Sensortoolkit—A Python Library for Standardizing the Ingestion, Analysis, and Reporting of Air Sensor Data for Performance Evaluation
Abstract
Highlights
- The U.S. EPA previously released a series of reports with recommendations to standardizing the summary and presentation of air sensor performance evaluations through collocation with federal reference and equivalent method instruments including recommended statistical metrics and figures.
- The U.S. EPA is introducing the free and open-source Python library called sensortoolkit for the analysis of air sensor performance evaluation data which handles a wide variety of data formats, calculates the metrics, and creates summary figures.
- The library will reduce the data processing effort and support the standardization of air sensor performance evaluation results.
- Consistency in reporting test results will help consumers compare performance results and make more informed purchasing decision.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Suggested User Experience
2.2. Required Software
2.3. Documentation
2.4. Design and Architecture
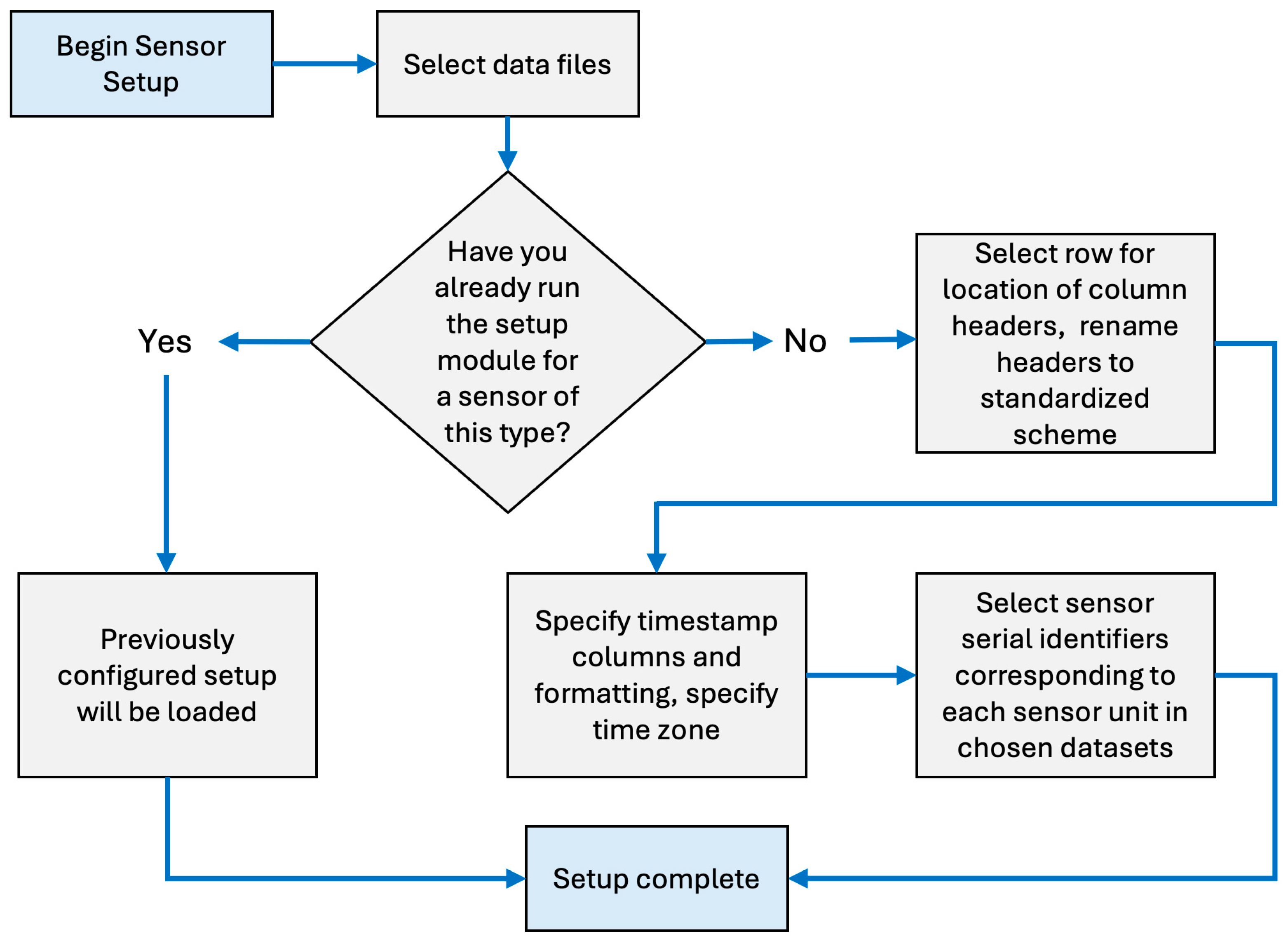
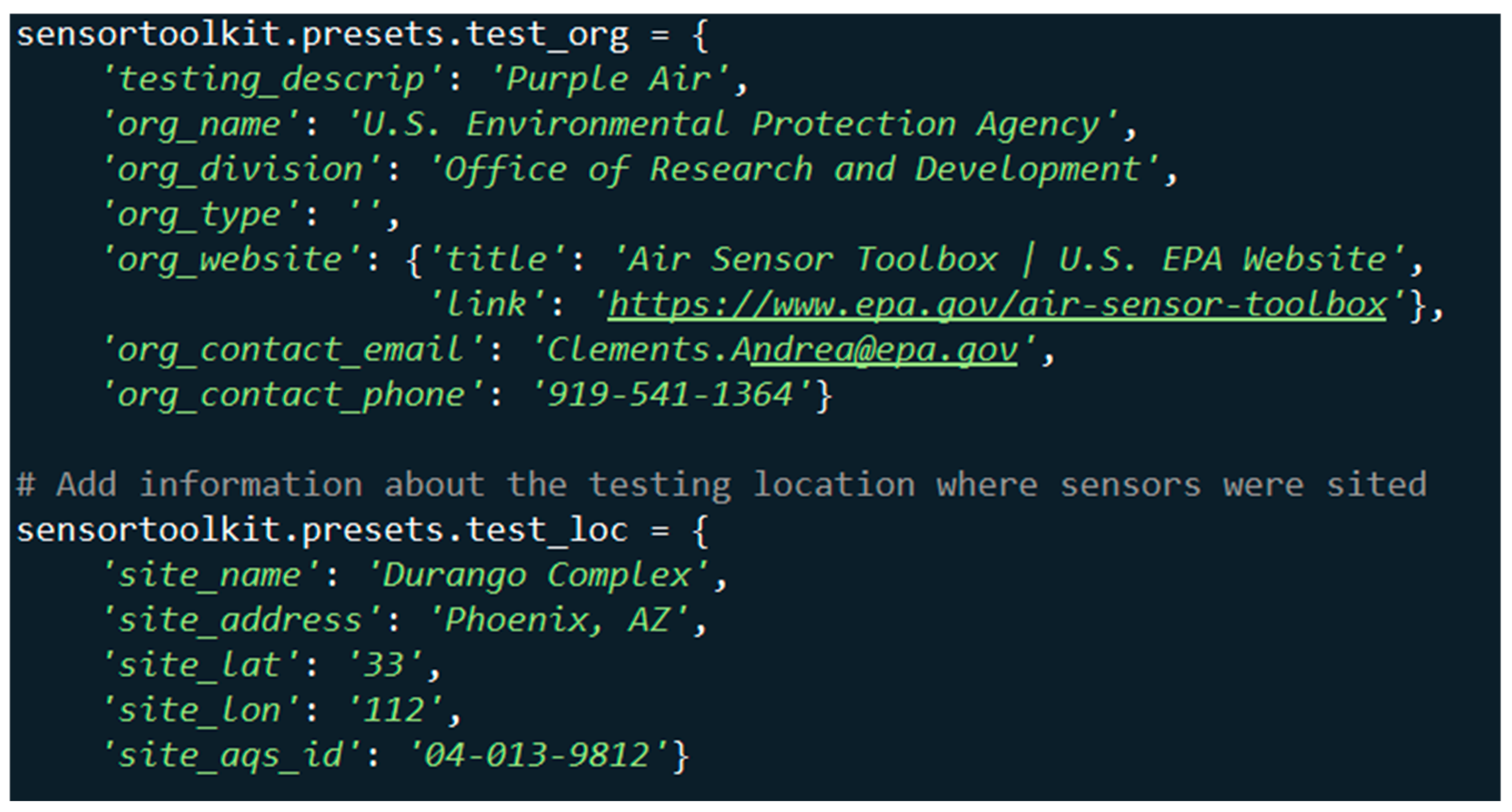
2.4.1. Testing Attribute Objects
2.4.2. Data Formatting Scheme
2.4.3. Sensor Evaluation Object
2.4.4. Performance Report Object
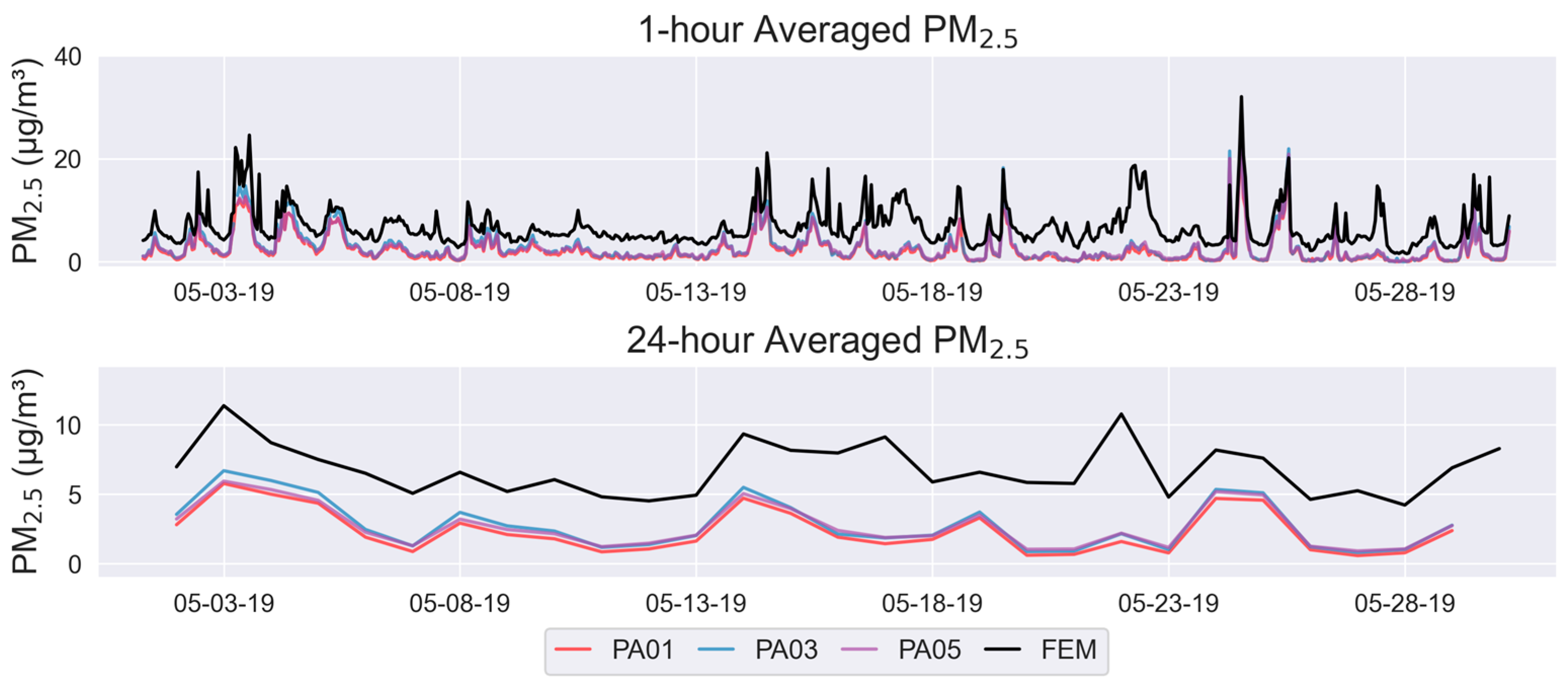
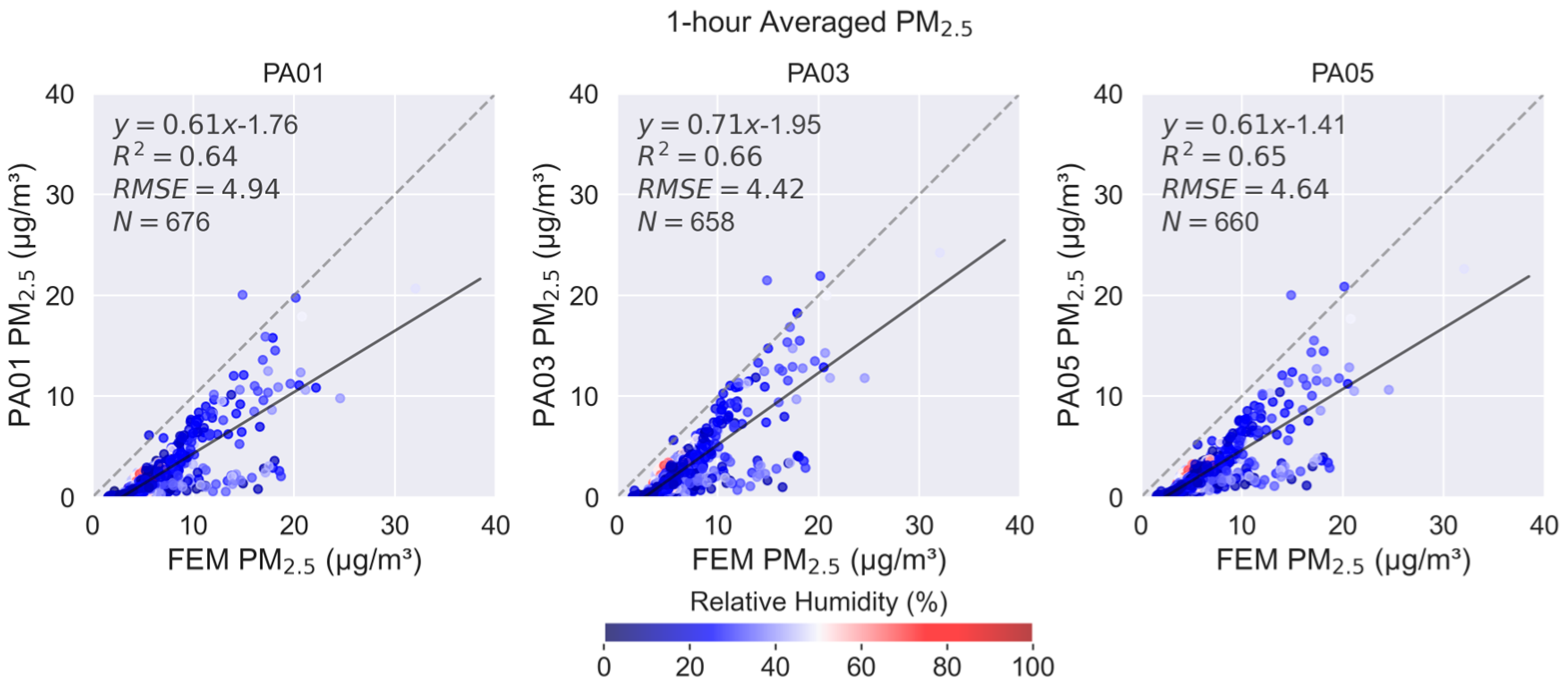
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The user needs that guided the creation of this tool;
- A data ingestion methodology to handle variation in data format;
- Standardization in performance metric calculations;
- Data visualizations;
- The motivations for the reporting template design.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| AQMD | Air Quality Management District |
| AQS | Air Quality System |
| AZ | Arizona |
| °C | Degrees Centigrade |
| CFR | Code of Federal Regulations |
| CO | Carbon Monoxide |
| CSV | Comma Separated Values |
| CV | Coefficient of Variation |
| °F | Degrees Fahrenheit |
| FEM | Federal Equivalent Method |
| FRM | Federal Reference Method |
| GMT | Greenwich Mean Time |
| ID | Identification Number |
| IDE | Integrated Development Environment |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| JSON | JavaScript Object Notation |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| N | Number of Data Points |
| NO2 | Nitrogen Dioxide |
| NRMSE | Normalized Root Mean Square Error |
| O3 | Ozone |
| ORAU | Oak Ridge Associated Universities |
| ORISE | Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education |
| P-TAQS | Phoenix-as-a-Testbed for Air Quality Sensors |
| PM | Particulate Matter |
| PM2.5 | Fine Particulate Matter |
| PMc or PM10-2.5 | Coarse Particulate Matter |
| PM10 | Particles with diameters that are generally less than 10 μm |
| PyPI | Python Packaging Index |
| R2 | Coefficient of Determination |
| RH | Relative Humidity |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| RTP | Research Triangle Park |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SDFS | Sensortoolkit Data Formatting Scheme |
| SO2 | Sulfur Dioxide |
| T | Temperature |
| U.S. EPA | United States Environmental Protection Agency |
| URL | Uniform Resource Locator |
| UTC | Coordinated Universal Time |
References
- Kelly, K.E.; Xing, W.W.; Sayahi, T.; Mitchell, L.; Becnel, T.; Gaillardon, P.E.; Meyer, M.; Whitaker, R.T. Community-Based Measurements Reveal Unseen Differences during Air Pollution Episodes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, W.; Shantz, N.; Neil, L.; Townend, T.; Adamescu, A.; Al-Abadleh, H.A. Air Quality Measurements in Kitchener, Ontario, Canada Using Multisensor Mini Monitoring Stations. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhwal, S.; Tripathi, S.N.; Bergin, M.H.; Bhave, P.; de Foy, B.; Reddy, T.V.R.; Chaudhry, S.K.; Jain, V.; Garg, N.; Lalwani, P. Evaluation of PM2.5 spatio-temporal variability and hotspot formation using low-cost sensors across urban-rural landscape in lucknow, India. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 319, 120302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, E.G.; Watkins, T.H.; Solomon, P.A.; Thoma, E.D.; Williams, R.W.; Hagler, G.S.W.; Shelow, D.; Hindin, D.A.; Kilaru, V.J.; Preuss, P.W. The Changing Paradigm of Air Pollution Monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11369–11377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoak, R.; Clements, A.; Duvall, R. Best Practices for Starting an Air Sensor Loan Program; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, WA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- D’eon, J.C.; Stirchak, L.T.; Brown, A.-S.; Saifuddin, Y. Project-Based Learning Experience That Uses Portable Air Sensors to Characterize Indoor and Outdoor Air Quality. J. Chem. Educ. 2021, 98, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griswold, W.; Patel, M.; Gnanadass, E. ‘One Person Cannot Change It; It’s Going to Take a Community’: Addressing Inequity through Community Environmental Education. Adult Learn. 2024, 35, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier-Oxandale, A.; Papapostolou, V.; Feenstra, B.; Boghossian, B.D.; Polidori, A. Towards the Development of a Sensor Educational Toolkit to Support Community and Citizen Science. Sensors 2022, 22, 2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, A.L.; Griswold, W.G.; Rs, A.; Johnston, J.E.; Herting, M.M.; Thorson, J.; Collier-Oxandale, A.; Hannigan, M. Low-Cost Air Quality Monitoring Tools: From Research to Practice (A Workshop Summary). Sensors 2017, 17, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.; Bejarano, E.; Carvlin, G.; Fellows, K.; King, G.; Lugo, H.; Jerrett, M.; Meltzer, D.; Northcross, A.; Olmedo, L.; et al. Combining Community Engagement and Scientific Approaches in Next-Generation Monitor Siting: The Case of the Imperial County Community Air Network. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, E.; Kobayaa, N.; Jaafar, W.; Torbatian, S.; Gamage, S.M.; Brook, J.; Chan, A.; Evans, G.; Jeong, C.-H.; Siegel, J.; et al. Campus–Community Partnership to Characterize Air Pollution in a Neighborhood Impacted by Major Transportation Infrastructure. ACS EST Air 2024, 1, 1601–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkjohn, K.K.; Clements, A.; Mocka, C.; Barrette, C.; Bittner, A.; Champion, W.; Gantt, B.; Good, E.; Holder, A.; Hillis, B.; et al. Air Quality Sensor Experts Convene: Current Quality Assurance Considerations for Credible Data. ACS EST Air 2024, 1, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feenstra, B.; Papapostolou, V.; Hasheminassab, S.; Zhang, H.; Boghossian, B.D.; Cocker, D.; Polidori, A. Performance evaluation of twelve low-cost PM2.5 sensors at an ambient air monitoring site. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 216, 116946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Duvall, R.; Kilaru, V.; Hagler, G.; Hassinger, L.; Benedict, K.; Rice, J.; Kaufman, A.; Judge, R.; Pierce, G.; et al. Deliberating performance targets workshop: Potential paths for emerging PM2.5 and O3 air sensor progress. Atmos. Environ. X 2019, 2, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvall, R.M.; Hagler, G.S.W.; Clements, A.L.; Benedict, K.; Barkjohn, K.; Kilaru, V.; Hanley, T.; Watkins, N.; Kaufman, A.; Kamal, A.; et al. Deliberating Performance Targets: Follow-on workshop discussing PM10, NO2, CO, and SO2 air sensor targets. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 246, 118099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, K.; Kelly, K.E. Performance evaluation of the Alphasense OPC-N3 and Plantower PMS5003 sensor in measuring dust events in the Salt Lake Valley, Utah. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 2455–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouimette, J.; Arnott, W.P.; Laven, P.; Whitwell, R.; Radhakrishnan, N.; Dhaniyala, S.; Sandink, M.; Tryner, J.; Volckens, J. Fundamentals of low-cost aerosol sensor design and operation. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, M.R.; Malings, C.; Pandis, S.N.; Presto, A.A.; McNeill, V.F.; Westervelt, D.M.; Beekmann, M.; Subramanian, R. From low-cost sensors to high-quality data: A summary of challenges and best practices for effectively calibrating low-cost particulate matter mass sensors. J. Aerosol Sci. 2021, 158, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, D.H.; Kroll, J.H. Assessing the accuracy of low-cost optical particle sensors using a physics-based approach. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 6343–6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Ning, Z.; Ye, S.; Sun, L.; Yang, F.; Wong, K.C.; Westerdahl, D.; Louie, P.K.K. Impact Analysis of Temperature and Humidity Conditions on Electrochemical Sensor Response in Ambient Air Quality Monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvall, R.M.; Clements, A.L.; Hagler, G.; Kamal, A.; Kilaru, V.; Goodman, L.; Frederick, S.; Barkjohn, K.K.; VonWald, I.; Greene, D.; et al. Performance Testing Protocols, Metrics, and Target Values for Fine Particulate Matter Air Sensors: Use in Ambient, Outdoor, Fixed Site, Non-Regulatory Supplemental and Informational Monitoring Applications; EPA/600/R-20/280; Office of Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, WA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Duvall, R.M.; Clements, A.L.; Hagler, G.; Kamal, A.; Kilaru, V.; Goodman, L.; Frederick, S.; Barkjohn, K.K.; VonWald, I.; Greene, D.; et al. Performance Testing Protocols, Metrics, and Target Values for Ozone Air Sensors: Use in Ambient, Outdoor, Fixed Site, Non-Regulatory Supplemental and Informational Monitoring Applications; EPA/600/R-20/279; Office of Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, WA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Duvall, R.; Clements, A.; Barkjohn, K.; Kumar, M.; Greene, D.; Dye, T.; Papapostolou, V.; Mui, W.; Kuang, M. NO2, CO, and SO2 Supplement to the 2021 Report on Performance Testing Protocols, Metrics, and Target Values for Ozone Air Sensors; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, WA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Levy Zamora, M.; Buehler, C.; Lei, H.; Datta, A.; Xiong, F.; Gentner, D.R.; Koehler, K. Evaluating the Performance of Using Low-Cost Sensors to Calibrate for Cross-Sensitivities in a Multipollutant Network. ACS EST Eng. 2022, 2, 780–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvall, R.; Clements, A.; Barkjohn, K.; Kumar, M.; Greene, D.; Dye, T.; Papapostolou, V.; Mui, W.; Kuang, M. PM10 Supplement to the 2021 Report on Performance Testing Protocols, Metrics, and Target Values for Fine Particulate Matter Air Sensors; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, WA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Collier-Oxandale, A.; Feenstra, B.; Papapostolou, V.; Polidori, A. AirSensor v1.0: Enhancements to the open-source R package to enable deep understanding of the long-term performance and reliability of PurpleAir sensors. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 148, 105256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feenstra, B.; Collier-Oxandale, A.; Papapostolou, V.; Cocker, D.; Polidori, A. The AirSensor open-source R-package and DataViewer web application for interpreting community data collected by low-cost sensor networks. Environ. Model. Softw. 2020, 134, 104832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, D.C.; Ropkins, K. Openair—An R package for air quality data analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 27–28, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, S.; Kumar, M. Sensortoolkit. Available online: https://github.com/USEPA/sensortoolkit (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Anaconda. Anaconda Software Distribution. Available online: https://www.anaconda.com/docs/getting-started/anaconda/main (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Landis, M.S.; Long, R.W.; Krug, J.; Colon, M.; Vanderpool, R.; Habel, A.; Urbanski, S.P. The US EPA wildland fire sensor challenge: Performance and evaluation of solver submitted multi-pollutant sensor systems. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 247, 118165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malings, C.; Tanzer, R.; Hauryliuk, A.; Saha, P.K.; Robinson, A.L.; Presto, A.A.; Subramanian, R. Fine particle mass monitoring with low-cost sensors: Corrections and long-term performance evaluation. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkjohn, K.K.; Gantt, B.; Clements, A.L. Development and application of a United States-wide correction for PM2.5 data collected with the PurpleAir sensor. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 4617–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magi, B.I.; Cupini, C.; Francis, J.; Green, M.; Hauser, C. Evaluation of PM2.5 measured in an urban setting using a low-cost optical particle counter and a Federal Equivalent Method Beta Attenuation Monitor. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaratne, R.; Liu, X.; Thai, P.; Dunbabin, M.; Morawska, L. The influence of humidity on the performance of a low-cost air particle mass sensor and the effect of atmospheric fog. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 4883–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkjohn, K.K.; Holder, A.L.; Frederick, S.G.; Clements, A.L. Correction and Accuracy of PurpleAir PM2.5 Measurements for Extreme Wildfire Smoke. Sensors 2022, 22, 9669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, J.J.; Mura, I.; Franco, J.F.; Akhavan-Tabatabaei, R. Aire—A web-based R application for simple, accessible and repeatable analysis of urban air quality data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 138, 104976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkjohn, K.K.; Seppanen, C.; Arunachalam, S.; Krabbe, S.; Clements, A.L. Air Sensor Data Unifier: R-Shiny Application. Air 2025, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkjohn, K.K.; Plessel, T.; Yang, J.; Pandey, G.; Xu, Y.; Krabbe, S.; Seppanen, C.; Bichler, R.; Tran, H.N.Q.; Arunachalam, S.; et al. Air Sensor Network Analysis Tool: R-Shiny Application. Preprints 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Real Time Geospatial Data Viewer (RETIGO). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/hesc/real-time-geospatial-data-viewer-retigo (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- Freeman, M.; Plessel, T.; Howard, T.; Xu, Y. Real Time Geospatial Data Viewer (RETIGO). Available online: https://github.com/USEPA/retigo (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- MacDonald, M.K.; Champion, W.M.; Thoma, E.D. SENTINEL: A Shiny app for processing and analysis of fenceline sensor data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2025, 189, 106462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


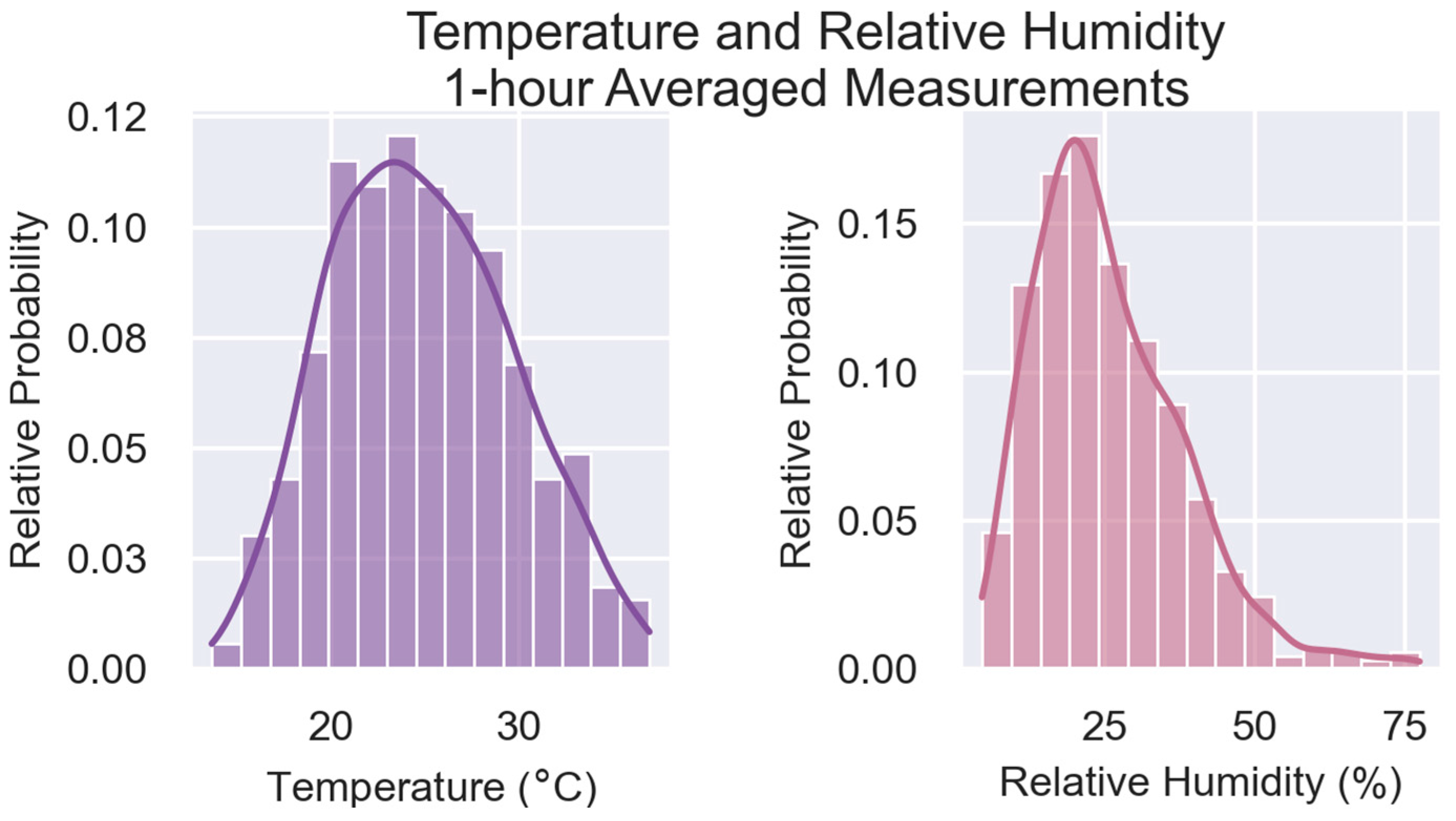


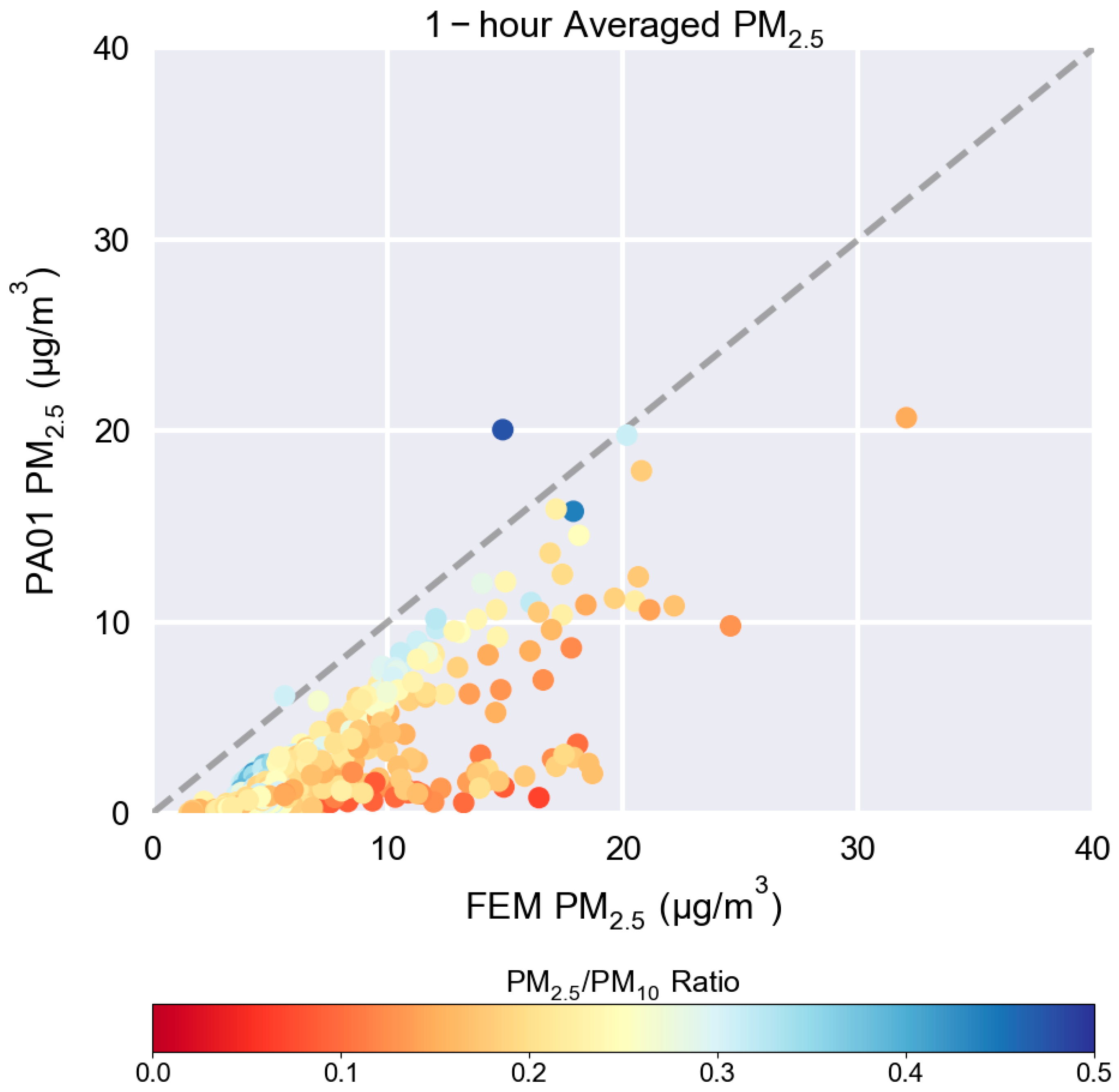
| Project | Location(s) Evaluated | Sensor(s) Evaluated | Pollutant(s) Evaluated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phoenix | Phoenix, Arizona | PurpleAir PA-II-SD | PM2.5, PM10 |
| Long-term performance project | Phoenix, Arizona Denver Colorado Wilmington, Delaware Decatur, Georgia Research Triangle Park, North Carolina Edmond, Oklahoma Milwaukee, Wisconsin | Aeroqual AQY | PM2.5, O3 |
| APT Maxima | PM2.5 | ||
| Clarity Node | PM2.5 | ||
| PurpleAir PA-II-SD | PM2.5 | ||
| SENSIT RAMP | PM2.5, O3 | ||
| QuantAQ AriSense | PM2.5 | ||
| Research Triangle Park | Research Triangle Park, North Carolina | Apis APM01 | O3 |
| Myriad Sensors PocketLab Air | O3 | ||
| Vaisala AQT420 | O3 |
| Developer | Software Package of Library (Language) | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Collaborative Development | aiRE (R/RShiny) [37] |
|
|
| Kings College London | OpenAir (R) [28] |
|
|
| South Coast Air Quality Management District | AirSensor (R) [26,27] |
|
|
| South Coast Air Quality Management District | Dataviewer (RShiny) [27] |
|
|
| U.S. EPA | Air Sensor Data Unifier (RShiny) [38] |
|
|
| U.S. EPA | Air Sensor Network Analysis Tool (RShiny) [39] |
|
|
| U.S. EPA | RETIGO (browser-based) [40,41] |
|
|
| U.S. EPA | sensortoolkit (Python) [29] |
|
|
| U.S. EPA | SENTINEL (RShiny) [42] |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, M.; Frederick, S.G.; Barkjohn, K.K.; Clements, A.L. Sensortoolkit—A Python Library for Standardizing the Ingestion, Analysis, and Reporting of Air Sensor Data for Performance Evaluation. Sensors 2025, 25, 5645. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185645
Kumar M, Frederick SG, Barkjohn KK, Clements AL. Sensortoolkit—A Python Library for Standardizing the Ingestion, Analysis, and Reporting of Air Sensor Data for Performance Evaluation. Sensors. 2025; 25(18):5645. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185645
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Menaka, Samuel G. Frederick, Karoline K. Barkjohn, and Andrea L. Clements. 2025. "Sensortoolkit—A Python Library for Standardizing the Ingestion, Analysis, and Reporting of Air Sensor Data for Performance Evaluation" Sensors 25, no. 18: 5645. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185645
APA StyleKumar, M., Frederick, S. G., Barkjohn, K. K., & Clements, A. L. (2025). Sensortoolkit—A Python Library for Standardizing the Ingestion, Analysis, and Reporting of Air Sensor Data for Performance Evaluation. Sensors, 25(18), 5645. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185645







