Finite Element Model Updating for a Continuous Beam-Arch Composite Bridge Based on the RSM and a Nutcracker Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of the Structural Natural Frequency
- Decompose the projection matrix into the product of the observable vector and the Kalman filter state vector , as shown below:
- From Equation (5), it can be concluded that:
2.2. Construction of a Surrogate Model Based on Response Surface Methodology
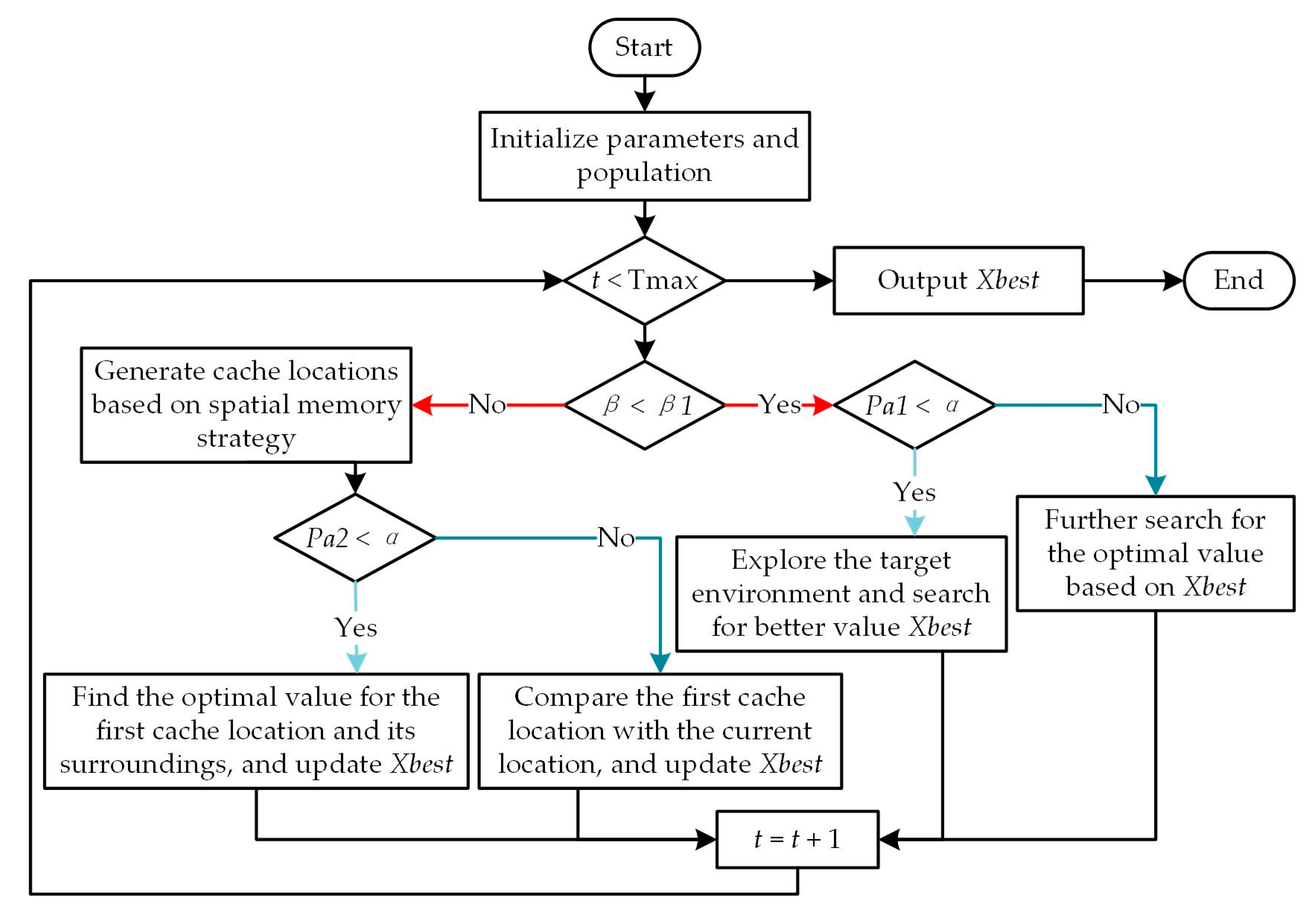
2.3. Parameter Optimization Process Based on the Nutcracker Optimization Algorithm
2.3.1. Foraging Stage
- Exploration sub-stage: searching for pinecones in summer and autumn
- Development sub-stage: pinecone storage
2.3.2. Retrieval Stage
- Exploration sub stage: winter search cache
- Development sub-stage: cache recovery
2.4. Model Updating Procedure Integrating the Response Surface Method and the Nutcracker Optimization Algorithm
3. Case Study
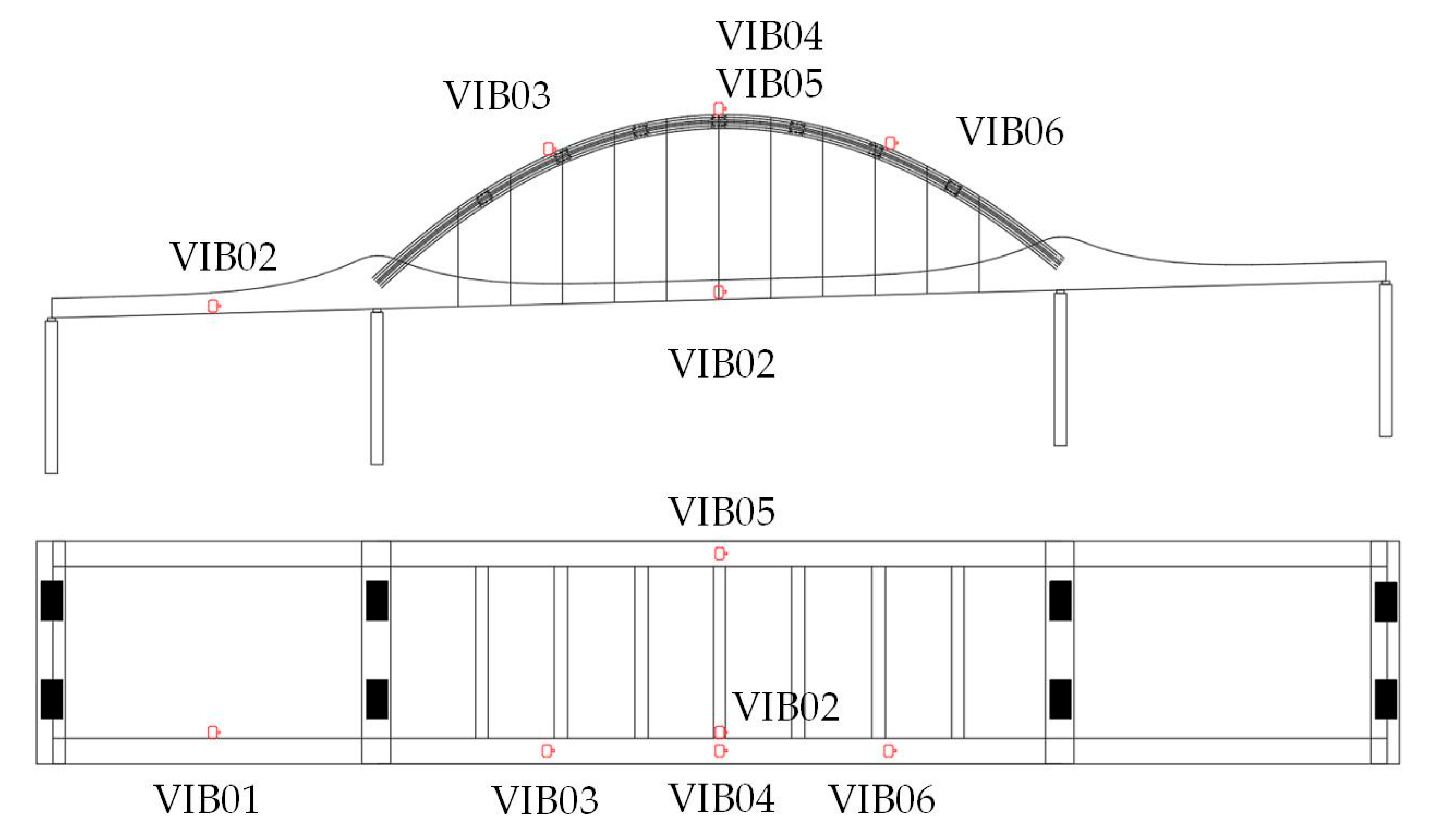
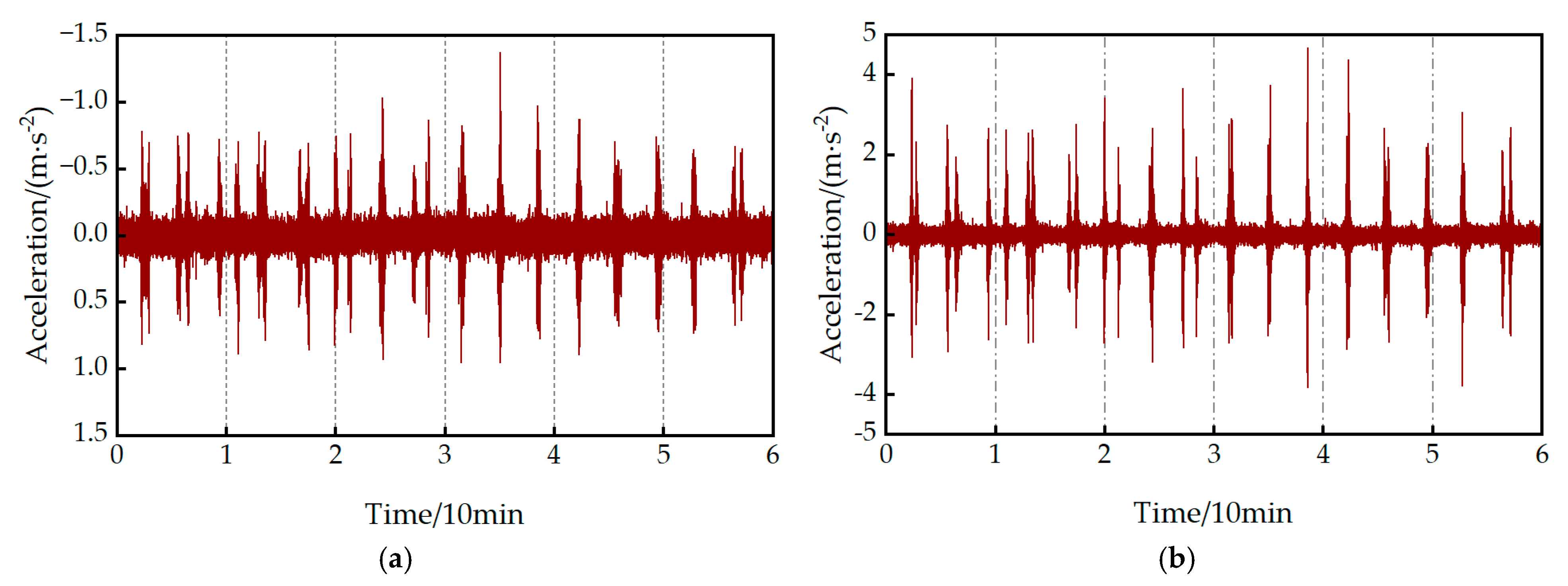
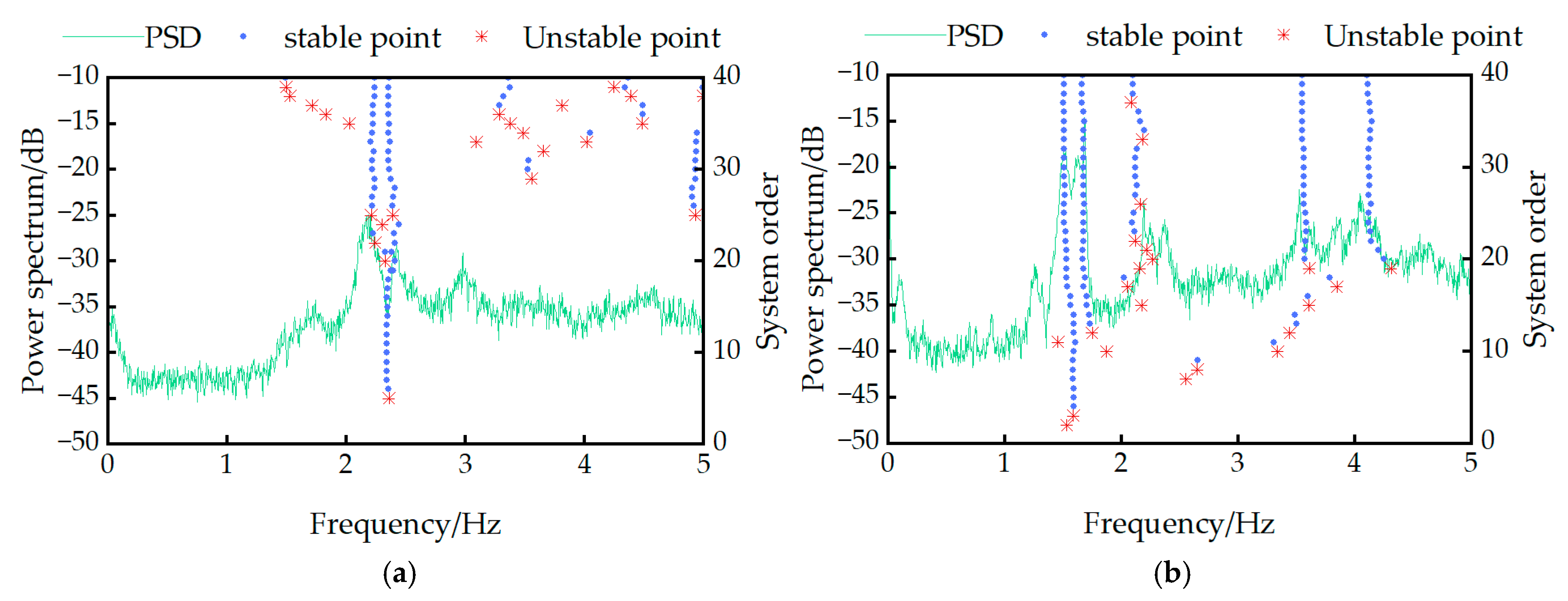
3.1. Comparison of Operational Bridge Frequency Identification
3.2. Finite Element Model of the Continuous Beam–Arch Composite Bridge and FE Model Results
3.3. Construction of the Response Surface Model
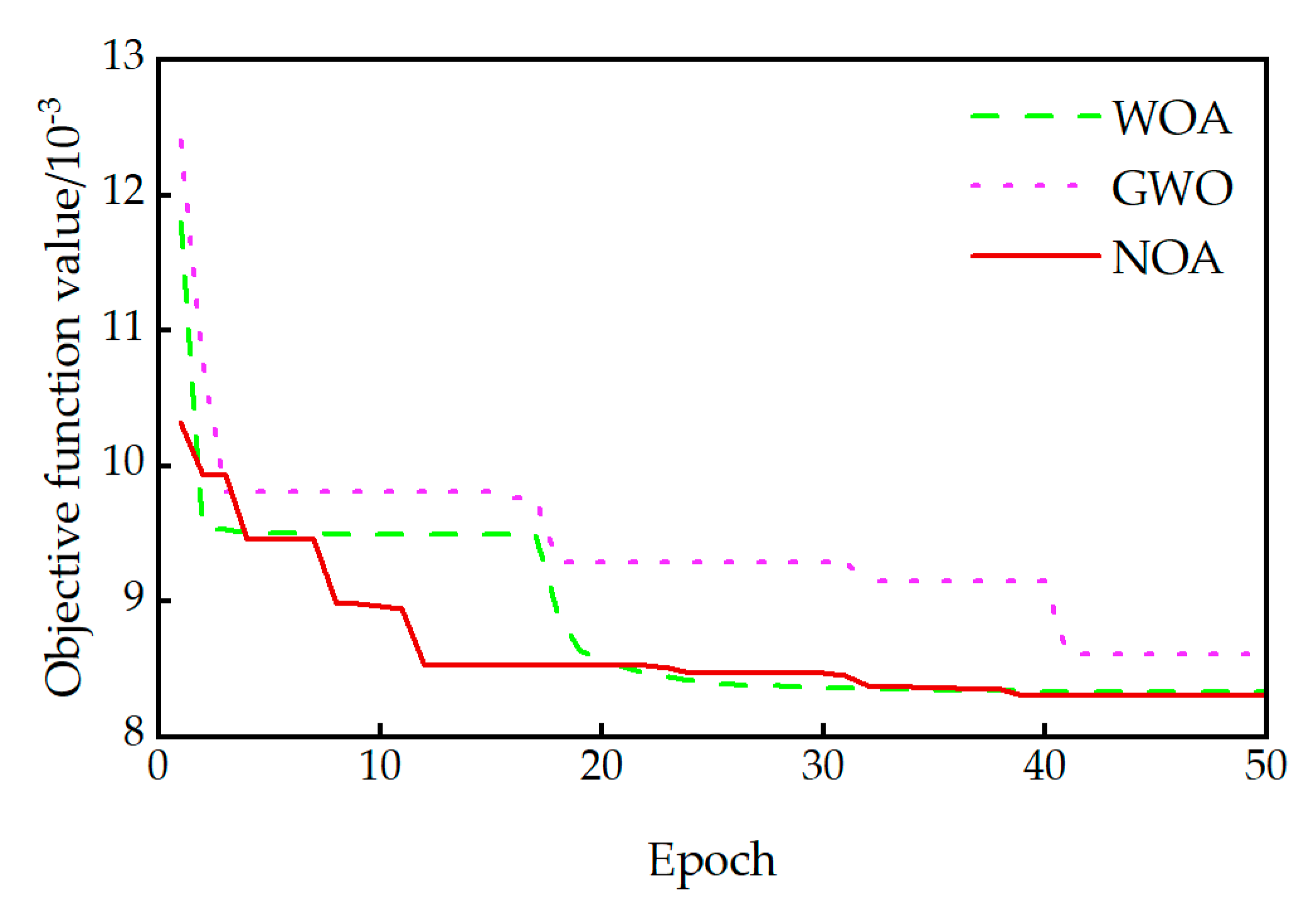
3.4. Optimization Algorithms and Model Updating Results
4. Conclusions
- The SSI method was employed to analyze the operational vibration response of an in-service municipal bridge, successfully extracting its second-order vibration frequencies. These experimentally identified frequencies served as the benchmark for subsequent model updating;
- The NOA features dual exploration strategies, enhancing its global optimum localization. Integrating RSM with NOA accelerated parameter identification compared to standalone methods. Experimental results confirmed that the NOA outperforms GWO and the WOA in convergence rates and enhanced model accuracy;
- Experimental validation indicates that the structural frequencies extracted from the updated FE model by the proposed method exhibit improved consistency with the frequencies identified from the structural health monitoring data, demonstrating the method’s effectiveness in enhancing numerical model accuracy. Moreover, the proposed RSM–NOA method reduced the average frequency error from 5.58% to 2.75% by updating the model parameters.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FE | Finite Element |
| RSM | Response Surface Model |
| NOA | Nutcracker Optimization Algorithm |
| SSI | Stochastic Subspace Identification |
| OMA | Operational Modal Analysis |
| PSD | Power Spectral Density |
| FEA | Finite Element Analysis |
| GWO | Grey Wolf Optimizer |
| WOA | Whale Optimization Algorithm |
References
- Bartilson, D.; Jang, J.; Smyth, A.W. Finite element model updating using objective-consistent sensitivity-based parameter clustering and Bayesian regularization. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2019, 114, 328–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Yang, D.; Yi, T.; Li, W.; Li, C. Bridge finite element model updating using stochastic vehicle-induced static response monitoring data. Eng. Struct. 2024, 301, 117280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottershead, J.E.; Friswell, M. Model updating in structural dynamics: A survey. J. Sound. Vib. 1993, 167, 347–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottershead, J.E.; Link, M.; Friswell, M.I. The sensitivity method in finite element model updating: A tutorial. Mech. Syst. Signal Proc. 2011, 25, 2275–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, D.; Li, Q.; Kha n, I.; Zhou, X. A novel finite element model updating method based on substructure and response surface model. Eng. Struct. 2015, 103, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, S.; Bakhary, N.; Abidin, A.R.Z. Response surface methodology for damage detection using frequency and mode shape. Measurement 2018, 115, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ansari, F.; Wu, B.; Li, S.; Morgese, M.; Zhou, J. LSTM approach for condition assessment of suspension bridges based on time-series deflection and temperature data. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2022, 25, 3450–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Zhou, B.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, T.; Wang, H. Bridge model updating based on wavelet neural network and wind-driven optimization. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 23, 9185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, L.; Wu, W.; Xu, L. Seismic fragility assessment framework for highway bridges based on an improved uniform design-response surface model methodology. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 18, 2329–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wu, N.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Fan, F.; Wang, J. Dynamic response of spatial train-track-bridge interaction system due to unsupported track using virtual work principle. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wu, N.; Cao, H.; Zhang, W. Two-stage stochastic model updating approach based on Bayesian framework and hybrid multi-population migrant genetic-metropolis-hastings algorithm for heavy-haul railway bridges. Eng. Optim. 2024, 57, 1343–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yan, Q.; Huang, S.; Zou, C.; Zhong, J.; Wang, W. Finite element model updating in bridge structures using kriging model and latin hypercube sampling method. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 11, 8980756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjneya, K.; Roy, K. Response surface-based structural damage identification using dynamic responses. Structures 2021, 29, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Sen, A. Adaptive response surface based efficient finite element model updating. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2014, 80, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Li, A.; Li, J.; Shi, H.; Duan, M.; Zhou, G. Model updating of an existing bridge with high-dimensional variables using modified particle swarm optimization and ambient excitation data. Measurement 2020, 159, 107754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Shao, T. Finite element model updating for improved box girder bridges with corrugated steel webs using the response surface method and fmincon algorithm. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 25, 586–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Chen, H. Finite element model updating in structural dynamics by using the response surface method. Eng. Struct. 2010, 32, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayekhi, M.; Santini-Bell, E. Three-dimensional multiscale finite element models for in-service performance assessment of bridges. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2019, 34, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Quek, S.; Li, A.; Li, J.; Duan, M. Hybrid approach to seismic reliability assessment of engineering structures. Eng. Struct. 2017, 153, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Shao, F.; He, L.; Xu, Q.; Bai, L. Multi-objective optimal design of steel beams based on genetic algorithm-response surface methodology. Transp. Res. Rec. 2025, 17, 03611981251327221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Cai, C. Bridge model updating using response surface method and genetic algorithm. J. Bridge Eng. 2010, 15, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.; Kim, C. Finite element model updating on small-scale bridge model using the hybrid genetic algorithm. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2013, 9, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, J. Feasibility study of improved particle swarm optimization in kriging metamodel based structural model updating. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2019, 70, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulkaibet, I.; Mthembu, L.; Neto, F.D.L.; Marwala, T. Finite element model updating using fish school search and volitive particle swarm optimization. Integr. Comput.-Aided Eng. 2015, 22, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cao, H.; Qin, S. Research on multi-alternatives problem of finite element model updating based on IAFSA and kriging model. Sensors 2020, 20, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Cheng, F.; Zou, C.; Zhang, R.; Li, C.; Huang, S.; Zhou, Y. Swarm intelligent optimization conjunction with kriging model for bridge structure finite element model updating. Buildings 2022, 12, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Yuan, Y.; Gan, Y.; Wang, Q. Improved metaheuristic algorithm based finite element model updating of a hybrid girder cable-stayed railway bridge. Buildings 2022, 12, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jiang, L.; Xu, F.; Gu, J.; Ye, Z.; Peng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, R. Safety evaluation for fabricated small box girder bridges based on fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and monitoring data. Sensors 2024, 24, 4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pioldi, F.; Ferrari, R.; Rizzi, E. Output-only modal dynamic identification of frames by a refined FDD algorithm at seismic input and high damping. Mech. Syst. Sig. Process. 2016, 68-69, 265–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynders, E. System identification methods for (operational) modal analysis: Review and comparison. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2012, 19, 51–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, A.; Altunisik, A.C.; Birinci, F.; Sevim, B.; Türker, T. Finite-element analysis and vibration testing of a two-span masonry arch bridge. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2010, 24, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu Kuan, Y.C. Mode shape-based damage detection of twin skewed bridges based on OMA and FE model updating. Struct. Eng. Int. 2024, 34, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Chen, C.; Kusbiantoro, A.; Lai, G. Finite element model of a cable-stayed bridge updated with vibration measurements and its application to investigate the variation of modal frequencies in monitoring. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2024, 20, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, L. Application of improved stabilization diagram in modal parameter identification by stochastic subspace identification. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Structural Health Monitoring of Intelligent Infrastructure, Shenzhen, China, 16–18 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Alimouri, P.; Moradi, S.; Chinipardaz, R. Updating finite element model using stochastic subspace identification method and bees optimization algorithm. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2018, 15, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.; Montgomery, D.C.; Anderson-Cook, C.M. Response Surface Methodology: Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Mohamed, R.; Jameel, M.; Abouhawwash, M. Nutcracker optimizer: A novel nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for global optimization and engineering design problems. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 262, 110248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Alonso, J.F.; Naranjo-Perez, J.; Pavic, A.; Sáez, A. Maximum likelihood finite-element model updating of civil engineering structures using nature-inspired computational algorithms. Struct. Eng. Int. 2021, 31, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lu, H.; Chen, X. A general 2d meshless interpolating boundary node method based on the parameter space. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 10, 3435751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhong, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Bian, X. Interpolating isogeometric boundary node method and isogeometric boundary element method based on parameter space. CMES-Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2020, 123, 807–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, H.; Cao, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, A.; Wu, N.; Liu, Z. Separation of temperature-induced response for bridge long-term monitoring data using local outlier correction and savitzky-golay convolution smoothing. Sensors 2023, 23, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Chen, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Fan, J. An integrated coupling element for vehicle-rail-bridge interaction system with a non-uniform continuous bridge. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 2015, 28, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Y.; Lu, N.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, X. Assessment of fatigue crack propagation and lifetime of double-sided U-rib welds considering welding residual stress relaxation. Ocean Eng. 2025, 332, 121400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


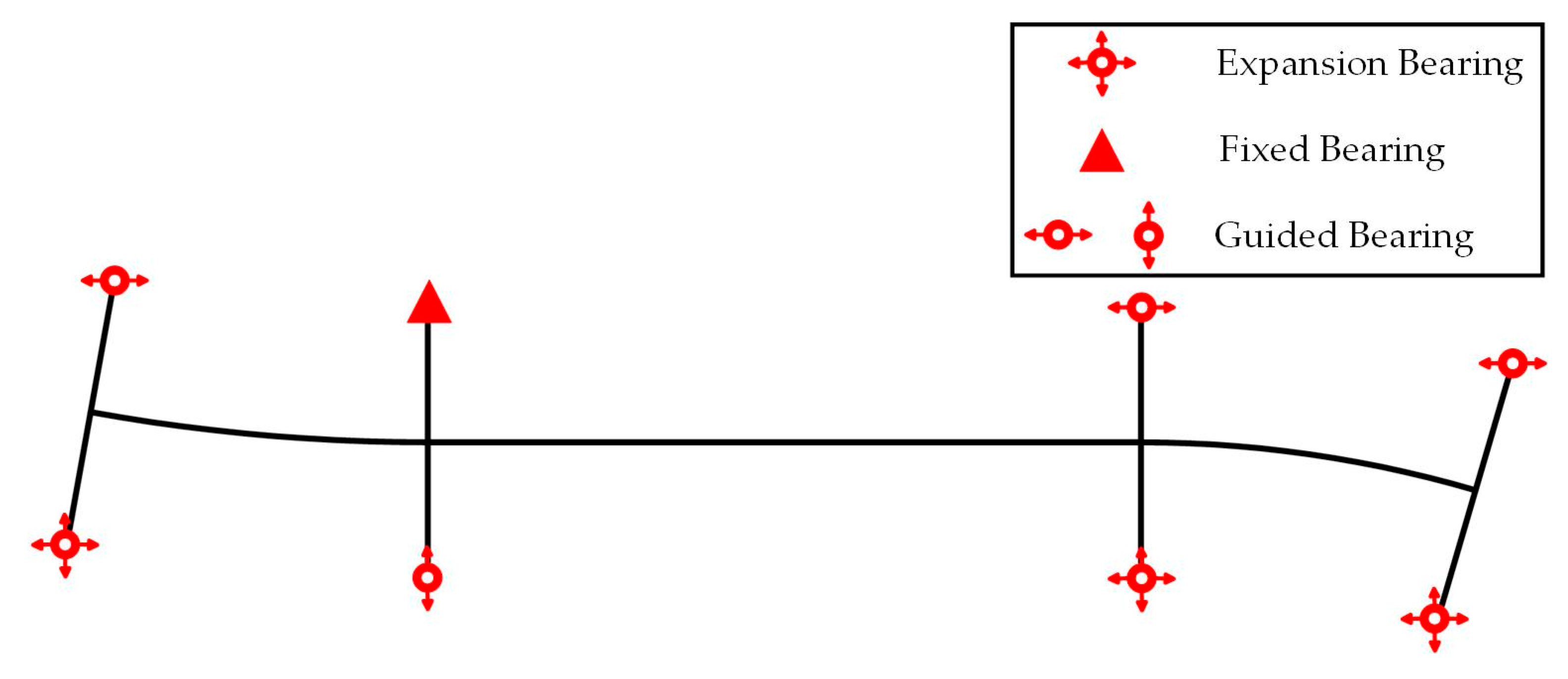

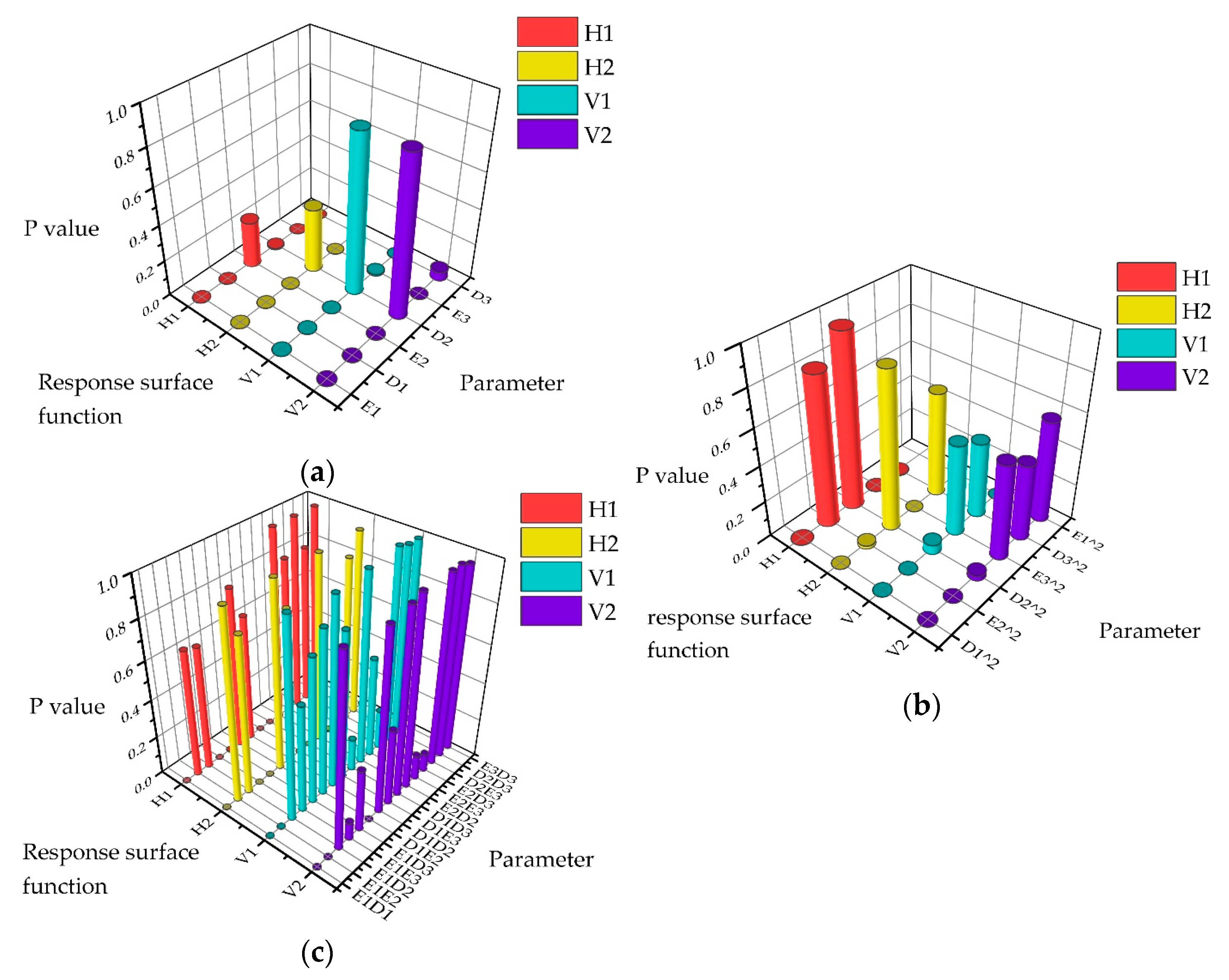
| Material | Mass Density/kg·m−3 | Elastic Modulus/MPa | Poisson’s Ratio | Structural Component |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C55 concrete | 2.55 × 103 | 3.55 × 104 | 0.2 | Main girder, steel tube infill |
| Steel | 8.0055 × 103 | 20.6 × 104 | 0.3 | Arch rib, wind bracing, bearing |
| Steel strand | 8.0055 × 103 | 19.5 × 104 | 0.2 | Hanger cables |
| Vibration Mode | FEA Calculated Value/Hz | Measured Value/Hz | Error/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical Bending 1 (V1) | 1.465 | 1.511 | 3 |
| Vertical Bending 2 (V2) | 1.567 | 1.684 | 7.4 |
| Horizontal Bending 1 (H1) | 2.108 | 2.187 | 3.6 |
| Horizontal Bending 2 (H2) | 2.22 | 2.422 | 8.3 |
| Frequency | H1 | H2 | V1 | V2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9998 | 0.9996 | 0.9983 | 0.9998 | |
| 0.00021 | 0.00032 | 0.00074 | 0.00059 |
| Parameter/Unit | Pre-Correction | Post-Correction | Change Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| E1/MPa | 35,500 | 33,122.78 | 6.7 |
| D1/kg·m−3 | 2.55 × 103 | 2.48 × 103 | 2.7 |
| E2/MPa | 195,000 | 151,841.69 | 22.1 |
| D2/kg·m−3 | 8.0055 × 103 | 10.4 × 103 | 29.9 |
| E3/MPa | 206,000 | 179,298.83 | 12.9 |
| D3/kg·m−3 | 8.0055 × 103 | 9.45 × 103 | 18 |
| Mode | Measured Value/Hz | GWO Correction | WOA Correction | NOA Correction | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calculated Value/Hz | Error/% | Calculated Value/Hz | Error/% | Calculated Value/Hz | Error/% | ||
| V1 | 1.511 | 1.501 | 0.6 | 1.508 | 0.2 | 1.505 | 0.3 |
| V2 | 1.684 | 1.765 | 4.8 | 1.757 | 4.3 | 1.763 | 4.6 |
| H1 | 2.187 | 2.036 | 6.9 | 2.03 | 7.1 | 2.103 | 3.8 |
| H2 | 2.422 | 2.475 | 2.2 | 2.467 | 1.9 | 2.477 | 2.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, W.; Yang, H.; Hao, J.; Zhai, M.; Cao, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, K. Finite Element Model Updating for a Continuous Beam-Arch Composite Bridge Based on the RSM and a Nutcracker Optimization Algorithm. Sensors 2025, 25, 4831. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154831
Zhou W, Yang H, Hao J, Zhai M, Cao H, Liu Z, Wang K. Finite Element Model Updating for a Continuous Beam-Arch Composite Bridge Based on the RSM and a Nutcracker Optimization Algorithm. Sensors. 2025; 25(15):4831. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154831
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Weihua, Hongyin Yang, Jing Hao, Mengxiang Zhai, Hongyou Cao, Zhangjun Liu, and Kang Wang. 2025. "Finite Element Model Updating for a Continuous Beam-Arch Composite Bridge Based on the RSM and a Nutcracker Optimization Algorithm" Sensors 25, no. 15: 4831. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154831
APA StyleZhou, W., Yang, H., Hao, J., Zhai, M., Cao, H., Liu, Z., & Wang, K. (2025). Finite Element Model Updating for a Continuous Beam-Arch Composite Bridge Based on the RSM and a Nutcracker Optimization Algorithm. Sensors, 25(15), 4831. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154831







