Improvements to Unsteady Pressure-Sensitive Paint Formulations
Abstract
Highlights
- Hydrophobic TiO2 particles generate smoother and thinner uPSP coatings.
- Choice of dispersant can greatly affect the linearity of the pressure sensitivity.
- Even after degradation, one of two dispersants tested showed minimal loss of pressure sensitivity.
- Use of this dispersant showed pressure sensitivity was less dependent on temperature.
- New PSP formulations showed minimal change in frequency response.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Pressure-Sensitive Paint Formulations
2.3. Measurements
3. Results
3.1. General Coating Properties
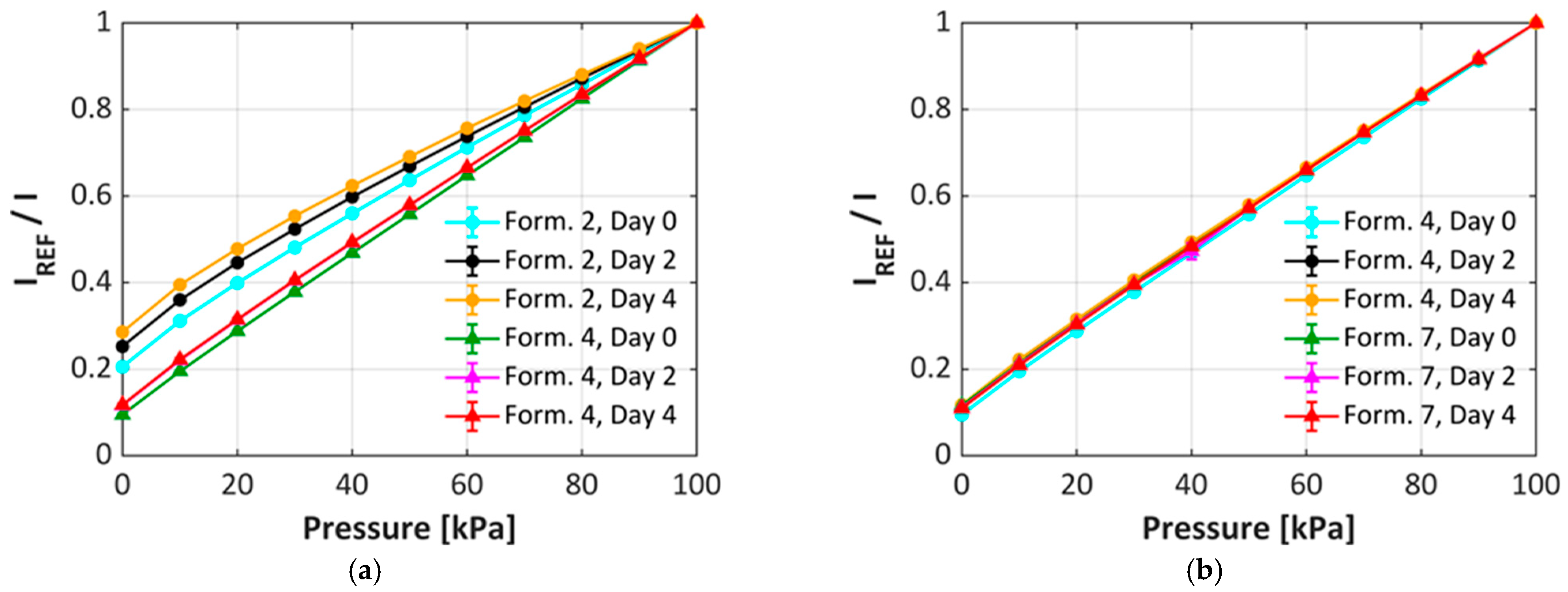
3.2. uPSP Calibration Performance
3.3. Degradation
3.4. Frequency Response
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PSP | Pressure-Sensitive Paint |
| uPSP | unsteady Pressure-Sensitive Paint |
| PtTfPP | 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorophenyl)porphyrin-22,24-diide platinum(II) |
| m-SiO2 | mesoporous silicon dioxide |
| TiO2 | titanium dioxide |
| CCD | Charge-coupled device |
| mm | millimeter |
| nm | nanometer |
| Hz | Hertz |
| kHz | kilohertz |
| kPa | kilopascal |
| fps | frames per second |
References
- McLachlan, B.; Bell, J. Pressure-Sensitive Paint in Aerodynamic Testing. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1995, 10, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Campbell, B.; Burns, S.; Sullivan, J. Temperature- and Pressure-Sensitive Luminescent Paints in Aerodynamics. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1997, 50, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Sullivan, J. Pressure and Temperature Sensitive Paints, 2nd ed.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavandi, J.; Callis, J.; Gouterman, M.; Khalil, G.; Wright, D.; Green, E.; Burns, D.; McLachlan, B. Luminescent Barometry in Wind Tunnels. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1990, 61, 3340–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.J.; Benne, M.E.; Crites, R.C.; Donovan, J.F. Aerodynamic Measurements Based on Photoluminescence. In Proceedings of the 31st Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 11–14 January 1993; pp. 93–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, M.E. Advances in AEDC’s Lifetime Pressure-Sensitive Paint Program. In Proceedings of the U.S. Air Force T&E Days, Nashville, TN, USA, 6–8 December 2005. AIAA Paper 2005-7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, M.E. AEDC’s Portable Pressure-Sensitive Paint Data Acquisition System. In Proceedings of the U.S. AirForce T&E Days, Destin, FL, USA, 13–15 February 2007. AIAA Paper 2007-1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, M.E. Pressure-Sensitive Paint Data on the Facility Aerodynamics Validation and Research (FAVOR) Model at AEDC, AEDC-TR-09-F-34, December 2009. Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/tr/pdf/ADA511418.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Sellers, M.E. Demonstration of a Temperature-Compensated Pressure Sensitive Paint on the Orion Launch Abort Vehicle. In Proceedings of the 29th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27–30 June 2011. AIAA Paper 2011-3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, M.E.; Nelson, M.A.; Crafton, J.W. Dynamic Pressure-Sensitive Paint Demonstration in AEDC Propulsion Win Tunnel 16T*. In Proceedings of the 2016 AIAA SciTech Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 4–8 January 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lakowicz, J. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.W.; Sakaue, H.; Liu, T.; Sullivan, J.P. Fast Pressure-Sensitive Paint for Flow and Acoustic Diagnostics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2014, 46, 303–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, O.D.; Watkins, A.N.; Ingram, J.L. Pressure Sensitive Paint Measurements on 15% Scale Rotor Blades in Hover. In Proceedings of the 35th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–9 June 2005. AIAA Paper 2005-5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, A.N.; Leighty, B.D.; Lipford, W.E.; Wong, O.D.; Oglesby, D.M.; Ingram, J.L. Development of a Pressure Sensitive Paint System for Measuring Global Surface Pressures on Rotorcraft Blades. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Congress on Instrumentation in Aerospace Simulation Facilities, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 10–14 June 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, O.D.; Watkins, A.N.; Goodman, K.Z.; Crafton, J.; Forlines, A.; Goss, L.; Gregory, J.W.; Juliano, T.J. Blade Tip Pressure Measurements Using Pressure Sensitive Paint. Blade Tip Pressure Measurements Using Pressure Sensitive Paint. J. Am. Helicopter Soc. 2018, 63, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, A.N.; Leighty, B.D.; Lipford, W.E.; Wong, O.D.; Goodman, K.Z.; Crafton, J.; Forlines, A.; Goss, L.P.; Gregory, J.W.; Juliano, T.J. Development of a Pressure Sensitive Paint System for Measuring Global Surface Pressures on Rotor-craft Blades in Simulated Forward Flight. In Proceedings of the 28th Aerodynamic Measurement Technology, Ground Testing, and Flight Testing Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 25–28 June 2012. AIAA Paper 2012-2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Torgerson, S.; Sullivan, J.; Johnston, R.; Fleeter, S. Rotor Blade Pressure Measurement in a High-Speed Axial compressor Using Pressure and Temperature Sensitive Paints. In Proceedings of the 35th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 6–9 January 1997. AIAA Paper 1997-0162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgerson, S.; Liu, T.; Sullivan, J. Rotor Blade Pressure Measurement in a Rotating Machinery Using Pressure and Temperature Sensitive Paints. In Proceedings of the AGARD-CP-598-Advanced Non-Intrusive Instrumentation for Propulsion Engines, 1998; pp. 19-1–19-9. Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/tr/pdf/ADA348957.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Bencic, T.J. Rotating pressure and temperature Measurements on Scale-Model Fans Using Luminescent Paints. In Proceedings of the 34th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Cleveland, OH, USA, 13–15 July 1998. AIAA Paper 1998-3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarra, K.; Goss, L.; Jordan, J.; Rabe, D.; Gord, J.; Car, D. Optical Measurements of Surface Pressure and Temperature in Turbomachinery. AGARD-CP-598-Advanced Non-Intrusive Instrumentation for Propulsion Engines, 1998; pp. 18-1–18-13. Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/tr/pdf/ADA348957.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Gregory, J.W. Porous Pressure-Sensitive Paint for Measurement of Unsteady Pressures in Turbomachinery. In Proceedings of the 42nd Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Reno, NV, USA, 5–8 January 2004. AIAA Paper 2004-0294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, M.E.; Nelson, M.A.; Roozeboom, N.H.; Burnside, N.H. Evaluation of Unsteady Pressure Sensitive Paint Measurement Technique for Space Launch Vehicle Buffet Determination. In Proceedings of the 55th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Grapevine, TX, USA, 9–13 January 2017. AIAA Paper 2017-1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozeboom, N.; Powell, J.; Baerny, J.; Murakami, D.; Ngo, C.; Garbeff, T.; Ross, J.; Flach, R. Development of Unsteady Pressure-Sensitive Paint Application on NASA Space Launch System. In Proceedings of the 2019 AIAA Aviation Forum, Dallas, TX, USA, 17–21 June 2019. AIAA 2019-3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozeboom, N.; Baerny, J.K.; Murakami, D.D.; Ngo, C.; Powell, J.M. Recent Developments in NASA’s Unsteady Pressure-Sensitive Paint Capability. In Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2020 Forum, Orlando, FL, USA, 6–10 January 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, K.; Zukowska, G.Z.; Korczagin, I.; Malanowski, P. Effect of TiO2 on UV stability of polymeric binder films used in waterborne façade paints. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 85, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pia, J.E.; Hussein, B.A.; Skrypai, V.; Sarycheva, O.; Adler, M.J. Porphyrin Silanes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 449, 214183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Park, Y.; Kim, W.; Choi, W. Surface modification of TiO2 photocatalyst for environmental applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2013, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, I.; Chawla, H.; Chandra, A.; Sagadevan, S.; Garg, S. Advances in the strategies for enhancing the photocatalytic activity of TiO2: Conversion from UV-light active to visible-light active photocatalyst. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 143, 109700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libanori, R.; Giraldi, T.R.; Longo, E.; Leite, E.R.; Ribeiro, C. Effect of TiO2 surface modification in Rhodamine B photodegradation. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2009, 49, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, A.; Massera, E.; Quercia, L.; Di Francia, G. Development of pressure sensitive paints based on silicon nanostructured powders. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 118, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Gu, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. A novel sprayable fast-responding pressure sensitive paint based on mesoporous silicon dioxide particles. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 279, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egami, Y.; Sato, Y.; Konishi, S. Development of Sprayable Pressure Sensitive Paint with a Response Time of Less Than 10 μs. AIAA J. 2019, 57, 2198–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egami, Y.; Fujii, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Niimi, T. Reduction of temperature Effects in Pressure Sensitive Paint Measurements. AIAA J. 2013, 51, 1779–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemours Ti-Pure. Titanium Dioxide Solutions for Paints & Coatings. Available online: https://www.tipure.com/en/products/coatings (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Kasai, M.; Suzuki, A.; Egami, Y.; Nonomura, T.; Asai, K. A platinum-based fast-response pressure sensitive paint containing hydrophobic titanium dioxide. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 350, 114140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton, L.G.P.; Koklu, M.; Andino, M.; Lin, J.C.; Edelman, L.M. Sweeping Jet Optimization Studies. In Proceedings of the 8th AIAA Flow Control Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 13–17 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraway, E.R.; Demas, J.N.; DeGraff, B.A.; Bacon, J.R. Photophysics and Photochemistry of Oxygen Sensors Based on Luminescent Transition-Metal Complexes. Anal. Chem. 1991, 63, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, J.R.; Demas, J.N. Determination of Oxygen Concentrations by Luminescence Quenching of a Polymer-Immobilized Transition-Metal Complex. Anal. Chem. 1987, 59, 2780–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Kong, D.; Huang, F.; Cai, G.; Aisi, S.; Chem, Y. Pressure-sensitivity stability of poly[1-(trimethylsilyl)-1-propyne]-based pressure-sensitive paint for low-pressure conditions. Measurement 2022, 196, 111012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egami, Y.; Konishi, S.; Sato, Y.; Matsuda, Y. Effects of solvents for luminophore on dynamic and static characteristics of sprayable polymer/ceramic pressure-sensitive paints. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 286, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
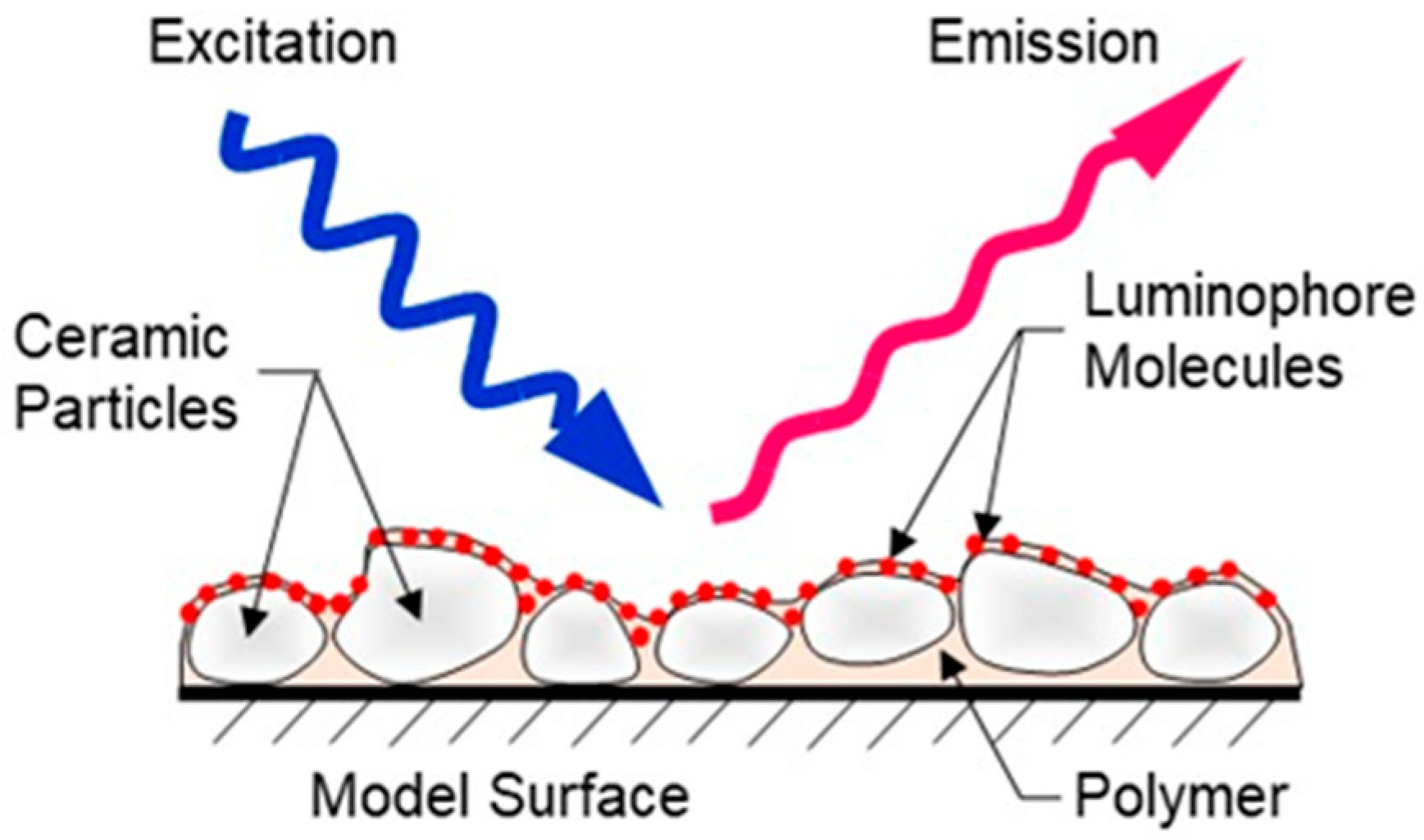
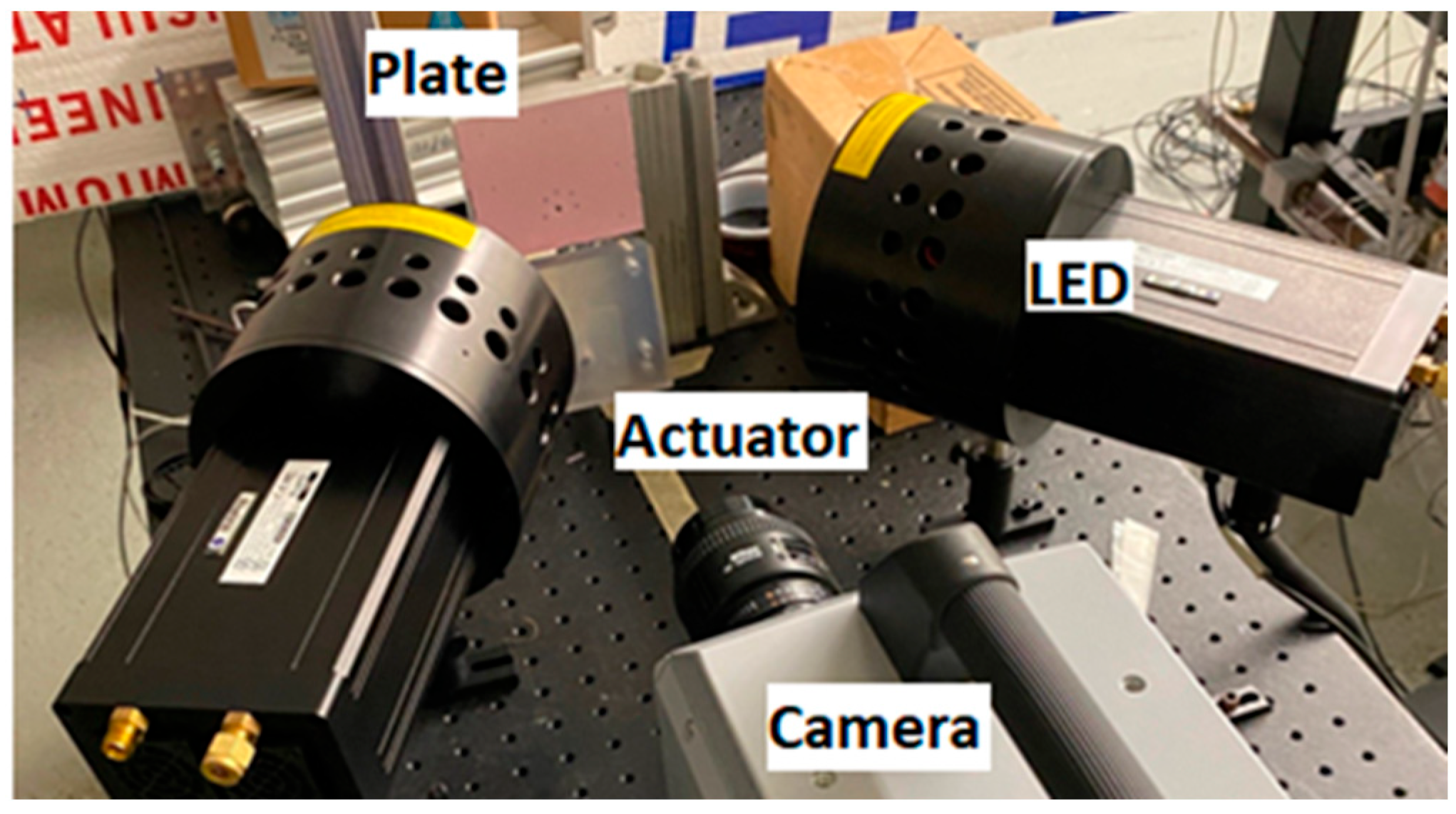
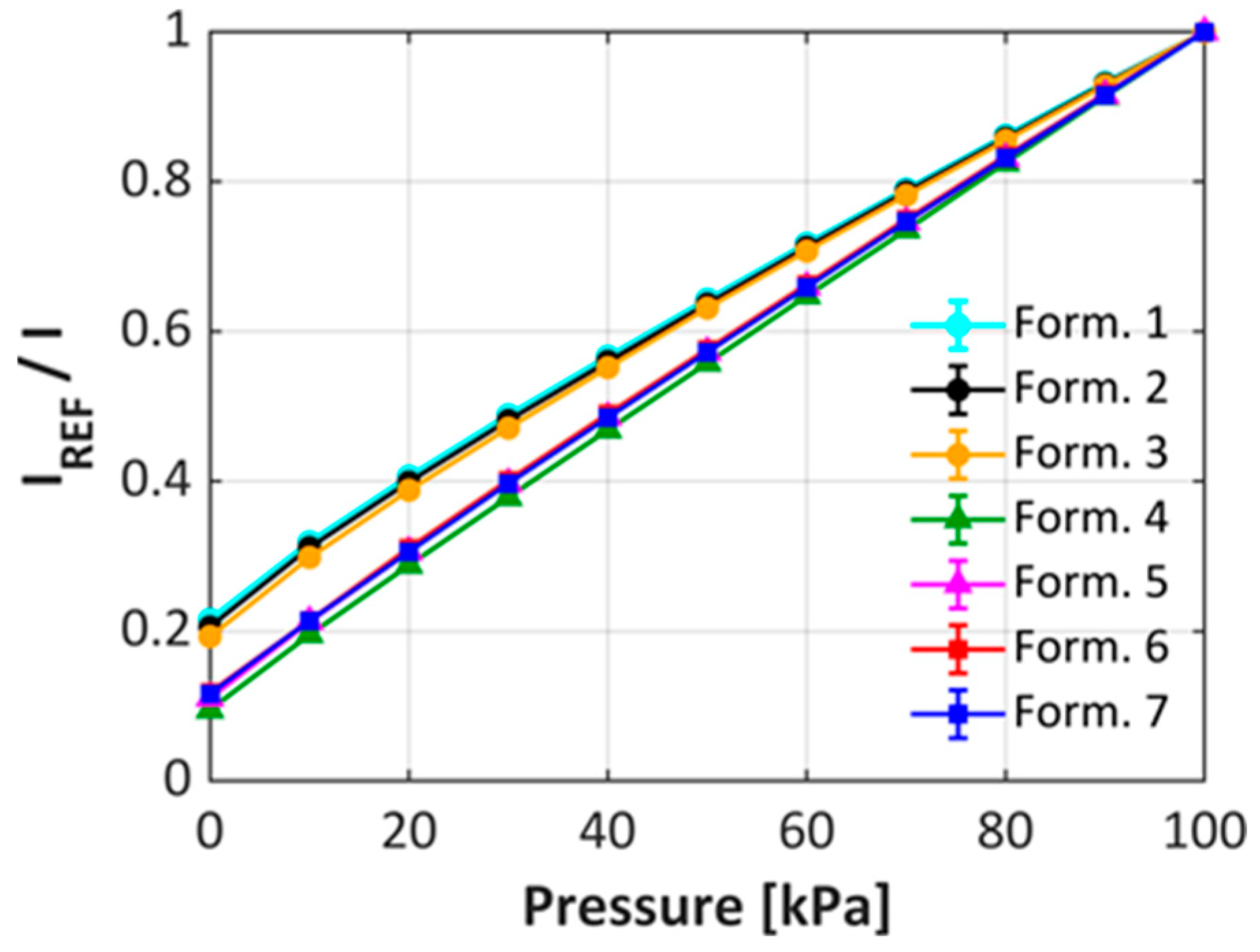
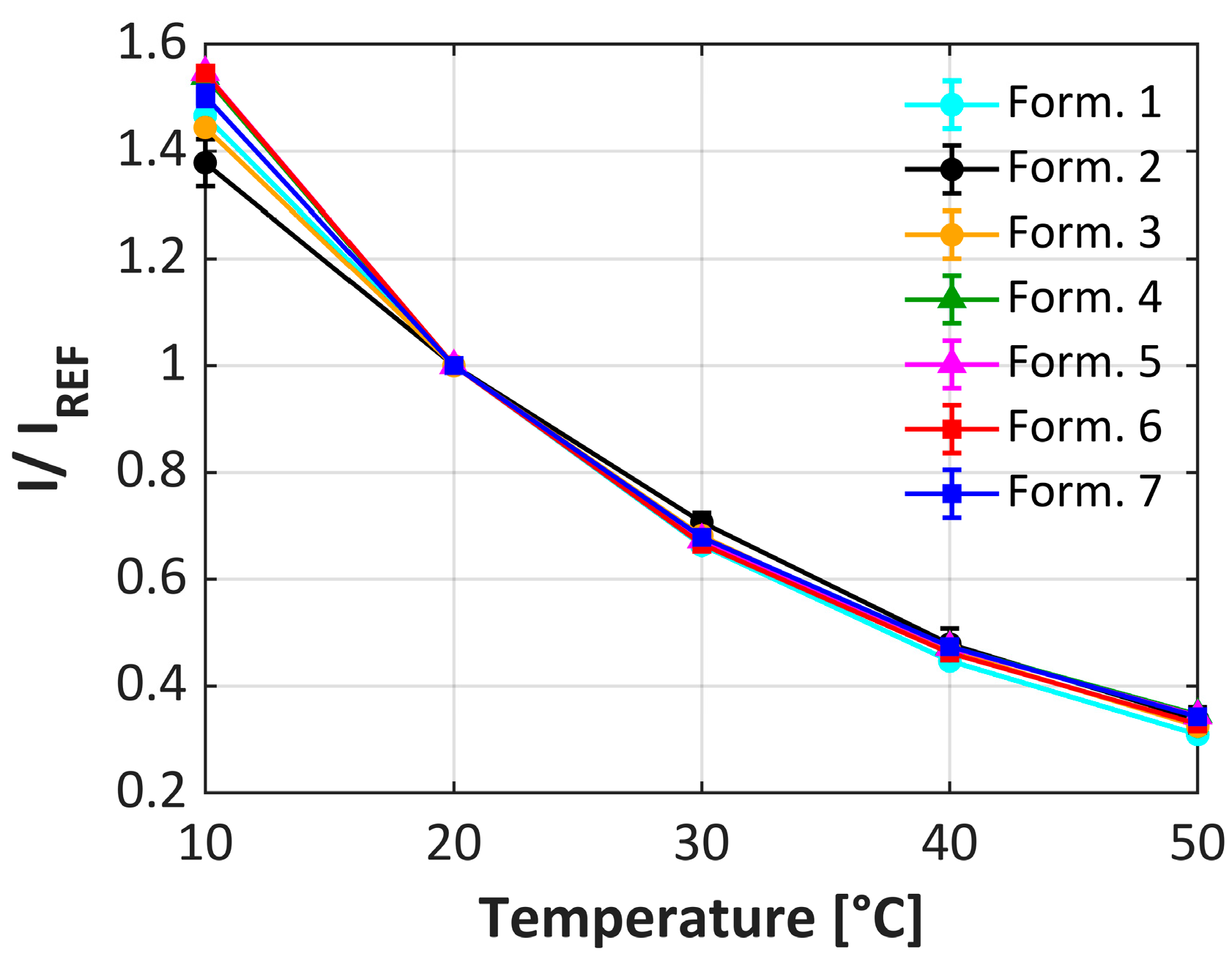


| Formulations | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 grade | I | II | III | II | III | IV | V |
| Hydrophilic (+) or Hydrophobic (−) | + | + | + | + | + | − | − |
| Silica wt% | 0 | 3 | 6.5 | 3 | 6.5 | 0 | 3.5 |
| Alumina wt% | 1.7 | 2.5 | 4.0 | 2.5 | 4.0 | 1.7 | 3.3 |
| Size of TiO2 particles (μm) | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.5 | 0.36 | 0.5 | 0.22 | 0.31 |
| Dispersant | A | A | A | B | B | B | B |
| Roughness (Ra, μm) | 6.0 ± 1.3 | 6.5 ± 1.3 | 6.4 ± 2.4 | 3.3 ± 0.8 | 4.1 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.4 | 3.9 ± 0.5 |
| Thickness (µm) | 55.9 ± 17.8 | 40.6 ± 17.8 | 66.0 ± 27.9 | 50.8 ± 17.8 | 30.5 ± 10.2 | 27.9 ± 7.6 | 27.9 ± 17.8 |
| TiO2 Formulations | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 grade | I | II | III | II | III | IV | V |
| Hydrophilic (+) or Hydrophobic (−) | + | + | + | + | + | − | − |
| Dispersant | A | A | A | B | B | B | B |
| Degradation rate (%/day) | −12.2 ± 6.2 | −13 ± 3.9 | −13.5 ± 4.6 | −7.3 ± 3.5 | −7.8 ± 3.1 | −5 ± 1.2 | −7.6 ± 2.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peak, S.M.; Reese, D.T.; Goodman, K.Z.; Watkins, A.N. Improvements to Unsteady Pressure-Sensitive Paint Formulations. Sensors 2025, 25, 5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185892
Peak SM, Reese DT, Goodman KZ, Watkins AN. Improvements to Unsteady Pressure-Sensitive Paint Formulations. Sensors. 2025; 25(18):5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185892
Chicago/Turabian StylePeak, Sarah M., Daniel T. Reese, Kyle Z. Goodman, and A. Neal Watkins. 2025. "Improvements to Unsteady Pressure-Sensitive Paint Formulations" Sensors 25, no. 18: 5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185892
APA StylePeak, S. M., Reese, D. T., Goodman, K. Z., & Watkins, A. N. (2025). Improvements to Unsteady Pressure-Sensitive Paint Formulations. Sensors, 25(18), 5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185892







