RTK-GNSS Increment Prediction with a Complementary “RTK-SeqNet” Network: Exploring Hybridization with State-Space Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
Choice of GRU over LSTM
3. Data Construction and Proposed Method
3.1. Data Collection and Processing
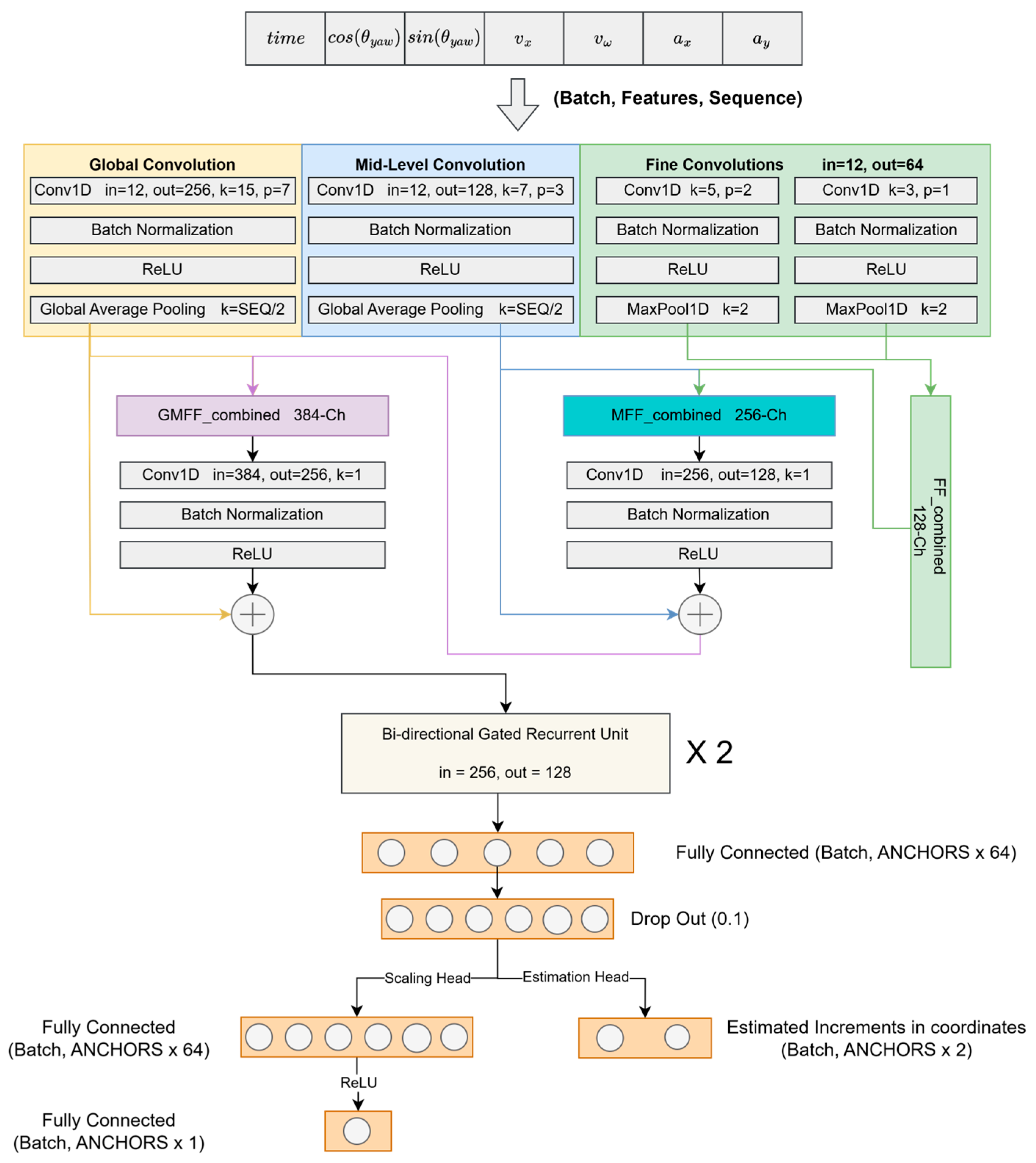
3.2. Proposed RTK-SeqNet Architecture
3.3. Optimization and Loss Functions
3.3.1. GNSS Loss
3.3.2. Directional Loss
3.3.3. Vector Loss
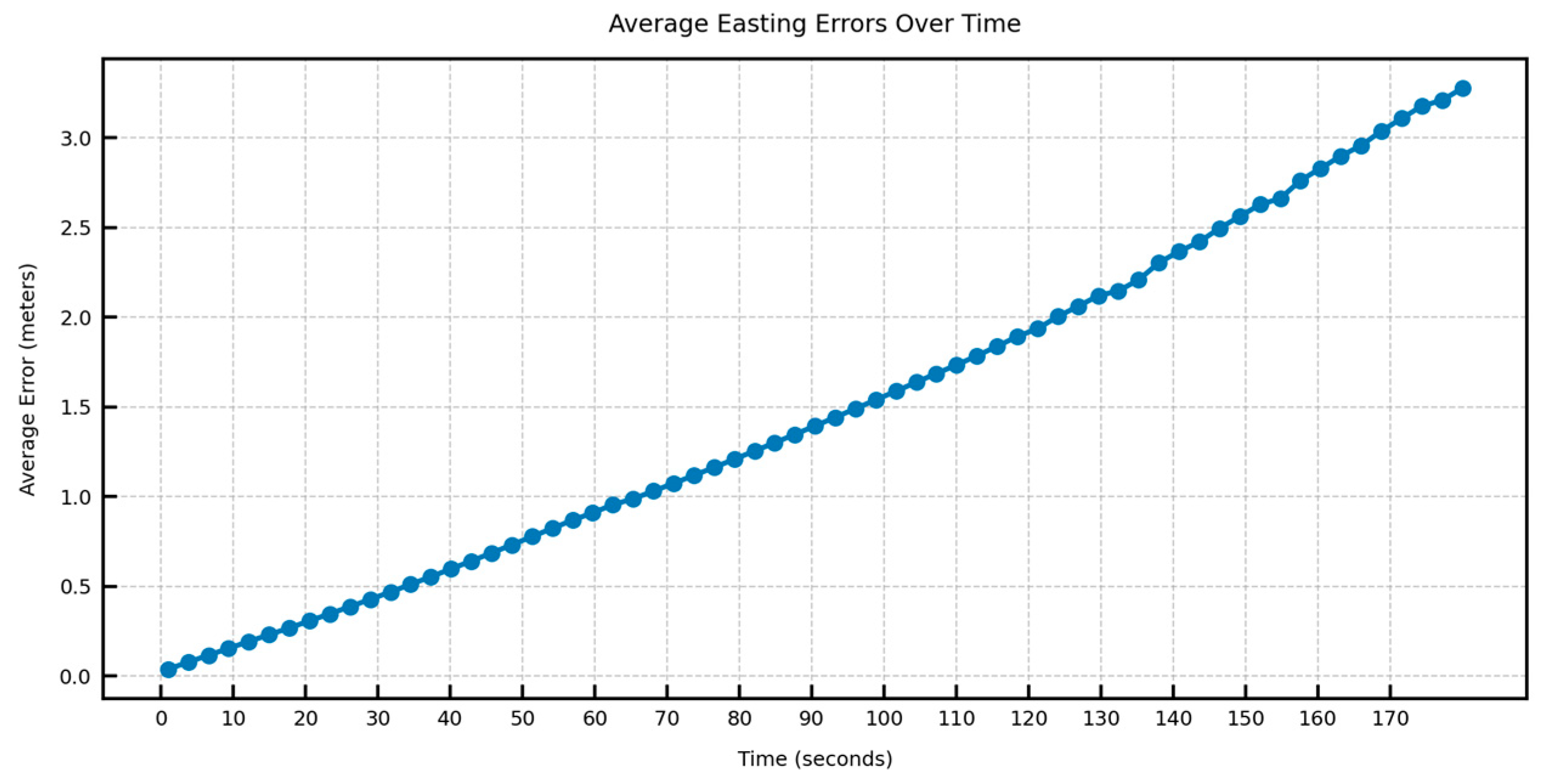
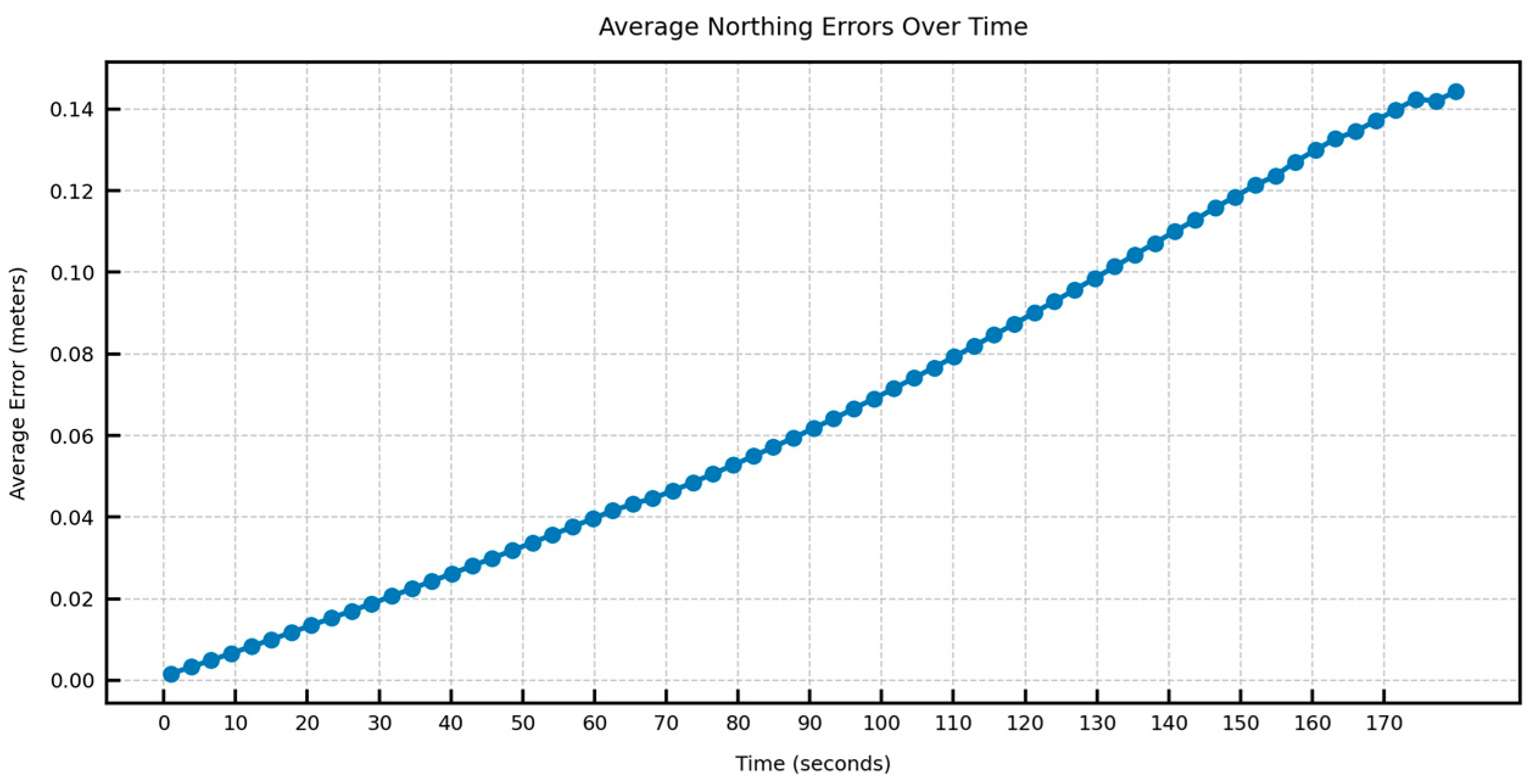
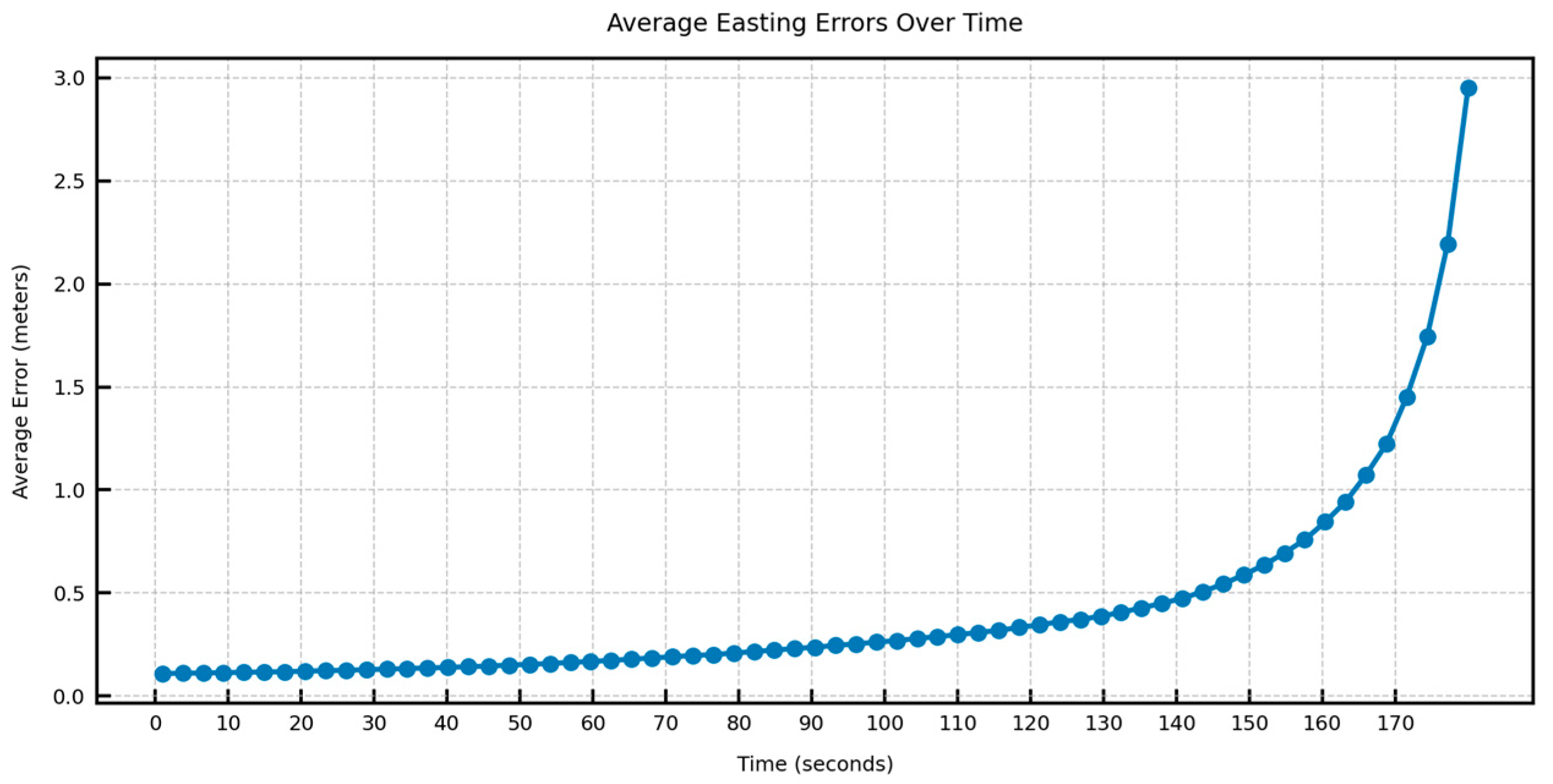
4. Experiments and Results
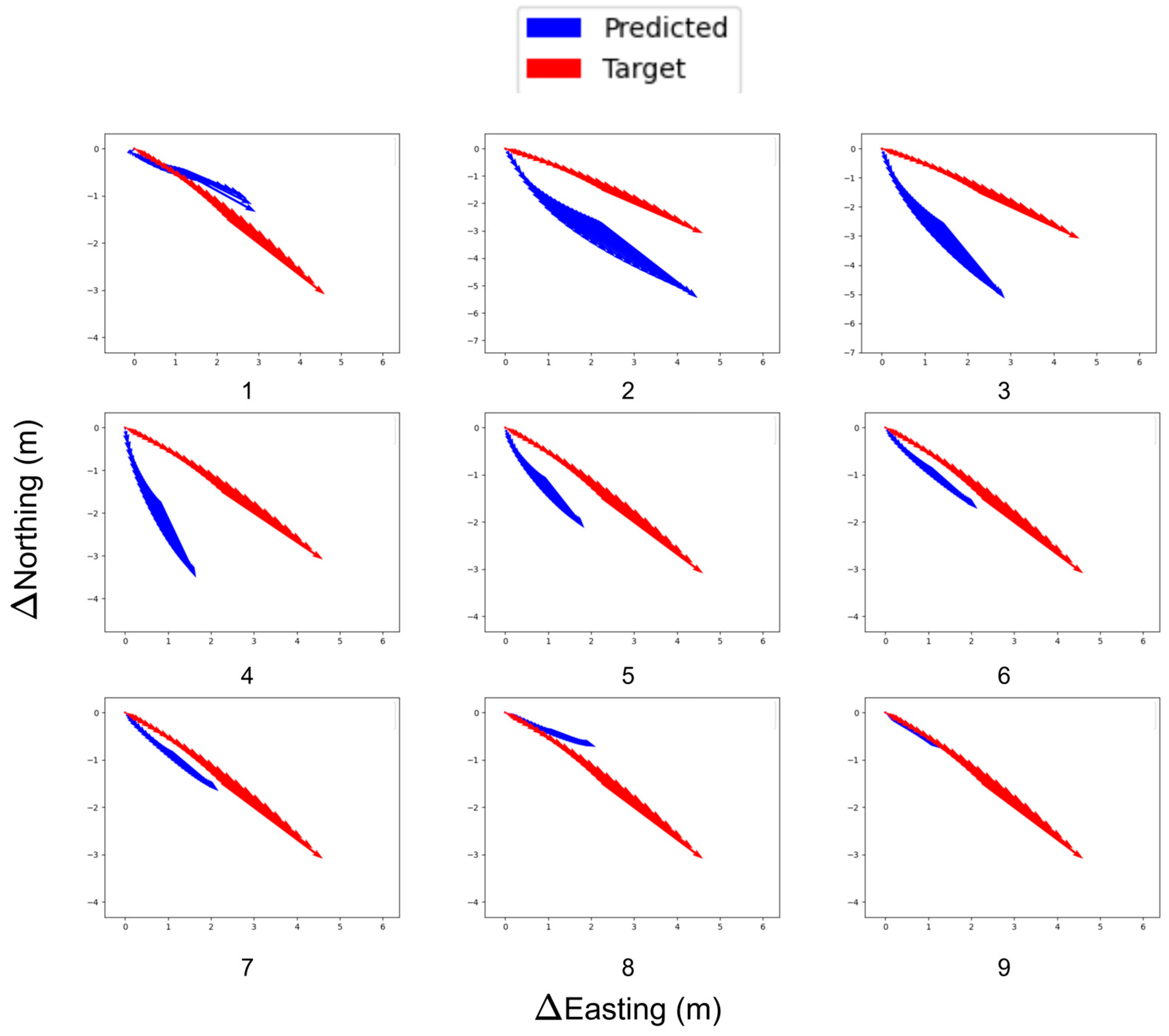
4.1. Vector Direction Progression
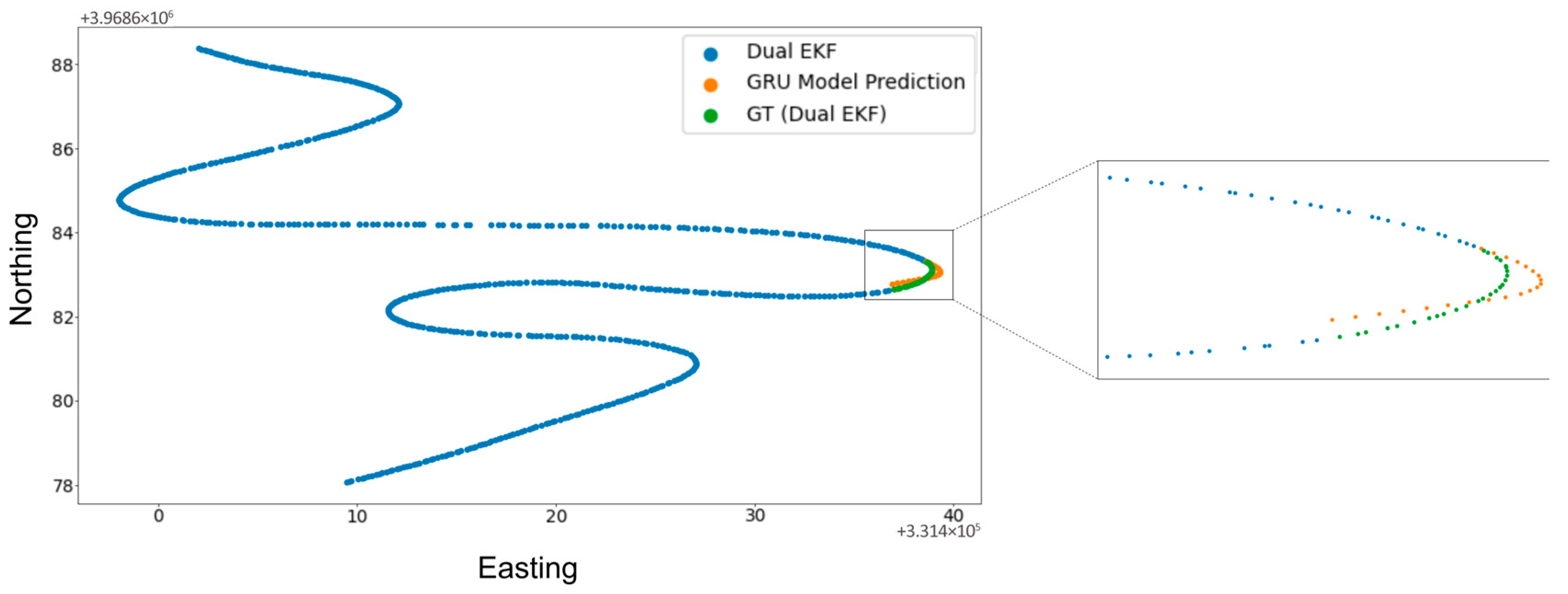
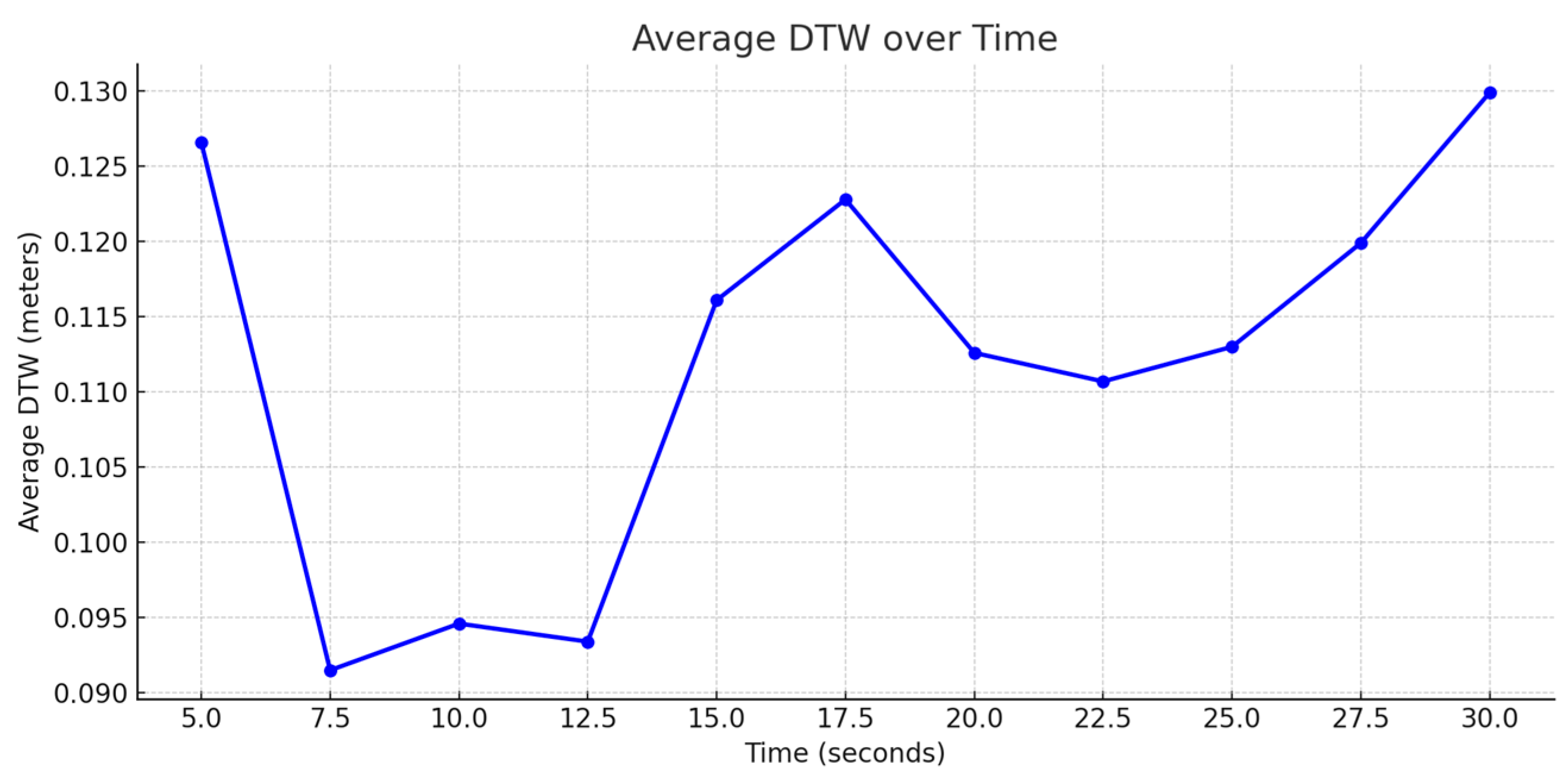
4.2. Model Performance
| Algorithm 1. Trajectory Update and Integration |
| 1: 2: from last iteration 3: Append placeholder to 4: for each pred in predictions do 5: do 6: try 7: |
| 8: 9: except Index Error do 10: 11: break 12: 13: end for |
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Kleusberg, A. GPS for Geodesy; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 477–478. [Google Scholar]
- Spilker, J.S., Jr.; Axelrad, P.; Parkinson, B.W.; Enge, P. Global Positioning System: Theory Applications Volume, I; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, P.D. Principles of GNSS, Inertial, and Multisensor Integrated Navigation Systems; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–824. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, T.; Stouch, D. A generalized extended kalman filter implementation for the robot operating system. Intelligent Autonomous Systems 13. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference IAS-13; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 335–348. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. In arXiv; 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, W.E.; Nielsen, G.A.; Tyler, D.A. Tyler. Precision navigation with GPS. Comput. Electron. Agric. 1994, 11, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anneveld, J.C. Mammoth vessels and coriolis force. J. Navig. 1971, 24, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfield, J.J. Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 2554–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepp, H.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Tang, R.; Bao, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Z. A real-time trajectory prediction method of small-scale quadrotors based on GPS data and neural network. Sensors 2020, 20, 7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, L.; Yan, X.; Chang, N.; Wan, Q.; Wu, Y. A Tractor Work Position Prediction Method Based on CNN-BiLSTM Under GNSS Signal Denial. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 16, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Herath, S.; Yan, H.; Furukawa, Y. RoNIN: Robust Neural Inertial Navigation in the Wild: Benchmark, Evaluations, & New Methods. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–1 August 2020; pp. 3146–3152. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Bai, H.; Jin, K.; Zou, G. An GNSS/INS integrated navigation algorithm based on PSO-LSTM in satellite rejection. Electronics 2023, 12, 2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Lin, J.; Sui, Z.; Qu, X.; Wang, R.; Sheng, K.; Zhang, B. An End-to-End Learning-Based Multi-Sensor Fusion for Autonomous Vehicle Localization. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.05088. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Zhao, H.; Chen, W. A Hybrid Algorithm of LSTM and Factor Graph for Improving Combined GNSS/INS Positioning Accuracy during GNSS Interruptions. Sensors 2024, 24, 5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, M.; Gerkey, B.; Smart, W.D. Programming Robots with ROS: A Practical Introduction to the Robot Operating System; O’Reilly Media: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Markov, A. Extension of the limit theorems of probability theory to a sum of variables connected in a chain. Dynam. Probabilist. Syst. 1971, 1, 552. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, P.J. Robust estimation of a location parameter. In Breakthroughs in Statistics: Methodology and Distribution; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 492–518. [Google Scholar]
- Sakoe, H.; Chiba, S. Dynamic programming algorithm optimization for spoken word recognition. In IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1978; Volume 26, pp. 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Levinson, J.; Askeland, J.; Becker, J.; Dolson, J.; Held, D.; Kammel, S.; Kolter, J.Z.; Langer, D.; Pink, O.; Pratt, V.; et al. Towards fully autonomous driving: Systems and algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Baden-Baden, Germany, 5–9 June 2011; pp. 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Mahony, R.; Hamel, T.; Pflimlin, J.-M. Nonlinear complementary filters on the special orthogonal group. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2008, 53, 1203–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Grift, T.E. Dual Extended Kalman Filter for Robust Localization of Agricultural Vehicles in GNSS-Challenged Fields. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2019, 16, 5. [Google Scholar]









| Gate | Role (LSTM) | Role (GRU) |
|---|---|---|
| Input Gate | Controls how much information flows into the cell state | (Handled by the update gate in GRU) |
| Forget Gate | Controls how much information is discarded from the cell state | (Also handled by the update gate in GRU) |
| Output Gate | Controls how much of the cell state is exposed as output | (Not present in GRU) |
| Update Gate | (Not present in LSTM) | Controls both input and memory retention |
| Reset Gate | (Not present in LSTM) | Decides how much of the previous state to keep when updating |
| Recurrent Unit | Parameters | Timing |
|---|---|---|
| Bi-GRU | 810,435 | 8.545 milliseconds |
| Bi-LSTM | 1,008,067 | 11.14 milliseconds |
| Sensor | Sensitivity (Temp Coefficient) | Accuracy/ Stability |
|---|---|---|
| Rate Gyroscope | ±0.04%/°C | 20° drift-s−1 |
| Accelerometer | ±0.02%/°C | ±0.75 mg/°C (X,Y), ±1.5 mg/°C (Z) |
| Heading | < | Static pitch/roll ± 1°, dynamic ± 3°; static yaw ± 3°, dynamic ± 5° |
| GNSS (u-blox ZED-F9P) | 0.01 m | - |
| Hyper Parameters | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Epoch | 350 |
| Optimizer | ADAM |
| Learning Rate | |
| Weight Decay | |
| Sequence Length | 64 |
| Anchors | 32 |
| Trajectories (180 s) | Average DTW | RMSE |
|---|---|---|
| 0–180 s | 2.5953 m | 6.5930 m |
| 15–195 s | 1.2809 m | 3.3427 m |
| 30–210 s | 1.5127 m | 5.3223 m |
| 50–230 s | 1.4278 m | 1.4995 m |
| 80–260 s | 1.0866 m | 1.3645 m |
| 120–300 s | 1.6238 m | 2.2825 m |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, H.; Waqar, M.M.; Ma, R.; Kim, S.C.; Baek, Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, H. RTK-GNSS Increment Prediction with a Complementary “RTK-SeqNet” Network: Exploring Hybridization with State-Space Systems. Sensors 2025, 25, 6349. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206349
Ali H, Waqar MM, Ma R, Kim SC, Baek Y, Kim J, Lee H. RTK-GNSS Increment Prediction with a Complementary “RTK-SeqNet” Network: Exploring Hybridization with State-Space Systems. Sensors. 2025; 25(20):6349. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206349
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Hassan, Malik Muhammad Waqar, Ruihan Ma, Sang Cheol Kim, Yujun Baek, Jongrin Kim, and Haksung Lee. 2025. "RTK-GNSS Increment Prediction with a Complementary “RTK-SeqNet” Network: Exploring Hybridization with State-Space Systems" Sensors 25, no. 20: 6349. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206349
APA StyleAli, H., Waqar, M. M., Ma, R., Kim, S. C., Baek, Y., Kim, J., & Lee, H. (2025). RTK-GNSS Increment Prediction with a Complementary “RTK-SeqNet” Network: Exploring Hybridization with State-Space Systems. Sensors, 25(20), 6349. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206349







