Low-Cost Spinning Disk Confocal Microscopy with a 25-Megapixel Camera
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
- cardiac perfusion with cold, freshly prepared 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA),
- fixation of the dissected brain with a 4% PFA solution on an orbital shaker overnight at 4 °C followed by washing three times with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at room temperature,
- sectioning the brain manually using a vibratome followed by clearing of the slice with RapiClear 1.52 (SunJin Lab) overnight at room temperature,
- mounting of the cleared sample with fresh RapiClear 1.52 reagent in a 0.25 mm-deep iSpacer microchamber (SunJin Lab).
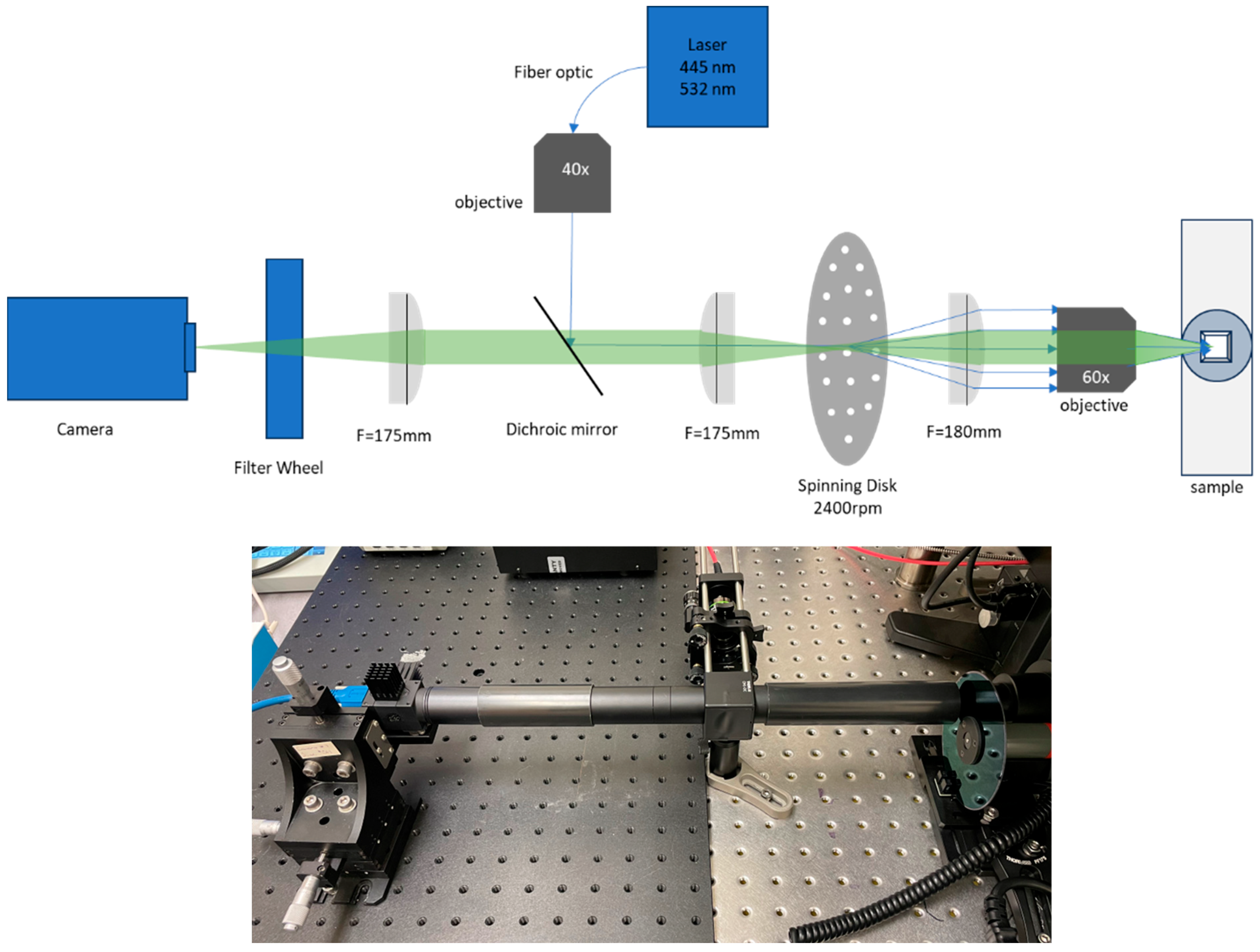
2.2. Microscope Setup
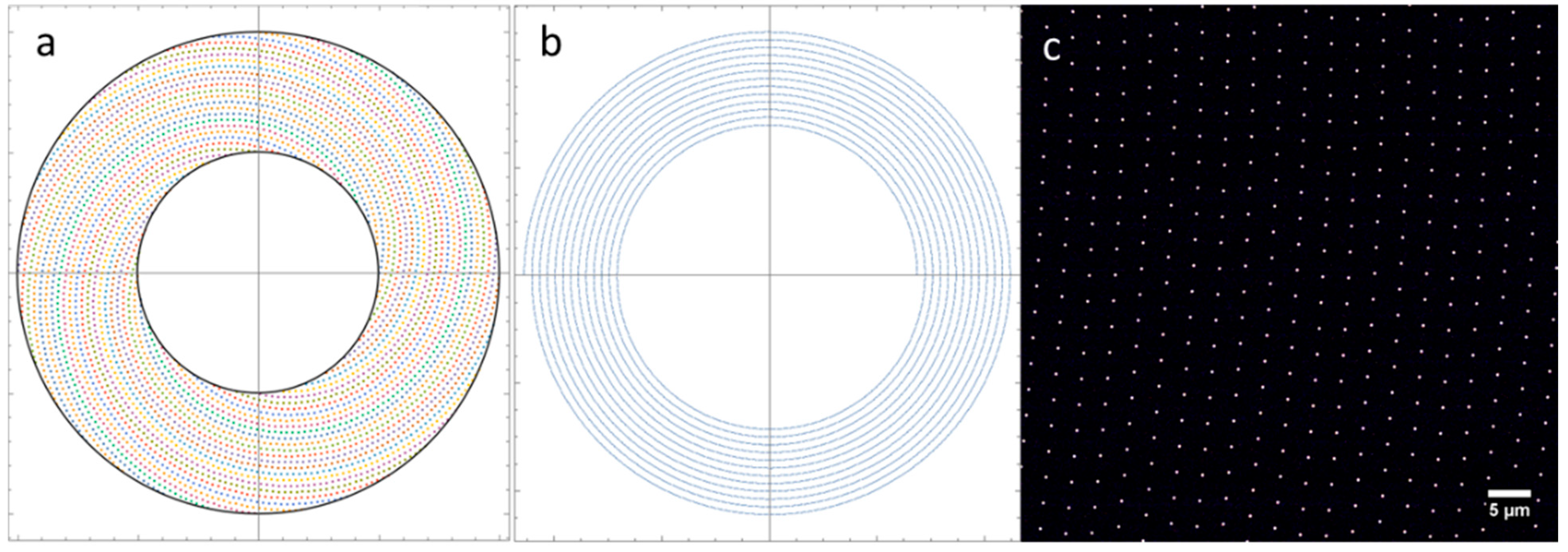
2.3. Spinning Disk Design
2.4. Machine Vision Camera
2.5. Low-Cost Lasers
3. Results and Discussion
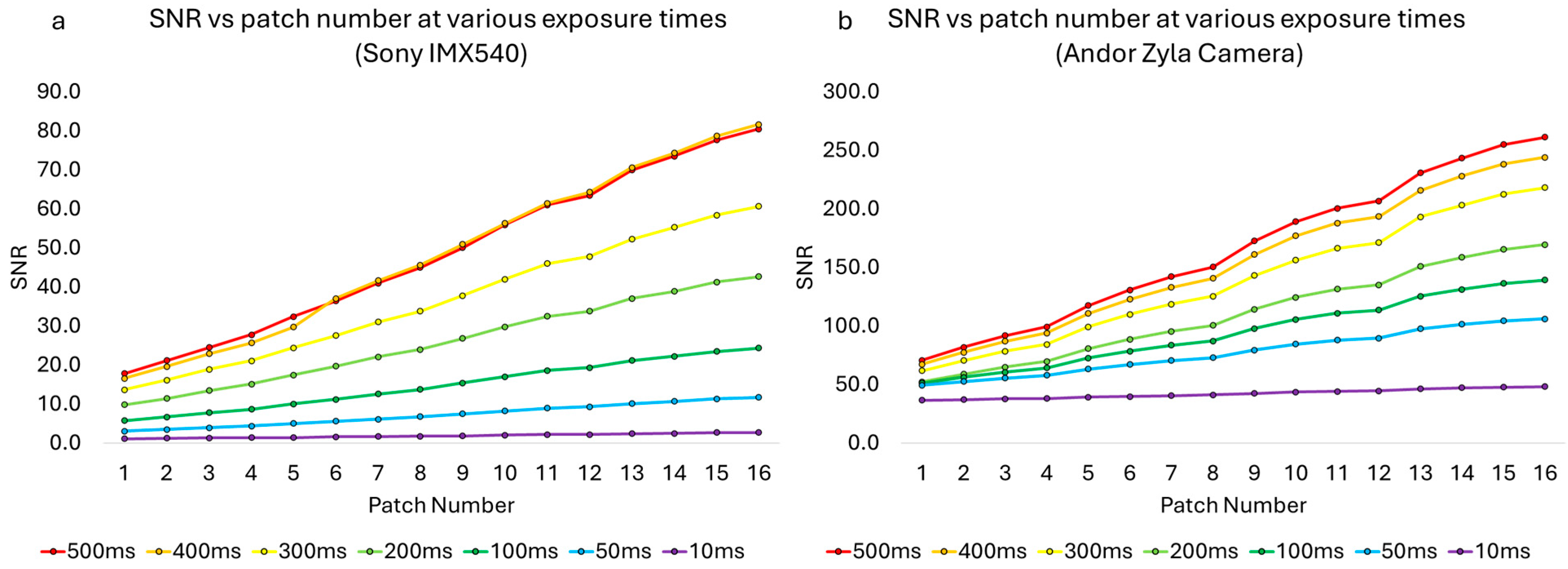
3.1. Characterization of the Camera
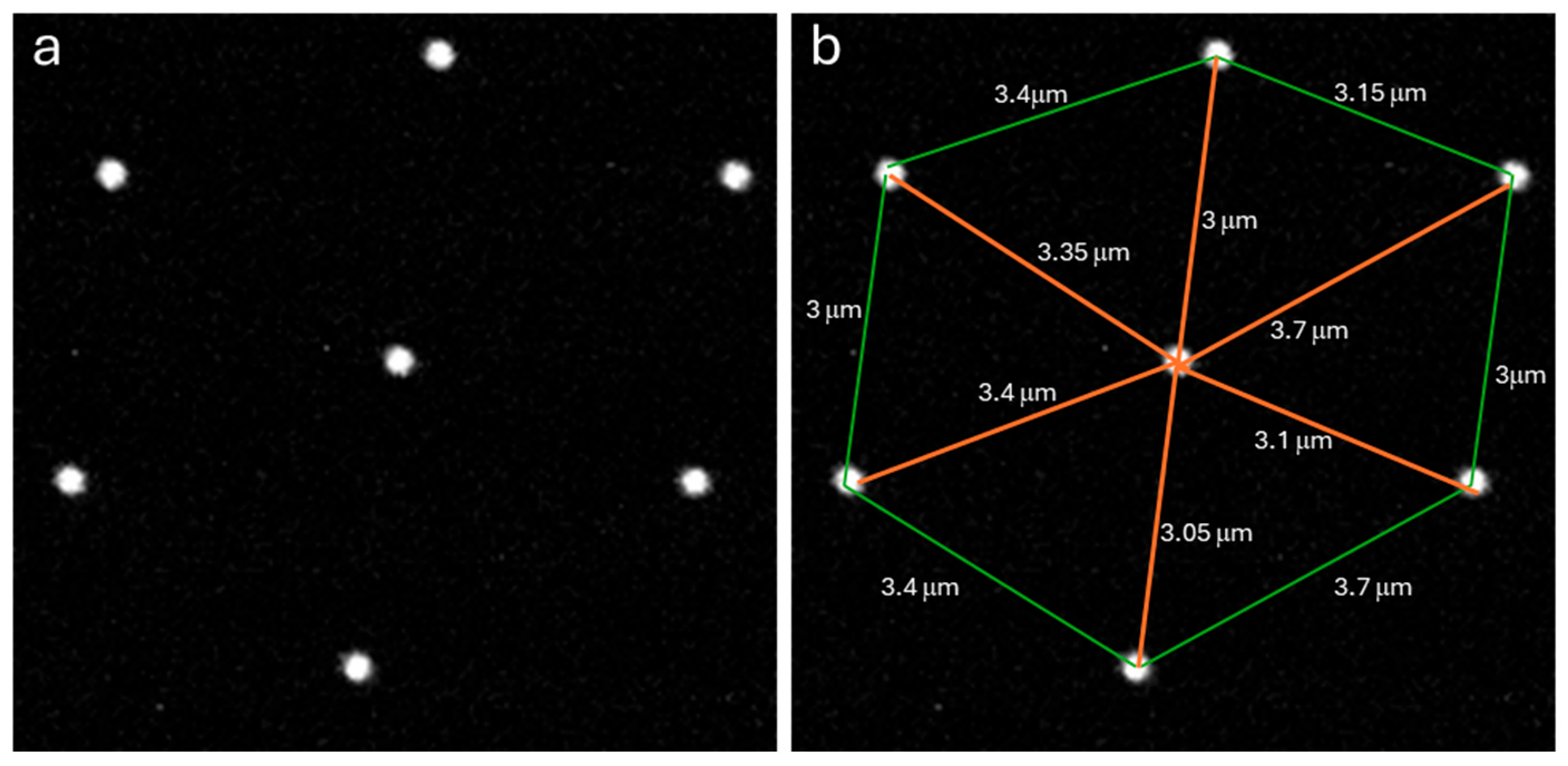
3.2. Resolution Measurements
3.3. Imaging of Biological Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NA | Numerical Aperture |
| MP | Megapixel |
| CMOS | Complementary metal oxide semiconductor |
| GFP | Green fluorescent protein |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| WF | Widefield |
| SD | Spinning disk |
| DPSS | Diode-pumped solid state |
| WD | Working distance |
References
- Cybulski, J.S.; Clements, J.; Prakash, M. Foldscope: Origami-based paper microscope. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehrer, A.C.; Martin-Villalba, A.; Diederich, B.; Ewers, H. An open-source, high-resolution, automated fluorescence microscope. Elife 2024, 12, RP89826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightley, J.; Kumar, S.; Lim, M.Q.; Garcia, E.; Görlitz, F.; Alexandrov, Y.; Parrado, T.; Hollick, C.; Steele, E.; Roßmann, K.; et al. openFrame: A modular, sustainable, open microscopy platform with single-shot, dual-axis optical autofocus module providing high precision and long range of operation. J. Microsc. 2023, 292, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitrone, P.G.; Schindelin, J.; Stuyvenberg, L.; Preibisch, S.; Weber, M.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Huisken, J.; Tomancak, P. OpenSPIM: An open-access light-sheet microscopy platform. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 598–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenegger, D.G.; Tran, C.H.T.; LeDue, J.; Zhou, N.; Gordon, G.R. A high performance, cost-effective, open-source microscope for scanning two-photon microscopy that is modular and readily adaptable. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospíšil, J.; Lukeš, T.; Bendesky, J.; Fliegel, K.; Spendier, K.; Hagen, G.M. Imaging tissues and cells beyond the diffraction limit with structured illumination microscopy and Bayesian image reconstruction. Gigascience 2019, 8, giy126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannebelle, M.T.M.; Raeth, E.; Leitao, S.M.; Lukeš, T.; Pospíšil, J.; Toniolo, C.; Venzin, O.F.; Chrisnandy, A.; Swain, P.P.; Ronceray, N.; et al. Open-source microscope add-on for structured illumination microscopy. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Ge, X.; Li, M.; Guan, M.; Hou, Y.; Fu, Y.; Xu, X.; Jiang, S.; et al. Open-3DSIM: An open-source three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy reconstruction platform. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 1183–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsamsam, M.N.; Kopūstas, A.; Jurevičiūtė, M.; Tutkus, M. The miEye: Bench-top super-resolution microscope with cost-effective equipment. HardwareX 2022, 12, e00368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelstein, A.D.; Tsuchida, M.A.; Amodaj, N.; Pinkard, H.; Vale, R.D.; Stuurman, N. Advanced methods of microscope control using μManager software. J. Biol. Methods 2014, 1, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovesný, M.; Křížek, P.; Borkovec, J.; Švindrych, Z.; Hagen, G.M. ThunderSTORM: A comprehensive ImageJ plug-in for PALM and STORM data analysis and super-resolution imaging. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2389–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, R.; Lelek, M.; Fornasiero, E.F.; Valtorta, F.; Zimmer, C.; Mhlanga, M.M. QuickPALM: 3D real-time photoactivation nanoscopy image processing in ImageJ. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swedlow, J.R. The Open Microscopy Environment: A Collaborative Data Modeling and Software Development Project for Biological Image Informatics. In Imaging Cellular and Molecular Biological Functions; Shorte, S.L., Frischknecht, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 71–92. ISBN 978-3-540-71331-9. [Google Scholar]
- Petráň, M.; Heydrovský, M.; Egger, M.D.; Galambos, R. Tandem-scanning reflected-light microscope. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1968, 58, 661–664. [Google Scholar]
- Oreopoulos, J.; Berman, R.; Browne, M. Spinning-disk confocal microscopy. present technology and future trends. Methods Cell Biol. 2014, 123, 153–175. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadian, S.; Lindsey, P.J.; Smeets, H.J.M.; van Tienen, F.H.J.; van Zandvoort, M.A.M.J. Spinning Disk Confocal Microscopy for Optimized and Quantified Live Imaging of 3D Mitochondrial Network. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehbens, S.; Pemble, H.; Murrow, L.; Wittmann, T. Imaging intracellular protein dynamics by spinning disk confocal microscopy. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 504, pp. 293–313. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao, Y.-T.; Wu, T.-Y.; Wu, B.-K.; Chu, S.-W.; Hsieh, C.-L. Spinning disk interferometric scattering confocal microscopy captures millisecond timescale dynamics of living cells. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 45233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conchello, J.-A.; Lichtman, J.W. Theoretical analysis of a rotating-disk partially confocal scanning microscope. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.Q.; Corle, T.R.; Kino, G.S. Real-time confocal scanning optical microscope. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1988, 53, 716–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juskaitis, R.; Wilson, T.; Neil, M.A.A.; Kozubek, M. Efficient real-time confocal microscopy with white light sources. Nature 1996, 383, 804–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, T.; Juskaitis, R.; Neil, M.A.A.; Kozubek, M. Confocal microscopy by aperture correlation. Opt. Lett. 1996, 23, 1879–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimozawa, T.; Yamagata, K.; Kondo, T.; Hayashi, S.; Shitamukai, A.; Konno, D.; Matsuzaki, F.; Takayama, J.; Onami, S.; Nakayama, H.; et al. Improving spinning disk confocal microscopy by preventing pinhole cross-talk for intravital imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3399–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, O.; Pieper, C.; Clever, M.; Pfaff, J.; Ruhlandt, A.; Kehlenbach, R.H.; Wouters, F.S.; Großhans, J.; Bunt, G.; Enderlein, J. Resolution doubling in fluorescence microscopy with confocal spinning-disk image scanning microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 21000–21005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaami, T.; Otsuki, S.; Tomosada, N.; Kosugi, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Ishida, H. High-speed 1-frame/ms scanning confocal microscope with a microlens and Nipkow disks. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, T.; Kei, T. Super-resolution spinning-disk confocal microscopy using optical photon reassignment. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 15003–15011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, A.R.; Lee, M.Y.; Howard, M.D.; Woodworth, M.A.; Nicovich, P.R.; Vaughan, J.C. Versatile, do-it-yourself, low-cost spinning disk confocal microscope. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Mellor, R.H.; Bernstein, M.; Keller-Peck, C.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Wallace, M.; Nerbonne, J.M.; Lichtman, J.W.; Sanes, J.R. Imaging Neuronal Subsets in Transgenic Mice Expressing Multiple Spectral Variants of GFP. Neuron 2000, 28, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.B.; Perrimon, N. The autosomal FLP-DFS technique for generating germline mosaics in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1996, 144, 1673–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grueber, W.B.; Ye, B.; Yang, C.H.; Younger, S.; Borden, K.; Jan, L.Y.; Jan, Y.N. Projections of Drosophila multidendritic neurons in the central nervous system: Links with peripheral dendrite morphology. Development 2007, 134, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesnicky, E.C.; Killian, D.J.; Garcia, E.; Morton, M.C.; Rathjen, A.R.; Sola, I.E.; Gavis, E.R. Extensive use of RNA-binding proteins in Drosophila sensory neuron dendrite morphogenesis. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2014, 4, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svindrych, Z.; Ovesný, M.; Hagen, G.M. PALM/STORM microscopy with a dual objective microscope. In Microscopy and Imaging Science: Practical Approaches to Applied Research and Education; Méndez-Vilas, A., Ed.; Formatex: Badajoz, Spain, 2017; pp. 620–627. ISBN 978-84-942134-9-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bertels, M.; Jutzi, B.; Ulrich, M. Automatic Real-Time Pose Estimation of Machinery from Images. Sensors 2022, 22, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.A.; Noble, D.; Machado, R.; Paul, T.C.; Hagen, G.M. Flexible Multiplane Structured Illumination Microscope with a Four-Camera Detector. Photonics 2022, 9, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, T.C.; Johnson, K.A.; Hagen, G.M. Super-Resolution Imaging of Neuronal Structures with Structured Illumination Microscopy. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K.B.J. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; ISBN 9780128161579. [Google Scholar]
- Allen Institute for Brain Science. Allen Mouse Brain Atlas [Dataset]. 2004. Available online: https://mouse.brain-map.org/ (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- Lein, E.S.; Hawrylycz, M.J.; Ao, N.; Ayres, M.; Bensinger, A.; Bernard, A.; Boe, A.F.; Boguski, M.S.; Brockway, K.S.; Byrnes, E.J.; et al. Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature 2007, 445, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotadia, S.; Crest, J.; Tram, U.; Riggs, B.; Sullivan, W. Blastoderm Formation and Cellularisation in Drosophila melanogaster. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sage, D.; Donati, L.; Soulez, F.; Fortun, D.; Schmit, G.; Seitz, A.; Guiet, R.; Vonesch, C.; Unser, M. DeconvolutionLab2: An open-source software for deconvolution microscopy. Methods 2017, 115, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshner, H.; Aguet, F.; Sage, D.; Unser, M. 3-D PSF fitting for fluorescence microscopy: Implementation and localization application. J. Microsc. 2013, 249, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, G.M.; Caarls, W.; Lidke, K.A.; De Vries, A.H.B.; Fritsch, C.; Barisas, B.G.; Arndt-Jovin, D.J.; Jovin, T.M. Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching and photoconversion in multiple arbitrary regions of interest using a programmable array microscope. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2009, 72, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, G.M.; Caarls, W.; Thomas, M.; Hill, A.; Lidke, K.A.; Rieger, B.; Fritsch, C.; van Geest, B.; Jovin, T.M.; Arndt-Jovin, D.J. Biological applications of an LCoS-based programmable array microscope (PAM). In Imaging, Manipulation, and Analysis of Biomolecules, Cells, and Tissues V; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2007; Volume 6441, pp. 218–229. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Babcock, H.P.; Zhuang, X. Dual-objective STORM reveals three-dimensional filament organization in the actin cytoskeleton. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Dai, Q.; Tang, M.; Shao, L.; Gou, W.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, B.; et al. Elucidating subcellular architecture and dynamics at isotropic 100-nm resolution with 4Pi-SIM. Nat. Methods 2025, 22, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

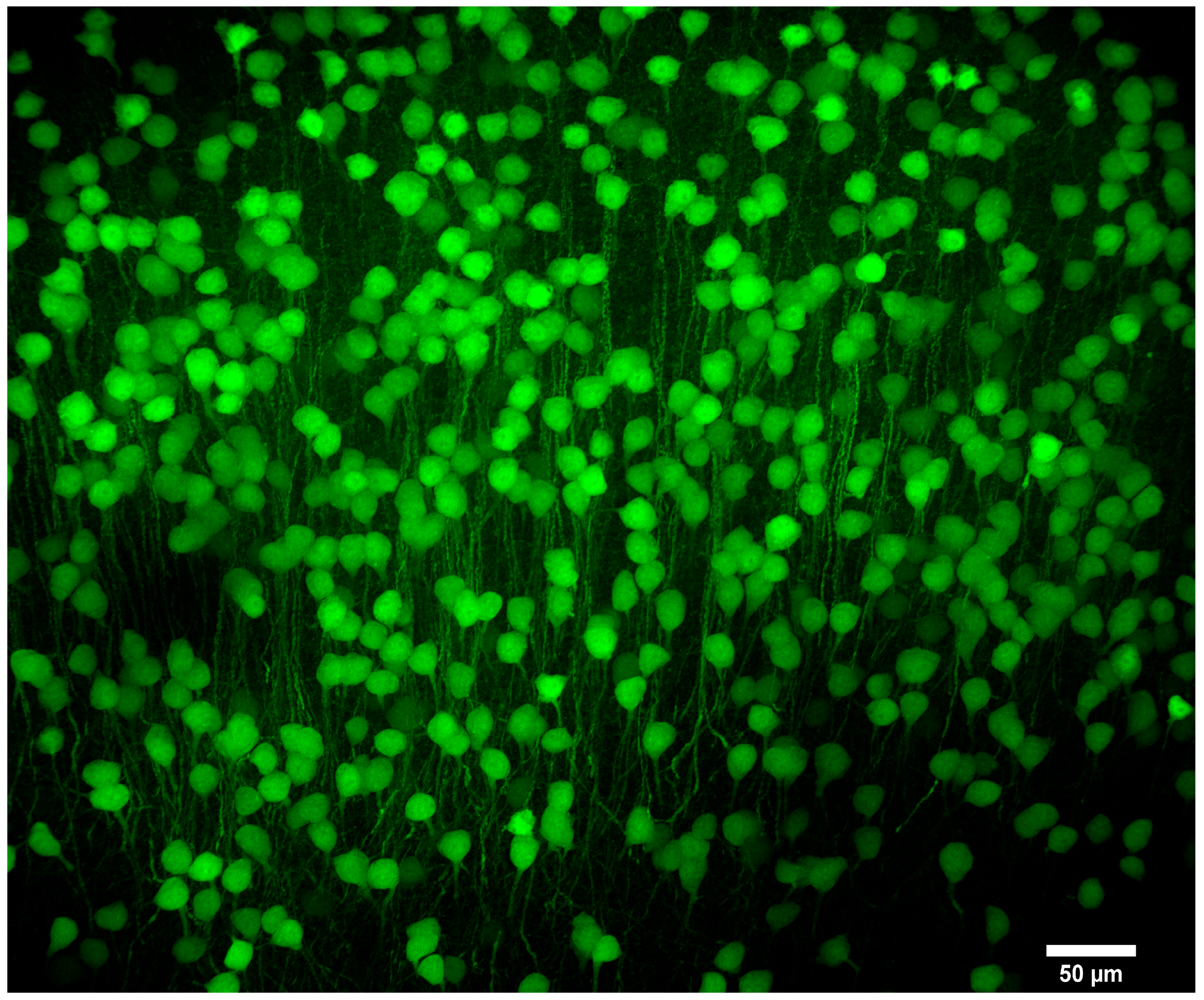
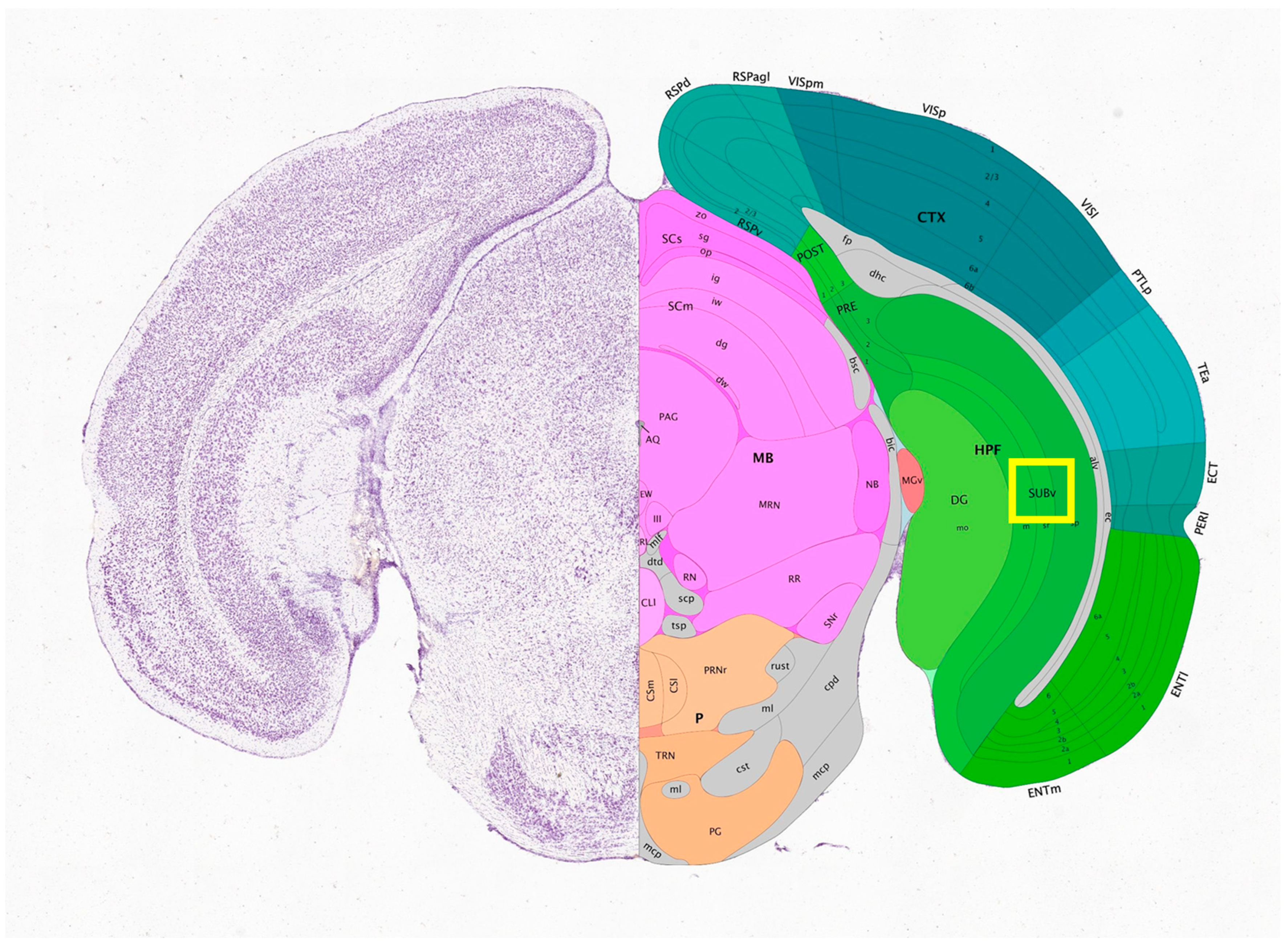
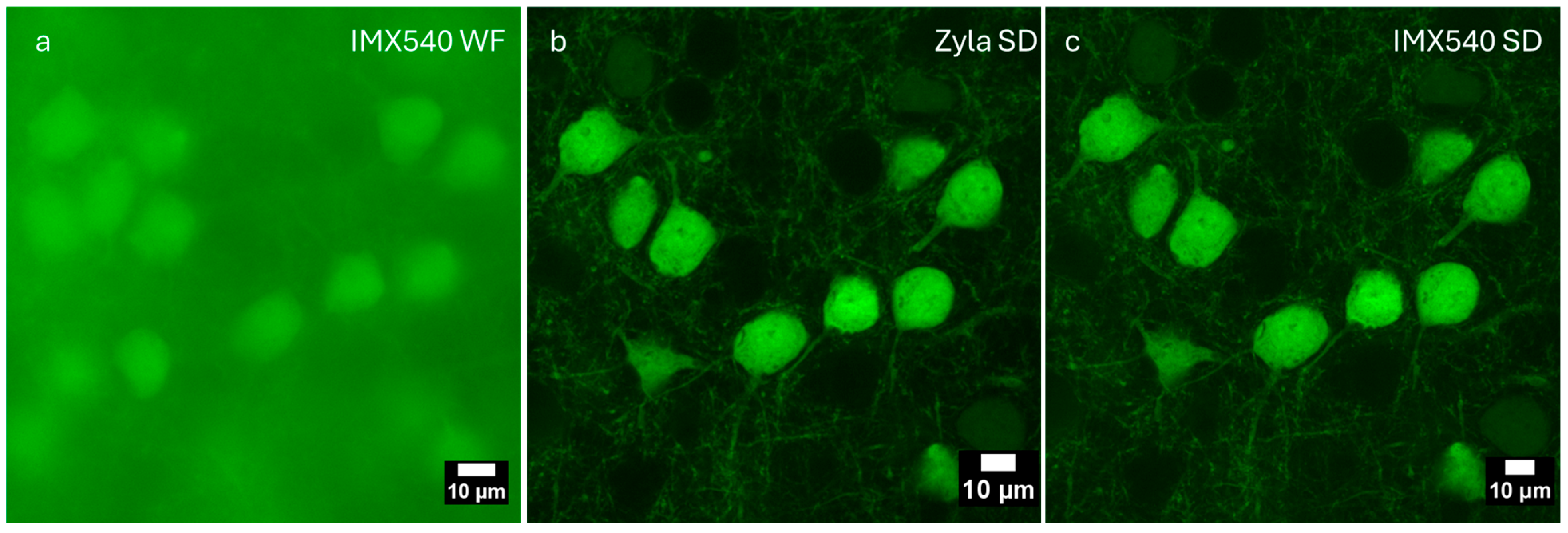

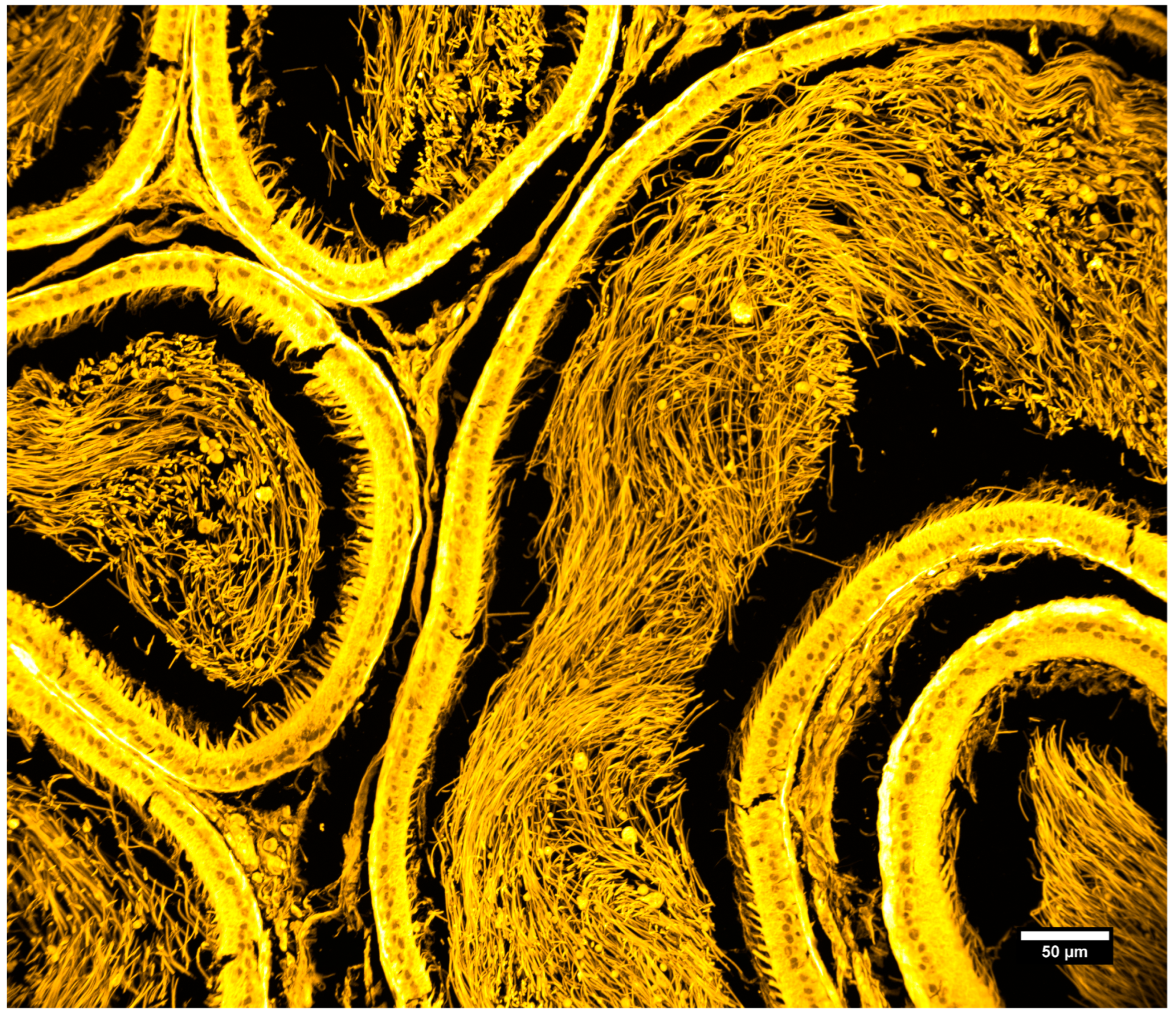
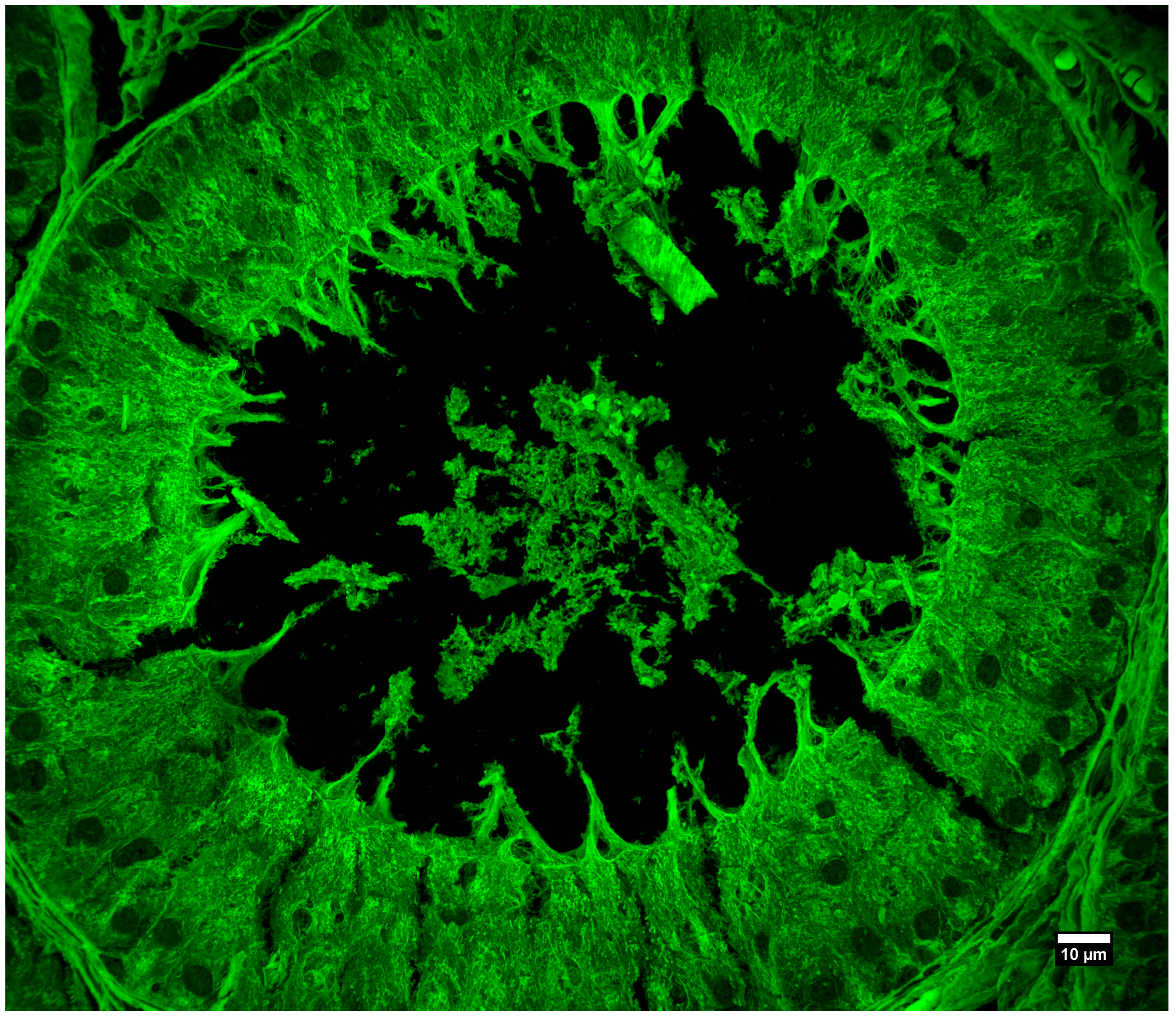
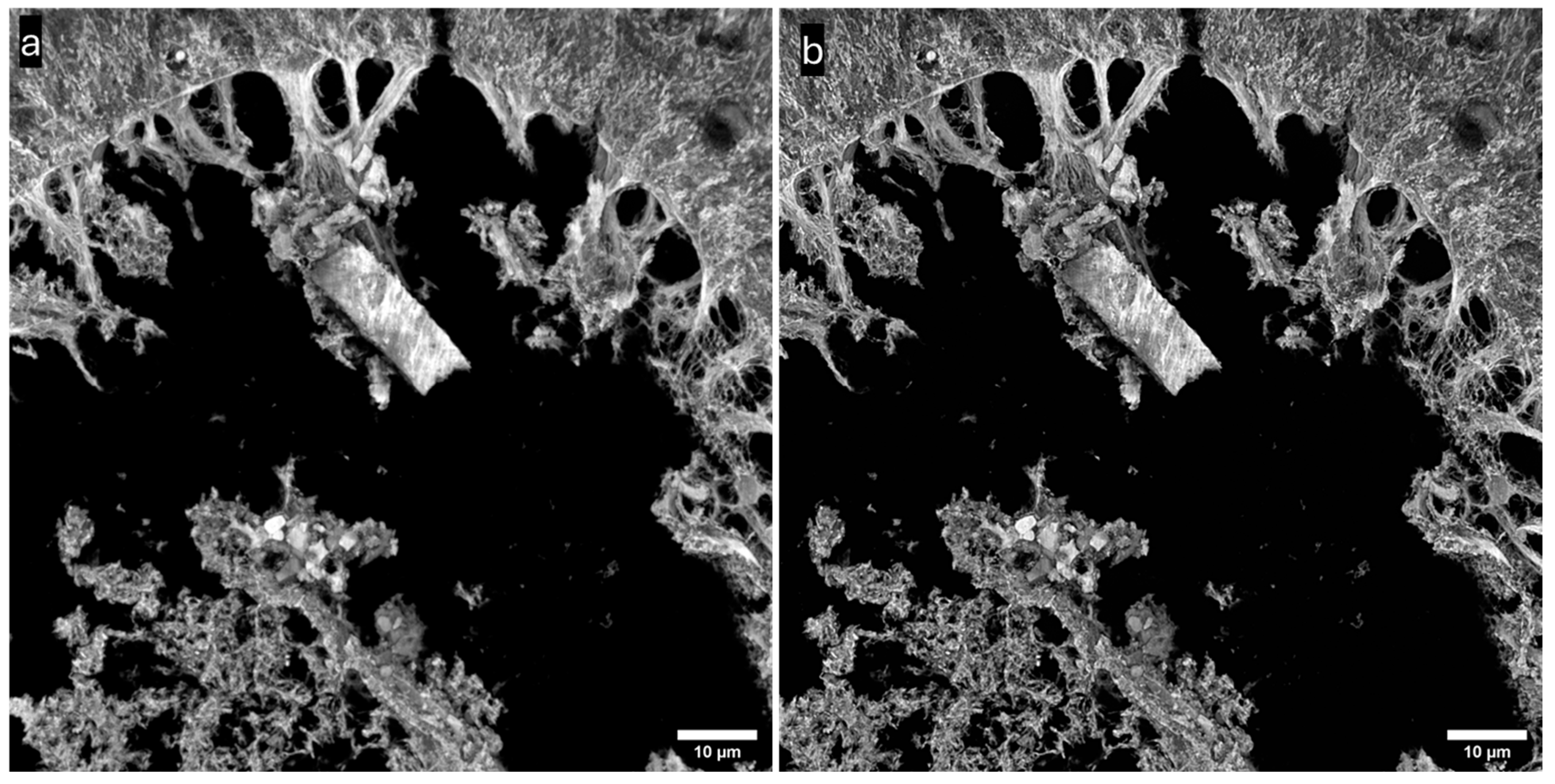
| Objective Mag. | Objective NA | Optimal Pinhole Diameter for λ = 515 nm (μm) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 1.40 | 44.88 |
| 60 | 1.42 | 26.55 |
| 30 | 1.05 | 17.95 |
| 20 | 0.85 | 14.78 |
| 10 | 0.40 | 15.71 |
| Camera | FLIR Blackfly S | Andor Zyla 4.2+ |
|---|---|---|
| Part number | BFS-U3-244S8M-C | ZYLA-4.2P-CL10 |
| Sensor type | Sony IMX540 (Pregius S) | Andor Zyla |
| Quantum efficiency | 69% at 525 nm | 82% at 555 nm |
| Read noise | 2.31 e− | 0.9 e− |
| Dark current | 0.3 e−/pixel/s | 0.1 e−/pixel/s |
| Pixel size | 2.74 um | 6.5 um |
| Full well capacity | 9648 e− | 30,000 e− |
| Pixel format | 5320 × 4600 (24.5 MP) | 2048 × 2048 (4.2 MP) |
| Maximum frame rate | 15 FPS | 100 FPS |
| Readout method | Global shutter | Rolling shutter |
| CMOS type | Back-illuminated | Front-illuminated |
| Sensor size | 14.599 × 12.626 mm | 13.3 × 13.3 mm |
| Interface | USB3 | Camera link |
| Weight of camera | 53 g | 1 kg |
| Size of camera | 29 × 29 × 39 mm | 133 × 80 × 82 mm |
| Approx. price | USD2225 | USD 18,000 |
| Objective Mag/NA | Expected Res. at 515 nm (nm) | Pixel Size (Sony, nm) | Sampling Rate (Sony) | Over- Sampled? (Sony) | Pixel Size Andor (nm) | Sampling Rate (Andor) | Over- Sampled? (Andor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10×/0.40 | 785 | 274 | 2.87 | Yes | 650 | 1.21 | No |
| 20×/0.85 | 370 | 137 | 2.70 | Yes | 325 | 1.14 | No |
| 30×/1.05 | 299 | 91 | 3.28 | Yes | 216 | 1.38 | No |
| 40×/0.95 | 330 | 68.5 | 4.83 | Yes | 162.5 | 2.03 | Yes |
| 60×/1.35 | 233 | 45.6 | 5.10 | Yes | 108 | 2.14 | Yes |
| 60×/1.42 | 221 | 45.6 | 4.85 | Yes | 108 | 2.05 | Yes |
| 100×/1.40 | 224 | 27.4 | 8.19 | Yes | 65 | 3.45 | Yes |
| Objective Mag/NA | XY | Z |
|---|---|---|
| 20×/0.85 | 384.8 nm | 1.932 μm |
| 60×/1.42 | 215.8 nm | 521.9 nm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hagen, G.M.; Lewis, B.; Levis, S.; Hamilton, J.R.; Paul, T.C. Low-Cost Spinning Disk Confocal Microscopy with a 25-Megapixel Camera. Sensors 2025, 25, 7183. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237183
Hagen GM, Lewis B, Levis S, Hamilton JR, Paul TC. Low-Cost Spinning Disk Confocal Microscopy with a 25-Megapixel Camera. Sensors. 2025; 25(23):7183. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237183
Chicago/Turabian StyleHagen, Guy M., Brian Lewis, Summer Levis, Joseph R. Hamilton, and Tristan C. Paul. 2025. "Low-Cost Spinning Disk Confocal Microscopy with a 25-Megapixel Camera" Sensors 25, no. 23: 7183. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237183
APA StyleHagen, G. M., Lewis, B., Levis, S., Hamilton, J. R., & Paul, T. C. (2025). Low-Cost Spinning Disk Confocal Microscopy with a 25-Megapixel Camera. Sensors, 25(23), 7183. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237183






