Imaging Through Scattering Tissue Based on NIR Multispectral Image Fusion Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Explanation
- Contrast: Contrast is typically measured using Michelson contrast [31] or RMS contrast [32]. However, in this application, a Laplacian filter was applied to the grayscale version of each image. The absolute value of the filter’s response was then calculated for each pixel. This method tends to assign higher weights to significant image features, such as edges and textures. This feature is denoted as C (the contrast weights) and is computed separately for each pixel in the image
- Exposure and Illumination power: Examining the unprocessed intensities within a channel allows us to assess the exposure quality of a pixel. Our objective is to retain intensities that are not close to zero (indicating underexposure) or one (indicating overexposure). We assign a weight to each intensity, denoted as i, based on its proximity to the pixel-normalized intensity middle value, 0.5, which is represented by employing a Gaussian curve:
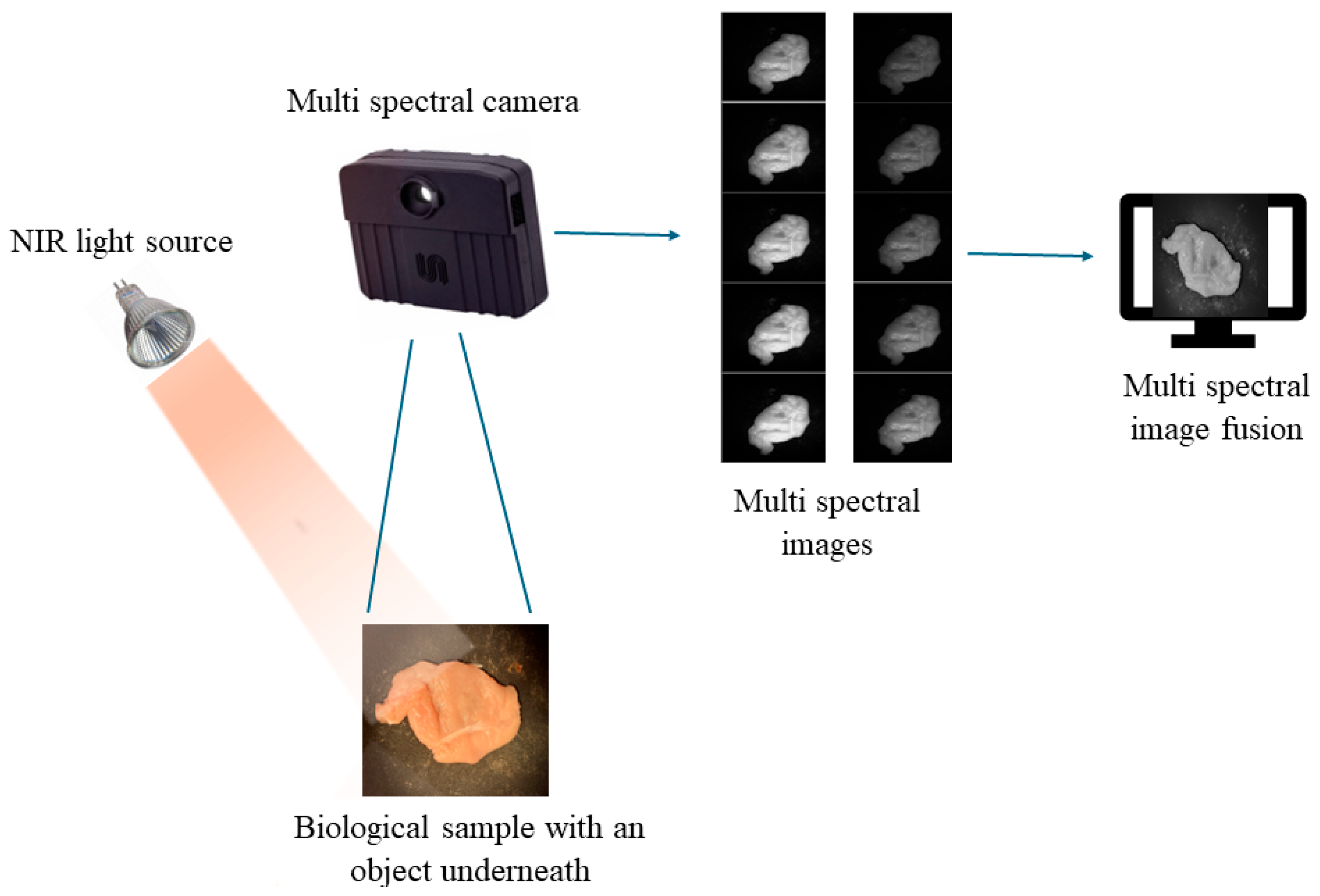
3. Experimental Setup
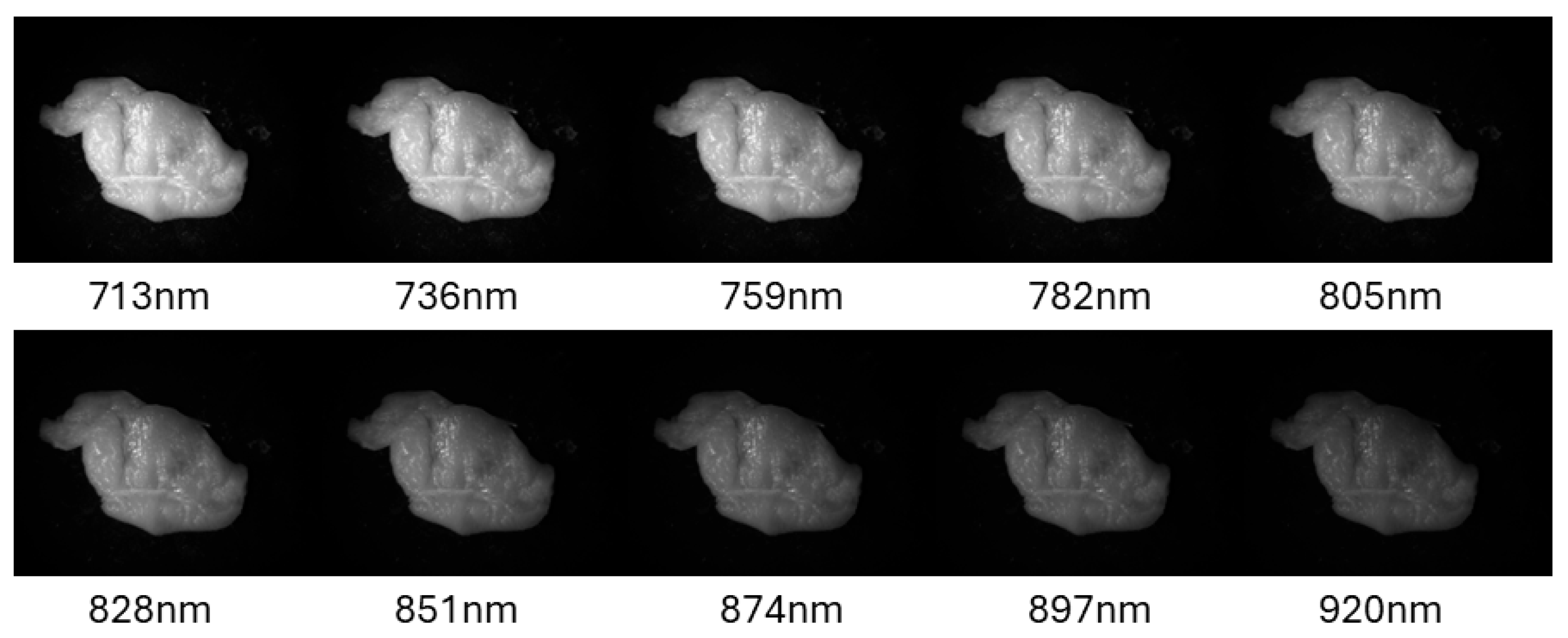
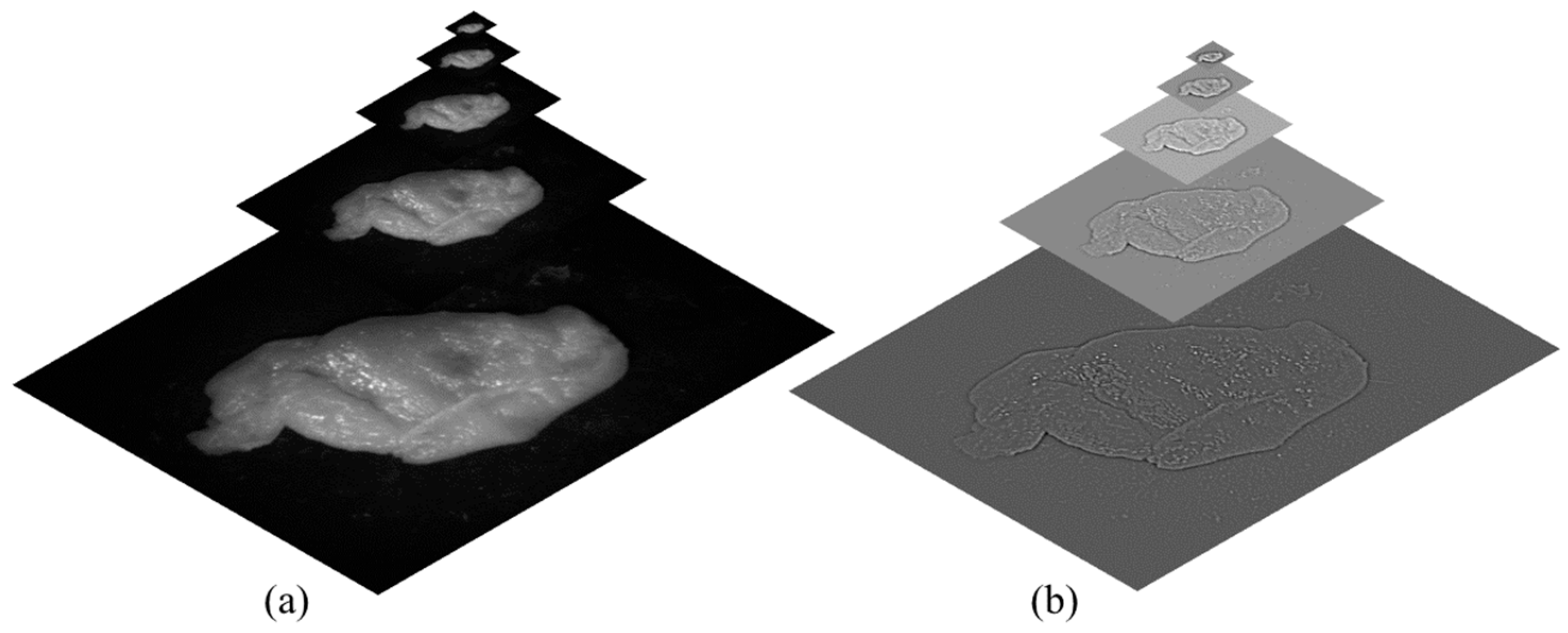
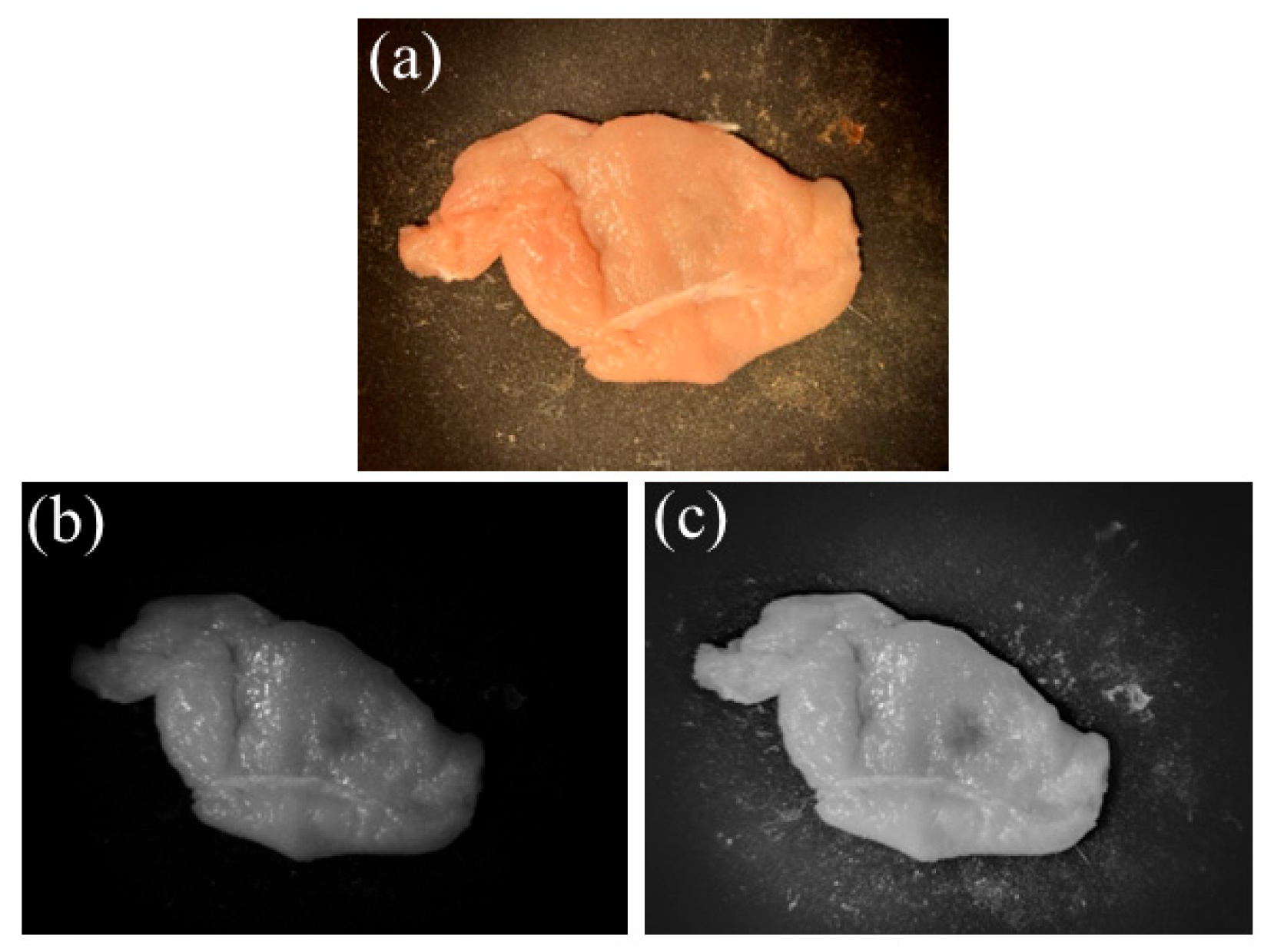
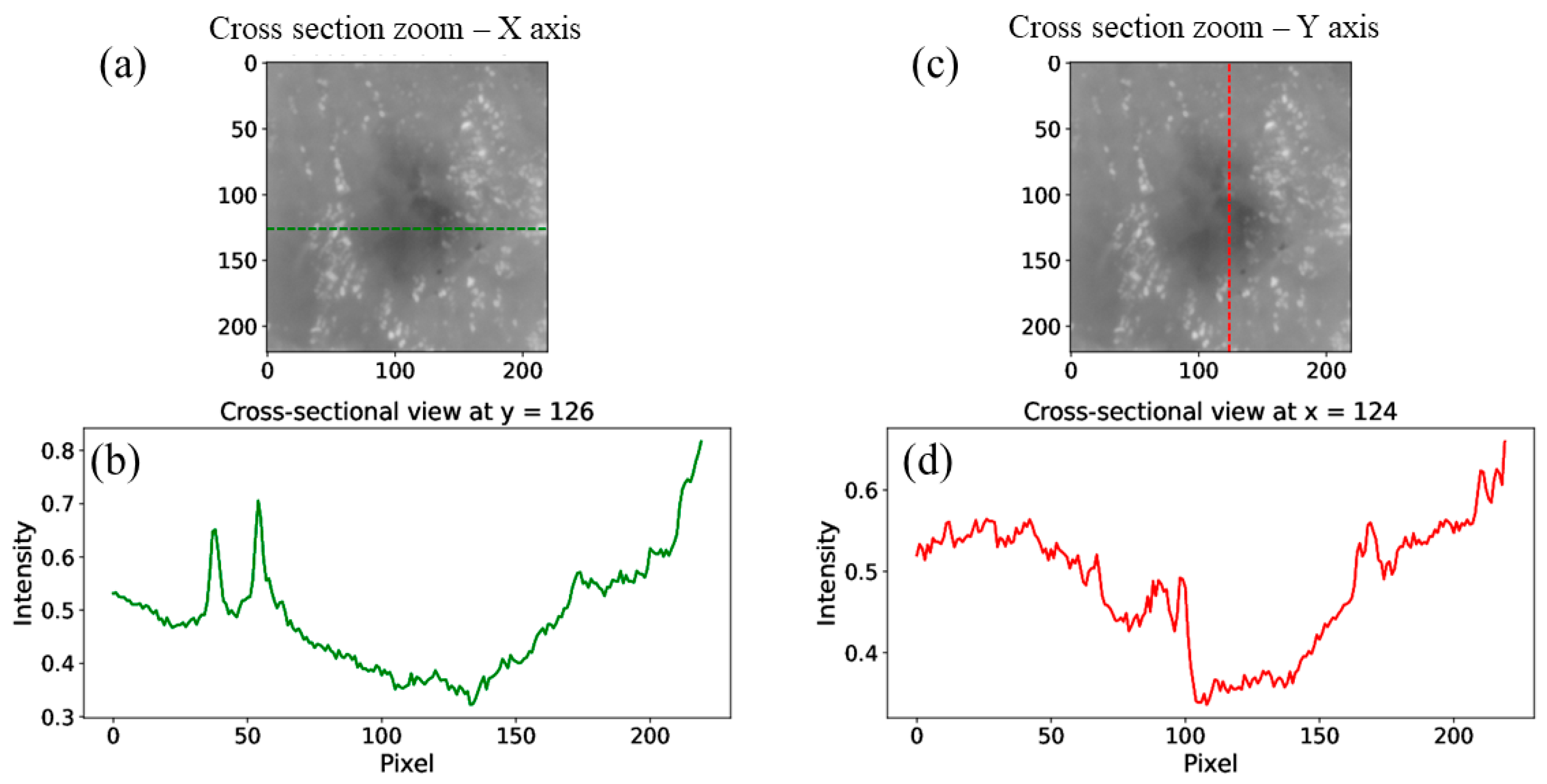
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NIR | Near Infrared |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| FWHM | Full-Width Half Maxima |
| RGB | Red, Green, Blue |
References
- Danan, Y.; Yariv, I.; Zalevsky, Z.; Sinvani, M. Improved Margins Detection of Regions Enriched with Gold Nanoparticles inside Biological Phantom. Materials 2017, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, J.; Hebisch, C.; Phipps, J.E.; Lagarto, J.L.; Kim, H.; Darrow, M.A.; Bold, R.J.; Marcu, L. Real-time Diagnosis and Visualization of Tumor Margins in Excised Breast Specimens using Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging and Machine Learning. Biomed. Opt. Exp. 2020, 11, 1216–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, A.I.; Câtoi, C. Chapter 14, Nervous System Tumors. In Comparative Oncology; The Publishing House of the Romanian Academy: Bucharest, Romania, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Heidkamp, J.; Scholte, M.; Rosman, C.; Manohar, S.; Fütterer, J.J.; Rovers, M.M. Novel Imaging Techniques for Intraoperative Margin Assessment in Surgical Oncology, A Systematic Review. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arica, S.; Altuntas, T.S.; Erbay, G. On Visualization and Quantification of Lesion Margin in CT Liver Images. In Proceedings of the Medical Technologies Congress (TIPTEKNO), Antalya, Turkey, 19–20 November 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Veluponnar, D.; Dashtbozorg, B.; Jong, L.-J.S.; Geldof, F.; Guimaraes, M.D.S.; Peeters, M.-J.T.F.D.V.; van Duijnhoven, F.; Sterenborg, H.J.C.M.; Ruers, T.J.M.; de Boer, L.L. Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy for Accurate Margin Assessment in Breast-Conserving Surgeries: Importance of an Optimal Number of Fibers. Biomed. Opt. Express 2023, 14, 4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluponnar, D.; de Boer, L.L.; Geldof, F.; Jong, L.-J.S.; Guimaraes, M.D.S.; Peeters, M.-J.T.F.D.V.; van Duijnhoven, F.; Ruers, T.; Dashtbozorg, B. Toward Intraoperative Margin Assessment using a Deep Learning-based Approach for Automatic Tumor Segmentation in Breast Lumpectomy Ultrasound Images. Cancers 2023, 15, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluponnar, D.; de Boer, L.L.; Dashtbozorg, B.; Jong, L.-J.S.; Geldof, F.; Guimaraes, M.D.S.; Sterenborg, H.J.C.M.; Vrancken-Peeters, M.-J.T.F.D.; van Duijnhoven, F.; Ruers, T. Margin Assessment During Breast Conserving Surgery using Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2024, 29, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong, L.J.S.; Veluponnar, D.; Geldof, F.; Sanders, J.; Guimaraes, M.D.S.; Peeters, M.-J.T.F.D.V.; van Duijnhoven, F.; Sterenborg, H.J.C.M.; Dashtbozorg, B.; Ruers, T.J.M. Toward Real-time Margin Assessment in Breast-conserving Surgery with Hyperspectral Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, K.; Deng, H.; Feng, J.; Fei, Y.; Jin, Y.; Liao, C.; Li, Q. CT Cinematic Rendering for Pelvic Primary Tumor Photorealistic Visualization. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2018, 8, 804–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Park, H.; Lim, K.M. Phototoxicity: Its Mechanism and Animal Alternative Test Methods. Toxicol. Res. 2015, 31, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernas, T.; Robinson, J.P.; Asem, E.K.; Rajwa, B. Loss of Image Quality in Photobleaching During Microscopic Imaging of Fluorescent Probes Bound to Chromatin. J. Biomed. Opt. 2005, 10, 064015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, A.J. Nonexponential Statistics of Fluorescence Photobleaching. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 121, 2899–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertzborn, D.; Nguyen, H.N.; Hüttmann, K.; Prengel, J.; Ernst, G.; Guntinas-Lichius, O.; von Eggeling, F.; Hoffmann, F. Intraoperative Assessment of Tumor Margins in Tissue Sections with Hyperspectral Imaging and Machine Learning. Cancers 2023, 15, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liao, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Han, D.; Jia, Z.; Qin, C.; Niu, S.; et al. Near-Infrared II Hyperspectral Imaging Improves the Accuracy of Pathological Sampling of Multiple Cancer Types. Lab Investig. 2023, 103, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasca, S.V.; Calin, M.A.; Manea, D.; Radvan, R. Hyperspectral Imaging with Machine Learning for in Vivo Skin Carcinoma Margin Assessment: A Preliminary Study. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2024, 47, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, T.; Kautz, J.; Van Reeth, F. Exposure Fusion. In Proceedings of the 15th Pacific Conference on Computer Graphics and Applications (PG’07), Maui, HI, USA, 29 October–2 November 2007; pp. 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.Y.; Cho, S.W.; Kim, Y.A.; Kim, D.; Oh, B.-C.; Park, D.J.; Park, Y.J. Cancers with Higher Density of Tumor-Associated Macrophages Were Associated with Poor Survival Rates. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2015, 49, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusmann, H.; Kölzer, J.; Otto, J.; Puls, R.; Friedrich, T.; Heywang-Koebrunner, S.; Zinth, W. Photon Transport in Highly Scattering Tissue; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1995; Volume 2326, p. 370. [Google Scholar]
- Mangold, K.; Shaw, J.; Vollmer, M. The physics of near-infrared photography. Eur. J. Phys. 2013, 34, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, A.M.K.; Heinrich, D.; Olajos, J.; Andersson-Engels, S. Near Infrared Diffuse Reflection and Laser-induced Fluorescence Spectroscopy for Myocardial Tissue Characterisation. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 1997, 53, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, T.A.; Morries, L.D. Near-infrared Photonic Energy Penetration: Can Infrared Phototherapy Effectively Reach the Human Brain? Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 2191–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bommel, W. Halogen Lamp. In Encyclopedia of Color Science and Technology; Luo, R., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojanen, M.; Kärhä, P.; Ikonen, E. Spectral Irradiance Model for Tungsten Halogen Lamps in 340–850 nm Wavelength Range. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmi, M.; Haruna, M. Ultra-High Resolution Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Using a Halogen Lamp as the Light Source. Opt. Rev. 2003, 10, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribbing, C.G. Chapter 8.2. Blackbody radiation. In Optical Thin Films and Coatings; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hessel, C. An Implementation of the Exposure Fusion Algorithm. Image Process. Line 2018, 8, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, X. Multi-Exposure Image Fusion Techniques: A Comprehensive Review. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Fang, L.; Hu, J.; Yin, H. Pixel-level Imageaw Fusion: A Survey of the State of the Art. Inf. Fusion 2017, 33, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelson, A. Studies in Optics; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1927. [Google Scholar]
- Peli, E. Contrast in Complex Images. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1990, 7, 2032–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, P.J.; Hanna, K.; Kolczynski, R.J. Enhanced image capture through fusion. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Augmented Visual Display Research, Berlin, Germany, 11–14 May 1993; pp. 207–224. [Google Scholar]
- Ogden, J.M.; Adelson, E.H.; Bergen, J.R.; Burt, P.J. Pyramid-based computer graphics. RCA Eng. 1985, 30, 4–15. [Google Scholar]
- Tet, A. Hierarchical image fusion. Mach. Vis. Appl. 1990, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atiya, N.; Shemer, A.; Schwarz, A.; Beiderman, Y.; Danan, Y. Imaging Through Scattering Tissue Based on NIR Multispectral Image Fusion Technique. Sensors 2025, 25, 4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164977
Atiya N, Shemer A, Schwarz A, Beiderman Y, Danan Y. Imaging Through Scattering Tissue Based on NIR Multispectral Image Fusion Technique. Sensors. 2025; 25(16):4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164977
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtiya, Nisan, Amir Shemer, Ariel Schwarz, Yevgeny Beiderman, and Yossef Danan. 2025. "Imaging Through Scattering Tissue Based on NIR Multispectral Image Fusion Technique" Sensors 25, no. 16: 4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164977
APA StyleAtiya, N., Shemer, A., Schwarz, A., Beiderman, Y., & Danan, Y. (2025). Imaging Through Scattering Tissue Based on NIR Multispectral Image Fusion Technique. Sensors, 25(16), 4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164977





