exploration 2022, 2, 20210112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Dong, X.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Zheng, Z.; Ugurlu, M.C.; Jiang, W.; Liu, H.; Sitti, M. Actuation-enhanced multifunctional sensing and information recognition by magnetic artificial cilia arrays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2308301120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Sun, B.; Chen, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Shao, J. Advances in micro/nano-engineered flexible sensor arrays for intelligent human-machine interaction. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klopfer, M.; Cordonier, C.; Inoue, K.; Li, G.-P.; Honma, H.; Bachman, M. Flexible, transparent electronics for biomedical applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 63rd Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 28–31 May 2013; pp. 494–499. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Zhong, S.; Zheng, Z.; Du, J.; Nie, R.; Shi, Q.; Huang, Q.; Wang, H. Magnetic shaftless propeller millirobot with multimodal motion for small-scale fluidic manipulation. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2025, 6, 0235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Xin, Z.; Hou, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.-W.; Sun, T.; Shi, Q.; Wang, H. Double-modal locomotion of a hydrogel ultra-soft magnetic miniature robot with switchable forms. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2024, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lee, S.; Yokota, T.; Someya, T. Skin electronics: Next-generation device platform for virtual and augmented reality. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.; Zadan, M.; Majidi, C. Soft tactile sensing skins for robotics. Curr. Robot. Rep. 2021, 2, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, K. Electronic skin: From flexibility to a sense of touch. Nature 2021, 591, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Shao, Q.; Tang, C.; Qiao, F.; Lu, T.; Li, X.; Liu, X.J.; Zhao, H. Conformable and compact multiaxis tactile sensor for human and robotic grasping via anisotropic waveguides. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2200595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanastasiou, D.T.; Harimurti, S.; Okuda, C.; Mimuro, M.; Yukita, W.; Yokota, T.; Someya, T. A novel thickness-gradient electrospun nanomesh for interface-free e-skin applications. Mater. Horiz. 2025, 12, 4676–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, Y.; Cho, S.; Choe, A.; Yeom, J.; Ro, Y.G.; Kim, J.; Kang, D.-H.; Lee, S.; Ko, H. Soft sensors and actuators for wearable human–machine interfaces. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 1464–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Hu, H.; Li, S.; Tian, H.; Fan, W.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Taylor, A.C.; Shao, J. Sensing-triggered stiffness-tunable smart adhesives. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Gu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lee, S.; Yokota, T.; Haick, H.; Someya, T. A 10-micrometer-thick nanomesh-reinforced gas-permeable hydrogel skin sensor for long-term electrophysiological monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadj5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Hu, J.; Yan, X. Review of fiber-or yarn-based wearable resistive strain sensors: Structural design, fabrication technologies and applications. Textiles 2022, 2, 81–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Li, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Zhang, M.; Sun, B. Bioinspired suspended sensing membrane array with modulable wedged-conductive channels for crosstalk-free and high-resolution detection. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2403645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Thangavel, G.; Xin, Y.; Gao, D.; Poh, W.C.; Chen, S.; Lee, P.S. Printed sustainable elastomeric conductor for soft electronics. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, S.; Arunagirinathan, R.S. Silver nanowires in stretchable resistive strain sensors. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, S.; Ravi Sankar, A. Intrinsically conducting polymers in flexible and stretchable resistive strain sensors: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 13152–13178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi-Mamoudan, F.; Ibarra-Castanedo, C.; Maldague, X.P. Advancements in and Research on Coplanar Capacitive Sensing Techniques for Non-Destructive Testing and Evaluation: A State-of-the-Art Review. Sensors 2024, 24, 4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.H.; Jafarizadeh, B.; Pala, N.; Wang, C. Wearable capacitive pressure sensor for contact and non-contact sensing and pulse waveform monitoring. Molecules 2022, 27, 6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayegani, A.; Saberian, M.; Delshad, Z.; Liang, J.; Sadiq, M.; Nazar, A.M.; Mohsan, S.A.H.; Khan, M.A. Recent advances in self-powered wearable sensors based on piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators. Biosensors 2022, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Wahab, M.A.; Will, G.; Karim, M.R.; Pan, T.; Gao, M.; Lai, D.; Lin, Y.; Miraz, M.H. Recent advances in stretchable and wearable capacitive electrophysiological sensors for long-term health monitoring. Biosensors 2022, 12, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Jiao, P.; Zhu, Z. Combination of piezoelectric and triboelectric devices for robotic self-powered sensors. Micromachines 2021, 12, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.-H.; Wang, F.; Hua, J.; Cheng, W.; Shi, Y.; Pan, L. Recent Advances in Flexible Self-Powered Sensors in Piezoelectric, Triboelectric, and Pyroelectric Fields. Nanoenergy Adv. 2024, 4, 235–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Chang, L.; Huber, J. Investigation of mechanical energy harvesting cycles using ferroelectric/ferroelastic switching. Nano Energy 2022, 93, 106862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Ji, G.; Huber, J.E. Mechanical energy harvesting: From piezoelectric effect to ferroelectric/ferroelastic switching. Nano Energy 2024, 133, 110489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Cui, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, B.; Liu, X.-J.; Zhao, H. Shape reconstruction of soft continuum robots via the fusion of local strains and global poses. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2024, 5, 10224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yang, J.; Kim, D.; Yun, D. Soft tactile sensor to detect the slip of a Robotic hand. Measurement 2022, 200, 111615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, F.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, X.; Yin, L.; Shi, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, H. A novel peak positioning method for nanometer displacement measurement by optical linear encoder. Measurement 2025, 242, 115888. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Ban, Y.; Wang, X.; Lei, B.; Wang, L.; Chen, B.; Gao, F.; Jiang, X.; Liu, H. Achieving High-Fold Optical Subdivision of a Blazed Grating Interferometer Through Near-Littrow Incidence. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Ban, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, P.; Niu, D.; Chen, B.; Jiang, W.; Gao, F.; Jiang, X. High-fold optical subdivision blazed grating interferometer based on Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Measurement 2025, 242, 116128. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, H.; Zhang, C.; Pan, C.; Hu, H.; Ji, K.; Sun, H.; Lyu, C.; Tang, D.; Li, T.; Fu, J. Split-type magnetic soft tactile sensor with 3D force decoupling. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2310145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, M.; Saleem, M.M.; Tiwana, M.I.; Shakoor, R.I.; Cheung, R. A soft multi-axis high force range magnetic tactile sensor for force feedback in robotic surgical systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhu, H.; Chen, R.; Hu, S.; Jia, Z.; Yu, H.; Qu, S. Design of 3D magnetic tactile sensors with high sensing accuracy guided by the theoretical model. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2200291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Xie, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, M.; Bao, X.; Shang, J.; Li, R.-W. Flexible magnetic sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karboul-Trojet, W.; Roussigné, Y.; Faurie, D.; Chérif, S. Static and dynamic study of magnetic properties in FeNi film on flexible substrate, effect of applied stresses. Eur. Phys. J. B 2012, 85, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arribas, A.; Combarro, L.; Goiriena-Goikoetxea, M.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Svalov, A.V.; Fernández, E.; Orue, I.; Feuchtwanger, J. Thin-film magnetoimpedance structures onto flexible substrates as deformation sensors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, H.; Yang, Y.; Kim, G.; Gim, D.; Ha, M. Anisotropy in magnetic materials for sensors and actuators in soft robotic systems. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 6778–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellebrekers, T.; Kroemer, O.; Majidi, C. Soft magnetic skin for continuous deformation sensing. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2019, 1, 1900025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, G.; Fang, Y.; Tat, T.; Xiao, X.; Song, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, J. Soft fibers with magnetoelasticity for wearable electronics. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-P.; Peng, K.-Y.; Chang, J.-Y. Increasing Sensitivity of Magnetic Tactile Sensors by Optimizing Arrangement of PM Array. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE SENSORS, Vienna, Austria, 29 October–1 November 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, C.; Silvestri, S.; Schena, E.; Massaroni, C. Smart Wristband Based on a Magnetic Soft Sensor for Pulse Wave Measurement. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 37142–37150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, C.; Pan, C.; Dai, H.; Sun, H.; Pan, Y.; Lai, X.; Lyu, C.; Tang, D.; Fu, J. Wireless flexible magnetic tactile sensor with super-resolution in large-areas. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 19271–19280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, W.; Song, C.; Pan, J.; Shen, Y. Soft magnetic skin for super-resolution tactile sensing with force self-decoupling. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabc8801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, V.; Ly, K.; Johnson, B.K.; Naris, M.; Anderson, M.P.; Humbert, J.S.; Correll, N.; Rentschler, M. Embedded magnetic sensing for feedback control of soft HASEL actuators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022, 39, 808–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripka, P. Sensors based on bulk soft magnetic materials: Advances and challenges. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 2466–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Han, M. Recent progress in soft electronics and robotics based on magnetic nanomaterials. Soft Sci. 2023, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, C.; Bao, B.; Karnaushenko, D.D.; Bandari, V.K.; Rivkin, B.; Li, Z.; Faghih, M.; Karnaushenko, D.; Schmidt, O.G. A new dimension for magnetosensitive e-skins: Active matrix integrated micro-origami sensor arrays. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Distance | Avg. Bx (mT) | Avg. By (mT) | Order of (Bx/By) |
|---|---|---|---|
| −3 mm | |||
| −9 mm | |||
| −15 mm |
| Method | Magnetic Source | Field Configuration | Sensing Principle | Signal Strength (at >10 mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hellebrekers (2019) [42] | Soft composite (particles) | Random particle distribution | Single 3-axis Magnetometer | μT-level (inferred) |
| Yan (2021) [47] | Soft composite (film) | Sinusoidal magnetization | 3-axis Hall Sensor | μT-level |
| Becker (2022) [51] | (External magnet) | 3D micro-origami cube | Anisotropic Magnetoresistance (AMR) | (N/A) |
| Rehan (2022) [36] | Discrete permanent magnets | 4-magnet simple array | 4x single-axis Hall Sensors | ≈7.3 mT at 6 mm |
| Dai (2024) [35] | Soft composite (film) | Centripetal magnetization | 3-axis Hall Sensor | ≈40 μT at 20 mm |
| Our Proposed Work | Discrete permanent magnets (N52) | Halbach Array | 3-axis Hall Sensor | ≈1 mT at 15 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wen, C.; Han, J.; Kang, W.; Zheng, Z. Numerical Investigation of Halbach-Array-Based Flexible Magnetic Sensors for Wide-Range Deformation Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 7240. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237240
Han Y, Zhang S, Wen C, Han J, Kang W, Zheng Z. Numerical Investigation of Halbach-Array-Based Flexible Magnetic Sensors for Wide-Range Deformation Detection. Sensors. 2025; 25(23):7240. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237240
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yina, Shuaiqi Zhang, Chenglin Wen, Jie Han, Wenbin Kang, and Zhiqiang Zheng. 2025. "Numerical Investigation of Halbach-Array-Based Flexible Magnetic Sensors for Wide-Range Deformation Detection" Sensors 25, no. 23: 7240. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237240
APA StyleHan, Y., Zhang, S., Wen, C., Han, J., Kang, W., & Zheng, Z. (2025). Numerical Investigation of Halbach-Array-Based Flexible Magnetic Sensors for Wide-Range Deformation Detection. Sensors, 25(23), 7240. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237240







