Application of Surface Electromyography (sEMG) in the Analysis of Upper Limb Muscle Activity in Women Aged 50+ During Torqway Riding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
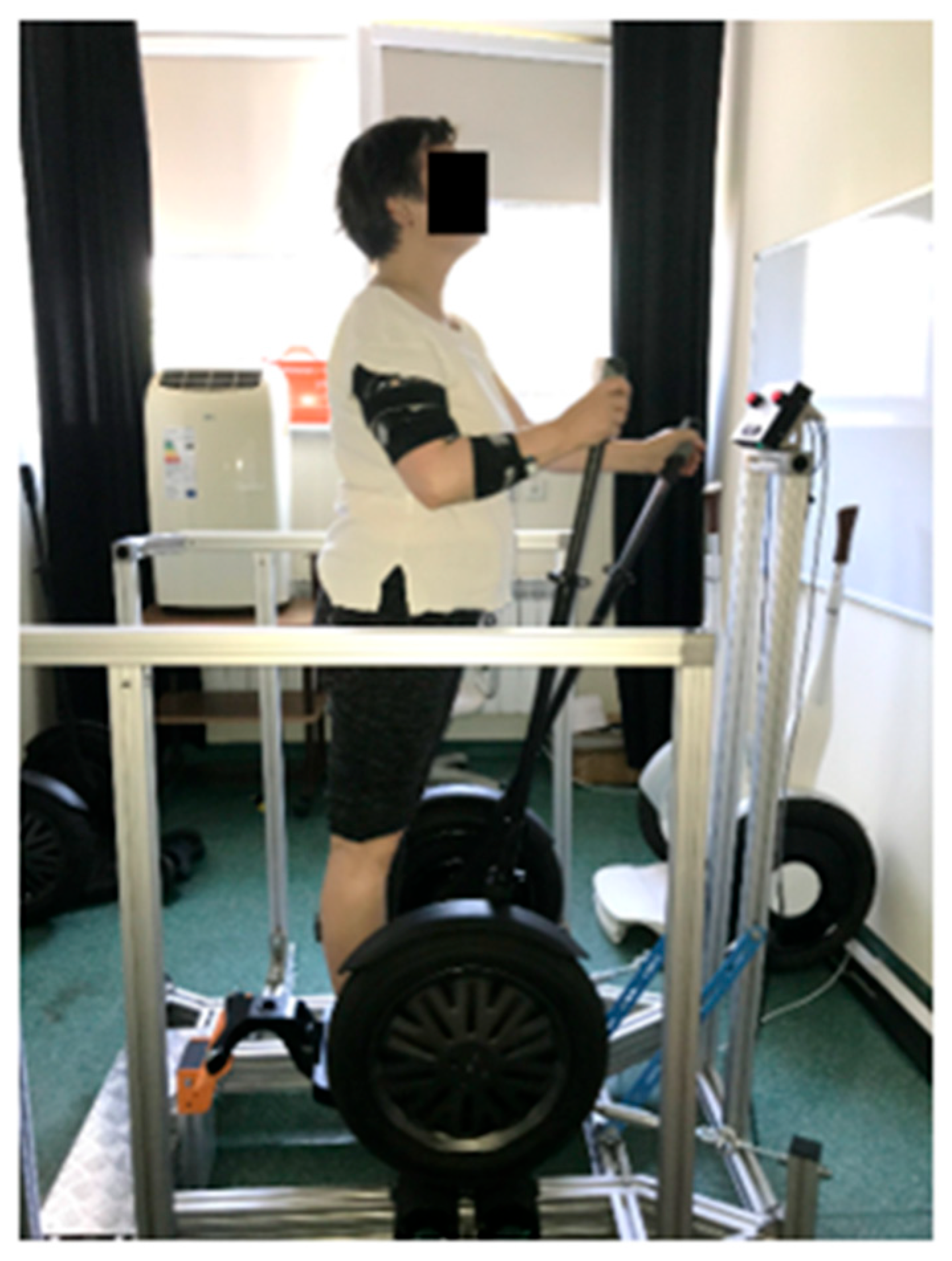
2.2. Test Environment and Equipment
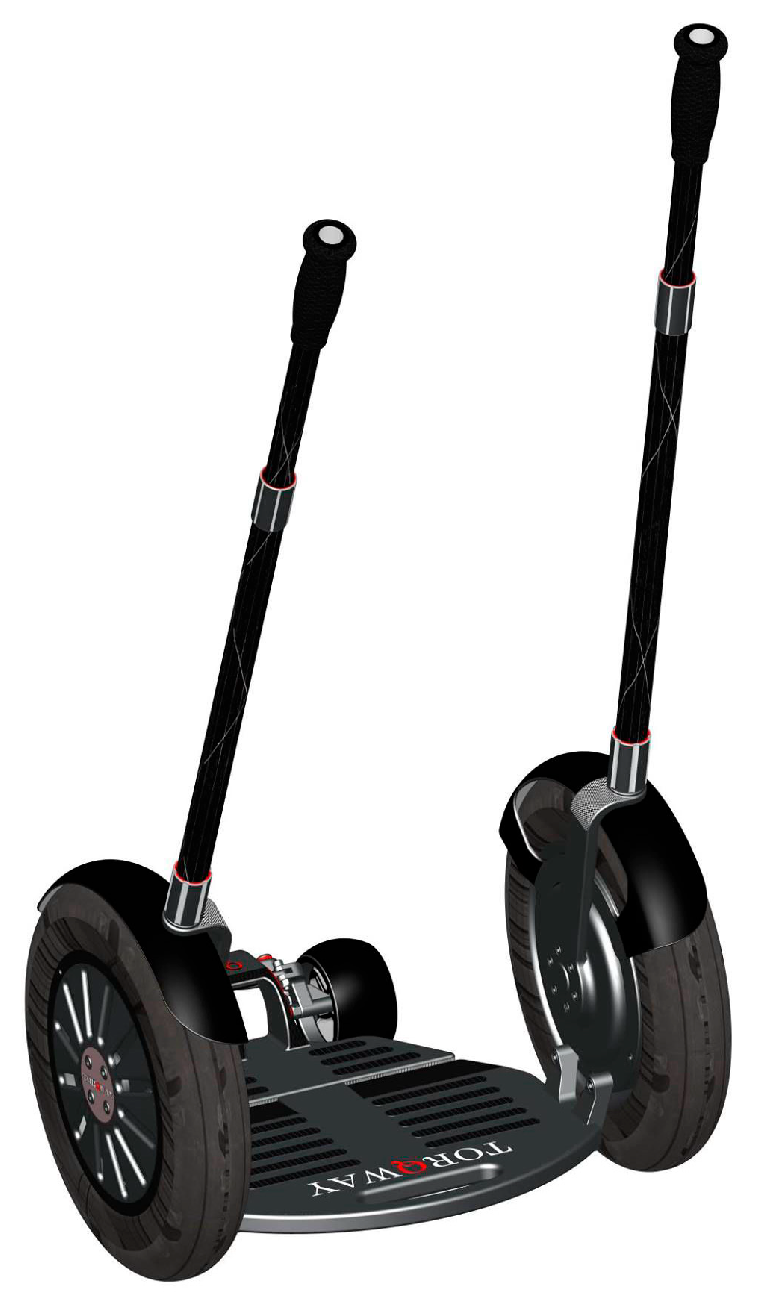
Description of the Torqway Device
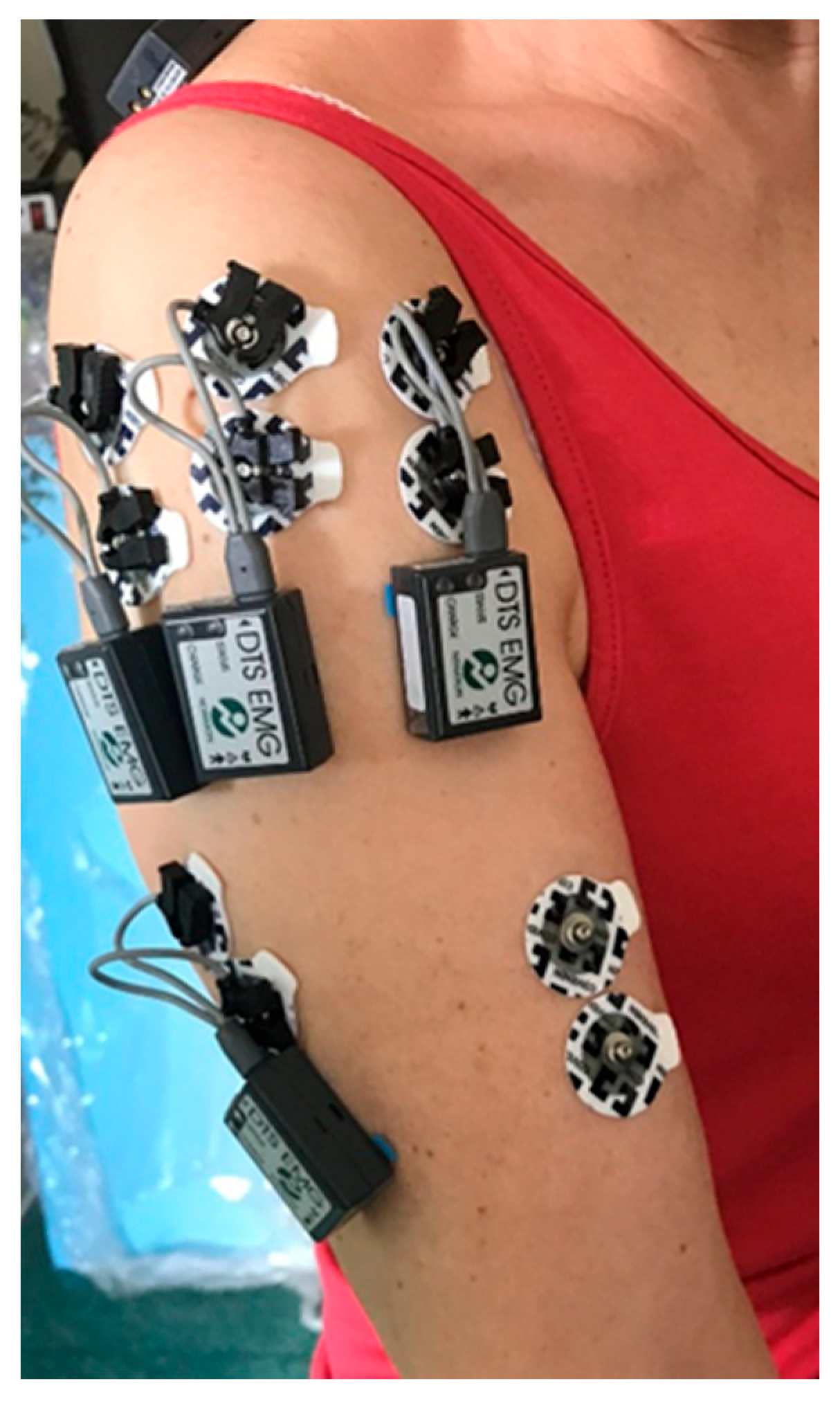
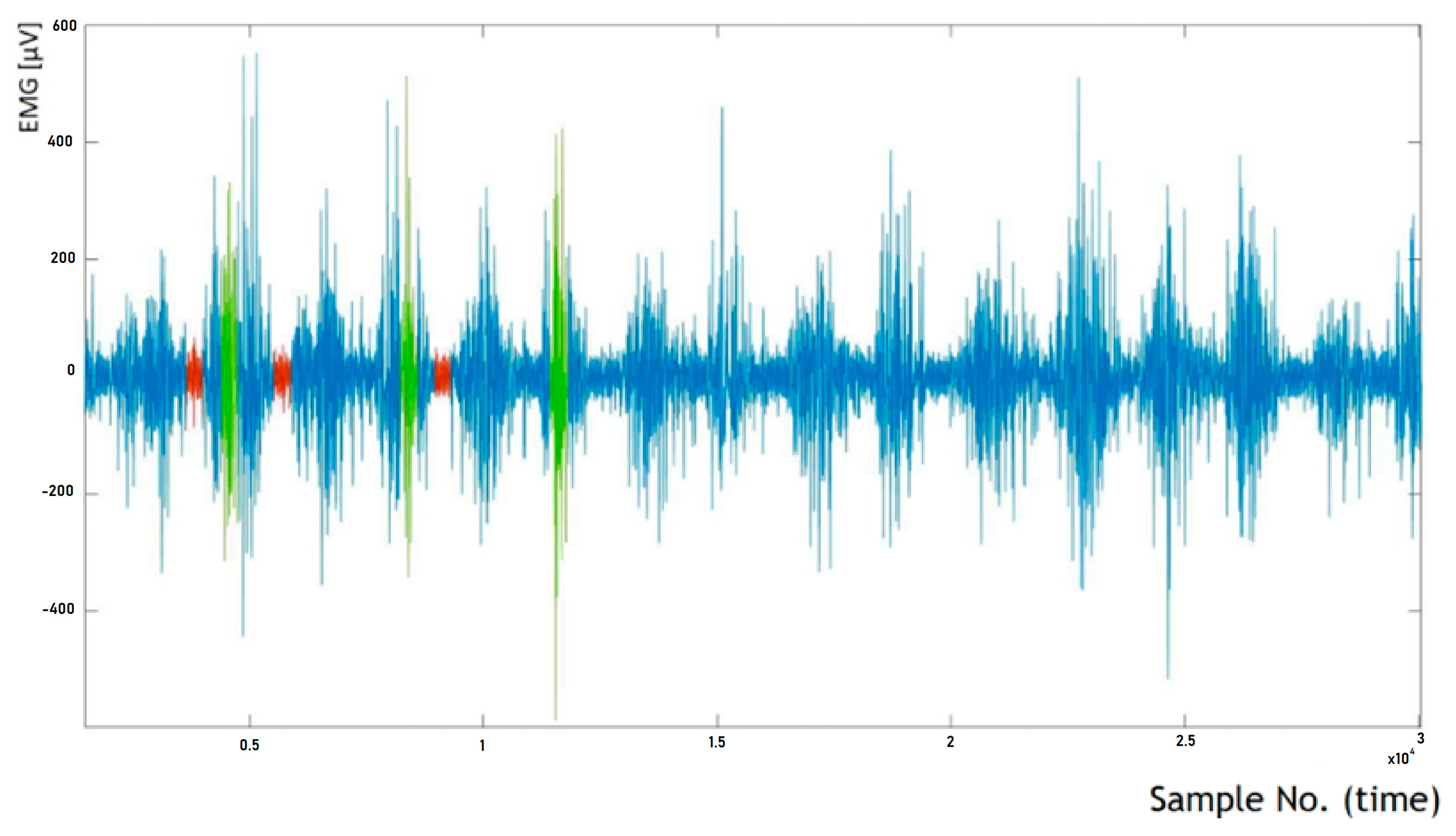
2.3. Surface Electromyography (sEMG) Measurement
2.4. Estimation of Time and Frequency-Domain sEMG Signal Parameters
2.5. Statistical Analysis
- —mean difference between pairs;
- sd—standard deviation of the differences;
- n—number of pairs of observations.
- —mean square within groups;
- —mean square between groups.
3. Experimental Studies
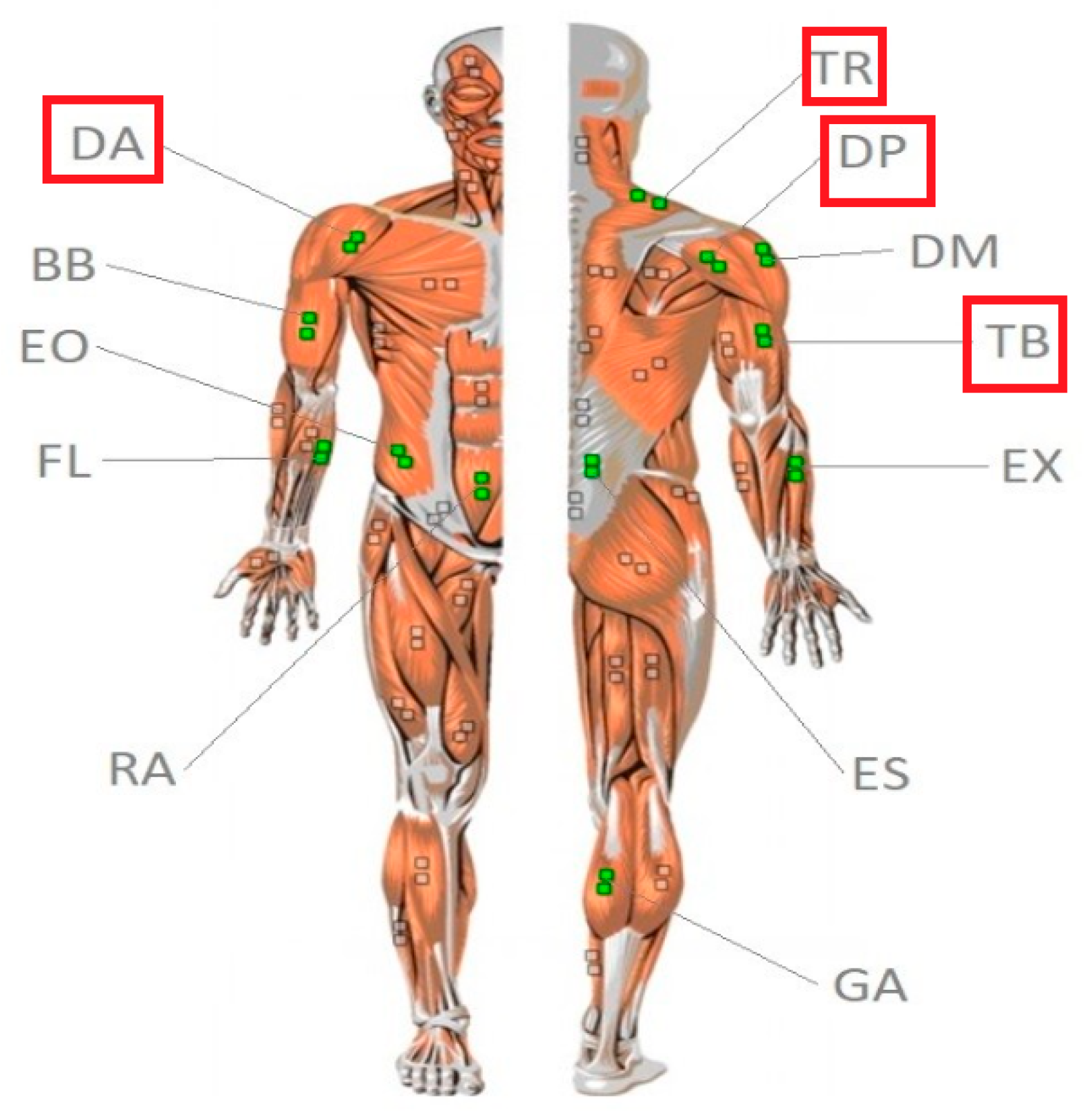
3.1. Muscles Tested
3.2. Experimental Procedure
- Triceps brachii (TB):Elbow flexed at 90°, shoulder in neutral position. Participants performed an isometric elbow extension against manual resistance applied at the distal forearm.
- Anterior deltoid (DA):Shoulder flexed to 90°, elbow extended, palm facing down. The participant resisted a downward force applied just above the wrist to produce isometric shoulder flexion.
- Posterior deltoid (DP):Shoulder abducted to 90° in the horizontal plane (reverse fly position), elbow flexed at 90°. The participant exerted isometric horizontal abduction against resistance applied at the lateral elbow.
- Upper trapezius (TR):Shoulder in neutral position, participant elevated (shrugged) the shoulder isometrically against manual downward pressure applied to the acromion process.
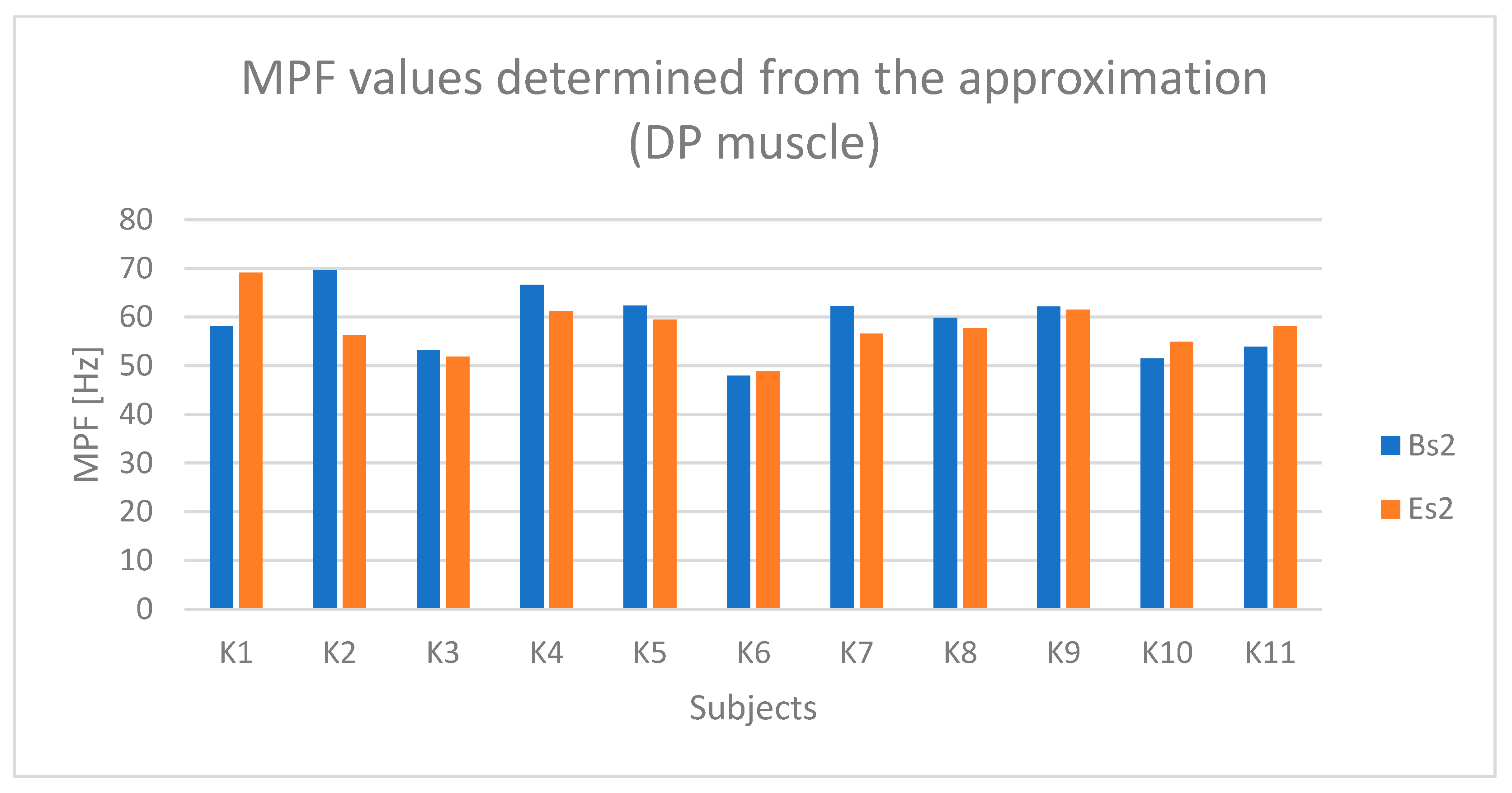
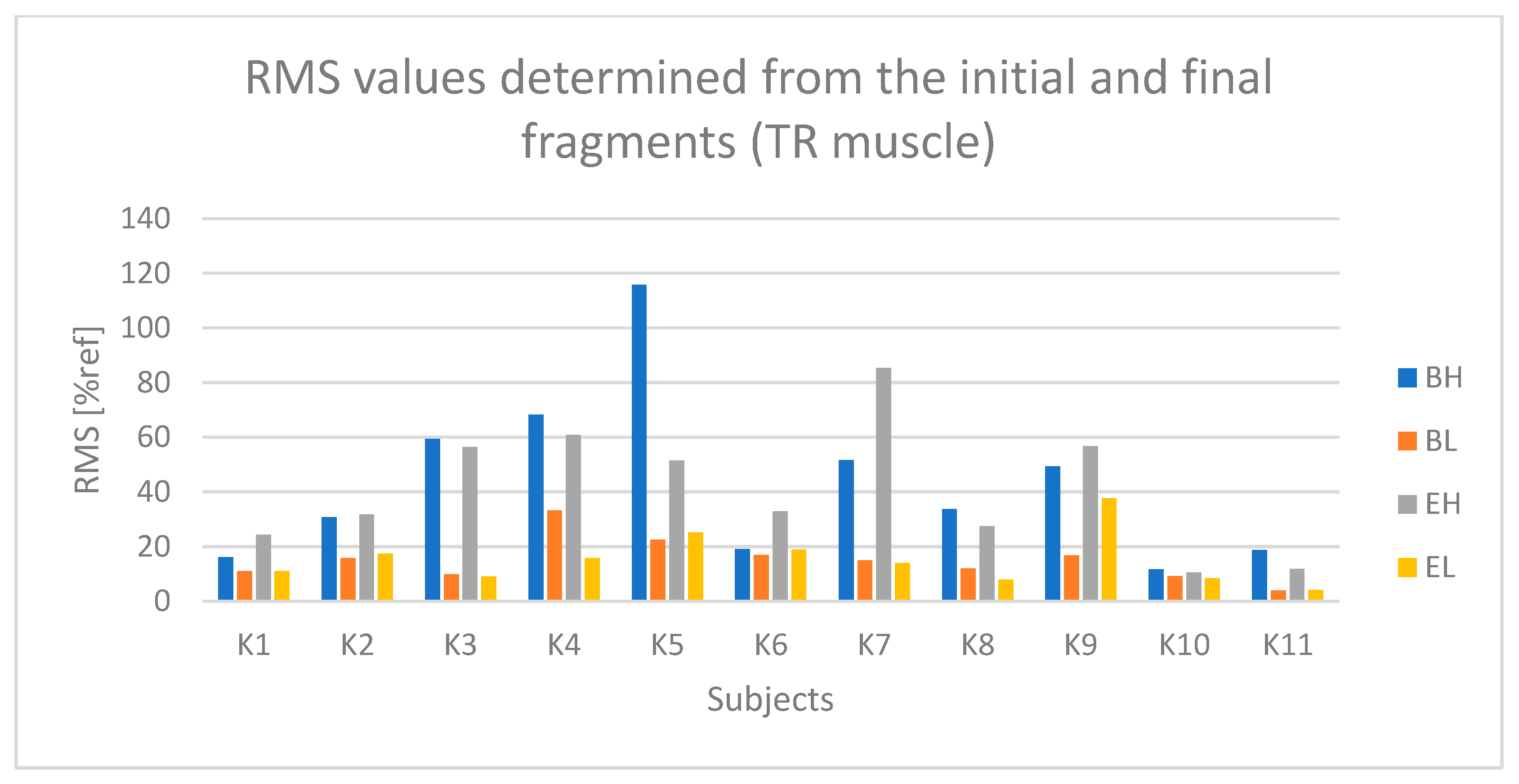
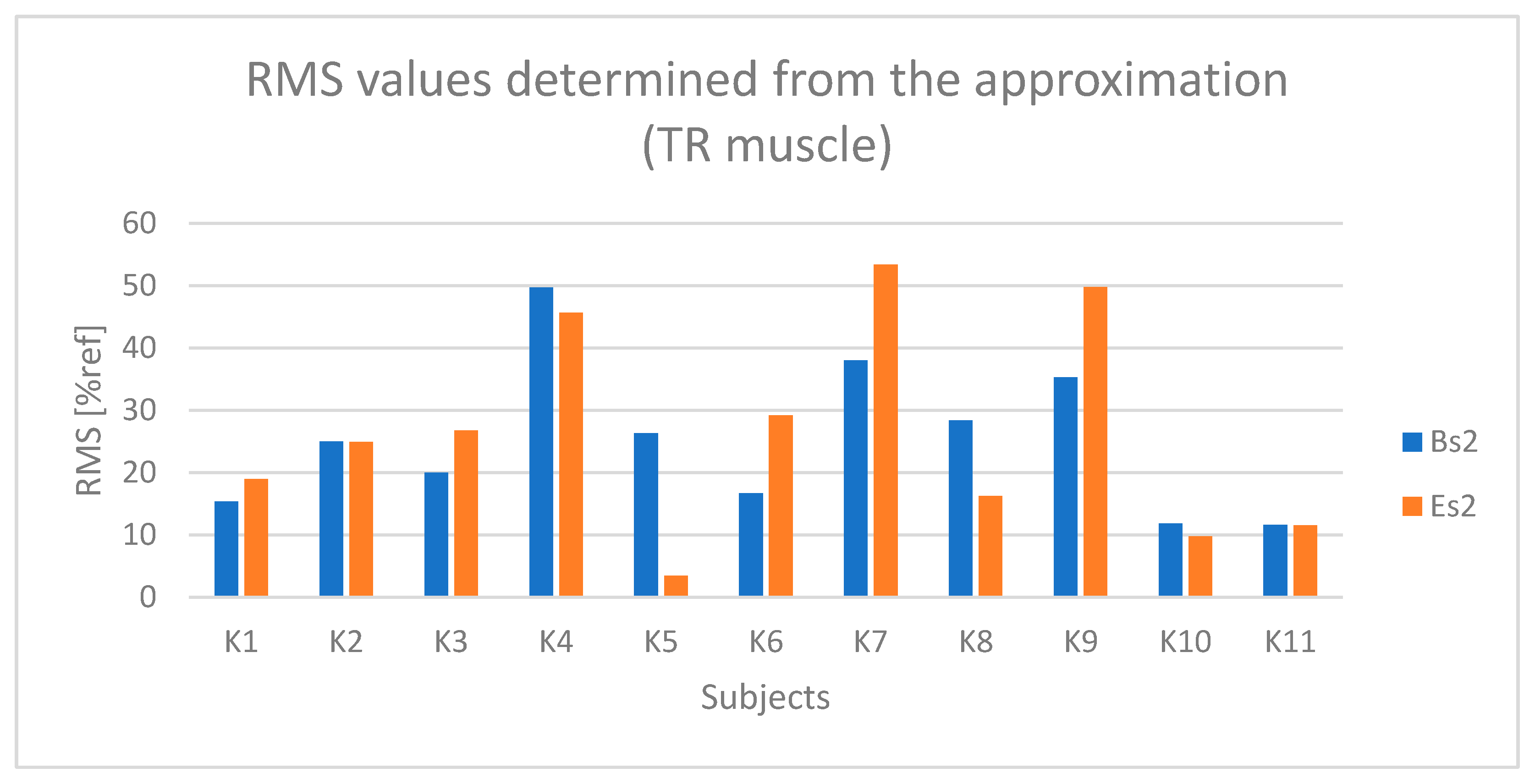
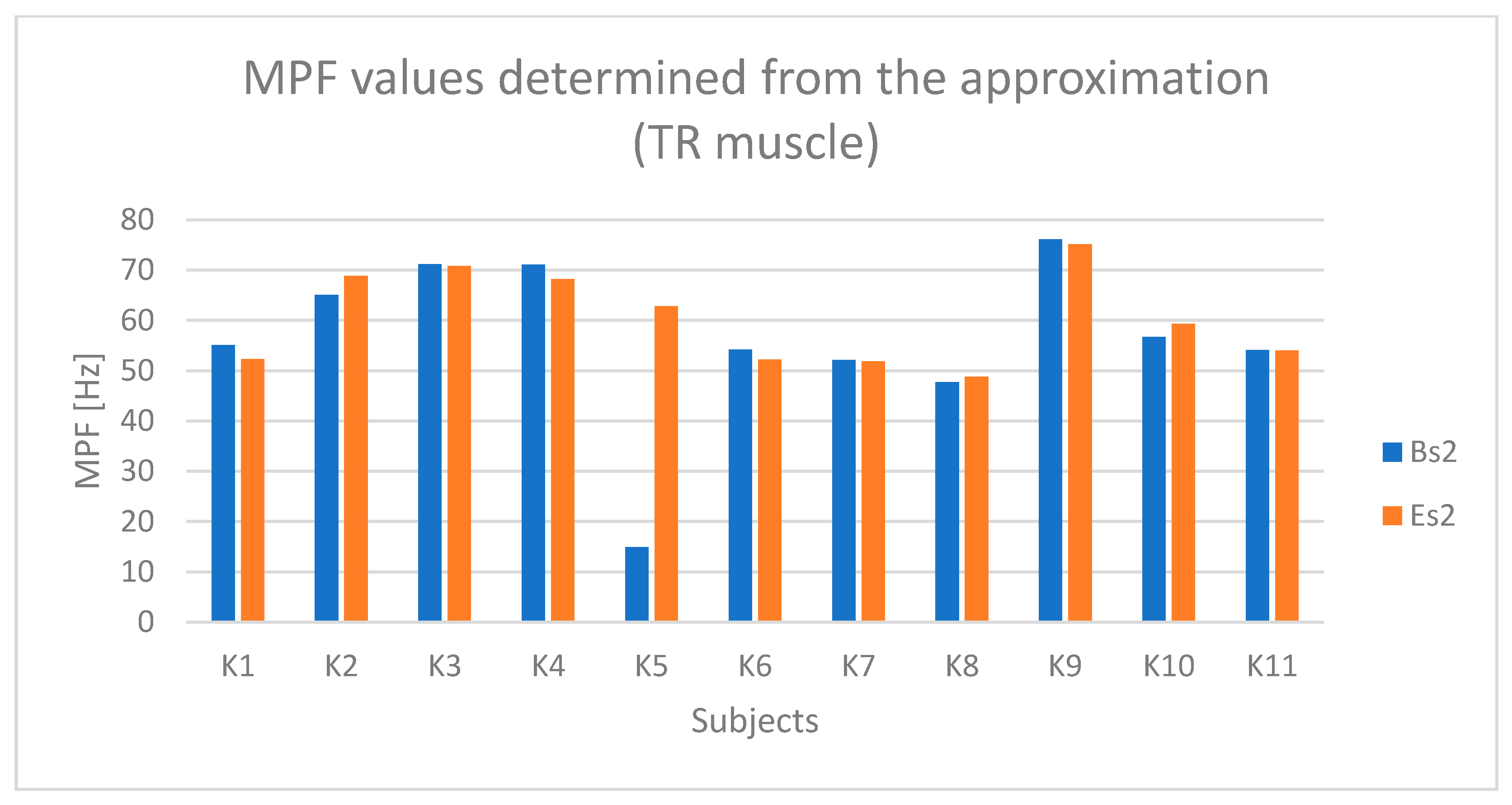
4. Results
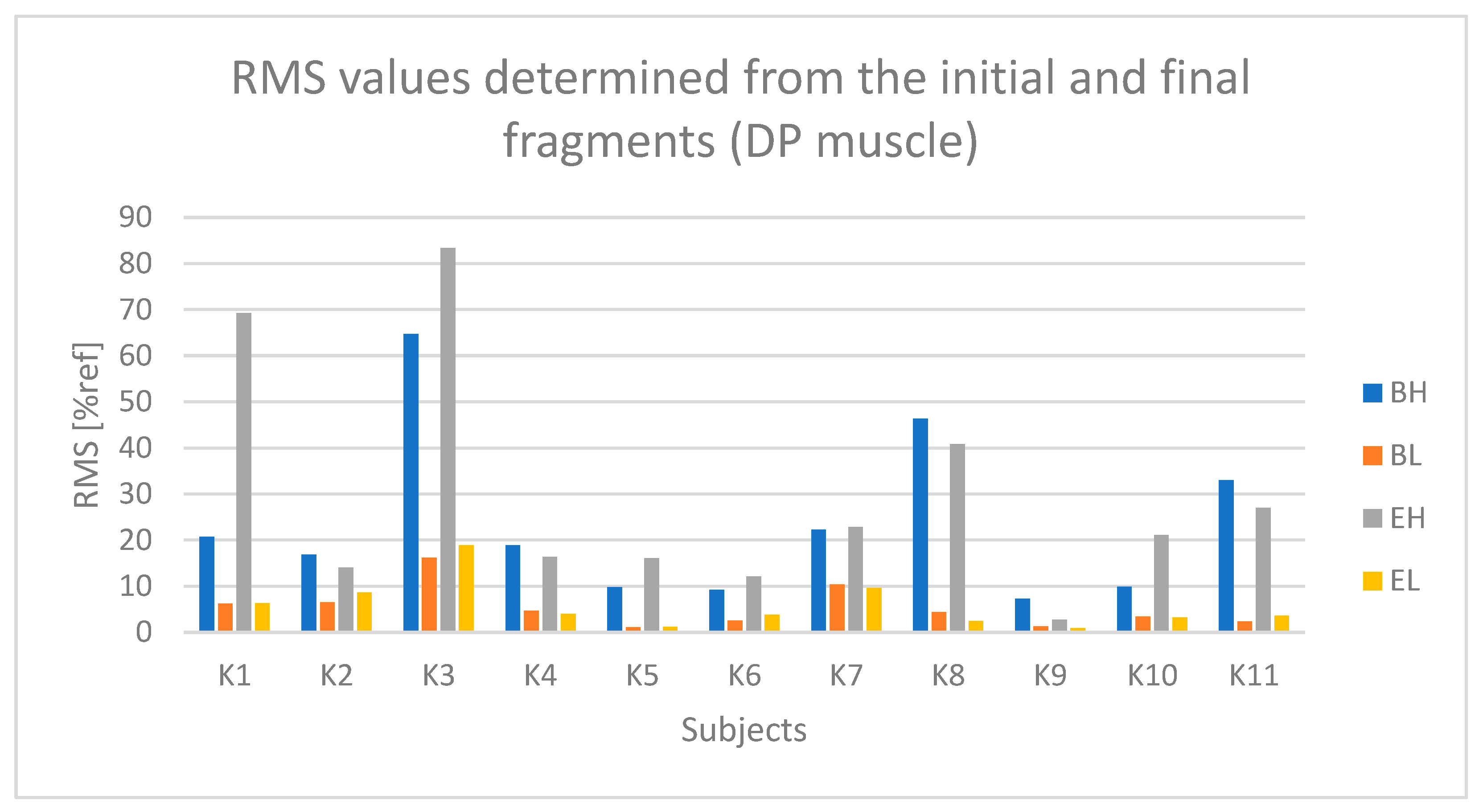
4.1. Analysis of Time-Dependent Muscle Activation
- The active phase from the initial seconds of riding (referred to as BH);
- The passive phase from the initial seconds of riding (BL);
- The active phase from the final seconds of riding (EH);
- The passive phase from the final seconds of riding (EL).
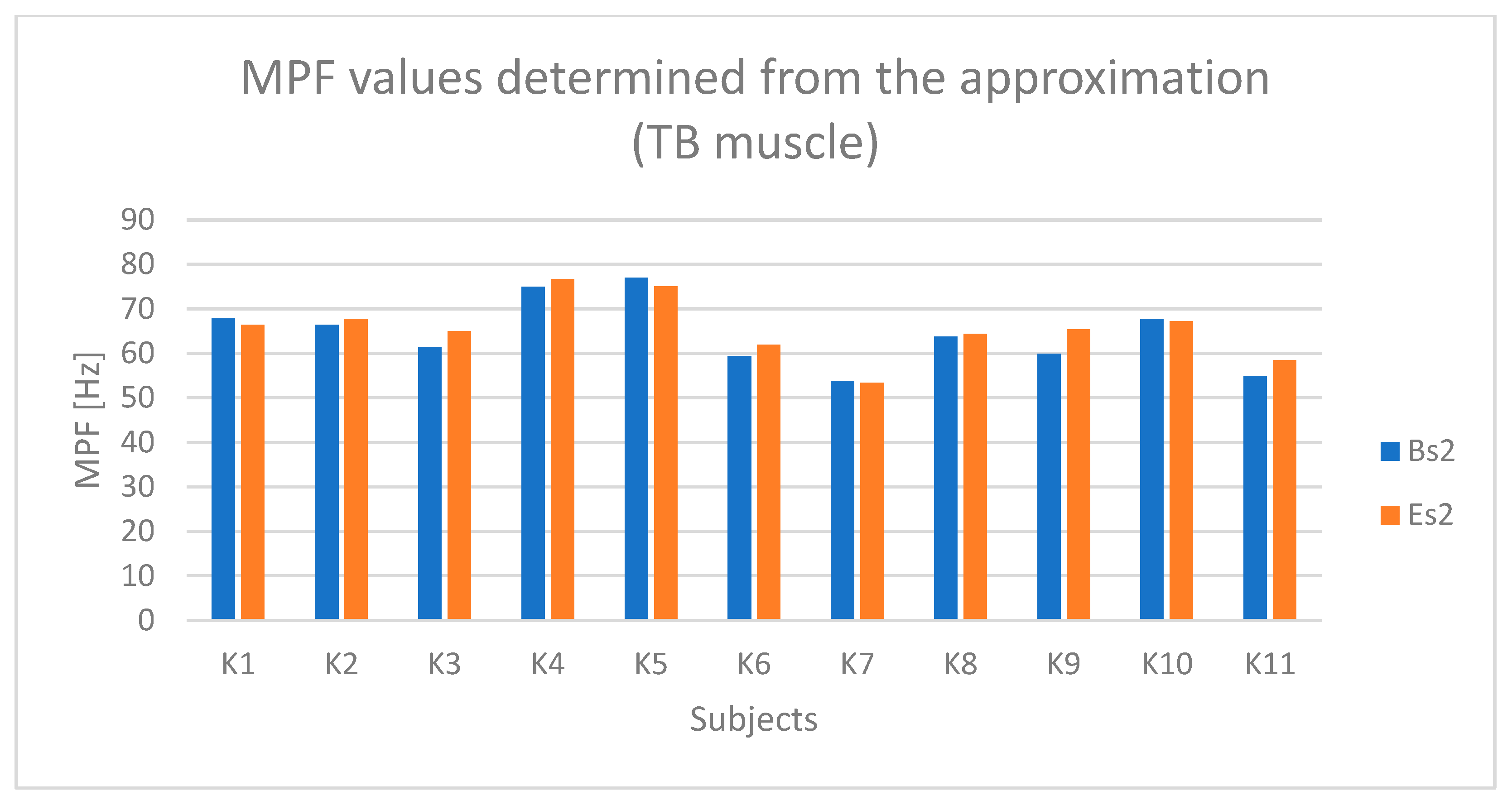
4.2. Statistical Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
7. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Yu, L.; Liu, H. Electromyographic Analysis of Lower Limb Muscles during Riding a Self-Balancing Electric Scooter. Sensors 2020, 20, 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Electromyographic Analysis of Lower Limb Muscles during Riding a Segway PT. Sensors 2019, 19, 5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.S.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Souza, M.F.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Souza, D.; Venturini, D.; Barbosa, D.S.; Cyrino, E.S. Traditional and pyramidal resistance training systems improve muscle quality and metabolic biomarkers in older women: A randomized crossover study. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 127, 110723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimaud, D.; Messonnier, L.; Castells, J.; Devillard, X.; Calmels, P.; Saboul, D. Electromyographic assessment of muscle activity between genders during unilateral weight-bearing tasks using adjusted distances. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2017, 34, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, R.; Sardella, F.; Zanetti, A.; Guccione, A.A. Electromyographic analysis of vastus medialis obliquus and vastus lateralis muscles during open kinetic chain and closed kinetic chain exercises in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome: A case–control study. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2018, 43, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.C.; Silva, Z.; Sousa, G.d.C.; Silva, L.F.; Marques, K.d.V.; Soares, A.B.; Cerqueira, E.P.; Liberti, E.A.; Bérzin, F. Electromyographic evaluation of upper limb muscles involved in armwrestling sport simulation during dynamic and static conditions. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2009, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarsingh, E.J.; Oud, M.; van Eykern, L.A.; Hoekstra, M.O.; van Aalderen, W.M. Electromyographic monitoring of respiratory muscle activity in dyspneic infants and toddlers. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2006, 150, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arghadeh, R.; Alizadeh, M.H.; Minoonejad, H.; Sheikhhoseini, R.; Asgari, M.; Jaitner, T. Electromyography of shoulder muscles in individuals without scapular dyskinesis during closed kinetic chain exercises on stable and unstable surfaces: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Sports Act. Living 2024, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Yu, L.; Liu, H. Electromyographic Analysis of Upper Limb Muscles during Riding a Self-Balancing Electric Unicycle. Sensors 2020, 20, 7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C.J. The Use of Surface Electromyography in Biomechanics. J. Appl. Biomech. 1997, 13, 135–163. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, K.R. The basics of electromyography. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, ii32–ii35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, J. Advances in Applied Electromyography; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-953-307-382-8. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/359 (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Preston, D.C.; Shapiro, B.E. Electromyography and Neuromuscular Disorders, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 9780323661805. [Google Scholar]
- Papagiannis, G.I.; Triantafyllou, A.I.; Roumpelakis, I.M.; Zampeli, F.; Garyfallia Eleni, P.; Koulouvaris, P.; Papadopoulos, E.C.; Papagelopoulos, P.J.; Babis, G.C. Methodology of surface electromyography in gait analysis: Review of the literature. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2019, 43, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellig, T.; Johnen, L.; Mertens, A.; Nitsch, V.; Brandl, C. Investigation of observational methods assessing workload of static working postures based on surface electromyography. Work 2019, 62, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinali, G.; Kara, S.; Yıldırım, M.S. Electromyographic analysis of an ergonomic risk factor: Overhead work. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 1924–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficek, K.; Gołas, A.; Pietraszewski, P.; Strózik, M.; Krzysztofik, M. The Effects of a Combined Pre- and Post-Operative Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Rehabilitation Program on Lower Extremity Muscle Imbalance. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. EMG-Triggered Pedaling Training on Muscle Activation, Gait, and Motor Function for Stroke Patients. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkar, R.; Momeni, K.; Ramanujam, A.; Ravi, M.; Garbarini, E.; Gail, F. Forrest; Use of Surface EMG in Clinical Rehabilitation of Individuals With SCI: Barriers and Future Considerations. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 578559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horyzont 2020 Projekt. Available online: https://torqway.com/pl (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Bęczkowska, S.A.; Grabarek, I.; Zysk, Z.; Gosek-Ferenc, K. Physical Activity and Ecological Means of Transport—Functional Assessment Methodology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noraxom.com. Available online: https://www.noraxon.com/ (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Seniam.com. Available online: http://www.seniam.org/ (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Alizadehkhaiyat, O.; Fisher, A.C. Electromyographic analysis of shoulder muscle activation during push-up variations on stable and unstable surfaces. Phys. Ther. Sport 2007, 8, 146–155. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Liu, J.Z.; Brown, R.W.; Yue, G.H. A dynamical model of muscle activation, fatigue, and recovery. Biophys. J. 2002, 82, 2344–2359. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Warth, R.; Millett, P. Physical Examination of the Shoulder: An Evidence-Based Approach; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, Y.; Lee, D. Surface Electromyography Analysis for Evaluating Muscle Fatigue in Upper Extremity Muscles. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2020, 55, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.H.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Bin Mohd Ali, M.A.; Bakar, A.A.; Chellappan, K.; Chang, T.G. Surface Electromyography Signal Processing and Classification Techniques. Sensors 2021, 21, 2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H. Electromyographic Analysis of Upper Limb Muscles during Nordic Walking. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2020, 53, 102400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y. Comparative Analysis of Muscle Activation during Walking with and without Nordic Walking Poles. Sensors 2021, 21, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamavuako, E.N.; Englehart, K.B. On the usability of intramuscular EMG for prosthetic control: A Fitts’ law approach. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2015, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Vecchio, A.; Holobar, A.; Falla, D. Large-scale detection of variability in fascicle conduction velocity reveals motor unit recruitment strategies. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 523–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenberg, L.A.; Hermens, H.J. Motor unit firing rate patterns during voluntary muscle force generation: A simulation study. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2018, 41, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzoni, M.; Celadon, N.; Mastrapasqua, D. Surface EMG applications in the assessment of neuromuscular function. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2017, 35, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, C.J. The use of surface electromyography in biomechanics. J. Appl. Biomech. 2019, 35, 86–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merletti, R.; Botter, A.; Troiano, A. Technology and instrumentation for detection and conditioning of the surface electromyographic signal: State of the art. Clin. Biomech. 2009, 24, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merletti, R.; Parker, P.A. (Eds.) Electromyography-Physiology, Engineering, and Noninvasive Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; ISBN 0-471-67580-6. [Google Scholar]
- Earp, J.E.; Newton, R.U.; Cormie, P.; Blazevich, A.J. Knee angle-specific EMG normalization: The use of polynomial based EMG-angle relationships. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2013, 23, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaudens, P.; Banse, X.; Mousny, M.; Detrembleur, C. Gait in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Kinematics and electromyographic analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2009, 18, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbehzadeh, S.; Mohseni Bandpei, M.A.; Ehsani, F. Knee muscle activity during gait in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injury: A systematic review of electromyographic studies. Knee Surg. Sport. Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2017, 25, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni-Bandpei, M.A.; Rajabzadeh, F.; Hamedinia, M.R.; Zarghami, M.; Motealleh, A. Electromyographic analysis of the effect of adding vibration to physical therapy for the management of low back pain. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2017, 21, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrington, L.; Waterman, R.; Smith, L. Electromyographic analysis of shoulder muscles during press-up variations and progressions. J Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2015, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, H.; Zheng, Y. Electromyographic Analysis of Thigh Muscles during Unconventional Bicycle Riding. Sensors 2020, 20, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S. EMG in sports rehabilitation. Br. J. Sport. Med. 2010, 44, i10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felici, F.; Vecchio, A.D. Surface Electromyography: What limits its use in exercise and sport physiology? Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 578504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sire, A.; Demeco, A.; Marotta, N.; Moggio, L.; Palumbo, A.; Iona, T.; Ammendolia, A. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury Prevention Exercises: Could a Neuromuscular Warm-Up Improve Muscle Pre-Activation before a Soccer Game? A Proof-of-Principle Study on Professional Football Players. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.; Catarino, A.; Carvalho, H.; Postolache, O.; Postolache, G.; Ferreira, F. Design of a Long Sleeve T-Shirt with ECG and EMG for Athletes and Rehabilitation Patients. In Innovation, Engineering and Entrepreneurship. HELIX 2018; Machado, J., Soares, F., Veiga, G., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 505, ISBN 978-3-319-91333-9. [Google Scholar]
- Signorile, J.F.; Avedesian, J.M.; Babamoto, B.N.; Yan, Z.; Magyari, P.M. Electromyographic analysis of hip adduction exercises in collegiate female soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dello Iacono, A.; Padulo, J.; Seitz, L.D.; Ardigo, L.P. Lower-limb electromyographic analysis during an incremental cycling exercise until exhaustion. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2018, 38, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. (Ed.) Electromyography in Ergonomics, 1st ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bęczkowska, S.; Celiński, D.; Grabarek, I.; Grzybowska, K.; Zysk, Z. (Nie)ergonomiczne warunki pracy ratownika w ambulansie medycznym. Med. Pr. Work. Health Saf. 2024, 75, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, W.S. Overview of Electromyography in Ergonomics. Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. Annu. Meet. 2000, 44, 5-534–5-536. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/154193120004403037?journalCode=proe (accessed on 20 April 2024). [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/352015010_A_Review_of_Electromyography_Signal_Analysis_of_Fatigue_Muscle_for_Manual_Lifting (accessed on 20 April 2024).
- Kupa, E.J.; Roy, S.H.; Kandarian, S.C.; De Luca, C.J. Effects of muscle fiber type and size on EMG median frequency and conduction velocity. J. Appl. Physiol. 1995, 79, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viitasalo, J.T.; Komi, P.V.; Hämäläinen, I. Changes in EMG frequency spectrum during fatigue. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1981, 46, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Tested Person | Age | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) | BMI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | 54 | 165 | 72 | 26.45 |
| k2 | 54 | 164 | 79 | 29.37 |
| k3 | 52 | 153 | 62 | 26.49 |
| k4 | 59 | 162 | 69 | 26.29 |
| k5 | 62 | 165 | 63 | 23.14 |
| k6 | 50 | 167 | 90 | 32.27 |
| k7 | 57 | 166 | 69 | 25 |
| k8 | 50 | 170 | 57 | 19.7 |
| k9 | 52 | 164 | 57 | 21.2 |
| k10 | 58 | 161,5 | 62 | 23.92 |
| k11 | 50 | 170 | 72 | 24.91 |
| Muscle/ Person | TB | DA | DP | TR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | x | x | ||
| K2 | x | x | ||
| K3 | x | x | ||
| K4 | ||||
| K5 | x | x | x | |
| K6 | x | |||
| K7 | ||||
| K8 | ||||
| K9 | x | |||
| K10 | x | |||
| K11 |
| Muscle/ Person | TB | DA | DP | TR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | 109/ 7 | 42/ 5 | 21/ 6 | 16/ 11 |
| K2 | 28/ 9 | 52/ 10 | 17/ 6 | 31/ 16 |
| K3 | 142/ 17 | 106/ 21 | 65/ 16 | 59/ 10 |
| K4 | 17/ 6 | 68/ 20 | 19/ 5 | 68/ 33 |
| K5 | 46/ 6 | 22/ 2 | 10/ 1 | 116/ 23 |
| K6 | 56/ 7 | 25/ 6 | 9/ 3 | 19/ 17 |
| K7 | 82/ 8 | 55/ 4 | 22/ 10 | 52/ 15 |
| K8 | 45/ 8 | 56/ 3 | 46/ 4 | 34/ 12 |
| K9 | 36/ 3 | 33/ 3 | 7/ 1 | 49/ 17 |
| K10 | 46/ 6 | 28/ 10 | 10/ 3 | 12/ 9 |
| K11 | 86/ 17 | 76/ 11 | 33/ 2 | 19/ 4 |
| Muscle | RMS Active (M ± SD) | RMS Passive (M ± SD) | Test t (p-Value) | MPF Active (M ± SD) | MPF Passive (M ± SD) | ANOVA (F, p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TB | 109 ± 7 | 28 ± 9 | t(10) = 5.62, p < 0.001 | 120 ± 8 | 95 ± 10 | F(1,10) = 12.34, p = 0.003 |
| DA | 106 ± 21 | 52 ± 10 | t(10) = 4.92, p < 0.005 | 115 ± 9 | 92 ± 12 | F(1,10) = 9.87, p = 0.007 |
| TR | 116 ± 23 | 31 ± 16 | t(10) = 6.21, p < 0.001 | 112 ± 7 | 90 ± 11 | F(1,10) = 11.45, p = 0.004 |
| DP | 98 ± 15 | 40 ± 12 | t(10) = 4.35, p < 0.005 | 110 ± 9 | 88 ± 13 | F(1,10) = 10.12, p = 0.005 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bęczkowska, S.A.; Grabarek, I.; Zysk, Z. Application of Surface Electromyography (sEMG) in the Analysis of Upper Limb Muscle Activity in Women Aged 50+ During Torqway Riding. Sensors 2025, 25, 4280. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144280
Bęczkowska SA, Grabarek I, Zysk Z. Application of Surface Electromyography (sEMG) in the Analysis of Upper Limb Muscle Activity in Women Aged 50+ During Torqway Riding. Sensors. 2025; 25(14):4280. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144280
Chicago/Turabian StyleBęczkowska, Sylwia Agata, Iwona Grabarek, and Zuzanna Zysk. 2025. "Application of Surface Electromyography (sEMG) in the Analysis of Upper Limb Muscle Activity in Women Aged 50+ During Torqway Riding" Sensors 25, no. 14: 4280. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144280
APA StyleBęczkowska, S. A., Grabarek, I., & Zysk, Z. (2025). Application of Surface Electromyography (sEMG) in the Analysis of Upper Limb Muscle Activity in Women Aged 50+ During Torqway Riding. Sensors, 25(14), 4280. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144280






