Design and Control of a Wheeled Bipedal Robot Based on Hybrid Linear Quadratic Regulator and Proportional-Derivative Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. System Modeling
2.1. Dual-Wheel Inverted Pendulum Model
2.2. Four-Link Motion Model
3. Analysis of Control Algorithm
3.1. Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR) Control
3.2. PD Control
3.3. Virtual Model Control
3.4. Linear Fitting
4. Modeling Simulation Verification
4.1. Definition of Connecting Rod Structure Parameters
4.2. Simulink Simulation Modeling
4.3. Slope Simulation Test
4.4. Jump Simulation Test
5. Webots Simulation Experiment
6. Experiments and Analysis of Results
6.1. Experimental Platform for Balance Control of Bipedal Wheel-Legged Robot
6.2. Robot Control Experiment
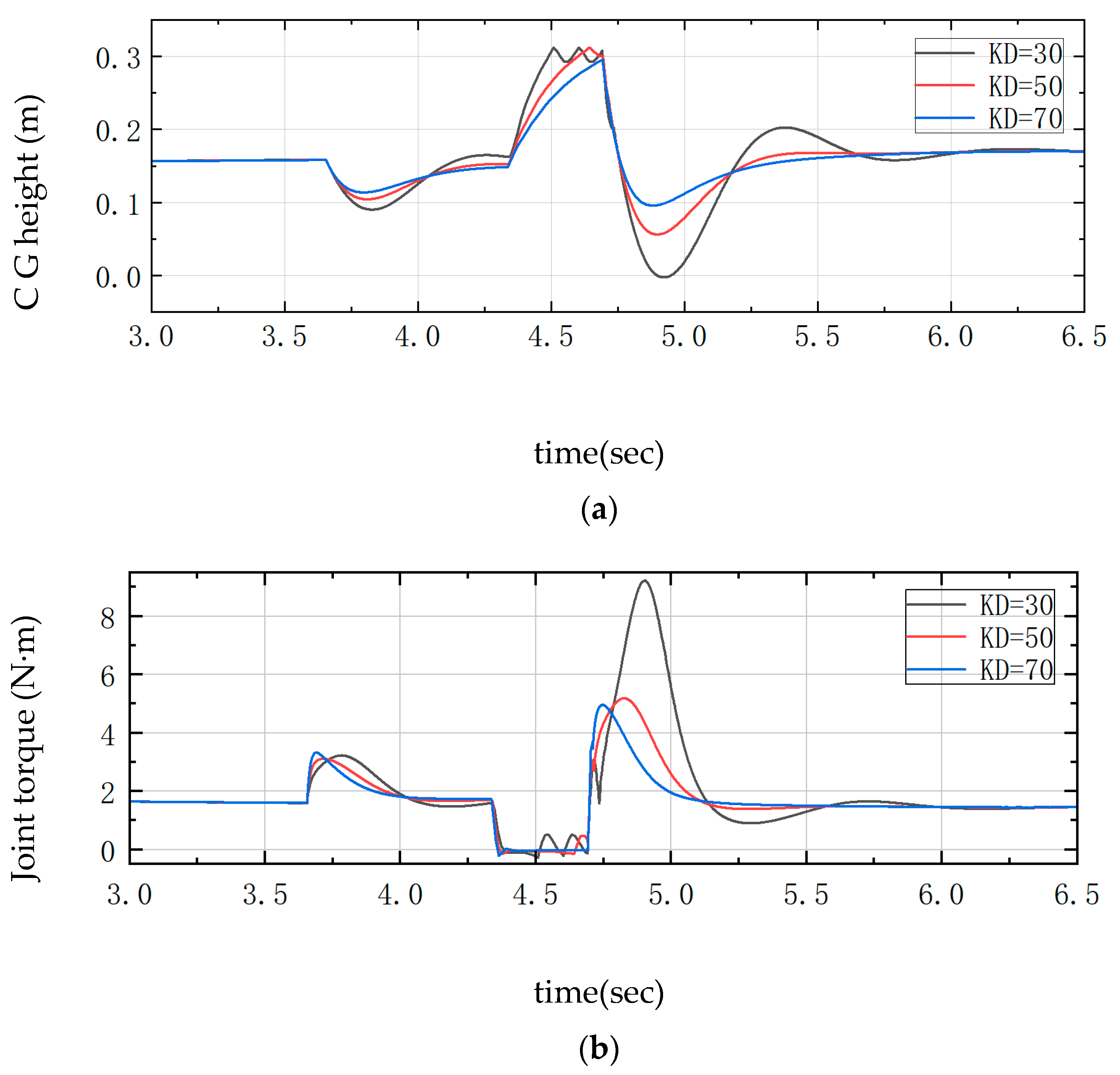
6.3. Experiments and Result Analysis of LQR-PD Control
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | Full name |
| WBRs | Wheeled Bipedal Robots |
| LQR | Linear Quadratic Regulator |
| VMC | Virtual Model Control |
| PID | Proportional-Integral-Derivative |
| PD | Proportional-Derivative |
| CG Height | Center of Gravity Height |
| IDA-PBC | Interconnection and Damping Distribution-Passive Control |
| UKF | Unscented Kalman Filter |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Unit |
| CAN | Controller Area Network |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| ITAE | Integral of Time-Weighted Absolute Error |
References
- Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Wen, S.; Cao, K.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ji, A. Development of wheel-legged biped robots: A review. J. Bionic Eng. 2024, 21, 607–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Poranne, R.; Coros, S. Go fetch!-Dynamic grasps using boston dynamics spot with external robotic arm. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 4488–4494. [Google Scholar]
- Klemm, V.; Morra, A.; Salzmann, C.; Tschopp, F.; Bodie, K.; Gulich, L.; Küng, N.; Mannhart, D.; Pfister, C.; Vierneisel, M.; et al. Ascento: A Two-Wheeled Jumping Robot. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 7515–7521. [Google Scholar]
- Kollarcík, A.; Gurtner, M. Modeling and Control of Two-Legged Wheeled Robot. Master’s Thesis, Czech Technical University, Prague, Czech Republic, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.X.; Zhang, L.Y. Balance Control of Wheel-Legged Robots. Inf. Control 2023, 52, 648–659. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.Y. Design and Control of a Wheel-Bipedswitchable Robot System; Harbin Institute of Technology: Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C. Research on System Design and Locomotion Control of a Bipedal Wheel-Legged Robot. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Lai, J.; Bing, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z. An Adaptive Approach to Whole-Body Balance Control of Wheel-Bipedal Robot Ollie. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 12835–12842. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Cui, L.; Zhang, J.; Lai, J.; Zhang, D.; Chen, K.; Jiang, Z.P. Balance control of a novel wheel-legged robot: Design and experiments. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 6782–6788. [Google Scholar]
- Dinev, T.; Xin, S.; Merkt, W.; Ivan, V.; Vijayakumar, S. Modeling and control of a hybrid wheeled jumping robot. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 2563–2570. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, H.; Yao, L.; Wang, Z. Trajectory Planning for Jumping and Soft Landing with a New Wheeled Bipedal Robot. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 13406–13415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yu, L.; Qin, S.; Jin, G.; Chen, Y. Design and Control of a Bio-Inspired Wheeled Bipedal Robot. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2025, 30, 2461–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, F.; Zhu, W.; Hayashibe, M. Balance Stability Augmentation for Wheel-Legged Biped Robot Through Arm Acceleration Control. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 54022–54031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydogmus, O.; Yilmaz, M. Comparative Analysis of Reinforcement Learning Algorithms for Bipedal Robot Locomotion. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 7490–7499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, B.; Hong, Z.; Shen, C.; Wensing, P.M.; Zhang, W. Underactuated Motion Planning and Control for Jumping With Wheeled-Bipedal Robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, J.; Yin, S.; Zhang, Y. Modeling and MPC-Based Pose Tracking for Wheeled Bipedal Robot. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 7881–7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Lu, B.; Cao, H.; Fang, Y. Somersaulting Jump of Wheeled Bipedal Robot: A Comprehensive Planning and Control Strategy. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 4460–4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Song, S.; Meng, M.Q.-H. Towards Terrain Adaptablity: In Situ Transformation of Wheel-Biped Robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 3819–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Yu, Z.; Chen, X.; Lai, J.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Huang, Q. Concept and Strategies: Equivalent Predictive Control and Handle Point Control for Bipedal-Vehicle Transformable Robots Under Various Disturbances. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 13470–13484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Cao, H.; Hao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Tang, S. A Planning and Control Scheme for the Run-and-Jump Motion of a Wheeled Bipedal Robot Considering Dynamic Constraints. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 1–12, 1206–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, N.; Xu, Z.; Dou, M.; He, L. Design and Implementation of a Novel Two-Wheeled Composite Self-Balancing Robot for Stationary Operations in Unknown Terrain. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 86032–86045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaa, M.Y.; Barambones, O.; Bencherif, A. Robust Adaptive Sliding Mode Control Using Stochastic Gradient Descent for Robot Arm Manipulator Trajectory Tracking. Electronics 2024, 13, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaa, M.Y.; Bencherif, A.; Barambones, O. Indirect Adaptive Control Using Neural Network and Discrete Extended Kalman Filter for Wheeled Mobile Robot. Actuators 2024, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajib, S.H. Risk Factors Contributing to Inland Water Transport Passenger Ferry Accidents in Bangladesh. J. Saf. Sustain. 2025, 2, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xin, Y.; Chen, C.; Song, Z.; Sun, B.; Guo, T. Whole-Body Control with Uneven Terrain Adaptability Strategy for Wheeled-Bipedal Robots. Electronics 2025, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, V.; Mannhart, D.; Siegwart, R. Design Optimization of a Four-Bar Leg Linkage for a Legged-Wheeled Balancing Robot. In Advances in Robotics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Klemm, V.; Morra, A.; Gulich, L.; Mannhart, D.; Rohr, D.; Kamel, M.; de Viragh, Y.; Siegwart, R. LQR-Assisted Whole-Body Control of a Wheeled Bipedal Robot with Kinematic Loops. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3745–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bareiss, D.; Van den Berg, J. Reciprocal collision avoidance for robots with linear dynamics using LQR-obstacles. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 3847–3853. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Li, H.X.; Miao, Z.H.; Cheng, H.F. Swing-up of double inverted pendulum based on variable gain LQR technique. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2011, 31, 1341–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.Q. Research on Structure Design and Motion Control System of Bipedal Wheeled Legged Robot. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing University of Technology, Chongqing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.Y. Research on Jump Control for Hydraulic Bipedal Wheel-Legged Robots. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, C.K. Stable Walking and Trajectory Tracking Control for Quadruped Robots Based on VMC. Master’s Thesis, Hunan University of Technology, Zhuzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, J.; Chen, S. Balance Control Method for Bipedal Wheel-Legged Robots Based on Friction Feedforward Linear Quadratic Regulator. Sensors 2025, 25, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Xin, Y.; Liu, S.; Rong, X.; Li, Y. Modeling and control of a wheeled biped robot. Micromachines 2022, 13, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




















| Symbol | Meaning, Unit |
|---|---|
| Body mass (kg) | |
| Wheel mass (kg) | |
| Distance from body center of mass to wheel center (m) | |
| Wheel radius (m) | |
| Distance between left and right wheels (m) | |
| Gravitational acceleration (m/s2) | |
| Machine pitch angle (rad), angular velocity (rad/s), angular acceleration (rad/s2) | |
| The driving torque of the wheel (N·m) | |
| The force between the body and the wheel in the x and y directions (N) | |
| The friction between the wheel and the ground (N) | |
| Wheel displacement m, velocity (m/s), acceleration (m/s2) | |
| Wheel rotation angular velocity (rad/s), acceleration (rad/s2) | |
| Wheel moment of inertia (kg·m2) | |
| Moment of inertia of the body around the x,y,z-axis (kg·m2) | |
| Course angle (rad), angular velocity (rad/s), angular acceleration (rad/s2) |
| Symbol | Meaning, Unit |
|---|---|
| The length of the corresponding rod (m) | |
| The distance between the joints (m) | |
| Distance (m) from the intersection point of the upper joint to the lower lever (m) | |
| Pendulum height (m) | |
| The angle between bar and the horizontal axis (rad) | |
| Angle between auxiliary connecting rod and (rad) | |
| Angle between auxiliary connecting rod and (rad) | |
| The angle between bar and the horizontal axis (rad) | |
| The angle between bar and the horizontal axis (rad) | |
| The angle between bar and the horizontal axis (rad) | |
| Desired leg length (m) | |
| Vertical coordinates of the center of mass of the connecting rod | |
| Height of the total center of gravity of the system (m) | |
| Height of the center of gravity of the pendulum (m) | |
| Drive wheel radius (m) | |
| Drive wheel mass (kg) | |
| Body mass (kg) | |
| Pendulum mass (kg) | |
| Total system mass (kg) | |
| Distance from center of gravity to wheel axle (m) | |
| Drive wheel moment of inertia (kg·m2) | |
| Moment of inertia of a pendulum (kg·m2) | |
| Normal force (N) | |
| Combined force of gravity and acceleration (N) | |
| Driving torque (N·m) |
| Motors | Rated Torque (N·m) | Rated Speed (RPM) | Power (W) | Control Frequency (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Joint Motors | 12 | 196 | 150 | 1000 |
| In-wheel Motors | 2 | 120 | 103 | 1000 |
| Type | Method | Mean | Variance | RMSE | ITAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position (mm) | LQR-PD PID-PID | 38.3085 66.5343 | 62,364.4706 63,661.0724 | 249.73 252.31 | 1285.6 1852.4 |
| Velocity (mm/s) | LQR-PD PID-PID | −5.2762 −6.9331 | 4958.3190 10,378.1216 | 70.42 101.87 | 542.1 896.3 |
| Pitch angle (10*deg) | LQR-PD PID-PID | −30.1684 −37.6911 | 13,543.1260 21,434.8167 | 116.37 146.41 | 987.5 1562.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, C. Design and Control of a Wheeled Bipedal Robot Based on Hybrid Linear Quadratic Regulator and Proportional-Derivative Control. Sensors 2025, 25, 5398. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175398
Xu Y, Wang Z, Lu C. Design and Control of a Wheeled Bipedal Robot Based on Hybrid Linear Quadratic Regulator and Proportional-Derivative Control. Sensors. 2025; 25(17):5398. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175398
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yu, Zhaoqiang Wang, and Chenhui Lu. 2025. "Design and Control of a Wheeled Bipedal Robot Based on Hybrid Linear Quadratic Regulator and Proportional-Derivative Control" Sensors 25, no. 17: 5398. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175398
APA StyleXu, Y., Wang, Z., & Lu, C. (2025). Design and Control of a Wheeled Bipedal Robot Based on Hybrid Linear Quadratic Regulator and Proportional-Derivative Control. Sensors, 25(17), 5398. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175398







