Occluded Person Re-Identification via Multi-Branch Interaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Multi-head attention is employed to supplement the high-level feature with discriminative cues.
- A dual-classifier fusion mechanism is designed to adaptively assign weights to different views, generating a comprehensive pedestrian representation.
- Mutual distillation is introduced to establish collaborative learning pathways across branches, enhancing the consistency of multi-branch features.
- Extensive experiments are conducted on five public person re-ID datasets to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
2. Related Works
2.1. Occluded Person Re-ID
2.2. Distillation Learning
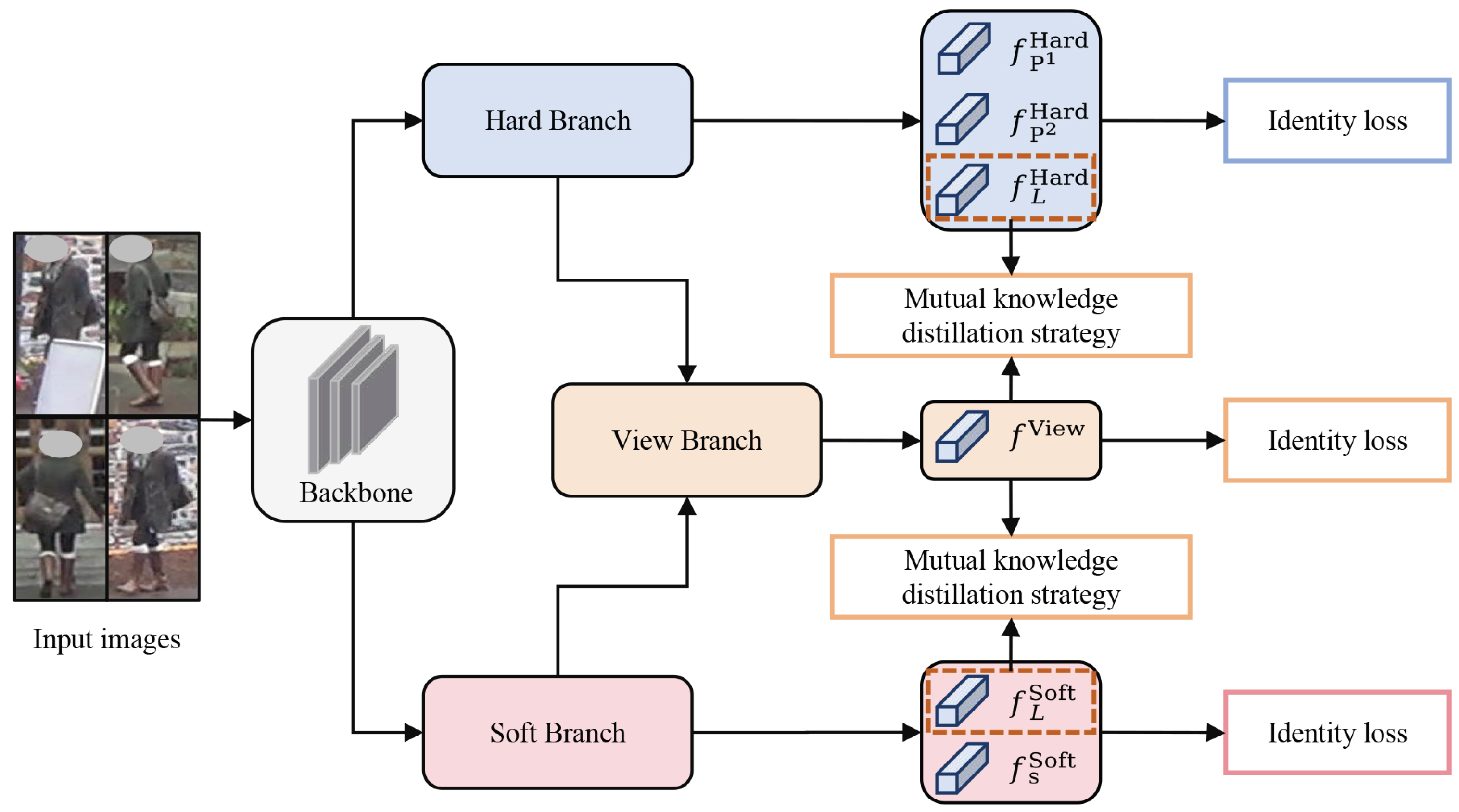
3. The Proposed Method
3.1. Hard Branch
3.2. Soft Branch
3.3. View Branch
3.4. Mutual Knowledge Distillation Strategy
3.5. Loss Function
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
4.1.1. Datasets
4.1.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.3. Performance Comparison
| Method | Occluded-DukeMTMC | Occluded-REID | P-DukeMTMC-reID | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | Rank-1 | mAP | Rank-1 | mAP | Rank-1 | |
| DSR [28] | 30.4 | 40.8 | 62.8 | 72.8 | 68.0 | 73.7 |
| PGFA [24] | 37.3 | 51.4 | - | - | 72.4 | 85.7 |
| PVPM [25] | 37.7 | 47.0 | 61.2 | 70.4 | - | - |
| HOReID [26] | 43.8 | 55.1 | 70.2 | 80.3 | - | - |
| Pirt [27] | 50.9 | 60.0 | - | - | - | - |
| PGFL-KD [38] | 54.1 | 63.0 | 70.3 | 80.7 | - | - |
| IGOAS [48] | 49.4 | 60.1 | 81.1 | 91.6 | - | - |
| OAMN [29] | 46.1 | 62.6 | - | - | 77.4 | 86.0 |
| DPD-PAT [14] | 53.6 | 64.5 | 72.1 | 81.6 | - | - |
| TransReID [43] | 55.7 | 64.2 | 67.3 | 70.2 | 68.6 | 71.3 |
| FED [30] | 56.4 | 68.1 | 79.3 | 86.3 | 80.5 | 83.1 |
| MHSANet [15] | 44.8 | 59.7 | - | - | 37.6 | 67.9 |
| QPM [16] | 53.3 | 66.7 | - | - | 74.4 | 89.4 |
| CAAO [4] | 55.8 | 67.8 | 83.4 | 87.1 | 79.5 | 90.5 |
| DRL-Net [21] | 50.8 | 65.0 | - | - | - | - |
| RTGAT [17] | 50.1 | 61.0 | 51.0 | 71.8 | 74.3 | 85.6 |
| SCAT [51] | 54.9 | 62.8 | 76.1 | 80.4 | - | - |
| ViT-SPT [32] | 57.4 | 68.6 | 81.3 | 86.8 | - | - |
| MVIIP [31] | 57.3 | 68.6 | 77.4 | 85.5 | 79.0 | 91.5 |
| DPEFormer [50] | 58.9 | 69.9 | 79.5 | 87.0 | - | - |
| MBIN (Ours) | 59.1 | 71.2 | 87.1 | 92.8 | 82.5 | 93.0 |
| Method | Market-1501 | DukeMTMC-reID | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | Rank-1 | mAP | Rank-1 | |
| BOT [19] | 85.7 | 94.1 | 76.4 | 86.4 |
| PGFA [24] | 76.8 | 91.2 | 79.5 | 89.6 |
| HOReID [26] | 84.9 | 94.2 | 75.6 | 86.9 |
| ISP [53] | 88.6 | 94.9 | 78.4 | 88.9 |
| Pirt [27] | 86.3 | 94.1 | 77.6 | 88.9 |
| PGFL-KD [38] | 87.2 | 95.3 | 79.5 | 89.6 |
| DPD-PAT [14] | 88.0 | 95.4 | 78.2 | 88.8 |
| CAAO [4] | 87.3 | 95.1 | 77.5 | 88.9 |
| RTGAT [17] | 88.2 | 93.3 | 76.9 | 88.0 |
| DRL-Net [21] | 86.9 | 94.7 | 76.6 | 88.1 |
| PAT [52] | 81.5 | 92.4 | - | - |
| ViT-SPT [32] | 86.2 | 94.5 | 79.1 | 89.4 |
| MBIN (Ours) | 89.1 | 96.1 | 80.1 | 91.2 |
4.4. Ablation Studies
4.4.1. Effectiveness of Each Component
4.4.2. Effectiveness of the MKD Strategy
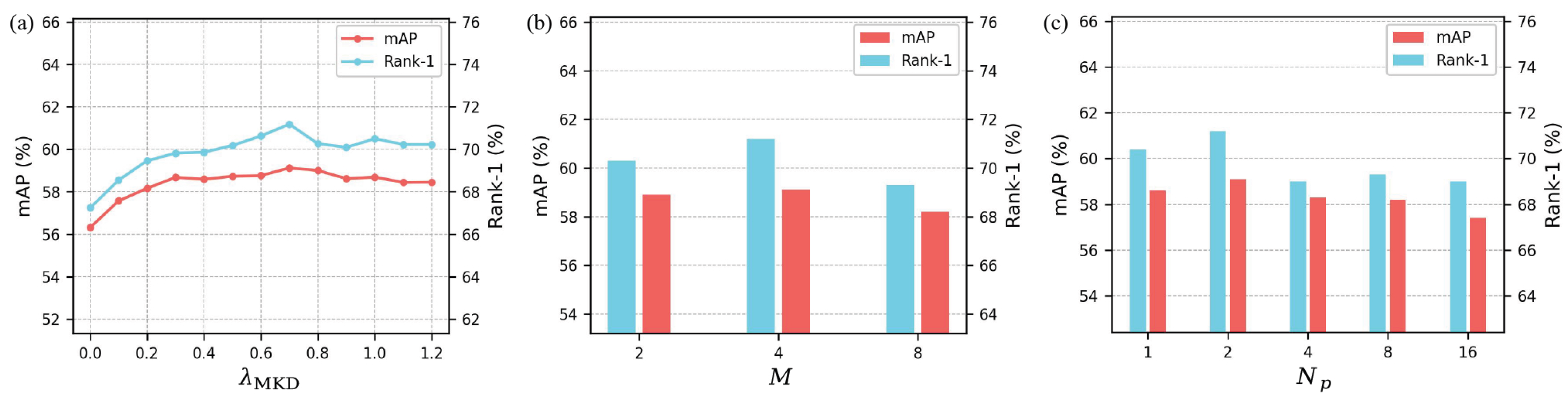
4.5. Parameter Analysis
4.5.1. Impact of the Hyperparameter
4.5.2. Impact of the Hyperparameter M
4.5.3. Impact of the Hyperparameter
4.6. Qualitative Analysis
4.6.1. Visualization of Retrieval Results
4.6.2. Visualization of Heatmap
4.7. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, N.; Liu, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Han, J. Deep learning for visible-infrared cross-modality person re-identification: A comprehensive review. Inf. Fusion 2023, 91, 396–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Chen, S.; Li, C.; Zheng, W.S.; Crandall, D.; Du, B. Transformer for object re-identification: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2024, 133, 2410–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, E.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Ning, X.; Tiwari, P. Occluded person re-identification with deep learning: A survey and perspectives. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 239, 122419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Qu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Tu, Y.; Bai, X. Content-adaptive auto-occlusion network for occluded person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 4223–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Kim, S.; Park, S.; Jeong, J. Person Re-Identification with Attribute-Guided, Robust-to-Low-Resolution Drone Footage Considering Fog/Edge Computing. Sensors 2025, 25, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; He, Y.; Hao, G. Identity Hides in Darkness: Learning Feature Discovery Transformer for Nighttime Person Re-Identification. Sensors 2025, 25, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asperti, A.; Naldi, L.; Fiorilla, S. An Investigation of the Domain Gap in CLIP-Based Person Re-Identification. Sensors 2025, 25, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Liu, W. Pedestrian Re-Identification Based on Fine-Grained Feature Learning and Fusion. Sensors 2024, 24, 7536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdoun, O.; Moutarde, F.; Stanciulescu, B.; Steux, B. Person re-identification in multi-camera system by signature based on interest point descriptors collected on short video sequences. In Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE International Conference on Distributed Smart Cameras, Palo Alto, CA, USA, 7–11 September 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kviatkovsky, I.; Adam, A.; Rivlin, E. Color invariants for person reidentification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 35, 1622–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, S.Z. Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Shenyang, China, 14–16 October 2015; pp. 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzani, L.; Cristani, M.; Murino, V. Symmetry-driven accumulation of local features for human characterization and re-identification. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2013, 117, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wang, S. Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 480–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F. Diverse part discovery: Occluded person re-identification with part-aware transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 2898–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Liu, X.; Yin, B.; Li, X. MHSA-Net: Multihead self-attention network for occluded person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 34, 8210–8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ding, C.; Shao, Z.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, S.; Tao, D. Quality-aware part models for occluded person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 3154–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Hou, C.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Z. Reasoning and tuning: Graph attention network for occluded person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 1568–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Nguyen, K.; Sridharan, S.; Fookes, C. AG-ReID. v2: Bridging aerial and ground views for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2024, 19, 2896–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Gu, Y.; Liao, X.; Lai, S.; Jiang, W. Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Y. Circle loss: A unified perspective of pair similarity optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6398–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Cheng, X.; Lu, S.; Zhang, J. Learning disentangled representation implicitly via transformer for occluded person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Peng, B.; Yan, W.Q. Dual knowledge distillation on multiview pseudo labels for unsupervised person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 7359–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Geng, X. Generalizable metric network for cross-domain person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 9039–9052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, P.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Y. Pose-guided feature alignment for occluded person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, J.; Lu, H.; Liu, Z. Pose-guided visible part matching for occluded person reid. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11744–11752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yu, G.; Zhou, E.; Sun, J. High-order information matters: Learning relation and topology for occluded person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6449–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J. Pose-guided inter-and intra-part relational transformer for occluded person re-identification. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Liang, J.; Li, H.; Sun, Z. Deep spatial feature reconstruction for partial person re-identification: Alignment-free approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7073–7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liu, W.; Dai, P.; Liu, J.; Ye, Q.; Xu, M.; Chen, Q.; Ji, R. Occlude them all: Occlusion-aware attention network for occluded person re-id. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11833–11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, F.; Tang, S.; Zhao, R.; He, L.; Song, J. Feature erasing and diffusion network for occluded person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4754–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Yan, S.; Tang, H.; Tang, J.; Zhang, L. Multi-view information integration and propagation for occluded person re-identification. Inf. Fusion 2024, 104, 102201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Xia, J.; Liu, W.; Dai, P.; Wu, Y.; Cao, L. Occluded person re-identification via saliency-guided patch transfer. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; pp. 5070–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yang, J.; Zhou, M.; Huang, Z.; Zheng, W.S.; Yang, X.; Ren, J. Learning from human educational wisdom: A student-centered knowledge distillation method. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 4188–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Liu, J.; Du, L.; Wan, S.; Yi, Z. Reciprocal teacher-student learning via forward and feedback knowledge distillation. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2024, 26, 7901–7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Tang, H.; Li, Z. Learning contrastive self-distillation for ultra-fine-grained visual categorization targeting limited samples. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 7135–7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiang, T.; Hospedales, T.M.; Lu, H. Deep mutual learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4320–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Lan, C.; Zeng, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zha, Z.J. Pose-guided feature learning with knowledge distillation for occluded person re-identification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 4537–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Mu, Y. Patch-based knowledge distillation for lifelong person re-identification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radenović, F.; Tolias, G.; Chum, O. Fine-tuning CNN image retrieval with no human annotation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 1655–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Luo, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Li, H.; Jiang, W. Transreid: Transformer-based object re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 15013–15022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, J.; Chen, Z.; Lai, J.; Wang, G. Occluded person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, San Diego, CA, USA, 23–27 July 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Shen, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, Q. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristani, E.; Solera, F.; Zou, R.; Cucchiara, R.; Tomasi, C. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In Proceedings of the European Eonference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 7–13 December 2016; pp. 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lv, X.; Dou, S.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, L. Incremental generative occlusion adversarial suppression network for person ReID. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 4212–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fu, K.; Zhao, Q. Dynamic patch-aware enrichment transformer for occluded person re-identification. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2025, 327, 114193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Fu, S.; Tang, Y. Skip connection aggregation transformer for occluded person reidentification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2023, 20, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Shen, H.T.; Song, J. Part-aware transformer for generalizable person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 11280–11289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Guo, H.; Liu, Z.; Tang, M.; Wang, J. Identity-guided human semantic parsing for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Dataset | Train | Qurey | Gallery | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID | Image | ID | Image | ID | Image | |
| Occluded-DukeMTMC | 702 | 15,618 | 519 | 2210 | 1110 | 17,661 |
| Occluded-REID | 100 | 1000 | 100 | 500 | 100 | 500 |
| P-DukeMTMC-reID | 665 | 12,927 | 634 | 2163 | 634 | 9053 |
| Market-1501 | 751 | 12,936 | 750 | 12,936 | 750 | 19,732 |
| DukeMTMC-reID | 702 | 16,522 | 702 | 2228 | 1110 | 17,661 |
| Method | mAP | Rank-1 | Rank-3 | Rank-5 | Rank-10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 54.0 | 62.4 | 71.4 | 75.2 | 80.2 |
| Baseline + MIA | 55.9 | 63.9 | 72.8 | 77.1 | 82.1 |
| Baseline + VI | 57.8 | 69.2 | 77.7 | 80.9 | 84.7 |
| Baseline + MIA + VI | 59.1 | 71.2 | 79.5 | 83.0 | 86.7 |
| Method | mAP | Rank-1 | Rank-3 | Rank-5 | Rank-10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 56.3 | 67.2 | 76.4 | 80.3 | 84.3 | |
| + | 58.4 | 69.0 | 78.1 | 81.4 | 85.7 |
| + | 58.6 | 69.5 | 78.3 | 81.7 | 85.5 |
| + + | 59.1 | 71.2 | 79.5 | 83.0 | 86.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Ding, J. Occluded Person Re-Identification via Multi-Branch Interaction. Sensors 2025, 25, 6526. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25216526
Huang Y, Ding J. Occluded Person Re-Identification via Multi-Branch Interaction. Sensors. 2025; 25(21):6526. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25216526
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yin, and Jieyu Ding. 2025. "Occluded Person Re-Identification via Multi-Branch Interaction" Sensors 25, no. 21: 6526. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25216526
APA StyleHuang, Y., & Ding, J. (2025). Occluded Person Re-Identification via Multi-Branch Interaction. Sensors, 25(21), 6526. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25216526






