Markerless Motion Capture Parameters Associated with Fall Risk or Frailty: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Primary Research Question
2.3. Secondary Research Questions
- How was the MMC technology set up for assessments (e.g., camera type, angle, distance from participant)?
- Were the results stratified by demographic or disease characteristics (sex, age, body mass index, etc.) and, if so, what differences were reported?
- What were the reported rates and reasons (if any) for poor or incomplete MMC data recording, and what reasons were provided (if any)?
2.4. Search Strategy
2.5. Eligibility Criteria
The Inclusion Criteria Consisted of the Following
2.6. Exclusion Criteria
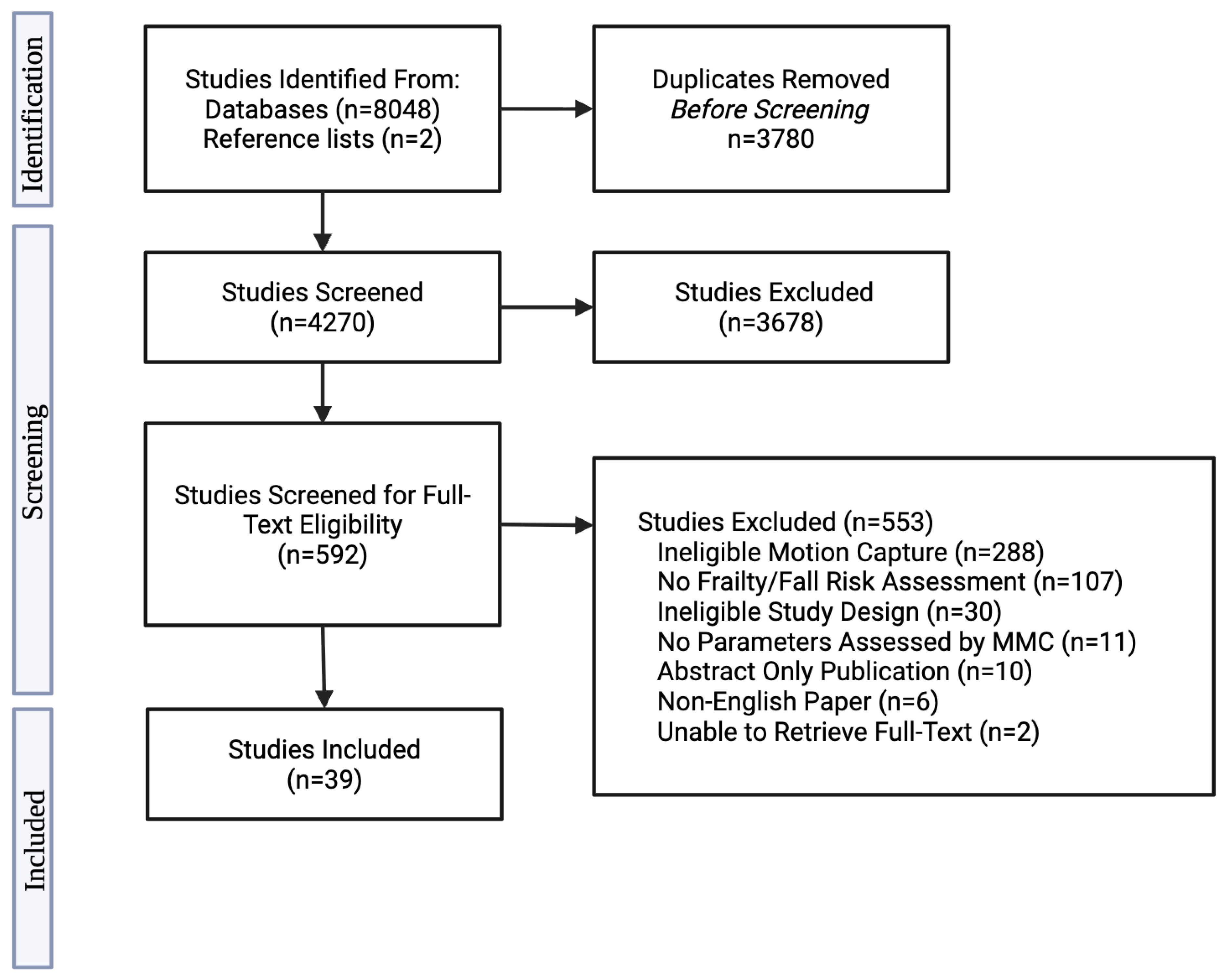
2.7. Study Selection
2.8. Data Extraction
2.9. Definition of Terms
3. Results
3.1. Study and Population Characteristics
3.2. Technology Characteristics
3.3. Assessment Characteristics
3.4. Accuracy, Sensitivity, and Specificity
3.5. Statistical Analyses Reported
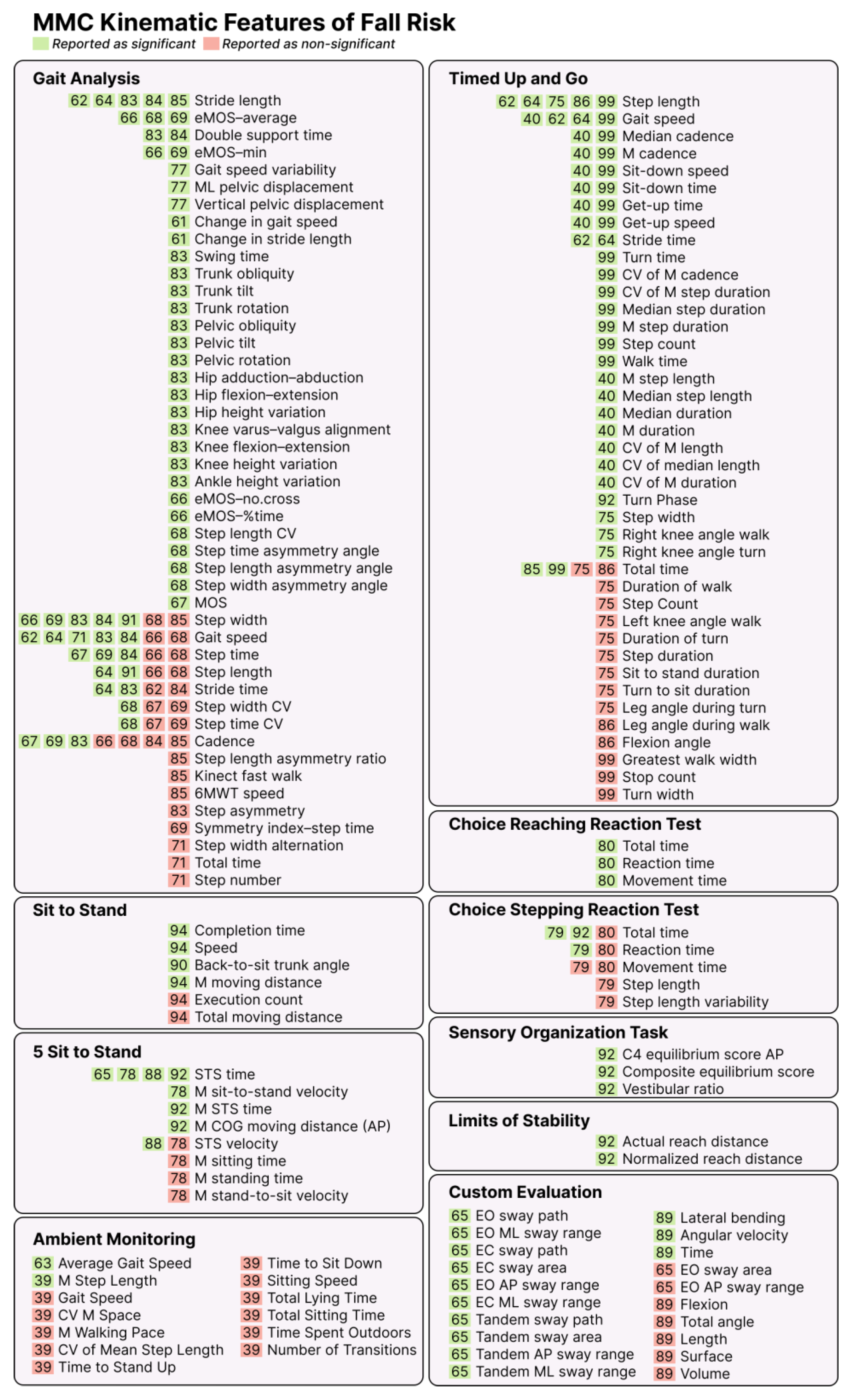
3.6. Kinematic Features of Fall Risk
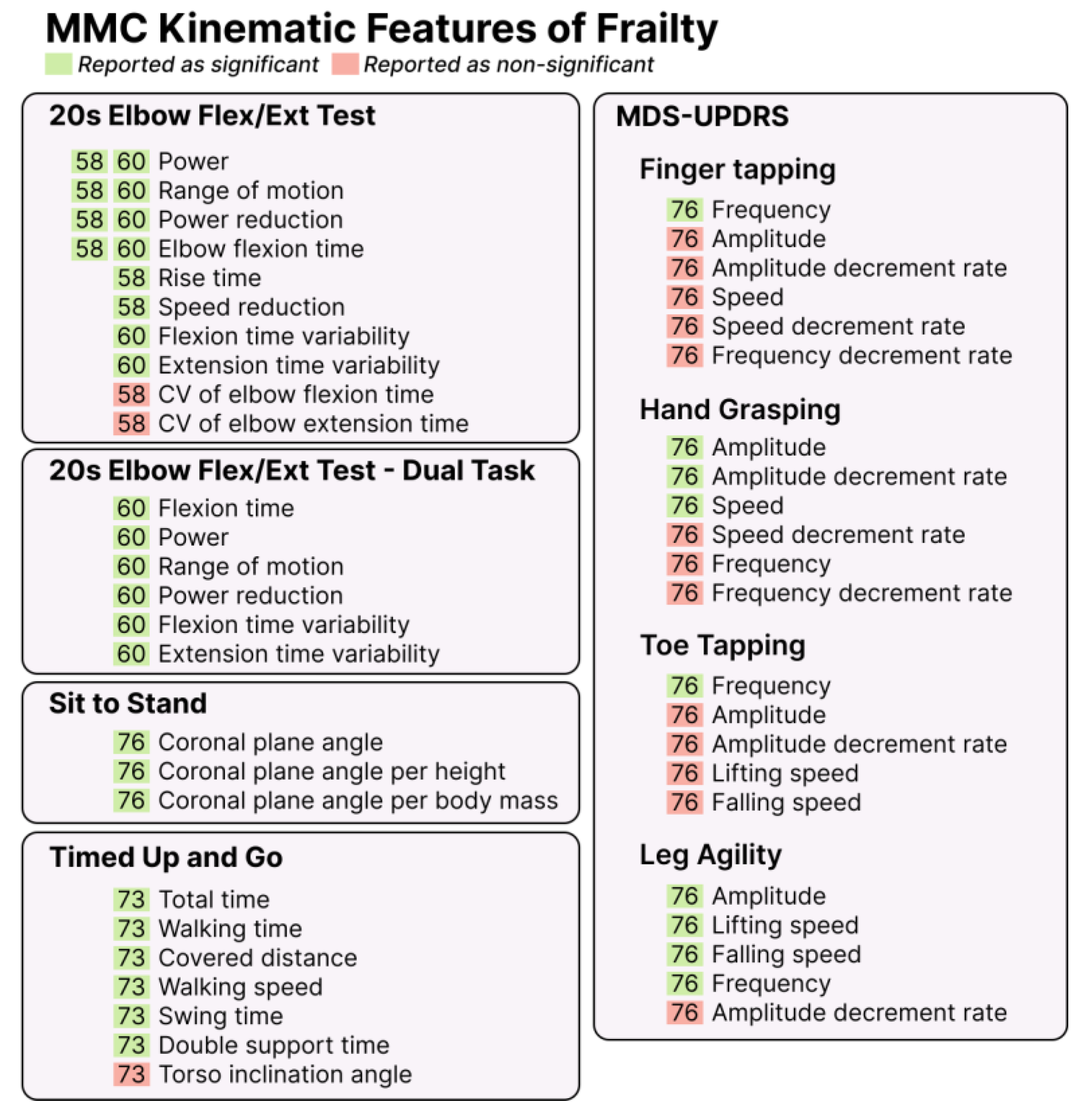
3.7. Kinematic Features of Frailty
3.8. Feature Sets
3.9. Rates of Errors in Recording
4. Discussion
4.1. Future Directions
4.2. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.H.; Rockwood, K. Frailty in Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmour, H.; Ramage-Morin, P.L. Association of frailty and pre-frailty with increased risk of mortality among older Canadians. Health Rep. 2021, 32, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.E.; Snih, S.A.; Berges, I.M.; Ray, L.A.; Markides, K.S.; Ottenbacher, K.J. Frailty and 10-year mortality in community-living Mexican American older adults. Gerontology 2009, 55, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensrud, K.E.; Ewing, S.K.; Cawthon, P.M.; Fink, H.A.; Taylor, B.C.; Cauley, J.A.; Dam, T.T.; Marshall, L.M.; Orwoll, E.S.; Cummings, S.R.; et al. A comparison of frailty indexes for the prediction of falls, disability, fractures, and mortality in older men. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2009, 57, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhodary, A.A.; Aljunid, S.M.; Ismail, A.; Nur, A.M.; Shahar, S. The economic Burden of Frailty Among Elderly People: A Review of the Current Literature. Malays. J. Public Health Med. 2020, 20, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, M.; Prince, M.; Thiyagarajan, J.A.; De Carvalho, I.A.; Bernabei, R.; Chan, P.; Gutierrez-Robledo, L.M.; Michel, J.P.; Morley, J.E.; Ong, P.; et al. Frailty: An Emerging Public Health Priority. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, N.; Darvishi, N.; Ahmadipanah, M.; Shohaimi, S.; Mohammadi, M. Global prevalence of falls in the older adults: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2022, 17, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishya, R.; Vaish, A. Falls in Older Adults are Serious. Indian. J. Orthop. 2020, 54, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori-Asenso, R.; Chin, K.L.; Mazidi, M.; Zomer, E.; Ilomaki, J.; Zullo, A.R.; Gasevic, D.; Ademi, Z.; Korhonen, M.J.; LoGiudice, D.; et al. Global Incidence of Frailty and Prefrailty Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e198398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health Agency of Canada. Surveillance Report on Falls Among Older Adults in Canada. 2024. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/healthy-living/surveillance-report-falls-older-adults-canada.html#a2.6 (accessed on 29 December 2024).
- Yang, Z.C.; Lin, H.; Jiang, G.H.; Chu, Y.H.; Gao, J.H.; Tong, Z.J.; Wang, Z.H. Frailty Is a Risk Factor for Falls in the Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2023, 27, 487–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhu, M.; Wang, R. Associations among frailty status, hypertension, and fall risk in community-dwelling older adults. Int. J. Nurs. Sci. 2024, 11, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.-H.; Chang, S.-F. Frailty as a Risk Factor for Falls Among Community Dwelling People: Evidence From a Meta-Analysis. J. Nurs. Scholarsh. 2017, 49, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensrud, K.E.; Ewing, S.K.; Taylor, B.C.; Fink, H.A.; Stone, K.L.; Cauley, J.A.; Tracy, J.K.; Hochberg, M.C.; Rodondi, N.; Cawthon, P.M.; et al. Frailty and risk of falls, fracture, and mortality in older women: The study of osteoporotic fractures. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2007, 62, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chittrakul, J.; Siviroj, P.; Sungkarat, S.; Sapbamrer, R. Physical Frailty and Fall Risk in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Aging Res. 2020, 2020, 3964973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, S.; Hosoi, T.; Yakabe, M.; Yunoki, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Kase, Y.; Miyawaki, M.; Ishii, M.; Ogawa, S. Preventative approaches to falls and frailty. Osteoporos. Sarcopenia 2025, 11 (Suppl. S2), 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Long, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wu, S. The association between cognitive frailty and the risk of fall occurrence in older adults: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1537240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Gan, P.; How, C.H. Approach to frailty in the elderly in primary care and the community. Singap. Med. J. 2018, 59, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrier, G.; Filipovic, A.; Wasan, H.; di Pietro, A.; Mittal, D.; Kamath, G.; Kharawala, S.; Mehmud, F. A targeted literature review on the impact of tailored interventions on patient outcomes in oncology. Oncogene 2025, 44, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dautzenberg, L.; Beglinger, S.; Tsokani, S.; Zevgiti, S.; Raijmann, R.; Rodondi, N.; Scholten, R.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Di Nisio, M.; Emmelot-Vonk, M.; et al. Interventions for preventing falls and fall-related fractures in community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2021, 69, 2973–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faller, J.W.; Pereira, D.D.N.; de Souza, S.; Nampo, F.K.; Orlandi, F.S.; Matumoto, S. Instruments for the detection of frailty syndrome in older adults: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, E.; Jang, I.Y. Frailty and Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panhwar, Y.N.; Naghdy, F.; Naghdy, G.; Stirling, D.; Potter, J. Assessment of frailty: A survey of quantitative and clinical methods. BMC Biomed. Eng. 2019, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, R., 2nd; Assadzandi, S.; Adelman, M. Frailty: Evaluation and Management. Am. Fam. Physician 2021, 103, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lameirinhas, J.; Gorostiaga, A.; Etxeberria, I. Definition and assessment of psychological frailty in older adults: A scoping review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 100, 102442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, L.; Needham, L.; McGuigan, P.; Bilzon, J. Applications and limitations of current markerless motion capture methods for clinical gait biomechanics. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancillao, A.; Aertbelien, E.; De Schutter, J. Effect of the soft tissue artifact on marker measurements and on the calculation of the helical axis of the knee during a gait cycle: A study on the CAMS-Knee data set. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2021, 80, 102866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvorkin, V.; Garcia-Fernandez, M.; Gonzalez-Casado, G.; Li, M.; Rovira-Garcia, A. Assessment of Noise of MEMS IMU Sensors of Different Grades for GNSS/IMU Navigation. Sensors 2024, 24, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuirk, T.E.; Perry, E.S.; Sihanath, W.B.; Riazati, S.; Patten, C. Feasibility of Markerless Motion Capture for Three-Dimensional Gait Assessment in Community Settings. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 867485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, B.; Seyres, M.; Philp, F.; Chadwick, E.K.; Blana, D. Healthcare applications of single camera markerless motion capture: A scoping review. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.W.T.; Tang, Y.M.; Fong, K.N.K. A systematic review of the applications of markerless motion capture (MMC) technology for clinical measurement in rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2023, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabbasi, H.; Gradinaru, A.; Moldoveanu, F.; Moldoveanu, A. Human motion tracking & evaluation using Kinect V2 sensor. In Proceedings of the E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB), Iasi, Romania, 19–21 November 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Microsoft Kinect sensor and its effect. IEEE Multimed. 2012, 19, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scataglini, S.; Abts, E.; Van Bocxlaer, C.; Van den Bussche, M.; Meletani, S.; Truijen, S. Accuracy, Validity, and Reliability of Markerless Camera-Based 3D Motion Capture Systems versus Marker-Based 3D Motion Capture Systems in Gait Analysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sensors 2024, 24, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Jiao, Y.; Meiring, R.M.; Sheng, B.; Zhang, Y. Reliability and validity of current computer vision based motion capture systems in gait analysis: A systematic review. Gait Posture 2025, 120, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, N.A.; Caccese, J.B.; Tracy, R.E.; Hagen, J.; Quatman-Yates, C.C.; On, A.J. The Validity and Usability of Markerless Motion Capture and Inertial Measurement Units for Quantifying Dynamic Movements. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2025, 57, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattananon, P.; Ebaugh, D.; Biely, S.A.; Smith, S.S.; Hicks, G.E.; Silfies, S.P. Kinematic characterization of clinically observed aberrant movement patterns in patients with non-specific low back pain: A cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, F.; Shim, J.; Wu, F.; Langer, P.; Fleisch, E. The Bitemporal Lens Model-toward a holistic approach to chronic disease prevention with digital biomarkers. JAMIA Open 2024, 7, ooae027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, A.; Bihl, T.; Bresciani, J.P. Identifying Fall Risk Predictors by Monitoring Daily Activities at Home Using a Depth Sensor Coupled to Machine Learning Algorithms. Sensors 2021, 21, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, A.; Bihl, T.; Bresciani, J.P. Automatic measurement of fall risk indicators in timed up and go test. Inf. Health Soc. Care 2019, 44, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorce, P. Musculoskeletal Disorders and Diseases: Biomechanical Modeling in Sport, Health, Rehabilitation and Ergonomics. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Park, D.; Rha, D.W.; Nam, H.S.; Jo, Y.J.; Kim, D.Y. Kinematic analysis of movement patterns during a reach-and-grasp task in stroke patients. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1225425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.W.; Chang, C.F. Biomechanics of human movement and its clinical applications. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2012, 28 (Suppl. S2), S13–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillon, K.; Kivimaki, M.; Hamer, M.; Sabia, S.; Fransson, E.I.; Singh-Manoux, A.; Gale, C.R.; Batty, G.D. Measures of frailty in population-based studies: An overview. BMC Geriatr. 2013, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strini, V.; Schiavolin, R.; Prendin, A. Fall Risk Assessment Scales: A Systematic Literature Review. Nurs. Rep. 2021, 11, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.; Connie, T.; Goh, M.K.O.; Saedon, N. Model-Based Feature Extraction and Classification for Parkinson Disease Screening Using Gait Analysis: Development and Validation Study. JMIR Aging 2025, 8, e65629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouca-Machado, R.; Branco, D.; Fonseca, G.; Fernandes, R.; Abreu, D.; Guerreiro, T.; Ferreira, J.J.; CNS Physiotherapy Study group. Kinematic and Clinical Outcomes to Evaluate the Efficacy of a Multidisciplinary Intervention on Functional Mobility in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 637620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyasingh-Jacob, J.; Crook-Rumsey, M.; Shah, H.; Joseph, T.; Abulikemu, S.; Daniels, S.; Sharp, D.J.; Haar, S. Markerless Motion Capture to Quantify Functional Performance in Neurodegeneration: Systematic Review. JMIR Aging 2024, 7, e52582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ruiz, L.; Jimenez, A.R.; Garcia-Villamil, G.; Seco, F. Detecting Fall Risk and Frailty in Elders with Inertial Motion Sensors: A Survey of Significant Gait Parameters. Sensors 2021, 21, 6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aromataris, E.; Lockwood, C.; Porritt, K.; Pilla, B.; Jordan, Z. (Eds.) JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; JBI: Adelaide, Australia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatesiktat, P.; Lim, G.M.; Lim, W.S.; Ang, W.T. Anatomical-Marker-Driven 3D Markerless Human Motion Capture. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 2024, 29, 6186–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchet, O.; Fantino, B.; Allali, G.; Muir, S.W.; Montero-Odasso, M.; Annweiler, C. Timed Up and Go test and risk of falls in older adults: A systematic review. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2011, 15, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, S.W.; Berg, K.; Chesworth, B.; Speechley, M. Use of the Berg Balance Scale for predicting multiple falls in community-dwelling elderly people: A prospective study. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wapp, C.; Mittaz Hager, A.G.; Hilfiker, R.; Zysset, P. History of falls and fear of falling are predictive of future falls: Outcome of a fall rate model applied to the Swiss CHEF Trial cohort. Front. Aging 2022, 3, 1056779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, L.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Walston, J.; Newman, A.B.; Hirsch, C.; Gottdiener, J.; Seeman, T.; Tracy, R.; Kop, W.J.; Burke, G.; et al. Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M146–M156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, K.; Song, X.; MacKnight, C.; Bergman, H.; Hogan, D.B.; McDowell, I.; Mitnitski, A. A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people. CMAJ 2005, 173, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahiri, M.; Wang, C.; Gardea, M.; Nguyen, H.; Shahbazi, M.; Sharafkhaneh, A.; Ruiz, I.T.; Nguyen, C.K.; Bryant, M.S.; Najafi, B. Remote Physical Frailty Monitoring-The Application of Deep Learning-Based Image Processing in Tele-Health. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 219391–219399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargar, B.A.H.; Mollahosseini, A.; Struemph, T.; Pace, W.; Nielsen, R.D.; Mahoor, M.H. Automatic measurement of physical mobility in Get-Up-and-Go Test using Kinect sensor. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2014, 2014, 3492–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan Rouzi, M.; Lee, M.; Beom, J.; Bidadi, S.; Ouattas, A.; Cay, G.; Momin, A.; York, M.K.; Kunik, M.E.; Najafi, B. Quantitative biomechanical analysis in validating a video-based model to remotely assess physical frailty: A potential solution to telehealth and globalized remote-patient monitoring. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2024, 14, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, L.J.; DeRoche, C.B.; Rantz, M.; Alexander, G.L.; Skubic, M.; Despins, L.; Abbott, C.; Harris, B.H.; Galambos, C.; Koopman, R.J. Using Embedded Sensors in Independent Living to Predict Gait Changes and Falls. West. J. Nurs. Res. 2017, 39, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantz, M.; Skubic, M.; Abbott, C.; Galambos, C.; Popescu, M.; Keller, J.; Stone, E.; Back, J.; Miller, S.J.; Petroski, G.F. Automated In-Home Fall Risk Assessment and Detection Sensor System for Elders. Gerontologist 2015, 55 (Suppl. S1), S78–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, E.; Skubic, M.; Rantz, M.; Abbott, C.; Miller, S. Average in-home gait speed: Investigation of a new metric for mobility and fall risk assessment of elders. Gait Posture 2015, 41, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rantz, M.J.; Skubic, M.; Abbott, C.; Galambos, C.; Pak, Y.; Ho, D.K.C.; Stone, E.E.; Rui, L.; Back, J.; Miller, S.J. In-home fall risk assessment and detection sensor system. J. Gerontol. Nurs. 2013, 39, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Aldunate, R.G.; Paramathayalan, V.R.; Ratnam, R.; Jain, S.; Morrow, D.G.; Sosnoff, J.J. Preliminary evaluation of a self-guided fall risk assessment tool for older adults. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2019, 82, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, S.; Dolatabadi, E.; Ng, K.-D.; Mansfield, A.; Flint, A.; Taati, B.; Iaboni, A. Vision-Based Assessment of Gait Features Associated with Falls in People with Dementia. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 1148–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, S.; Nabavi, H.; Sabo, A.; Arora, T.; Iaboni, A.; Taati, B. The Toronto older adults gait archive: Video and 3D inertial motion capture data of older adults’ walking. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdizadeh, S.; Sabo, A.; Ng, K.-D.; Mansfield, A.; Flint, A.J.; Taati, B.; Iaboni, A. Predicting Short-Term Risk of Falls in a High-Risk Group with Dementia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2021, 22, 689–695.e681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.-D.; Mehdizadeh, S.; Iaboni, A.; Mansfield, A.; Flint, A.; Taati, B. Measuring Gait Variables Using Computer Vision to Assess Mobility and Fall Risk in Older Adults with Dementia. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2020, 8, 2100609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamahori, K.; Zin, T.T. A Study on Assessment of Falling Risk in the Elderly Using a Balance Task. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 12th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Nara, Japan, 10–13 October 2013; pp. 513–514. [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka, H.; Tanaka, N.; Eng, M.; Saeki, K.; Kiriyama, T.; Eura, N.; Ikeda, M.; Izumi, T.; Kitauti, T.; Furiya, Y.; et al. Risk of falling in Parkinson’s disease at the Hoehn-Yahr stage III. Eur. Neurol. 2011, 66, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuguchi, Y.; Nakao, M.; Nagai, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Abe, T.; Kakinoki, S.; Imagawa, S.; Matsutani, K.; Saito, T.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Machine learning-based gait analysis to predict clinical frailty scale in elderly patients with heart failure. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2024, 5, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshima, N.; Kohama, T.; Kusunoki, M.; Fujita, E.; Okada, S.; Kato, Y.; Kofuku, K.; Islam, M.M.; Brechue, W.F. Development of Simple, Objective Chair-Standing Assessment of Physical Function in Older Individuals Using a KinectTM Sensor. J. Frailty Aging 2019, 8, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, A.; Bresciani, J.-P. Validation of an ambient system for the measurement of gait parameters. J. Biomech. 2018, 69, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cao, J.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, M.; Luo, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, L.; Tsui, K.-L.; Zhao, Y. Identifying sensors-based parameters associated with fall risk in community-dwelling older adults: An investigation and interpretation of discriminatory parameters. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Hong, R.; Wu, Z.; Yue, L.; Peng, K.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Jin, L.; Guan, Q. Kinect-based objective assessment for early frailty identification in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2023, 35, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, J. A Fall Risk Assessment Model for Community-Dwelling Elderly Individuals Based on Gait Parameters. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 120857–120867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejupi, A.; Brodie, M.; Gschwind, Y.J.; Lord, S.R.; Zagler, W.L.; Delbaere, K. Kinect-Based Five-Times-Sit-to-Stand Test for Clinical and In-Home Assessment of Fall Risk in Older People. Gerontology 2015, 62, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejupi, A.; Brodie, M.; Gschwind, Y.J.; Schoene, D.; Lord, S.; Delbaere, K. Choice stepping reaction time test using exergame technology for fall risk assessment in older people. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2014, 2014, 6957–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejupi, A.; Gschwind, Y.J.; Brodie, M.; Zagler, W.L.; Lord, S.R.; Delbaere, K. Kinect-based choice reaching and stepping reaction time tests for clinical and in-home assessment of fall risk in older people: A prospective study. Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act. Off. J. Eur. Group. Res. Into Elder. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Colagiorgio, P.; Romano, F.; Sardi, F.; Moraschini, M.; Sozzi, A.; Bejor, M.; Ricevuti, G.; Buizza, A.; Ramat, S. Affordable, automatic quantitative fall risk assessment based on clinical balance scales and Kinect data. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2014, 2014, 3500–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianaria, E.; Grangetto, M.; Roppolo, M.; Mulasso, A.; Rabaglietti, E. Kinect-based gait analysis for automatic frailty syndrome assessment. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 1314–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Latorre, J.; Colomer, C.; Alcaniz, M.; Llorens, R. Gait analysis with the Kinect v2: Normative study with healthy individuals and comprehensive study of its sensitivity, validity, and reliability in individuals with stroke. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, I.; Latorre, J.; Aguilar, M.; Pastor, P.; Llorens, R. Validity and sensitivity of instrumented postural and gait assessment using low-cost devices in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, K.; Thilarajah, S.; Pua, Y.-H.; Williams, G.; Tan, D.; Mentiplay, B.; Denehy, L.; Clark, R. Dynamic balance and instrumented gait variables are independent predictors of falls following stroke. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, S.; Paterson, K.; Bower, K.; McGinley, J.; Miller, K.; Pua, Y.-H.; Clark, R.A. Quantifying individual components of the timed up and go using the kinect in people living with stroke. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2015, 29, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Banerjee, A. Low-cost visual postural feedback with Wii balance board and Microsoft Kinect—A feasibility study. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Point-of-Care Healthcare Technologies (PHT), Bangalore, India, 16–18 January 2013; pp. 291–294. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, B.K.; Jain, H.; Vijay, V.; Yadav, S.K.; Mathur, A.; Hewson, D.J. A Comparison of Four Approaches to Evaluate the Sit-to-Stand Movement. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. A Publ. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2020, 28, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnechère, B.; Sholukha, V.; Omelina, L.; Van Vooren, M.; Jansen, B.; Van Sint Jan, S. Dynamic balance assessment of elderly patients using serious games. In REHAB ‘16: Proceedings of the 4th Workshop on ICTs for Improving Patients Rehabilitation Research Techniques, Lisbon Portugal, 13–14 October 2016; ACM Digital Library: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bourrelier, J.; Hassani, A.; Mourey, F.; Brost, V.; Yang, F.; Kubicki, A. Back to sit transfer in aging: Motor planning impairments and functional abilities in frail aged adults. Mov. Sports Sci. Sci. Et. Mot. 2016, 93, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargos, J.C.V.; Magalhaes, G.V.; Avellar, L.M.; Frizera, A.; Rinaldi, N.M. Increased Risk of Falling in Older Adults When Coordinating Obstacle Avoidance and Grasping. Mot. Control 2023, 27, 880–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Yu, X.; Xiong, S. A multifactorial fall risk assessment system for older people utilizing a low-cost, markerless Microsoft Kinect. Ergonomics 2024, 67, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Z.K.; Connie, T.; Goh, M.K.O.; Saedon, N.I.B. Fall risk prediction using temporal gait features and machine learning approaches. Front. Artif. Intell. 2024, 7, 1425713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.L.; Lee, C.H.; Lai, C.L.; Jiang, B.C. Correlating common clinical postural stability measurements with balance assessments. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2020, 20, 1950067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.R.; Chakravarty, K.; Sinha, A. Eigen Posture Based Fall Risk Assessment System Using Kinect. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, A.; Bihl, T.; Bresciani, J.-P. Automating the Timed Up and Go Test Using a Depth Camera. Sensors 2017, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejupi, A.; Gschwind, Y.J.; Valenzuela, T.; Lord, S.R.; Delbaere, K. A Kinect and Inertial Sensor-Based System for the Self-Assessment of Fall Risk: A Home-Based Study in Older People. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2016, 31, 261–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Bobadilla, A.V.; Schmitt, V.; Maier, C.S.; Mensing, S.; Stodtmann, S. Practical guide to SHAP analysis: Explaining supervised machine learning model predictions in drug development. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2024, 17, e70056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, H.; Yu, L.; Yeung, E.H.K.; Luo, J.; Tsui, K.L.; Zhao, Y. A Systematic Review of Wearable Sensor-Based Technologies for Fall Risk Assessment in Older Adults. Sensors 2022, 22, 6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Sosnoff, J.J. Novel sensing technology in fall risk assessment in older adults: A systematic review. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, A.; Fritz, S.L.; Lusardi, M. Walking speed: The functional vital sign. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2015, 23, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abellan van Kan, G.; Rolland, Y.; Andrieu, S.; Bauer, J.; Beauchet, O.; Bonnefoy, M.; Cesari, M.; Donini, L.M.; Gillette Guyonnet, S.; Inzitari, M.; et al. Gait speed at usual pace as a predictor of adverse outcomes in community-dwelling older people an International Academy on Nutrition and Aging (IANA) Task Force. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, C.E.; Fitzpatrick, A.L.; Leary, C.S.; Hajat, A.; Ilango, S.D.; Park, C.; Phelan, E.A.; Semmens, E.O. Change in gait speed and fall risk among community-dwelling older adults with and without mild cognitive impairment: A retrospective cohort analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardell, M.; Dolgoy, N.; Bernard, S.; Bayless, K.; Hirsche, R.; Dennett, L.; Tandon, P. Movement Outcomes Acquired via Markerless Motion Capture Systems Compared with Marker-Based Systems for Adult Patient Populations: A Scoping Review. Biomechanics 2024, 4, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Park, K. Improving Gait Analysis Techniques with Markerless Pose Estimation Based on Smartphone Location. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Shimatani, K.; Hasegawa, M.; Kurita, Y.; Ishige, Y.; Takemura, H. Accuracy of Temporo-Spatial and Lower Limb Joint Kinematics Parameters Using OpenPose for Various Gait Patterns with Orthosis. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 2666–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, N.A.; Eghobamien, I.J.; Nwaokoro, V.I.; Pamukoff, D.N. The influence of motion capture method, sex, and body mass index on lower extremity kinematics and intersession reliability during a drop-vertical jump. J. Sports Sci. 2025, 43, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Kim, K.I.; Choi, Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Kang, E.; Oh, H.K.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, E.K.; Yoon, Y.S.; Kang, S.B.; et al. Comparison of multidimensional frailty score, grip strength, and gait speed in older surgical patients. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study Characteristics | Population Characteristics | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Year | FR or F | N | Health Status | Sex M/F | Age Mean (SD) | Population at Risk of Falls or Frail n (%) | ||
| O | C | P | |||||||
| [84] | 2020 | FR | 97 | Patients with PD | 49/48 a | NR | 67.8 (NR) | NR | 6 (6.2) |
| [89] | 2016 | FR | 22 | Older adults | 5/17 a | 82 (8) | 22 (100) | ||
| [90] | 2016 | Both | 60 | Older adults | 27/33 | 84 (5.2) | 85.8 (5.2) | 82.6 (4.7) | 35 (58.3) |
| [85] | 2019 | FR | 81 | Stroke survivors | 43/48 | 62.8 (12.3) | 62.8 (12.3) | 63.4 (15.6) | 23 (28.4) |
| [91] | 2023 | FR | 26 | Older adults | NR | NR | 66.1 (3.8) | 66.2 (3.9) | 13 (50) |
| [81] | 2014 | FR | 79 | Older adults | NR | NR | 26 (5) | 76 (10) | 32 (40.5) |
| [60] | 2024 | F | 65 | Older adults | 16/49 | 56.0 (18.7) | NR | NR | NR |
| [39] | 2021 | FR | 30 | Hospital in-patients | 12/18 | 83.3 (8.5) | NR | NR | 21 (70) |
| [40] | 2019 | FR | 43 | Older adults | 16/27 | 83 (NR) | NR | NR | 21 (48.8) |
| [96] | 2017 | FR | 37 | Hospital in-patients | 14/23 | 83.6 (NR) | NR | NR | 21 (56.8) |
| [78] | 2015 | FR | 94 | Older adults | 28/66 a | 79.7 (6.4) | NR | NR | 29 (30.9) |
| [79] | 2014 | FR | 104 | Older adults | 34/70 | 80.7 (7.0) | NR | NR | 68 (65.4) |
| [80] | 2016 | FR | 94 | Older adults | 32/62 a | 80.6 (6.9) | NR | NR | 19 (20.2) |
| [82] | 2016 | F | 30 | Older adults | 5/25 | 75.6 (7.5) | NR | NR | 17 (56.8) |
| [70] | 2023 | FR | 6 | University students | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| [59] | 2014 | FR | 12 | Older adults | NR | NR | NR | NR | 7 (58.3) |
| [71] | 2011 | FR | 30 | Patients with PD | 14/16 a | 68.3 (7) | NR | NR | 15 (50) |
| [92] | 2024 | FR | 106 | Older adults | 0/106 | NR | 74.2 (5.1) | 76.6 (5) | 22 (20.8) |
| [83] | 2019 | FR | 437 | Stroke survivors | 224/213 a | NR | 48.3 (16.1) | 43.3 (18.6) | 18 (4.1) |
| [93] | 2024 | FR | 65 | MMU-FRiP: non-fallers Mendeley: fallers | MMU-FRiP: 18/3 Mendeley: 7/37 a | NR | NR | 70.0 (8.6) | 44 (67.7) |
| [66] | 2020 | FR | 52 | Older adults | 28/24 | 76.3 (8) | NR | NR | 28 (53.8) |
| [67] | 2022 | FR | 14 | Older adults | 3/11 | 86.7 (6.2) | NR | NR | NR |
| [68] | 2021 | FR | 51 | Patients with dementia | 23/28 | 76.3 (7.9) | NR | NR | 51 (100) |
| [72] | 2024 | F | 417 | Patients with heart failure | 222/194 | VC: 82.5 (5.2) DC: 82.3 (4.9) | NR | NR | 417 (100) |
| [69] | 2020 | FR | 32 | Dementia | 18/11 | 75.5 (8.6) | 78.3 (8.9) | 17 (54.8) | |
| [61] | 2017 | FR | 23 | Older adults | 7/16 | 85.2 (NR) | 13 (56.5) | ||
| [62] | 2015 | FR | 19 | Older adults | 9/10 a | 87 (NR) | NR | ||
| [64] | 2013 | FR | 32 | Older adults | 7/8 a | 56.5 (11.5) | 87.5 (7.9) | NR | |
| [88] | 2020 | FR | 37 | Older adults | NR | 28.3 (6.8) | 67.2 (6.7) | 16 (43.2) | |
| [63] | 2015 | FR | 16 | Older adults | 7/9 | 85.8 (8.0) | NR | NR | NR |
| [94] | 2020 | FR | 15 | Stroke survivors | 13/2 | 58.6 (8.7) | NR | NR | NR |
| [65] | 2019 | FR | 30 | Bone clinic patients | 0/30 | NR | 74.5 (6.2) | 80.8 (9.2) | 10 (33.3) |
| [73] | 2019 | F | 402 | Older adults | 136/266 a | 73.7 (7.5) | NR | NR | 90 (22.4) |
| [95] | 2018 | FR | 224 | Patients with neurological disorders | 144/80 | 67.5 (14) | NR | NR | 45 (20.1) |
| [86] | 2015 | FR | 30 | Stroke survivors | 21/9 | 68 (15) | NR | NR | NR |
| [75] | 2024 | FR | 41 | Older adults | 5/36 | NR | 77.4 (5.3) | 82.0 (7.4) | 15 (36.6) |
| [76] | 2023 | F | 52 | Patients with PD | 24/28 | 65.5 (8.9) | 65.5 (NR) | 69 (NR) | 32 (61.5) |
| [58] | 2020 | F | 21 | Patients with COPD | NR | 67.8 (10.7) | NR | NR | NR |
| [77] | 2023 | FR | 46 | Older adults | 15/31 | 71.4 (5.11) | NR | NR | 10 (21.7) |
| Hardware | MMC Set-Up | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Device | n of Devices | Set-Up | Additional Equipment | Algorithm | Key Points | Features | Features or Feature Set? |
| Alvarez 2020 [84] | Kinect v2 | 1 | H: 0.8 m D: 1.5 Frontal plane | WBB, table, laptop | NR | NR | 20 | Features |
| Bonnechère 2016 [89] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | Frontal plane | WBB, table, display screen | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | NR | 8 | Features |
| Bourrelier 2016 [90] | Kinect | 1 | D: 2.5 m A: 20 degrees Sagittal plane | Chair with armrests | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | NR | 2 | Features |
| Bower 2019 [85] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | D: 1.8–4.0 m | Table, laptop | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | NR | 9 | Features |
| Camargos 2023 [91] | Kinect | 3 | NR | Leap motion controller | NR | NR | 20 | Features |
| Colagiorgio 2014 [81] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | D: 2 m Frontal plane | NR | NR | NR | 80 | Features |
| Dehghan Rouzi 2024 [60] | Smartphones or Tablet cameras | 1 | Sagittal plane | NR | Google’s MediaPipe | 32 | 14 | Features |
| Dubois 2017 [96] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | D: 4 m Sagittal plane | Stopwatch | Custom algorithm | NR | 21 | Features |
| Dubois 2019 [40] | Kinect | 1 | D: 4 m H: 1.7 m A: 20 degrees Sagittal plane | NR | Custom algorithm | NR | 17 features Set of 1–3 features | Feature set + features |
| Dubois 2021 [39] | Kinect v2 | 1 | A: 20 degrees | Tripod | Custom algorithm | NR | 15 features Set of 2 features | Feature set + features |
| Ejupi 2014 [79] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | D: 2 m H: 0.8 m Frontal plane | TV, tripod/table | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | NR | 6 | Features |
| Ejupi 2015 [78] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | D: 2 m H: 0.8 m Frontal plane | Monitor | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | NR | 5 | Features |
| Ejupi 2016 [80] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | D: 2 m H: 0.8 m Frontal plane | TV screen | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | NR | 8 | Features |
| Gianaria 2016 [82] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | D: 4 m H: 2 m | NR | Custom algorithm | 25 | 7 | Features |
| Kamahori 2023 [70] | Intel RealSense D435 2D camera | 1 | D: 3.25 m H: 1.1 m | Tripod | Custom algorithm | NR | Set of 5 features | Feature sets |
| Kargar 2014 [59] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | D: 3.5 m H: 1.2 m | Table, chair | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | 20 | 5 | Features |
| Kataoka 2011 [71] | Unspecified camera | 1 | NR | NR | Manual labeling | NR | 21 | Features |
| Kim 2024 [92] | Kinect | 1 | D: 3.2 m H: 0.7 m Frontal plane | Table, chair, cone, balance pad | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | 25 | 66 | Features |
| Latorre 2019 [83] | Kinect v2 | 1 | D: 6 m | NR | Custom algorithm | 25 | 23 | Features |
| Lim 2024 [93] | ||||||||
| Mehdizadeh 2020 [66] | Kinect V2 | 1 | Ceiling mount | RFID tags | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | NR | 30 | Features |
| Mehdizadeh 2021 [68] | Kinect | 1 | Ceiling mount | RFID tags | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | NR | 12 | Features |
| Mehdizadeh 2022 [67] | Motorola Moto G5 Play cell phones | 2 | D: 1.1–2 m | IMUs | Alphapose, OpenPose, and Detectron | NR | 24 | Features |
| Mizuguchi 2024 [72] | iPod touch, seventh generation | 1 | D: 4 m H: 1 m | Tripod, floor markers, chair | OpenPose | 25 | Set of 45 features | Feature sets |
| Ng 2020 [69] | Kinect V2 | 1 | Ceiling mount | NR | Openpose | 13 | 7 | Features |
| Phillips 2017 [61] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | NR | NR | Custom algorithm | NR | 3 | Features |
| Rantz 2013 [64] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | Ceiling mount | NR | Custom algorithm | NR | 3 | Features |
| Rantz 2015 [62] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | Ceiling mount | NR | Custom algorithm | NR | 3 | Features |
| Shukla 2020 [88] | Kinect | 2 | D: 2.3 m Frontal plane | NR | Custom algorithm | 15 | 2 | Features |
| Stone 2015 [63] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | Ceiling mount | NR | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | NR | 1 | Features |
| Sun 2019 [65] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | D: 2 m H: 1 m | PC-based computer and a display screen | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | NR | 13 | Features |
| Sun 2020 [94] | Xbox 360 Kinect | 1 | Frontal plane | Display | Unity3D software | NR | 5 | Features |
| Takeshima 2019 [73] | Microsoft Kinect | D: 3 m H: 0.1 m | Tripod, laptop | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | 25 | 3 | Features | |
| Tripathy 2018 [95] | Kinect Xbox 360 (Kinect 1) and Kinect Xbox One (Kinect 2) | 2 | D: 3 m Frontal plane | NR | Custom algorithm | 20 | Set of 7 features | Feature sets |
| Vernon 2015 [86] | Kinect Xbox 360 | 1 | Frontal plane | Table, chair | Custom algorithm | 7 | 7 | Features |
| Wang 2024 [75] | Microsoft Kinect | 1 | NR | Chair, tripod | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | 25 | 142 | Features |
| Xie 2023 [76] | Azure Kinect | 1 | D: 1.2–2.2 m H: 1 m | Table, chair | Custom algorithm | 32 | 22 | Features |
| Zahiri 2020 [58] | Samsung Galaxy Tablet | 1 | Sagittal plane | Tripod, IMU | OpenPose | 3 | 20 | Features |
| Zhang 2023 [77] | Azure Kinect | 1 | D: 0.8 m Frontal plane | IMUs | Kinect-based skeletal tracking | 32 | 8 | Features |
| Frailty/Fall Risk Reference Assessment (Non-MMC) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Type | Reference Measure | Administered By | MMC Task/Activity |
| Alvarez 2020 [84] | Clinical | POMA | Neurologist | Gait analysis |
| Bonnechère 2016 [89] | Clinical | Tinetti, BBS, TUG, 30 s STS | Clinical evaluation | Video game |
| Bourrelier 2016 [90] | Clinical | TUG and gait speed | PT | STS |
| Bower 2019 [85] | Clinical | Step test, TUG, prospective fall monitoring | PT and EP | Gait analysis |
| Camargos 2023 [91] | Self-report | Fall history | Self-report | Gait analysis |
| Colagiorgio 2014 [81] | Clinical | Tinetti test | Clinician | Tinetti test |
| DehghanRouzi 2024 [60] | Clinical | Frailty meter assessment protocol | Research staff | 20 s elbow flexion and extension test |
| Dubois 2017 [96] | Clinical | TUG | Healthcare professional | TUG |
| Dubois 2019 [40] | Clinical | TUG | Healthcare professional | TUG |
| Dubois 2021 [39] | Clinical | Tinetti test, TUG | PT | Ambient monitoring |
| Ejupi 2014 [79] | Self-report | Fall history | Self-report | CSRT |
| Ejupi 2015 [78] | Clinical | 5STS, fall history | Research staff | 5STS |
| Ejupi 2016 [80] | Clinical | PPA and prospective fall reporting | Research staff | Choice reaction times |
| Gianaria 2016 [82] | Self-report | TUG, TFI | Self-report | TUG |
| Kamahori 2023 [70] | Clinical | Tinetti test | NR | Balance task |
| Kargar 2014 [59] | Clinical | Get up and go task | Physician | TUG |
| Kataoka 2011 [71] | Self-report | Fall history | Self-report | Gait analysis |
| Kim 2024 [92] | Self-report | Prospective fall monitoring | Self-report | TUG |
| Latorre [83] | Clinical | BBS | NR | Gait analysis |
| Lim 2024 [93] | Clinical | POMA and JHFRAT | Unspecified | TUG |
| Mehdizadeh 2020 [66] | Self-report | Prospective fall monitoring | Research Staff | Gait analysis |
| Mehdizadeh 2021 [68] | Self-report | Prospective fall monitoring | Research Staff | Gait analysis |
| Mehdizadeh 2022 [67] | Clinical | BBS, POMA, TUG | Research staff | Gait analysis |
| Mizuguchi 2024 [72] | Clinical | Clinical frailty scale | Cardiologists | Gait analysis |
| Ng 2020 [69] | Self-report | Prospective fall monitoring, POMA | Research staff and healthcare professional | Ambient monitoring |
| Phillips 2017 [61] | Self-report | Prospective fall monitoring | Self-report | Gait analysis |
| Rantz 2013 [64] | Clinical | BBS, TUG, SPPB, SLS, HGS, FAP | Research staff | Gait analysis |
| Rantz 2015 [62] | Clinical | HGS, FRT, BBS, TUG, SPPB, SLS | Research staff | Gait analysis |
| Shulka 2020 [88] | Clinical | 5STS | “Expert” | 5STS |
| Stone 2015 [63] | Clinical | TUG, HGS, BBS, MDRT | Research staff | Ambient monitoring |
| Sun 2019 [65] | Clinical | TUG, BBS, FES | Research staff | Video game |
| Sun 2020 [94] | Clinical | Biodex balance system and TUG | PT and research staff | Video game |
| Takeshima 2019 [73] | Clinical | Functional independence measure | PT | STS |
| Tripathy 2018 [95] | Clinical | BBS | NR | SLS |
| Vernon 2015 [86] | Clinical | Step test, TUG, FRT | Assessor | TUG |
| Wang 2024 [75] | Clinical | BBS, TUG | NR | TUG |
| Xie 2023 [76] | Clinical | Fried’s frailty criteria | Movement disorder specialist | MDS-UPDRS-III |
| Zahiri 2020 [58] | Clinical | Fried’s frailty criteria | Validated IMU assessment | 20 s elbow flexion and extension test |
| Zhang 2023 [77] | Self-report | Fall history | Self-report | Gait analysis |
| Reference | Fall Risk or Frailty? | MMC Task/Activity | # of Features | Top 10 Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colagiorgio 2014 [81] | Fall risk | Tinetti test | 8 | Maximum amplitude of chest pitch, velocity of the steps, chest pitch during standing from chair, standing eyes open-Ks (postural control), standing eyes open SD, sit down chest pitch, standing eyes open mean velocity, sternal nudge changes in txc (postural control) |
| Kamahori 2023 [70] | Fall risk | Clinical test of sensory interaction and balance | 5 | M displacement of the center of gravity, the instantaneous max displacement of the center of gravity, the M displacement before and after the center of gravity, the instantaneous max displacement before and after the center of gravity, the variance in the arm swing width |
| Kargar 2014 [59] | Fall risk | TUG | 7 | Number of steps, duration of each step, number of steps in turning phase, distance between two elbows, angle between the legs, right and left knee angles |
| Lim 2024 [93] | Fall risk | TUG | 4 | Ave step time, cadence, ave stride time, ave stance time |
| Mizuguchi 2024 [72] | Frailty | Gait analysis | 45 | Gait speed, total gait time, spine angle in frontal walking, stance phase time, elbow angle (median), ankle swing speed (max), heel angle (min), trajectory of the ankle distance (max), ankle lift speed (max), cornering time… * |
| Tripathy 2018 [95] | Fall risk | BBS | 7 | Zero crossing rate, SLS duration, spectral entropy, disease, gender, fall history, postural deviation |
| Zahiri 2020 [58] | Frailty | 20 s arm flexion–extension test | 5 | Range of motion, percentage of decline in power, flexion time, flexion time variability, extension time variability |
| Zhang 2023 [77] | Fall risk | Gait analysis | 20 | Step frequency, BMI, gait cycle variability, hypertension, eye diseases, dyslipidemia, age, CV disease, diabetes, stride CV… * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osness, E.; Isley, S.; Bertrand, J.; Dennett, L.; Bates, J.; Van Decker, N.; Stanhope, A.; Omkar, A.; Dolgoy, N.; Ezeugwu, V.E.; et al. Markerless Motion Capture Parameters Associated with Fall Risk or Frailty: A Scoping Review. Sensors 2025, 25, 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185741
Osness E, Isley S, Bertrand J, Dennett L, Bates J, Van Decker N, Stanhope A, Omkar A, Dolgoy N, Ezeugwu VE, et al. Markerless Motion Capture Parameters Associated with Fall Risk or Frailty: A Scoping Review. Sensors. 2025; 25(18):5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185741
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsness, Emma, Serena Isley, Jennifer Bertrand, Liz Dennett, Jack Bates, Nathan Van Decker, Alexis Stanhope, Ayushi Omkar, Naomi Dolgoy, Victor E. Ezeugwu, and et al. 2025. "Markerless Motion Capture Parameters Associated with Fall Risk or Frailty: A Scoping Review" Sensors 25, no. 18: 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185741
APA StyleOsness, E., Isley, S., Bertrand, J., Dennett, L., Bates, J., Van Decker, N., Stanhope, A., Omkar, A., Dolgoy, N., Ezeugwu, V. E., & Tandon, P. (2025). Markerless Motion Capture Parameters Associated with Fall Risk or Frailty: A Scoping Review. Sensors, 25(18), 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185741






