HC-SPA: Hyperbolic Cosine-Based Symplectic Phase Alignment for Fusion Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We have designed a novel gradient coordination mechanism that projects gradients from different modalities onto a shared hyperbolic space. By utilizing hyperbolic metrics to define and compute the geometric relationships between these modalities, this mechanism effectively coordinates their gradient flows, thereby reducing inter-modality conflicts and enhancing the quality of feature fusion through more cooperative updates.
- We have developed a symplectic phase alignment strategy that employs symplectic transformations to rigorously synchronize the gradient update phases across each modality. This design ensures that optimization steps maintain directional consistency, which in turn avoids destructive interference between disparate gradient influences and significantly improves both the stability and convergence speed of the training process.
- We also demonstrate through experiments on several public datasets and different models that the HC-SPA optimizer significantly enhances model performance across various application scenarios. Particularly in tasks involving complex modal relationships, the optimizer effectively improves gradient coordination, reduces phase conflicts, and thereby enhances training stability and fusion performance.
2. Related Work
2.1. Multimodal Fusion
2.2. Hyperbolic Approaches
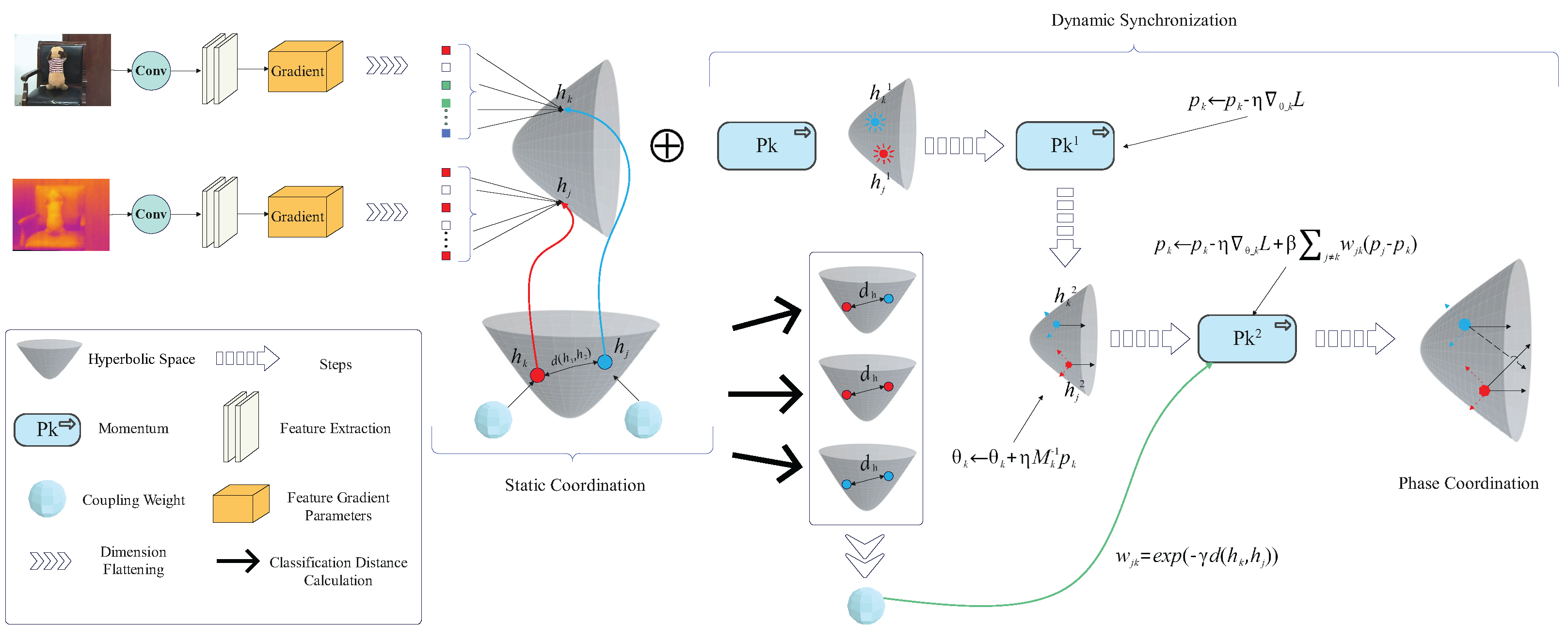
3. Materials and Methods
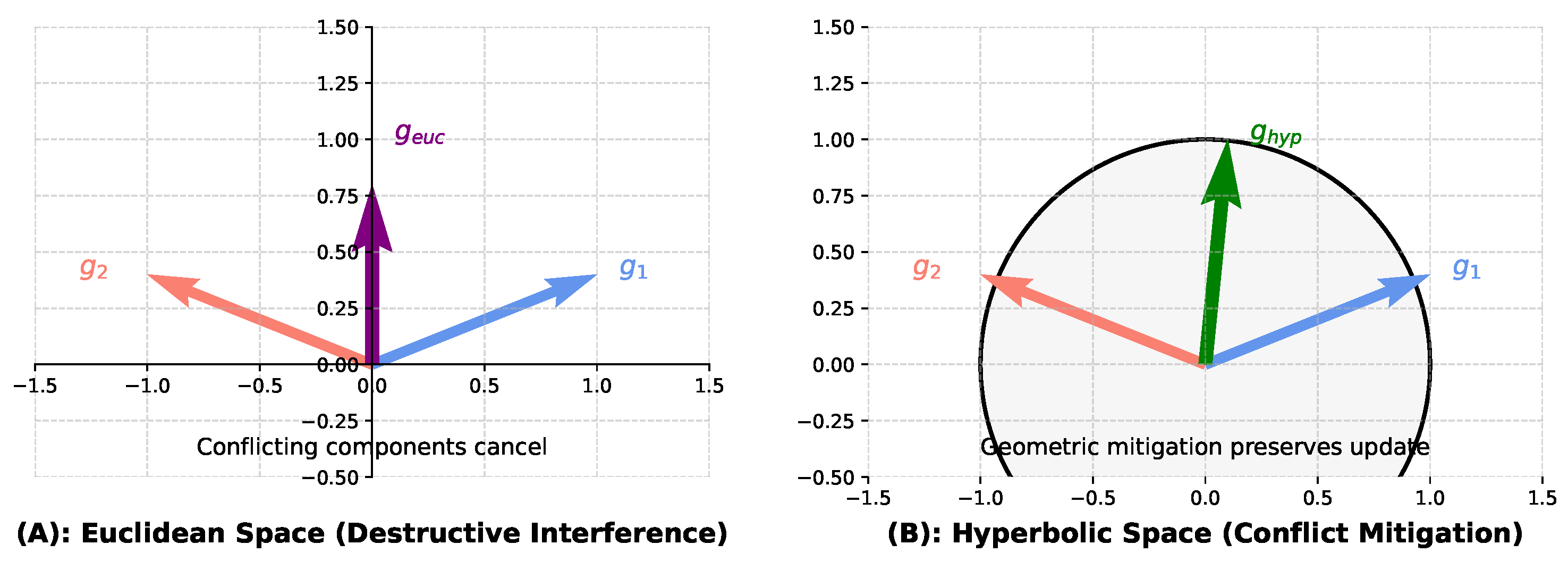
3.1. Motivations
3.2. Coordinating Heterogeneous Gradient Flows
3.2.1. Mapping Parameters to the Hyperbolic Space
3.2.2. Justification for Choosing the Lorentz Model
3.2.3. Computing the Hyperbolic Distance
3.2.4. Momentum Adjustment and Gradient Scaling
3.3. Synchronizing Gradient Update Phases
3.3.1. Gradient Synchronization
3.3.2. Constructing the Update Rule
3.3.3. Phase Coordination Mechanism
3.4. Integration with Deep Learning Models and Modularity
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Configurations
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Comparative Experiments
Quantitative Results
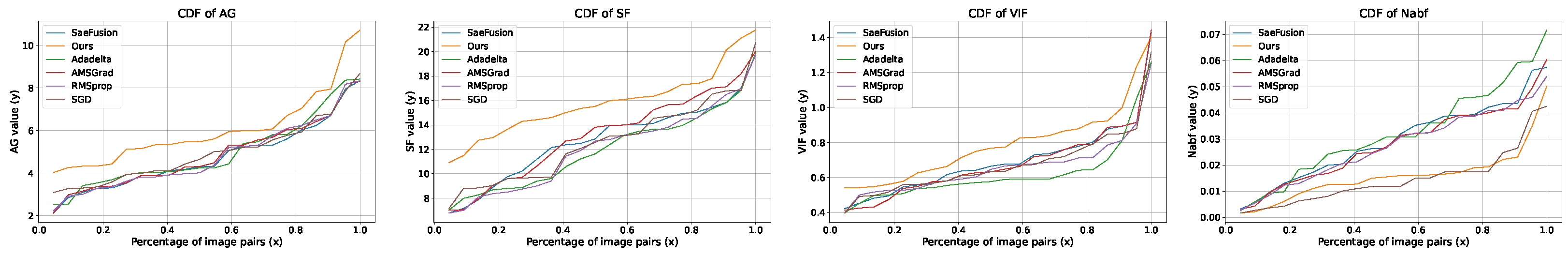
4.4. Analysis of Metric Variations and Optimizer Efficacy
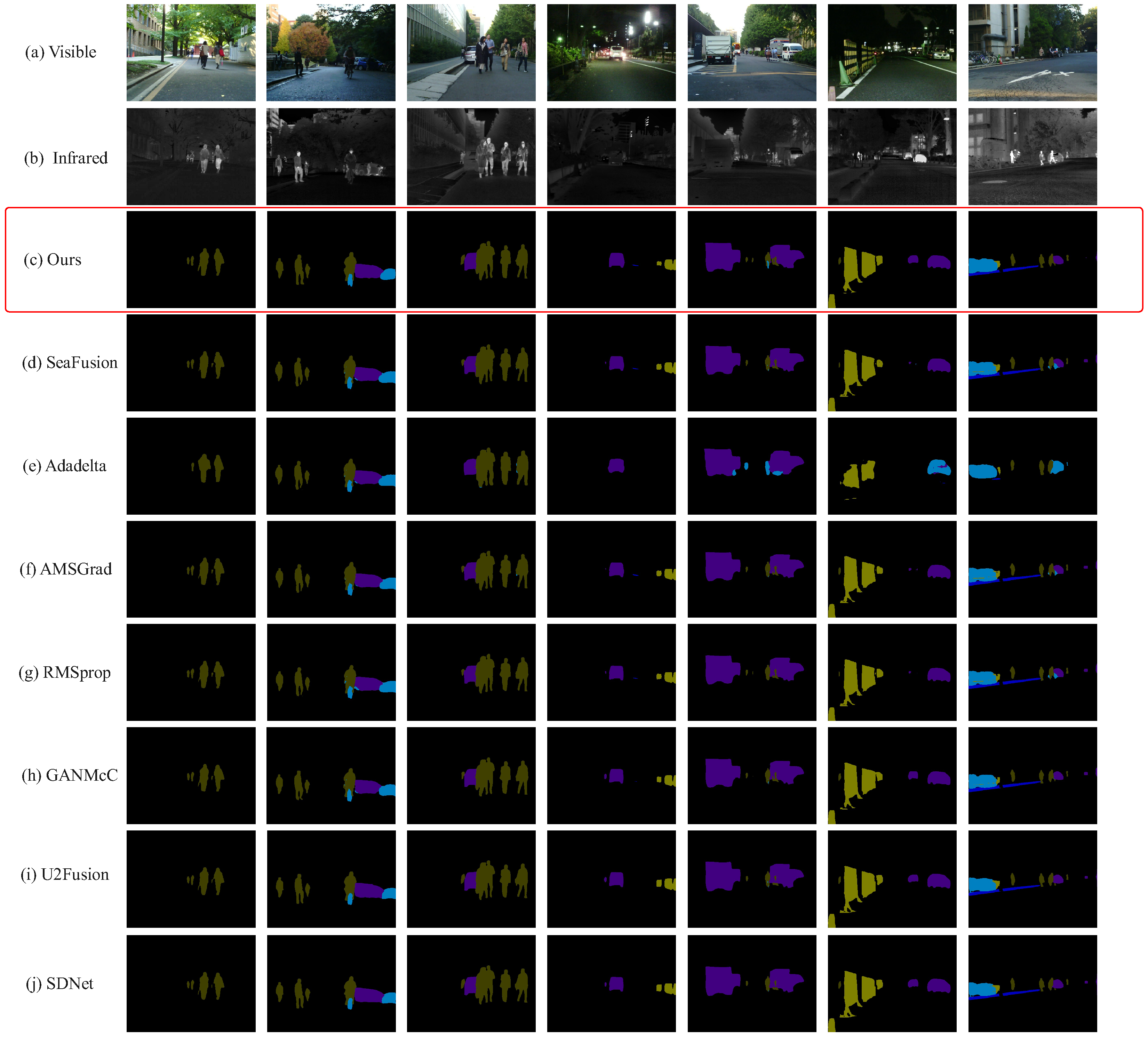
4.5. Semantic Segmentation Performance
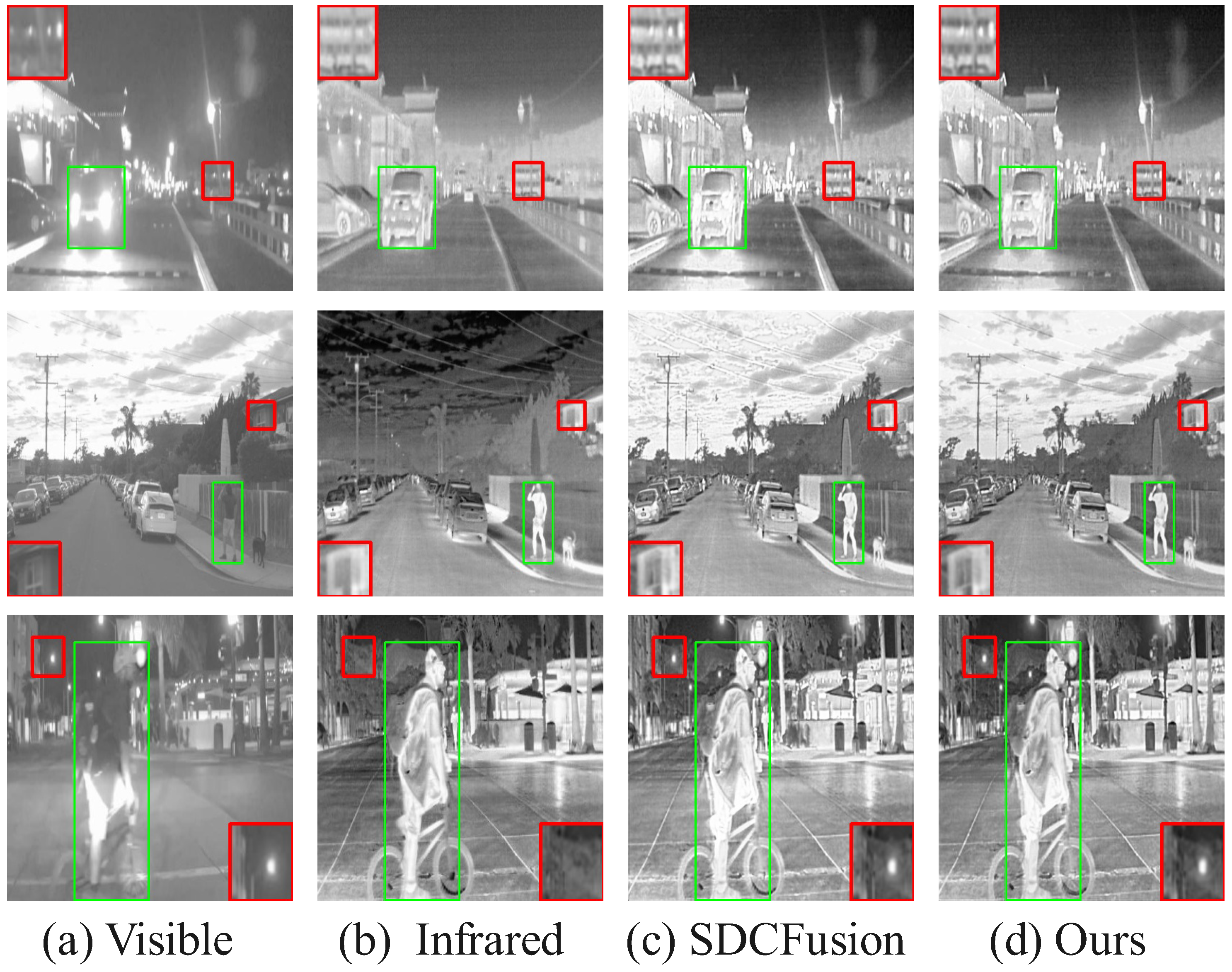
4.6. Validation Experiment
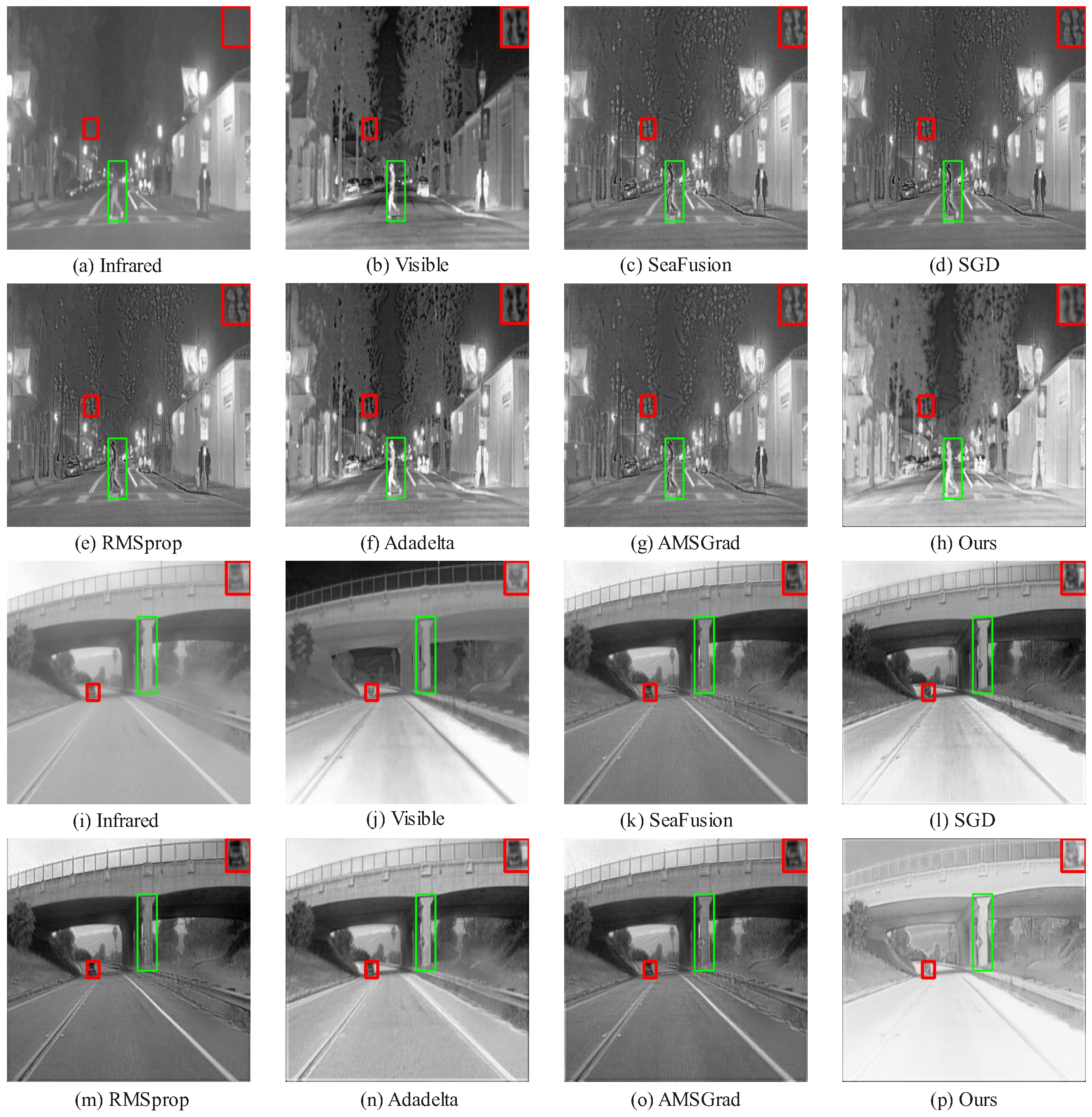
4.6.1. Qualitative Results
4.6.2. Quantitative Results
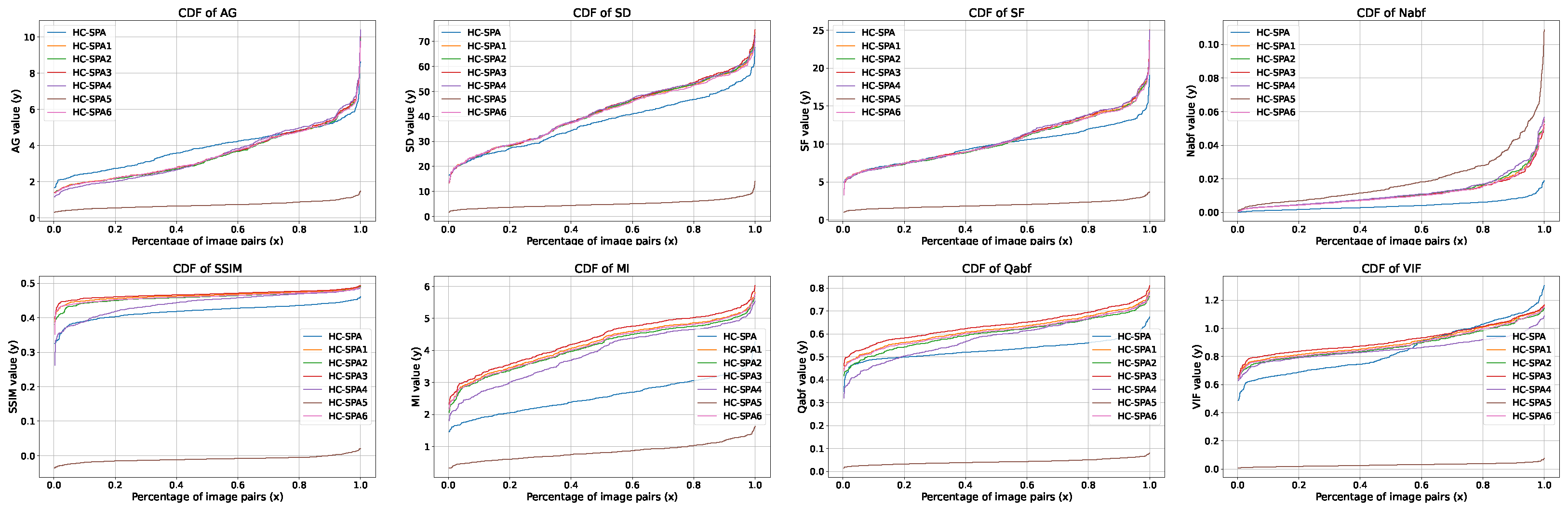
4.7. Hyperparameter Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hutahaean, N.D.; Siregar, I.J.; Lumbantobing, A.S.; Togatorop, P.R.; Simanjuntak, H.T.A.; Situmeang, S.I.G.; Lumbantobing, A.B. Data integration automation from heterogeneous data sources for smart farming data lake. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2025; Volume 3250. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Li, J.; Jiang, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, Q.; Gao, E.; Yue, T. Autonomous Data Association and Intelligent Information Discovery Based on Multimodal Fusion Technology. Symmetry 2024, 16, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Shen, T.; Wang, Q. Advancing RGB-IR Image Fusion: Exploiting Hyperbolic Geometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 6007–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fu, Y. FCDFusion: A fast, low color deviation method for fusing visible and infrared image pairs. Comput. Vis. Media 2025, 11, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Gao, J.; Zhou, S.; Li, C.; Shi, J.; Guo, F. Cross-Modality Target Detection Using Infrared and Visible Image Fusion for Robust Objection recognition. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2025, 123, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayhan, F.; Joshi, J.; Ren, G.; Hernandez, L.; Petreca, B.; Baurley, S.; Berthouze, N.; Cho, Y. Advancing Textile Damage Segmentation: A Novel RGBT Dataset and Thermal Frequency Normalization. Sensors 2025, 25, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Er, M.J. Mitigating gradient conflicts via expert squads in multi-task learning. Neurocomputing 2025, 614, 128832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alison, R.; Jonathan, W.; Suhartono, D. Analyzing the Effects of Combining Gradient Conflict Mitigation Methods in Multi-Task Learning. CommIT (Commun. Inf. Technol.) J. 2024, 18, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, D.; Jiang, Z.; Ma, L.; Zhong, W.; Fan, X.; Liu, R. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion: From Data Compatibility to Task Adaption. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 47, 2349–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Ma, J. Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: A semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network. Inf. Fusion 2022, 82, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Jiang, J.; Mei, X.; Zhang, X.P. DDcGAN: A dual-discriminator conditional generative adversarial network for multi-resolution image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4980–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Fan, F.; Huang, J.; Mei, X.; Ma, Y. SwinFusion: Cross-domain Long-range Learning for General Image Fusion via Swin Transformer. IEEE/CAA. Automat 2022, 9, 1200–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Fang, L.; Xia, S.; Deng, Y.; Ma, J. Dif-fusion: Towards high color fidelity in infrared and visible image fusion with diffusion models. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 5705–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Ma, J. Rethinking the necessity of image fusion in high-level vision tasks: A practical infrared and visible image fusion network based on progressive semantic injection and scene fidelity. Inf. Fusion 2023, 99, 101870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, H.; Gong, M.; Ma, J. DIVFusion: Darkness-free infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2023, 91, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zou, H.; Li, W.; Li, D.; Kuang, Y. HiViT-IDS: An Efficient Network Intrusion Detection Method Based on Vision Transformer. Sensors 2025, 25, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinemre, I.; Mehmood, K.; Kralevska, K.; Mahmoodi, T. Gradient-Based Optimization for Intent Conflict Resolution. Electronics 2024, 13, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Hu, J.F.; Zhao, Z.P.; Liu, Y. MCFNet: Research on small target detection of RGB-infrared under UAV perspective with multi-scale complementary feature fusion. IET Image Process. 2025, 19, e13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jia, C.; Li, Z.; Wei, X.; Chen, M. A survey of geometric optimization for deep learning: From Euclidean space to Riemannian manifold. ACM Comput. Surv. 2025, 57, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I. Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, 3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, R.S.; Liu, Z. Combination of multimodal image fusion and pattern recognition for pipeline inspection. Inf. Fusion 2006, 7, 272–282. [Google Scholar]
- Baltrušaitis, T.; Ahuja, C.; Morency, L.P. Multimodal machine learning: A survey and taxonomy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2019, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guan, Z.; Qian, W.; Cao, J.; Ma, R.; Bi, C. A degradation-aware guided fusion network for infrared and visible image. Inf. Fusion 2025, 118, 102931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, L.; Ma, J. Text-IF: Leveraging Semantic Text Guidance for Degradation-Aware and Interactive Image Fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 27026–27035. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Chen, W.; Xing, X.; He, S.; Luo, X.; Lyu, X.; Shen, L.; Qiu, G. HySurvPred: Multimodal Hyperbolic Embedding with Angle-Aware Hierarchical Contrastive Learning for Survival Prediction. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25 February–4 March 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Mandica, P.; Franco, L.; Kallidromitis, K.; Petryk, S.; Galasso, F. Hyperbolic Learning with Multimodal Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.05097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcehre, C.; Denil, M.; Genc, Y.; de Freitas, N. Hyperbolic Attention Networks. In Proceedings of the ICLR, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chami, I. Representation Learning and Algorithms in Hyperbolic Spaces. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vidal, À.P.; Nasrollahi, K.; Moeslund, T.B.; Escalera, S. Machine Unlearning in Hyperbolic vs. Euclidean Multimodal Contrastive Learning: Adapting Alignment Calibration to MERU. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2503.15166. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Multimodal sentiment and emotion recognition in hyperbolic space. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 250, 123456. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.; Zhou, W.; Peng, C.; Hoshyar, A.N.; Xu, C.; Naseem, U.; Xia, F. Multimodal Hyperbolic Graph Learning for Alzheimer’s Disease Detection. In Proceedings of the Australasian Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Melbourne, Australia, 25–29 November 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 390–403. [Google Scholar]
- Shamir, O.; Zhang, T. Stochastic Gradient Descent for Non-smooth Optimization: Convergence Results and Optimal Averaging Schemes. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. (NeurIPS) 2013, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Huo, H.; Li, J.; Pang, S.; Zheng, B. A semantic-driven coupled network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2024, 108, 102352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Q.; Watanabe, K.; Karasawa, T.; Ushiku, Y.; Harada, T. MFNet: Towards real-time semantic segmentation for autonomous vehicles with multi-spectral scenes. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 5108–5115. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Le, Z.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X. FusionDN: A Unified Densely Connected Network for Image Fusion. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 12484–12491. [Google Scholar]
- Toet, A. The TNO multiband image data collection. Data Brief 2017, 15, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieleman, T.; Hinton, G. Root Mean Square Propagation (RMSProp). In Coursera: Neural Networks for Machine Learning; Lecture 6.5; Coursera: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D. ADADELTA: An Adaptive Learning Rate Method. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1212.5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddi, S.J.; Kale, S.; Kumar, S. On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E. Digital Image Processing; Standard reference for image quality metrics including MSE and PSNR; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Athanasopoulos, G. Forecasting: Principles and Practice; Statistical basis for standard deviation; OTexts: Melbourne, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh-Thu, Q.; Ghanbari, M. The scope of PSNR in image and video quality assessment. Electron. Lett. 1993, 44, 800–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M.; Thomas, J.A. Elements of Information Theory; Foundational theory for mutual information; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, New Jersey, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh, H.R.; Bovik, A.C. Image information and visual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2006, 15, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Fang, L. Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 22, 2864–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, K. Note on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1895, 58, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piella, G. A general framework for multiresolution image fusion: From pixels to regions. Inf. Fusion 2003, 4, 259–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Shao, Z.; Liang, P.; Xu, H. GANMcC: A Generative Adversarial Network With Multiclassification Constraints for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Ling, H. U2Fusion: A Unified Unsupervised Image Fusion Network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, J. SDNet: A versatile squeeze-and-decomposition network for real-time image fusion. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 2761–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







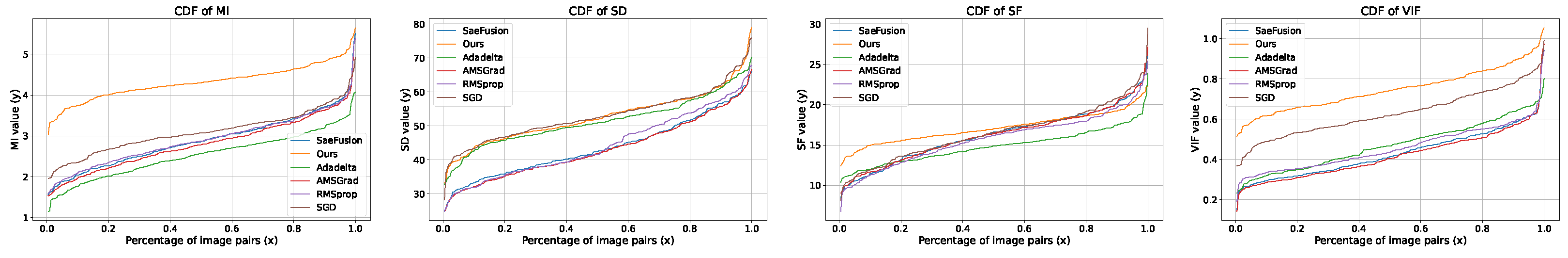



| Model | MSE | SD | PSNR | AG | CC | EN | Nabf | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeaFusion | 0.039 | 40.20 | 63.89 | 3.077 | 0.540 | 6.659 | 0.014 | 0.3104 |
| SGD | 0.038 | 40.13 | 64.03 | 3.040 | 0.611 | 6.703 | 0.008 | 0.4951 |
| RMSprop | 0.037 | 39.37 | 64.06 | 3.036 | 0.536 | 6.607 | 0.013 | 0.3142 |
| Adadelta | 0.039 | 39.46 | 63.80 | 3.015 | 0.596 | 6.643 | 0.014 | 0.3104 |
| AMSGrad | 0.038 | 40.02 | 63.96 | 3.096 | 0.542 | 6.658 | 0.013 | 0.3026 |
| Ours | 0.034 | 41.46 | 64.49 | 3.286 | 0.674 | 6.675 | 0.003 | 0.4781 |
| Model | MSE | SD | VIF | AG | CC | SF | Nabf | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeaFusion | 0.024 | 41.23 | 0.676 | 3.879 | 0.339 | 11.17 | 0.043 | 0.1489 |
| Adadelta | 0.024 | 39.87 | 0.589 | 4.243 | 0.535 | 8.797 | 0.036 | 0.3802 |
| AMSGrad | 0.024 | 41.53 | 0.648 | 3.886 | 0.400 | 10.61 | 0.041 | 0.1272 |
| RMSprop | 0.016 | 48.80 | 0.678 | 3.823 | 0.399 | 8.746 | 0.040 | 0.1759 |
| SGD | 0.086 | 37.69 | 0.756 | 4.115 | 0.611 | 9.644 | 0.017 | 0.4227 |
| Ours | 0.019 | 41.66 | 0.878 | 5.993 | 0.624 | 12.96 | 0.012 | 0.4038 |
| Model | MSE | SD | VIF | EN | CC | SF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeaFusion | 0.062 | 38.66 | 0.483 | 6.885 | 0.339 | 12.97 |
| Adadelta | 0.052 | 42.18 | 0.496 | 7.012 | 0.084 | 12.99 |
| AMSGrad | 0.062 | 39.11 | 0.467 | 6.894 | 0.275 | 12.85 |
| RMSprop | 0.063 | 38.89 | 0.516 | 6.839 | 0.080 | 12.41 |
| SGD | 0.051 | 45.91 | 0.671 | 7.343 | 0.093 | 13.65 |
| Ours | 0.048 | 47.40 | 0.847 | 7.405 | 0.284 | 15.90 |
| Method | Background | Car | Person | Bike | Curve | Car Stop | Cuadrail | Color Tone | Bump | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visible | 98.26 | 89.03 | 59.94 | 70.00 | 60.69 | 71.43 | 77.90 | 63.42 | 75.31 | 74.00 |
| Infrared | 98.24 | 87.33 | 70.46 | 69.23 | 58.74 | 68.85 | 65.57 | 56.93 | 72.72 | 72.01 |
| GANMcC | 98.47 | 89.26 | 72.11 | 71.74 | 62.71 | 72.94 | 74.05 | 63.26 | 77.42 | 75.77 |
| U2Fusion | 98.49 | 89.78 | 72.93 | 71.96 | 62.84 | 70.95 | 79.25 | 63.59 | 77.32 | 76.35 |
| SDNet | 98.52 | 90.43 | 73.41 | 71.61 | 63.68 | 75.59 | 85.25 | 61.82 | 81.41 | 76.11 |
| Adadelta | 95.44 | 58.06 | 49.53 | 25.69 | 9.55 | 26.92 | 45.71 | 35.7 | 13.57 | 40.02 |
| AMSGrad | 98.46 | 90.72 | 66.24 | 68.75 | 56.73 | 73.24 | 83.14 | 66.55 | 80.4 | 76.02 |
| RMSprop | 98.44 | 90.54 | 65.37 | 68.70 | 56.13 | 72.76 | 83.41 | 66.46 | 80.42 | 76.80 |
| SeaFusion | 98.45 | 90.62 | 65.47 | 68.81 | 56.79 | 73.16 | 82.99 | 66.56 | 80.11 | 75.88 |
| Ours | 98.62 | 91.06 | 75.61 | 71.98 | 63.92 | 74.84 | 77.89 | 67.31 | 77.13 | 77.59 |
| Dataset | Method | SD | PSNR | MSE | MI | SDC | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNO | SDCFusion | 45.35 | 61.48 | 0.046 | 2.236 | 1.866 | 0.490 |
| TNO | Ours1 | 45.37 | 61.99 | 0.041 | 2.387 | 1.836 | 0.494 |
| TNO | Ours2 | 45.82 | 62.03 | 0.040 | 2.365 | 1.850 | 0.497 |
| RoadScene | SDCFusion | 44.47 | 58.66 | 0.088 | 2.620 | 1.778 | 0.398 |
| RoadScene | Ours1 | 47.87 | 58.99 | 0.081 | 3.340 | 1.647 | 0.410 |
| RoadScene | Ours2 | 50.43 | 58.82 | 0.085 | 3.187 | 1.620 | 0.410 |
| MSRS | SDCFusion | 42.37 | 64.37 | 0.348 | 4.442 | 1.665 | 0.497 |
| MSRS | Ours1 | 42.28 | 64.41 | 0.345 | 4.869 | 1.601 | 0.493 |
| MSRS | Ours2 | 42.79 | 64.26 | 0.336 | 4.944 | 1.586 | 0.497 |
| Model | MSE | VIF | PSNR | AG | CC | SCD | SF | Nabf | alpha | beta | gamma |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC-SPA | 0.034 | 0.843 | 64.49 | 3.286 | 0.674 | 1.717 | 8.769 | 0.003 | 2.0 | 0.90 | 5.0 |
| HC-SPA1 | 0.039 | 0.942 | 63.84 | 3.031 | 0.604 | 1.472 | 9.400 | 0.009 | 0.5 | 0.90 | 2.0 |
| HC-SPA2 | 0.037 | 0.927 | 64.08 | 2.987 | 0.606 | 1.490 | 9.268 | 0.009 | 1.0 | 0.90 | 10.0 |
| HC-SPA3 | 0.037 | 0.945 | 64.11 | 2.995 | 0.608 | 1.516 | 9.309 | 0.009 | 1.0 | 0.95 | 10.0 |
| HC-SPA4 | 0.041 | 0.909 | 63.75 | 3.079 | 0.595 | 1.394 | 9.560 | 0.009 | 1.0 | 0.90 | 20.0 |
| HC-SPA5 | 0.068 | 0.027 | 49.83 | 0.779 | 0.131 | 0.249 | 1.975 | 0.016 | 2.0 | 0.90 | 10.0 |
| HC-SPA6 | 0.042 | 0.934 | 63.68 | 3.075 | 0.602 | 1.434 | 9.460 | 0.008 | 2.0 | 0.95 | 20.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Fang, A.; Li, Y.; Wei, Y. HC-SPA: Hyperbolic Cosine-Based Symplectic Phase Alignment for Fusion Optimization. Sensors 2025, 25, 5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165003
Zhang W, Fang A, Li Y, Wei Y. HC-SPA: Hyperbolic Cosine-Based Symplectic Phase Alignment for Fusion Optimization. Sensors. 2025; 25(16):5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165003
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenlong, Aiqing Fang, Ying Li, and Yan Wei. 2025. "HC-SPA: Hyperbolic Cosine-Based Symplectic Phase Alignment for Fusion Optimization" Sensors 25, no. 16: 5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165003
APA StyleZhang, W., Fang, A., Li, Y., & Wei, Y. (2025). HC-SPA: Hyperbolic Cosine-Based Symplectic Phase Alignment for Fusion Optimization. Sensors, 25(16), 5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165003






