In-Wheel Motor Fault Diagnosis Method Based on Two-Stream 2DCNNs with DCBA Module
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. 2DCNN
2.2. Attention Mechanism (AM)
3. The Proposed Approaches
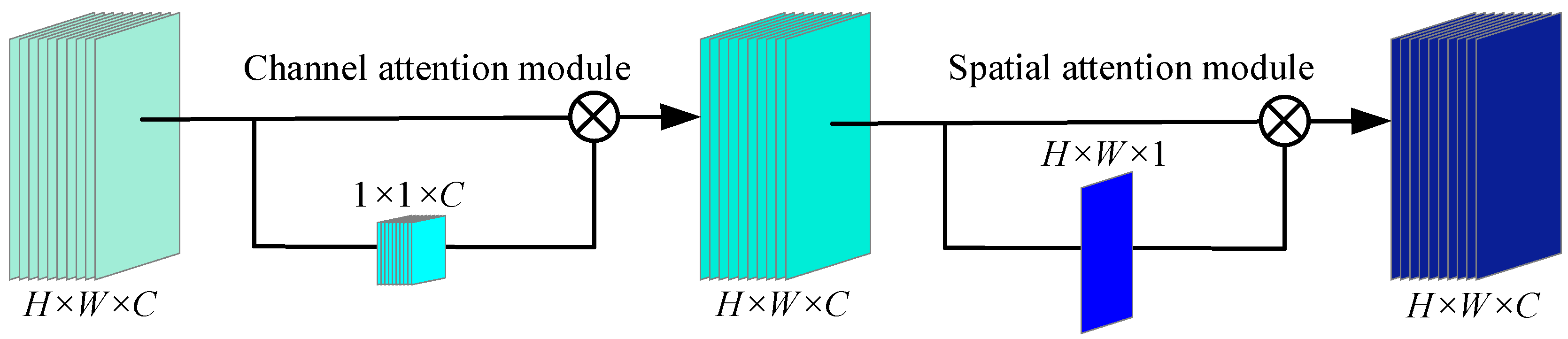
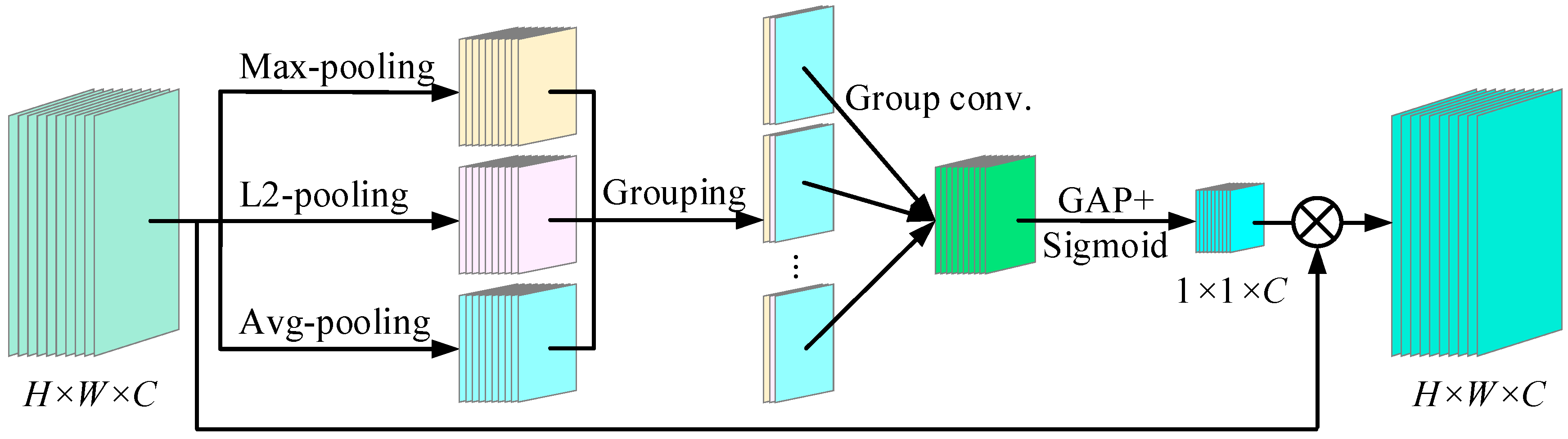
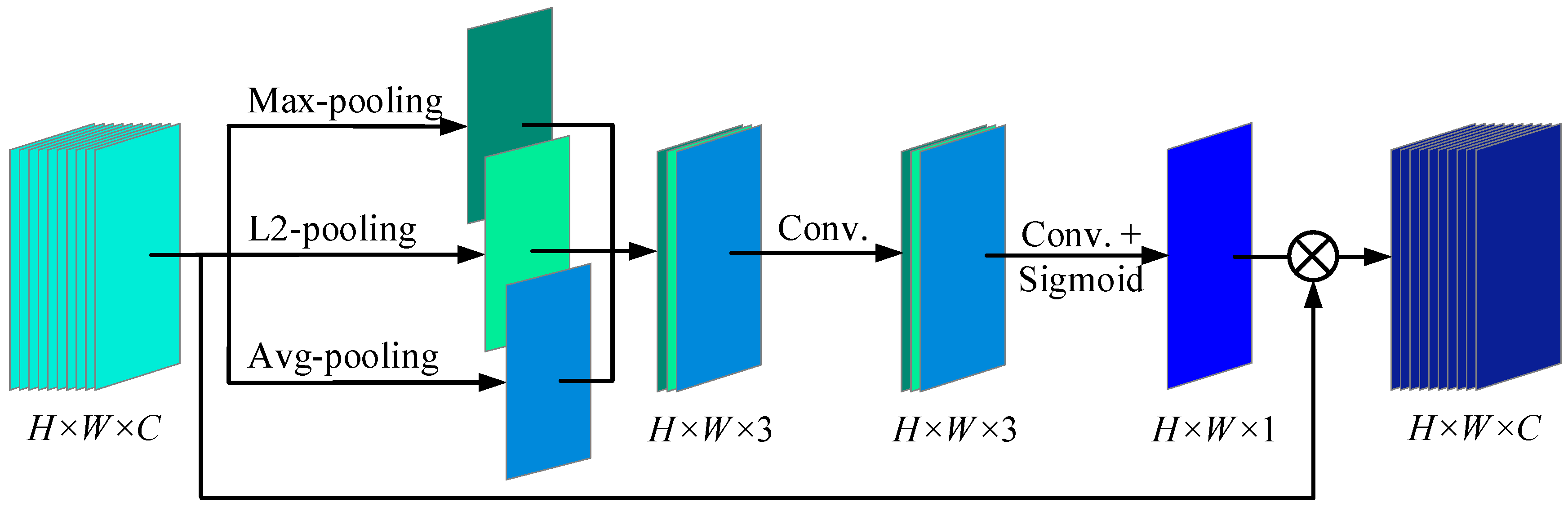
3.1. Depthwise Convolution Block Attention (DCBA)
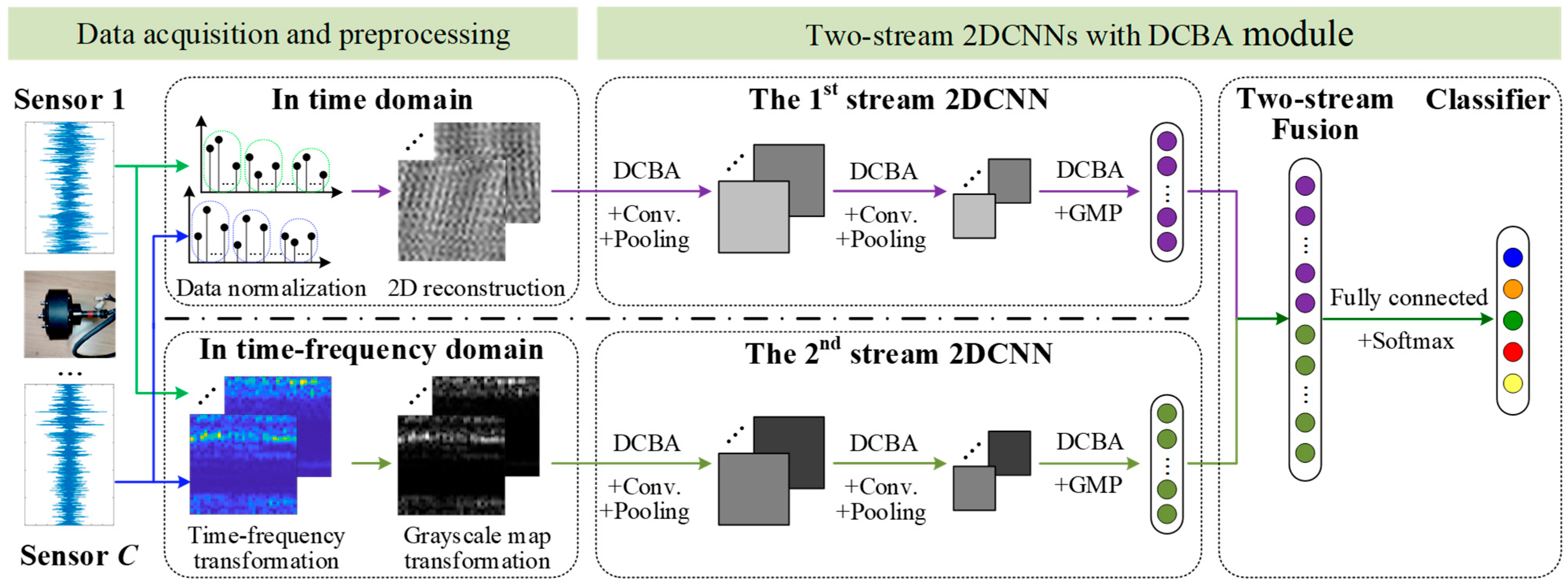
3.2. Network Structure of Two-Stream 2DCNNs with DCBA Module
3.3. Diagnosis Model of In-Wheel Motors’ Faults
4. Performance Verification
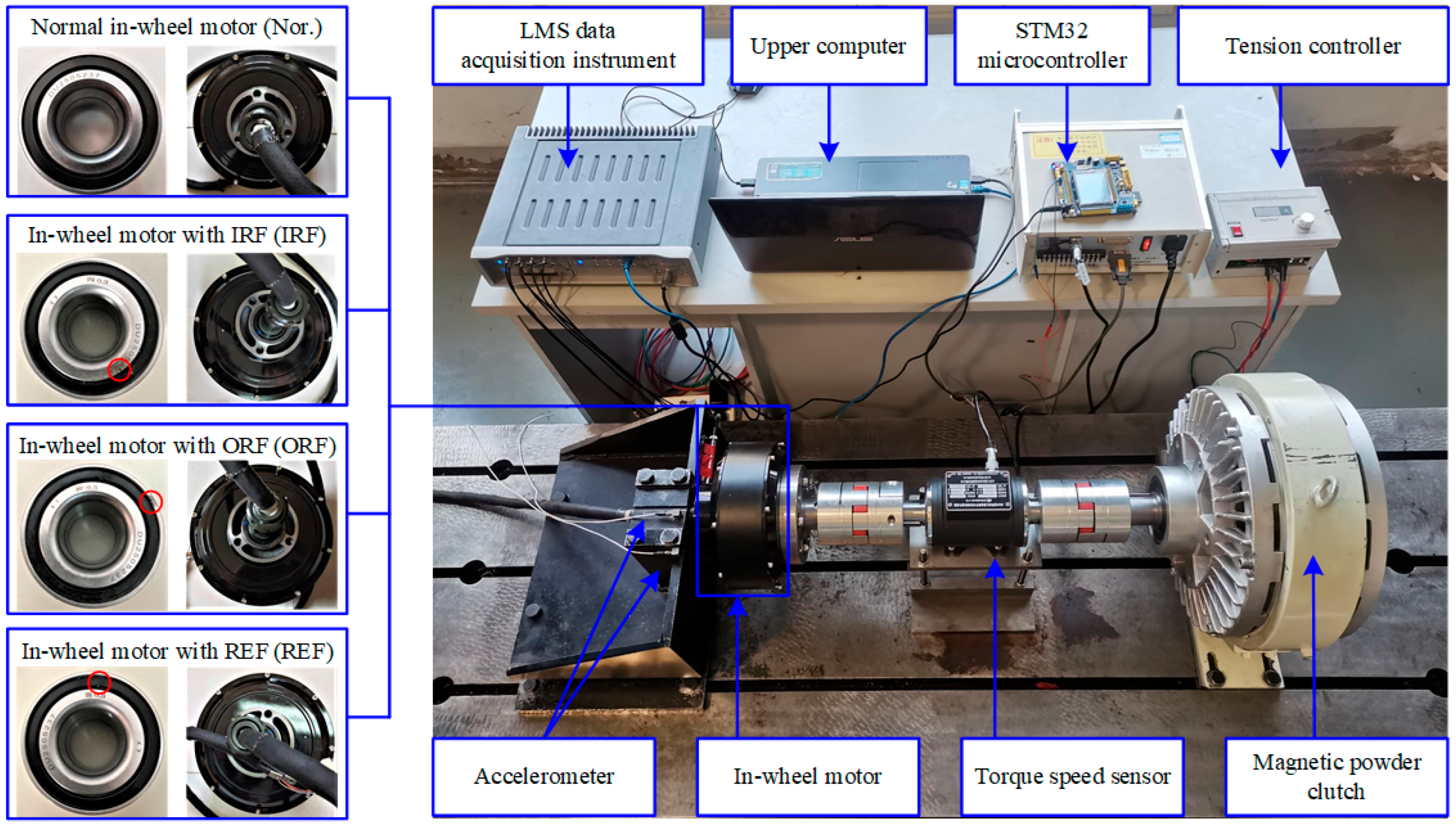
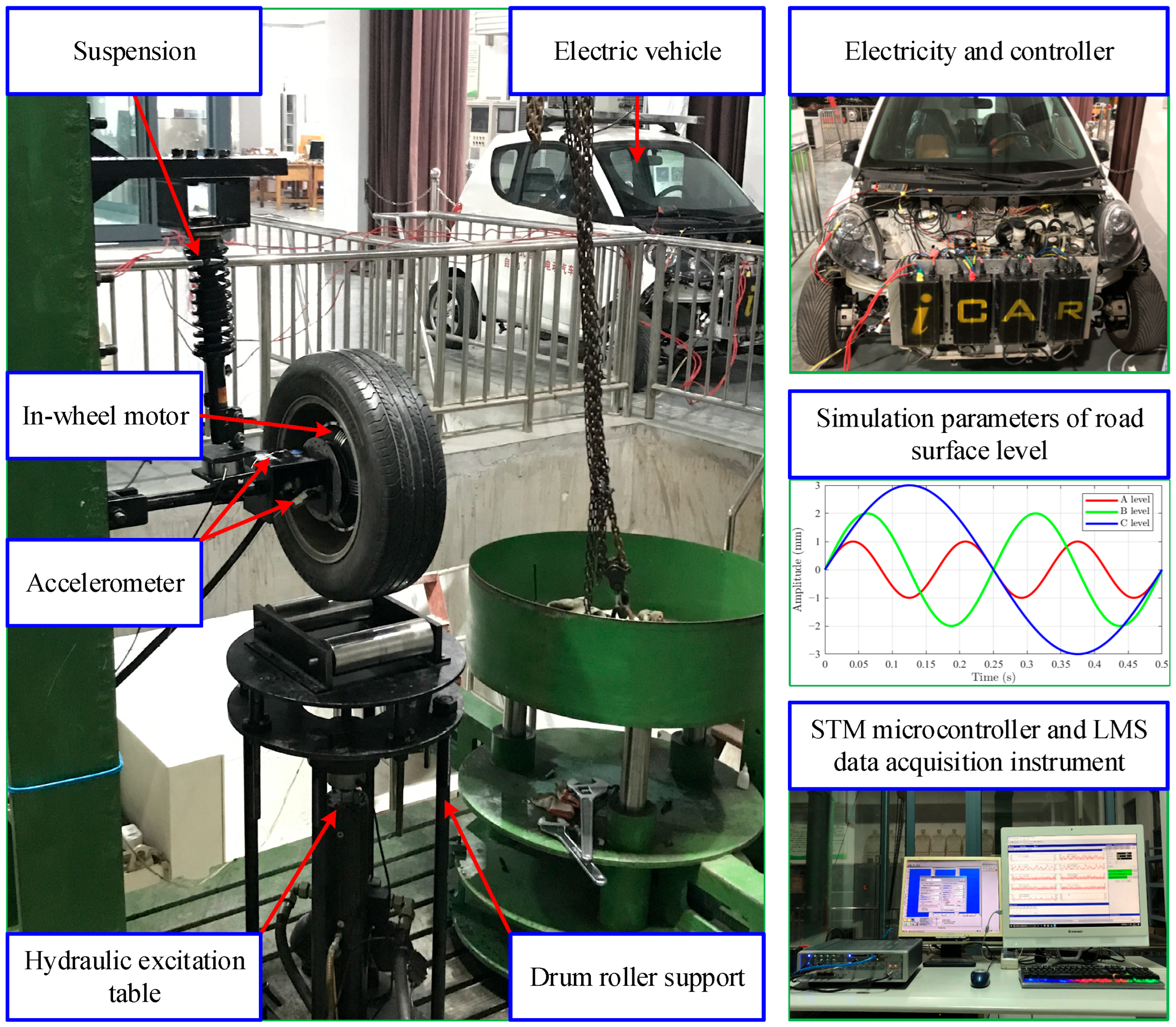
4.1. Case 1: In-Wheel Motor Experiment Under Static Interference
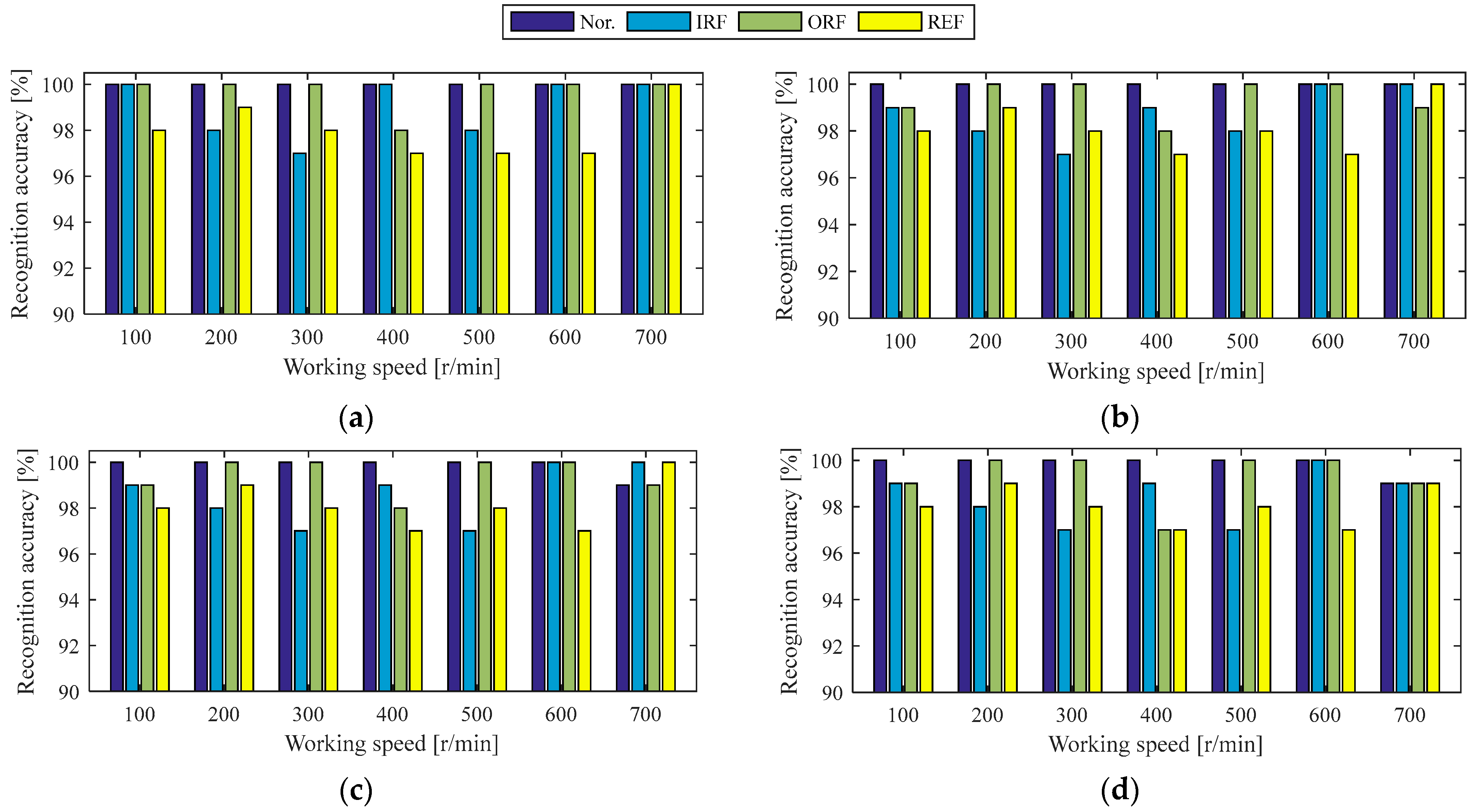
4.1.1. Holdout-Validation of Diagnosis Model Under the Same Working Condition of Case 1
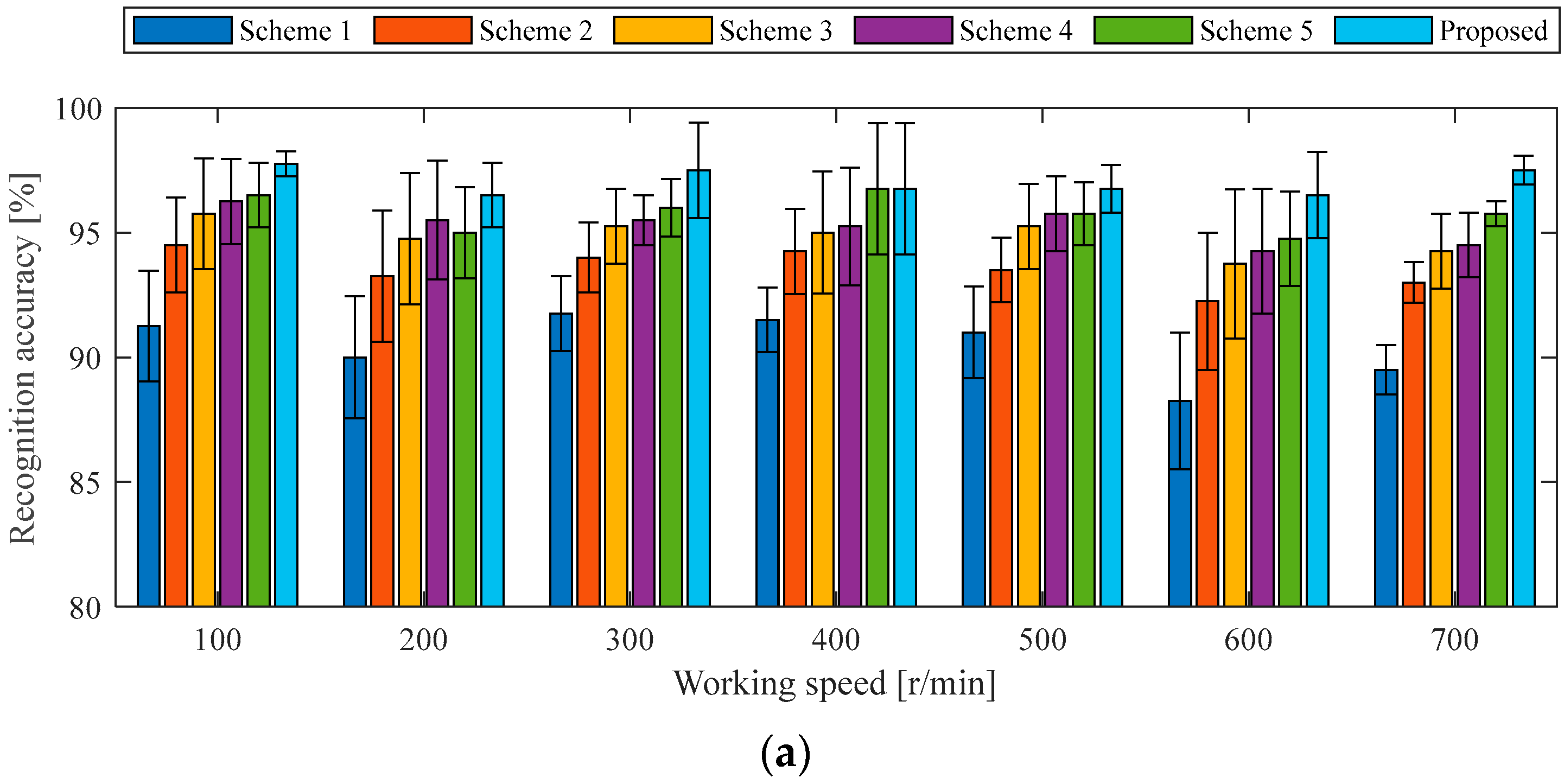
4.1.2. Cross-Validation of Diagnosis Model Under Similar Working Conditions to the Case 1 Experiment
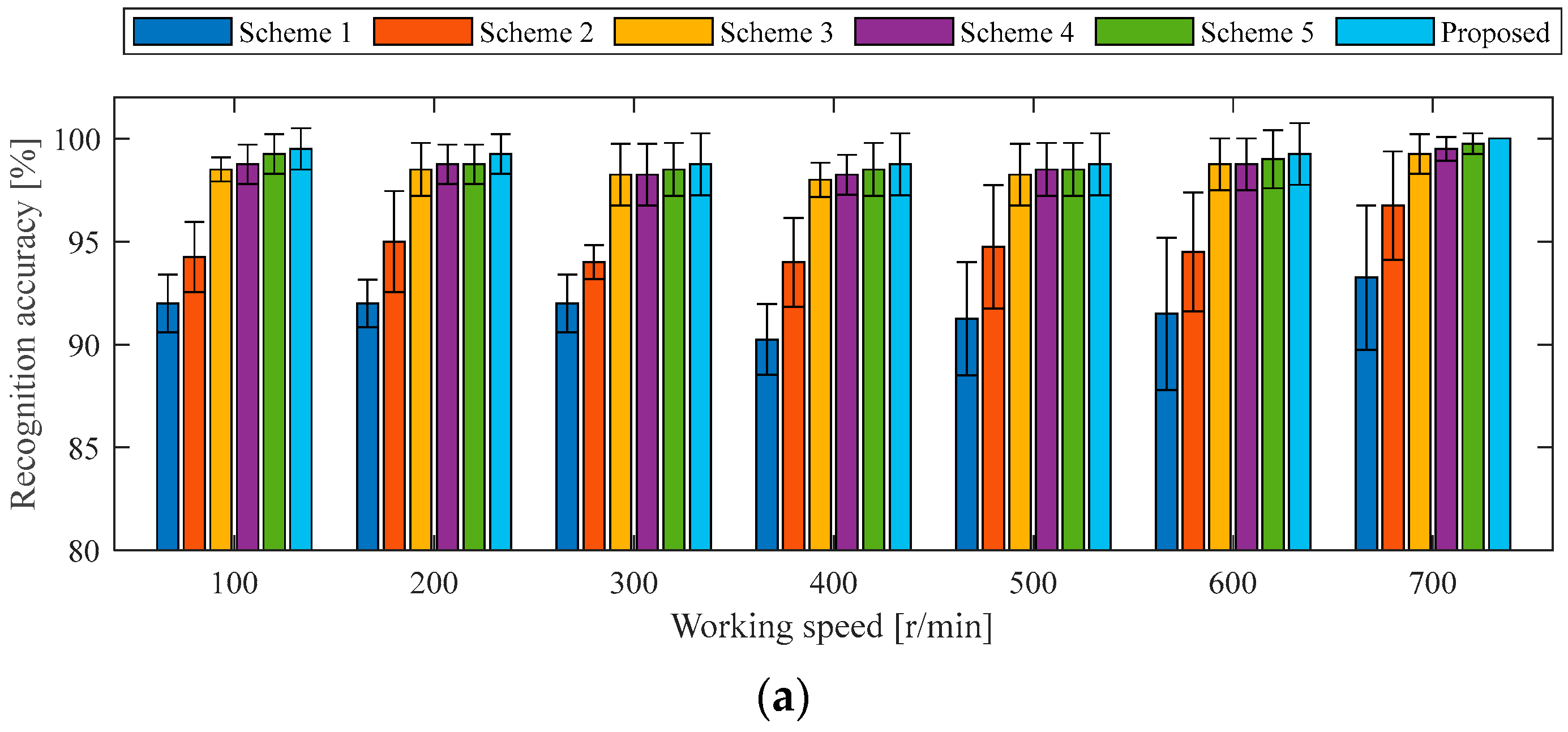
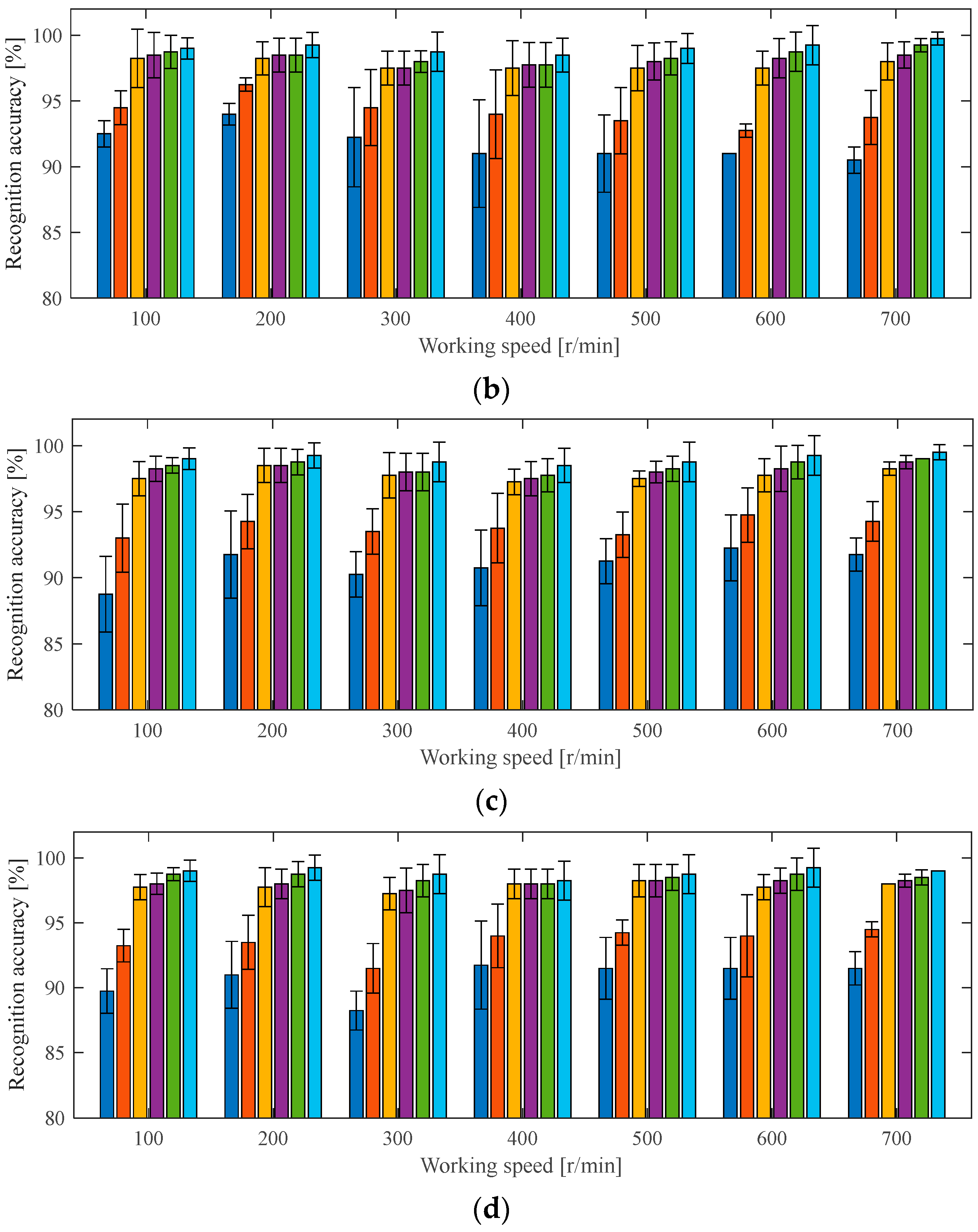
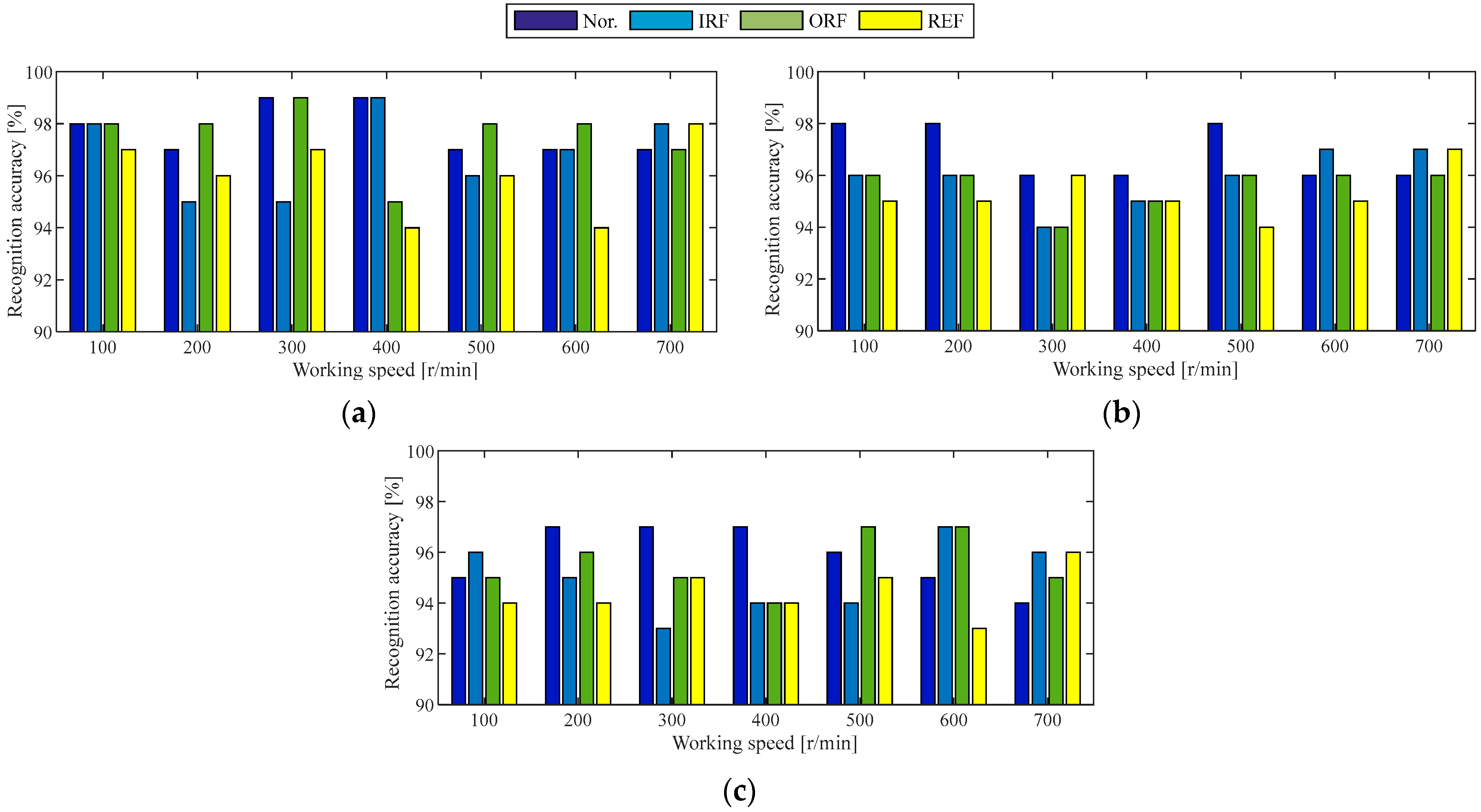
4.1.3. Ablation Experiment Under the Same Working Conditions as the Case 1 Experiment
4.2. Case 2: In-Wheel Motor Experiment Under Dynamic Disturbance
4.2.1. Holdout-Validation of Diagnosis Model Under the Same Working Conditions as the Case 2 Experiment
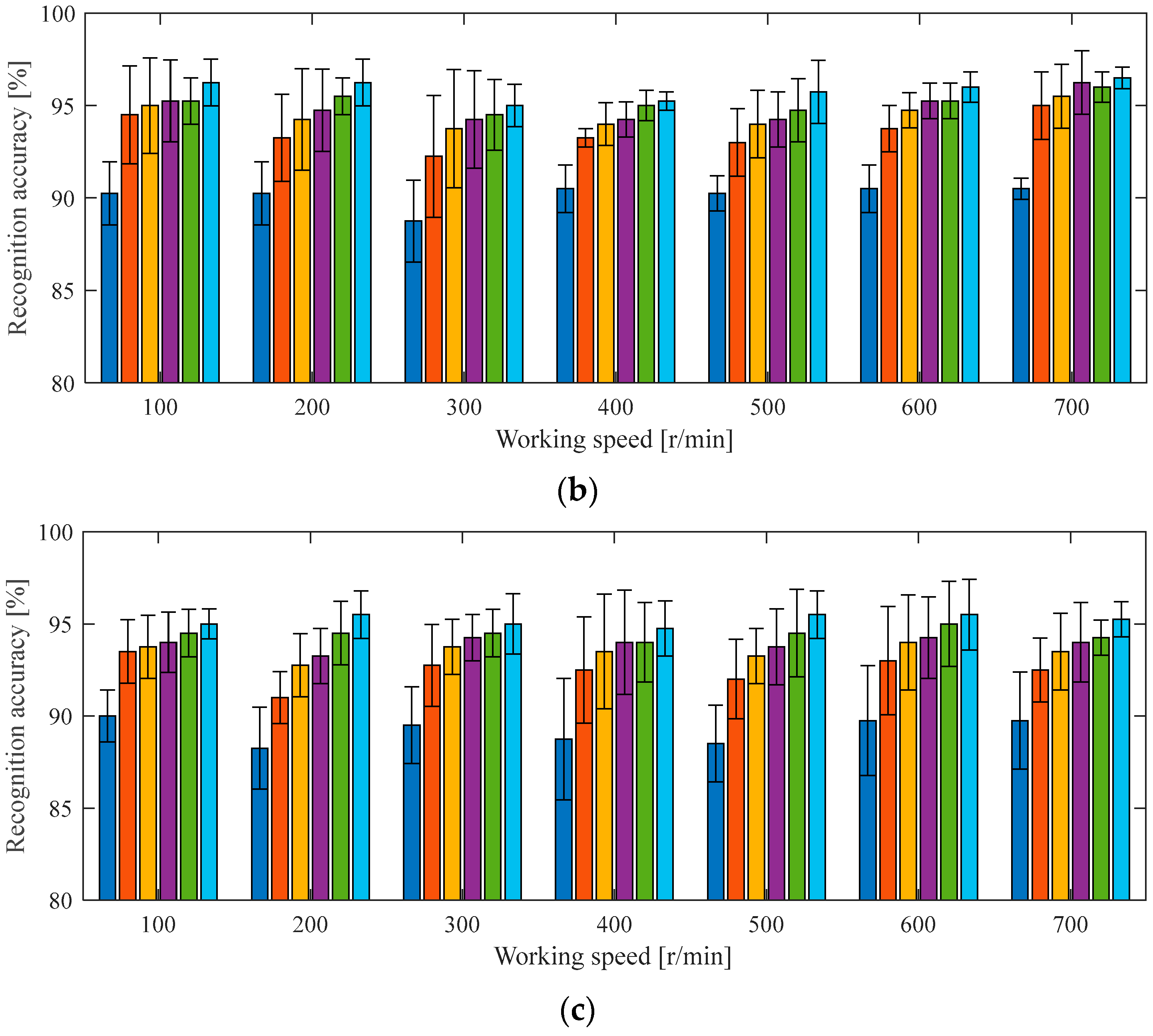
4.2.2. Cross-Validation of Diagnosis Model Under Similar Working Conditions as the Case 2 Experiment
4.2.3. Ablation Experiment Under the Same Working Conditions as the Case 2 Experiment
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, X.Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Quan, Z.Q.; Cai, Y.F.; Chen, L.; Bei, S.Y. DYC design for autonomous distributed drive electric vehicle considering tire nonlinear mechanical characteristics in the PWA form. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 11030–11046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.H.; Chai, X.Y.; Xu, L.Z.; Quan, L.; Yuan, C.C.; Tian, S.C. Design and performance of a distributed electric drive system for a series hybrid electric combine harvester. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 236, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Y.; Xiong, R.; Cai, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, R.X. Regenerative braking control strategy for distributed drive electric vehicles based on slope and mass co-estimation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 14610–14619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, L.; Xu, X.; Cai, Y.F.; Jiang, H.B.; Sun, X.Q. Passive fault-tolerant path following control of autonomous distributed drive electric vehicle considering steering system fault. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 123, 298–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yan, S.C.; Shen, Y.; Li, C.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Hussain, F. Model predictive control system based on direct yaw moment control for 4WID self-steering agriculture vehicle. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.T.; Ding, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.M.; Wu, M.; Wang, H.Q. A fuzzy system of operation safety assessment using multi-model linkage and multi-stage collaboration for in-wheel motor. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 30, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Tao, Y.K.; Feng, J.B.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xue, H.T.; Wang, T.S.; Xu, X.; Chen, P. Fault-tolerant collaborative control of four-wheel-drive electric vehicle for one or more in-wheel motors’ faults. Sensors 2025, 25, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Ta, Y.; Li, Y.F. Research on a remaining useful life prediction method for degradation angle identification two-stage degradation process. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 184, 109747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.Y.; Wang, H.Q.; Chen, P. Vibration-based intelligent fault diagnosis for roller bearings in low-speed rotating machinery. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 1887–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.T.; Liu, B.C.; Ding, D.Y.; Zhou, J.W.; Cui, X.L. Diagnosis method based on hidden Markov model and Weibull mixture model for mechanical faults of in-wheel motors. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, D.Z.; Yan, R.Q.; Mao, K.Z.; Shen, F.; Wang, J.J. Machine health monitoring using local feature-based gated recurrent unit networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.F.; Fu, S.; Feng, K.Y.; Han, X.; Hu, Y.Y.; Zhu, Q.Z.; Wei, X.H. Analysis of vibration characteristics of tractor-rotary cultivator combination based on time domain and frequency domain. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.J.; Song, X.J. A current noise cancellation method based on fractional linear prediction for bearing fault detection. Sensors 2024, 24, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.L.; Wang, H.B.; Zhao, D.Z.; Xu, H. Synchronous odd symmetric transform for rolling bearing fault diagnosis. Measurement 2024, 226, 114184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.Z.; Tang, Z.; Wang, K.J.; Li, P.C. Failure feature identification of vibrating screen bolts under multiple feature fusion and optimization method. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Adaptive staged remaining useful life prediction method based on multi-sensor and multi-feature fusion. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 231, 109033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.L.; Zhao, X.Y.; Liu, D.D.; Wang, H.Q. A novel spectral coherence-based weighted envelope spectrum analysis method for bearing fault diagnosis. Struct. Health Monit. 2023, 23, 2457–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.Y.; Fan, W.; Xu, Z.Y. An improved dual-kurtogram-based T2 control chart for condition monitoring and compound fault diagnosis of rolling bearings. Shock. Vib. 2021, 2021, 6649125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Dai, J.S.; Xu, W.C.; Chang, C.Q. Sparse bayesian learning approach for compound bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 1562–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Y.; Fan, W.; Chen, C.; Peng, Z.K. Adaptive two-stage model for bearing remaining useful life prediction using gaussian process regression with matched kernels. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2024, 73, 1958–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdaoui, H.; Ngiejungbwen, L.A.; Gu, J.A.; Tang, S.X. Improved signal processing for bearing fault diagnosis in noisy environments using signal denoising, time-frequency transform, and deep learning. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2023, 45, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhao, Y.F.; Geng, G.S.; Dustdar, S.; Donta, P.K.; Ji, G.J. A new fault feature extraction method of rolling bearings based on the improved self-selection ICEEMDAN-permutation entropy. ISA Trans. 2023, 143, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Mian, T.; Fatima, S.; Panigrahi, B.K. Fault diagnosis of electric two-wheeler under pragmatic operating conditions using wavelet synchrosqueezing transform and CNN. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 6254–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.Y.; Tong, Q.B.; Feng, Z.W.; Wan, Q.Z. Unbalanced bearing fault diagnosis under various speeds based on spectrum alignment and deep transfer convolution neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 8295–8306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.K.; Ge, C.; Feng, H.; Xue, H.T.; Yao, M.Y.; Tang, H.H.; Liao, Z.Q.; Chen, P. A novel approach for adaptively separating and extracting compound fault features of the in-wheel motor bearing. ISA Trans. 2025, 159, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.Y.; Xue, H.T.; Liu, B.C. Feature extraction method based on optimized SSD and enhance MOMEDA for bearing faults of in-wheel motor. Proc. Chin. Soc. Electr. Eng. 2023, 43, 9721–9732. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.C.; Xue, H.T.; Ding, D.Y.; Sun, N.; Chen, P. In-wheel motor fault diagnosis using affinity propagation minimum-distance discriminant projection and weibull-kernel-function-based SVDD. Sensors 2023, 23, 4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.H.; Yang, R.; Xue, Y.H.; Huang, M.J.; Ferrero, R.; Wang, Z.D. Deep Transfer learning for bearing fault diagnosis: A systematic review since 2016. Measurement 2023, 72, 3508221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhao, S.Y.; Liu, J.Z. Fused-deep-features based grape leaf disease diagnosis. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Y.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J.Z.; Wu, S. Tomato leaf disease diagnosis based on improved convolution neural network by attention module. Agronomy 2021, 11, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, D.M.; Chen, J.; Yan, X.A.; Zhao, X.L.; Pecht, M. Diversity maximization-based transfer diagnosis approach of rotating machinery. Struct. Health Monit.-Int. J. 2023, 23, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Fu, J.M.; Lu, C.Q.; Zhu, Y. Research on rolling bearing fault diagnosis of small dataset based on a new optimal transfer learning network. Measurement 2021, 177, 109285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.S.; So, H.C. Group-sparsity learning approach for bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 4566–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Li, Q.; Sun, D.Y.; Cao, W.; Fan, F.J. An intelligent fault diagnosis method of small sample bearing based on improved auxiliary classification generative adversarial network. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 19543–19555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.H.; Tang, Y.M.; Su, Y.X.; Feng, W.W.; Wang, B.; Chen, P.; Zuo, D.W. Feature extraction of multi-sensors for early bearing fault diagnosis using deep learning based on minimum unscented kalman filter. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 127, 107138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.H.; Jiang, X.X.; Yang, R.; Zhang, H.Y.; Liu, J.; Shen, C.Q. Actively imaginative data augmentation for machinery diagnosis under large-speed-fluctuation conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 8484–8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wang, J.; Yao, L.Q.; Huang, W.G.; Zhu, Z.K. Categorical feature GAN for imbalanced intelligent fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 3525212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Y.; Zeng, Y.T.; Shao, H.D.; Hu, H.W.; Xu, X.Q. Novel motor fault detection scheme based on one-class tensor hyperdisk. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 262, 110259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husari, F.; Seshadrinath, J. Stator turn fault diagnosis and severity assessment in converter-fed induction motor using flat diagnosis structure based on deep learning approach. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 5649–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.G.; Adade, S.Y.S.S.; Wang, Z.; Jiao, T.H.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, H.H.; Chen, Q.S. Deep learning and feature reconstruction assisted vis-NIR calibration method for on-line monitoring of key growth indicators during kombucha production. Food Chem. 2024, 463, 141411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Yang, P.K.; Yu, H.; Bai, J.; Feng, W.W.; Su, Y.X.; Si, Y.L. A 2DCNN-RF model for offshore wind turbine high-speed bearing-fault diagnosis under noisy environment. Energies 2022, 15, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.B.; Ju, Z. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on 2D CNN and hybrid kernel fuzzy SVM. Adv. Theory Simul. 2025, 8, 2400793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awais, M.; Li, W.; Hussain, S.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Li, W.G.; Song, R.; Liu, C.C. Comparative evaluation of land surface temperature images from unmanned aerial vehicle and satellite observation for agricultural areas using in situ data. Agriculture 2022, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Xiao, S.Q.; Zhang, F.B.; Huang, J.F.; Xie, Z.J.; Kong, X.W. A fault diagnosis method with AT-ICNN based on a hybrid attention mechanism and improved convolutional layers. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 225, 110191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Wang, A.C.; Shen, Y.D.; Lu, Z.M.; Peng, F.T.; Wei, X.H. Peach Flower density detection based on an improved CNN incorporating attention mechanism and multi-scale feature fusion. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, M.Y.; Pan, Q.M.; Jin, X.T.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Hu, Y.G. Identification of tea plant cultivars based on canopy images using deep learning methods. Sci. Hortic. 2025, 339, 113908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, H.X.; Chen, J.M.; Chen, Z.X.; Pu, T.; Zhang, X.Q.; Liu, F.B. LCRNet: Local cross-channel recalibration network for liver cancer classification based on CT images. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2023, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Pan, Y.; Xu, B.; Wang, J.C. A real-time apple targets detection method for picking robot based on shufflenetV2-YOLOX. Agriculture 2022, 12, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Module | Layer Type | Kernel Size | Stride |
|---|---|---|---|
| Channel attention | max-pooling | 2 × 2 | 2 |
| L2-pooling | 2 × 2 | 2 | |
| avg-pooling | 2 × 2 | 2 | |
| Conv | 1 × 1 × 3 | 1 | |
| Spatial attention | max-pooling | / | / |
| L2-pooling | / | / | |
| avg-pooling | / | / | |
| Conv1 | 3 × 3 × 3 | 1 |
| Process | Layer Type | Kernel Number @ Size/Stride/Padding | Output Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st-stream 2DCNN | Input | 2 @ 32 × 32 | |
| DCBA module | 2 @ 32 × 32 | ||
| Conv1 | 16 @ 3 × 3/1/1 | 16 @ 32 × 32 | |
| Pooling1 | 2 × 2/2/0 | 16 @ 16 × 16 | |
| DCBA module | 16 @ 16 × 16 | ||
| Conv2 | 32 @ 3 × 3/1/1 | 32 @ 16 × 16 | |
| Pooling2 | 2 × 2/2/0 | 32 @ 8 × 8 | |
| DCBA module | 32 @ 8 × 8 | ||
| GMP | 32 @ 1 × 1 | ||
| 2nd-stream 2DCNN | Input | 2 @ 33 × 33 | |
| DCBA module | 2 @ 33 × 33 | ||
| Conv1 | 16 @ 3 × 3/1/1 | 16 @ 33 × 33 | |
| Pooling1 | 2 × 2/2/0 | 16 @ 16 × 16 | |
| DCBA module | 16 @ 16 × 16 | ||
| Conv2 | 32 @ 3 × 3/1/1 | 32 @ 16 × 16 | |
| Pooling2 | 2 × 2/2/0 | 32 @ 8 × 8 | |
| DCBA module | 32 @ 8 × 8 | ||
| GMP | 32 @ 1 × 1 | ||
| Fusion and decision | Two-stream fusion | 64 @ 1 × 1 | |
| Fully connected layer | 5 @ 1 × 1 |
| Condition of Training Data | Condition of Testing Data | Recognition Accuracy of Each State | Average Accuracy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load | Speed | Load | Speed | Nor. | IRF | ORF | REF | |
| 0 | 100 and 300 | 0 | 200 | 98.0% | 94.8% | 96.8% | 96.0% | 96.4% |
| 0 | 200 and 400 | 0 | 300 | 96.4% | 94.0% | 95.2% | 94.0% | 94.9% |
| 10 | 200 and 400 | 10 | 300 | 97.6% | 94.4% | 96.0% | 95.2% | 95.8% |
| 10 | 300 and 500 | 10 | 400 | 95.6% | 94.0% | 94.8% | 94.0% | 94.6% |
| 20 | 300 and 500 | 20 | 400 | 94.4% | 93.2% | 94.0% | 93.6% | 93.8% |
| 20 | 400 and 600 | 20 | 500 | 95.2% | 93.2% | 94.4% | 94.4% | 94.3% |
| 30 | 400 and 600 | 30 | 500 | 95.6% | 93.6% | 96.0% | 94.8% | 95.0% |
| 30 | 500 and 700 | 30 | 600 | 96.0% | 94.0% | 95.6% | 95.2% | 95.2% |
| 0 and 20 | 100 | 10 | 100 | 96.8% | 94.4% | 96.0% | 96.8% | 96.0% |
| 0 and 20 | 200 | 10 | 200 | 96.4% | 92.8% | 95.6% | 93.6% | 94.6% |
| 0 and 20 | 300 | 10 | 300 | 97.2% | 93.2% | 95.2% | 95.2% | 95.2% |
| 10 and 30 | 400 | 20 | 400 | 96.4% | 93.6% | 95.6% | 94.4% | 95.0% |
| 10 and 30 | 500 | 20 | 500 | 96.0% | 94.8% | 95.6% | 95.2% | 95.4% |
| 10 and 30 | 600 | 20 | 600 | 95.6% | 94.4% | 95.2% | 94.0% | 94.8% |
| 10 and 30 | 700 | 20 | 700 | 95.6% | 94.4% | 96.8% | 94.4% | 95.3% |
| Condition of Training Data | Condition of Testing Data | Recognition Accuracy of Each State | Average Accuracy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load Surface | Speed | Load Surface | Speed | Nor. | IRF | ORF | REF | |
| A | 100 and 300 | A | 200 | 95.6% | 92.4% | 95.6% | 95.2% | 94.7% |
| A | 200 and 400 | A | 300 | 96.0% | 93.2% | 94.8% | 94.0% | 94.5% |
| A | 300 and 500 | A | 400 | 96.4% | 92.8% | 94.4% | 94.4% | 94.5% |
| B | 200 and 400 | B | 300 | 95.6% | 93.2% | 94.8% | 94.8% | 94.6% |
| B | 300 and 500 | B | 400 | 95.2% | 92.8% | 94.0% | 93.6% | 93.9% |
| B | 400 and 600 | B | 500 | 94.0% | 92.4% | 93.6% | 93.6% | 93.4% |
| C | 300 and 500 | C | 400 | 94.0% | 91.6% | 93.6% | 93.2% | 93.1% |
| C | 400 and 600 | C | 500 | 94.4% | 92.4% | 94.4% | 94.4% | 93.9% |
| C | 500 and 700 | C | 600 | 93.6% | 92.8% | 94.0% | 94.0% | 93.6% |
| A and C | 100 | B | 100 | 95.2% | 92.8% | 94.8% | 95.2% | 94.5% |
| A and C | 200 | B | 200 | 94.8% | 92.8% | 95.2% | 94.0% | 94.2% |
| A and C | 300 | B | 300 | 95.6% | 92.0% | 94.4% | 94.4% | 94.1% |
| B and C | 300 | A | 300 | 94.0% | 93.2% | 93.6% | 92.8% | 93.4% |
| B and C | 400 | A | 400 | 94.4% | 92.8% | 94.0% | 92.4% | 93.4% |
| B and C | 500 | A | 500 | 94.0% | 94.0% | 92.8% | 91.6% | 93.1% |
| A and B | 500 | C | 500 | 94.0% | 94.4% | 93.2% | 93.2% | 93.7% |
| A and B | 600 | C | 600 | 94.4% | 93.2% | 92.4% | 92.8% | 93.2% |
| A and B | 700 | C | 700 | 94.8% | 93.2% | 93.6% | 94.0% | 93.9% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Ouyang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xue, H.; Yue, H.; Feng, H. In-Wheel Motor Fault Diagnosis Method Based on Two-Stream 2DCNNs with DCBA Module. Sensors 2025, 25, 4617. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154617
Zhu J, Ouyang X, Jiang Z, Xu Y, Xue H, Yue H, Feng H. In-Wheel Motor Fault Diagnosis Method Based on Two-Stream 2DCNNs with DCBA Module. Sensors. 2025; 25(15):4617. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154617
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Junwei, Xupeng Ouyang, Zongkang Jiang, Yanlong Xu, Hongtao Xue, Huiyu Yue, and Huayuan Feng. 2025. "In-Wheel Motor Fault Diagnosis Method Based on Two-Stream 2DCNNs with DCBA Module" Sensors 25, no. 15: 4617. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154617
APA StyleZhu, J., Ouyang, X., Jiang, Z., Xu, Y., Xue, H., Yue, H., & Feng, H. (2025). In-Wheel Motor Fault Diagnosis Method Based on Two-Stream 2DCNNs with DCBA Module. Sensors, 25(15), 4617. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154617






