ColorX: A Fitness Tracker-Based Device for Rapid, Optical Sensing of Water Quality Parameters
Abstract
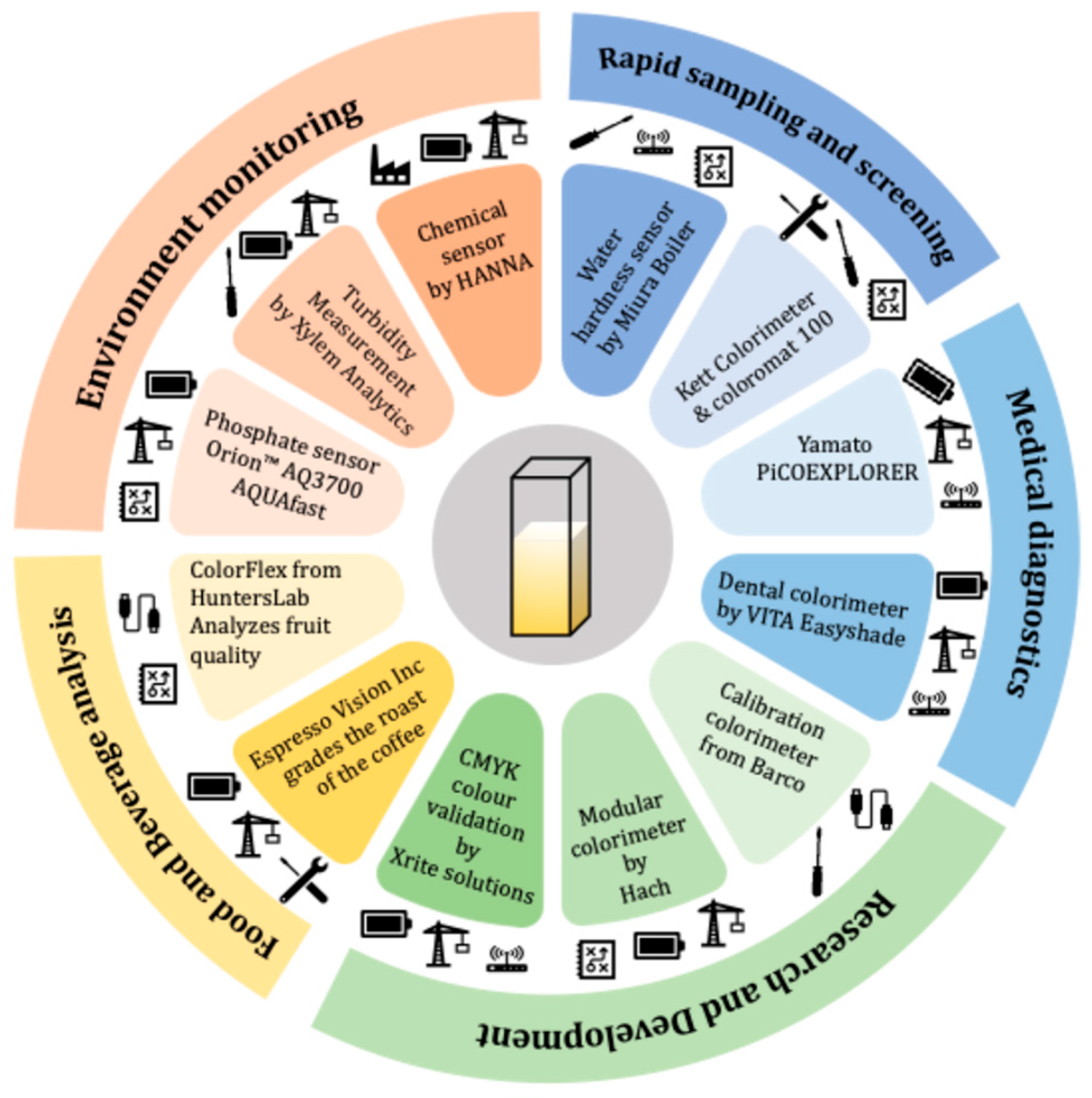
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
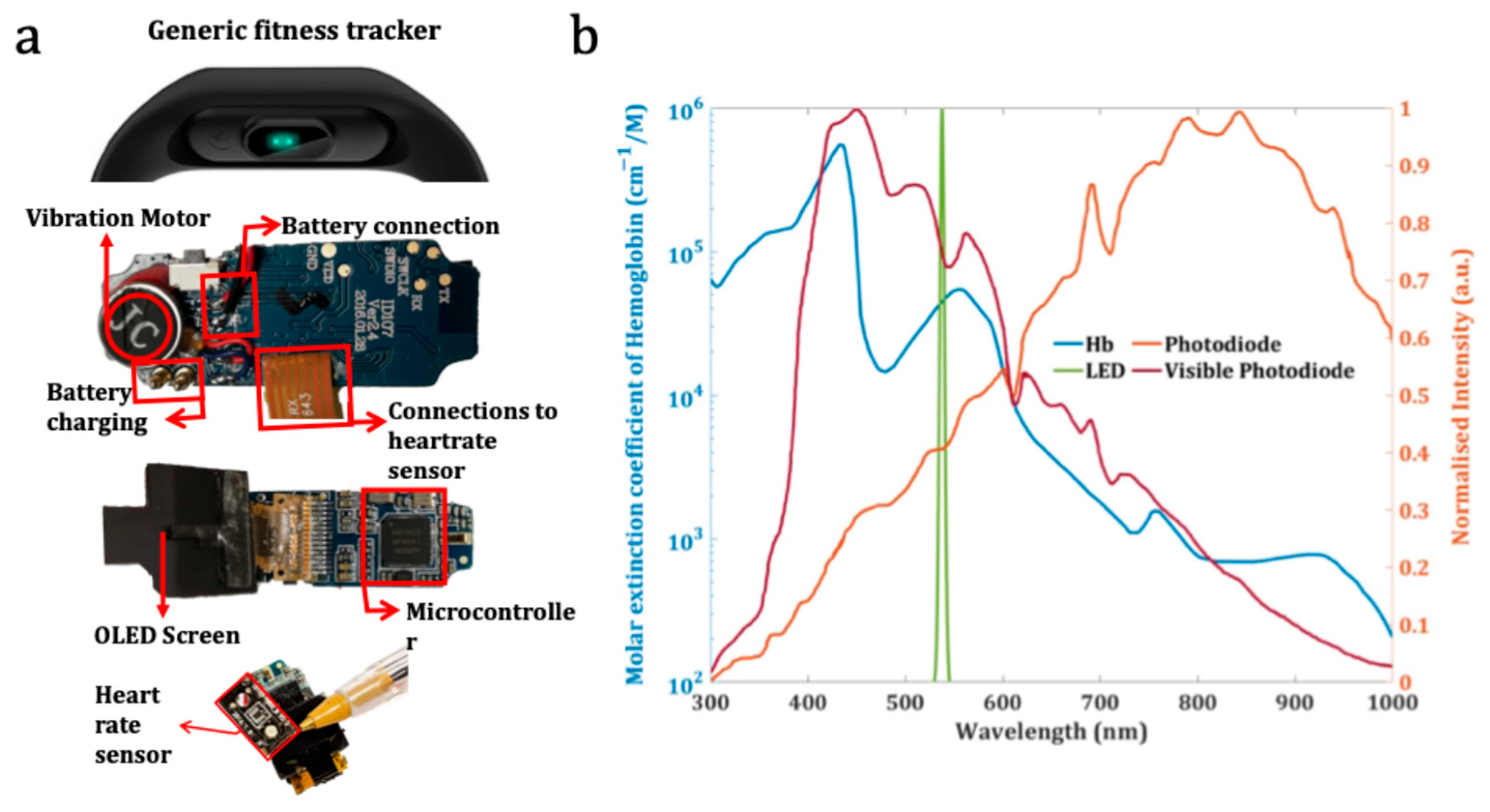
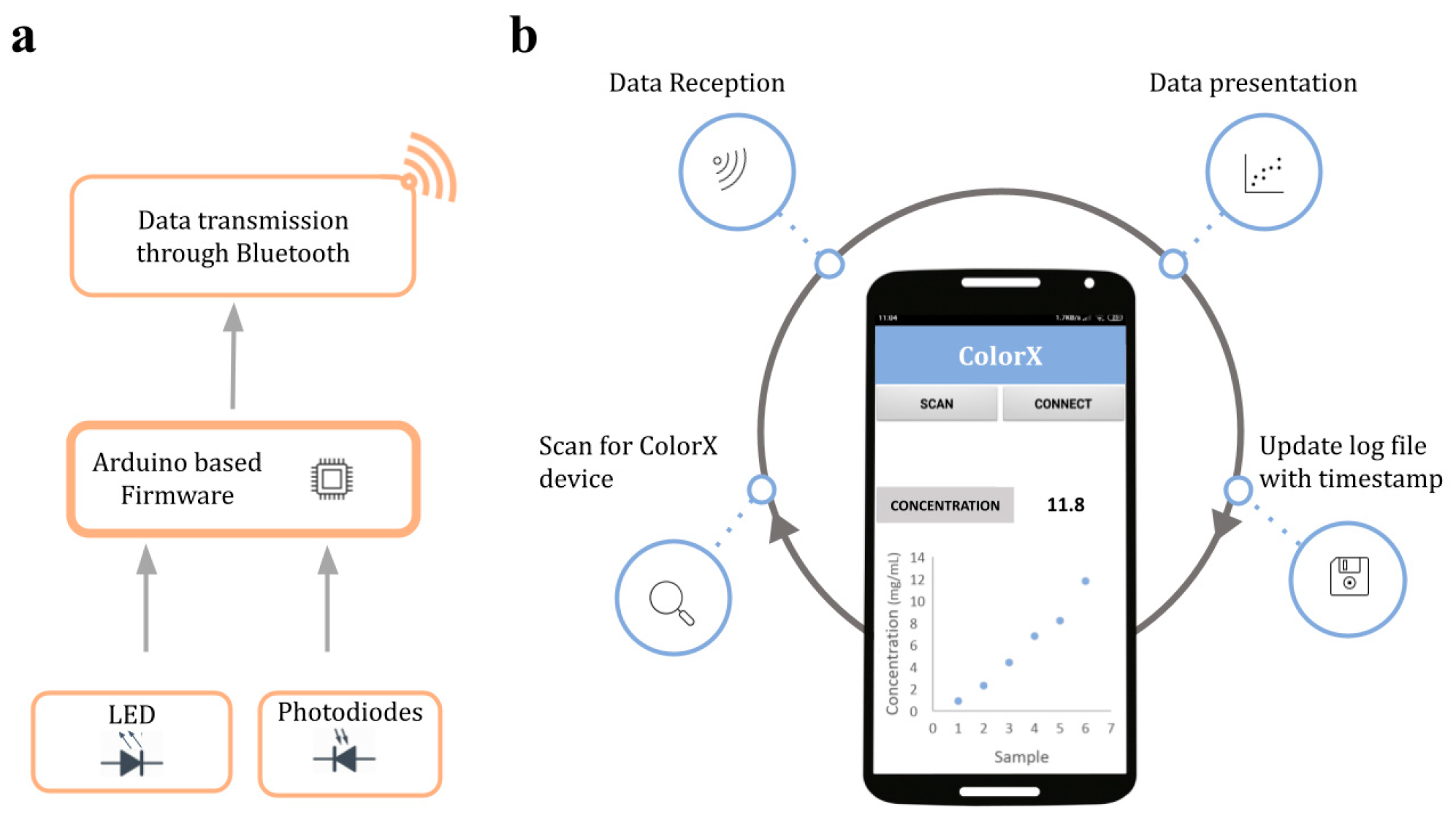
2.1. ColorX Hardware Parts and Components
2.2. Standard Solutions for ColorX Testing
3. Results and Discussion
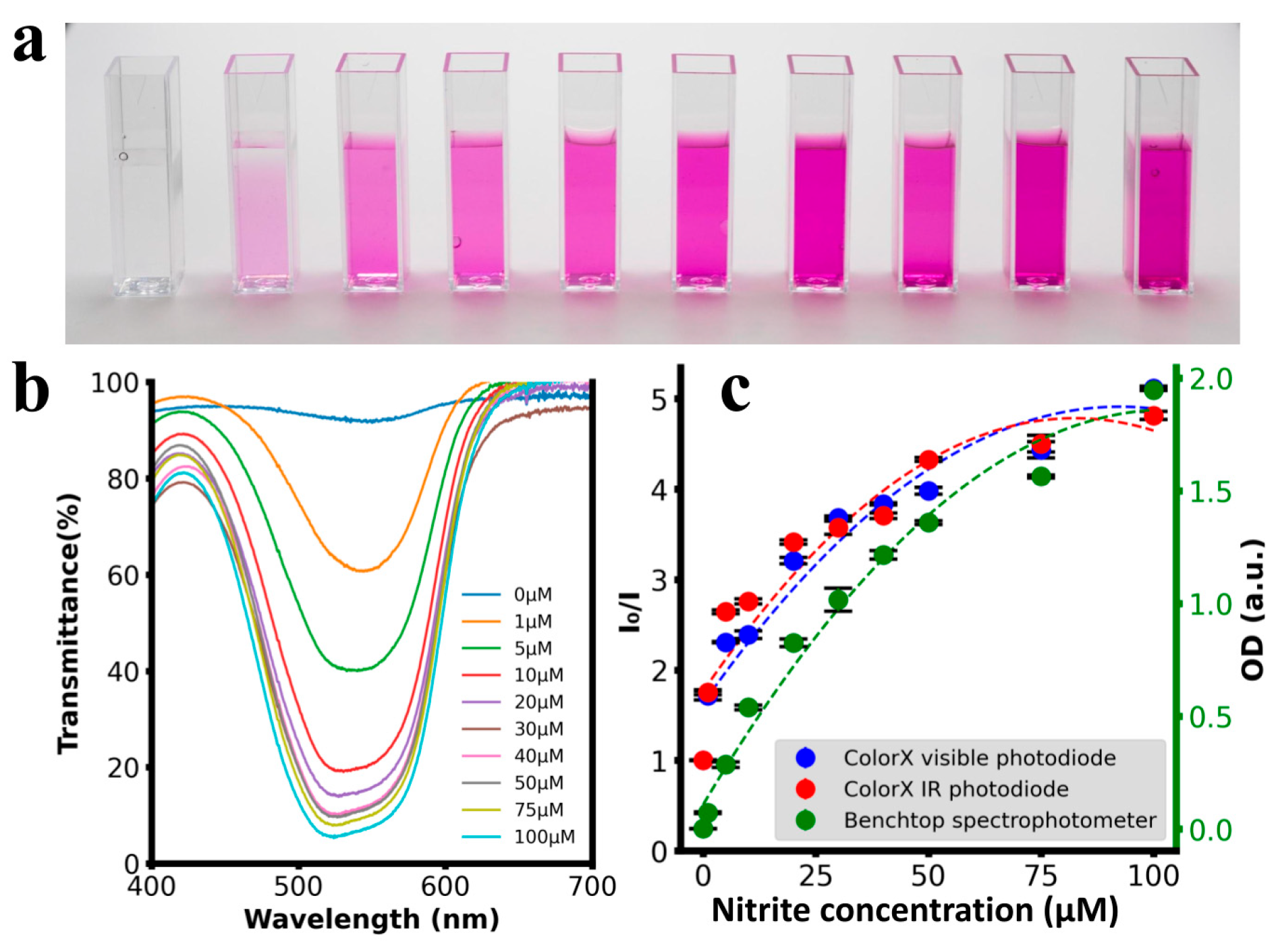
3.1. ColorX vs. Benchtop Spectrophotometer
3.2. Advantages of ColorX vs. Existing Colorimetric Solutions
3.3. Limitations of ColorX
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Popov-Raljić, J.V.; Mastilović, J.S.; Laličić-Petronijević, J.G.; Popov, V.S. Investigations of Bread Production with Postponed Staling Applying Instrumental Measurements of Bread Crumb Color. Sensors 2009, 9, 8613–8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov-Raljić, J.V.; Laličić-Petronijević, J.G. Sensory Properties and Color Measurements of Dietary Chocolates with Different Compositions during Storage for up to 360 Days. Sensors 2009, 9, 1996–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov-Raljić, J.V.; Lakić, N.S.; Laličić-Petronijević, J.G.; Barać, M.B.; Sikimić, V.M. Color Changes of UHT Milk during Storage. Sensors 2008, 8, 5961–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, X.; Guo, X.; Kong, B.; Zhang, M.; Qian, X.; Mi, S.; Sun, W. The Boom in 3D-Printed Sensor Technology. Sensors 2017, 17, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.; Valiulis, S.; Cheng, Q. Advances in Optical Sens-Ing and Bioanalysis Enabled by 3D Printing. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 2475–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.M. Materials Science. Building Research Equipment with Free, Open-Source Hardware. Science 2012, 337, 1303–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, D.K.; Gould, P.J. Open-Source Hardware Is a Low-Cost Alternative for Scientific Instrumentation and Research. Mod. Instrum. 2012, 1, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, G.L.; Lec, R.M.; Pishko, M.V. Emerging Biomedical Sensing Technologies and Their Applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2003, 3, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiei, E.; Tabrizian, M.; Hoorfar, M. A Review of Digital Mi-Crofluidics as Portable Platforms for Lab-on a-Chip Applica-Tions. Lab. Chip 2016, 16, 2376–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoui, R.; Blecker, C. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Measurement for Quality Assessment of Food Systems—A Review. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2011, 4, 364–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yallapragada, V.V.B.; Gowda, U.; Wong, D.; O’Faolain, L.; Tangney, M.; Devarapu, G.C.R. ODX: A Fitness Tracker-Based Device for Continuous Bacterial Growth Monitoring. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12329–12335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clydesdale, F.M.; Ahmed, E.M. Colorimetry—Methodology and Applications∗. CRC Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1978, 10, 243–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulahoum, H.; Ghorbanizamani, F.; Zihnioglu, F.; Turhan, K.; Timur, S. How Should Diagnostic Kits Development Adapt Quickly in COVID-19-like Pandemic Models? Pros and Cons of Sensory Platforms Used in COVID-19 Sensing. Talanta 2021, 222, 121534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zhuang, J.; Wei, G. Recent Advances in the Design of Colorimetric Sensors for Environmental Monitoring. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 2195–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.-Y.; Cay-Durgun, P.; Lai, T.; Sprowls, M.; Thomas, L.; Lind, M.L. Colorimetric Optoelectronic Dynam-Ics Analyzer for Measuring Total Ammonia of Biological Samples. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2018, 6, 2800610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, G.; Mshana, R.N.; Miörner, H. Evaluation of a Colorimet-Ric Assay Based on 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-Yl)-2,5-Diphenyl Tetrazolium Bromide (MTT) for Rapid Detection of Rifampicin Resistance in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 1998, 2, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Carrilho, E.; Thomas, S.W., 3rd; Sindi, H.; Whitesides, G.M. Simple Telemedicine for Developing Regions: Camera Phones and Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices for Real-Time, off-Site Diagnosis. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3699–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Musto, C.J.; Suslick, K.S. A Simple and Highly Sensi-Tive Colorimetric Detection Method for Gaseous Formaldehyde. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4046–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-S.; Jeon, B.G.; Ihm, C.; Park, J.-K.; Jung, M.Y. A Simple and Smart Telemedicine Device for Developing Regions: A Pocket-Sized Colorimetric Reader. Lab. Chip 2011, 11, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.-Y. Smartphone-Based Chemistry Instrumentation: Digitization of Colorimetric Measurements. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulstich, K.; Haberstroh, K.; Gruler, R.; Eberhard, M.; Wiest, T.; Lentzsch, D. Handheld and portable test systems for immunodiagnostics, nucleic acid detection and more. In Proceedings of the SPIE 6945, Optics and Photonics in Global Homeland Security IV, 69450H (15 April 2008); SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 15 April 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.-G.; Liu, P.; Hou, C.-J.; Huo, D.-Q.; Dong, J.-L.; Fa, H.-B. A Novel Chemical Detector Using Colorimetric Sensor Array and Pattern Recognition Methods for the Concentration Analy-Sis of NH3. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2010, 81, 105113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priye, A.; Bird, S.W.; Light, Y.K.; Ball, C.S.; Negrete, O.A.; Meagher, R.J. A Smartphone-Based Diagnostic Platform for Rapid Detec-Tion of Zika, Chikungunya, and Dengue Viruses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingles, J.M.; da Pereira, F. Smartphone-Based Nitrate Sensor. Ph.D. Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sa, A.-W. Sick Building Syndrome: In Public Build-Ings and Workplaces; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.; Mowlem, M.; Kraft, M.; Morgan, H. A Simple, Low-Cost Double Beam Spectrophotometer for Colorimetric Detection of Nitrite in Seawater. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-C.; Chen, Y.; Pang, Y.; Slavik, J.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Wu, X.-M.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S.-F.; Ren, T.-L. A Miniaturized Colorimeter with a Novel Design and High Precision for Photometric Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimeroff, I. Precision Measurement and Calibration Selected NBS Papers on Colorimetry; National Bureau of Standards: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari Shrestha, Y.; Krishna Shrestha, S. Fundamentals of Colorimetry. In Advances in Colorimetry; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chaloupka, K.; Varanka-Martin, M.; Pringle, D.L. Crepe Paper Colorimetry. J. Chem. Educ. 1995, 72, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PCE Americas Inc. Test Instruments. Colorimeter PCE-CSM 1. Available online: https://www.pce-instruments.com/english/measuring-instruments/test-meters/colorimeter-pce-instruments-colorimeter-pce-csm-1-det_2219781.htm (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- SpinLab HVI. Available online: https://www.uster.com/fileadmin/user_upload/Downloads/1_Products/1.2_Laboratory_Systems/Cotton_Classing/Uster_HVI_1000_brochure_web_en_18.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- PicoExplorer. Available online: https://www.yamato-scientific.com/product/show/picoexplorer// (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Zahnfabrik, V.; VITA Easyshade® V. VITA Zahnfabrik. Available online: https://www.vita-zahnfabrik.com/pdb_GG2G50G200_en,98478.html (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- EspressoVision. Available online: https://github.com/juztins-lab/roast-meter/ (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Hunterlab. Available online: https://www.hunterlab.com/blog/self-tanner-analysis-monitoring-color-formulas-with-spectrophotometric-technology/ (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Barco. Available online: https://www.medicalexpo.com/prod/barco/product-75282-664749.html (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Manufactures Water Quality Testing and Analytical Instruments & Reagents. Available online: https://ie.hach.com/ (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Colormetry Hardness Detector. Miura Boiler. Available online: https://www.miuraboiler.com/products/colormetry-hardness-detection-system/ (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Whiteness Meters and Colorimeters Rice and Powders. Kett. Available online: https://kett.com/whiteness-meters-colorimeters-rice-powders/ (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- BRS. Available online: https://www.brs.be/instruments/ (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- HZDG. Food Color Measurement Devices. Available online: https://www.hunterlab.com/solutions/color-measurement-applications/food/ (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Xrite. Available online: https://www.xrite.com/categories/portable-spectrophotometers/exact (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Hanna Inst. Available online: https://www.hannainst.com/hi96701-free-chlorine-portable-photometer.html (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Xylem Analytics. Available online: https://www.xylemanalytics.com/en/parameters/turbidity-and-tss (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- OrionTM AQ3700 AQUAfastTM Colorimeter. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/AC37A13#/AC37A13 (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Bonato, P. Advances in Wearable Technology and Applications in Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2005, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelson, Y.; Duckworth, R.J.; Comtois, G. A Wearable Re-Flectance Pulse Oximeter for Remote Physiological Monitoring. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2006, 2006, 912–915. [Google Scholar]
- Nihtianov, S.; Luque, A. Smart Sensors and MEMS: Intelli-Gent Devices and Microsystems for Industrial Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Beeby, S.P.; Ensel, G.; Kraft, M. MEMS Mechanical Sensors; Artech Print on Demand: Boston, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bogue, R. MEMS Sensors: Past, Present and Future. Sens. Rev. 2007, 27, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirvonen, J.-M.; Poikonen, T.; Vaskuri, A.; Kärhä, P.; Ikonen, E. Spectrally Adjustable Quasi-Monochromatic Radiance Source Based on LEDs and Its Application for Measuring Spectral Re-Sponsivity of a Luminance Meter. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2013, 24, 115201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.W.; Chia, K.S. A Review on Recent near Infrared Spectroscopic Measurement Setups and Their Challenges. Measurement 2021, 171, 108732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- nRF51822—Nordic Semiconductor. Available online: https://www.nordicsemi.com/Products/Low-power-short-range-wireless/nRF51822 (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- Cui, X.; Bray, S.; Reiss, A.L. Functional near Infrared Spectros-Copy (NIRS) Signal Improvement Based on Negative Correla-Tion between Oxygenated and Deoxygenated Hemoglobin Dy-Namics. Neuroimage 2010, 49, 3039–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, S. Arduino-nRF5: Arduino Core for Nordic Semiconductor nRF5 Based Boards. Available online: https://github.com/sandeepmistry/arduino-nRF5 (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- MIT App Inventor. Available online: https://appinventor.mit.edu/ (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- European Medicines Agency. Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology; Q2 (R1); Somatek Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, C.D.; Krolick, A.; Brunner, L.; Burklund, A.; Kahn, D.; Ball, W.P.; Weber-Shirk, M. An Affordable Open-Source Turbidimeter. Sensors 2014, 14, 7142–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coss, A.; Cantor, K.P.; Reif, J.S.; Lynch, C.F.; Ward, M.H. Pancre-Atic Cancer and Drinking Water and Dietary Sources of Nitrate and Nitrite. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 159, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korostynska, O.; Mason, A.; Al-Shamma’a, A. Monitoring of Nitrates and Phosphates in Wastewater: Current Technologies and Further Challenges. Int. J. Smart Sens. Intell. Syst. 2012, 5, 149–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maticic, B. The Impact of Agriculture on Ground Water Quality in Slovenia: Standards and Strategy. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 40, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, R.; Orozco, M.; Chávez, G.; Márquez-Lucero, A. The Evaluation of a Low-Cost Colorimeter for Glucose Detection in Salivary Samples. Sensors 2017, 17, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Huang, M.; Lan, J.; Chung, L.W.; Li, X.; Xie, X. Colori-Metric Calcium Probe with Comparison to an Ion-Selective Optode. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12476–12481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalise, L.; Cosoli, G. Wearables for Health and Fitness: Meas-Urement Characteristics and Accuracy. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Houston, TX, USA, 14–17 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, H. Wearable Bracelets with Variable Sam-Pling Frequency for Measuring Multiple Physiological Parame-Ter of Human. Comput. Commun. 2020, 161, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pine Time BY PINE64. Available online: https://pine64.org/devices/pinetime/ (accessed on 21 October 2024).


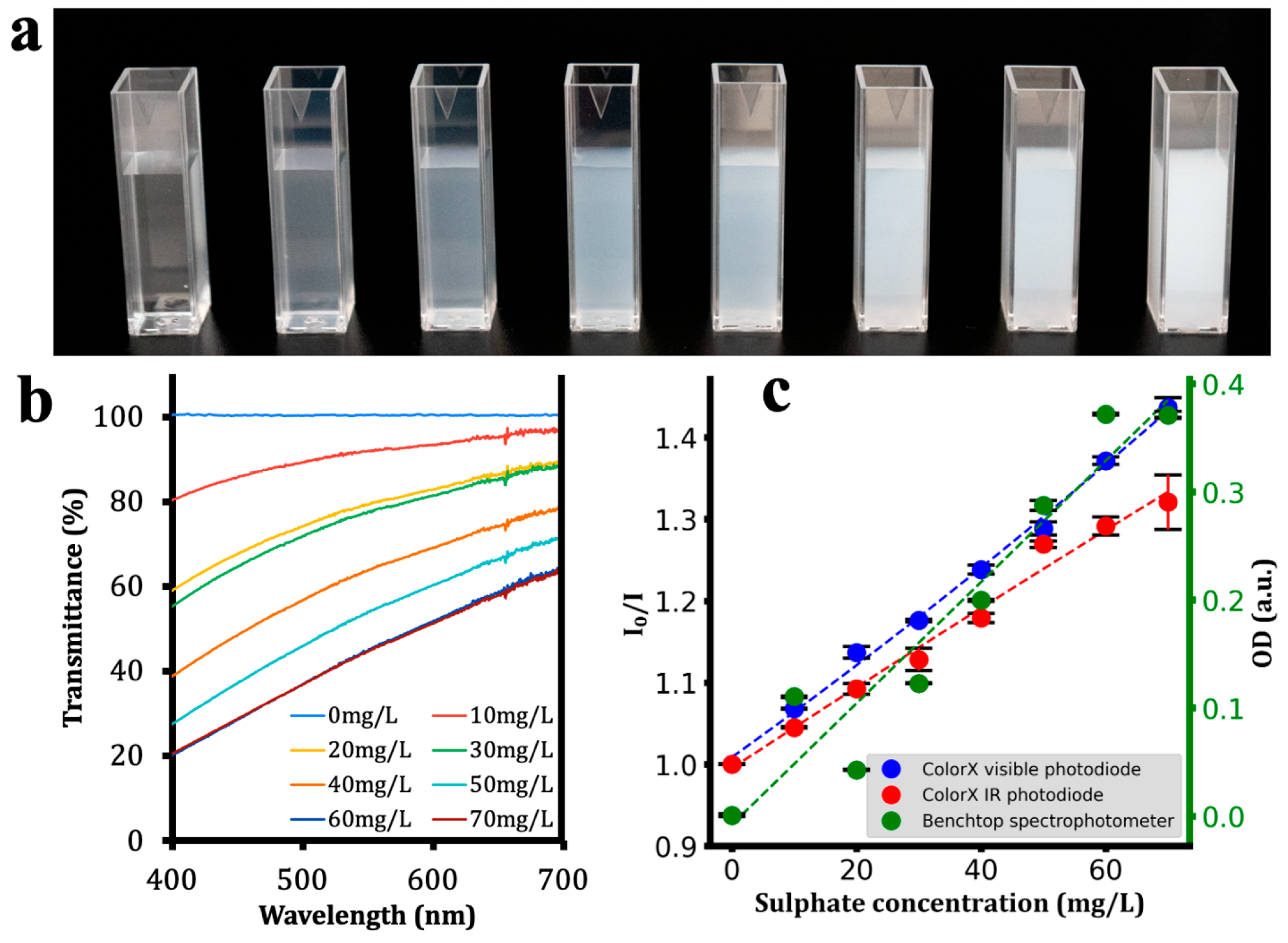
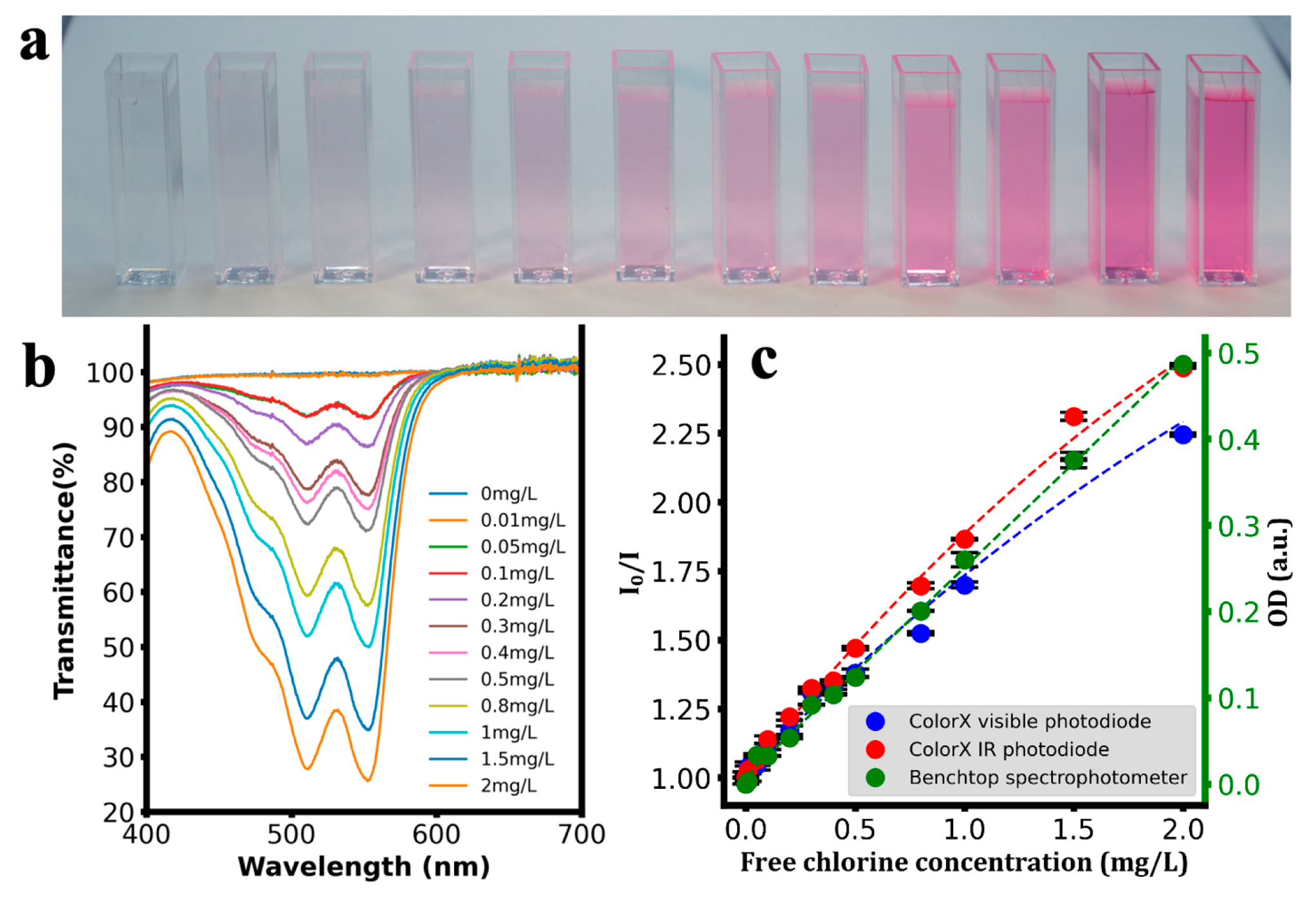
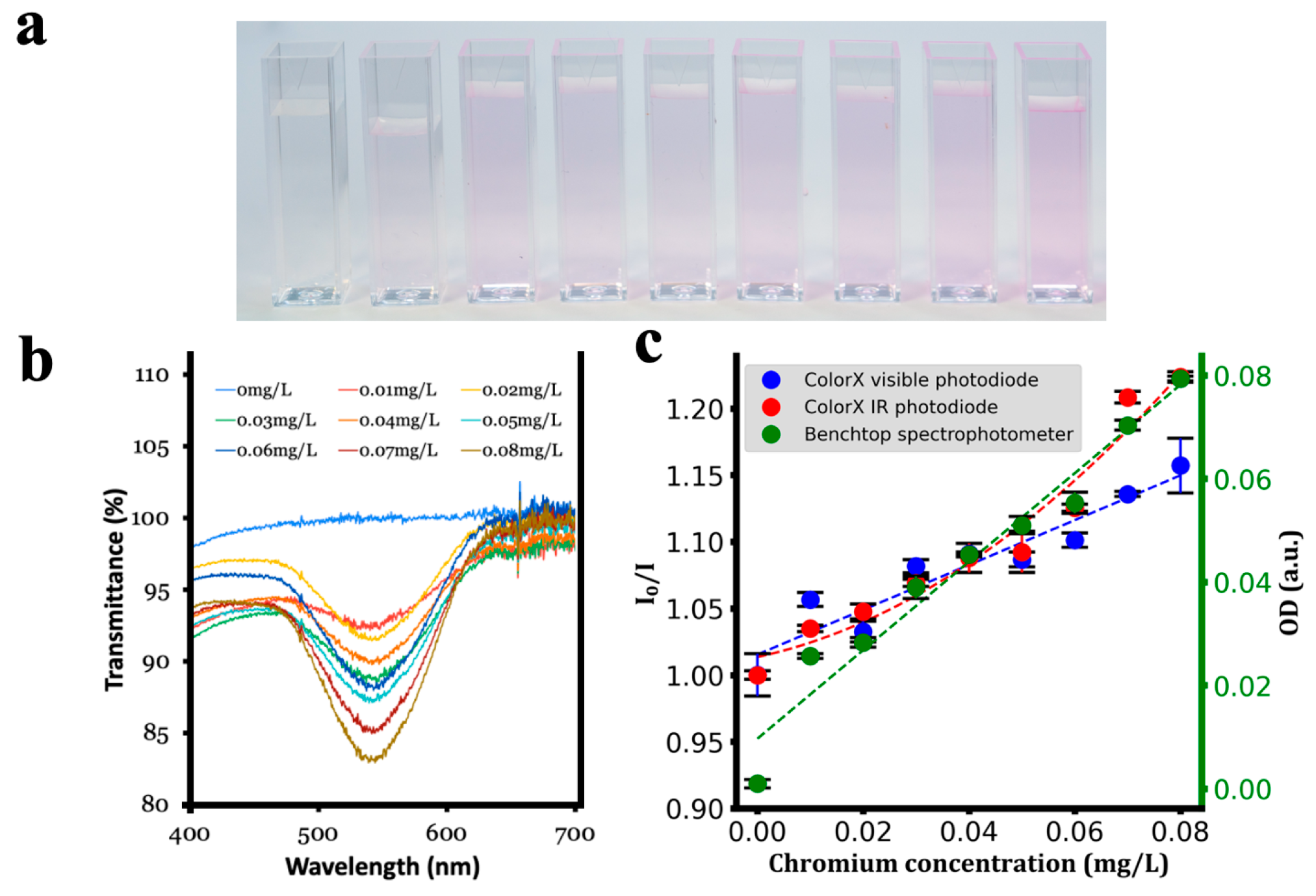
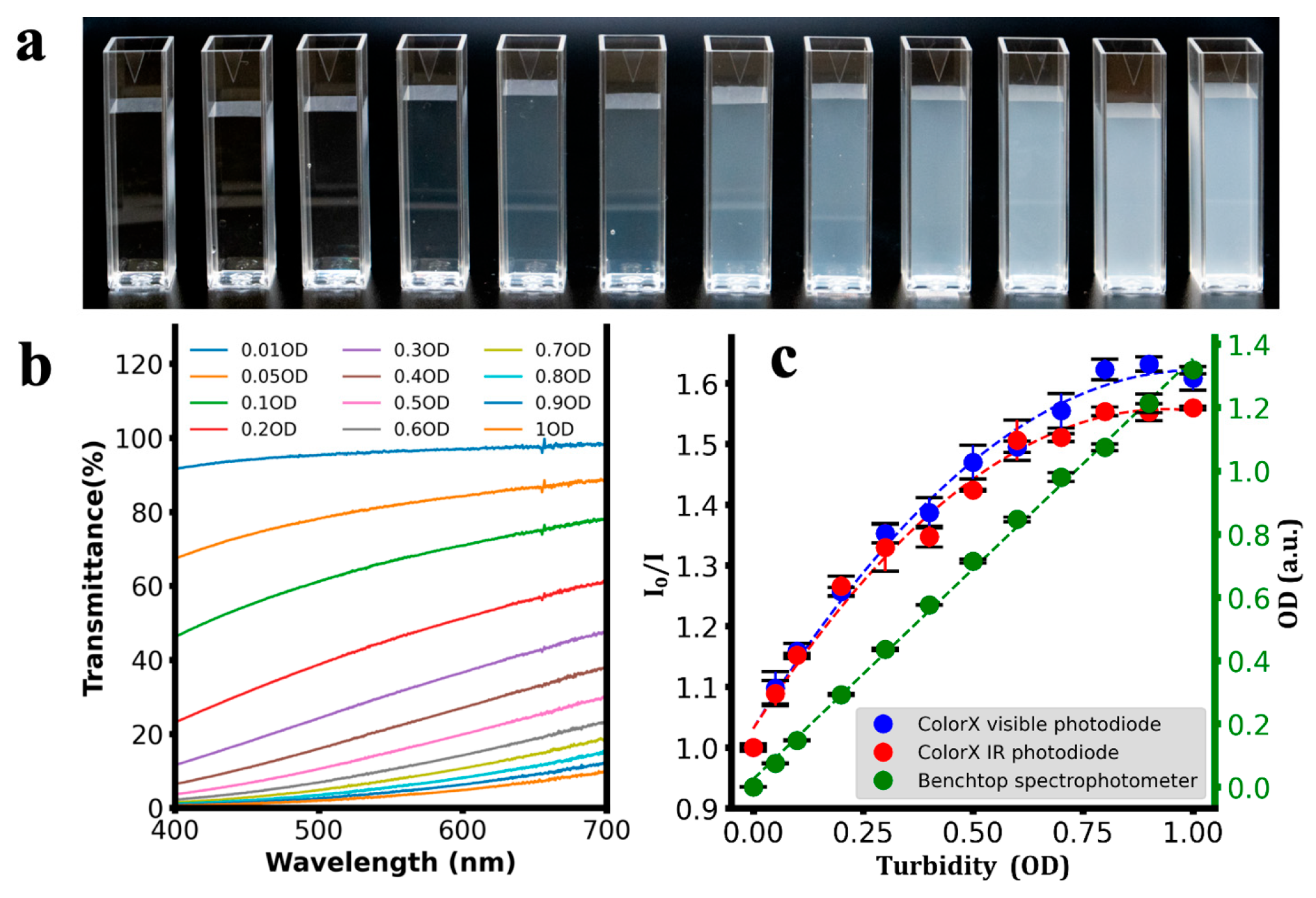
| Analyte | Calibration Equation | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrite | [VIS] Absorbance = 1.631 + 0.07093[X] − 0.0003834[X]2 | 0.938 |
| [IR] Absorbance = 1.764 + 0.07325[X] − 0.0004441[X]2 | 0.905 | |
| [Benchtop spec] Absorbance = 0.1082 + 0.03383[X] − 0.0001633[X]2 | 0.980 | |
| Sulfate | [VIS] Absorbance = 1.009 + 0.005449[X] − 8.708 × 10−6[X]2 | 0.996 |
| [IR] Absorbance = 0.995 + 0.004994[X] − 2.314 × 10−6[X]2 | 0.985 | |
| [Benchtop spec] Absorbance = 0.005613[X] − 0.008083 | 0.918 | |
| Free-Chlorine | [VIS] Absorbance = 1.019 + 0.7936[X] − 0.07866[X]2 | 0.985 |
| [IR] Absorbance = 1.015 + 0.9859[X] − 0.1167[X]2 | 0.995 | |
| [Benchtop spec] Absorbance = 0.2422[X] − 0.008548 | 0.997 | |
| Chromium | [VIS] Absorbance = 1.015 + 1.678[X] + 0.02142[X]2 | 0.900 |
| [IR] Absorbance = 1.014 + 0.8624[X] − 22.41[X]2 | 0.958 | |
| [Benchtop spec] Absorbance = 0.8556[X] + 0.009704 | 0.959 | |
| Turbidity | [VIS]Absorbance = 1.031 + 1.173[X] − 0.582[X]2 | 0.990 |
| [IR]Absorbance = 1.031 + 1.121[X] − 0.5966[X]2 | 0.988 | |
| [Benchtop spec] Absorbance = 1.329[X] + 0.02493 | 0.997 |
| Analyte | EPA/CDC Guidelines | ColorX LOD and %Avg CV | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VIS PD | IR PD | ||
| NITRITE | 1 mg/L | 0.07 mg/L, 1.06 | 0.1081 mg/L, 1.10 |
| SULFATE | 250 mg/L | 46 mg/L, 0.39 | 18 mg/L, 0.75 |
| FREE CHLORINE | 44 mg/L | 0.07 mg/L, 1.03 | 0.005 mg/L, 0.68 |
| CHROMIUM | 0.1 mg/L | 0.018 mg/L, 0.69 | 0.002 mg/L, 051 |
| TURBIDITY | 1 NTU | 2.97 NTU, 1.21 | 9.09 NTU, 1.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yallapragada, V.V.B.; Ananthachar, A.; Gowda, U.; ní Chlochasaigh, F.; O’Faolain, L.; Devarapu, G.C.R. ColorX: A Fitness Tracker-Based Device for Rapid, Optical Sensing of Water Quality Parameters. Sensors 2025, 25, 4935. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164935
Yallapragada VVB, Ananthachar A, Gowda U, ní Chlochasaigh F, O’Faolain L, Devarapu GCR. ColorX: A Fitness Tracker-Based Device for Rapid, Optical Sensing of Water Quality Parameters. Sensors. 2025; 25(16):4935. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164935
Chicago/Turabian StyleYallapragada, Venkata V. B., Adarsh Ananthachar, U. Gowda, F. ní Chlochasaigh, L. O’Faolain, and G. C. R. Devarapu. 2025. "ColorX: A Fitness Tracker-Based Device for Rapid, Optical Sensing of Water Quality Parameters" Sensors 25, no. 16: 4935. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164935
APA StyleYallapragada, V. V. B., Ananthachar, A., Gowda, U., ní Chlochasaigh, F., O’Faolain, L., & Devarapu, G. C. R. (2025). ColorX: A Fitness Tracker-Based Device for Rapid, Optical Sensing of Water Quality Parameters. Sensors, 25(16), 4935. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25164935






