A Method for Determining Parameters of Mid-Scale Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TID | Traveling ionospheric disturbances |
| TEC | Total electron content |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| CORS | Continuous Operating Reference Station |
| DCB | Differential Code Biases |
| AGW | Acoustic gravity waves |
Appendix A
| No. | Date | Max Ap-Index | Mean Ap-Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 January 2023 | 20 | 11 |
| 2 | 29 January 2023 | 20 | 10 |
| 3 | 13 February 2023 | 20 | 9 |
| 4 | 24 February 2023 | 23 | 11 |
| 5 | 1 March 2023 | 30 | 17 |
| 6 | 8 March 2023 | 30 | 17 |
| 7 | 17 March 2023 | 23 | 13 |
| 8 | 28 March 2023 | 17 | 8 |
| 9 | 8 April 2023 | 20 | 12 |
| 10 | 16 April 2023 | 17 | 9 |
| 11 | 3 May 2023 | 20 | 6 |
| 12 | 18 May 2023 | 7 | 2 |
| 13 | 26 May 2023 | 17 | 13 |
| 14 | 7 June 2023 | 20 | 7 |
| 15 | 8 June 2023 | 17 | 11 |
| 16 | 27 June 2023 | 23 | 20 |
| 17 | 1 July 2023 | 20 | 11 |
| 18 | 2 July 2023 | 17 | 10 |
| 19 | 4 July 2023 | 10 | 8 |
| 20 | 23 July 2023 | 23 | 14 |
| 21 | 24 July 2023 | 23 | 15 |
| 22 | 15 August 2023 | 10 | 6 |
| 23 | 23 August 2023 | 17 | 6 |
| 24 | 29 August 2023 | 20 | 9 |
| 25 | 4 September 2023 | 27 | 15 |
| 26 | 10 September 2023 | 13 | 5 |
| 27 | 11 September 2023 | 20 | 13 |
| 28 | 16 September 2023 | 30 | 12 |
| 29 | 21 September 2023 | 27 | 21 |
| 30 | 23 September 2023 | 27 | 20 |
| 31 | 3 October 2023 | 23 | 16 |
| 32 | 8 October 2023 | 23 | 15 |
| 33 | 11 October 2023 | 10 | 5 |
| 34 | 23 October 2023 | 7 | 2 |
| 35 | 3 November 2023 | 10 | 5 |
| 36 | 29 November 2023 | 17 | 10 |
| 37 | 7 December 2023 | 20 | 11 |
| 38 | 11 December 2023 | 10 | 2 |
| 39 | 25 December 2023 | 13 | 6 |
| 40 | 26 December 2023 | 17 | 12 |
| 41 | 28 December 2023 | 17 | 4 |
References
- Komjathy, A. Global Ionospheric Total Electron Content Mapping Using the Global Positioning System. Ph.D. Thesis, University of New Brunswick, Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, Fredericton, NB, Canada, 1997; Technical Report No. 188. Available online: https://gge.ext.unb.ca/Pubs/TR188.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Heelis, R.A.; Maute, A. Challenges to understanding the Earth’s ionosphere and thermosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2019JA027497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, T.; Otsuka, Y.; Coster, A.J.; Saito, A. Medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances detected with dense and wide TEC maps over North America. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L22101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, M.; Tsugawa, T.; Kubota, M.; Ishii, M. Concentric waves and short-period oscillations observed in the ionosphere after the 2013 Moore EF5 tornado. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5581–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wu, H.; Heale, C.; England, S.; Zhang, S. Impacts of thunderstorm-generated gravity waves on the ionosphere-thermosphere using TIEGCM-NG/MAGIC simulations and comparisons with GNSS TEC, ICON, and COSMIC 2 observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2024, 129, e2024JA032854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchin, P.A.; Bhatt, A.; Bramberger, M.; Chakraborty, S.; Debchoudhury, S.; Heale, C. Atmospheric and ionospheric responses to orographic gravity waves prior to the December 2022 cold air outbreak. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2024, 129, e2024JA032485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, G.; Azeem, I.; Reynolds, A.; Duly, T.M.; McBride, P.; Winkler, C.; Hunton, D. Analysis of traveling ionospheric disturbances (TIDs) in GPS TEC launched by the 2011 Tohoku earthquake. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makela, J.J.; Lognonné, P.; Hébert, H.; Gehrels, T.; Rolland, L.; Allgeyer, S.; Kherani, A.; Occhipinti, G.; Astafyeva, E.; Coïsson, P.; et al. Imaging and modeling the ionospheric airglow response over Hawaii to the tsunami generated by the Tohoku earthquake of 11 March 2011. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L00G02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.P.; Schubert, G.; Walterscheid, R.L. Propagation of tsunami-driven gravity waves into the thermosphere and ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, A08304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afraimovich, E.L.; Perevalova, N.P.; Plotnikov, A.V.; Uralov, A.M. The shock-acoustic waves generated by earthquakes. Ann. Geophys. 2001, 19, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Themens, D.R.; Watson, C.; Žagar, N.; Vasylkevych, S.; Elvidge, S.; McCaffrey, A.; Prikryl, P.; Reid, B.; Wood, A.; Jayachandran, P.T. Global propagation of ionospheric disturbances associated with the 2022 Tonga volcanic eruption. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L. Ionospheric disturbances of the January 15, 2022, Tonga volcanic eruption observed using the GNSS network in New Zealand. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchin, P.A.; Deshpande, K.B.; Egan, S.; Lay, E.H.; Obenberger, K.S.; Zettergren, M.D.; Snively, J.B. Ionospheric disturbances in GNSS TEC data: SpaceX Falcon 9 deorbit maneuvers over CONUS in April–May 2024. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2025, 52, e2024GL112364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasyukevich, Y.V.; Vesnin, A.M.; Astafyeva, E.; Maletckii, B.M.; Lebedev, V.P.; Padokhin, A.M. Supersonic waves generated by the 18 November 2023 Starship flight and explosions: Unexpected northward propagation and a man-made non-chemical depletion. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL109284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afraimovich, E.L.; Astafyeva, E.I.; Demyanov, V.V.; Edemskiy, I.K.; Gavrilyuk, N.S.; Ishin, A.B.; Kosogorov, E.A.; Leonovich, L.A.; Lesyuta, O.S.; Palamartchouk, K.S.; et al. A review of GPS/GLONASS studies of the ionospheric response to natural and anthropogenic processes and phenomena. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2013, 3, A27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-L.; Wan, Q.-T.; Ma, G.-Y.; Li, J.-H.; Fan, J.-T. The influence of ionospheric thin shell height on TEC retrieval from GPS observation. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 16, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenbeis, J.; Occhipinti, G.; Astafyeva, E.; Rolland, L. Short- and long-wavelength TIDs generated by the Great American eclipse of 21 August 2017. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 9486–9493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günzkofer, F.; Pokhotelov, D.; Stober, G.; Mann, I.; Vadas, S.L.; Becker, E.; Tjulin, A.; Kozlovsky, A.; Tsutsumi, M.; Gulbrandsen, N.; et al. Inferring neutral winds in the ionospheric transition region from atmospheric-gravity-wave traveling-ionospheric-disturbance (AGW-TID) observations with the EISCAT VHF radar and the Nordic Meteor Radar Cluster. Ann. Geophys. 2023, 41, 409–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komjathy, A.; Yang, Y.; Meng, X.; Verkhoglyadova, O.; Mannucci, A.J.; Langley, R.B. Review and perspectives: Understanding natural-hazards-generated ionospheric perturbations using GPS measurements and coupled modeling. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Yokoyama, T.; Ssessanga, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Liu, P. On using a double-thin-shell approach and TEC perturbation component to sound night-time mid-latitude E–F coupling. Earth Planets Space 2022, 74, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belehaki, A.; Tsagouri, I.; Altadill, D.; Blanch, E.; Borries, C.; Buresova, D.; Chum, J.; Galkin, I.; Juan, J.M.; Segarra, A.; et al. An overview of methodologies for real-time detection, characterisation and tracking of traveling ionospheric disturbances developed in the TechTIDE project. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2020, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savastano, G.; Komjathy, A.; Verkhoglyadova, O.; Mazzoni, A.; Crespi, M.; Wei, Y.; Mannucci, A.J. Real-time detection of tsunami ionospheric disturbances with a stand-alone GNSS receiver: A preliminary feasibility demonstration. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonah, O.F.; Zhang, S.; Coster, A.J.; Goncharenko, L.P.; Erickson, P.J.; Rideout, W.; de Paula, E.R.; de Jesus, R. Understanding inter-hemispheric traveling ionospheric disturbances and their mechanisms. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-R.; Vierinen, J.; Aa, E.; Goncharenko, L.P.; Erickson, P.J.; Rideout, W.; Coster, A.J.; Spicher, A. 2022 Tonga volcanic eruption induced global propagation of ionospheric disturbances via lamb waves. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2022, 9, 871275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.-H.; Lin, C.; Otsuka, Y.; Liu, H.; Rajesh, P.K.; Chen, C.-H.; Lin, J.-T.; Chang, M.T. Statistical study of medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances in low-latitude ionosphere using an automatic algorithm. Earth Planets Space 2021, 73, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenbeis, J. Ionospheric Dynamics by GNSS Total Electron Content Observations: The Effect of Solar Eclipses and the Mystery of Earthquake Precursors. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris Cité, Paris, France, 2020. Available online: http://www.theses.fr/2020UNIP7027/document (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- van Vugt, M.K.; Sederberg, P.B.; Kahana, M.J. Comparison of spectral analysis methods for characterizing brain oscillations. J. Neurosci. Methods 2007, 162, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreyev, A.; Kapytin, V.; Mukasheva, S.; Somsikov, V. Development of a system for detecting traveling ionospheric disturbances based on GNSS data. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasyukevich, Y.V.; Mylnikova, A.A.; Kunitsyn, V.E.; Padokhin, A.M. Influence of GPS/GLONASS differential code biases on the determination accuracy of the absolute total electron content in the ionosphere. Geomagn. Aeron. 2015, 55, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasyukevich, Y.; Mylnikova, A.; Vesnin, A. GNSS-based non-negative absolute ionosphere total electron content, its spatial gradients, time derivatives and differential code biases: Bounded-variable least-squares and taylor series. Sensors 2020, 20, 5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Z.; An, J. GPS differential code biases considering the second-order ionospheric term. GPS Solutions. 2017, 21(4), 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astafyeva, E. Ionospheric detection of natural hazards. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 1265–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, K.; Romero-Andrade, R.; Sharma, G.; Colonna, R. Sequential evolution of ionospheric TEC anomalies and acoustic-gravity wave precursors associated with the February 8, 2025, Mw 7.6 Cayman Islands earthquake. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2025, 274, 106582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmons, D.J.; Dao, E.V.; Knippling, K.K.; McNamara, L.F.; Nava, O.A.; Obenberger, K.S.; Colman, J.J. Estimating horizontal phase speeds of a traveling ionospheric disturbance from Digisonde single site vertical ionograms. Radio Sci. 2020, 55, e2020RS007089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufiqurrahman, E.; Soepardjo, A.H.; Muslim, B. The propagation speed of travelling ionospheric disturbance (TID) in ionosphere and vertical gravity wave caused by Sumatra–Andaman tsunami on December 26, 2004. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2023; p. 020241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, S.T.; Sherstyukov, R.O.; Kozlovsky, A.; Ulich, T.; Lester, M. Statistics of traveling ionospheric disturbances at high latitudes using a rapid-run ionosonde. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2024, 129, e2023JA031694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotake, N.; Otsuka, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Tsugawa, T.; Saito, A. Statistical study of medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances observed with the GPS networks in Southern California. Earth Planets Space 2007, 59, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
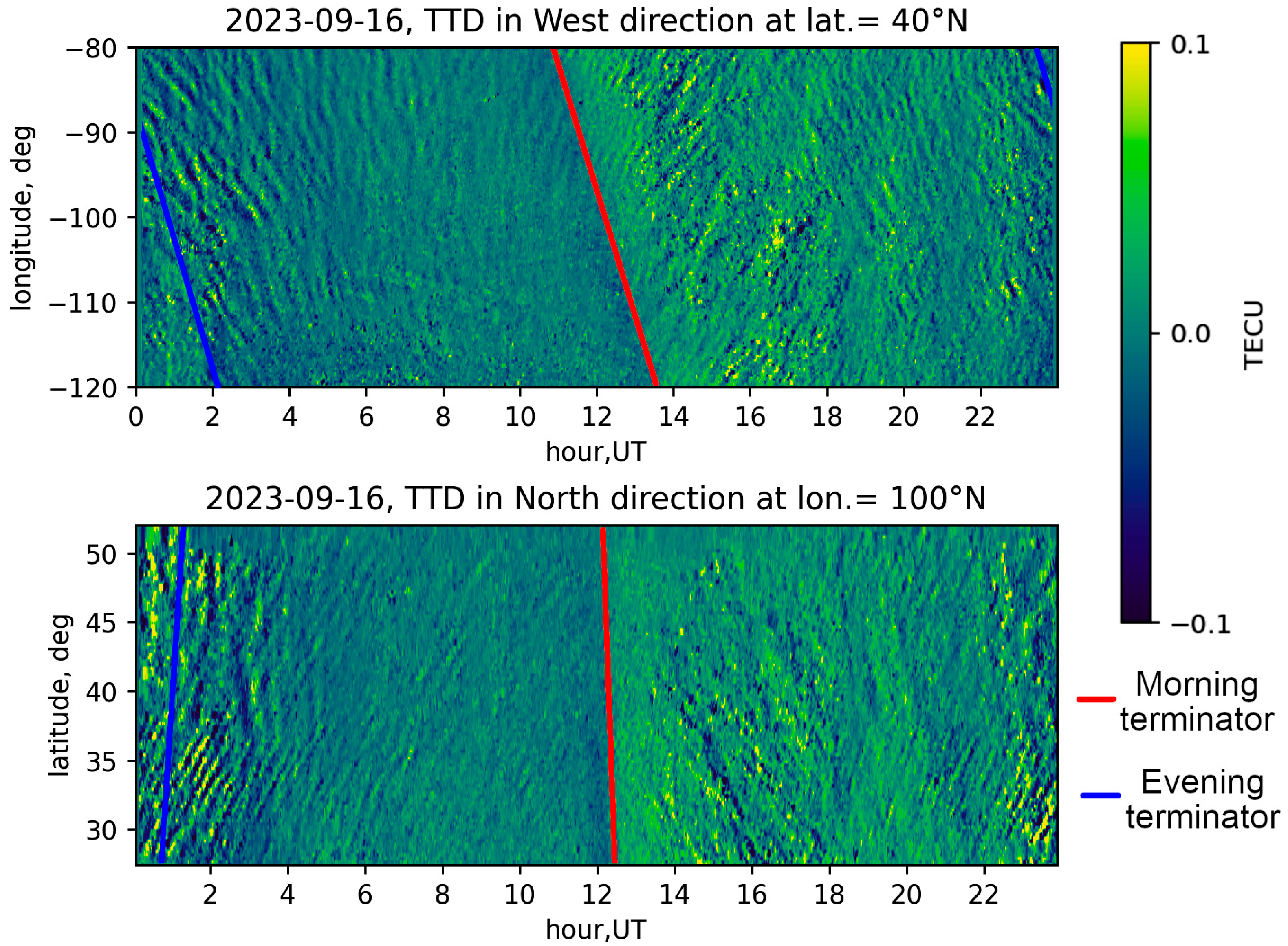

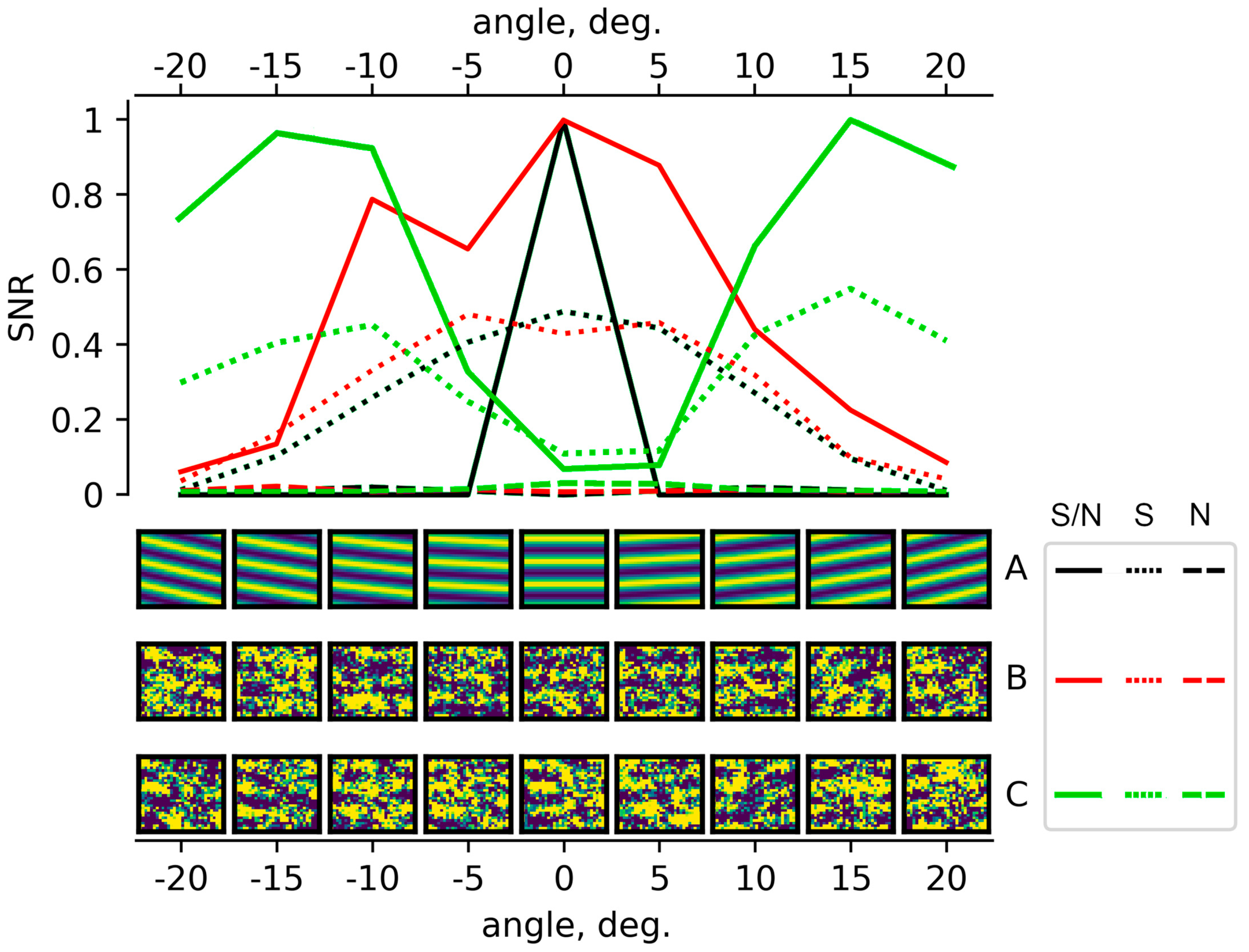



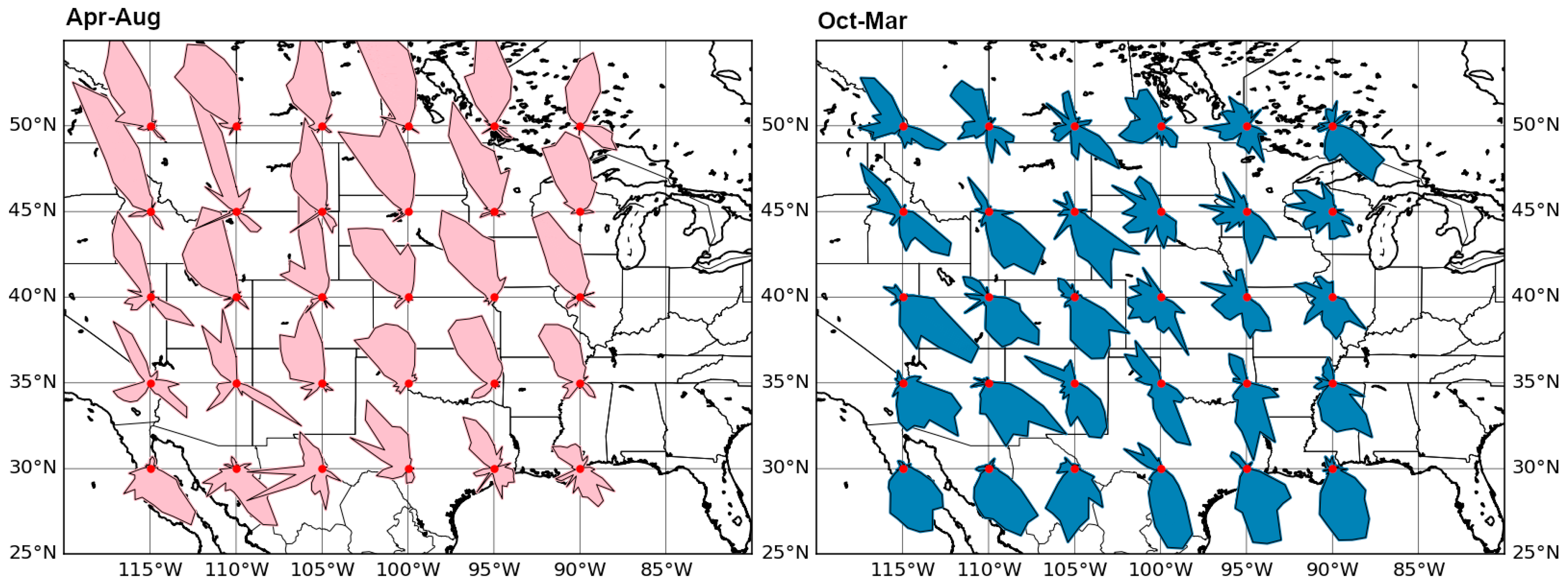
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andreyev, A.; Kapytin, V.; Yakovets, A.; Chsherbulova, Y. A Method for Determining Parameters of Mid-Scale Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances. Sensors 2025, 25, 5377. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175377
Andreyev A, Kapytin V, Yakovets A, Chsherbulova Y. A Method for Determining Parameters of Mid-Scale Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances. Sensors. 2025; 25(17):5377. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175377
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndreyev, Alexey, Vitaliy Kapytin, Artur Yakovets, and Yekaterina Chsherbulova. 2025. "A Method for Determining Parameters of Mid-Scale Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances" Sensors 25, no. 17: 5377. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175377
APA StyleAndreyev, A., Kapytin, V., Yakovets, A., & Chsherbulova, Y. (2025). A Method for Determining Parameters of Mid-Scale Traveling Ionospheric Disturbances. Sensors, 25(17), 5377. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175377





