Cor-Esc-25: A Low-Cost Prototype for Monitoring Brace Adherence and Pressure in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
Abstract
Highlights
- We propose a novel, economical, and practical open-system prototype, which we have named Cor-Esc-25, to measure brace adherence and adjustment in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis.
- Comparative analysis of the available non-invasive temperature and pressure sensors and creation of an organic system adaptable for any type of brace, which could help future researchers to understand the effectiveness of adherence and pressure in the correction of a Cobb curve.
- This study addresses a critical gap by establishing a universal, cost-effective prototype that provides researchers with objective data to study brace prescription effects.
- Its ease of application across different types of braces and low cost make Cor-Esc-25 a highly attractive solution for resource-constrained environments, and a promising foundation for future research.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
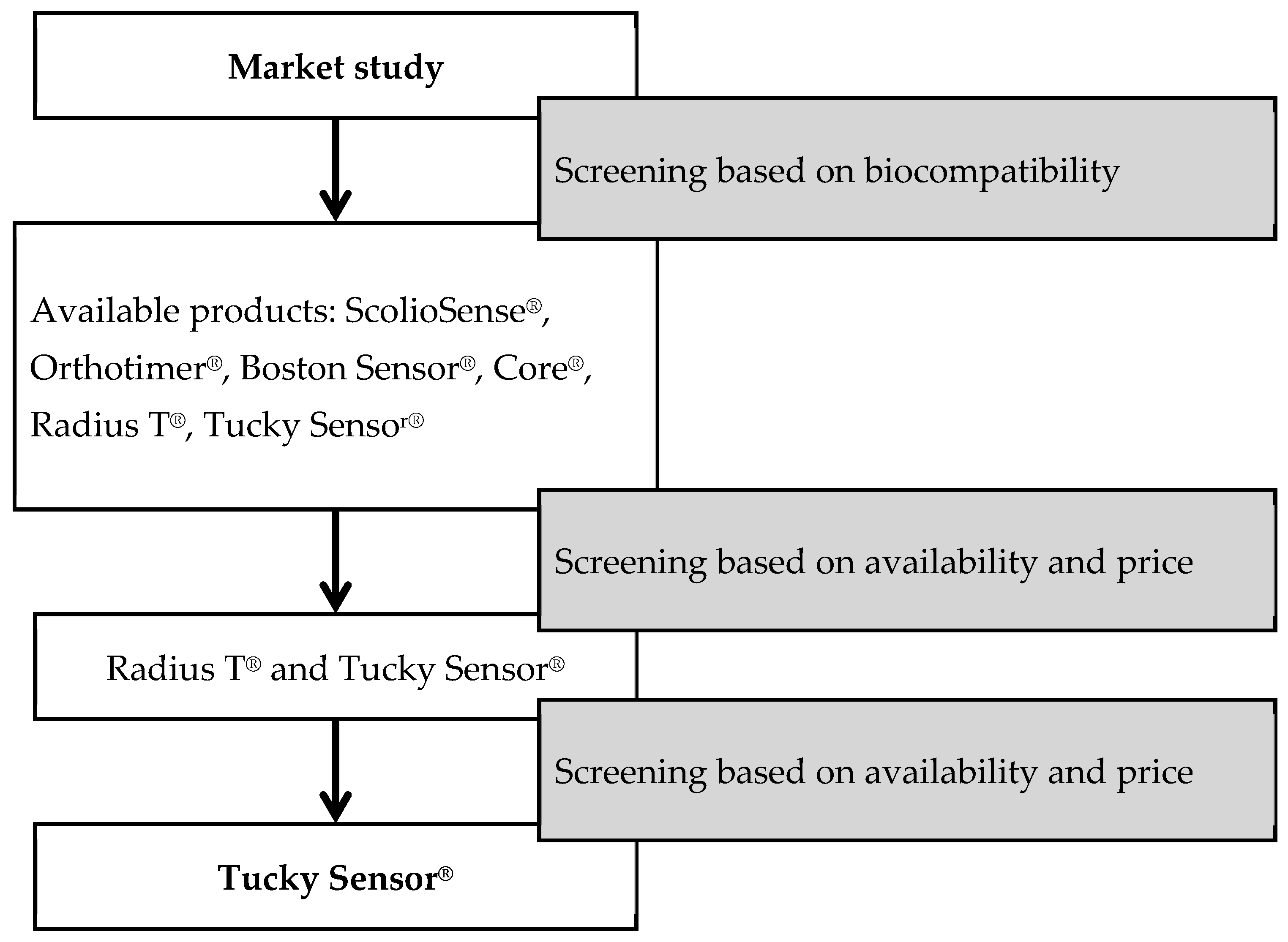
2.1. Brace Selection
2.2. Sensor Selection
2.3. Sensor Calibration
2.4. Preliminary Design of Cor-Esc-25
2.5. Patient Testing
3. Results
3.1. Temperature Sensor
- ScolioSense Temperature Sensor®: A lightweight, discreet sensor specifically designed to integrate into the Boston brace. It provides effective monitoring of adherence to AIS treatment and includes a proprietary mobile app. Battery lasts 21 days. Price not available [15].
- Orthotimer®: A very compact thermal sensor (13 × 9 × 5 mm) for documenting adherence. It offers 400 days of storage, customizable recording intervals (from 1 s to 60 min), USB reader, Bluetooth data transfer, and cloud-based analysis software. Price: EUR 2830 [16].
- Boston Sensor®: A wireless device placed inside the brace that records internal temperature every 15 min. About the size of a 50-cent coin, it includes an app (iOS/Android) and generates usage reports easily. One-year battery, replaceable with a standard watch battery. Compatible only with its dedicated app for privacy. Price not available [17].
- Core®: A clinically validated, portable, non-invasive device for continuous core temperature monitoring. Features ANT+ and Bluetooth connectivity, waterproof, compact design, and a rechargeable battery lasting up to 6 days. Price: USD 298.95 [18].
- Radius T®: A wireless, portable sensor that continuously measures body temperature every minute. Includes Bluetooth connectivity, water-resistant reusable adhesive, and a battery life of 8 days. Single-patient use. Indicated for patients aged 5 and older. Price: USD 49.99 [19].
- Tucky®: A thin, flexible, biocompatible thermometer in patch form developed by e-TakesCare, intended for non-invasive temperature monitoring under the armpit in preschool children. Transmits data via Bluetooth to a free smartphone app (iOS/Android), with real-time cloud syncing accessible to caregivers and clinicians. ISO13485 certified. Market price: ~EUR 70 [20].
3.2. Pressure Sensor
- ScolioSense Pressure Sensor®: Designed to ensure effective AIS treatment by tracking brace wear time. This lightweight and discreet device integrates easily into the brace and connects to a mobile app. It provides real-time data on treatment progress. Battery lasts 21 days. Price quote not obtained [15].
- F-Socket Tucky®: Used to evaluate and monitor the effectiveness of orthotic braces in AIS treatment. Sensors are placed inside the brace, offering real-time pressure data for immediate adjustments. Data can be stored and analyzed over time. Price: EUR 25,549 [21].
- Spondylos Tucky®: Measures, records, and analyzes the forces exerted by a Boston-type brace. Portable and lightweight, it includes a microprocessor, microSD card, and warning LEDs that activate when pressure drops below a set threshold. Price not available [22].
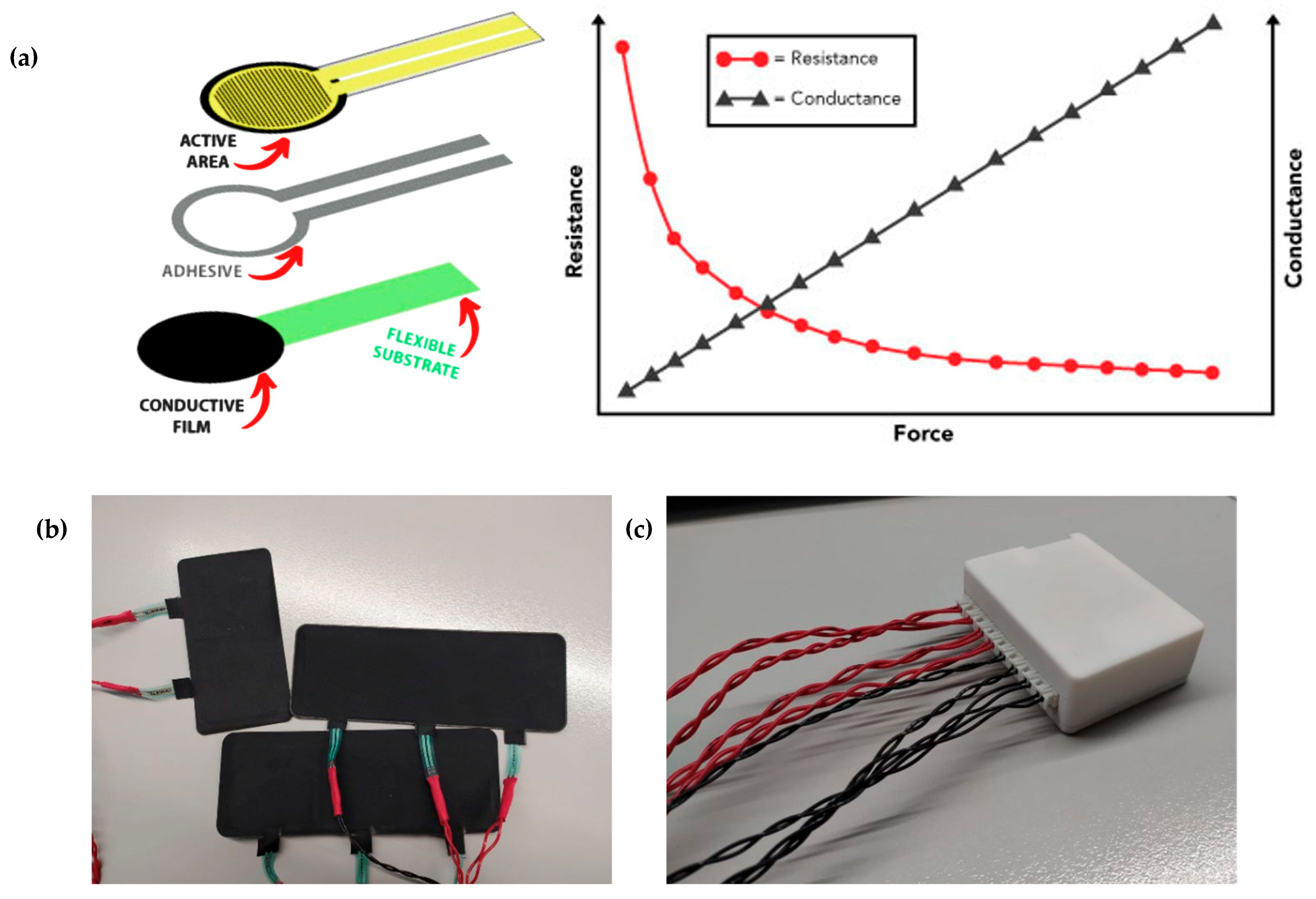
3.3. Cor-Esc-25 Design
3.4. Data Reading
- 1.
- Adherence Monitoring: Using the Tucky® app, once connected, the sensor continuously measures body temperature. Data are stored on the mobile device and synced with a secure online platform (Figure 5). Clinicians can log in, define a date range, and export records in Excel format.
- 2.
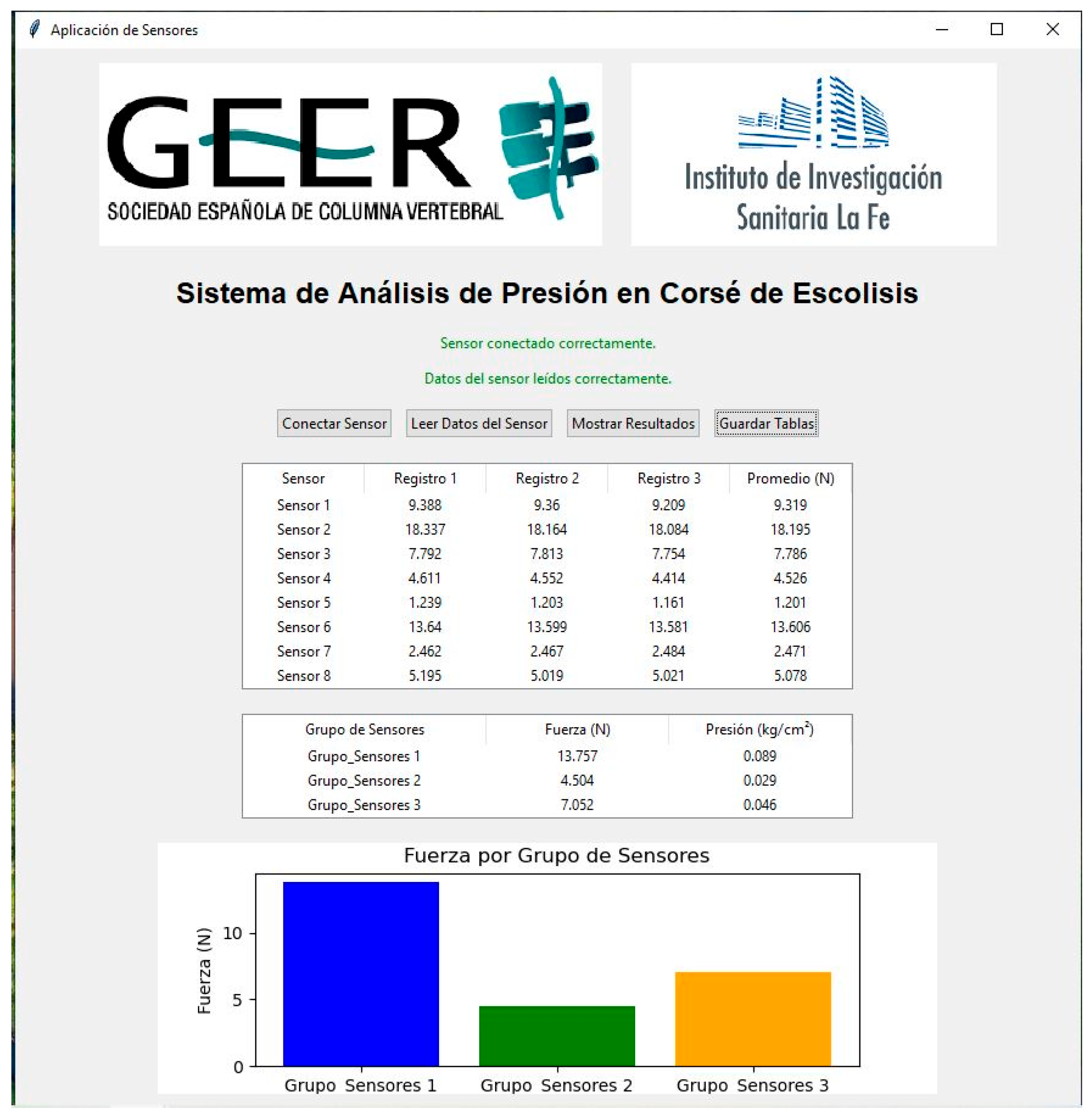
- Brace Fit Monitoring: A custom application was developed for pressure readings. For each reading, the clinician performs 10 consecutive measurements, stored in a matrix. The system then displays processed data, calculates averages per sensor and region (thoracic, lumbar, pelvic), and presents the results in two tables (individual records and cumulative values) and a bar graph (Figure 6).
3.5. Patient Pilot Testing
4. Discussion
4.1. Validation of the Temperature Sensor
4.2. Validation of the Pressure Sensor
4.3. Final Design of Cor-Esc-25
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIS | Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis |
References
- Weinstein, S.L.; Dolan, L.A.; Cheng, J.C.; Danielsson, A.; Morcuende, J.A. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Lancet 2008, 371, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konieczny, M.R.; Senyurt, H.; Krauspe, R. Epidemiology of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Child. Orthop. 2013, 7, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitosugi, M.; Shigeta, A.; Takatsu, A. An autopsy case of sudden death in a patient with idiopathic scoliosis. Med. Sci. Law 2000, 40, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, M.T.; Rabczuk, T. Evaluation of the efficiency of Boston brace on scoliotic curve control: A review of literature. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2020, 43, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Lou, E.; Wong, M.S. The Application of Integrated Force and Temperature Sensors to Enhance Orthotic Treatment Monitoring in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Pilot Study. Sensors 2025, 25, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalmers, E.; Lou, E.; Hill, D.; Zhao, H.V. An advanced compliance monitor for patients undergoing brace treatment for idiopathic scoliosis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2015, 37, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, E.; Hill, D.; Hedden, D.; Mahood, J.; Moreau, M.; Raso, J. An objective measurement of brace usage for the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2011, 33, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuss, F.K.; Ahmad, A.; Tan, A.M.; Razman, R.; Weizman, Y. Pressure Sensor System for Customized Scoliosis Braces. Sensors 2021, 21, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Wu, Q.; Xiao, B.; Wang, J.; Luo, C.; Yu, Q.; Liu, L.; Song, Y. A compliance real-time monitoring system for the management of the brace usage in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients: A pilot study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandal, S.; Rivard, C.H.; Bradet, R. Measuring the compliance behavior of adolescents wearing orthopedic braces. Issues Compr. Pediatr. Nurs. 1999, 22, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, T.; Sample, W.; Yorgova, P.; Neiss, G.; Rogers, K.; Shah, S.; Gabos, P.; Kritzer, D.; Bowen, J.R. Electronic monitoring of orthopedic brace compliance. J. Child. Orthop. 2015, 9, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, G.P.; Ferguson-Pell, M.W.; Smith, K.; Edgar, M.; Morley, T. Quantitative measurement of spinal brace use and compliance in the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2002, 91, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Périé, D.; Aubin, C.E.; Petit, Y.; Beauséjour, M.; Dansereau, J.; Labelle, H. Boston brace correction in idiopathic scoliosis: A biomechanical study. Spine 2003, 28, 1672–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tymińska, P.; Zaborowska-Sapeta, K.; Janczak, D.; Giżewski, T. TLSO with Graphene Sensors-An Application to Measurements of Corrective Forces in the Prototype of Intelligent Brace. Sensors 2022, 22, 4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ScolioSense. New Era in the Treatment of Scoliosis with a Brace. Available online: https://scoliosense.com (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Orthotimer. The Innovation for Documenting the Real Wear Timer of Orthopedic Aids. Available online: https://orthotimer.com/en/ (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- The Boston Sensor|Improve Scoliosis Brace Compliance. Available online: https://www.bostonoandp.com/products/scoliosis-and-spine/boston-sensor/ (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- CORE Body Temperature Sensor. CORE. Available online: https://corebodytemp.com/ (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Masimo—Radius T. Available online: https://www.mymasimo.com/products/radius-t/ (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- e-TakesCare—Soluciones de Supervisión a Distancia. e-TakesCare. Available online: https://www.e-takescare.com/es (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Pressure Mapping in Prosthetics|Tekscan. Available online: https://www.tekscan.com/products-solutions/systems/f-socket-system (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Force Sensors Data Recorder. SPONDYLOS Κέντρο Σκολίωσης Κύφωσης. Available online: https://www.spondylos.gr/en/force-sensors-data-recorder-2 (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Force Sensing Resistor, 0.5 N → 20 N, 18.53 mm, Analog Output. RS Online. Available online: https://es.rs-online.com/web/p/sensores-de-fuerza/2122460?gb=s (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Wong, M.S.; Evans, J.H. Biomechanical evaluation of the Milwaukee brace. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 1998, 22, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Abu Osman, N.A.; Mokhtar, H.; Mehmood, W.; Kadri, N.A. Analysis of the interface pressure exerted by the Chêneau brace in patients with double-curve adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2019, 233, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, V.M.; Houilliez, A.; Schill, A.; Carpentier, A.; Herbaux, B.; Thevenon, A. Study of the pressures applied by a Chêneau brace for correction of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2008, 32, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Hout, J.A.; van Rhijn, L.W.; van den Munckhof, R.J.; van Ooy, A. Interface corrective force measurements in Boston brace treatment. Eur. Spine J. 2002, 11, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Product | Price | Specific for Brace | Connection | Memory | Battery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ScolioSense® | - | Yes | Bluetooth | - | 21 days |
| Orthotimer® | EUR 2646 | Yes | Bluetooth | Internal (400 days) | 4–5 months |
| Boston Sensor® | - | Yes | Bluetooth | Online platform | 1 year |
| Core® | USD 298.95 | No | Bluetooth and ANT+ | Online platform | 6 days |
| Radius T® Masimo | USD 49.99 | No | Bluetooth | Online platform | 8 days |
| Tucky Sensor® | EUR 69.90 | No | Bluetooth | Online platform | 5 days |
| Site | Mean Pressure (MPa) | SD | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor 1 (Thoracic) | 0.018 | 0.0043 | 0.011–0.022 |
| Sensor 2 (Lumbar) | 0.0184 | 0.0082 | 0.006–0.029 |
| Sensor 3 (Pelvic) | 0.0222 | 0.0084 | 0.02–0.039 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ulldemolins, P.; Rubio, P.; Morales, J.; Pérez, S.; Bas, J.L.; Bas, P.; Lamas, M.; Baydal, J.M.; Bovea, M.; Atienza, C.M.; et al. Cor-Esc-25: A Low-Cost Prototype for Monitoring Brace Adherence and Pressure in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Sensors 2025, 25, 5616. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185616
Ulldemolins P, Rubio P, Morales J, Pérez S, Bas JL, Bas P, Lamas M, Baydal JM, Bovea M, Atienza CM, et al. Cor-Esc-25: A Low-Cost Prototype for Monitoring Brace Adherence and Pressure in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Sensors. 2025; 25(18):5616. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185616
Chicago/Turabian StyleUlldemolins, Pablo, Pedro Rubio, Jorge Morales, Silvia Pérez, Jose Luis Bas, Paloma Bas, Mario Lamas, Jose María Baydal, Miquel Bovea, Carlos María Atienza, and et al. 2025. "Cor-Esc-25: A Low-Cost Prototype for Monitoring Brace Adherence and Pressure in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis" Sensors 25, no. 18: 5616. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185616
APA StyleUlldemolins, P., Rubio, P., Morales, J., Pérez, S., Bas, J. L., Bas, P., Lamas, M., Baydal, J. M., Bovea, M., Atienza, C. M., & Bas, T. (2025). Cor-Esc-25: A Low-Cost Prototype for Monitoring Brace Adherence and Pressure in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Sensors, 25(18), 5616. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185616






