Integration of Multi-Sensor Fusion and Decision-Making Architecture for Autonomous Vehicles in Multi-Object Traffic Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
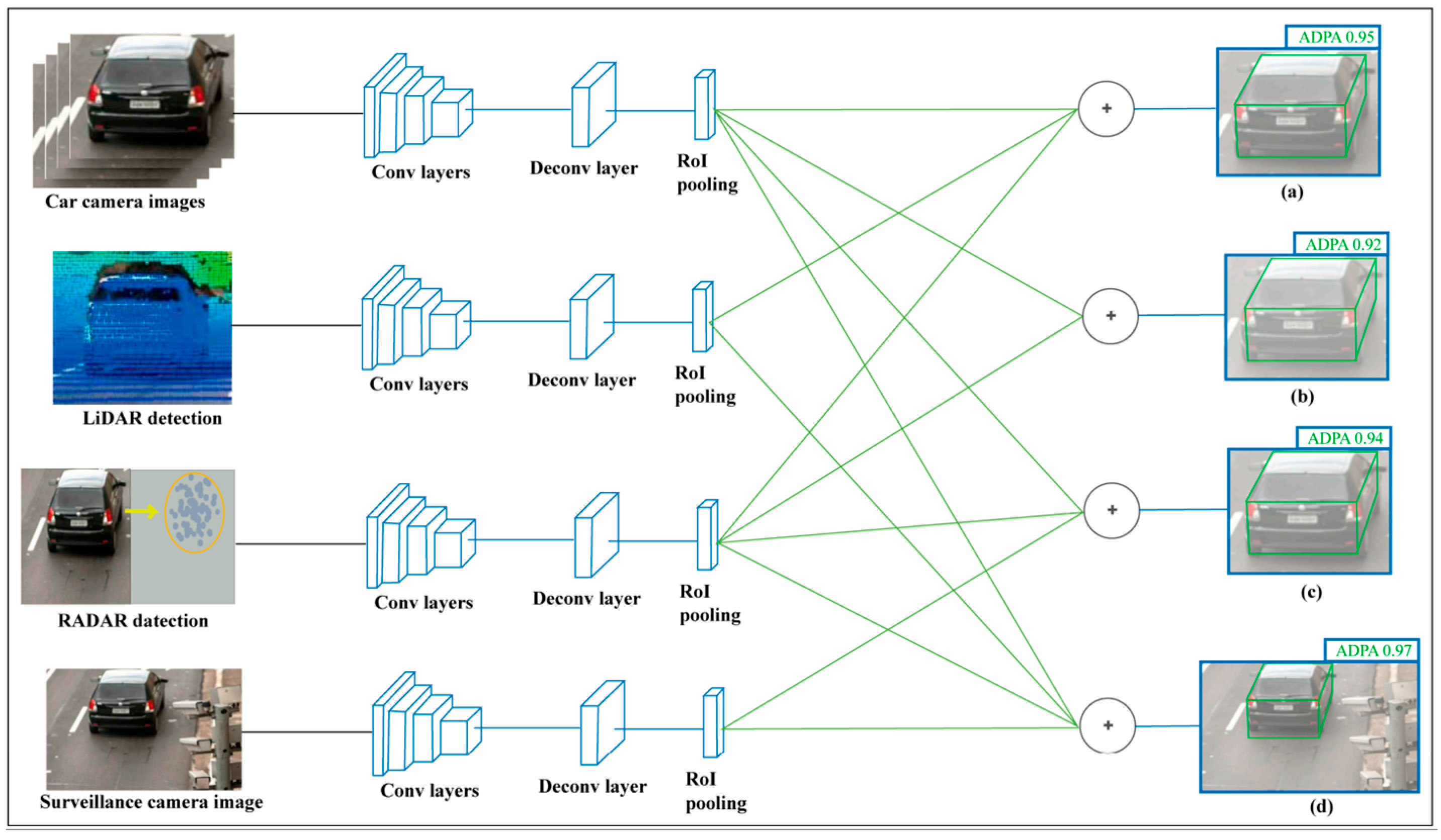
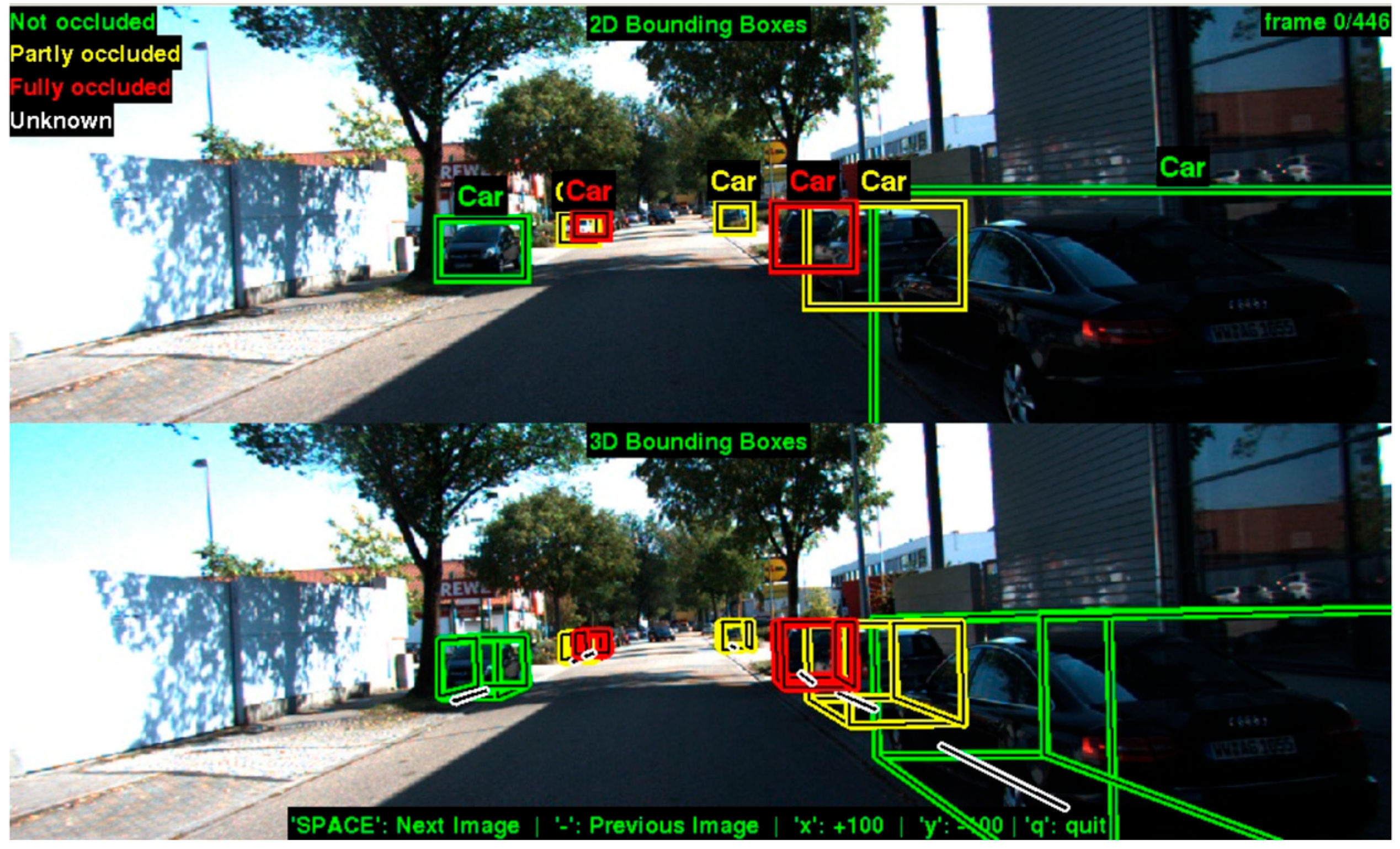
2.1. Camera Segmentation and LiDAR Signal Representation
2.2. Decision-Making for Autonomous Vehicles
2.3. Route Planning and PathFinding
2.4. Novelty of the Proposed Approach
3. System Architecture and Implementation
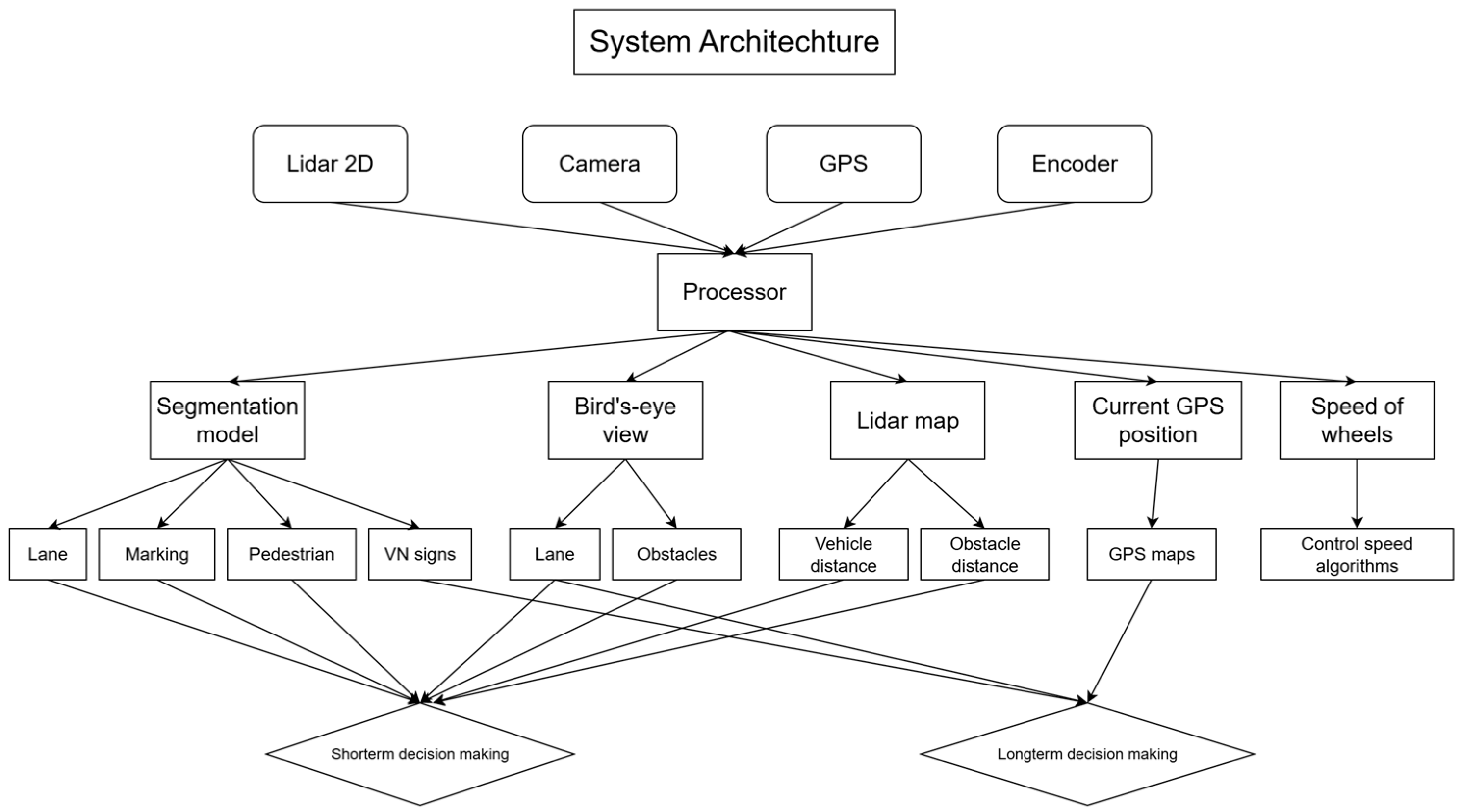
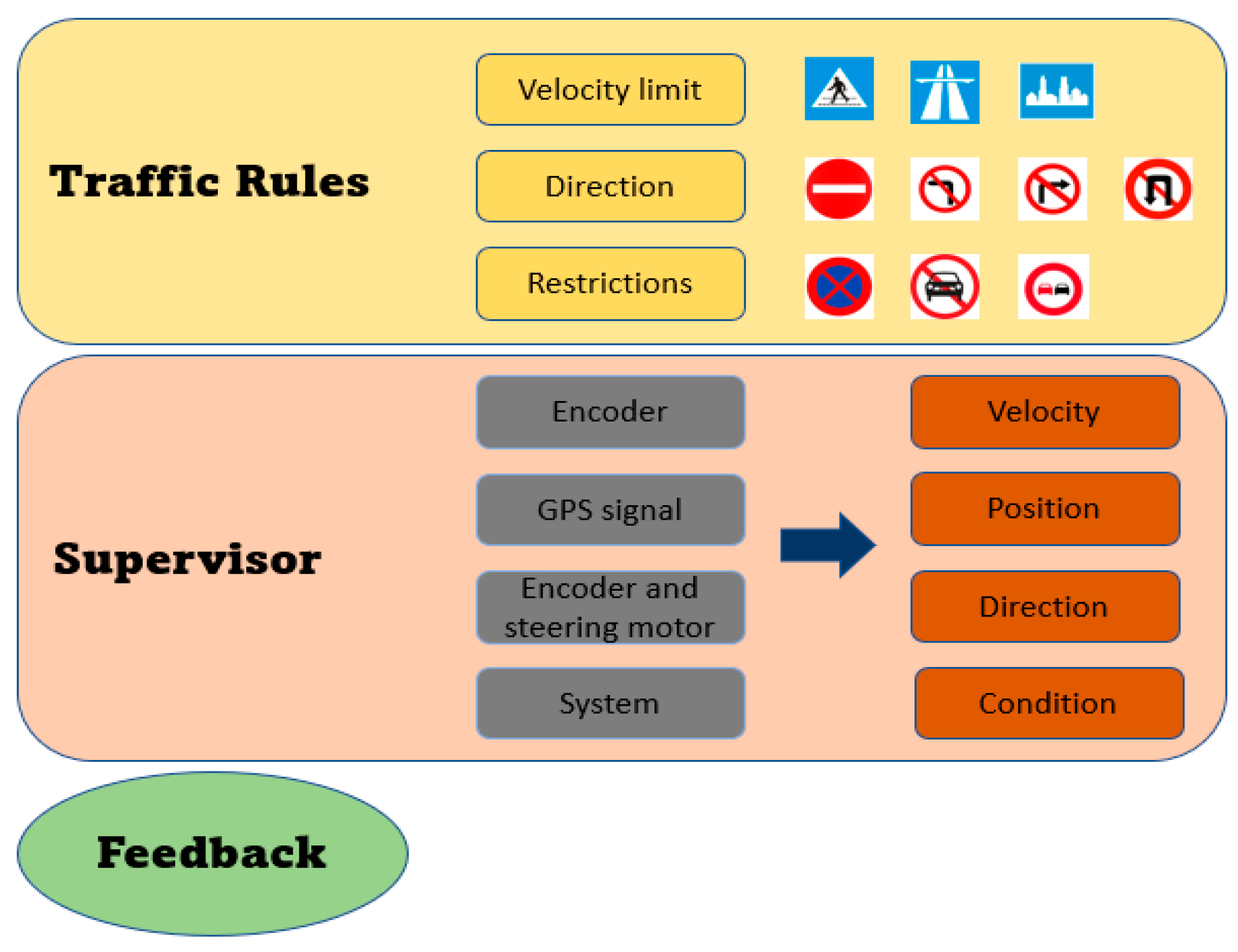
3.1. System Architecture Proposal
3.2. Implementations
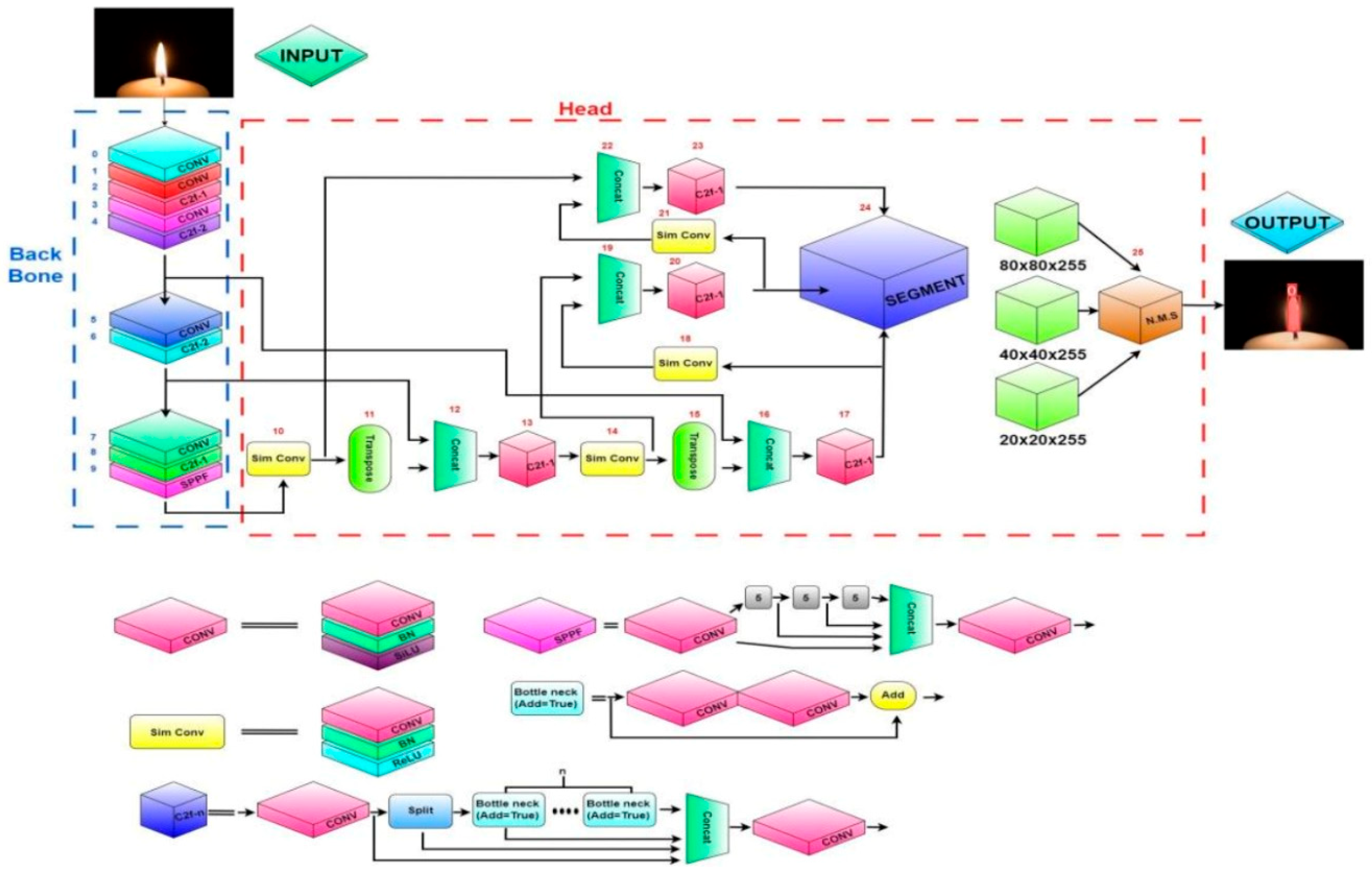
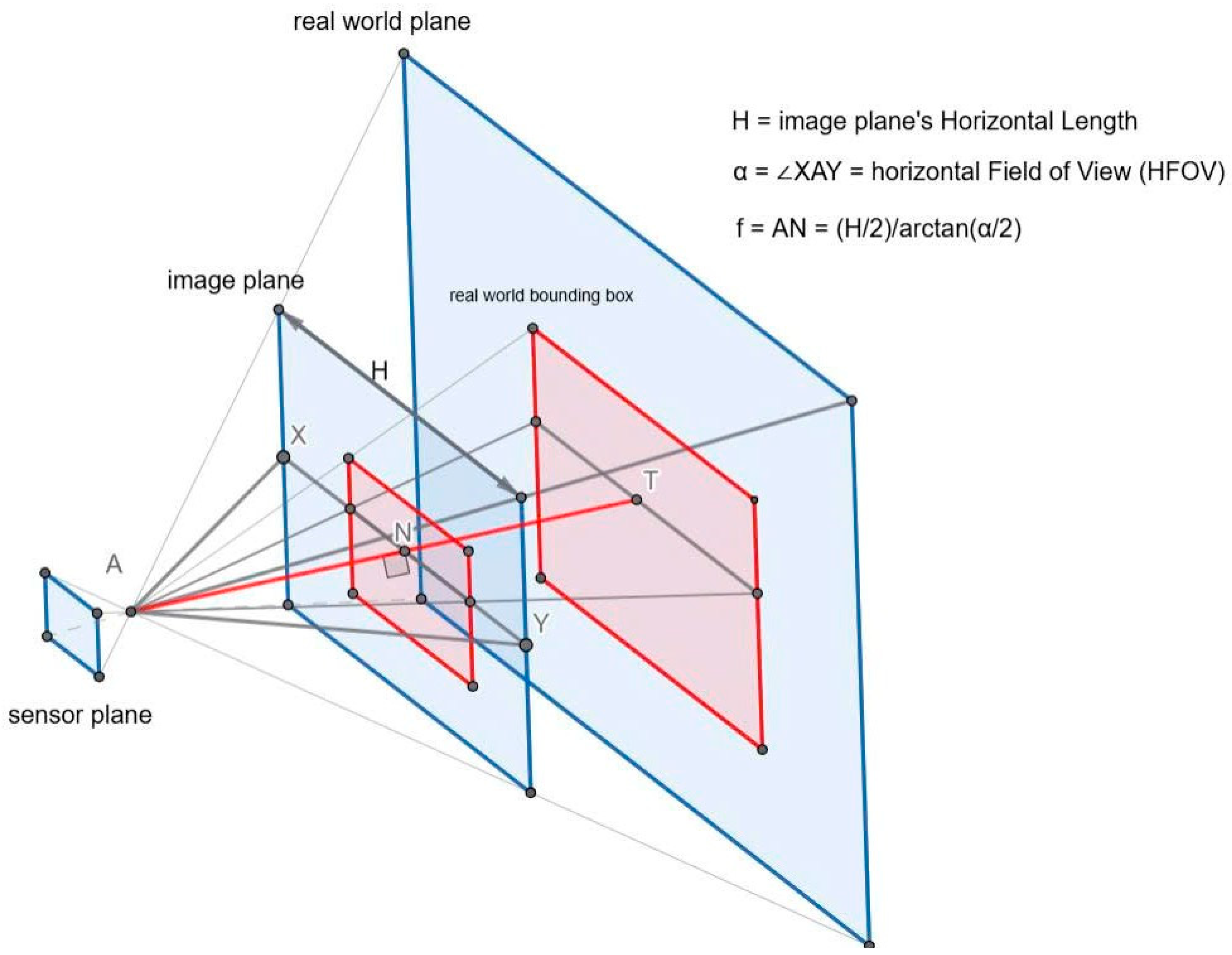
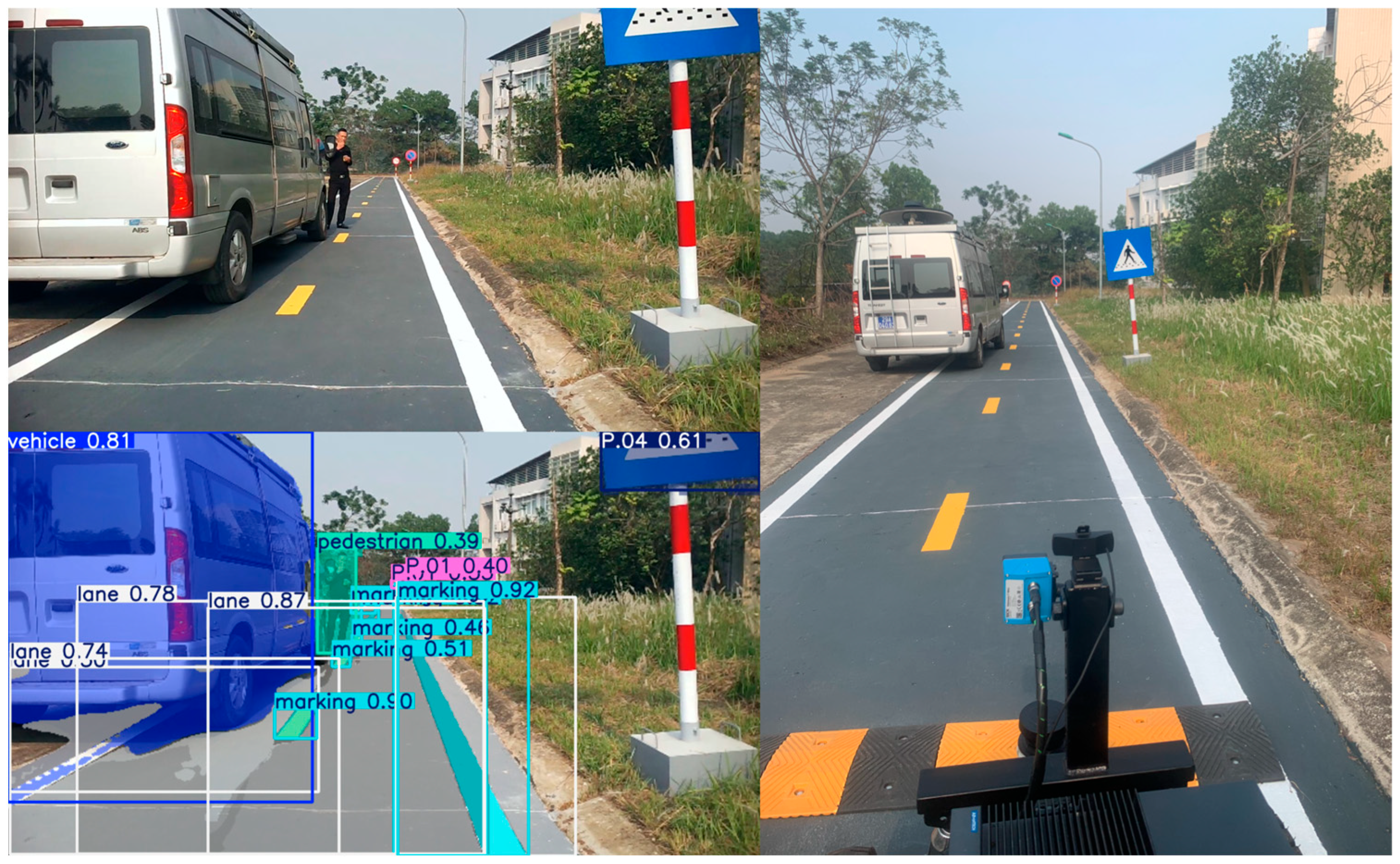
3.2.1. YOLOv8 Instance Segmentation and 2D LiDAR Fusion and Perception Visualization
3.2.2. Long-Short-Term Decision-Making Architecture Based on Sensor Exploitation
4. Experiments and Results
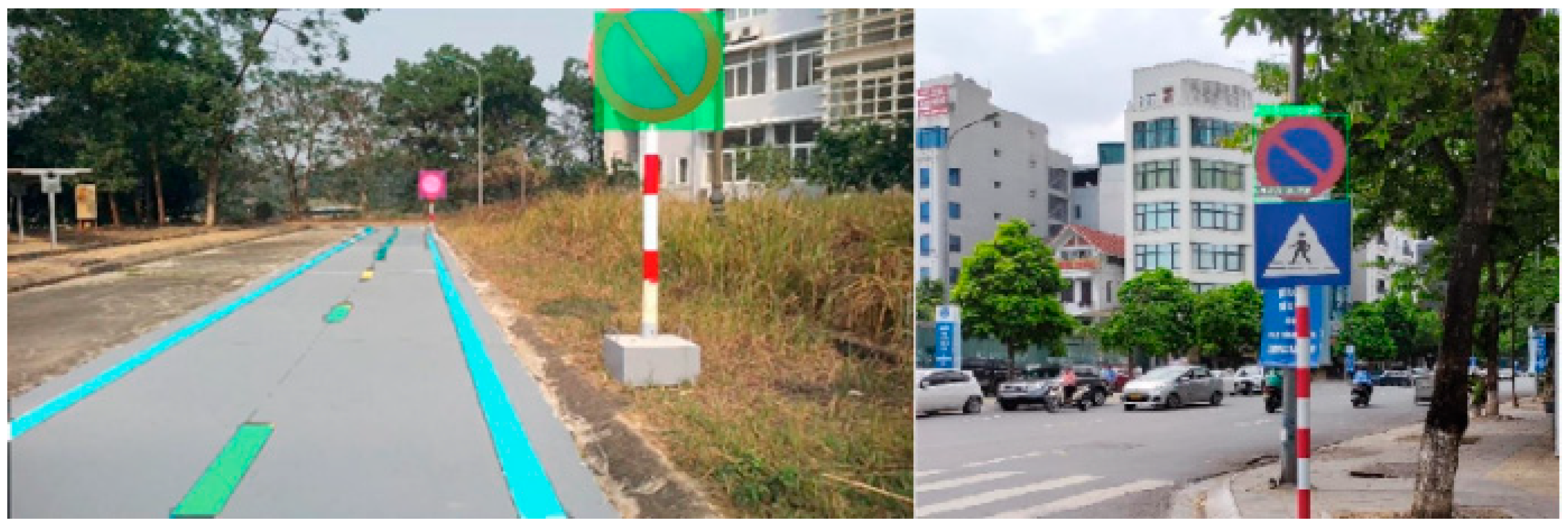
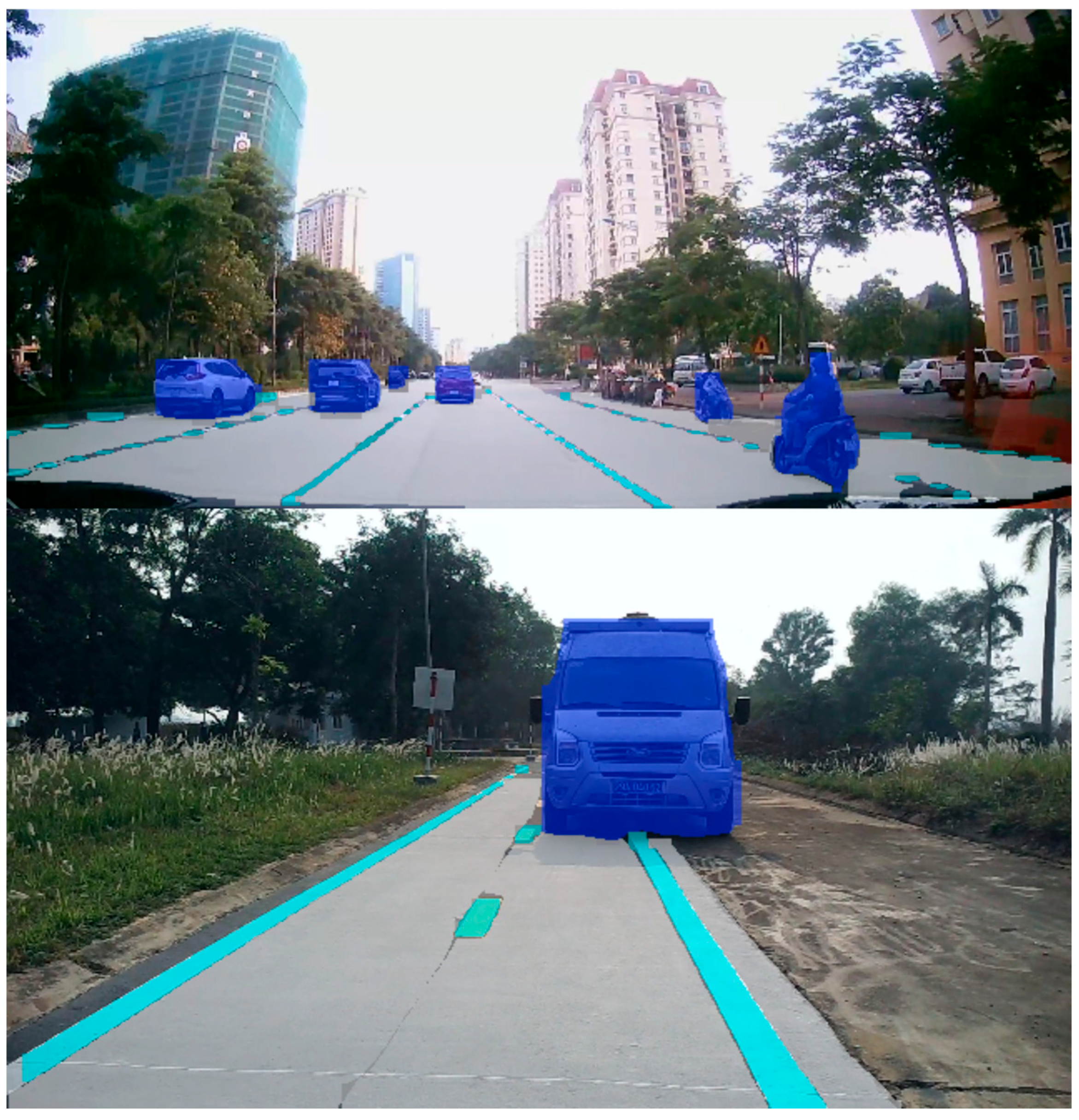
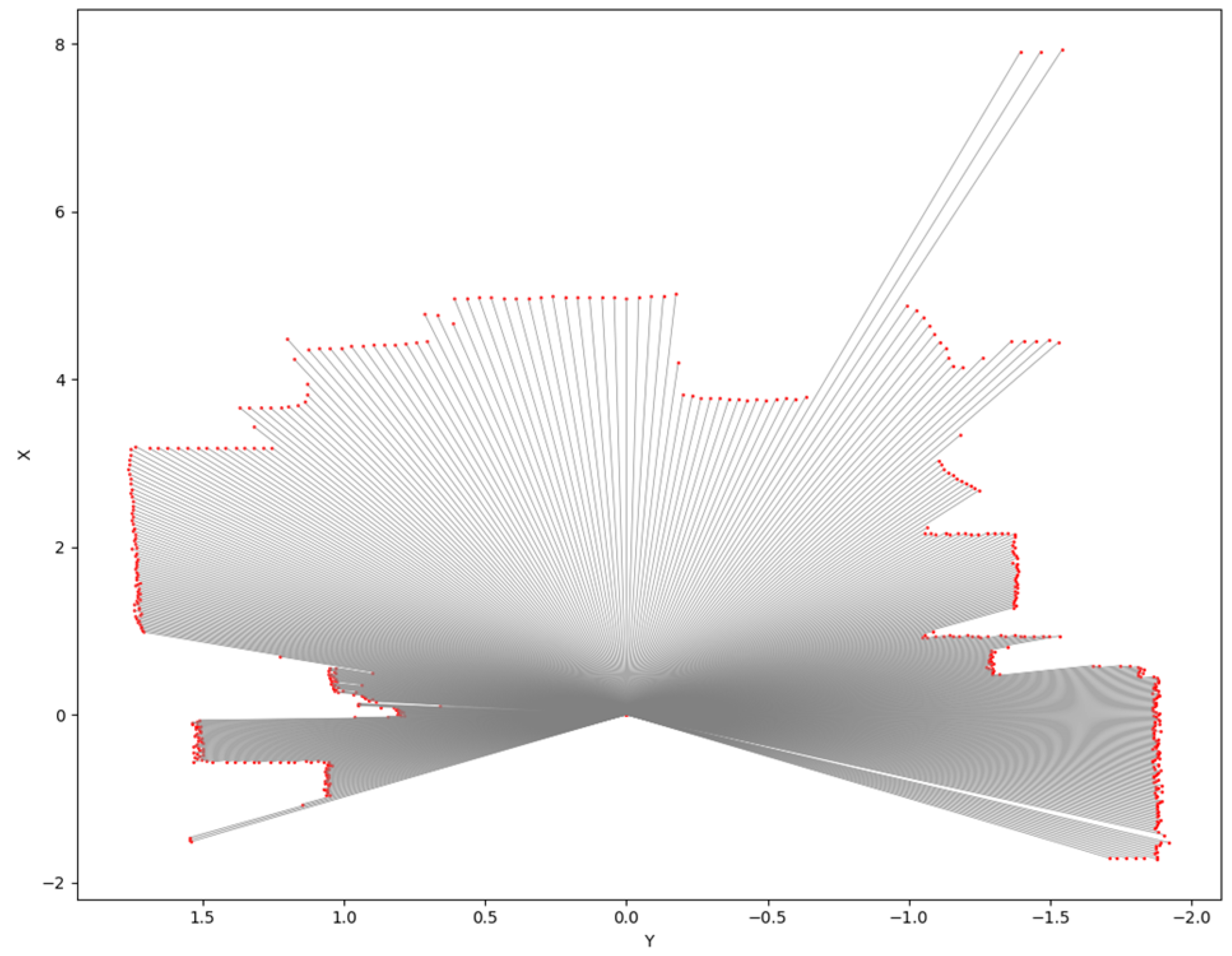
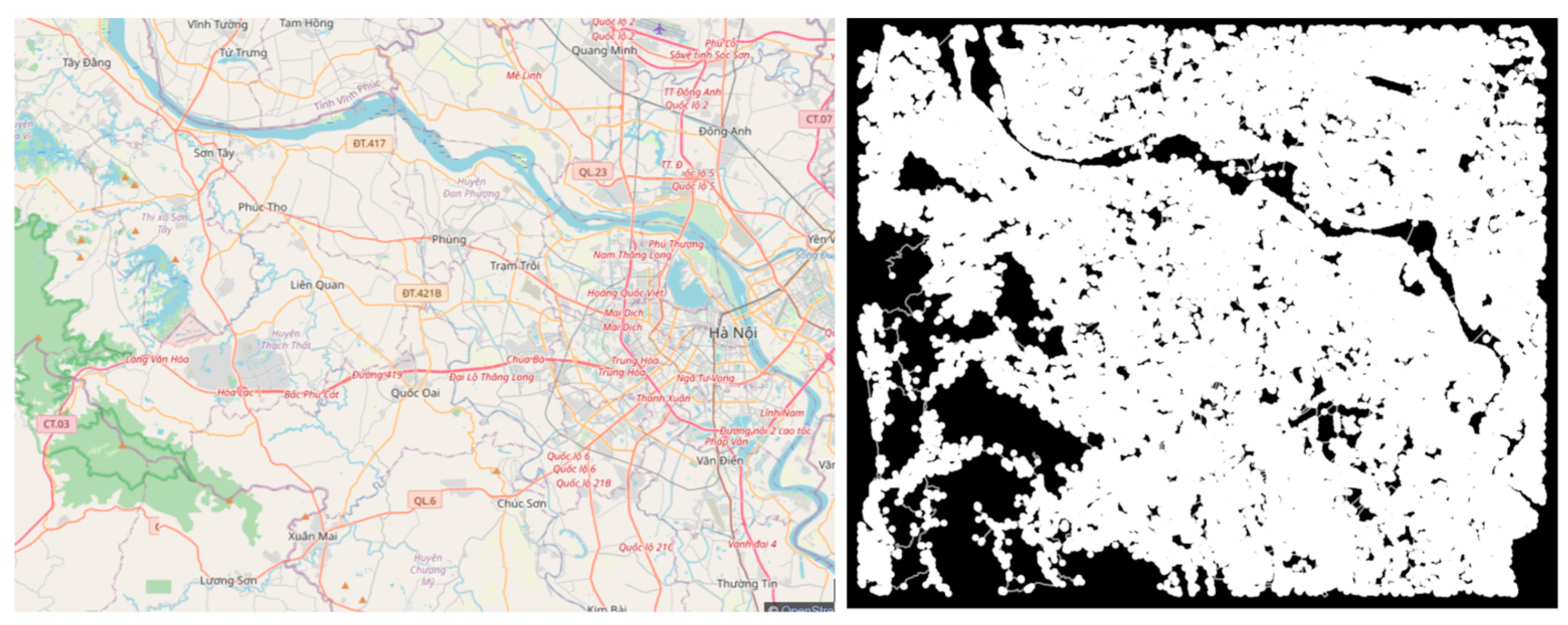
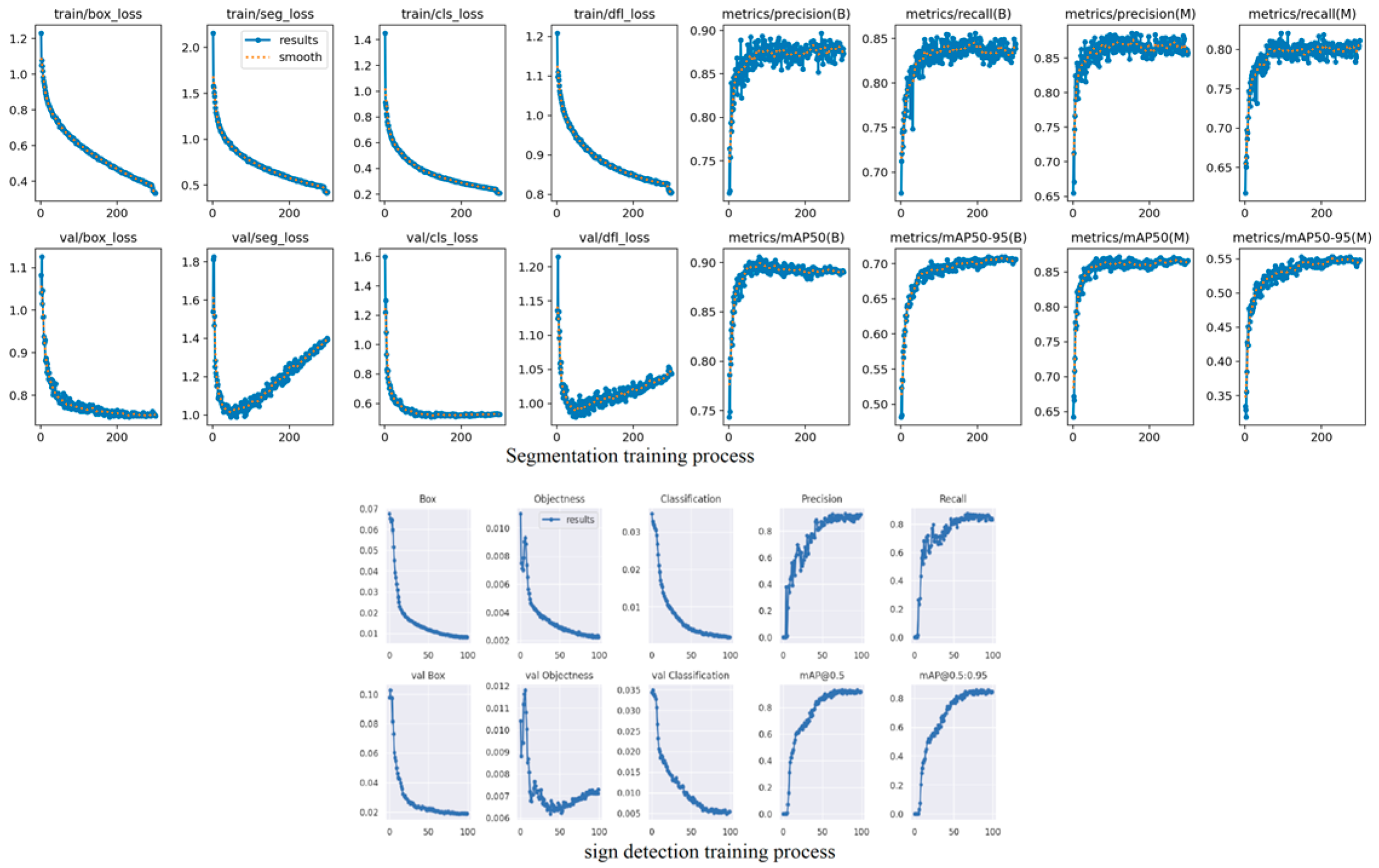
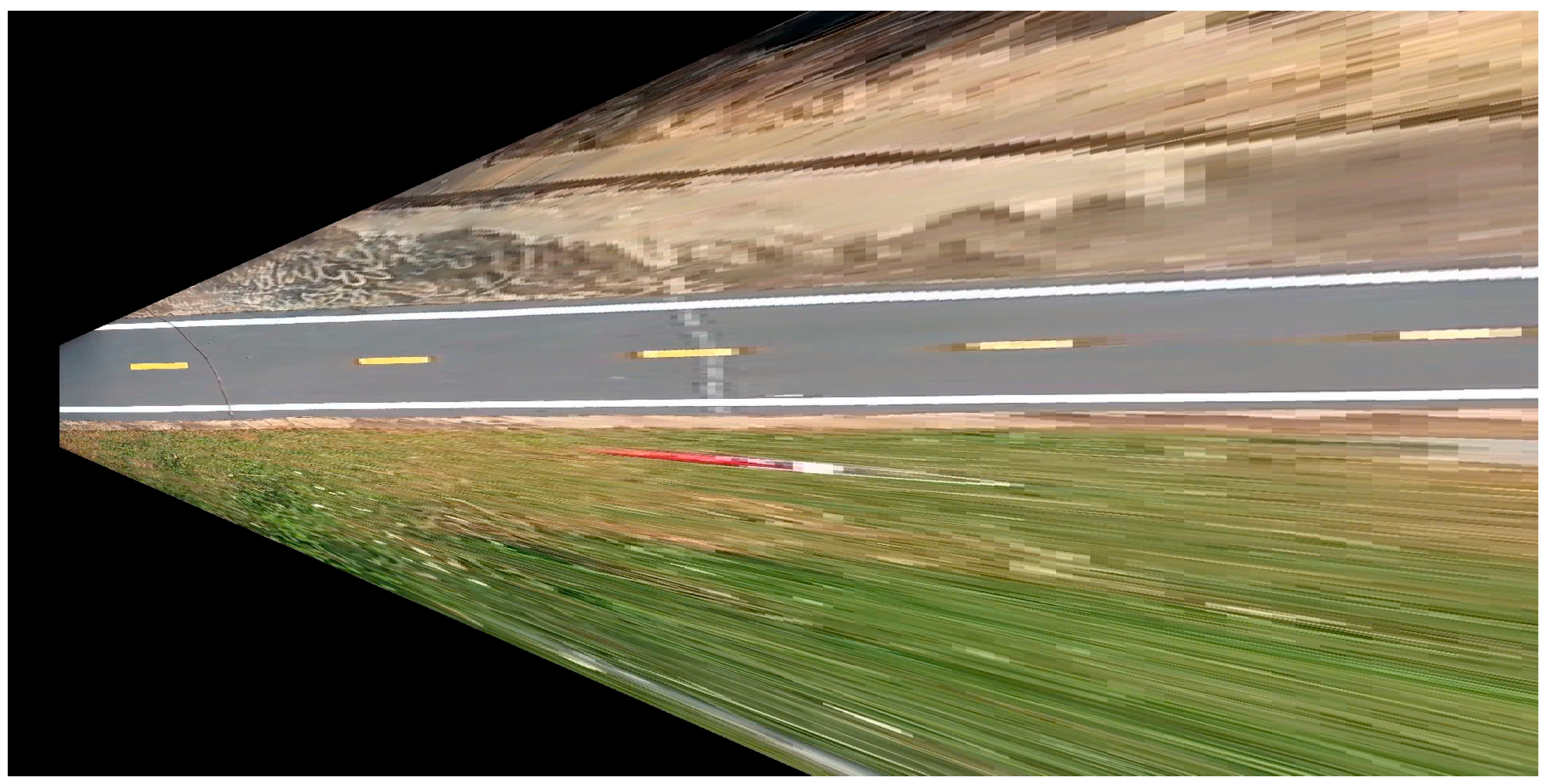
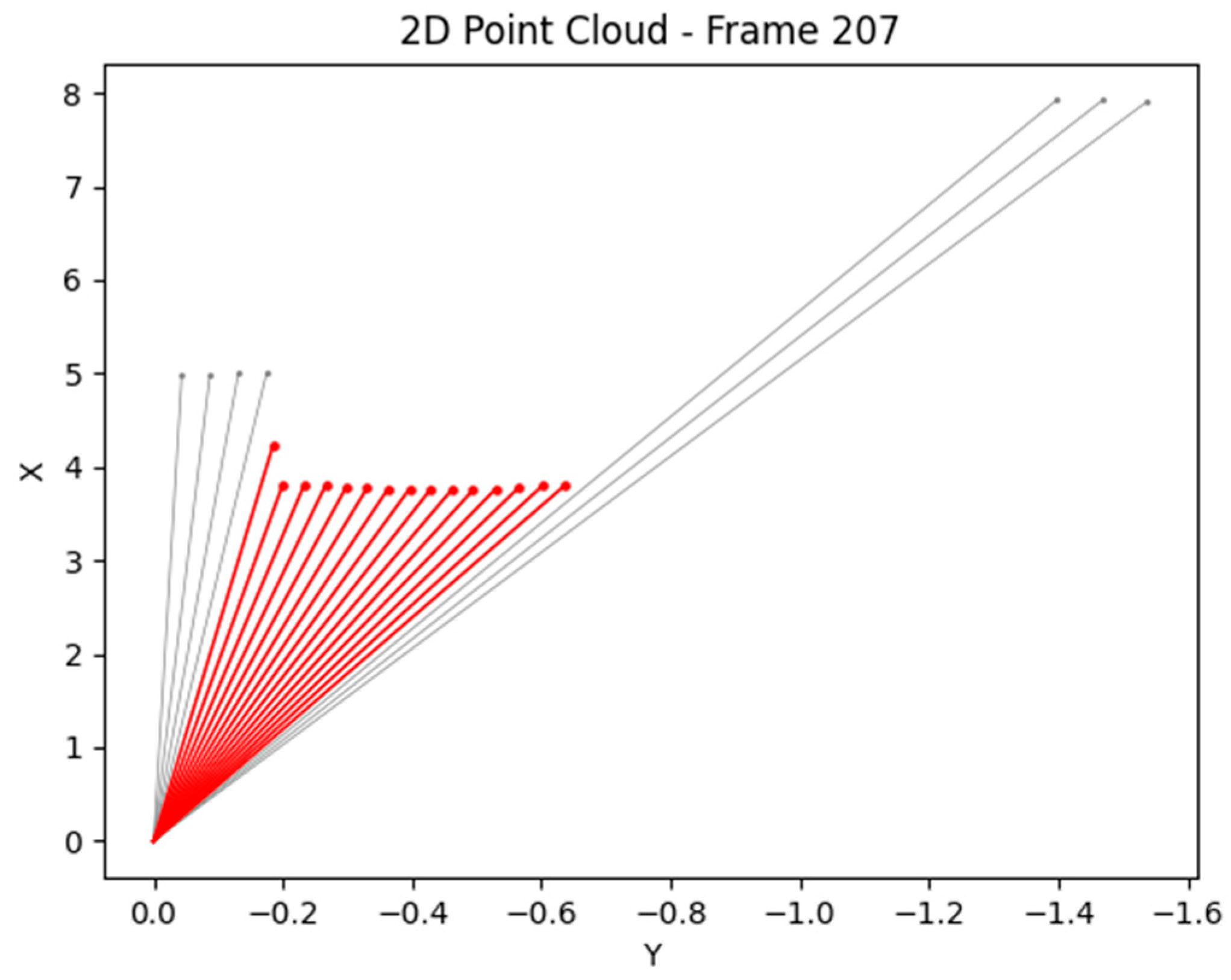
4.1. Results of YOLOv8 Instance Segmentation and 2D LiDAR Fusion and Top View for Vehicle Front-View Visualization
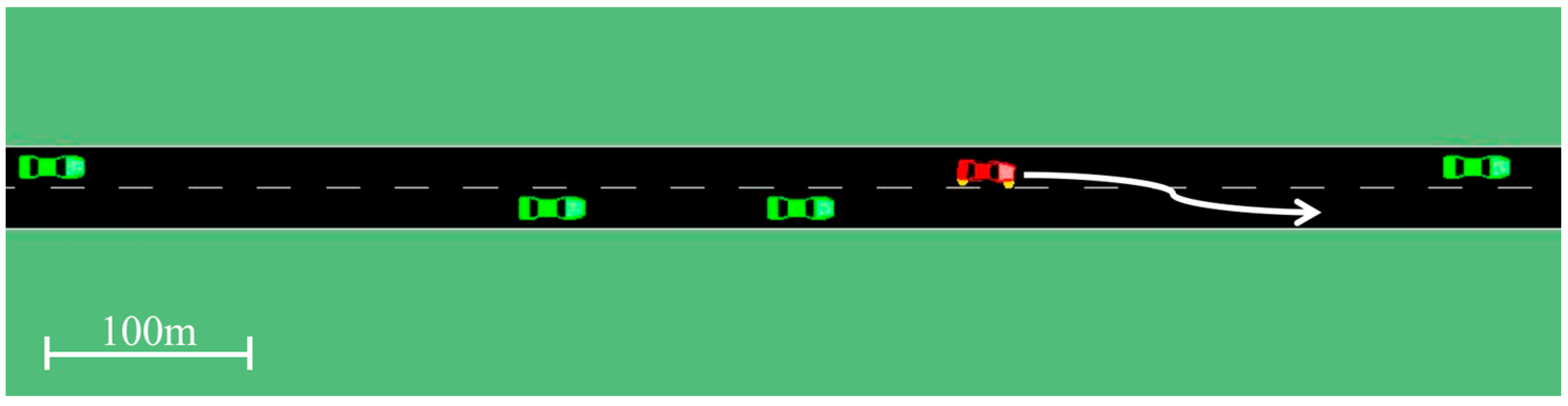
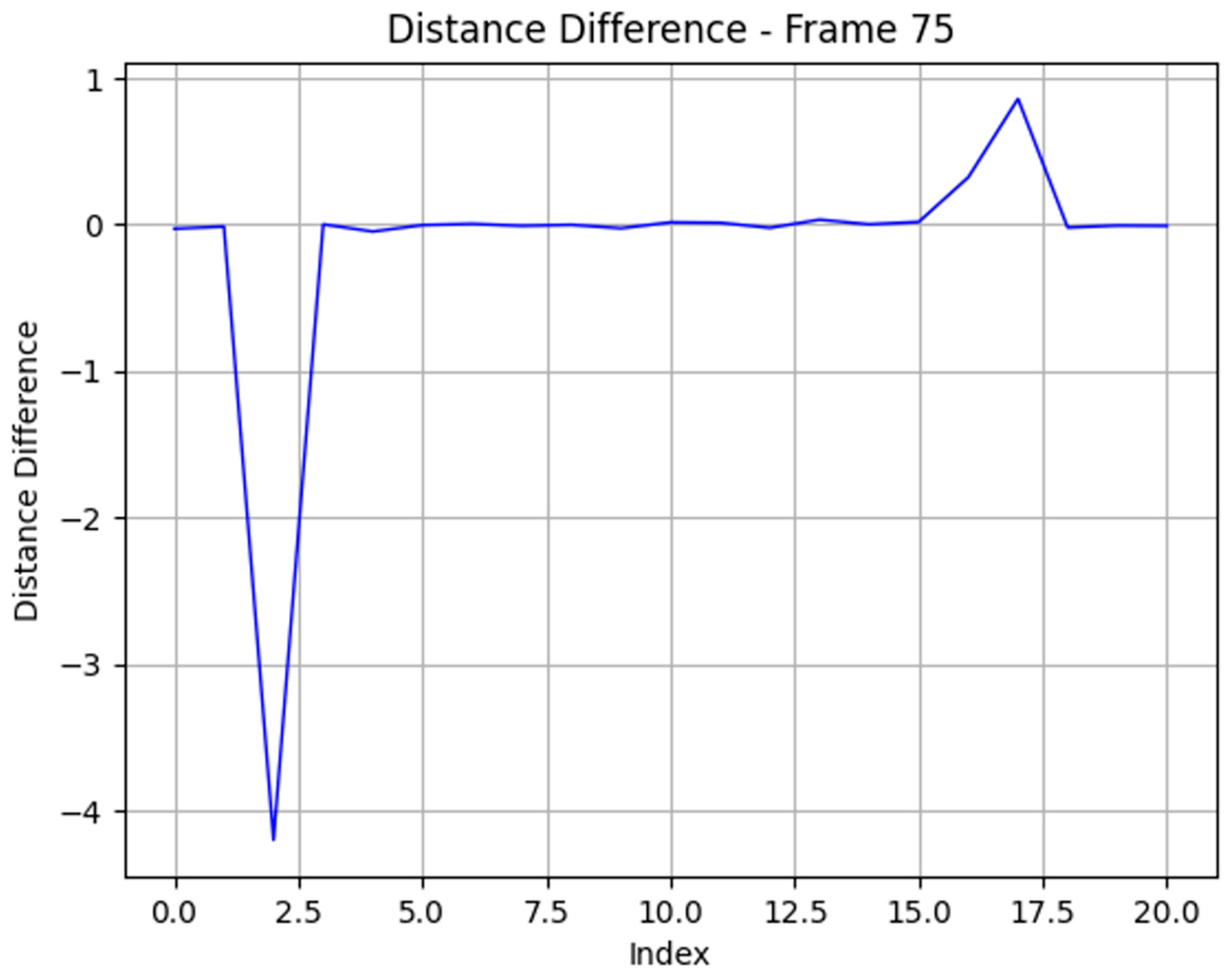
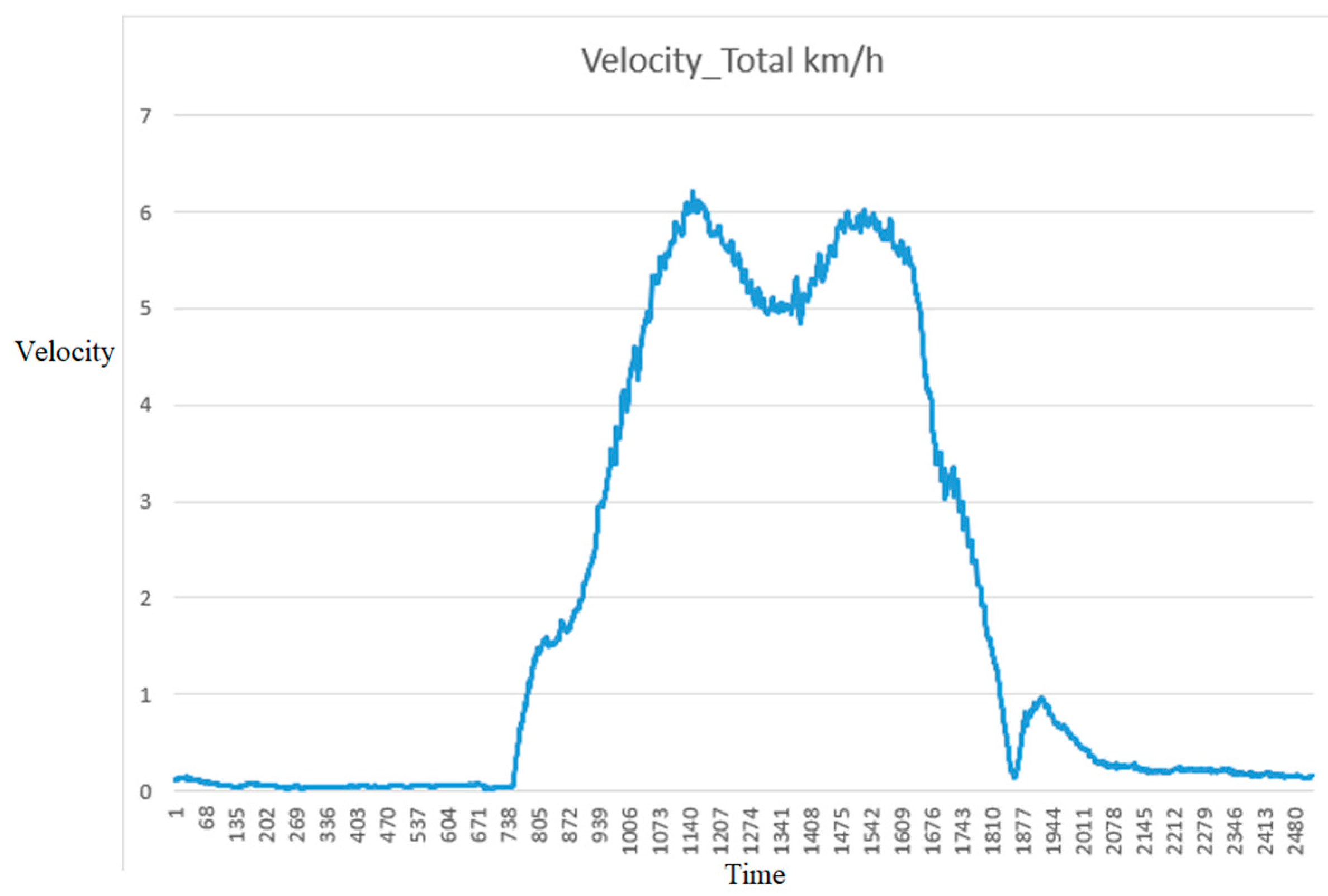
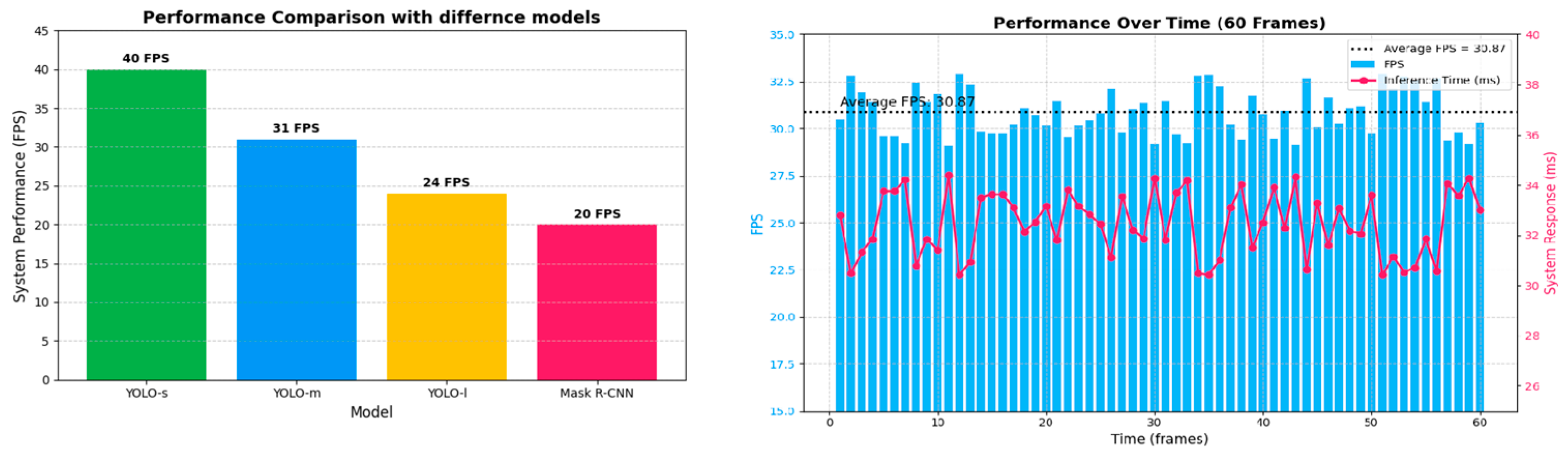
4.2. Result of System Response
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| YOLO | You Only Look Once |
| BEV | Bird’s-eye view |
| ROS | Robot Operating System |
References
- Ghraizi, D.; Talj, R.; Francis, C. An overview of decision-making in autonomous vehicles. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2023, 56, 10971–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.P.; Luong, T.N.; Xuan, T.P.; Duc, M.T.; Van Bach, N.P.; Minh, T.P.; Trong, T.B.; Huy, H.L. Study on a method for detecting and tracking multiple traffic signals at the same time using YOLOv7 and SORT object tracking. Int. Conf. Robot. Autom. Eng. 2023, 8, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, P.X.; Thien, N.L.; Ngoc, P.V.B.; Vu, M.H. Research and Development of a Traffic Sign Recognition Module in Vietnam. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2024, 14, 12740–12744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Y.Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Hu, L. Vehicle–pedestrian detection method based on improved YOLOv8. Electronics 2024, 13, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Improved YOLOv8 for small traffic sign detection under complex environmental conditions. Frankl. Open 2024, 8, 100167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ma, J.; Zhao, P. SDG-YOLOv8: Single-domain generalized object detection based on domain diversity in traffic road scenes. Displays 2025, 87, 102944. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanujjaman, M.; Chowdhury, M.Z.; Jang, Y.M. Sensor Fusion in Autonomous Vehicle with Traffic Surveillance Camera System: Detection, Localization, and AI Networking. Sensors 2023, 23, 3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Guan, Z.; Chen, Q.; Xu, Y.; Sun, F. Enhanced object detection in autonomous vehicles through LiDAR—Camera sensor fusion. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurtsever, E.; Lambert, J.; Carballo, A.; Takeda, K. A survey of autonomous driving: Common practices and emerging technologies. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 58443–58469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Stiller, C.; Urtasun, R. Vision meets robotics: The KITTI dataset. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.; Chitta, K.; Geiger, A. Multi-modal fusion transformer for end-to-end autonomous driving. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.09224. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Fu, W.; Song, Q.; Zhou, J. Potential risk assessment for safe driving of autonomous vehicles under occluded vision. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Q. Evolutionary decision-making and planning for autonomous driving based on safe and rational exploration and exploitation. Engineering 2024, 33, 108–120. [Google Scholar]
- Badue, C.; Guidolini, R.; Carneiro, R.V.; Azevedo, P.; Cardoso, V.B.; Forechi, A.; Jesus, L.; Berriel, R.; Paixão, T.; Mutz, F.; et al. Self-driving cars: A survey. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 165, 113816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Qu, X.; Lyu, N.; Li, S.E. Decision making of autonomous vehicles in lane change scenarios: Deep reinforcement learning approaches with risk awareness. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2022, 134, 103452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gong, X.; Chen, Y.H.; Huang, J.; Zhong, Z. Integrated Path Planning-Control Design for Autonomous Vehicles in Intelligent Transportation Systems: A Neural-Activation Approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 7602–7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viadero-Monasterio, F.; Meléndez-Useros, M.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, H.; Boada, B.; Boada, M. Motion Planning and Robust Output-Feedback Trajectory Tracking Control for Multiple Intelligent and Connected Vehicles in Unsignalized Intersections. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meléndez-Useros, M.; Viadero-Monasterio, F.; Jiménez-Salas, M.; López-Boada, M.J. Static Output-Feedback Path-Tracking Controller Tolerant to Steering Actuator Faults for Distributed Driven Electric Vehicles. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wu, X.; He, X.S. Vibration-Theoretic Approach to Vulnerability Analysis of Nonlinear Vehicle Platoons. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 11334–11344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xie, A.; Liu, X. Autonomous Vehicle Decision and Control through Reinforcement Learning with Traffic Flow Randomization. Machines 2024, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmin, A.; Shen, B.; Cheema, M.A.; Toosi, A.N.; Ali, M.E. Efficient alternative route planning in road networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 1234–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X. Deep reinforcement learning based dynamic route planning for minimizing travel time. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–23 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Verbytskyi, Y. Delivery routes optimization using machine learning algorithms. East. Eur. Econ. Bus. Manag. 2023, 38, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viadero-Monasterio, F.; Alonso-Rentería, L.; Pérez-Oria, J.; Viadero-Rueda, F. Radar-Based Pedestrian and Vehicle Detection and Identification for Driving Assistance. Vehicles 2024, 6, 1185–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A. Sampling-based path planning algorithms: A survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.14839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, P.; Thakur, A. Real-time obstacle avoidance algorithm for dynamic environment on probabilistic road map. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Symposium of Asian Control Association on Intelligent Robotics and Industrial Automation (IRIA), Goa, India, 20–22 September 2021; pp. 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F.; Rafique, S.; Khan, S.; Hasan, L. Smart Fire Safety: Real-Time Segmentation and Alerts Using Deep Learning. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Technol. (IJIST) 2024, 6, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Mulyanto, A.; Borman, R.I.; Prasetyawana, P.; Sumarudin, A. 2D LiDAR and camera fusion for object detection and object distance measurement of ADAS using Robotic Operating System (ROS). JOIV Int. J. Inform. Vis 2020, 4, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Szeliski, R. Computer Vision: Algorithms and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; p. 66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Guan, H.; Jia, X. An interpretable decision-making model for autonomous driving. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2024, 16, 16878132241255455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Guo, L. Localization and Mapping Based on Multi-feature and Multi-sensor Fusion. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2024, 25, 1503–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Ding, W.; Yang, M.; Zhu, H.; Dai, P. Benchmarking Perception to Streaming Inputs in Vision-Centric Autonomous Driving. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, H.N.; Luong, T.N.; Minh, T.P.; Hong, N.M.T.; Anh, K.T.; Hong, Q.B.; Bach, N.P.V. Integration of Multi-Sensor Fusion and Decision-Making Architecture for Autonomous Vehicles in Multi-Object Traffic Conditions. Sensors 2025, 25, 7083. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227083
Nguyen HN, Luong TN, Minh TP, Hong NMT, Anh KT, Hong QB, Bach NPV. Integration of Multi-Sensor Fusion and Decision-Making Architecture for Autonomous Vehicles in Multi-Object Traffic Conditions. Sensors. 2025; 25(22):7083. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227083
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Hai Ngoc, Thien Nguyen Luong, Tuan Pham Minh, Nguyen Mai Thi Hong, Kiet Tran Anh, Quan Bui Hong, and Ngoc Pham Van Bach. 2025. "Integration of Multi-Sensor Fusion and Decision-Making Architecture for Autonomous Vehicles in Multi-Object Traffic Conditions" Sensors 25, no. 22: 7083. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227083
APA StyleNguyen, H. N., Luong, T. N., Minh, T. P., Hong, N. M. T., Anh, K. T., Hong, Q. B., & Bach, N. P. V. (2025). Integration of Multi-Sensor Fusion and Decision-Making Architecture for Autonomous Vehicles in Multi-Object Traffic Conditions. Sensors, 25(22), 7083. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227083





