An Analytical Model of Motion Artifacts in a Measured Arterial Pulse Signal—Part II: Tactile Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Arterial Wall Displacement as the True Pulse Signal
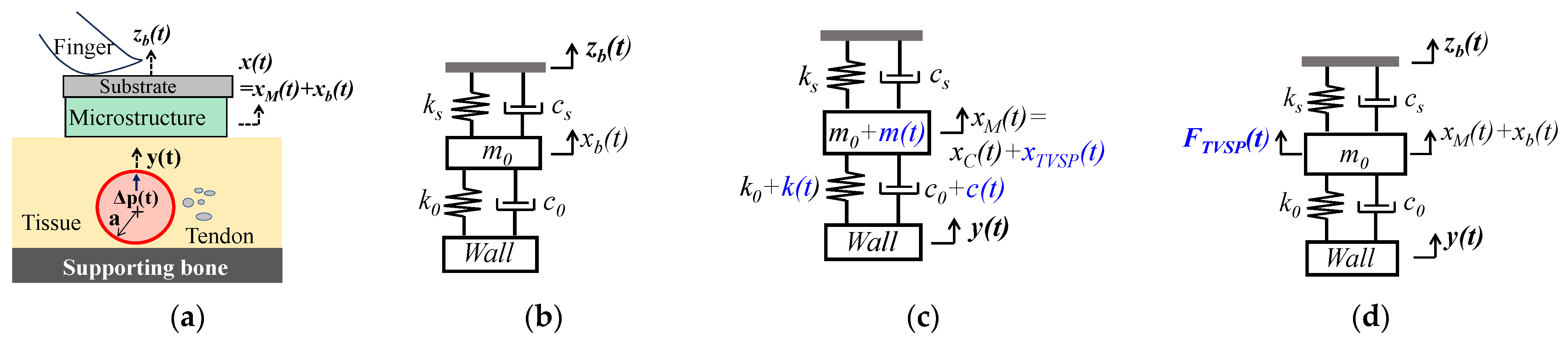
2.1.1. MA as Baseline Drift and TVSP
2.1.2. MA as Equivalent Forces
2.2. Arterial Pulsatile Pressure as the True Pulse Signal
2.2.1. MA as Baseline Drift and TVSP
2.2.2. MA as Equivalent Forces
2.3. Numerical Calculation
3. Results
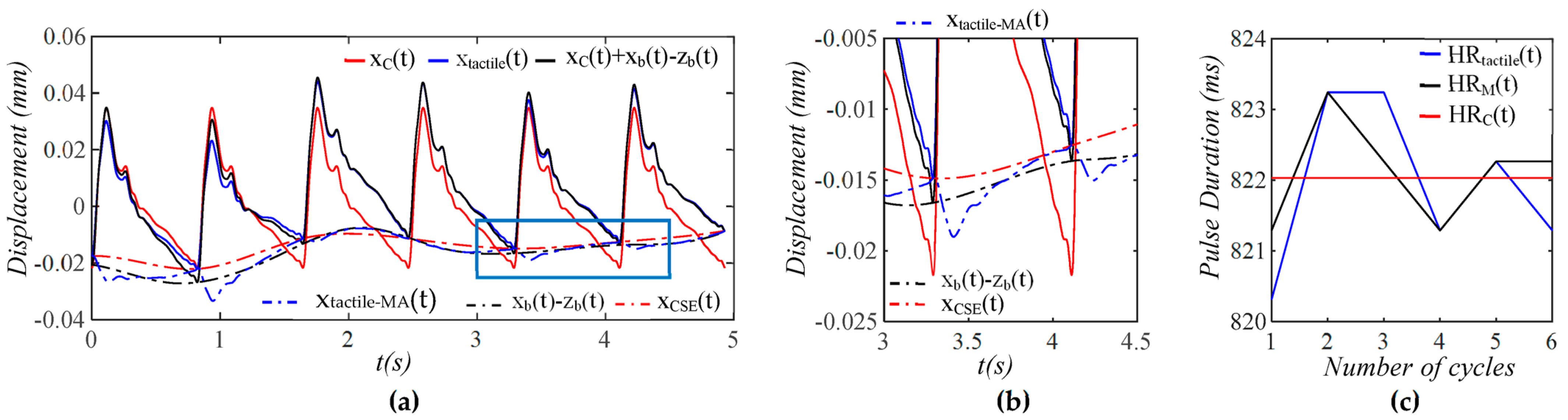
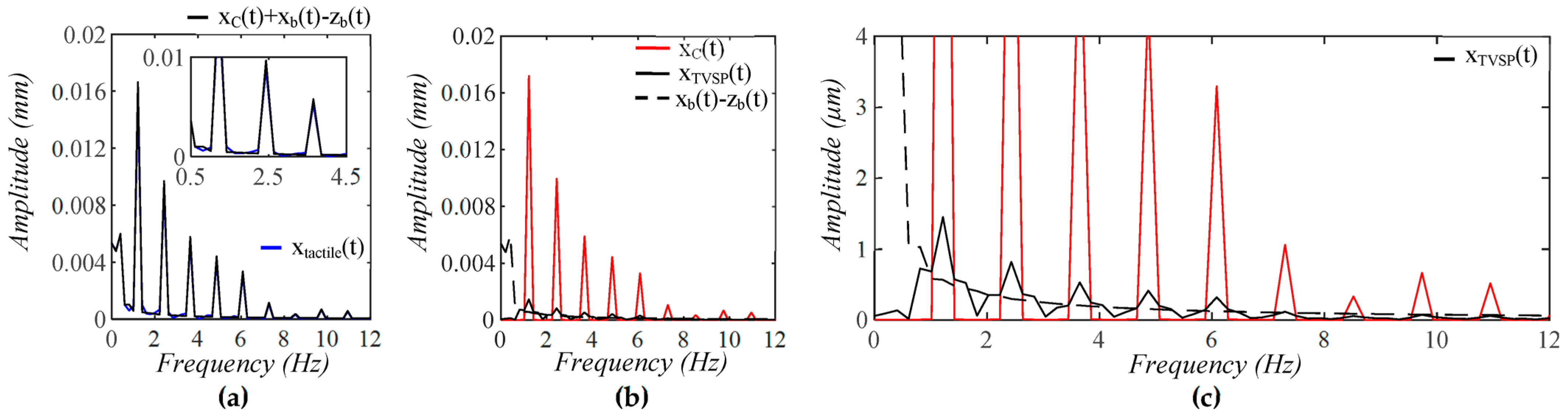
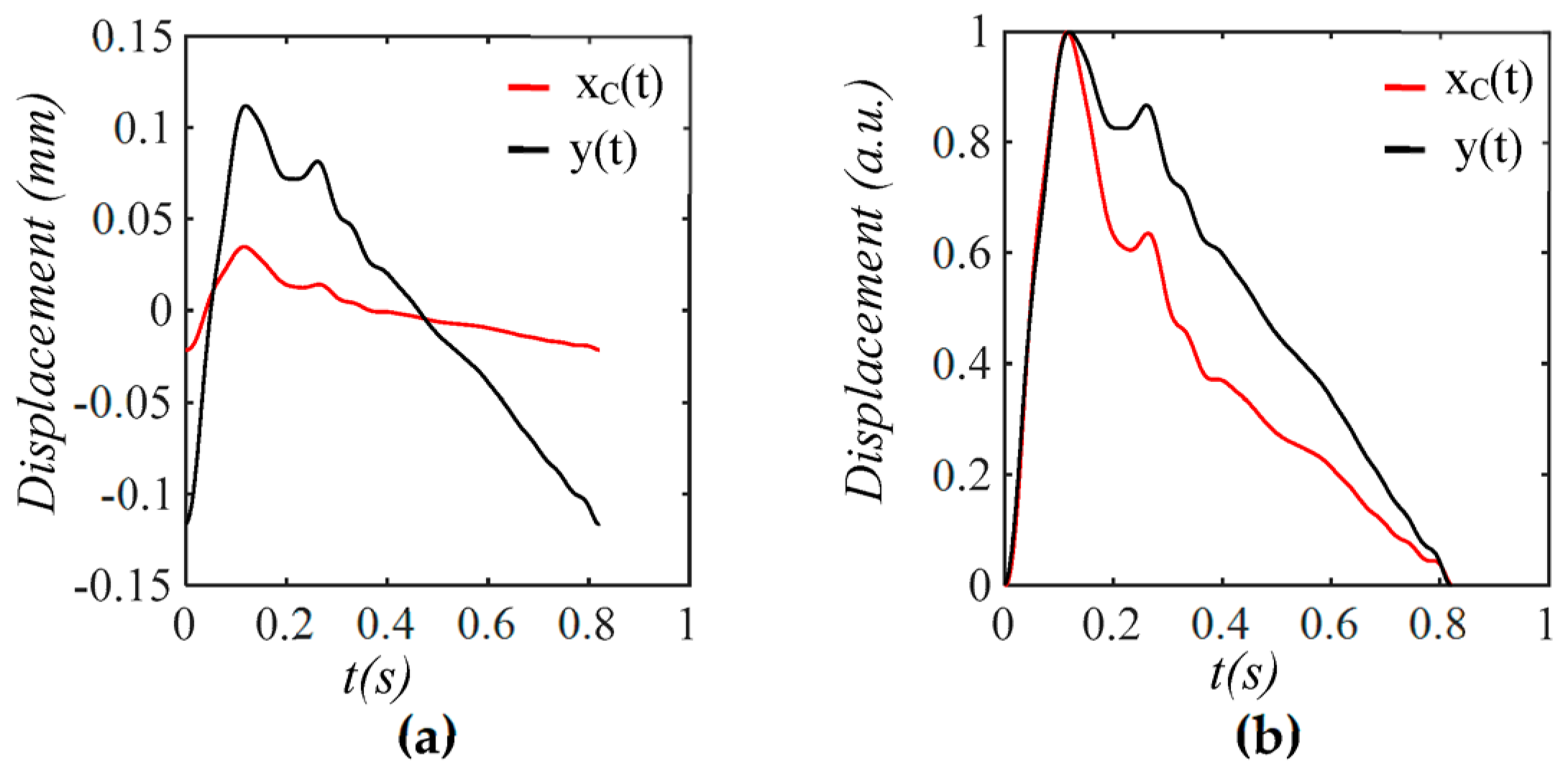
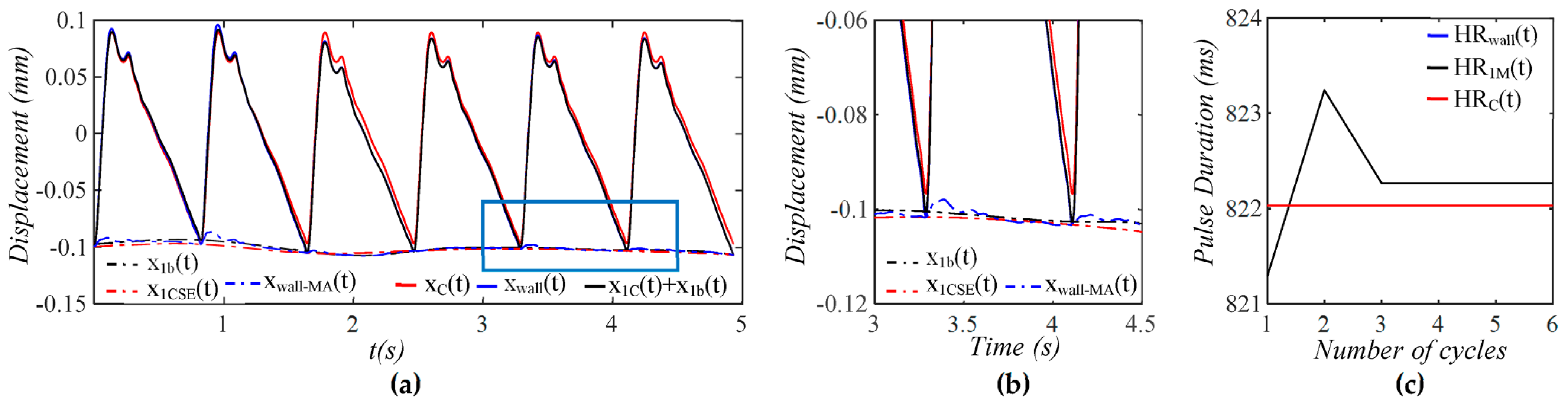
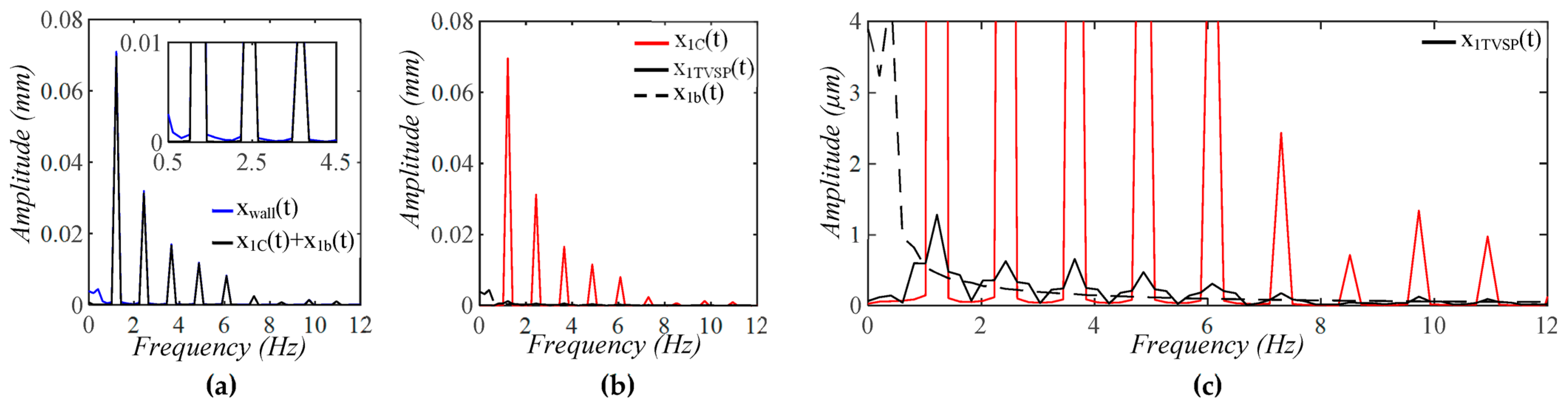
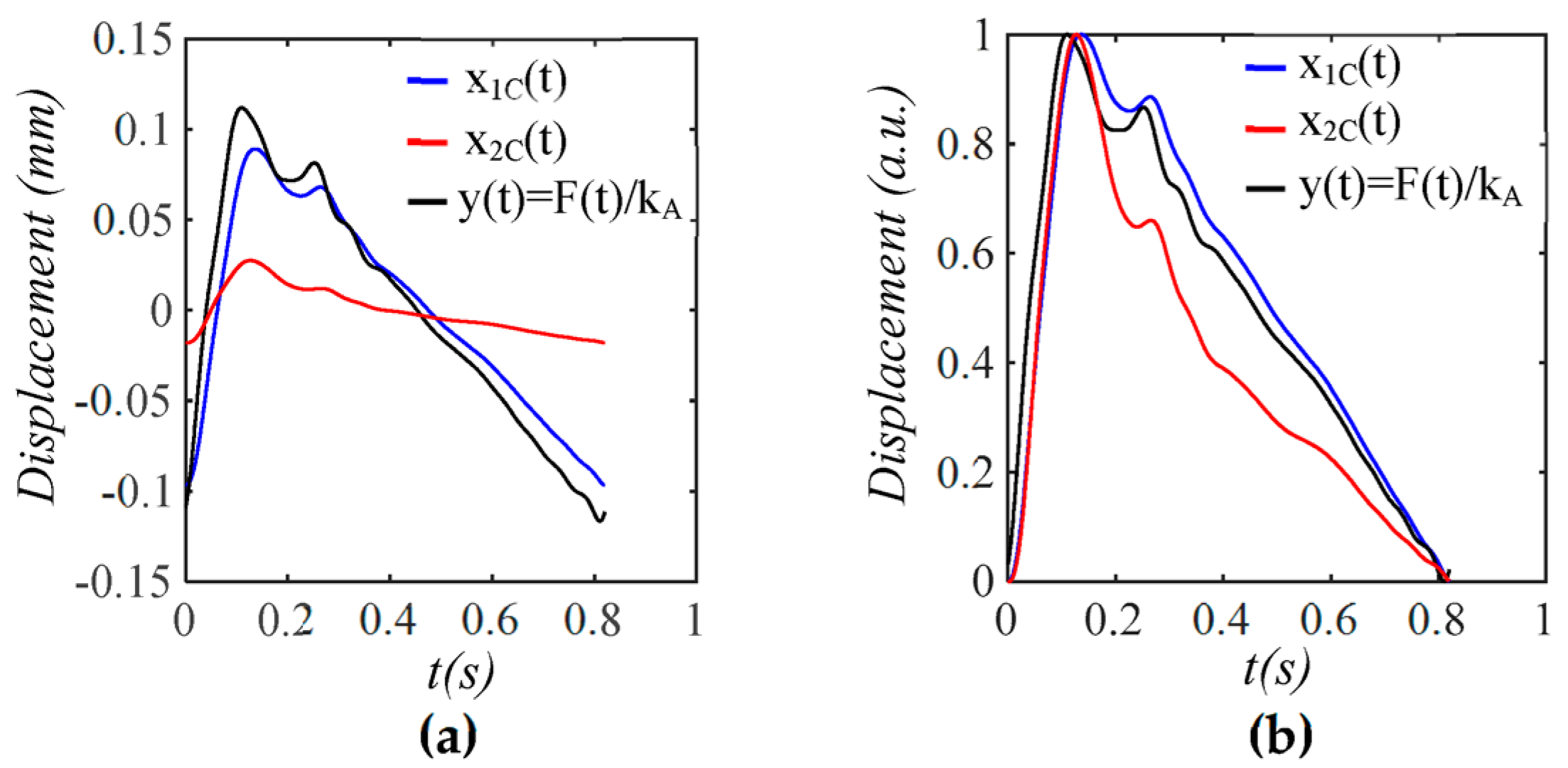
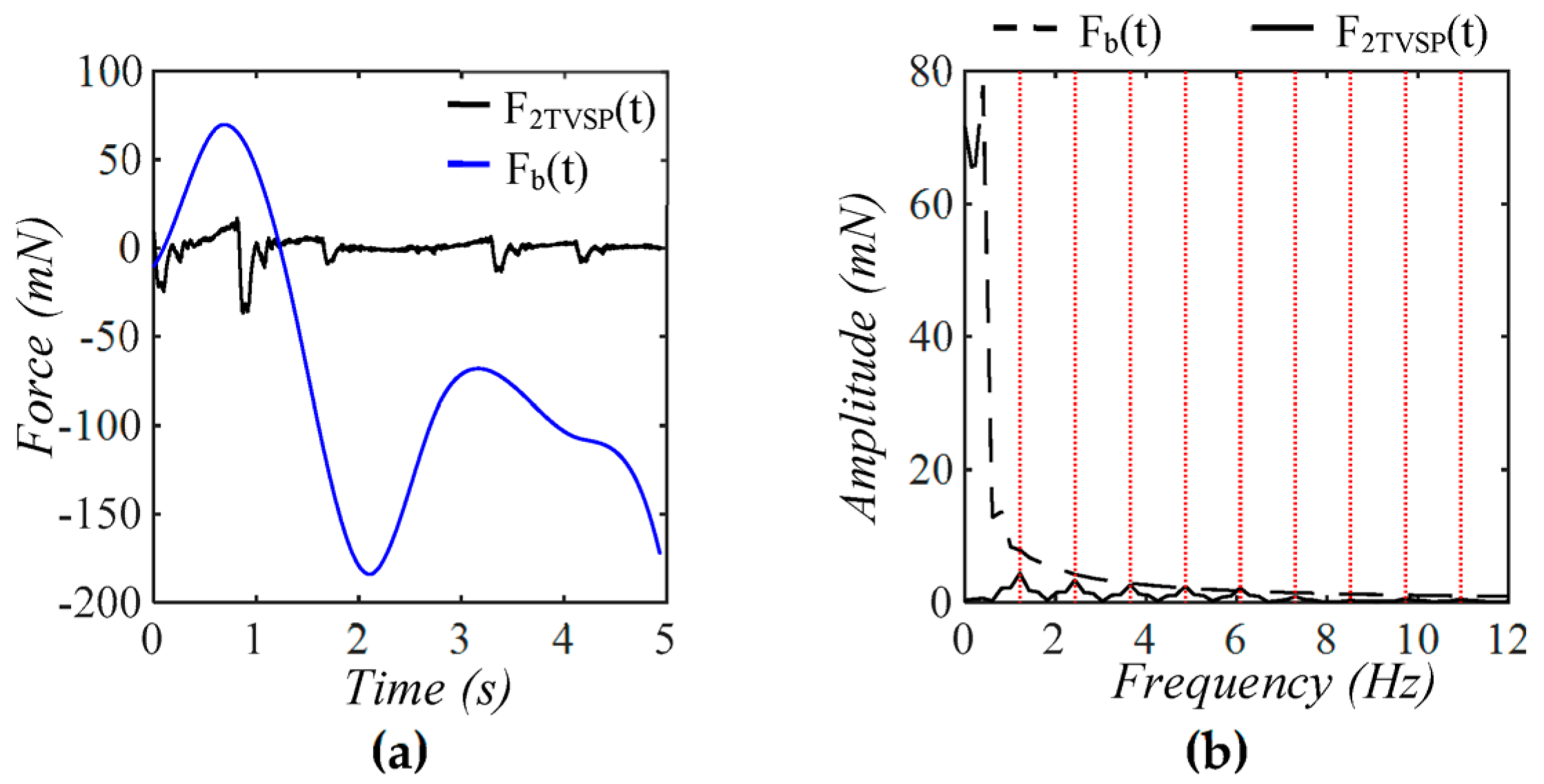
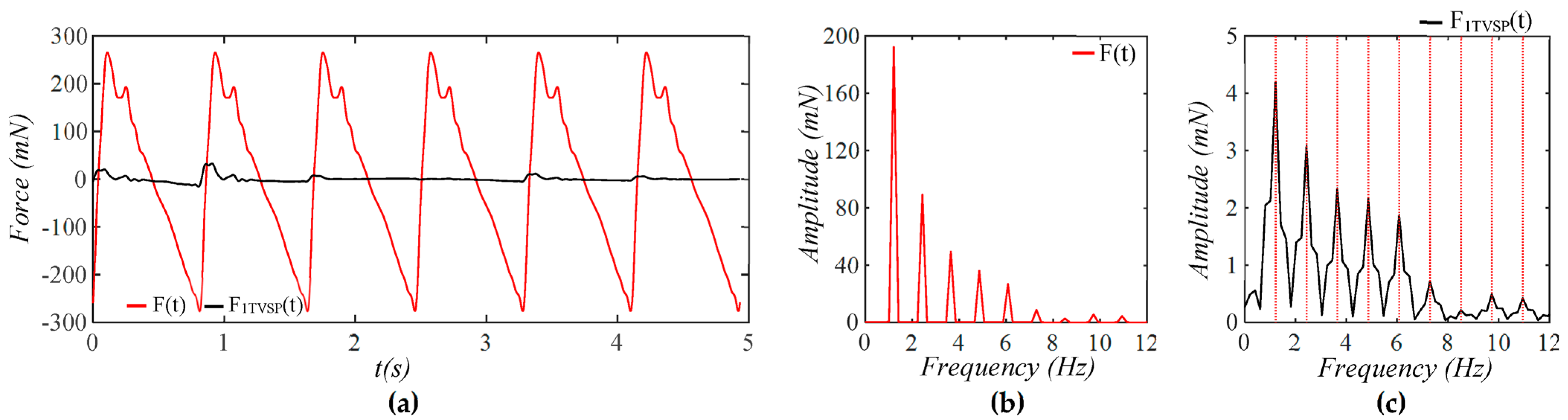
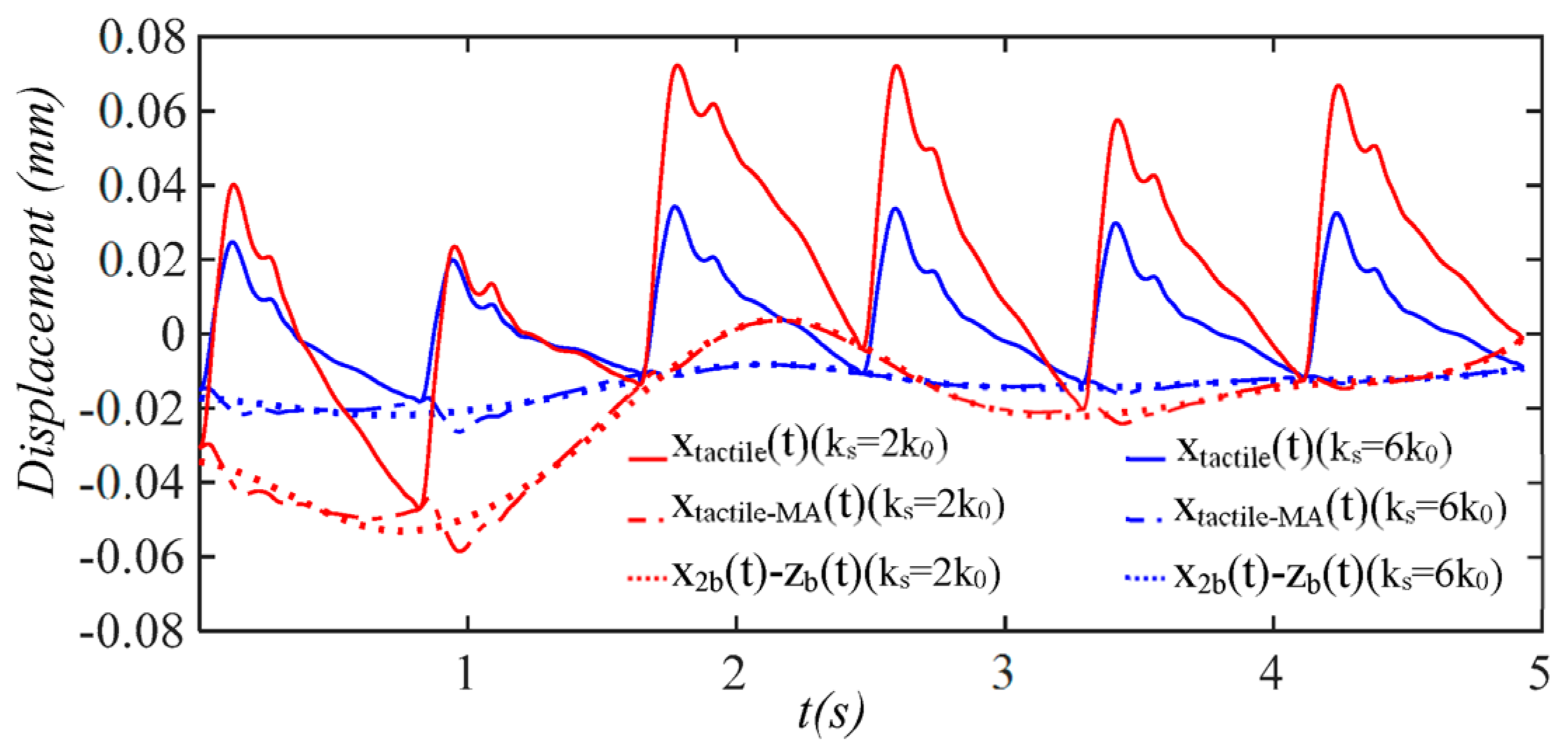
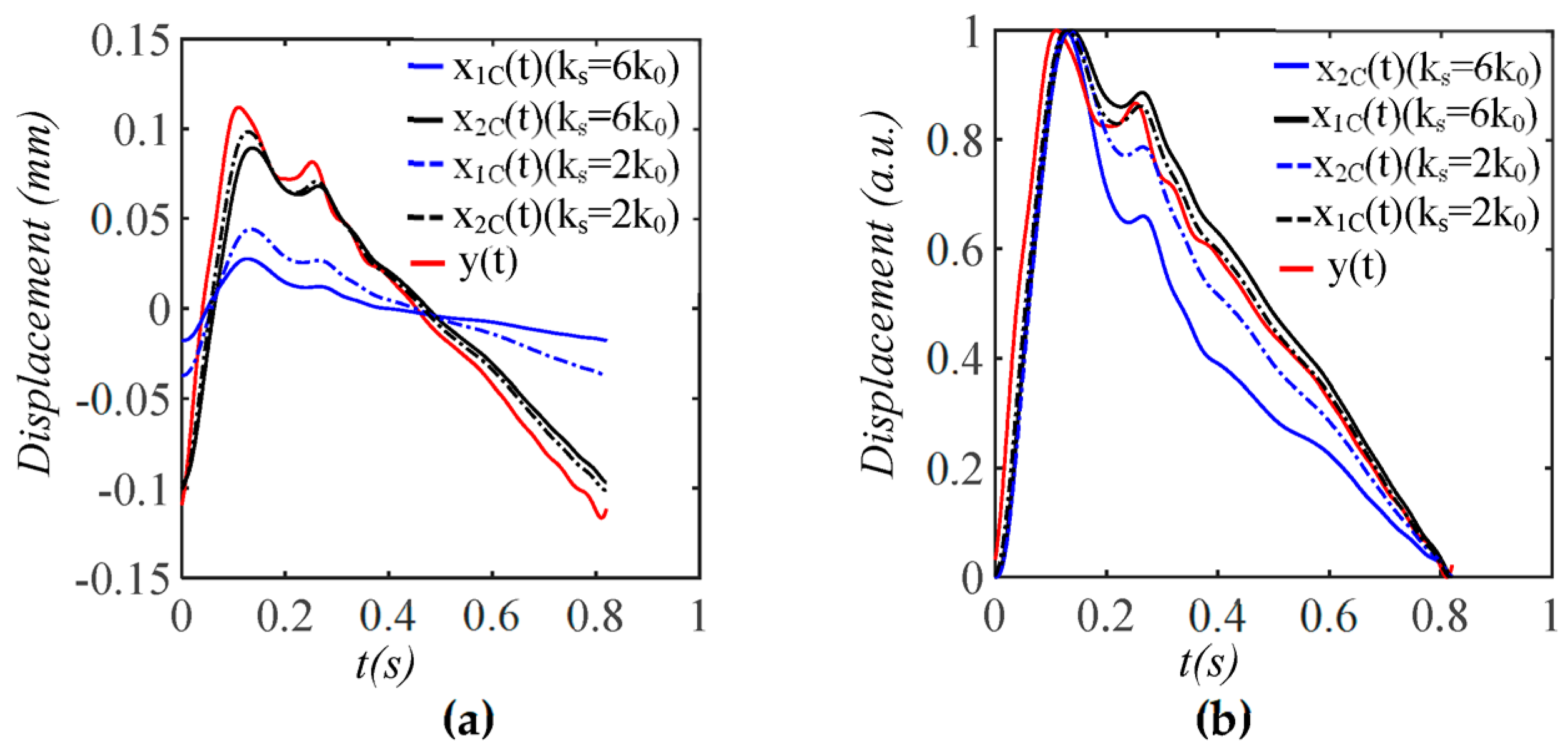
3.1. Arterial Wall Displacement as the True Pulse Signal
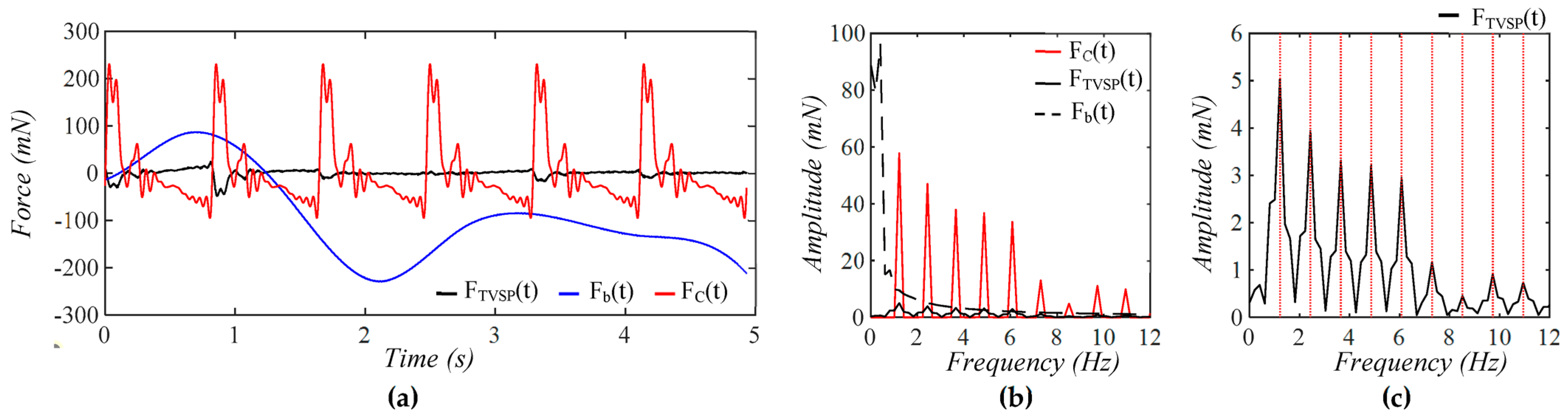
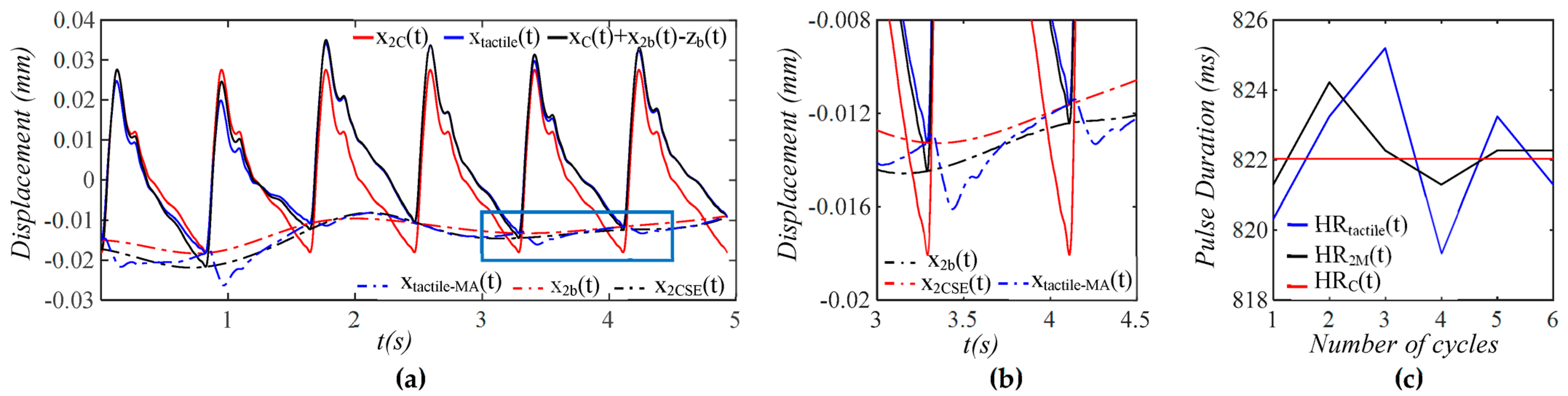
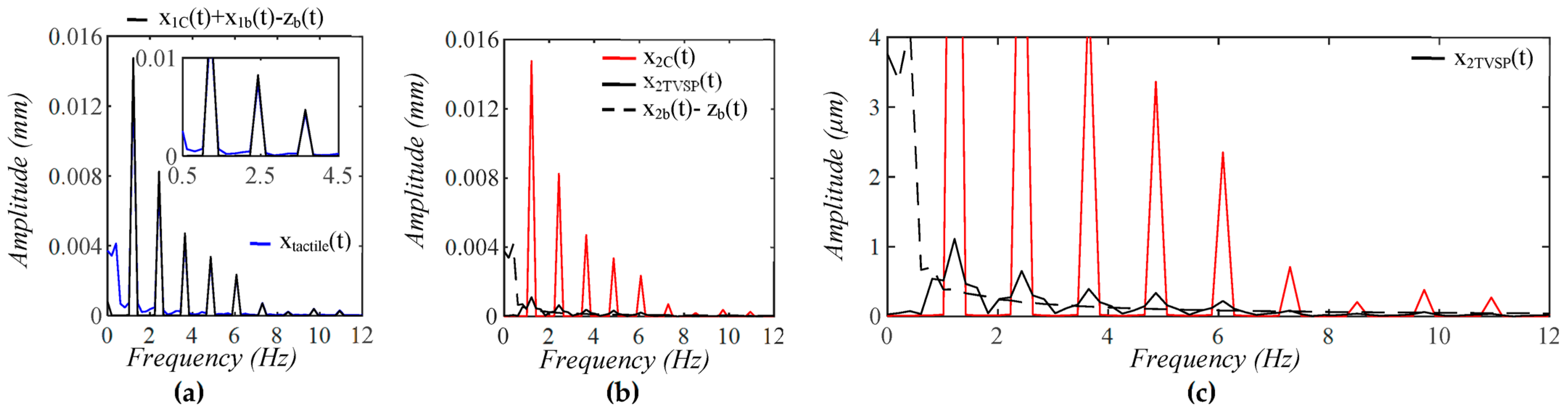
3.2. Pulsatile Pressure as the True Pulse Signal
4. Discussion
4.1. Baseline Drift Versus TVSP-Generated Distortion
4.2. Existence of TVSP
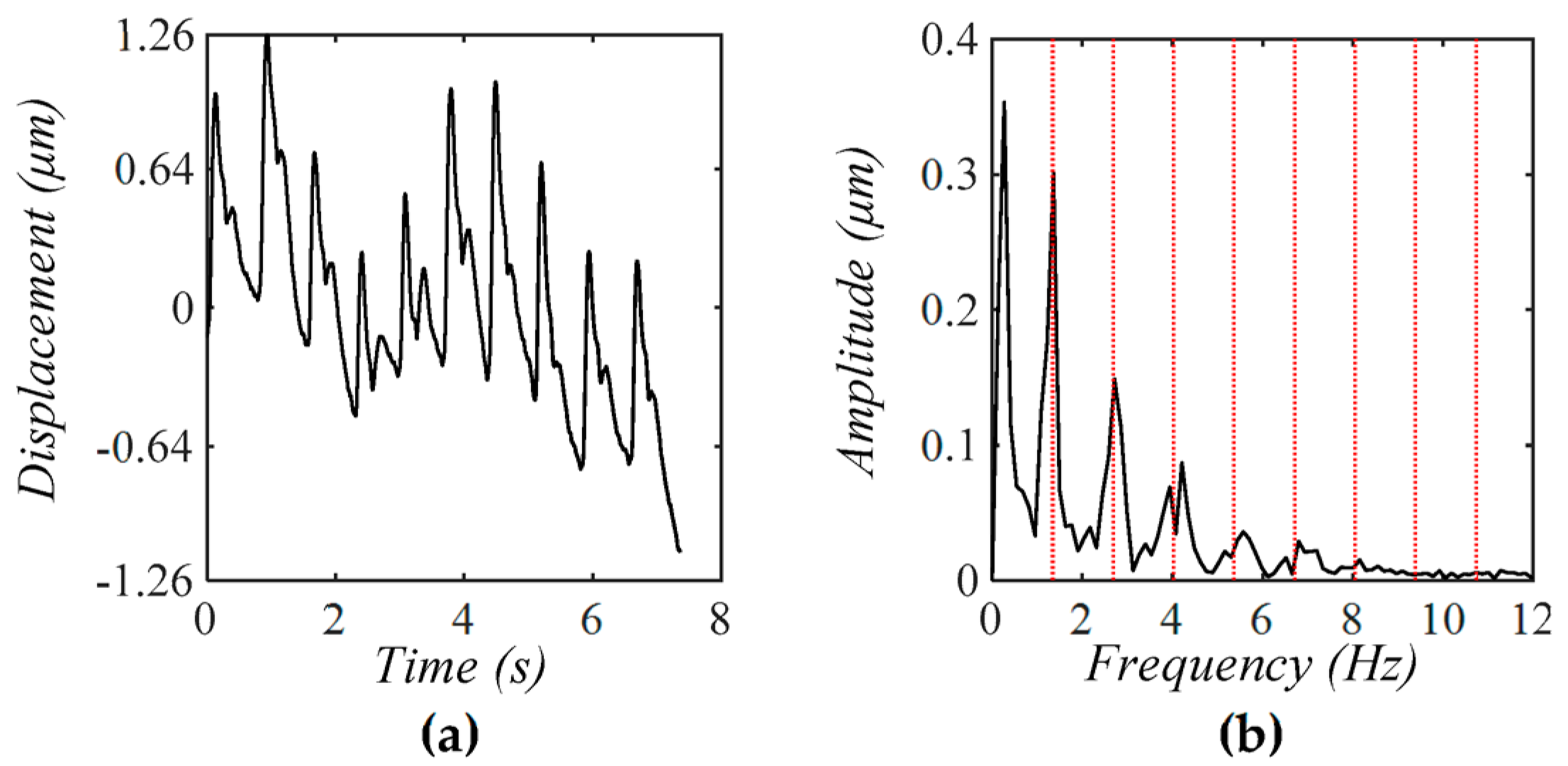
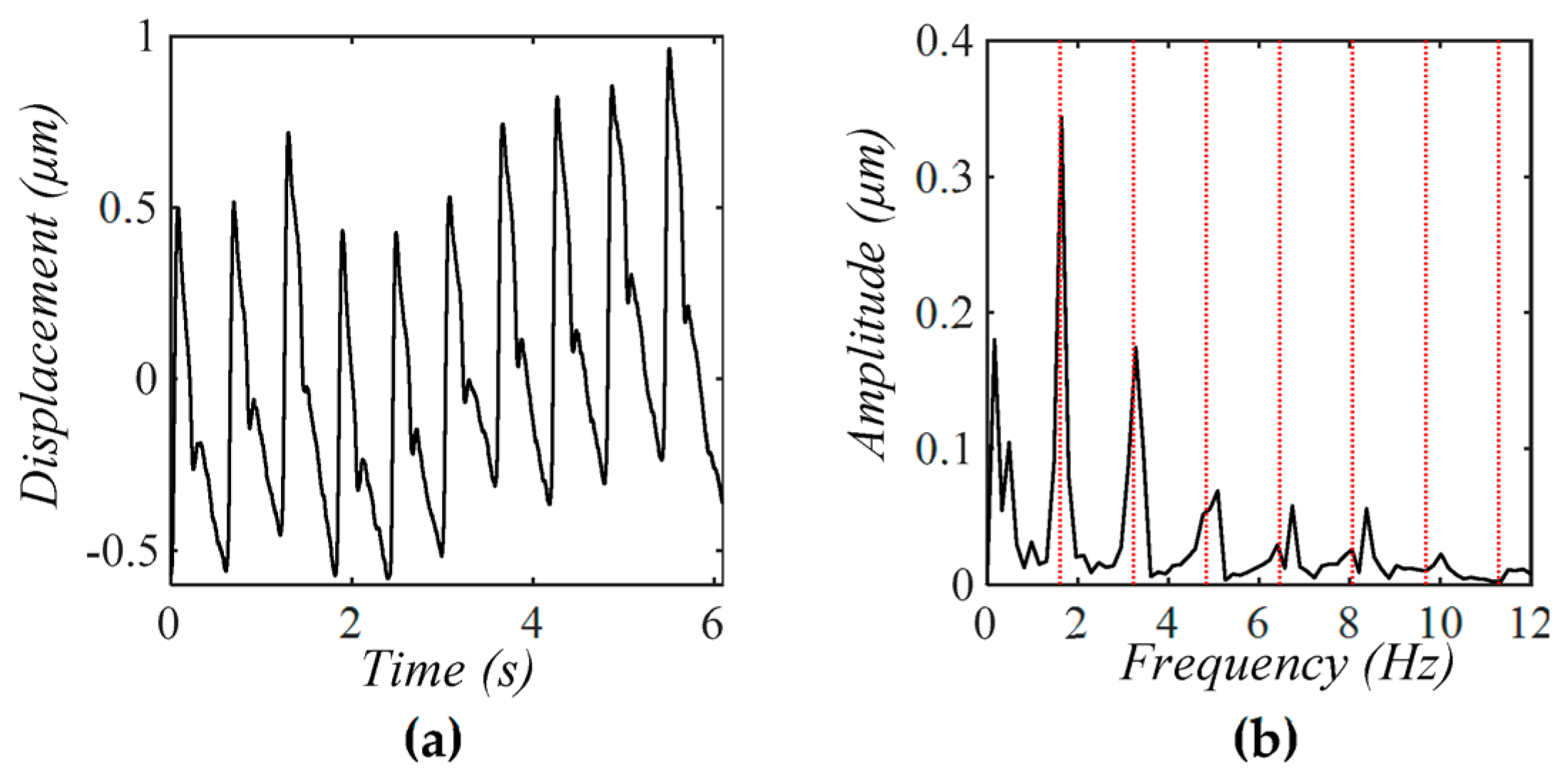
4.3. Comparison of a Tactile Sensor and an Accelerometer
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BD | Baseline drift |
| DOF | Degree-of-freedom |
| TVSP | Time-varying system parameters |
| MA | Motion artifacts |
| TCS | Tissue-contact-sensor |
| HR | Heart rate |
References
- Sun, X.; Liu, T.; Zhou, J.; Yao, L.; Liang, S.; Zhao, M.; Liu, C.; Xue, N. Recent Applications of Different Microstructure Designs in High Performance Tactile Sensors: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 10291–10303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shen, J.; Mei, L.; Qian, S.; Li, J.; Hao, Z. Performance Investigation of a Wearable Distributed-Deflection Sensor in Arterial Pulse Waveform Measurement. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 3994–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Reynolds, L.; Alberts, T.; Vahala, L.; Hao, Z. Model-based analysis of arterial pulse signals for tracking changes in arterial wall parameters: A pilot study. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2019, 18, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Wang, D. Arterial Pulse Signal Amplification by Adding a Uniform PDMS Layer to a Pyrex-Based Microfluidic Tactile Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 2164–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, C.; Lee, G.-Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.N.; Ahn, S.-H.; Suh, K.-Y. A flexible and highly sensitive strain-gauge sensor using reversible interlocking of nanofibres. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Di, C.-a.; Zhu, D. Advances of flexible pressure sensors toward artificial intelligence and health care applications. Mater. Horiz. 2014, 2, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagdeviren, C.; Su, Y.; Joe, P.; Yona, R.; Liu, Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Huang, Y.; Damadoran, A.R.; Xia, J.; Martin, L.W.; et al. Conformable amplified lead zirconate titanate sensors with enhanced piezoelectric response for cutaneous pressure monitoring. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, C.; Koo, J.H.; Nguyen, A.; Caves, J.M.; Kim, M.G.; Chortos, A.; Kim, K.; Wang, P.J.; Tok, J.B.; Bao, Z. Highly skin-conformal microhairy sensor for pulse signal amplification. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drotlef, D.M.; Amjadi, M.; Yunusa, M.; Sitti, M. Bioinspired Composite Microfibers for Skin Adhesion and Signal Amplification of Wearable Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Shim, J.; Jeong, S.; Yi, G.R.; Chae, H.; Bae, J.W.; Kim, S.O.; Pang, C. Microtopography-Guided Conductive Patterns of Liquid-Driven Graphene Nanoplatelet Networks for Stretchable and Skin-Conformal Sensor Array. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ding, H.; Tan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Kang, R.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Baughman, R.; Yin, Z.; et al. Multifaceted Mechanical Responsive Metamaterials: Mechanisms, Fabrications, and Applications. Innovation 2025, 101070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Qu, J.; Chen, L.; Li, F. Hofmeister effect regulated gel iontronic sensors for wide-range pressure perception. Innov. Mater. 2024, 2, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z. A 2-DOF Model of the Artery-Sensor System for Interpreting Variability in Measured Arterial Pulse Waveform. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 22668–22678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z. Harmonics of Pulsatile Pressure at Different Ages and Its Effect on Other Pulsatile Parameters and Waveform-Based Clinical Indices. J. Eng. Sci. Med. Diagn. Ther. 2023, 7, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, P.H.; Mariscal Harana, J.; Vennin, S.; Li, Y.; Chowienczyk, P.; Alastruey, J. Modeling arterial pulse waves in healthy aging: A database for in silico evaluation of hemodynamics and pulse wave indexes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2019, 317, H1062–H1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alastruey, J.; Khir, A.W.; Matthys, K.S.; Segers, P.; Sherwin, S.J.; Verdonck, P.R.; Parker, K.H.; Peiró, J. Pulse wave propagation in a model human arterial network: Assessment of 1-D visco-elastic simulations against in vitro measurements. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 2250–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-C.; Ren, W.-X.; Chen, G. Time–frequency analysis and applications in time-varying/nonlinear structural systems: A state-of-the-art review. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2018, 21, 1562–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neild, S.A.; McFadden, P.D.; Williams, M.S. A review of time-frequency methods for structural vibration analysis. Eng. Struct. 2003, 25, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Ajjarapu, V.; Vaidya, U. Data-Driven Identification of Nonlinear Power System Dynamics Using Output-Only Measurements. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2022, 37, 3458–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Yin, Z.; Han, Q.; Du, X. Output-only structural identification with random decrement technique. Structures 2023, 51, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Přibil, J.; Přibilová, A.; Frollo, I. Heart Pulse Transmission Parameters of Multi-Channel PPG Signals for Cuffless Estimation of Arterial Blood Pressure: Preliminary Study. Electronics 2024, 13, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, N.; Yao, Y.; Hao, L.; Xu, L.; Greenwald, S.E. Quantitative Comparison of the Performance of Piezoresistive, Piezoelectric, Acceleration, and Optical Pulse Wave Sensors. Front. Physiol. 2020, 10, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arathy, R.; Nabeel, P.M.; Abhidev, V.V.; Sivaprakasam, M.; Joseph, J. An Accelerometric Sensor System With Integrated Hydrostatic Pressure Correction to Assess Carotid Arterial Stiffness. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 11163–11175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payette, J.; Vaussenat, F.; Cloutier, S.G. Heart Rate Measurement Using the Built-In Triaxial Accelerometer from a Commercial Digital Writing Device. Sensors 2024, 24, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, C.; Schena, E.; Formica, D.; Massaroni, C. Comparison between Chest-Worn Accelerometer and Gyroscope Performance for Heart Rate and Respiratory Rate Monitoring. Biosensors 2022, 12, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zeng, W.; Hu, D.; Liu, H. Robust Heart Rate Monitoring by a Single Wrist-Worn Accelerometer Based on Signal Decomposition. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 15962–15971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
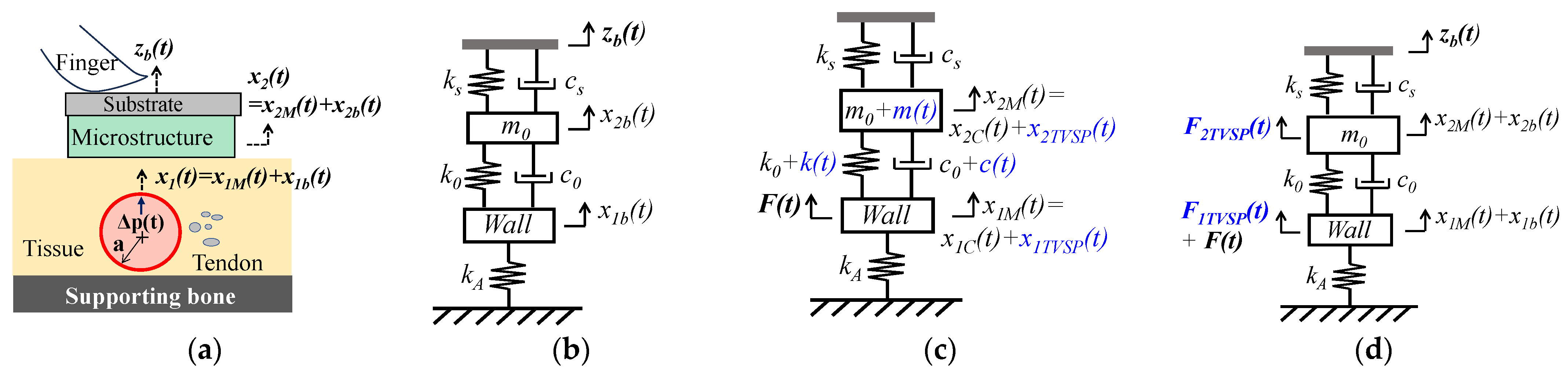


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, M.M.; Toraskar, S.; Hasan, M.; Hao, Z. An Analytical Model of Motion Artifacts in a Measured Arterial Pulse Signal—Part II: Tactile Sensors. Sensors 2025, 25, 5700. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185700
Rahman MM, Toraskar S, Hasan M, Hao Z. An Analytical Model of Motion Artifacts in a Measured Arterial Pulse Signal—Part II: Tactile Sensors. Sensors. 2025; 25(18):5700. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185700
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Md Mahfuzur, Subodh Toraskar, Mamun Hasan, and Zhili Hao. 2025. "An Analytical Model of Motion Artifacts in a Measured Arterial Pulse Signal—Part II: Tactile Sensors" Sensors 25, no. 18: 5700. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185700
APA StyleRahman, M. M., Toraskar, S., Hasan, M., & Hao, Z. (2025). An Analytical Model of Motion Artifacts in a Measured Arterial Pulse Signal—Part II: Tactile Sensors. Sensors, 25(18), 5700. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185700





