A 0.6-V All-Digital Temperature Sensor with Reduced Supply Sensitivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Operating Principle
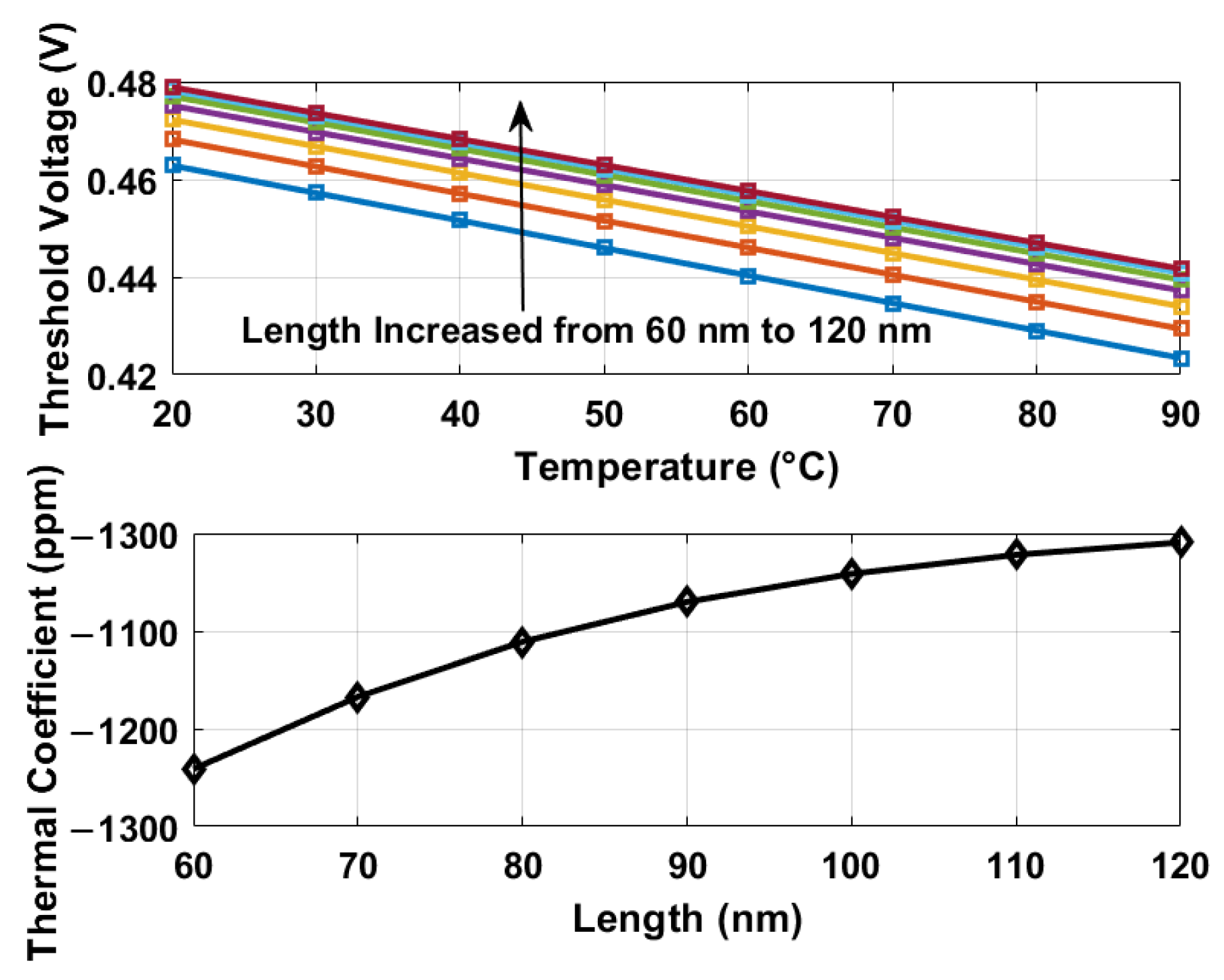
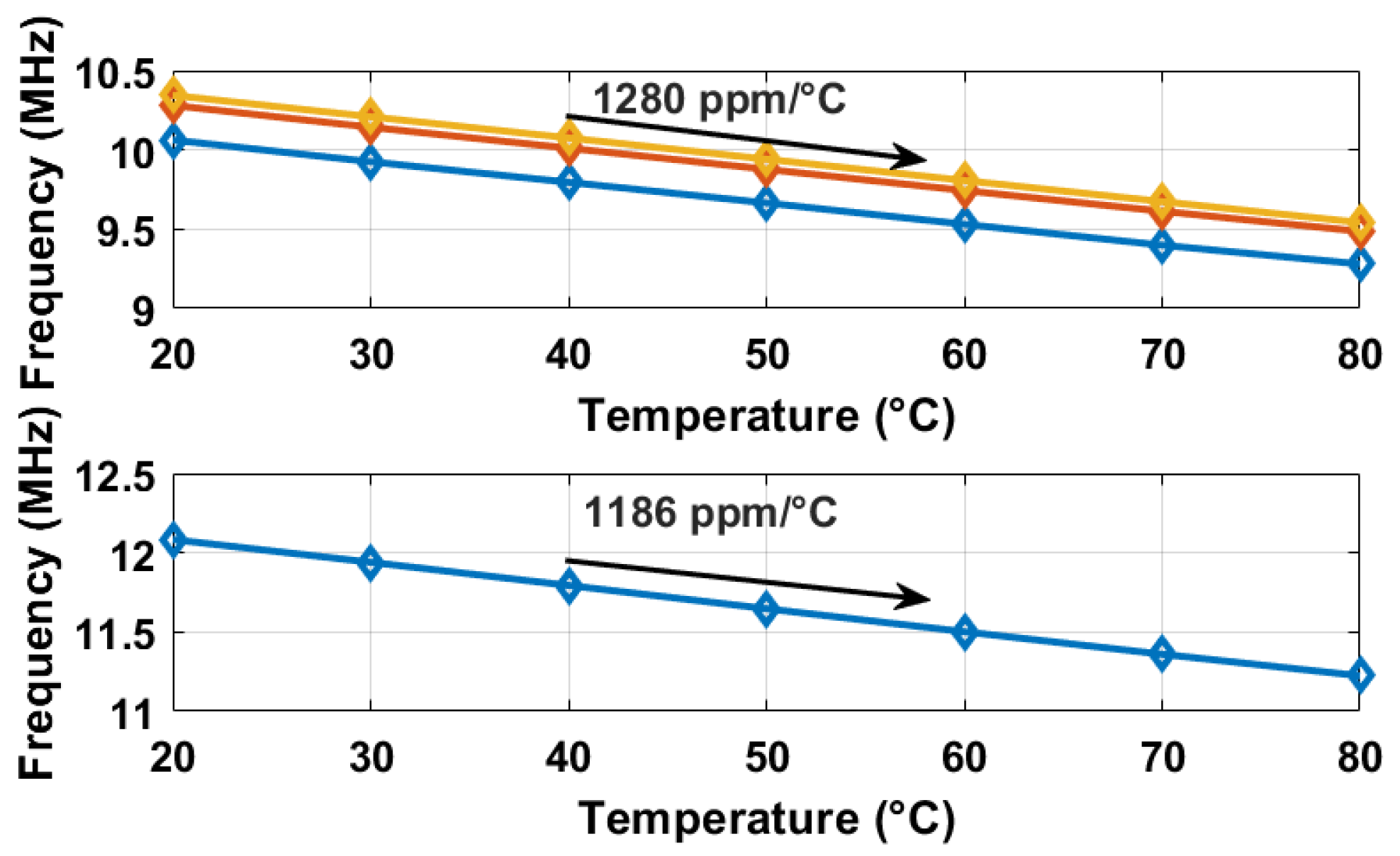
2.1. Physical Principles of Delay Line Thermal Coefficients (TCs)
2.2. Thermally Dependent Threshold Voltages
2.3. Thermally Dependent Propagation Delay Versus Supply Voltage
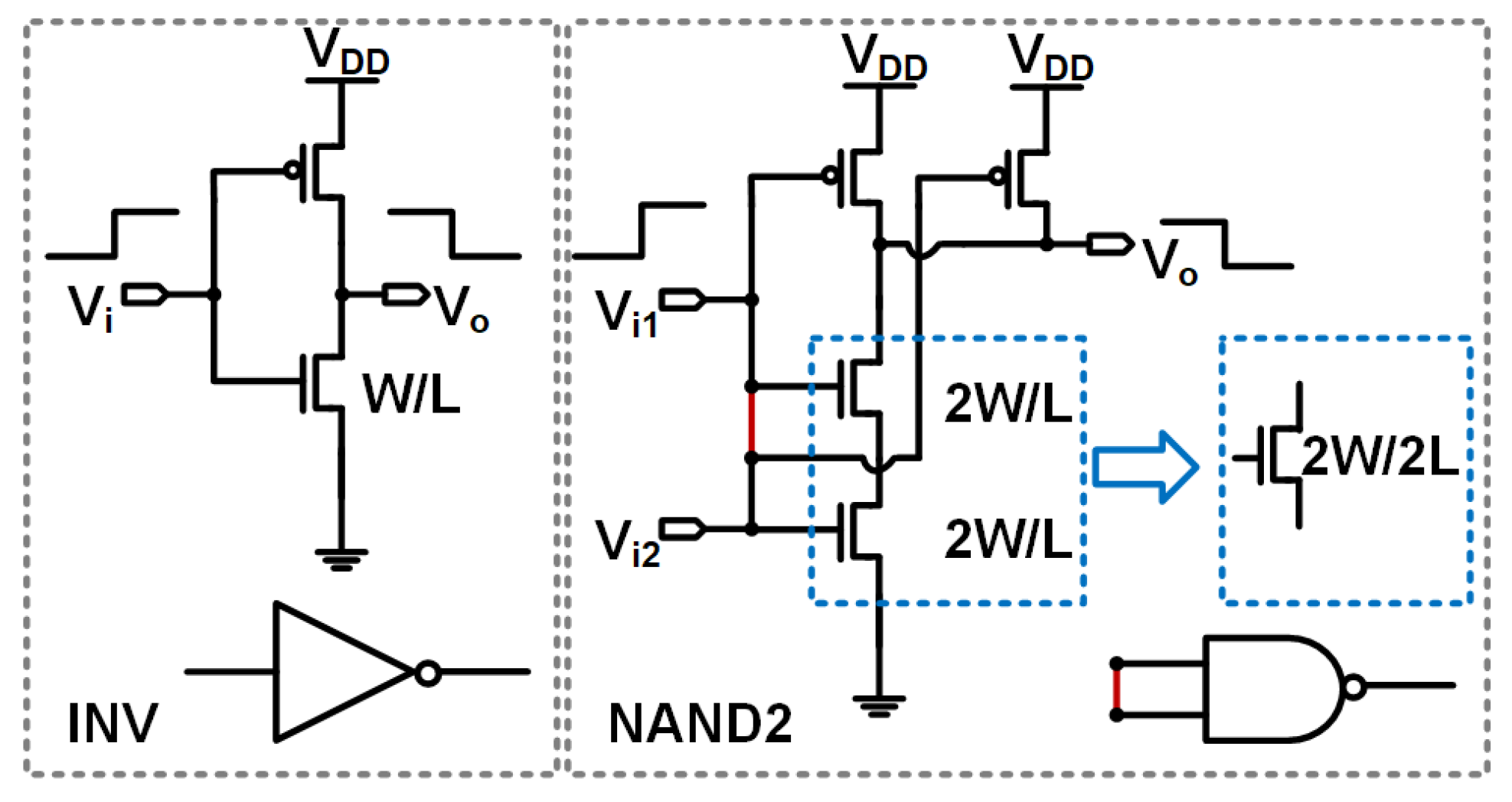
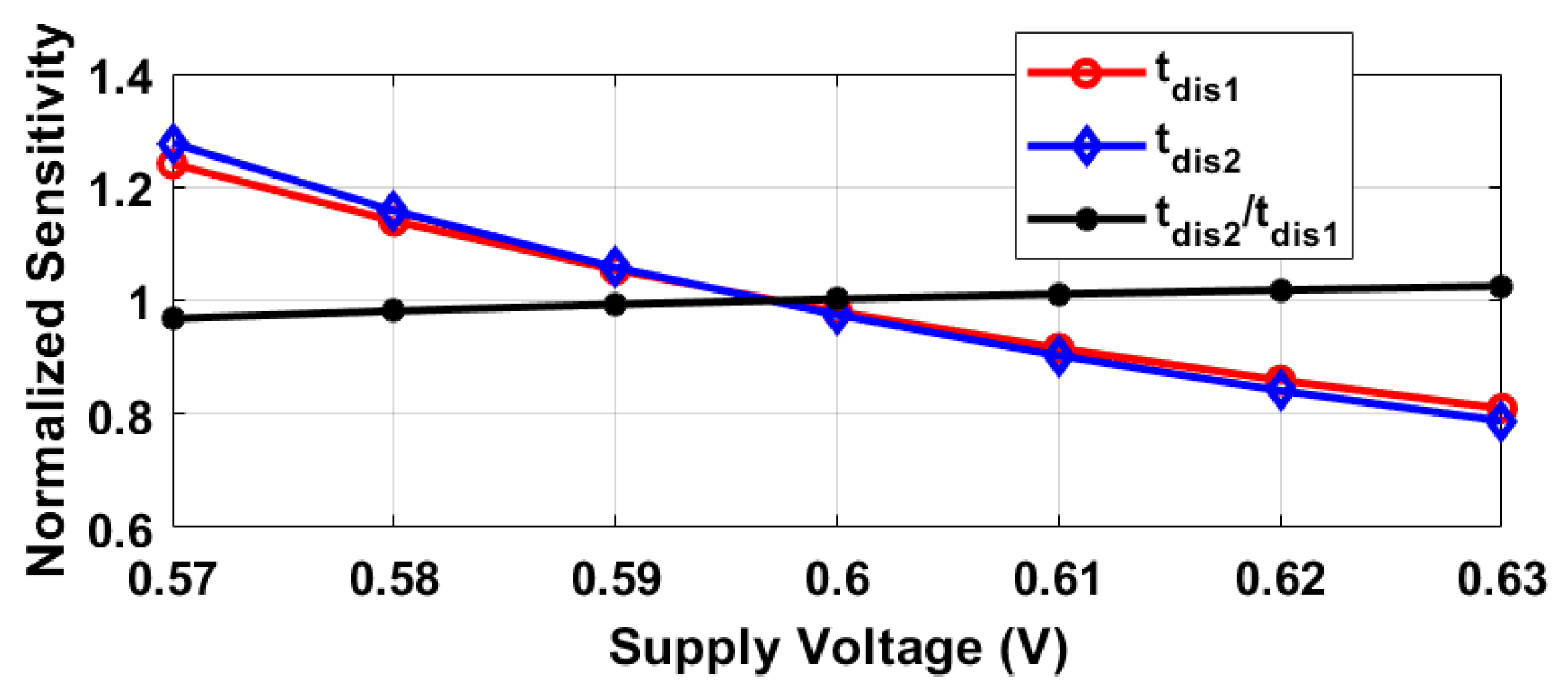
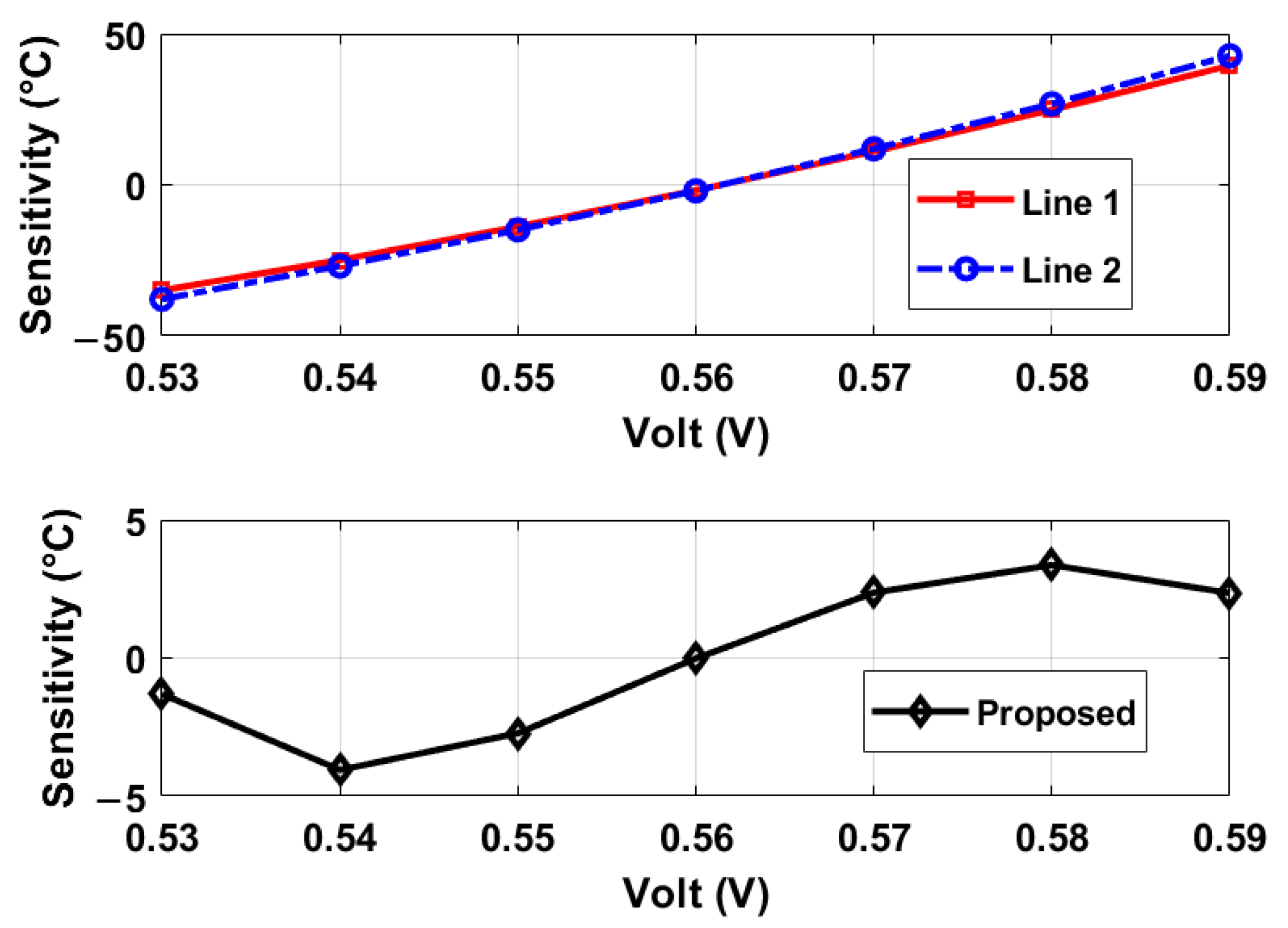
2.4. Power Supply Sensitivity Reduction
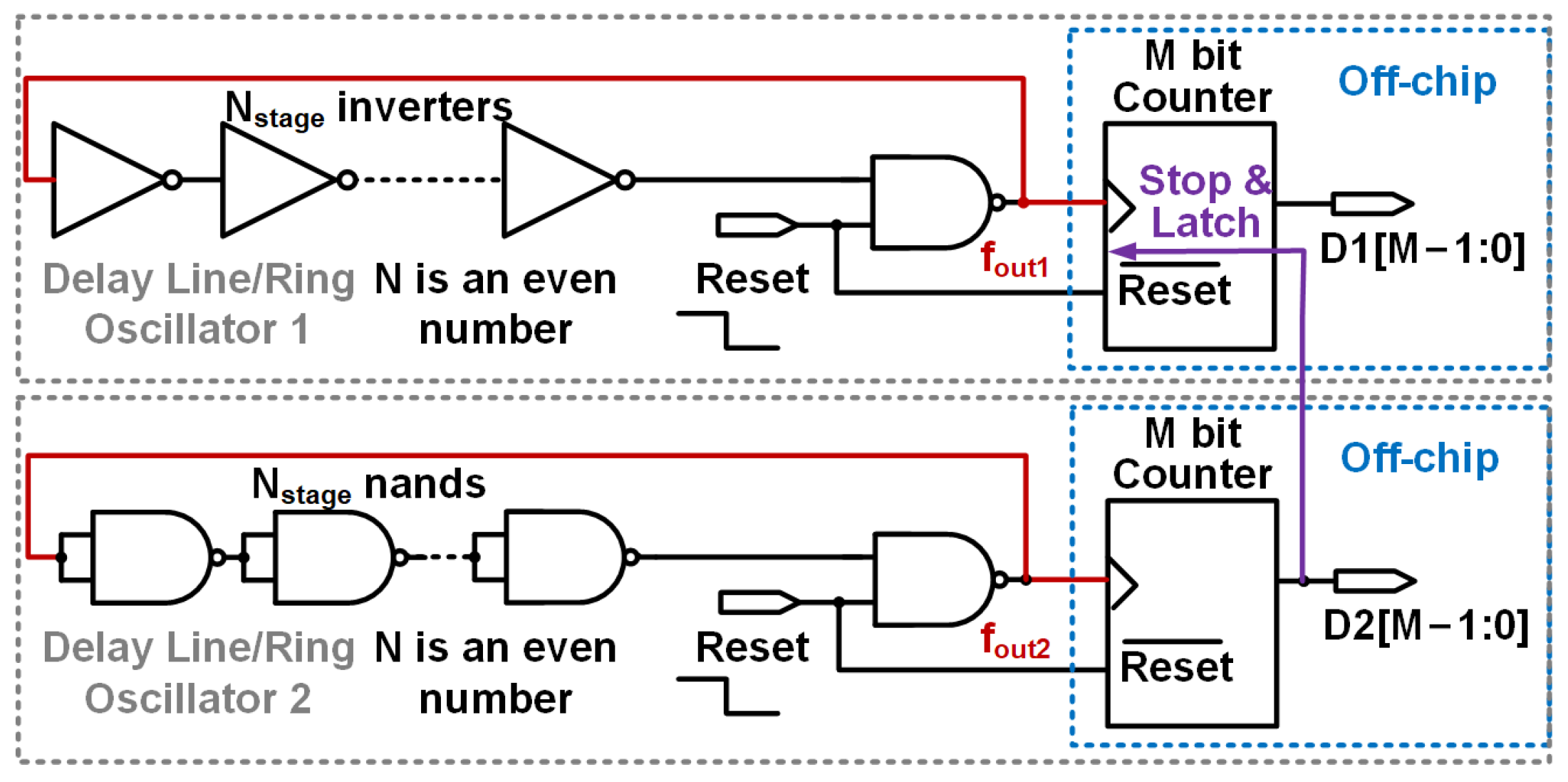
3. Circuit Architecture
3.1. Thermal Dependent Digital Outputs
3.2. Resolution of the Temperature Sensor
3.3. Limitations of Supply Voltage
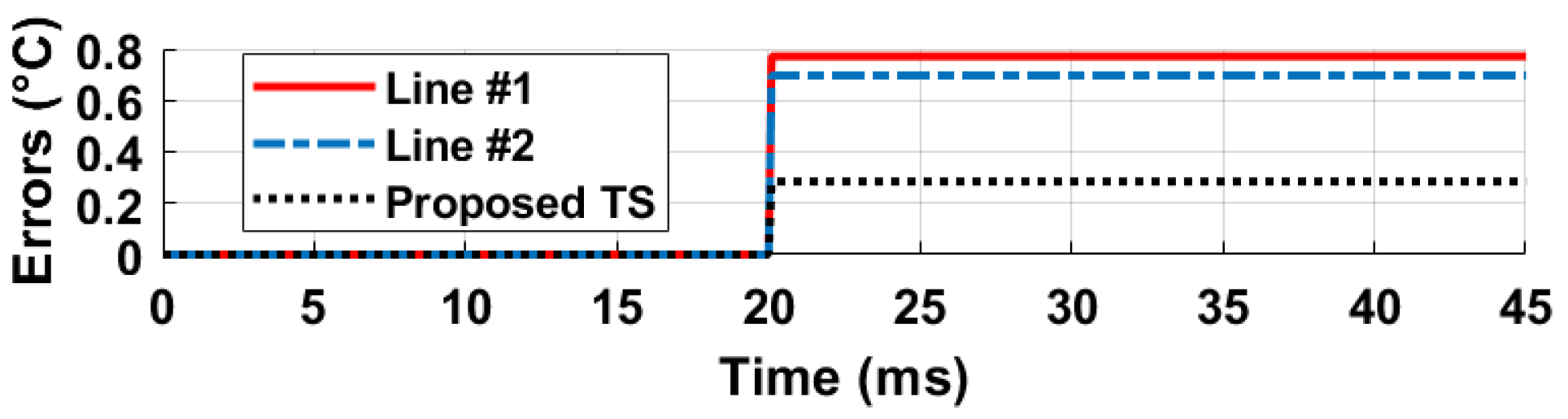
3.4. Phase Noise Analysis
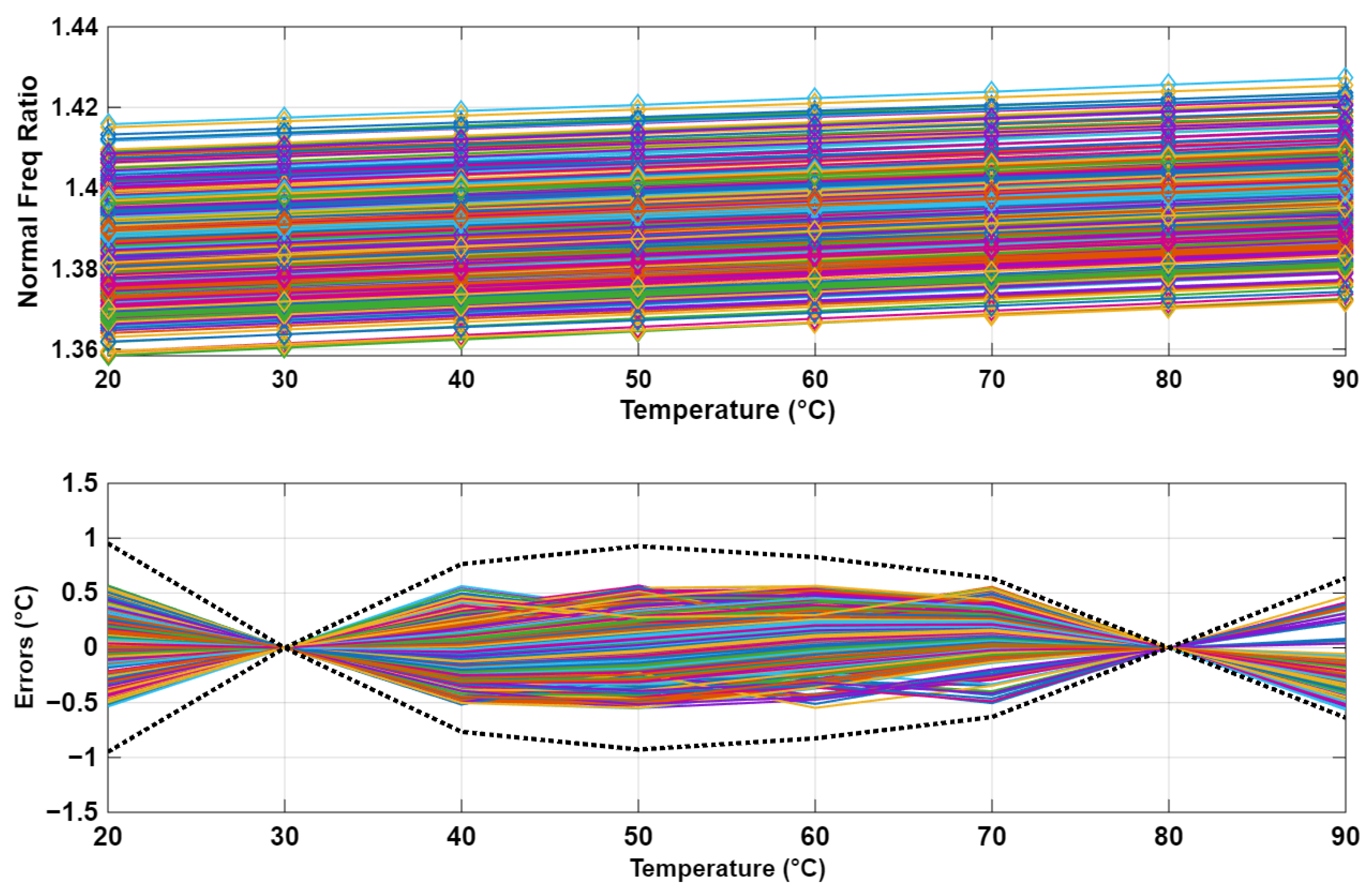
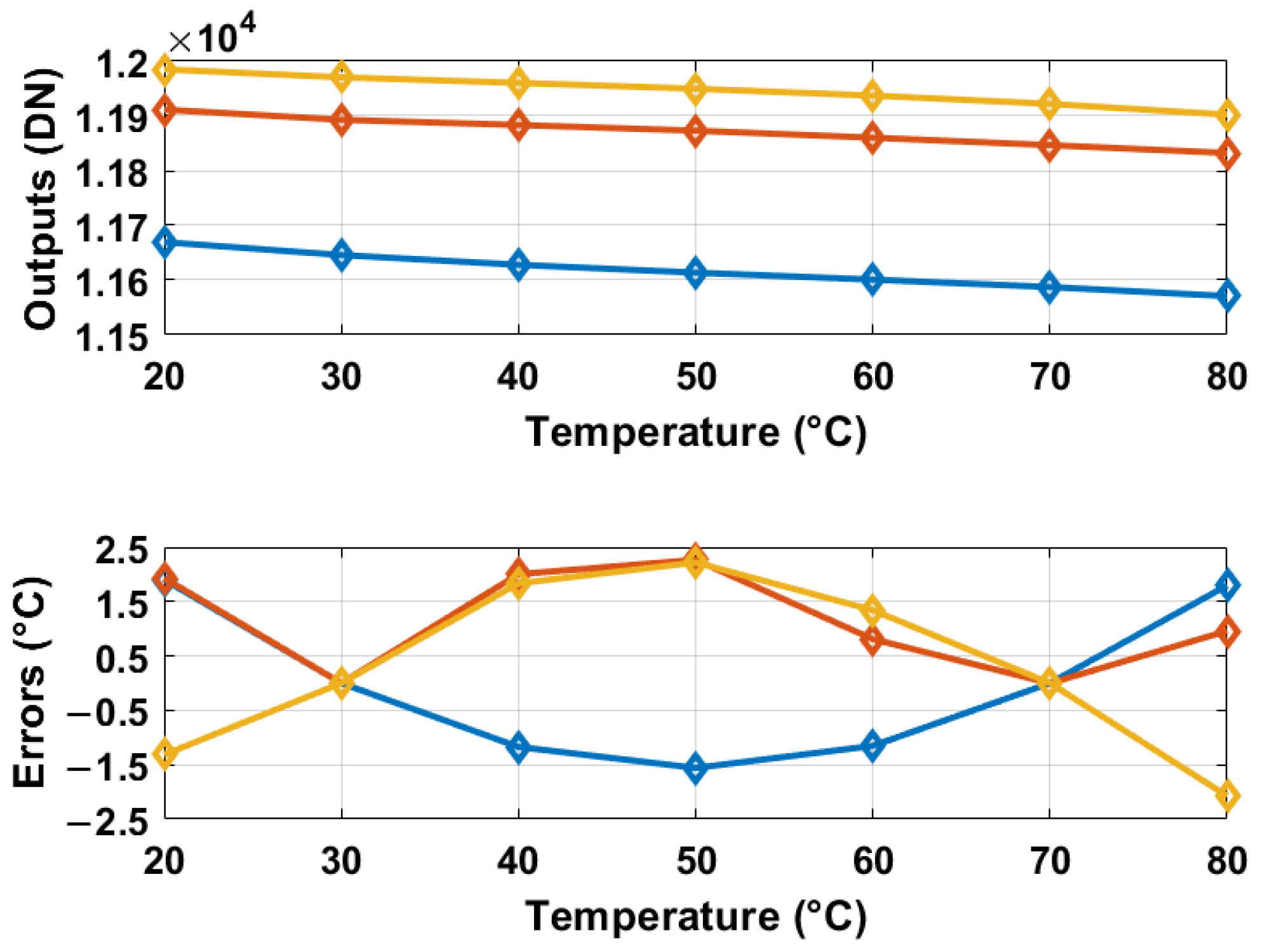
4. Monte Carlo Simulation Results
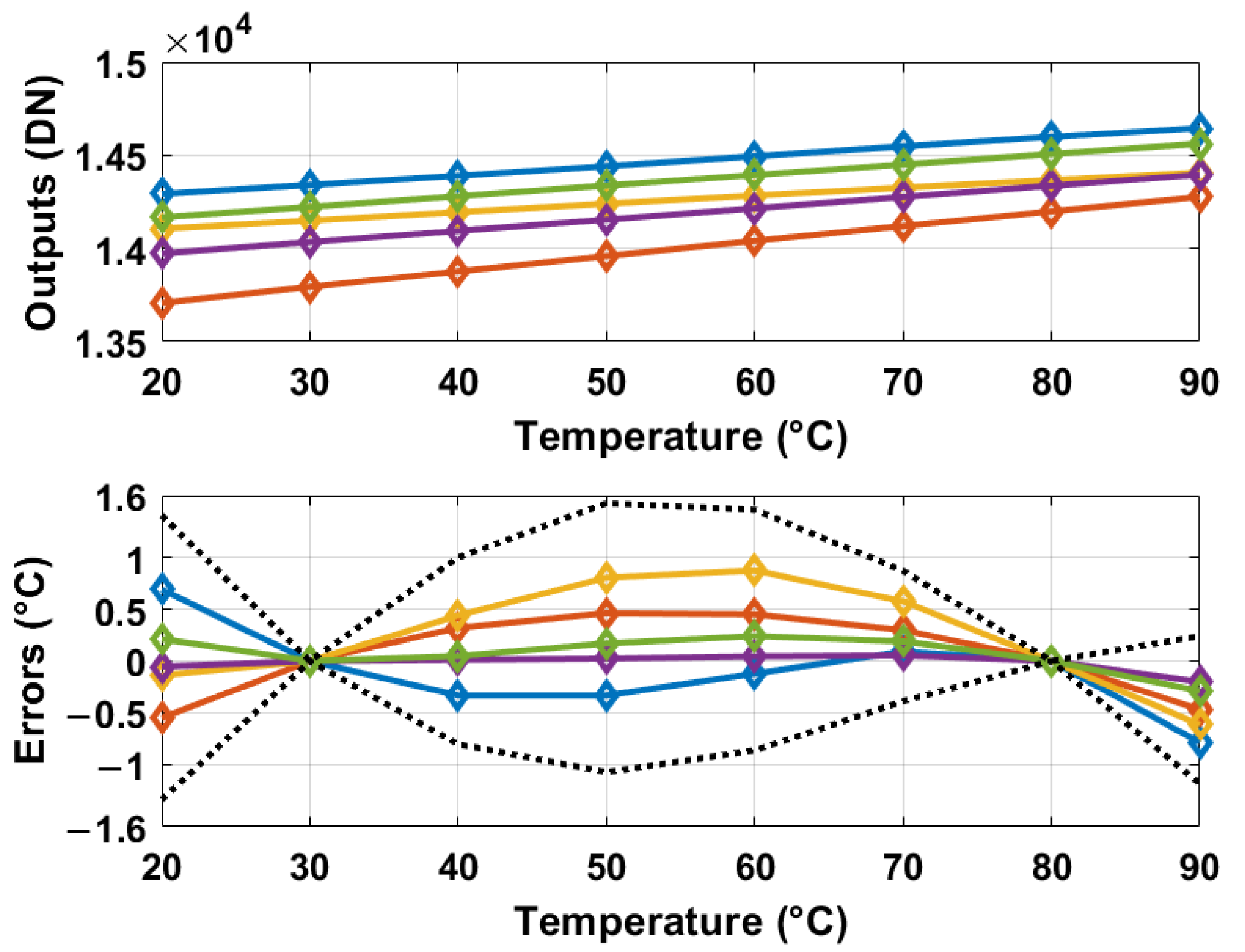
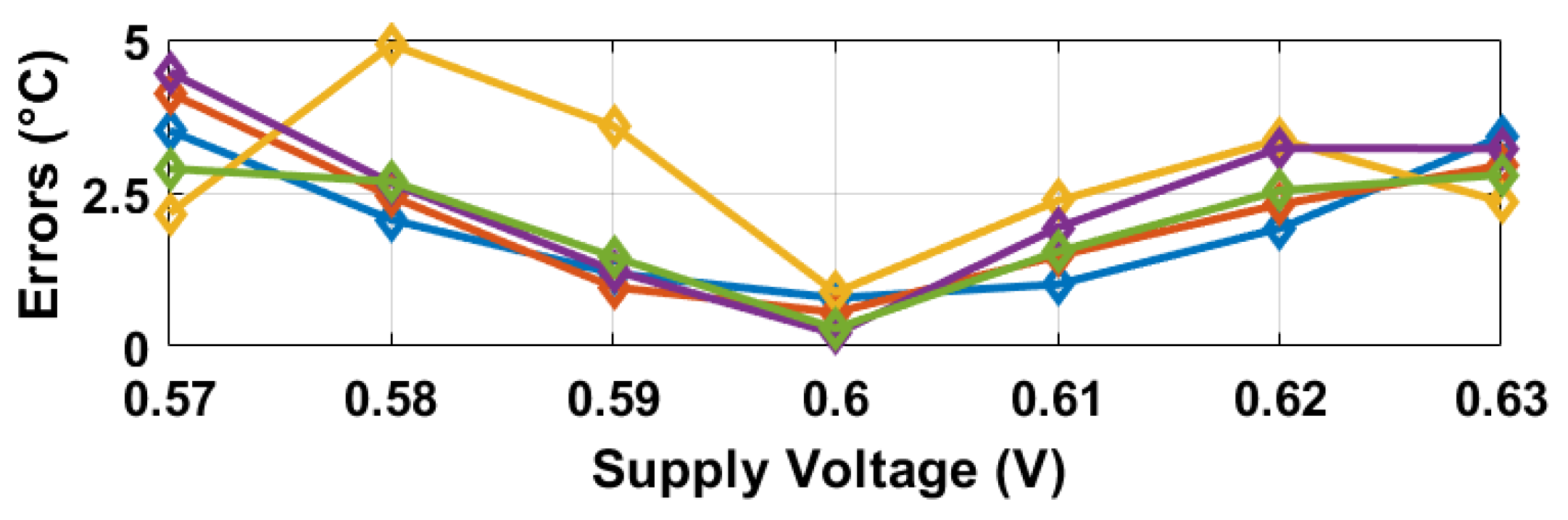
5. Measurement Results and Discussion
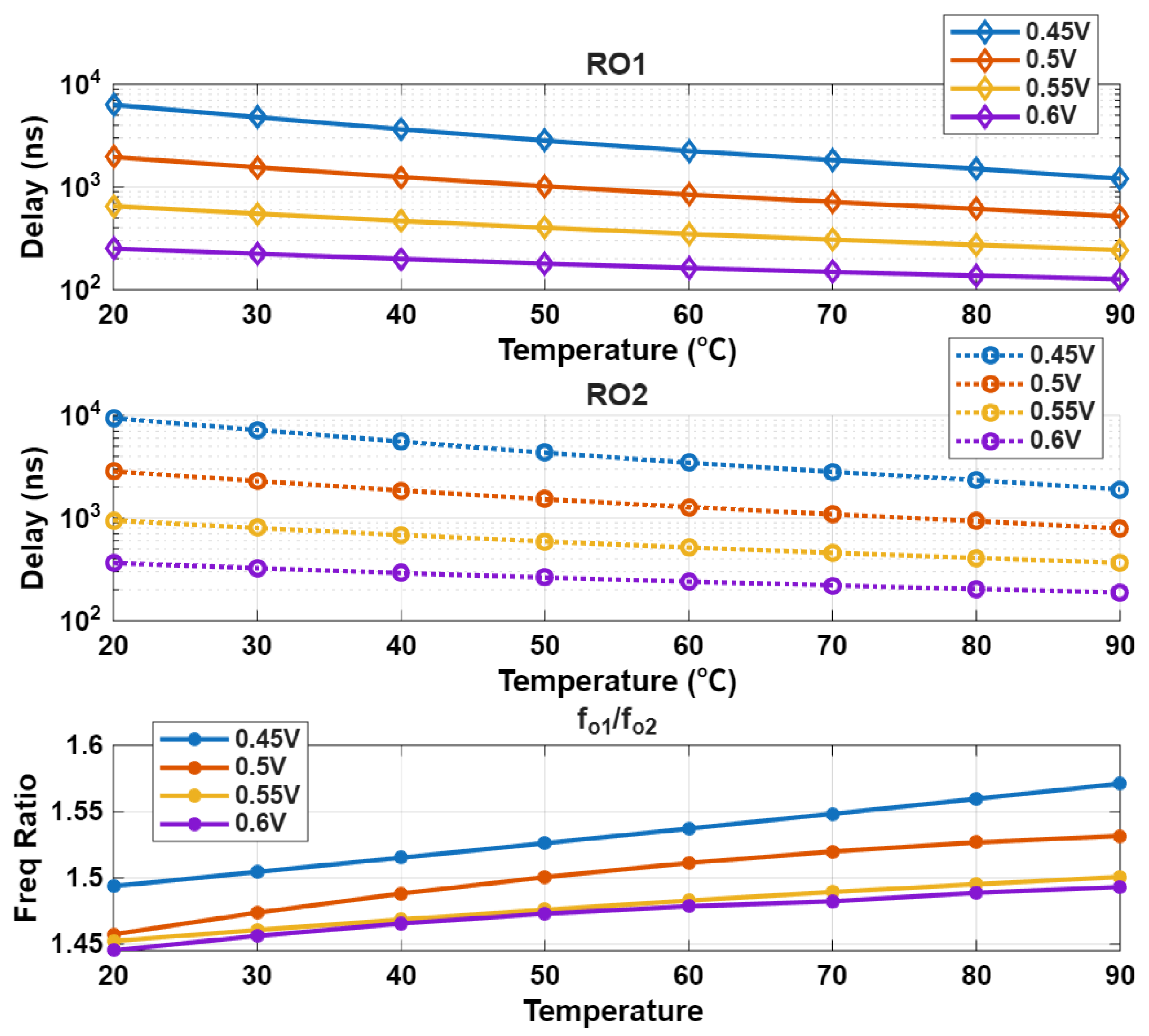
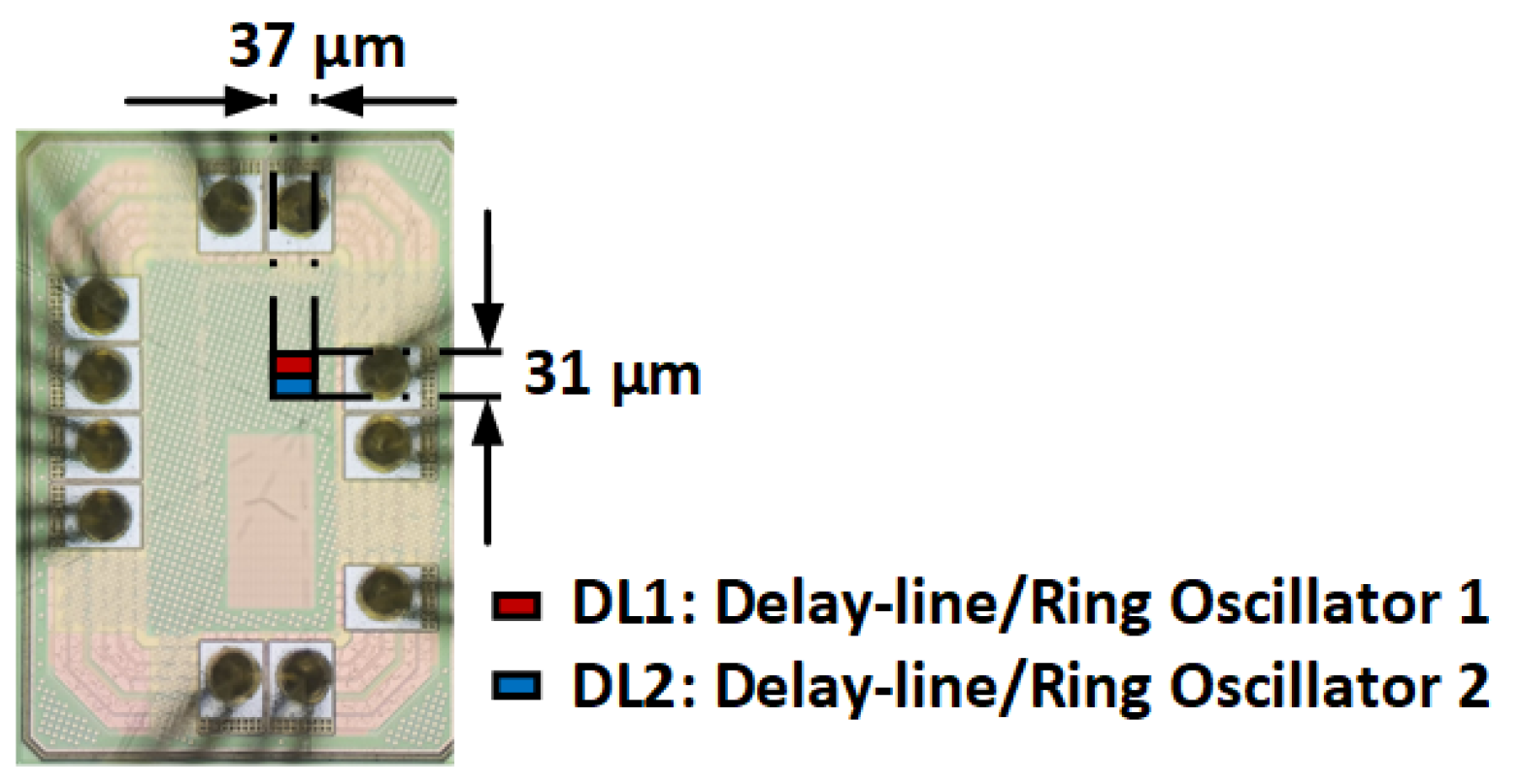
5.1. 55 nm CMOS Prototype
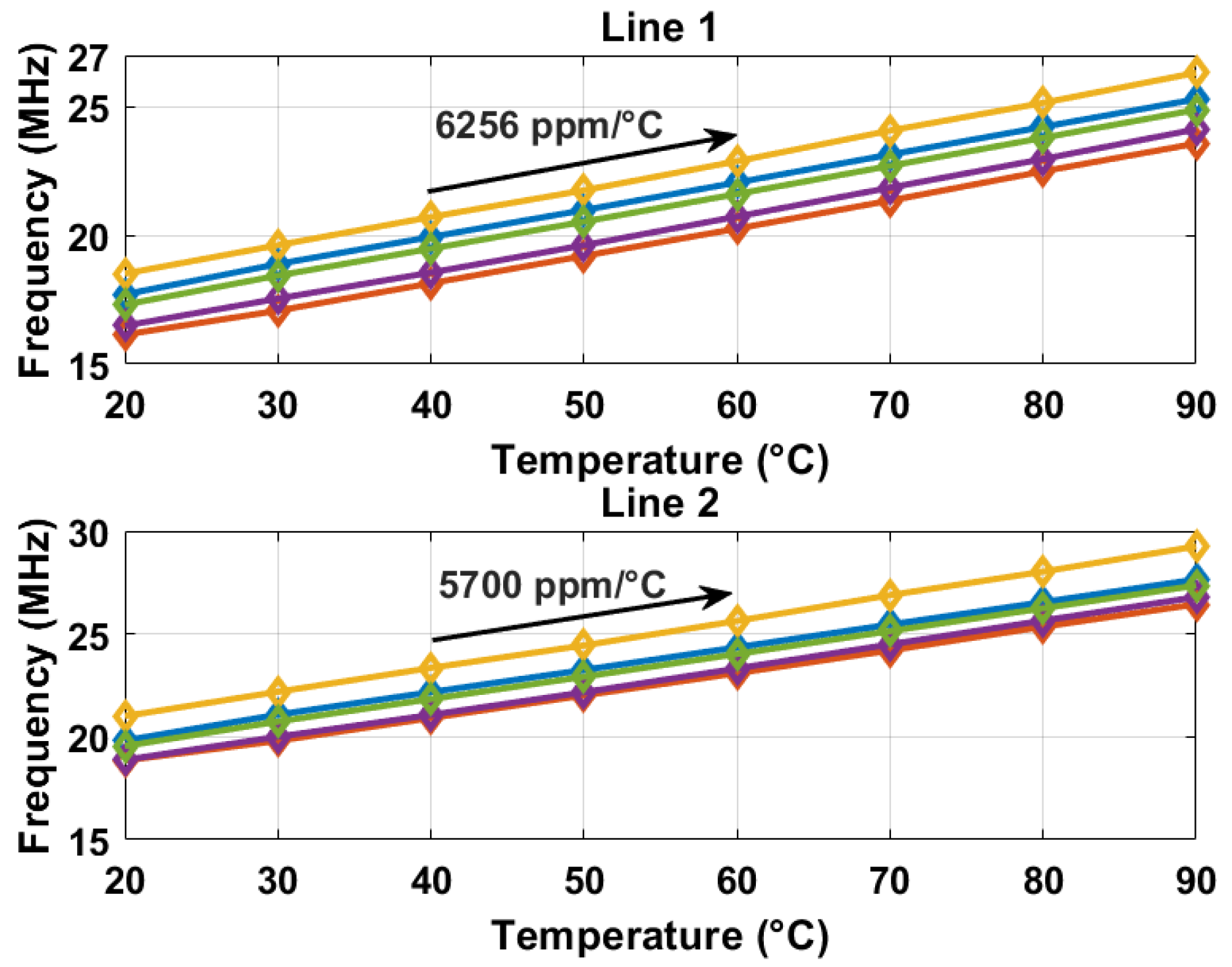
5.2. FPGA-Synthesized Temperature Sensor
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/236773/intel-core-i9-processor-14900k-36m-cache-up-to-6-00-ghz.html (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Available online: https://ark.intel.com/content/www/us/en/ark/products/230490/intel-core-i7-13700-processor-30m-cache-up-to-5-20-ghz.html (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Available online: https://edc.intel.com/content/www/us/en/design/products/platforms/processor-and-core-i3-n-series-datasheet-volume-1-of-2/001/digital-thermal-sensor/ (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Anand, T.; Makinwa, K.A.; Hanumolu, P.K. A self-referenced VCO-based temperature sensor with 0.034 c/mv supply sensitivity in 65 nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2015 Symposium on VLSI Circuits (VLSI Circuits) (2015), Kyoto, Japan, 17–19 June 2015; pp. C200–C201. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, D.; Woo, K.; Meninger, S.; Xanthopoulos, T.; Crain, E.; Ham, D. Time-domain cmos temperature sensors with dual delay-locked loops for microprocessor thermal monitoring. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2012, 20, 1590–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, S.-C.; Shen, Y.-S.; Peng, Y.-J. All-digital time-domain smart temperature sensor with an inter-batch inaccuracy of −0.7 °C–+0.6 °C after one-point calibration. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2011, 58, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, C.-C.; Peng, Y.-H.; Wang, K.-M.; Wang, Y.-S. A time-domain sar smart temperature sensor with curvature compensation and a 3 sigma inaccuracy of −0.4 °C–+0.6 °C over a 0 °C to 90 °C range. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, T.-K.; Wang, Y.-S.; Chen, C.-C. A time-domain sub-micro watt temperature sensor with digital set-point programming. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Koo, J.; Kim, K.; Lee, H.; Kim, C. A 0.008 mm2 500 μW 469 ks/s frequency-to-digital converter based cmos temperature sensor with process variation compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2013, 60, 2241–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, A.; Ubarretxena, A.; Zalbide, I.; Pardo, D.; Solar, H.; Garcia-Alonso, A.; Berenguer, R. Full passive UHF tag with a temperature sensor suitable for human body temperature monitoring. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2010, 57, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Lee, J.; Cho, N.; Burm, J. An ultralow power time-domain temperature sensor with time-domain delta–sigma TDC. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2017, 64, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Chen, C.-L.; Lin, Y.; You, S.-Q. An all-digital time-domain smart temperature sensor with a cost-efficient curvature correction. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2019, 27, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lin, Y.; Ning, N.; Yu, Q. A +0.44 °C/−0.4 °C inaccuracy temperature sensor with multi-threshold mosfet-based sensing element and cmos thyristor-based vco. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2021, 68, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, F.; Ria, A.; Piotto, M.; Bruschi, P. A CMOS Current Reference with Novel Temperature Compensation Based on Geometry-Dependent Threshold Voltage Effects. Electronics 2025, 14, 2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, B.; Park, H.J.; Sim, J.Y. A 192-pW Voltage Reference Generating Bandgap—Vth with Process and Temperature Dependence Compensation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 12, 3281–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzou, J.; Yao, C.; Cheung, R.; Chan, H. The temperature dependence of threshold voltages in submicrometer cmos. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 1985, 6, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.K.; Sze, S.M. Physics of Semiconductor Devices; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Elmasry, M. Digital MOS Integrated Circuits; IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://analogcircuitdesign.com/level-shifter-circuit/#level-shifter-using-mosfet-bidirectional-level-shifter (accessed on 7 November 2025).
- Homayoun, A.; Razavi, B. Relation between delay line phase noise and ring oscillator phase noise. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 2, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Ng, W.T. An all-digital self-calibrated delay-line based temperature sensor for VLSI thermal sensing and management. Integr. VLSI J. 2015, 51, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.ti.com/product/TMP75 (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Xie, S.; Prouza, A.A.; Theuwissen, A. A cmos-imager-pixel-based temperature sensor for dark current compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Chen, C.-L.; Fang, W.; Chu, Y.-C. All-digital cmos time-to-digital converter with temperature-measuring capability. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2020, 28, 2079–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://ei.tudelft.nl/smart_temperature/ (accessed on 25 December 2023).
| Parameters | This Work | This Work | [13] | [24] | [12] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2023 | 2023 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 |
| Technology | 55 | FPGA | 130 | 350 | FPGA |
| (nm) | |||||
| All-digital? | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Synthesized? | No | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Supply | |||||
| Sensitivity | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.014 | N/A | N/A |
| (C/mV) | |||||
| Calibration | 2-point | 2-point | 2-point | 2-point | 2-point |
| Method | +linear | +linear | +linear | +linear | +poly |
| Supply (V) | 0.6 | 1.2 | 3.3 | 0.95 | 1.2 |
| Area () | 0.0011 | 80 inv | 0.019 | 0.004 | 74 inv |
| PP IA | 1 | 2.5 | 0.84 | 1.35 | 0.9 |
| Min (C) | 20 | 20 | 0 | 0 | −20 |
| Max (C) | 90 | 80 | 80 | 90 | 100 |
| Rel. IA 1 | 1.42 | 4.17 | 1.05 | 1.5 | 1.1 |
| Conversion | 0.8 | 0.24 | 59 | 0.1 | 1 |
| Time (ms) | |||||
| Power (µW) | 2.5 | 12 | 0.196 | 5 | 90 |
| Energy (nJ) per conversion | 2 | 2.88 | 11.56 | 0.5 | 90 |
| Resolution (C) | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| 0.08 | 0.72 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.225 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S. A 0.6-V All-Digital Temperature Sensor with Reduced Supply Sensitivity. Sensors 2025, 25, 7181. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237181
Zhou H, Wang Y, Xie S. A 0.6-V All-Digital Temperature Sensor with Reduced Supply Sensitivity. Sensors. 2025; 25(23):7181. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237181
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Hui, Yi Wang, and Shuang Xie. 2025. "A 0.6-V All-Digital Temperature Sensor with Reduced Supply Sensitivity" Sensors 25, no. 23: 7181. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237181
APA StyleZhou, H., Wang, Y., & Xie, S. (2025). A 0.6-V All-Digital Temperature Sensor with Reduced Supply Sensitivity. Sensors, 25(23), 7181. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237181





