Towards Precision Nutrition: A Novel Smartphone-Connected Biosensor for Point-of-Care Detection of β-Hydroxybutyrate in Human Blood and Saliva
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
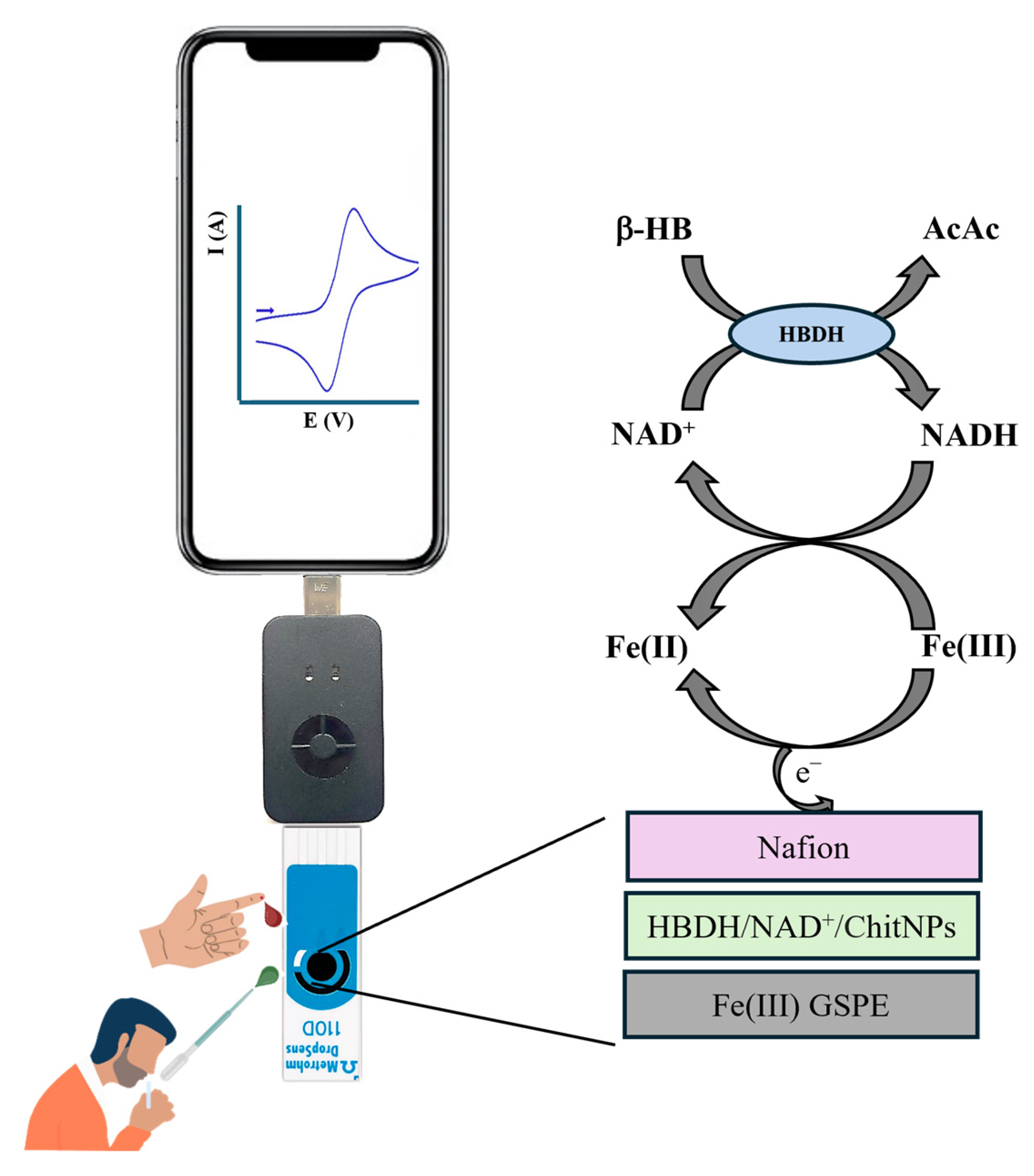
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Biosensor Fabrication
2.4. Real Samples Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
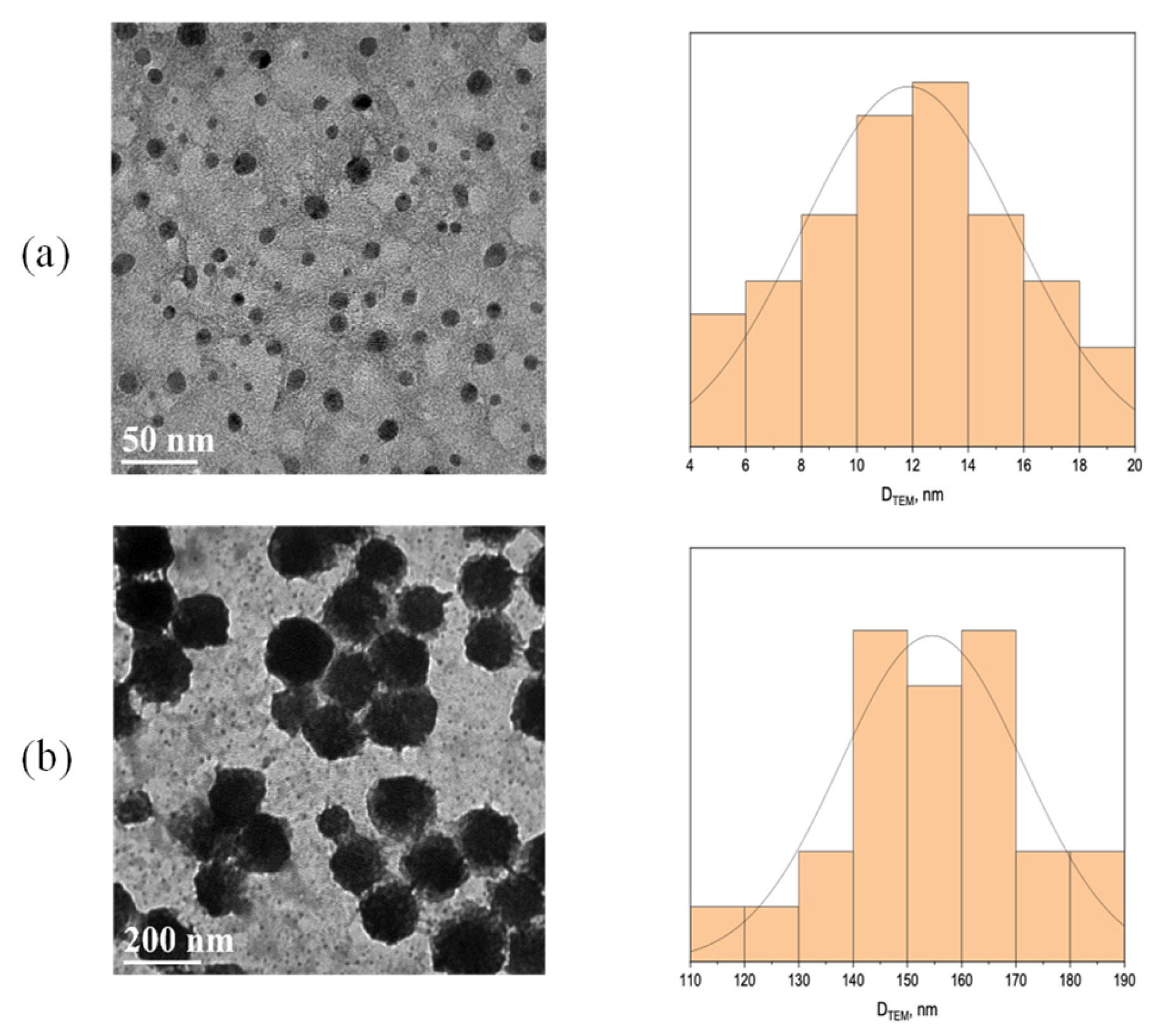
3.1. TEM Characterization
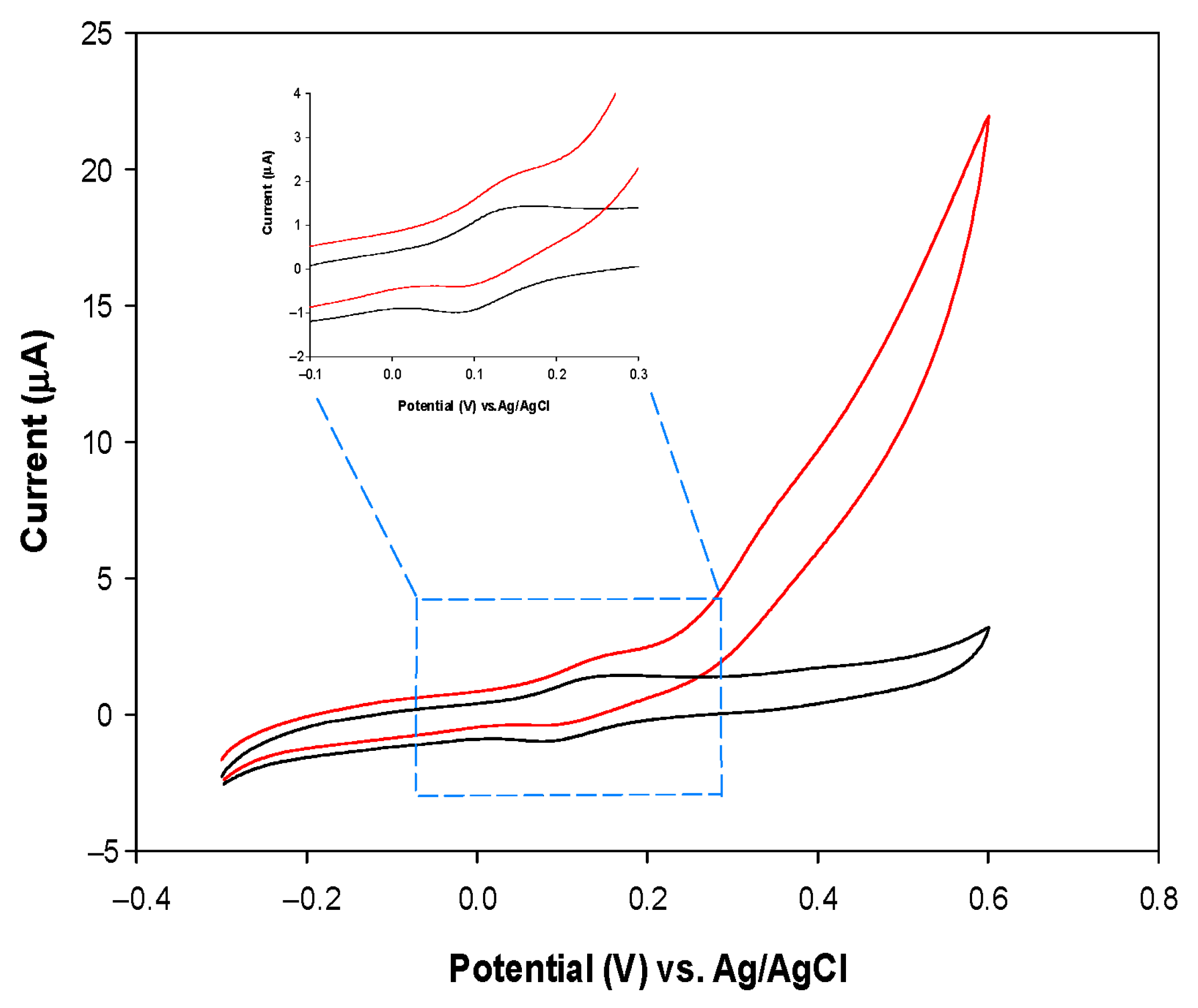
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization of the PVC/HBDH/NAD+/ChitNPs/Fe(III)GSPE Platform
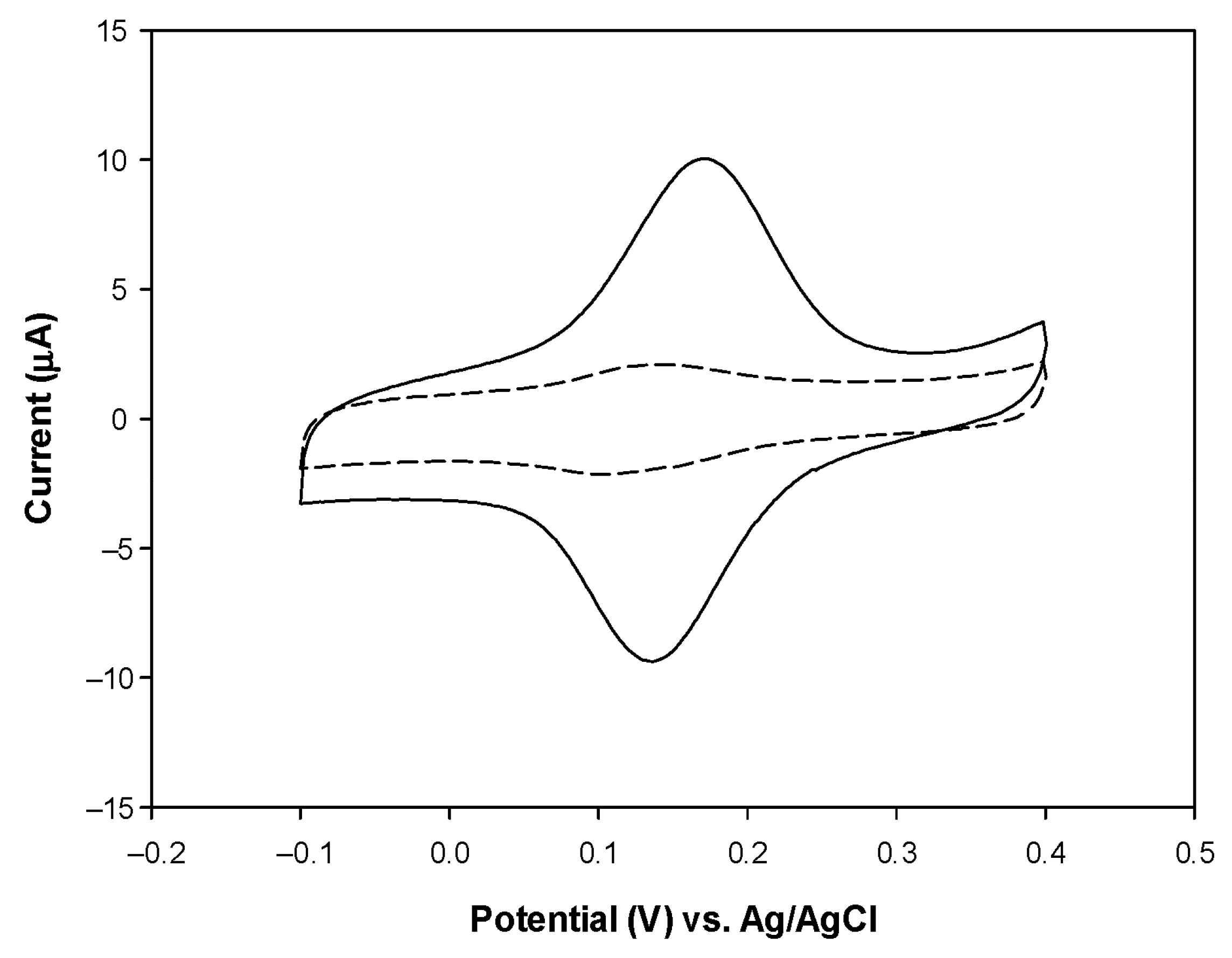
3.3. Effect of NAD+ and pH on Biosensor Current Response
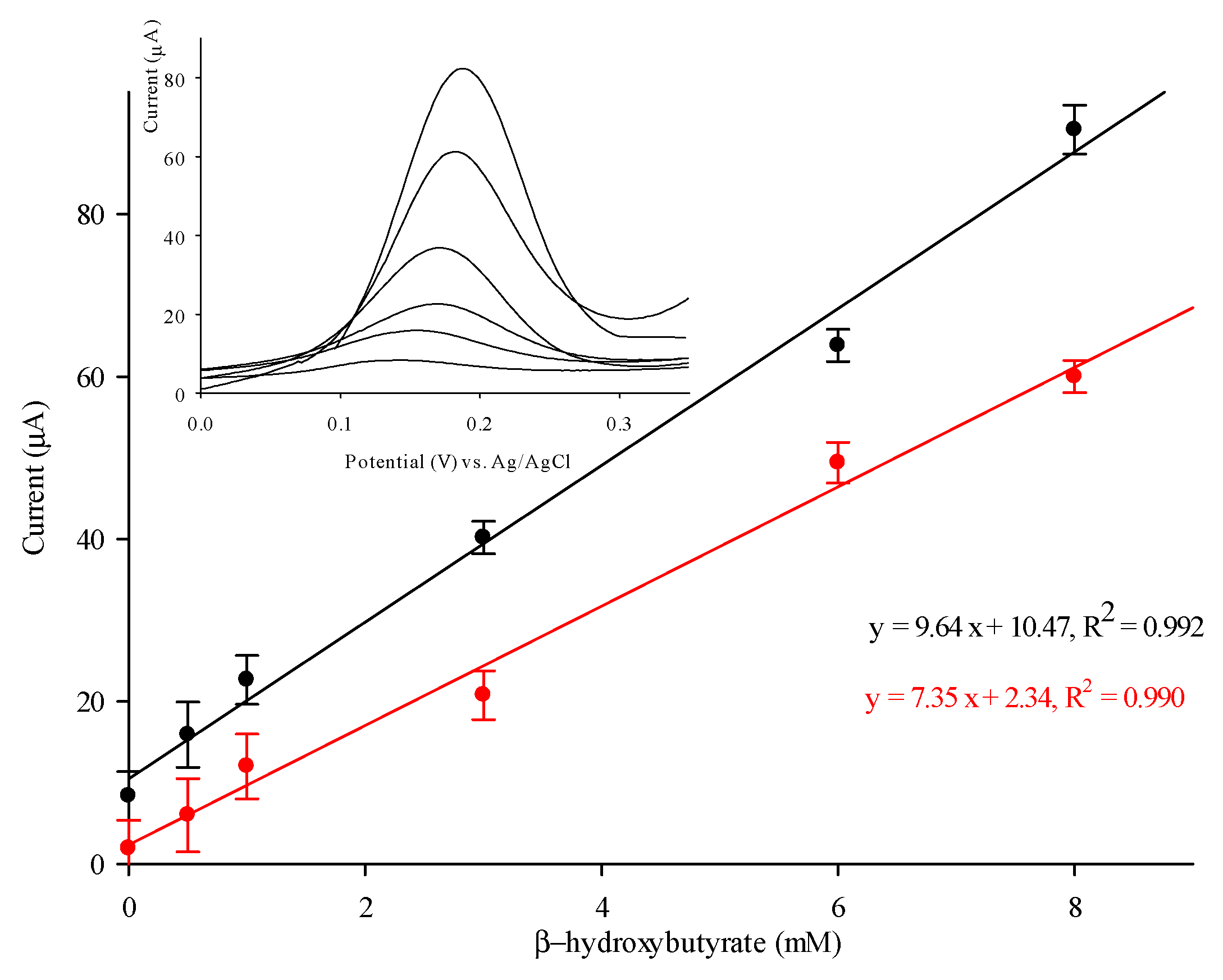
3.4. Detection of β-HB with PVC/HBDH/NAD+/ChitNPs/Fe(III)GSPE Biosensor
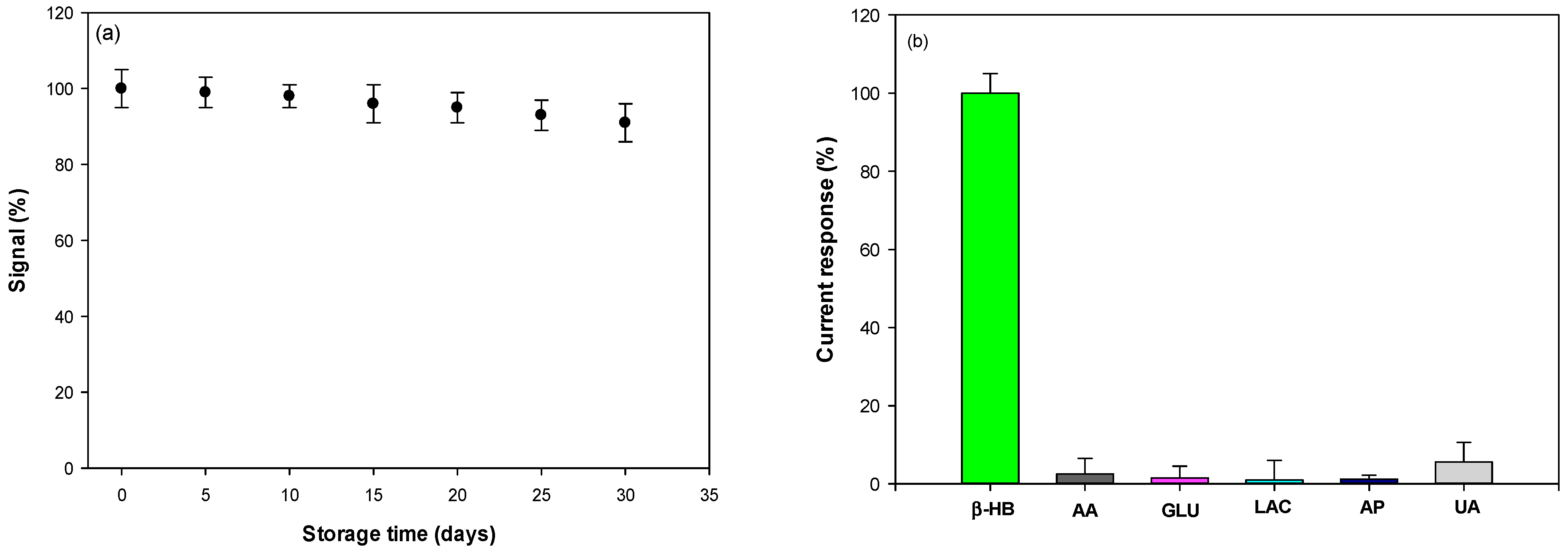
3.5. Reproducibility, Stability, and Selectivity
3.6. Detection of β-HB in Human Blood and Saliva
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wallace, T.M.; Matthews, D.R. Recent advances in the monitoring and management of diabetic ketoacidosis. QJM Int. J. Med. 2004, 97, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laffel, L. Ketone bodies: A review of physiology, pathophysiology and application of monitoring to diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 1999, 15, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempionatto, J.R.; Montiel, V.R.V.; Vargas, E.; Teymourian, H.; Wang, J. Wearable and mobile sensors for personalized nutrition. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1745–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, A.; Park, S.R.; Ku, Y.; Sun, M.; Yeon, S.; Lee, J.-K.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, M.-H. Highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) by measuring ketone bodies in urine. Sensors 2021, 21, 4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Caño, R.; Saha, T.; Moonla, C.; De la Paz, E.; Wang, J. Ketone bodies detection: Wearable and mobile sensors for personalized medicine and nutrition. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 159, 116938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, M.; Totani, M. A chemiluminescence-flow injection analysis of serum 3-hydroxybutyrate using a bioreactor consisting of 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase and NADH oxidase. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 229, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Matsuoka, A.; Hayashi, K.; Kimura, Y. Head-space gas-chromatographic determination of 3-hydroxybutyrate in plasma after enzymic reactions, and the relationship among the three ketone bodies. Clin. Chem. 1985, 31, 596–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avogaro, A.; Bier, D.M. Contribution of 3-hydroxyisobutyrate to the measurement of 3-hydroxybutyrate in human plasma: Comparison of enzymatic and gas-liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry assays in normal and in diabetic subjects. J. Lipid Res. 1989, 30, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, L.K.; Rittig, N.F.; Holmquist, E.F.; Jørgensen, K.A.; Jørgensen, J.O.L.; Møller, N.; Johannsen, M. Simultaneous determination of beta-hydroxybutyrate and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate in human whole blood using hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsand, F.; Darziani Azizi, M.; Naeemy, A.; Larijani, B.; Omidfar, K. An electrochemical biosensor for 3-hydroxybutyrate detection based on screen-printed electrode modified by coenzyme functionalized carbon nanotubes. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 2327–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrow, N.J.; Sanghera, G.S.; Walters, S.J.; Watkin, J.L. Development of a commercial amperometric biosensor electrode for the ketone D-3-hydroxybutyrate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 20, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ma, N.Z.; Wang, Y. A new handheld biosensor for monitoring blood ketones. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 109, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J. Smartphone-powered electrochemical dongle for point-of-care monitoring of blood β-ketone. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8609–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-García, G.; Pérez-Julián, E.; Agüí, L.; Cabré, N.; Joven, J.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. An electrochemical enzyme biosensor for 3-hydroxybutyrate detection using screen-printed electrodes modified by reduced graphene oxide and thionine. Biosensors 2017, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, T.; Sumiya, T.; Ono, M.; Ito, T.; Hanaoka, T.A. A novel, disposable, screen-printed amperometric biosensor for ketone 3-β-hydroxybutyrate fabricated using a 3-β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase-mesoporous silica conjugate. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerapandian, M.; Hunter, R.; Neethirajan, S. Ruthenium dye sensitized graphene oxide electrode for on-farm rapid detection of beta-hydroxybutyrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonla, C.; Reynoso, M.; Casanova, A.; Chang, A.Y.; Djassemi, O.; Balaje, A.; Abbas, A.; Li, Z.; Mahato, K.; Wang, J. Continuous ketone monitoring via wearable microneedle patch platform. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mugo, S.M.; Zhang, Q. Integrated wearable sensors for sensing physiological pressure signals and β-hydroxybutyrate in physiological fluids. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonla, C.; Del Caño, R.; Sakdaphetsiri, K.; Saha, T.; De la Paz, E.; Düsterloh, A.; Wang, J. Disposable screen-printed electrochemical sensing strips for rapid decentralized measurements of salivary ketone bodies: Towards therapeutic and wellness applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 220, 114842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourian, H.; Moonla, C.; Tehrani, F.; Vargas, E.; Aghavali, R.; Barfidokht, A.; Tangkuaram, T.; Mercier, P.P.; Dassau, E.; Wang, J. Microneedle-based detection of ketone bodies along with glucose and lactate: Toward real-time continuous interstitial fluid monitoring of diabetic ketosis and ketoacidosis. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 2291–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.B. From personalized nutrition to precision medicine: The rise of consumer genomics and digital health. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigli, V.; Tortolini, C.; Capecchi, E.; Angeloni, A.; Lenzi, A.; Antiochia, R. Novel amperometric biosensor based on tyrosinase/chitosan nanoparticles for sensitive and interference-free detection of total catecholamine. Biosensors 2022, 12, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baluchi, A.; Homaei, A. Immobilization of L-asparaginase on chitosan nanoparticles for the purpose of long-term application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, F.; Mandal, T.; Leech, D.; Magner, E. An electrochemical NADH biosensor based on a nanoporous gold electrode modified with diaphorase and an osmium polymer. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2022, 4, 100117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wang, S.-H.; Liu, C.-C. An electrochemical biosensor of the ketone 3-β-hydroxybutyrate for potential diabetic patient management. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 129, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chick, S.; Kachouei, M.A.; Knowlton, K.; Ali, M.A. Functionalized graphene-based biosensors for early detection of subclinical ketosis in dairy cows. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 51932–51943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, I.M.; Treloar, P.H.; Vadgama, P. Plasticized poly(vinyl chloride) as a permselective barrier membrane for high-selectivity amperometric sensors and biosensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 1992, 269, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenbacher, S.; Yang, C.-Y.; Kuan, T.-C.; Demircik, F.; Hanna, M.; Pfützner, A. System accuracy assessments with a blood glucose meter with combined glucose and β-hydroxybutyrate measurement capabilities. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 19, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.R.; Holland-Winkler, A.M.; Ansley, J.K.; Boone, E.D.H.; Schulte, M.K.O.R. Reliability and diagnostic performance of a new blood ketone and glucose meter in humans. Sports Nutr. Rev. J. 2021, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Electrode Platform | Electrochemical Signal | Sensing Modalities | Linear Range (mM) | LOD (µM) | Test Samples | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iridium–carbon ink/HBDH/NAD+/BSA | NADH oxidation | Amperometry | 0–10 | - | Bovine serum | [25] |
| CarbonSPE/K3[Fe(CN)6]/HBDH/NAD+ | Mediator oxidation | Amperometry | 0.01–5.28 | 14.41 | Human blood and serum | [12] |
| Graphene nanosheets/CarbonSPE/ferro-ferricyanide/HBDH/NAD+/glycerol | Ferrocyanide oxidation | CV | 0.00001–0.1 0.25–3.0 | 0.0002 | Spiked bovine serum | [26] |
| Carbon SPE/RGO/thionine/HBDH/NAD+ | Thionine oxidation | Amperometry | 0.01–1 | 9 | Spiked human serum | [14] |
| Carbon ink/Fe(III)-Fe(II)/BHDH/NAD+ | Fe(II) oxidation | CA | 0–4 | - | Human blood | [13] |
| Au coated/carbon SPE/TBO/HBDH/NAD+/ MWCNTs/Chit/PVC | TBO oxidation | Amperometry | 0.1–1 1–3 | 65 | Human saliva | [19] |
| Au/GA/BSA/HBDH/NAD+ | NADH oxidation | CV | 0.6–1 | 600 | Human urine | [4] |
| GSPE/Ru(II)/GO/HBDH/NAD+ | Ru(II) oxidation | Amperometry | 0.2–2.0 | - | Bovine serum | [16] |
| Fe(III)GSPE/HBDH/NAD+/ ChitNPs/PVC | Fe(II) oxidation | DPV | 0.4–8 | 0.2 | Human blood and saliva | this work |
| Human Sample | Human Blood and Saliva b-HB Concentration (mM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biosensor * (Blood) | Ketone Meter * (Blood) | Biosensor * (Saliva) | ELISA (Blood) | ELISA (Saliva) | |
| 1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.2 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.1 |
| 2 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.1 |
| 3 | 1.6 ± 0.2 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 1.4 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tortolini, C.; Caprio, M.; Gianfrilli, D.; Lenzi, A.; Antiochia, R. Towards Precision Nutrition: A Novel Smartphone-Connected Biosensor for Point-of-Care Detection of β-Hydroxybutyrate in Human Blood and Saliva. Sensors 2025, 25, 4336. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144336
Tortolini C, Caprio M, Gianfrilli D, Lenzi A, Antiochia R. Towards Precision Nutrition: A Novel Smartphone-Connected Biosensor for Point-of-Care Detection of β-Hydroxybutyrate in Human Blood and Saliva. Sensors. 2025; 25(14):4336. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144336
Chicago/Turabian StyleTortolini, Cristina, Massimiliano Caprio, Daniele Gianfrilli, Andrea Lenzi, and Riccarda Antiochia. 2025. "Towards Precision Nutrition: A Novel Smartphone-Connected Biosensor for Point-of-Care Detection of β-Hydroxybutyrate in Human Blood and Saliva" Sensors 25, no. 14: 4336. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144336
APA StyleTortolini, C., Caprio, M., Gianfrilli, D., Lenzi, A., & Antiochia, R. (2025). Towards Precision Nutrition: A Novel Smartphone-Connected Biosensor for Point-of-Care Detection of β-Hydroxybutyrate in Human Blood and Saliva. Sensors, 25(14), 4336. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144336









