Comb-Tipped Coupled Cantilever Sensor for Enhanced Real-Time Detection of E. coli Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
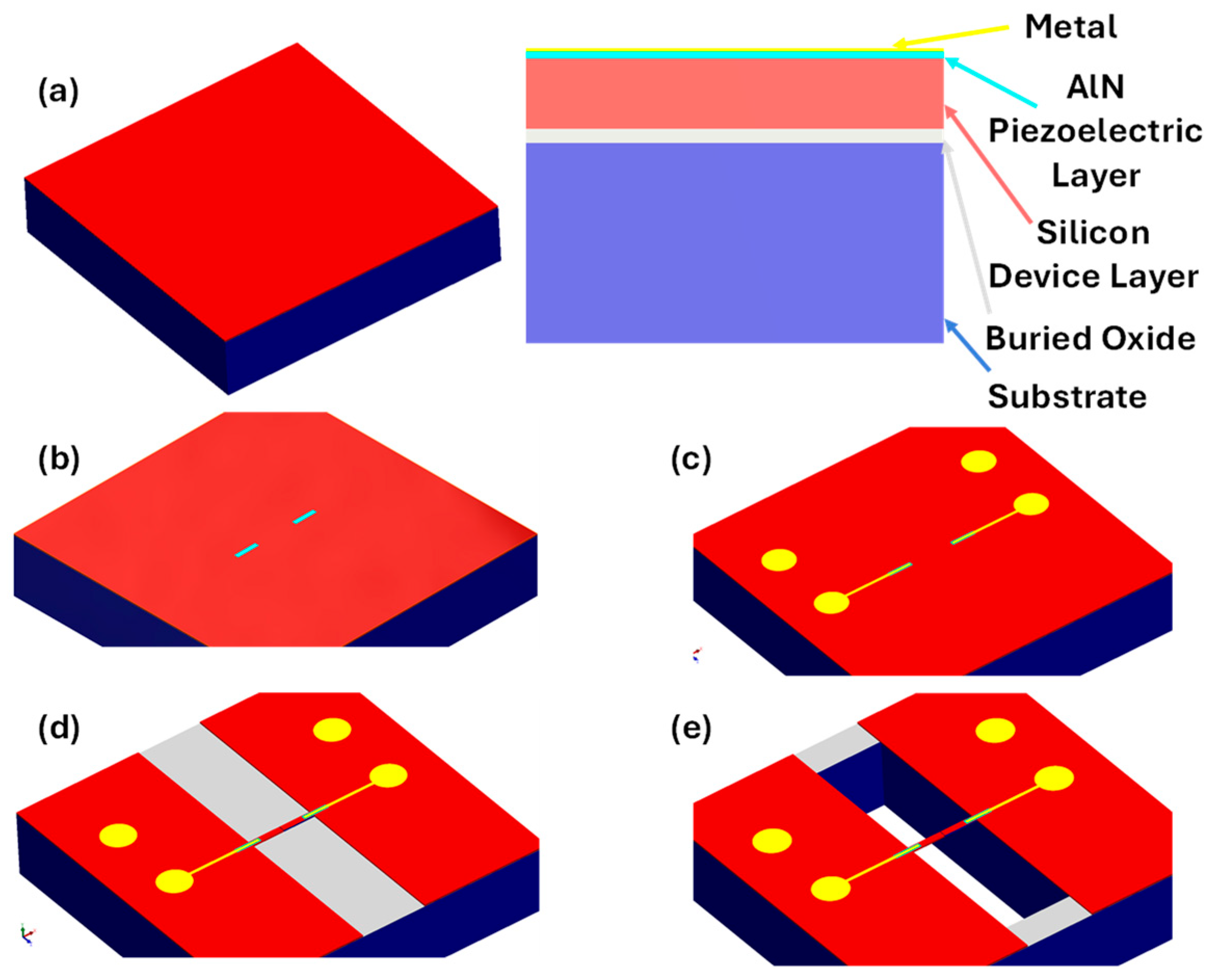
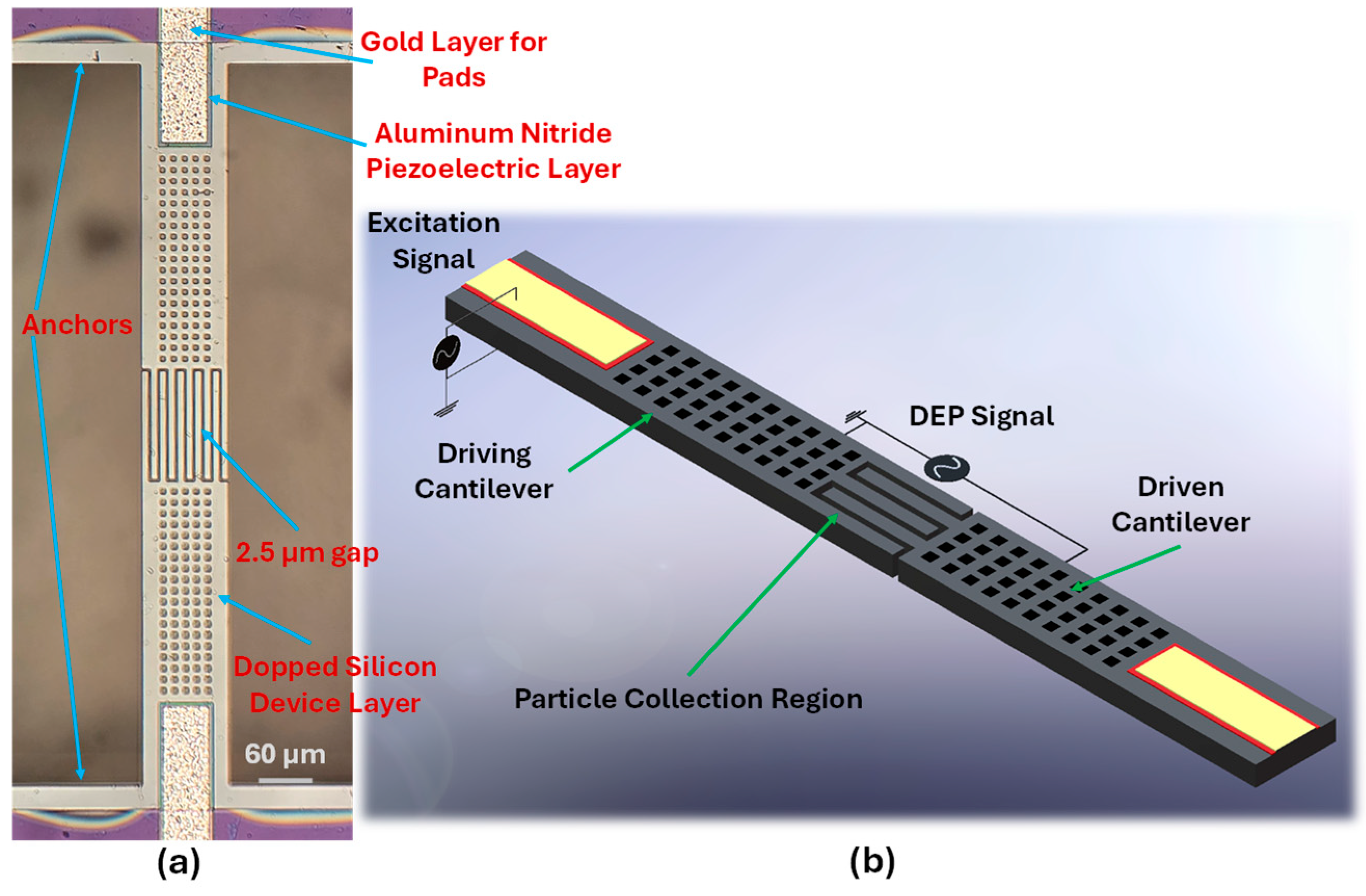
2.1. Design and Fabrication
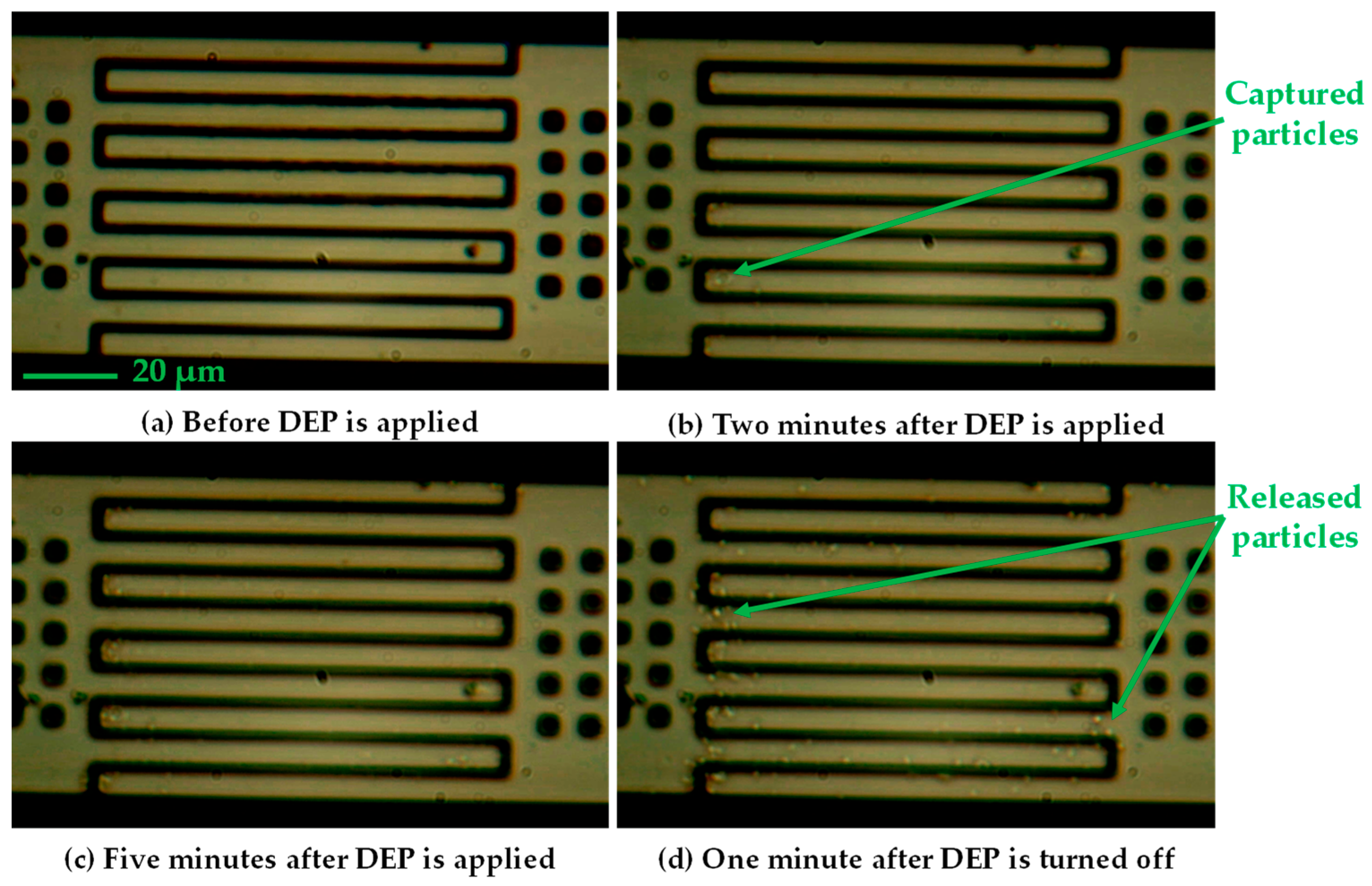
2.2. Operation of the Device
2.3. Experimetal Setup and Methodology
2.3.1. Experimental Setup
2.3.2. Preparation of Samples
2.3.3. Experimental Methodology
3. Results
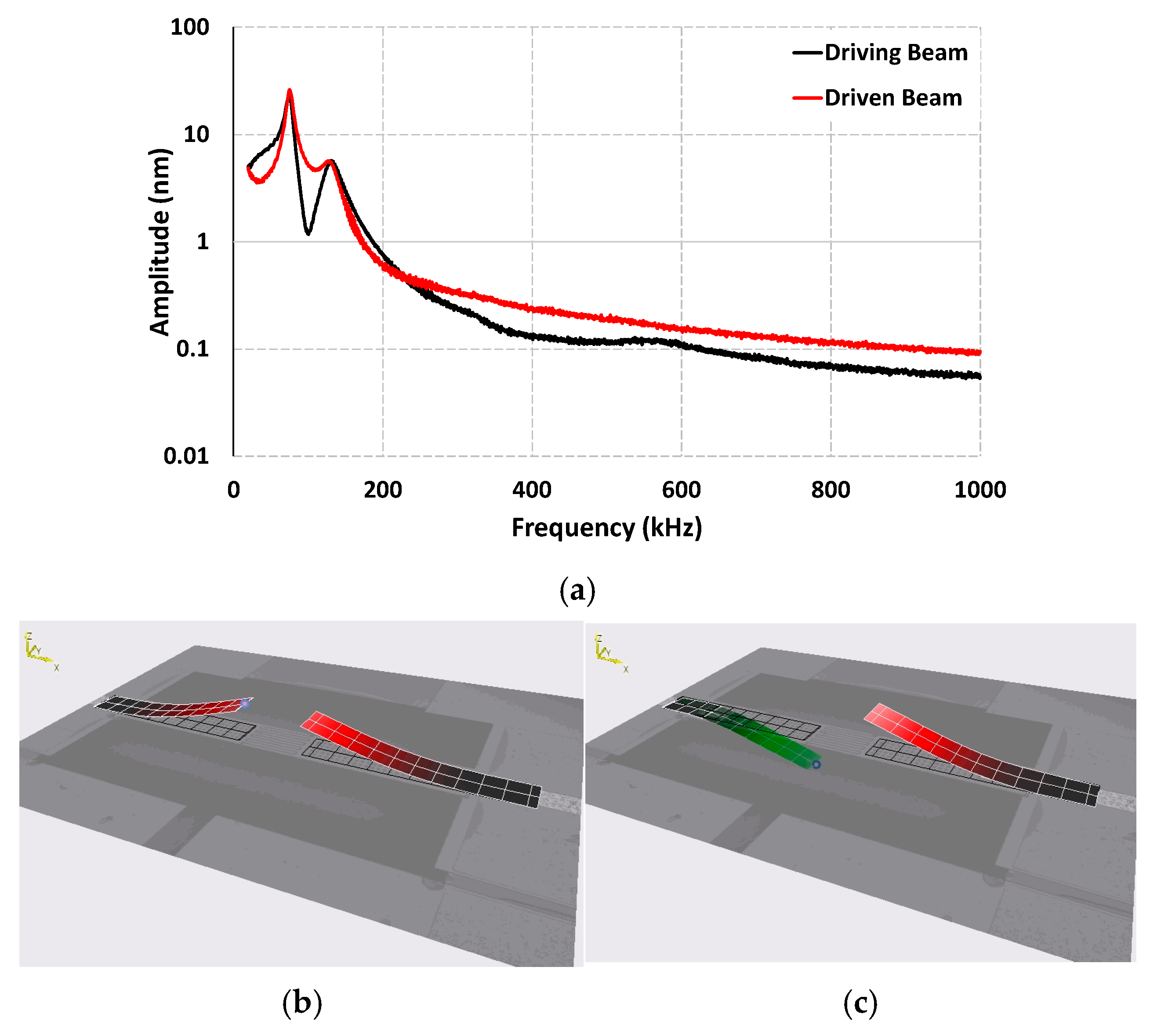
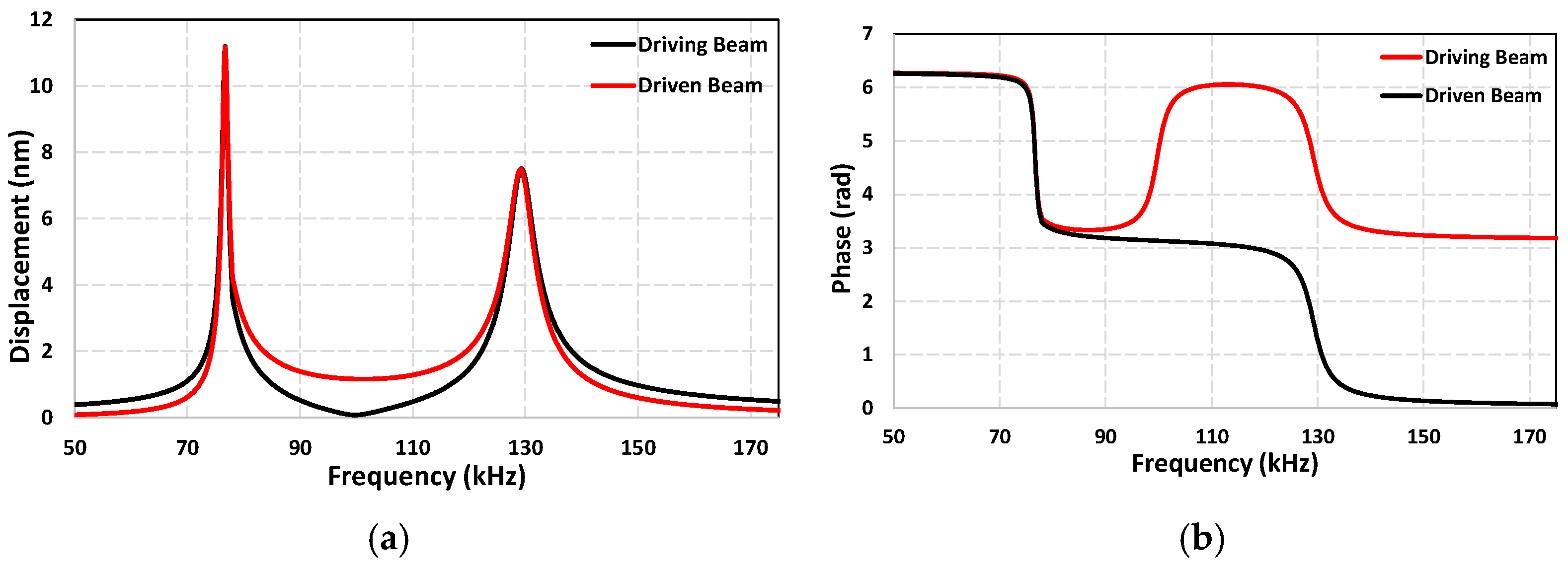
3.1. Dynamic Response of the Sensor
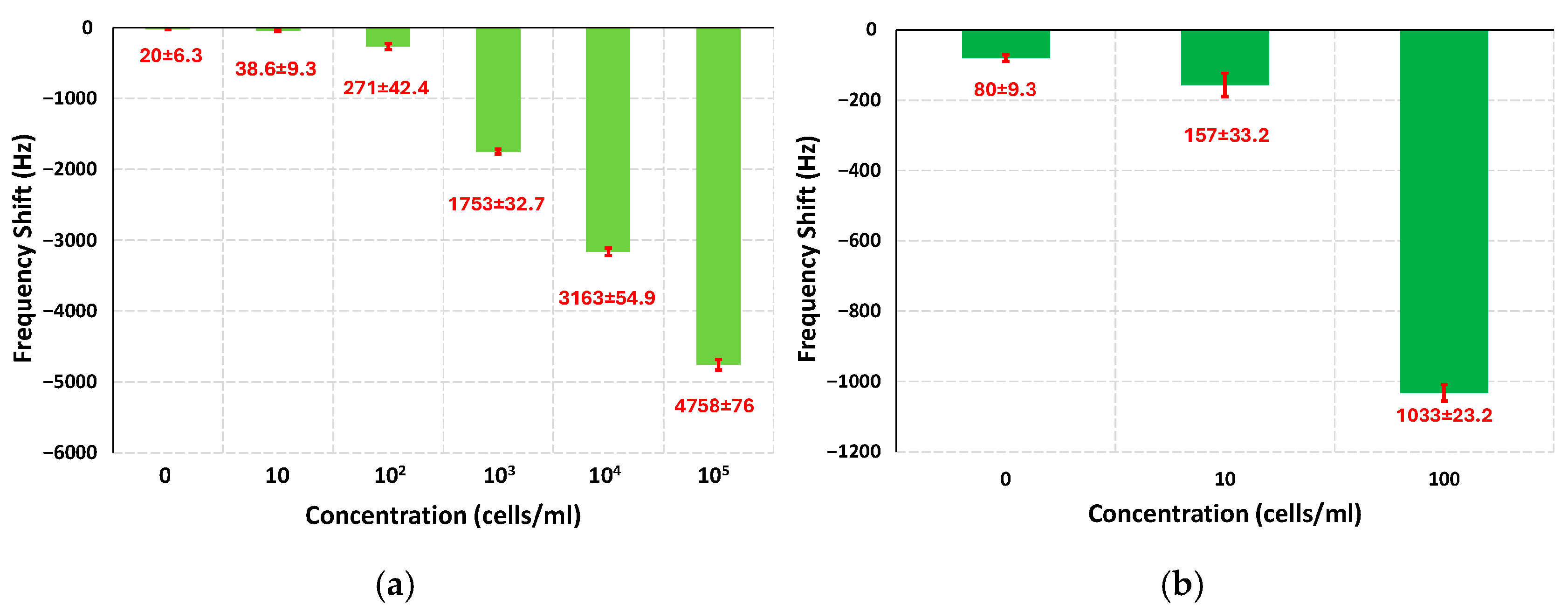
3.2. Frequency Shifts at Different Concentrations of E. coli
3.3. Limit of Detection, Signal to Noise Ratio, and Dynamic Range of the Sensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leikauf, G.D.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, A.S. Mechanisms of ultrafine particle-induced respiratory health effects. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, J.I.; Gać, P. Short-and Long-Term Effects of Inhaled Ultrafine Particles on Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Cejudo-Ruiz, F.R.; Stommel, E.W.; González-Maciel, A.; Reynoso-Robles, R.; Silva-Pereyra, H.G.; Pérez-Guille, B.E.; Soriano-Rosales, R.E.; Torres-Jardón, R. Sleep and Arousal Hubs and Ferromagnetic Ultrafine Particulate Matter and Nanoparticle Motion Under Electromagnetic Fields: Neurodegeneration, Sleep Disorders, Orexinergic Neurons, and Air Pollution in Young Urbanites. Toxics 2025, 13, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fode-Vaughan, K.A.; Maki, J.S.; Benson, J.A.; Collins, M.L. Direct PCR detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 37, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.M.; Domingues, L. On the track for an efficient detection of Escherichia coli in water: A review on PCR-based methods. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wityk, P.; Terebieniec, A.; Nowak, R.; Łubiński, J.; Mroczyńska-Szeląg, M.; Wityk, T.; Kostrzewa-Nowak, D. Reusable Biosensor for Easy RNA Detection from Unfiltered Saliva. Sensors 2025, 25, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.T.; Su, L.; Zhang, X.; Bennett, G.N.; Silberg, J.J.; Ajo-Franklin, C.M. Real-time bioelectronic sensing of environmental contaminants. Nature 2022, 611, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thavarajah, W.; Silverman, A.D.; Verosloff, M.S.; Kelley-Loughnane, N.; Jewett, M.C.; Lucks, J.B. Point-of-use detection of environmental fluoride via a cell-free riboswitch-based biosensor. ACS Synth. Biol. 2019, 9, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazial, F.F.; Tan, L.L.; Zubairi, S.I. Bienzymatic creatine biosensor based on reflectance measurement for real-time monitoring of fish freshness. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 269, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemian, H.; Ghaedi, M.; Dashtian, K.; Khan, S.; Mosleh, S.; Hajati, S.; Razmjoue, D. Highly sensitive fluorometric ammonia detection utilizing Solenostemon scutellarioides (L.) extracts in MOF-tragacanth gum hydrogel for meat spoilage monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 406, 135354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.A.; Grazhdan, D.; Fiutowski, J.; Nebling, E.; Blohm, L.; Lofink, F.; Rubahn, H.G.; de Oliveira Hansen, R. Meat and fish freshness evaluation by functionalized cantilever-based biosensors. Microsyst. Technol. 2020, 26, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik-Karpinska, E.; Ceremuga, M.; Niemcewicz, M.; Podogrocki, M.; Stela, M.; Cichon, N.; Bijak, M. Immunosensors—The future of pathogen real-time detection. Sensors 2022, 22, 9757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoubi, M.; Rahimi, F.; Negahdari, B.; Rezayan, A.H.; Shafiekhani, A. A lectin-coupled porous silicon-based biosensor: Label-free optical detection of bacteria in a real-time mode. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Hasan, M.R.; Hossain, S.I.; Ahommed, M.S.; Daizy, M. Ultrasensitive detection of pathogenic viruses with electrochemical biosensor: State of the art. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisen, A.; Thundat, T. Design & fabrication of cantilever array biosensors. Mater. Today 2009, 12, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.; Wang, T.; Ji, W.; Feng, L.; Yin, P.; Lu, J.; Yin, L. A2-Mode Lamb Passive-Wireless Surface-Acoustic-Wave Micro-Pressure Sensor Based on Cantilever Beam Structure. Sensors 2025, 25, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.N.; Mutharasan, R. Biosensing using dynamic-mode cantilever sensors: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 32, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.K.; Basu, A.; Bhattacharya, S. Micro/Nano fabricated cantilever based biosensor platform: A review and recent progress. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2020, 139, 109558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertke, M.; Kirsch, I.; Uhde, E.; Peiner, E. Ultrafine aerosol particle sizer based on piezoresistive microcantilever resonators with integrated air-flow channel. Sensors 2021, 21, 3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertke, M.; Xu, J.; Setiono, A.; Kirsch, I.; Uhde, E.; Peiner, E. Fabrication of a microcantilever-based aerosol detector with integrated electrostatic on-chip ultrafine particle separation and collection. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2019, 30, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Peiner, E. Resonant Silicon Microcantilevers for Particle and Gas Sensing. In Piezoelectric Sensors; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 291–338. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liao, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Yang, F. A high accuracy cantilever array sensor for early liver cancer diagnosis. Biomed. Microdevices 2016, 18, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahimi, K.M.; Kumar, R.; Pakhira, W.; Panwala, F.C. Enhanced design and analysis of the microcantilever-based bio-sensor to detect carcinoembryonic antigen tumor biomarkers. Comput. Assist. Methods Eng. Sci. 2023, 30, 347–367. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, S.; Mishra, S.; Mukhopadhyay, R. Enhancing sensitivity in a piezoresistive cantilever-based label-free DNA detection assay using ssPNA sensor probes. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, B.; Yang, Y.; Craighead, H.G. Virus detection using nanoelectromechanical devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 2604–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timurdogan, E.; Alaca, B.E.; Kavakli, I.H.; Urey, H. MEMS biosensor for detection of Hepatitis A and C viruses in serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, D.K.; Nandwana, V.; Henrich, S.E.; Josyula, V.P.; Thaxton, C.S.; Qi, C.; Simons, L.M.; Hultquist, J.F.; Ozer, E.A.; Shekhawat, G.S.; et al. Highly sensitive and ultra-rapid antigen-based detection of SARS-CoV-2 using nanomechanical sensor platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 195, 113647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndieyira, J.W.; Watari, M.; Barrera, A.D.; Zhou, D.; Vögtli, M.; Batchelor, M.; Cooper, M.A.; Strunz, T.; Horton, M.A.; Abell, C.; et al. Nanomechanical detection of antibiotic–mucopeptide binding in a model for superbug drug resistance. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.M.; Ji, H.F.; Wu, G.; Datar, R.; Cote, R.; Majumdar, A.; Thundat, T. Cantilever-based optical deflection assay for discrimination of DNA single-nucleotide mismatches. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 1567–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchelli, L.; Todorov, G.; Stavrov, V.; Ganev, B.; Todorov, T. Investigating a Detection Method for Viruses and Pathogens Using a Dual-Microcantilever Sensor. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahma, L.; Guha, K.; Karumuri, S.R. Design and analysis of novel MEMS cantilever biosensor with special focus on SCR for tuberculosis detection. Microsyst. Technol. 2025, 31, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, D.K.; Kushagra, A.; Ashwin, M.; Shukla, A.S.; Palaparthy, V. Sensitive detection of cardiac troponin-I protein using fabricated piezoresistive microcantilevers by a novel method of asymmetric biofunctionalization. Nanotechnology 2019, 31, 115503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmendra Kumar, R. MEMS based cantilever biosensors for cancer detection using potential bio-markers present in VOCs: A survey. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 3253–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Yang, F. A high-throughput cantilever array sensor for multiple liver cancer biomarkers detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 4675–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, J.; Cuervo, A.; Carrascosa, J.L. Nanomechanical detection of Escherichia coli infection by bacteriophage T7 using cantilever sensors. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 17689–17698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.; Shin, S.M.; Kim, B. Cantilever-type electrode array-based high-throughput microparticle sorting platform driven by gravitation and negative dielectrophoretic force. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 21, 015015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, S.; Lai, Y. A cantilever biosensor based on a gap method for detecting Escherichia coli in real time. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, J.; Jia, Z.; Lai, Y. Real-time ultralow bacterial detection with a gap-method microcantilever biosensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 24, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, S.; Lai, Y. Doubling the quality factor of cantilevers in liquid through fluid coupling-based actuation. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 164507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.A.; Alaei, E.; Lai, Y. Coupled cantilever biosensor utilizing a novel approach to gap-method for real-time detection of E. coli in low concentrations. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 435, 137665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, A.; Hames, G.; Glukh, K.; Hardy, B. PiezoMUMPs Design Handbook; MEMSCAP Inc.: Durham, NC, USA, 2014; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Azimi, S.; Moridsadat, M.; Shastri, B.; Banfield, B.W.; Escobedo, C.; Docoslis, A. Fast and sensitive virus detection using a plasmonic sensor that integrates electrokinetically assisted sampling and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2025, 9, 100273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, N.; Keeler, W.J.; Nandakumar, K.; Leung, K.T. The bactericidal effect of ultraviolet and visible light on Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 99, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, S.; Lai, Y. Regenerating silicon biosensors through thermal ablation with a hot plate. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2015, 6, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spletzer, M.; Raman, A.; Wu, A.Q.; Xu, X.; Reifenberger, R. Ultrasensitive mass sensing using mode localization in coupled microcantilevers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 254102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Montaseri, M.H.; Wood, G.S.; Pu, S.H.; Seshia, A.A.; Kraft, M. A review on coupled MEMS resonators for sensing applications utilizing mode localization. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 249, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manav, M.; Phani, A.S.; Cretu, E. Mode localization and sensitivity in weakly coupled resonators. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 19, 2999–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, T.J.; Hossen, I.; Bashir, R.; Chang, W.J.; Lee, C.H. Localized dielectric loss heating in dielectrophoresis devices. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braff, W.A.; Pignier, A.; Buie, C.R. High sensitivity three-dimensional insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1327–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabowo, B.A.; Cabral, P.D.; Freitas, P.; Fernandes, E. The challenges of developing biosensors for clinical assessment: A review. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zou, H.; Li, M.; Sun, C.; Ren, D.; Li, Y. Fiber optic surface plasmon resonance sensor for detection of E. coli O157: H7 based on antimicrobial peptides and AgNPs-rGO. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangenehzadeh, S.; Agocs, E.; Schröder, F.; Amroun, N.; Biedendieck, R.; Jahn, D.; Günther, A.; Zheng, L.; Roth, B.; Johannes, H.H.; et al. Polarization modulated spectroscopic ellipsometry-based surface plasmon resonance biosensor for E. coli K12 detection. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudsari, Z.O.; Khoramrooz, S.S.; Rouhi, S.; Ghasem, H.; Khatami, S.H.; Alizadeh, M.; Khosravi, N.A.; Mansoriyan, A.; Ghasemi, E.; Movahedpour, A.; et al. Electrochemical and optical biosensors for the detection of E. coli. Clin. Chim. Acta 2024, 565, 119984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovszki, D.; Valkai, S.; Gora, E.; Tanner, M.; Bányai, A.; Fürjes, P.; Dér, A. An integrated electro-optical biosensor system for rapid, low-cost detection of bacteria. Microelectron. Eng. 2021, 239, 111523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargol Zadeh, S.; Kashanian, S.; Nazari, M. A label-free carbohydrate-based electrochemical sensor to detect Escherichia coli pathogenic bacteria using d-mannose on a glassy carbon electrode. Biosensors 2023, 13, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setterington, E.B.; Alocilja, E.C. Rapid electrochemical detection of polyaniline-labeled Escherichia coli O157: H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2208–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Lu, Q.; Ge, S.; Cai, Q.; Grimes, C.A. Detection of pathogen Escherichia coli O157: H7 with a wireless magnetoelastic-sensing device amplified by using chitosan-modified magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 147, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Kosel, J. A magnetic biosensor system for detection of E. coli. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 3492–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bukhari, S.A.R.; Alaei, E.; Jia, Z.; Lai, Y. Comb-Tipped Coupled Cantilever Sensor for Enhanced Real-Time Detection of E. coli Bacteria. Sensors 2025, 25, 4145. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134145
Bukhari SAR, Alaei E, Jia Z, Lai Y. Comb-Tipped Coupled Cantilever Sensor for Enhanced Real-Time Detection of E. coli Bacteria. Sensors. 2025; 25(13):4145. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134145
Chicago/Turabian StyleBukhari, Syed Ali Raza, Elham Alaei, Zongchao Jia, and Yongjun Lai. 2025. "Comb-Tipped Coupled Cantilever Sensor for Enhanced Real-Time Detection of E. coli Bacteria" Sensors 25, no. 13: 4145. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134145
APA StyleBukhari, S. A. R., Alaei, E., Jia, Z., & Lai, Y. (2025). Comb-Tipped Coupled Cantilever Sensor for Enhanced Real-Time Detection of E. coli Bacteria. Sensors, 25(13), 4145. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134145






