Evaluation of Reaction Time and Hand–Eye Coordination in Schoolchildren Using Wearable Sensor-Based Systems: A Study with Neural Trainer Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Instrumentation
- Visual activity with red color selection only;
- Four nodes per station, approximately 20 cm apart;
- Motion sensor set to low mode;
- Light duration: 10 s;
- Start with an automatic countdown.
2.4. Evaluation Protocol
2.4.1. Evaluation Conditions
2.4.2. Implemented Tests
- (a)
- First evaluation: Time to complete 10 repetitions
- (b)
- Second evaluation: Number of hits in 15 s
- Test P1—10 timed repetitions, bimanual
- Duration: 10 repetitions;
- Modality: Both hands;
- Variable measured: Total time in seconds;
- Record: Time, hits, and average reaction time.
- Test P2—10 timed repetitions, left hand
- Duration: 10 repetitions;
- Modality: Left hand only;
- Variable measured: Total time in seconds;
- Record: Time, hits, and average reaction time.
- Test P3—10 timed repetitions, right hand (see Figure 2)
- Duration: 10 repetitions;
- Modality: Right hand only;
- Variable measured: Total time in seconds;
- Record: Time, hits, and average reaction time.
- Test P4—Hits, bimanual
- Duration: 15 s;
- Modality: Both hands;
- Variable measured: Number of hits;
- Record: Hits, errors, and average reaction time.
- Test P5—Hits, left hand
- Duration: 15 s;
- Modality: Left hand only;
- Variable measured: Number of hits;
- Record: Hits, errors, and average reaction time.
- Test P6—Hits, right hand
- Duration: 15 s;
- Modality: Right hand only;
- Variable measured: Number of hits;
- Record: Hits, errors, and average reaction time.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Data Distribution Analysis
3.3. Correlation Analysis
- P5 (15 s hits, left hand) and P6 (15 s hits, right hand) (r = 0.533, p < 0.001): moderate positive correlation between left- and right-handed guesses.
- P4 (15 s hits, bimanual) and P5 (15 s hits, left hand) (r = 0.481, p < 0.001): moderate positive correlation between bimanual and left-handed guesses.
- P2 (10-repetition time, left hand) and P3 (10-repetition time, right hand) (r = 0.392, p < 0.01): moderate positive correlation between left- and right-handed guesses.
3.4. Analysis of Lateral Differences
3.4.1. Comparison of Times (P2 vs. P3)
3.4.2. Comparison of Hits (P5 vs. P6)
3.5. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
3.5.1. Time Tests
3.5.2. Hit Tests
3.6. Visualization of Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diamond, A. Executive Functions. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2013, 64, 135–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, L.M.R.; Collado, N.R.; Sanz, J.L.G.; Nieto, M.P.; Coll, M.V.G. GRAMI-2: Desarrollo de un test para evaluar la coordinación motriz global en la educación primaria. Rev. Iberoam. Psicol. Ejerc. Deporte 2015, 10, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- de Brito, M.A.; Fernandes, J.R.; Esteves, N.S.; Müller, V.T.; Alexandria, D.B.; Pérez, D.I.V.; Slimani, M.; Brito, C.J.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Miarka, B. The Effect of Neurofeedback on the Reaction Time and Cognitive Performance of Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 868450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irawan, R.; Yenes, R.; Mario, D.T.; Komaini, A.; García-Fernández, J.; Orhan, B.E.; Ayubi, N. Design of a sensor technology-based hand-eye coordination measuring tool: Validity and reliability. Retos 2024, 56, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, N.; Moscatelli, F.; Di Padova, M.; Mancini, S.; Basta, A.; Guerriero, M.A.; Di Pace, A.; Limone, P.; Colella, D.; Grosu, V.T. The relationship between reaction time and agility performance in young athletes: A study using perception–action technological devices. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2024, 24, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, C.L.; Hendry, D.; Thomas, G.; Beynon, A.; Stearne, S.; Zabatiero, J.; Davey, P.; Larsen, J.R.; Rohl, A.L.; Straker, L.; et al. Evaluation of the Motus wearable sensor based system to accurately classify postures and movements in 3–14 aged children. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado de León, F.; Cortes, R. Tremün: Plataforma Para Entrenamiento Cognitivo Aplicado al Deporte. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Nacional de La Plata, La Plata, Argentina, 2020. Available online: https://sedici.unlp.edu.ar/handle/10915/118513 (accessed on 10 September 2025).
- Johnson, K.T.; Picard, R.W. Advancing neuroscience through wearable devices. Neuron 2020, 108, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouder, J.N.; Haaf, J.M. A psychometrics of individual differences in experimental tasks. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2019, 26, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ticona, N.P.; Salas, N.C.; Riveros, M.V.; Torres, J.S. Analysis of Psychophysical Performance with Neural Trainer Equipment and smartwatch in University Students: Study Based on Reaction Times and Successes in Motor Sequences. In INTED2025 Proceedings; Universidad Católica de Santa María: Arequipa, Peru, 2025; pp. 6795–6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L. Relationships between Motor Skills and Academic Achievement in School-Aged Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Children 2024, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Ye, D.; Zuo, J.; Liu, L. Research progress on the relationship between fine motor skills and academic ability in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Sports Act. Living 2025, 6, 1386967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Lee, H.; Li, W. Neural interfaces: Bridging the brain to the world beyond healthcare. Exploration 2024, 4, 20230146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuraltrainer.com—Boost Your Brain. Available online: https://neuraltrainer.com/ (accessed on 5 October 2025).
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykiert, D.; Der, G.; Starr, J.M.; Deary, I.J. Age differences in intra-individual variability in simple and choice reaction time: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goble, D.J.; Brown, S.H. Upper Limb Asymmetries in the Matching of Proprioceptive Versus Visual Targets. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 99, 3063–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decraene, L.; Orban de Xivry, J.-J.; Kleeren, L.; Crotti, M.; Verheyden, G.; Ortibus, E.; Feys, H.; Mailleux, L.; Klingels, K. In-depth quantification of bimanual coordination using the Kinarm exoskeleton robot in children with unilateral cerebral palsy. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2023, 20, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, S.E.; Sudgen, D.A.; Barnett, A.L. Movement Assessment Battery for Children-2:(Movement ABC-2); Pearson Education Limited: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Frikha, M.; Alharbi, R.S. Optimizing Fine Motor Coordination, Selective Attention and Reaction Time in Children: Effect of Combined Accuracy Exercises and Visual Art Activities. Children 2023, 10, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mia, M.R.; Ahamed, S.I.; Fial, A.; Nemanich, S. A Scoping Review on Mobile Health Technology for Assessment and Intervention of Upper Limb Motor Function in Children with Motor Impairments. Games Health J. 2024, 13, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, E.; Airaksinen, M.; Gallen, A.; Immonen, T.; Ilén, E.; Palsa, T.; Haataja, L.M.; Vanhatalo, S. Quantified Assessment of Infant’s Gross Motor Abilities Using a Multisensor Wearable. J. Vis. Exp. 2024, 207, e65949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Wang, X.; Lian, P.; Lu, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, X.; Hu, Q.; Zheng, H. Wearable Sensor-Based Multi-modal Fusion Network for Automated Gait Dysfunction Assessment in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2024, 6, 2300845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, S.A.; Feldman, J.F.; Jankowski, J.J. Modeling a cascade of effects: The role of speed and executive functioning in preterm/full-term differences in academic achievement: Executive function in preterm adolescents. Dev. Sci. 2011, 14, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prichard, E.; Propper, R.E.; Christman, S.D. Degree of handedness, but not direction, is a systematic predictor of cognitive performance. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






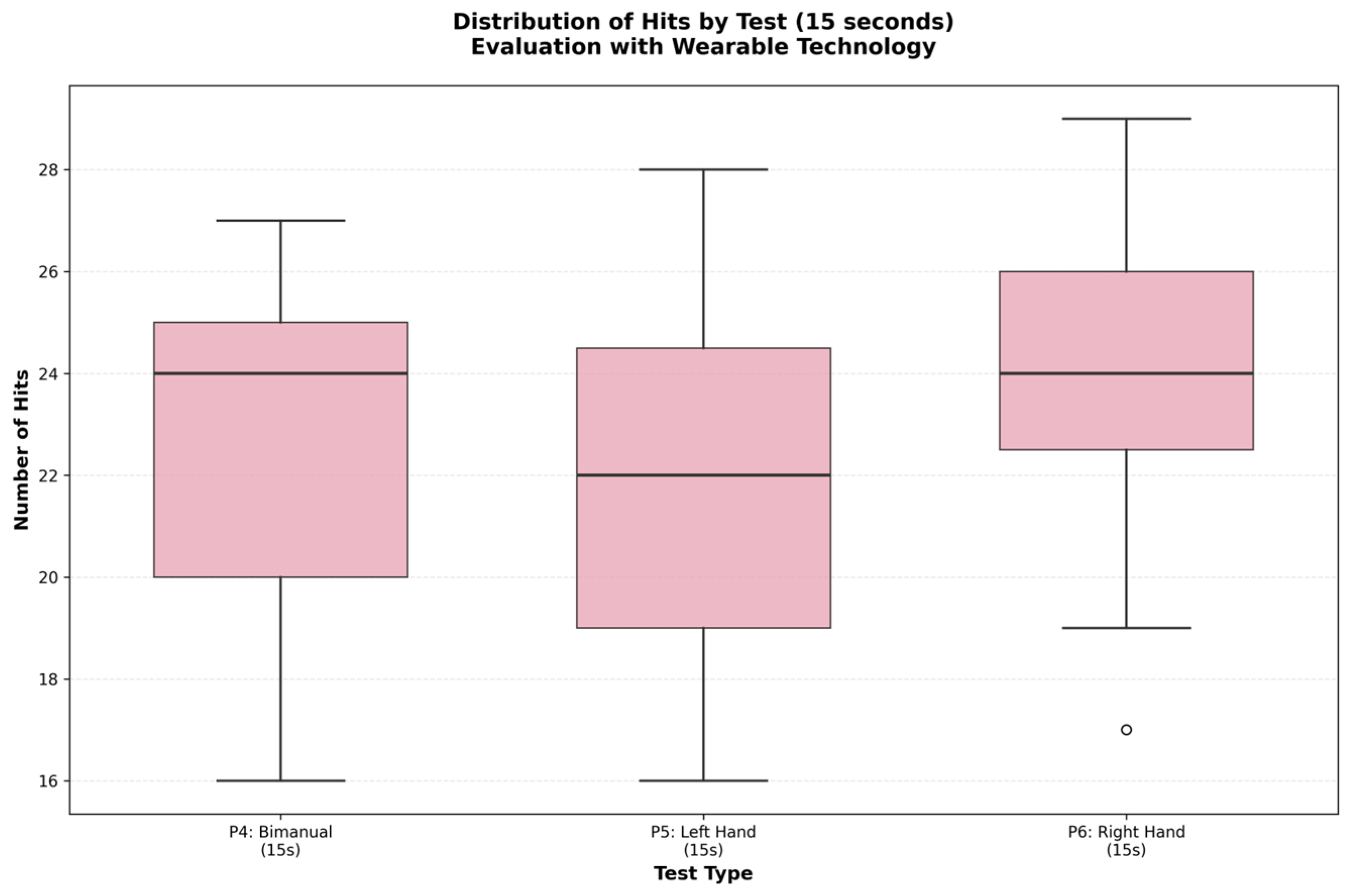
| Tests | Description | N | Mean | S.D. | Min | Max | Q1 | Q3 | IC95_inf | IC95_sup |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | Time 10 reps, bimanual. | 59 | 8.6949 | 1.4414 | 6 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 8.3271 | 9.0627 |
| P2 | Time 10 reps, left hand. | 59 | 8.8983 | 1.2958 | 5 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 8.5676 | 9.2289 |
| P3 | Time 10 reps, right hand. | 59 | 8.8305 | 1.2885 | 6 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 8.5017 | 9.1593 |
| P4 | Hits, bimanual. | 59 | 22.8983 | 3.1000 | 16 | 27 | 20 | 25 | 22.1072 | 23.6893 |
| P5 | Hits, left hand. | 59 | 22 | 3.3987 | 16 | 28 | 19 | 24.5 | 21.1327 | 22.8672 |
| P6 | Hits, right hand. | 59 | 24.4237 | 2.7241 | 17 | 29 | 22.5 | 26 | 23.7286 | 25.1188 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sulla-Torres, J.A.; Chavez-Salas, N.Y.; Valverde-Riveros, M.F.; Iquira-Becerra, D.A.; Rosas-Paredes, K.; Cossio-Bolaños, M.A. Evaluation of Reaction Time and Hand–Eye Coordination in Schoolchildren Using Wearable Sensor-Based Systems: A Study with Neural Trainer Devices. Sensors 2025, 25, 7006. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227006
Sulla-Torres JA, Chavez-Salas NY, Valverde-Riveros MF, Iquira-Becerra DA, Rosas-Paredes K, Cossio-Bolaños MA. Evaluation of Reaction Time and Hand–Eye Coordination in Schoolchildren Using Wearable Sensor-Based Systems: A Study with Neural Trainer Devices. Sensors. 2025; 25(22):7006. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227006
Chicago/Turabian StyleSulla-Torres, José Alfredo, Nadia Yunorvi Chavez-Salas, María Fernanda Valverde-Riveros, Diego Alonso Iquira-Becerra, Karina Rosas-Paredes, and Marco Antonio Cossio-Bolaños. 2025. "Evaluation of Reaction Time and Hand–Eye Coordination in Schoolchildren Using Wearable Sensor-Based Systems: A Study with Neural Trainer Devices" Sensors 25, no. 22: 7006. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227006
APA StyleSulla-Torres, J. A., Chavez-Salas, N. Y., Valverde-Riveros, M. F., Iquira-Becerra, D. A., Rosas-Paredes, K., & Cossio-Bolaños, M. A. (2025). Evaluation of Reaction Time and Hand–Eye Coordination in Schoolchildren Using Wearable Sensor-Based Systems: A Study with Neural Trainer Devices. Sensors, 25(22), 7006. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25227006






