Piezoelectric Effect of k-Carrageenan as a Tool for Force Sensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
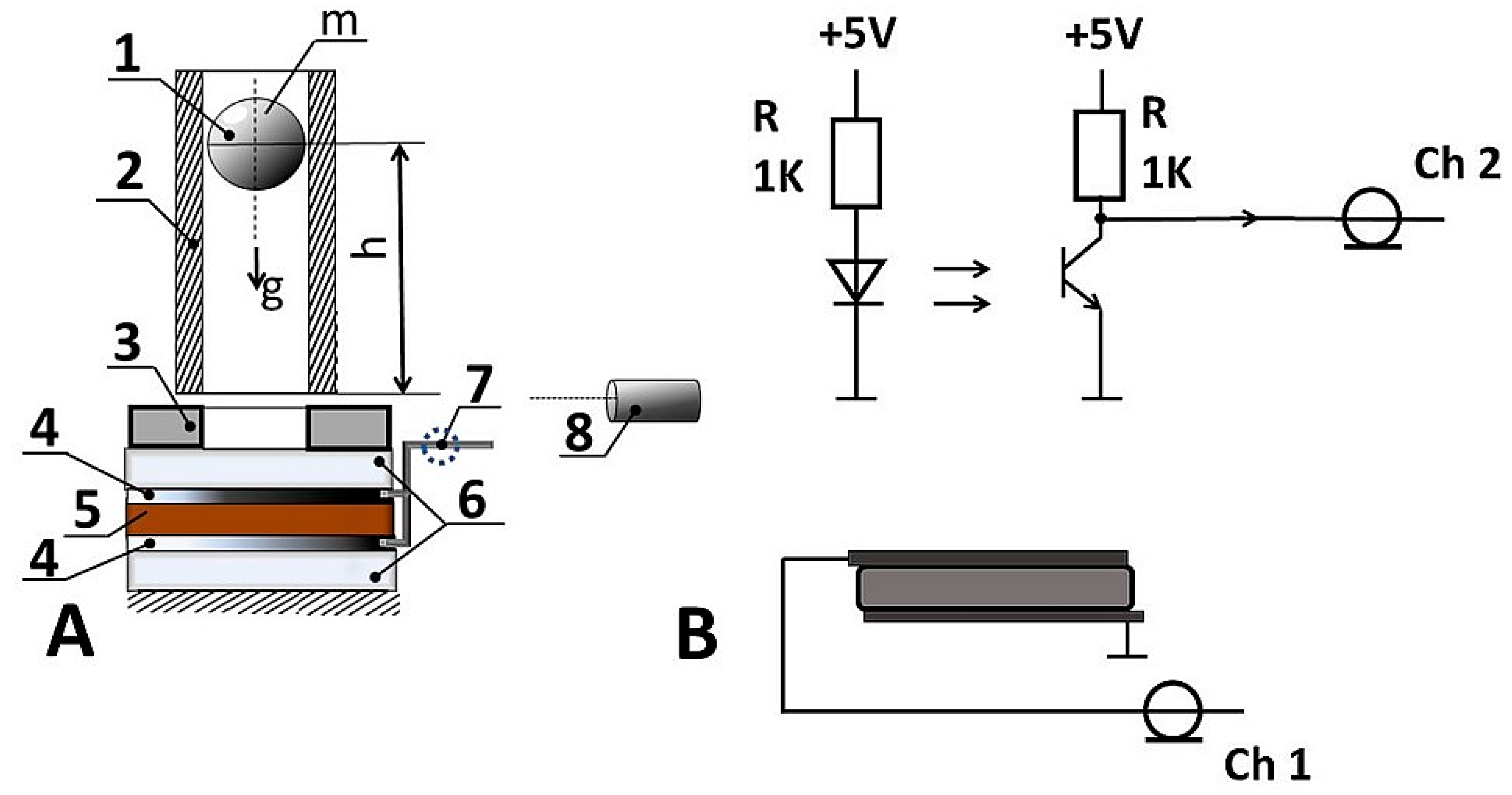
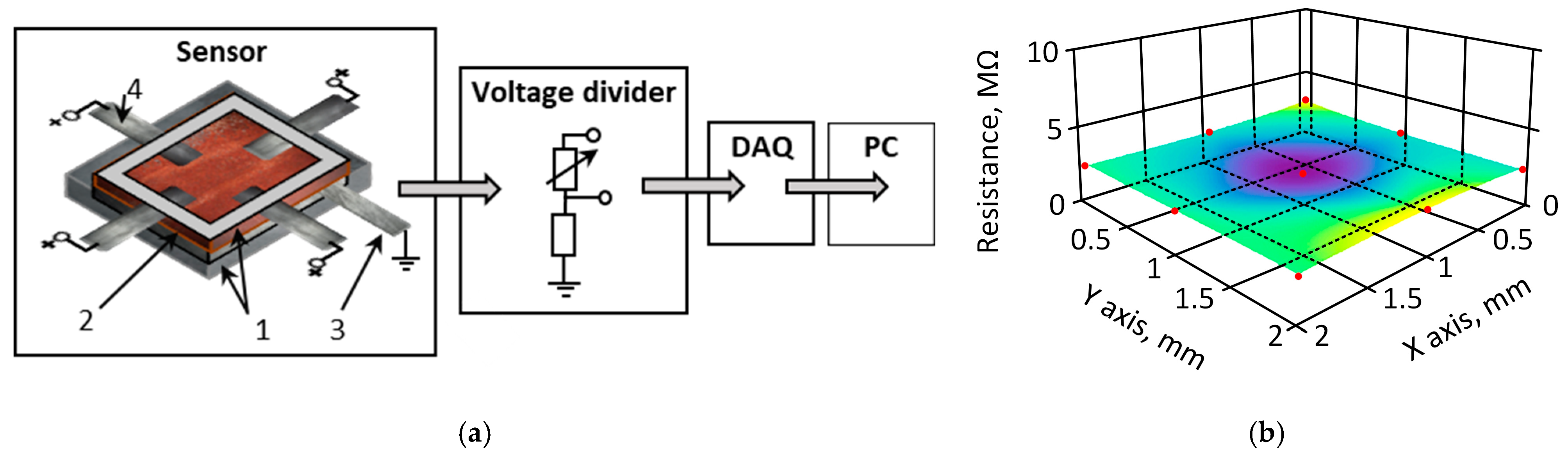
2. Materials and Methods
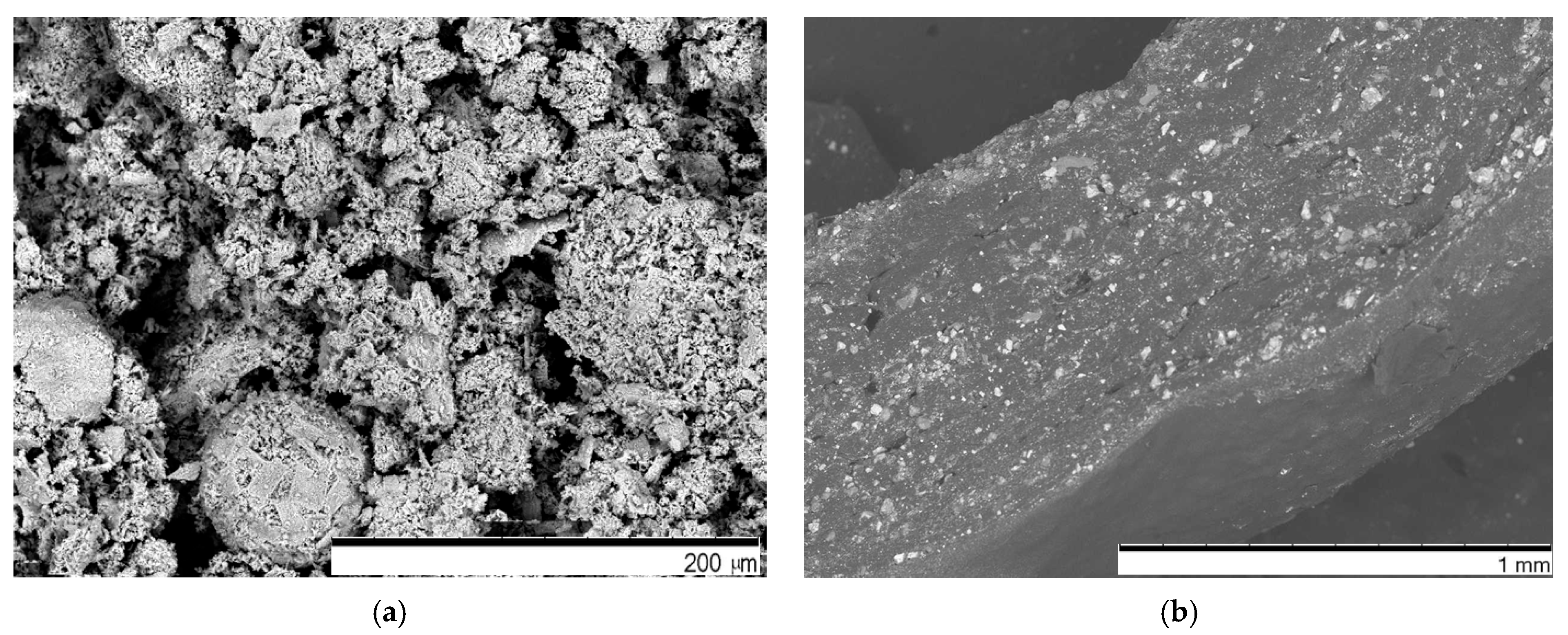
Characterization of the Material
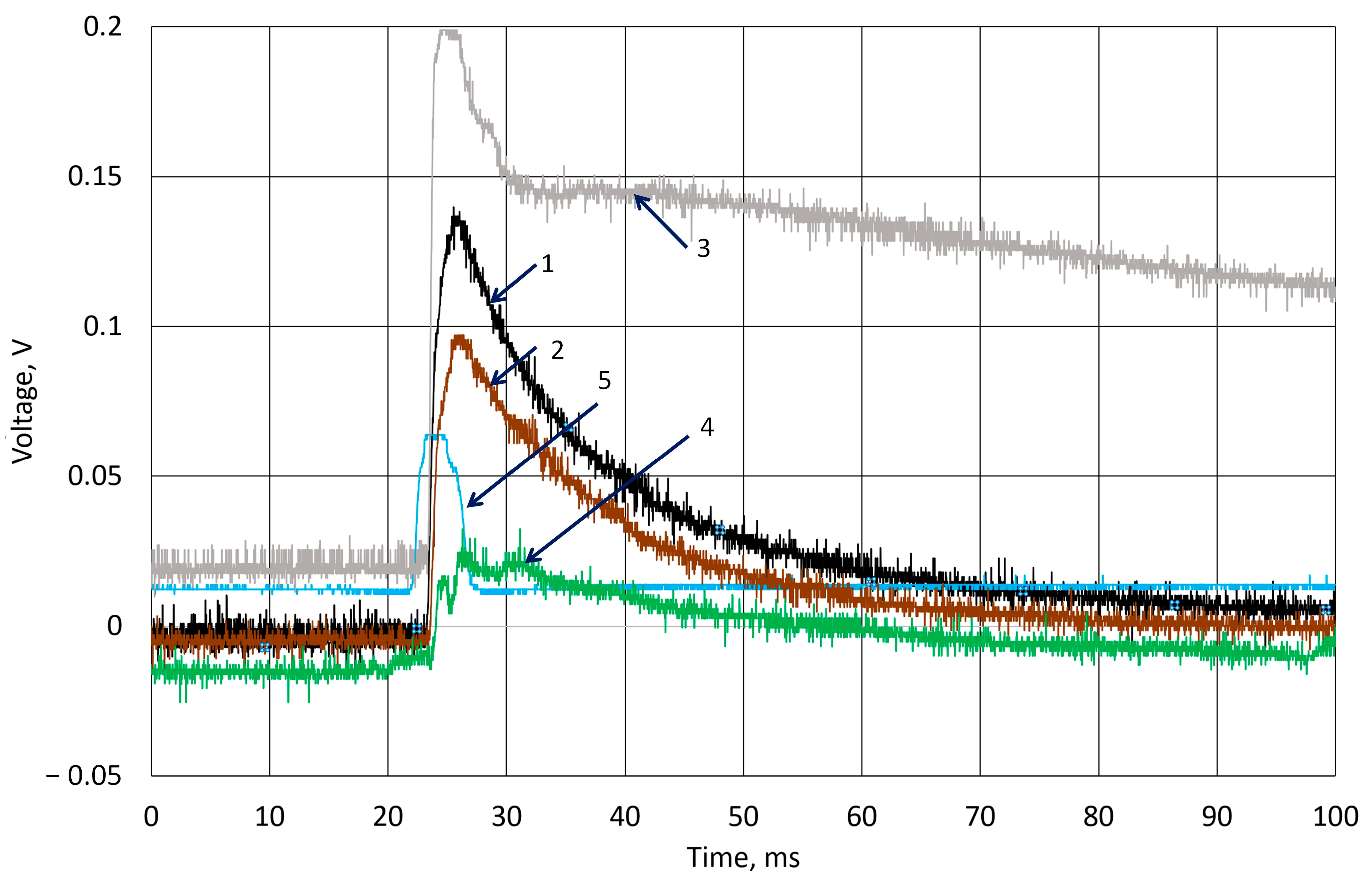
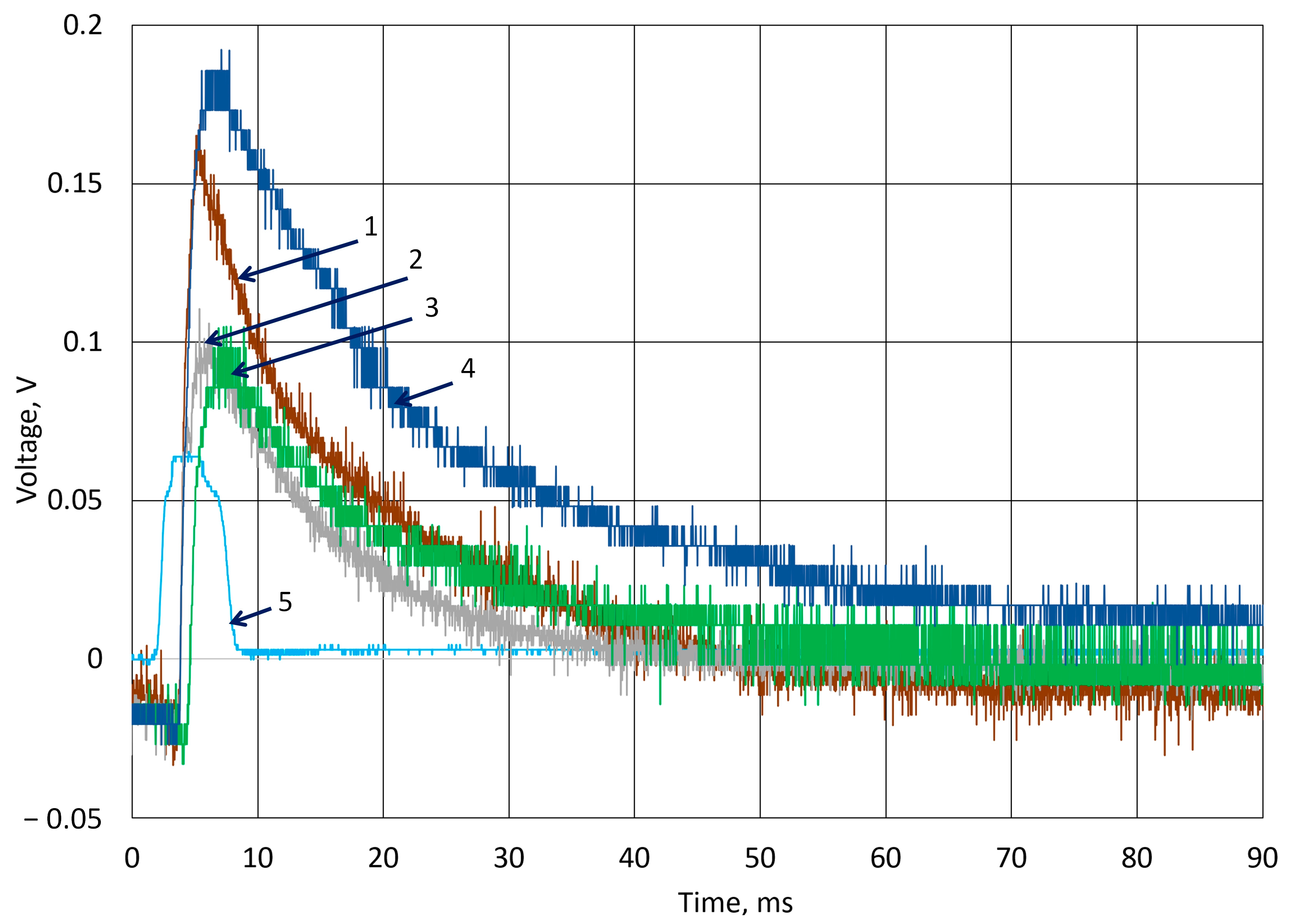
3. Results and Discussion
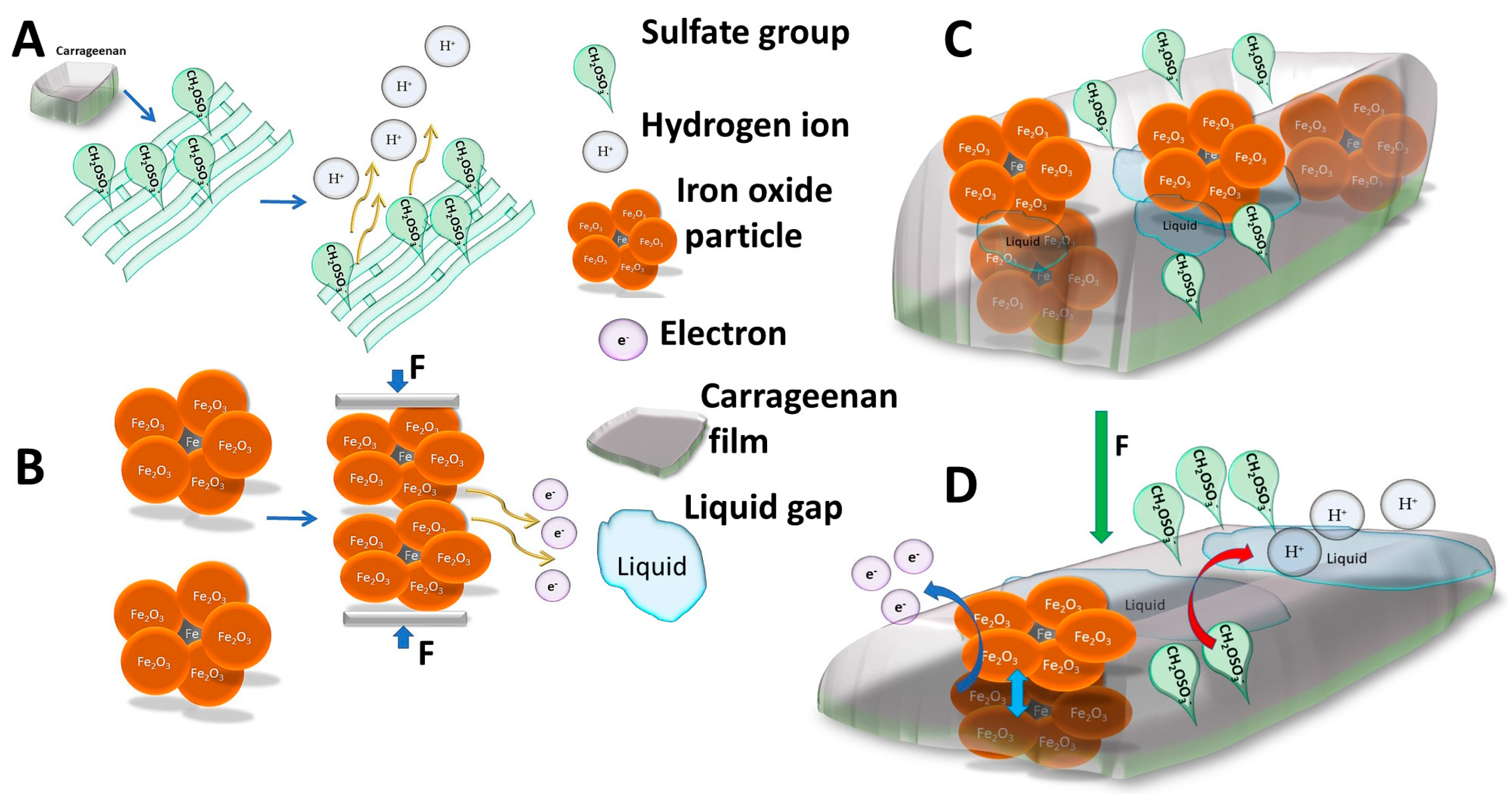
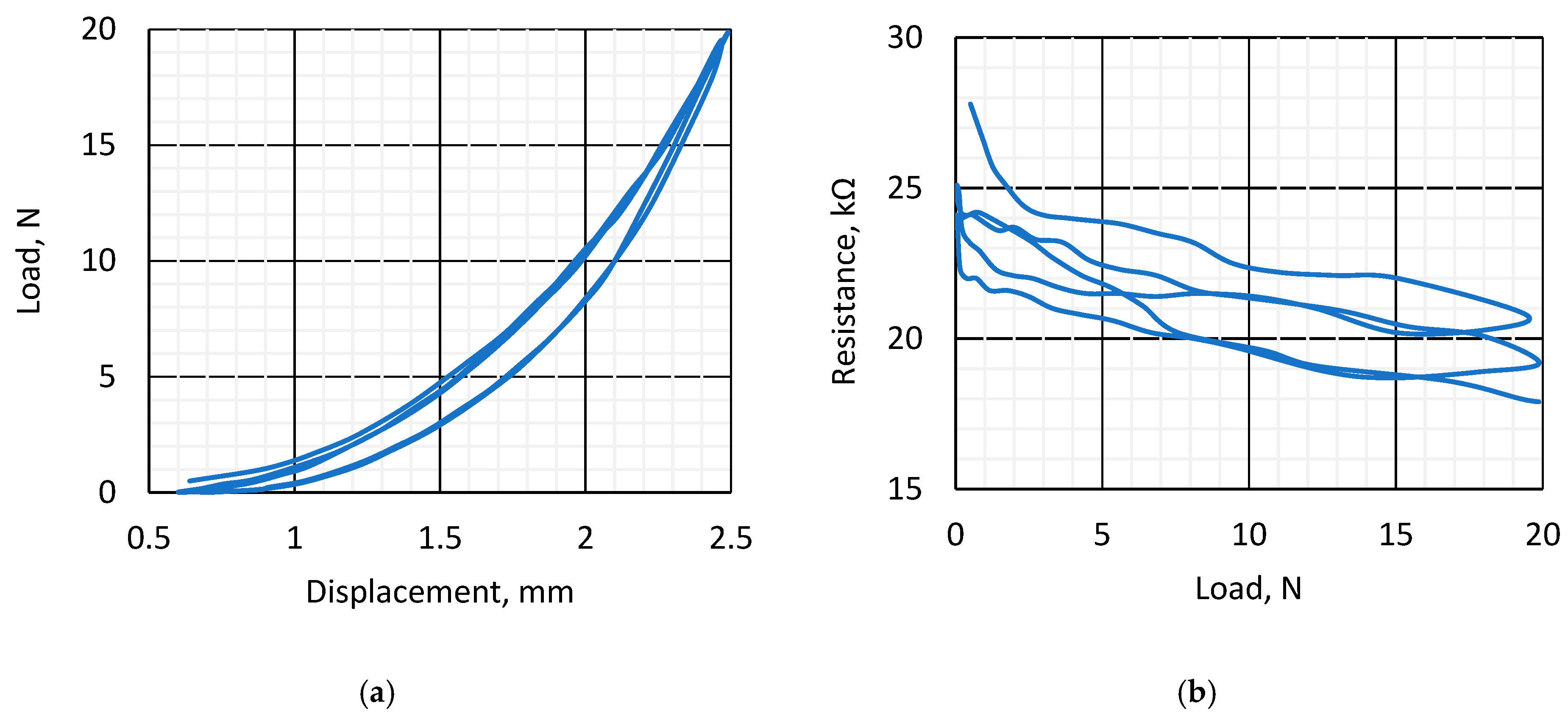
3.1. Piezoresistive and Surface Conductivity and Visual Investigation of k-Carrageenan Film
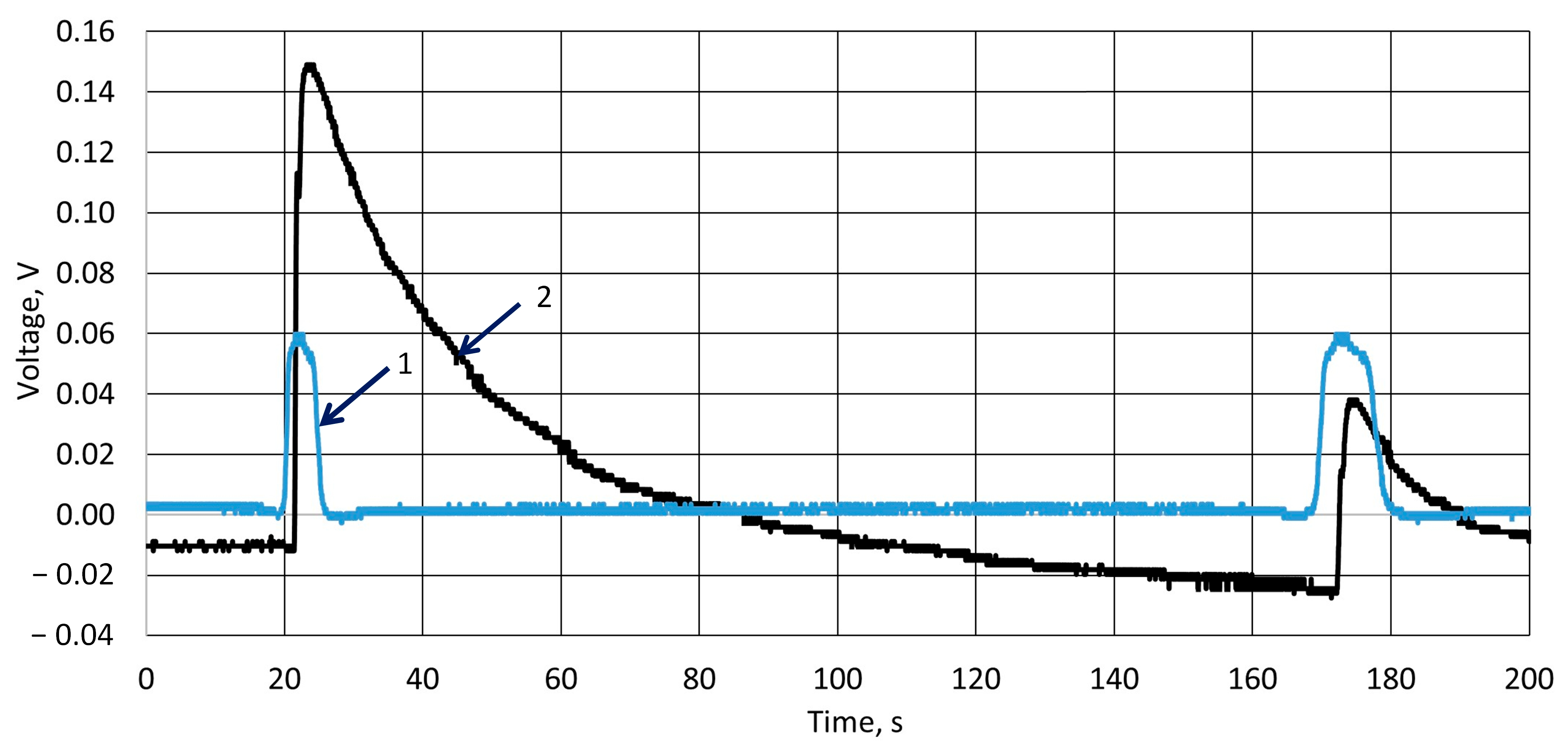
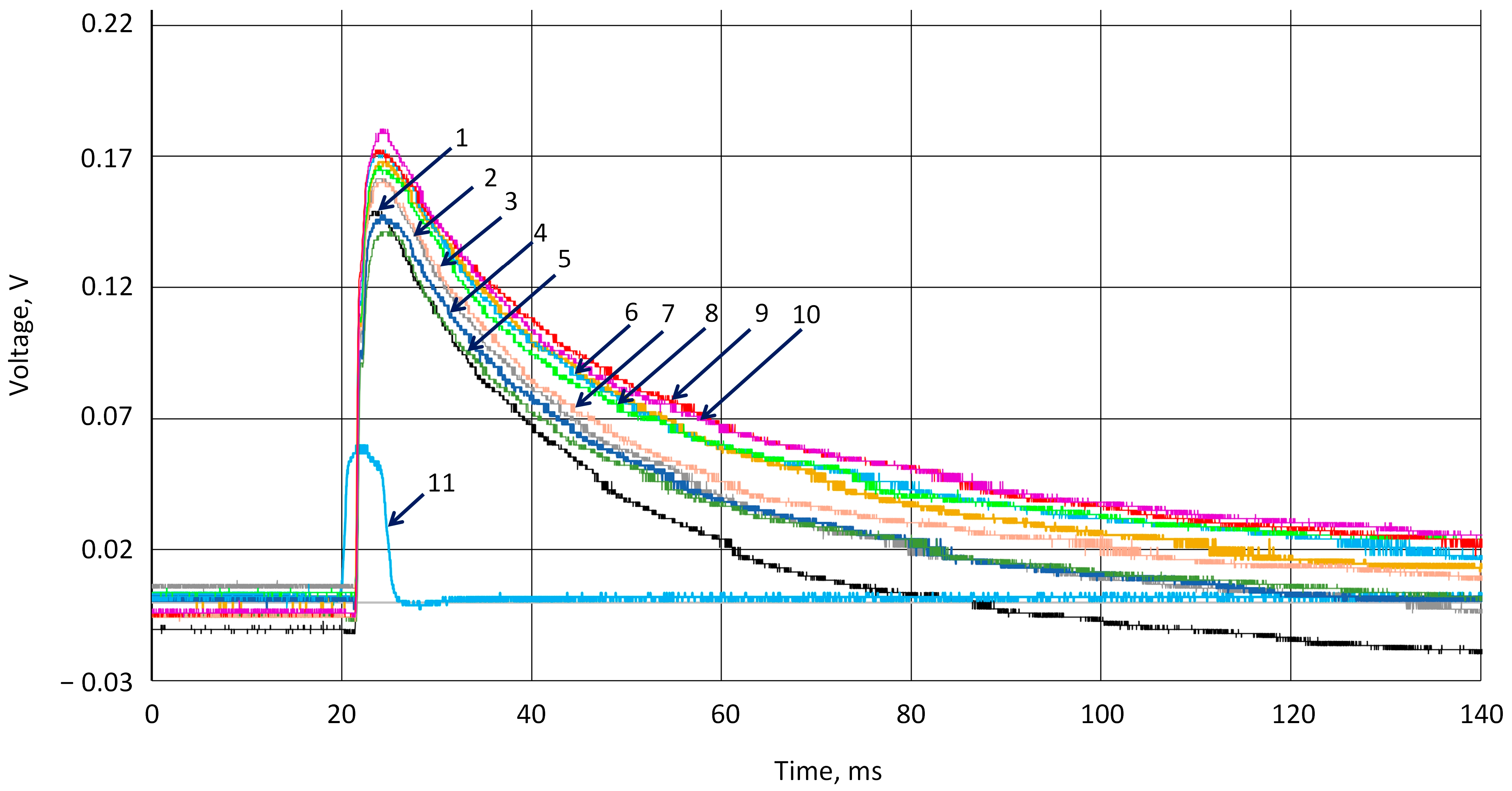
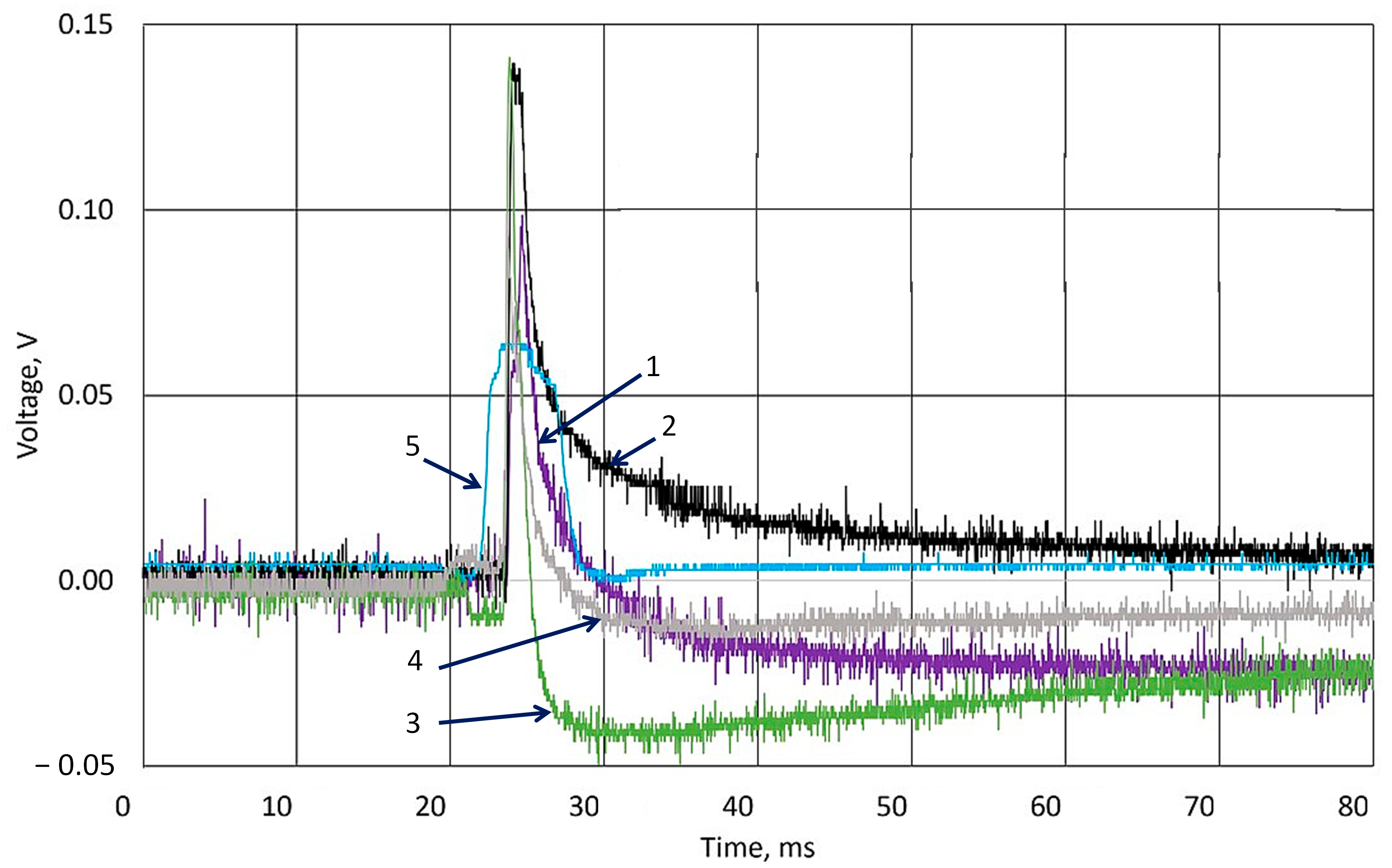
3.2. Investigation of Piezoelectric Behavior of k-Carrageenan Film
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Du, L.; Ma, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Ran, Z.; Zhou, L.; Dong, Q.; Zheng, W.; et al. Highly conductive and stable double network carrageenan organohydrogels for advanced strain sensing and signal recognition arrays. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Li, C.; Li, G.; Yu, D.; Song, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, W. Development of Conductive Hydrogels for Fabricating Flexible Strain Sensors. Small 2022, 18, 2101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bideau, J.; Viau, L.; Vioux, A. Ionogels, ionic liquid based hybrid materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, B.; Lou, Z.; Han, W.; Wang, L. The advancement of intelligent dressings for monitoring chronic wound infections. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, A.C.; Riley, L.; Segura, T.; Burdick, J.A. Hydrogel microparticles for biomedical applications. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 20–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Han, W. A wearable strain sensor based on self-healable MXene/PVA hydrogel for bodily motion detection. Microelectron. Eng. 2024, 291, 112197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Li, S.; Fu, X.; Han, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, G. Research Progress of Flexible Piezoresistive Sensors Based on Polymer Porous Materials. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 3848–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jariwala, T.; Ico, G.; Tai, Y.; Park, H.; Myung, N.V.; Nam, J. Mechano-Responsive Piezoelectric Nanofiber as an On-Demand Drug Delivery Vehicle. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 3706–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lv, C.; Ye, X.; Ping, J.; Ying, Y.; Lan, L. Hydrogel-based pressure sensors for electronic skin systems. Matter 2025, 8, 101992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Shiblee, M.N.I. 4D printing of soft sensors in robotics. In Smart Materials in Additive Manufacturing, Volume 3; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 99–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomatsu, I.; Peng, K.; Kros, A. Photoresponsive hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Li, X.; Hu, X. An Antibacterial, Highly Sensitive Strain Sensor Based on an Anionic Copolymer Interpenetrating with κ-Carrageenan. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 5641–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wu, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, S.; Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Dual Cross-Linked Ion-Based Temperature-Responsive Conductive Hydrogels with Multiple Sensors and Steady Electrocardiogram Monitoring. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 7670–7678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassab, Z.; Aziz, F.; Hannache, H.; Ben Youcef, H.; El Achaby, M. Improved mechanical properties of k-carrageenan-based nanocomposite films reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, B.; Liao, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, D.; Guo, D. Piezoelectric Properties of Fe2O3 Doped BiYbO3-Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 High Curie Temperature Ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 11485–11491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setter, N.; Damjanovic, D.; Eng, L.; Fox, G.; Gevorgian, S.; Hong, S.; Kingon, A.; Kohlstedt, H.; Park, N.Y.; Stephenson, G.B.; et al. Ferroelectric thin films: Review of materials, properties, and applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 051606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichý, J.; Erhart, J.; Kittinger, E.; Přívratská, J. Fundamentals of Piezoelectric Sensorics. Mechanical, Dielectric, and Thermodynamical Properties of Piezoelectric Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 1–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, N.A. Bio-piezoelectricity: Fundamentals and applications in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Biophys. Rev. 2022, 14, 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sappati, K.K.; Bhadra, S. Piezoelectric Polymer and Paper Substrates: A Review. Sensors 2018, 18, 3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Manikkavel, A.; Yewale, M.A.; Alam, M.N.; Park, S.S. Lightweight, compressible, stretchable, ultra-soft, and mechanically stable composites for piezo-electric energy generators and strain sensing. Mater. Res. Bull. 2024, 179, 112962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, E.J.; Ke, K.; Chorsi, M.T.; Wrobel, K.S.; Miller, A.N.; Patel, A.; Kim, I.; Feng, J.; Yue, L.; Wu, Q.; et al. Biodegradable piezoelectric force sensor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fundamentals of Piezoelectricity; Arnau, A.; Soares, D. Fundamentals on Piezoelectricity. In Piezoelectric Transducers and Applications; Arnau Vives, A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. An Introduction to the Theory of Piezoelectricity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Miao, L.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, P. Research Progress of Flexible Piezoresistive Pressure Sensor: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 31624–31644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, J.; Berger, J.; Boz, N.; Tekampe, S.; Oeser, M.; Liu, P. Mechanical and piezoresistive performance of polymethyl methacrylate modified with carbon nanotubes for sensitive road surface. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, N.; Shaler, S. The application of nanoindentation for determination of cellulose nanofibrils (CNF) nanomechanical properties. Mater. Res. Express 2016, 3, 105017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, S.; Dong, S.; Li, Z.; Ouyang, J.; Yu, X.; Han, B. Piezoresistivity, mechanisms and model of cement-based materials with CNT/NCB composite fillers. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 125704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yao, W.; Kawasaki, H. Piezoelectric nanomaterials for antibacterial strategies. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 40, 102419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wu, F.; Qin, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Fan, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Facile fabrication and characterization of double network starch/PVA/NaCl composite hydrogel for flexible strain sensor. React. Funct. Polym. 2025, 208, 106163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, D.; Xu, P.; Xue, W.; Liao, N. Highly sensitive hybrid silicon carbonitride piezoresistive sensors enabled by coupling piezoelectric effect. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Chang, L.; Ren, B.; Han, J.; Li, J. Enhanced braille recognition based on piezoresistive and piezoelectric dual-mode tactile sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 366, 115000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, J.; Jiang, X.; Kim, T. Static Force Measurement Using Piezoelectric Sensors. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 6664200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Yin, F.; Kim, E.S.; Wang, W.; Yoon, D.Y.; Wang, C.; Liang, J.; Li, Y.; Kim, N.Y. Advances in flexible sensors for intelligent perception system enhanced by artificial intelligence. InfoMat 2023, 5, e12412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaimis, U.; Ozolina, S.; Kukuskins, A. Recycled Algae Paper Density Control System for Quality Screening With Adjustable Light Source Wavelength. In Proceedings of the 21st International Scientific Conference on Engineering for Rural Development, Jelgava, Latvia, 25–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žaimis, U.; Petronienė, J.J.; Dzedzickis, A.; Bučinskas, V. Biodegradable Carrageenan-Based Force Sensor: An Experimental Approach. Sensors 2023, 23, 9423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgallas, A.; Landry, G. The coefficient of restitution of pressurized balls: A mechanistic model. Can. J. Phys. 2015, 94, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, R. Differences Between Bouncing Balls, Springs, and Rods. Am. J. Phys. 2008, 76, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gun’ko, V.M.; Savina, I.N.; Mikhalovsky, S.V. Properties of Water Bound in Hydrogels. Gels 2017, 3, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Chen, Y.; Lv, S.; Zuo, J.; Liu, L.; Mu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. One-step fabrication of dual-network cellulose-based hydrogel sensors with high flexibility and conductivity under ZnCl2 solvent method for flexible sensing properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 295, 139440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, A. Piezoelectric Materials. In Advanced Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 43–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toroń, B.; Szperlich, P.; Nowak, M.; Starczewska, A. A novel method for measuring piezoelectric coefficients. Measurement 2023, 206, 112274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.M.; Yun, K.S.; Ballenger, L.W.; Hackerman, N. Semiconductor Properties of Iron Oxide Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1979, 126, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, G.S. Iron oxide surfaces. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2016, 71, 272–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.G.B.; Scherer, M.M. Spectroscopic evidence for Fe(II)-Fe(III) electron transfer at the iron oxide-water interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4782–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Miao, Q.; Wu, D. Data simulation of the impact of ball strikes on the bottom of electric vehicle battery packs based on finite element analysis. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2024, 53, 102757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Azwan Ismail, K.; Ahmad, M.; Ismail, K.; Mat, F. Impact models and coefficient of restitution: A review. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2016, 11, 6549–6555. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/304883246 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Pongali, P.; Kasim, N.; Hanibah, H.; Rosli, N.H.A.; Rani, M.S.A.; Noor, S.A.M.; Abdullah, N.; Shamsudin, I.J. Glutaryl kappa-carrageenan: Synthesis, characterization and investigation of potential as gel-based biopolymer electrolyte. Polym. Bull. 2025, 82, 5693–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masalskyi, V.; Petroniene, J.J.; Petkevicius, S.; Piliukaityte, U.; Zaimis, U.; Malani, U.; Dzedzickis, A.; Bučinskas, V. Characterization of k-Carrageenan and Iron (III) Oxide Based Piezoresistive Film by Microrobotic System. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE Open Conference of Electrical, Electronic and Information Sciences (eStream), Vilnius, Lithuania, 24 April 2025; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, V.D.; Arul, N.S. Review on α-Fe2O3 based negative electrode for high performance supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 2016, 327, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Yudewitz, N.; Subhash, G.; Spearot, D.E. Effect of water concentration on the shock response of polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA) hydrogels: A molecular dynamics study. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 90, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bučinskas, V.; Žaimis, U.; Udris, D.; Petronienė, J.J.; Dzedzickis, A. Piezoelectric Effect of k-Carrageenan as a Tool for Force Sensor. Sensors 2025, 25, 4594. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154594
Bučinskas V, Žaimis U, Udris D, Petronienė JJ, Dzedzickis A. Piezoelectric Effect of k-Carrageenan as a Tool for Force Sensor. Sensors. 2025; 25(15):4594. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154594
Chicago/Turabian StyleBučinskas, Vytautas, Uldis Žaimis, Dainius Udris, Jūratė Jolanta Petronienė, and Andrius Dzedzickis. 2025. "Piezoelectric Effect of k-Carrageenan as a Tool for Force Sensor" Sensors 25, no. 15: 4594. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154594
APA StyleBučinskas, V., Žaimis, U., Udris, D., Petronienė, J. J., & Dzedzickis, A. (2025). Piezoelectric Effect of k-Carrageenan as a Tool for Force Sensor. Sensors, 25(15), 4594. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25154594









